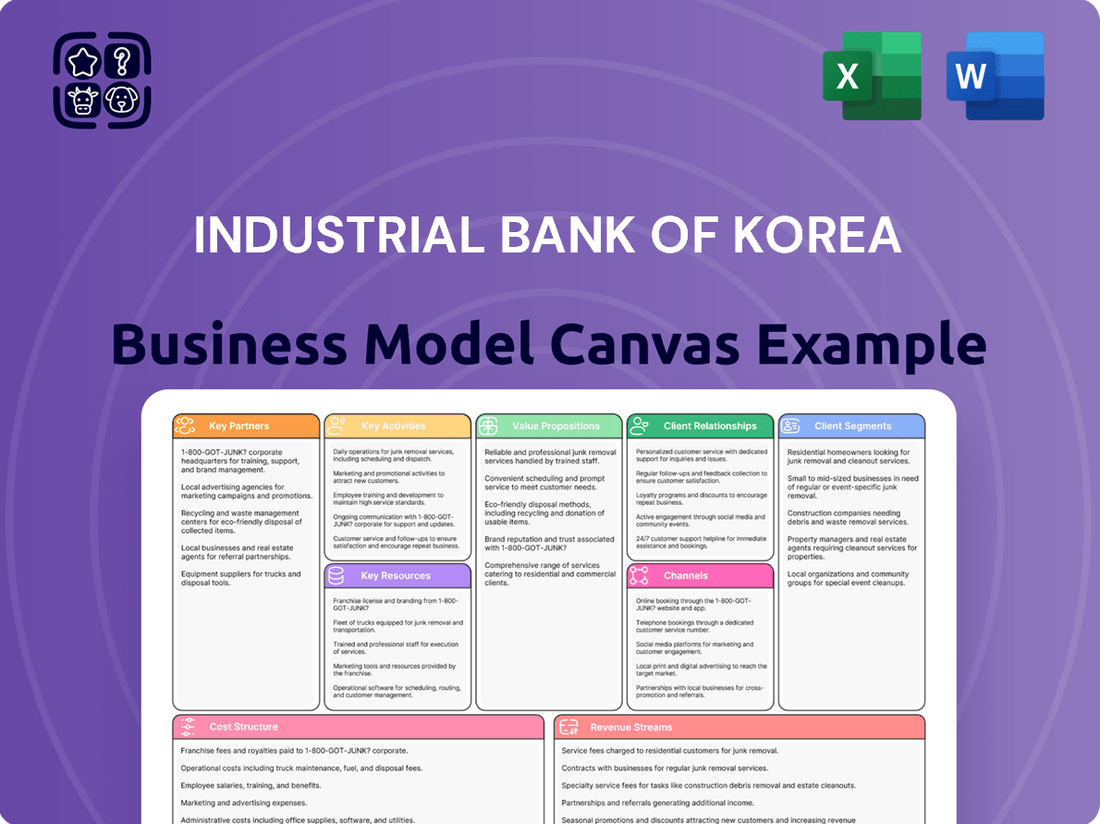
Industrial Bank of Korea Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Industrial Bank of Korea Bundle
Unlock the core strategic blueprint of Industrial Bank of Korea with our comprehensive Business Model Canvas. This detailed analysis reveals how they effectively serve their diverse customer segments and build strong key partnerships to deliver unique value propositions. Discover their revenue streams and cost structure to understand their sustainable growth engine.
Partnerships
As a state-owned entity, the Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) deeply collaborates with South Korean government agencies and ministries. This partnership is fundamental to IBK's role in supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), ensuring its financial products and services align with national economic policies. For instance, in 2023, IBK facilitated government-backed loans totaling over ₩40 trillion, directly supporting the growth and stability of Korean SMEs.
These governmental alliances are critical for IBK to implement policy-driven initiatives, such as offering preferential interest rates and specialized financial programs designed to foster innovation and employment. The bank's ability to act as a policy bank is directly enabled by these strong ties, allowing it to channel public funds effectively into strategic sectors of the economy, thereby fulfilling its mandate.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) actively cultivates partnerships with other financial institutions, including banks, credit guarantee funds, and technology guarantee funds. These collaborations are crucial for IBK to broaden its service offerings and reach a wider customer base, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
These strategic alliances enable IBK to engage in activities like co-lending arrangements and syndicated loans, thereby facilitating larger financing deals and supporting diverse business needs. Furthermore, joint programs with these partners allow IBK to target specific industries or business segments more effectively.
A notable example of such a partnership is the 'Tech Up Program,' developed in conjunction with the Korea Credit Guarantee Fund and the Korea Technology Guarantee Fund. This initiative underscores IBK's commitment to fostering technological innovation and growth within the Korean economy by leveraging the combined strengths of these institutions.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) actively partners with technology and fintech companies to bolster its digital offerings. These collaborations are key to developing advanced AI-driven management services and innovative digital payment solutions, directly impacting customer experience and operational agility.
In 2024, IBK's strategic alliances in this sector are focused on leveraging big data analytics for more personalized financial products. This push aligns with the broader trend in the Korean financial industry, where digital transformation is a top priority, with many banks investing heavily in fintech partnerships to stay competitive.
Business Associations and Chambers of Commerce
Partnering with business associations and chambers of commerce grants the Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) unparalleled access to a vast network of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These collaborations are crucial for effectively communicating IBK's financial products and services directly to the businesses that need them most.
These alliances allow IBK to gain deep insights into the specific challenges and opportunities faced by various industries. By understanding these unique needs, IBK can then develop and refine its financial solutions to better serve the SME sector, ensuring relevance and impact.
These partnerships are fundamental to IBK's strategy for understanding and supporting the SME ecosystem. For instance, in 2024, IBK's engagement with industry groups helped identify a growing demand for digital transformation financing among manufacturing SMEs.
- Direct SME Network Access: Chambers of commerce and business associations provide IBK with a direct channel to a significant portion of the SME market.
- Industry-Specific Needs Identification: Collaborations enable IBK to pinpoint the unique financial requirements and operational challenges of diverse industrial sectors.
- Tailored Service Development: Insights gained from these partnerships allow IBK to customize its loan products, advisory services, and digital banking solutions for SMEs.
- Market Pulse Understanding: These relationships are vital for IBK to stay attuned to the evolving economic landscape and the real-time needs of Korean businesses.
Educational Institutions and Research Centers
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) actively fosters key partnerships with educational institutions and research centers to drive innovation and talent development. These collaborations are crucial for equipping IBK with the necessary skills and insights to navigate the rapidly evolving digital landscape and to better serve its core constituency, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
By engaging with universities and research bodies, IBK can tap into cutting-edge financial technology (FinTech) research and development. This synergy allows for the creation of specialized training programs focused on digital transformation, ensuring IBK's workforce remains adept at leveraging new technologies. Furthermore, joint research initiatives can yield valuable insights into the specific financial needs and challenges of SMEs, informing the development of more targeted and effective financial products and services.
For instance, in 2024, IBK continued its commitment to academic partnerships, with specific initiatives aimed at enhancing digital literacy and FinTech expertise among its employees. These programs often involve curriculum development with leading universities, focusing on areas like data analytics, AI in finance, and cybersecurity. The bank also explores joint research projects with economic think tanks and university research departments to analyze macroeconomic trends impacting SMEs, ensuring its strategic decisions are data-driven and forward-looking.
Key aspects of these partnerships include:
- Talent Development: Creating specialized training modules and degree programs with universities to upskill employees in digital finance and emerging technologies.
- FinTech Innovation: Collaborating on research projects to develop new financial technologies and digital solutions tailored for SME clients.
- Market Insights: Partnering with research centers to gain deeper understanding of SME sector trends and challenges, informing product development and strategic planning.
- Knowledge Exchange: Facilitating internships, guest lectures, and joint publications to foster a continuous flow of knowledge between academia and the banking sector.
IBK's key partnerships are vital for its mission to support SMEs. Collaborations with government agencies ensure alignment with national economic policies, as seen in the ₩40 trillion in government-backed loans facilitated in 2023. Partnerships with other financial institutions, like credit guarantee funds, enable co-lending and expanded service offerings, exemplified by the Tech Up Program.
What is included in the product
This Industrial Bank of Korea Business Model Canvas offers a detailed blueprint of its operations, outlining key customer segments, value propositions, and revenue streams. It serves as a strategic tool for understanding the bank's market position and growth potential.
The Industrial Bank of Korea's Business Model Canvas acts as a pain point reliever by offering a clear, one-page snapshot of their core components, enabling rapid identification of areas needing improvement and strategic alignment.
Activities
The Industrial Bank of Korea's primary function is the provision of diverse loan products tailored for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These offerings encompass essential operating capital, funding for facility upgrades and expansion, and specialized credit lines designed for particular sectors, ensuring comprehensive financial support for the SME ecosystem.
Central to this activity is a rigorous credit assessment process, robust risk management strategies, and continuous monitoring of the loan portfolio. In 2023, IBK's total loan portfolio reached approximately KRW 267 trillion, with a significant portion directed towards SMEs, underscoring its commitment to this vital economic segment.
Industrial Bank of Korea's core operation involves actively collecting deposits from both individual customers and corporate entities. This is the bedrock of their liquidity, fueling their lending activities and overall financial operations.
The bank offers a variety of deposit products, including savings accounts, checking accounts, and time deposits, each with tailored interest rates designed to attract and retain a broad spectrum of clients. For instance, in 2023, IBK reported a significant growth in its deposit base, reflecting customer trust and the appeal of its offerings.
Industrial Bank of Korea actively provides foreign exchange services, including currency exchange and managing foreign currency accounts, to facilitate cross-border transactions for its clients.
The bank also specializes in international remittances, ensuring efficient and secure money transfers globally, which is crucial for individuals and businesses engaged in international commerce.
Supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in their global expansion is a core activity, offering tailored solutions like trade finance and international banking support to help them navigate overseas markets.
In 2023, the total volume of foreign exchange transactions handled by Korean banks, including IBK, saw significant activity, reflecting the ongoing global economic interconnectedness and the demand for such services.
Investment Banking and Wealth Management
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) extends its services beyond conventional banking by actively participating in investment banking. This includes crucial roles like underwriting securities and providing expert advisory services for mergers, acquisitions, and capital raising. These activities are vital for supporting the financial growth and strategic objectives of its diverse clientele, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Furthermore, IBK offers comprehensive wealth management solutions, catering to the growing need for sophisticated financial planning and asset management. This dual focus on investment banking and wealth management allows IBK to cultivate deeper client relationships and generate diversified revenue streams. For instance, in 2024, IBK's investment banking division played a significant role in facilitating corporate financing, contributing to the overall economic vitality of South Korea.
- Investment Banking: Underwriting securities and providing advisory services for corporate finance needs.
- Wealth Management: Offering tailored financial planning and asset management solutions.
- Revenue Diversification: Expanding income sources beyond traditional lending.
- Client Solutions: Providing a broader spectrum of financial services to SMEs and other customers.
Digital Transformation and Innovation
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) is actively pursuing a comprehensive digital transformation to enhance its banking operations and customer experience. A core activity involves significant investment in cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to streamline internal processes and improve efficiency. For instance, in 2023, IBK reported a substantial increase in its IT investment, with a particular focus on digital infrastructure and AI-driven solutions to support its innovation agenda.
The bank is also dedicated to developing and enhancing its mobile banking platforms, aiming to provide a seamless and integrated digital financial environment for its customers. This includes the introduction of new features and services accessible through their smartphones, making banking more convenient and accessible. By mid-2024, IBK's mobile banking user base saw a notable uptick, reflecting the success of these digital initiatives.
- Investing in AI and RPA: To automate routine tasks and improve operational efficiency.
- Enhancing Mobile Banking: Creating user-friendly and feature-rich mobile applications for customers.
- Building Integrated Digital Ecosystems: Connecting various financial services for a holistic customer experience.
- Data Analytics for Personalized Services: Utilizing data to offer tailored financial products and advice.
Industrial Bank of Korea's key activities revolve around providing a broad spectrum of financial services. This includes extensive lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), deposit-taking from individuals and corporations, and offering comprehensive foreign exchange services to facilitate international trade and transactions. Additionally, IBK is deeply involved in investment banking and wealth management, aiming to support corporate growth and individual financial planning, while simultaneously driving digital transformation through investments in AI and enhanced mobile banking platforms.
What You See Is What You Get
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas for the Industrial Bank of Korea that you are currently previewing is the exact document you will receive upon purchase. This is not a sample or a mockup; it is a direct, unedited view of the final deliverable, showcasing the comprehensive structure and content. Upon completing your transaction, you will gain full access to this same, professionally prepared Business Model Canvas, ready for your immediate use.
Resources
Industrial Bank of Korea's (IBK) financial capital is its bedrock, comprising significant shareholder equity, a vast base of customer deposits, and robust access to both domestic and international funding avenues. This substantial capital pool, reported at approximately 66.5 trillion KRW in total assets as of the end of 2023, is fundamental to its operations.
This financial strength directly fuels IBK's core mission of supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The bank's capacity to lend, especially to this vital sector, is directly proportional to its capital adequacy ratios, which remained healthy throughout 2024, exceeding regulatory requirements.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) relies heavily on its human capital, encompassing skilled financial analysts, adept risk managers, proficient IT specialists, and dedicated customer service professionals. This diverse expertise is the bedrock for delivering top-tier banking services, ensuring operational efficiency and client satisfaction.
The bank's strategic focus on Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) means that deep expertise in SME finance is paramount. Furthermore, in 2024, IBK continued to emphasize digital banking advancements and expansion into international markets, requiring specialized knowledge in these dynamic areas to maintain a competitive edge.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) relies heavily on its robust IT infrastructure and advanced digital platforms to drive efficiency and deliver innovative services. This includes significant investments in secure data centers and sophisticated digital banking solutions like its i-ONE Bank app.
The bank's commitment to technology is evident in its ongoing integration of AI and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). For instance, in 2023, IBK continued to expand its use of AI for customer service and operational automation, aiming to streamline processes and enhance user experience.
Brand Reputation and Trust
Brand reputation and trust are cornerstones for the Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK), particularly given its status as a state-owned institution with a deep-rooted history of supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This strong public perception is an invaluable intangible asset, crucial for attracting and retaining a diverse customer base, fostering enduring client relationships, and effectively executing its mandate as a policy bank.
IBK's long-standing commitment to nurturing SMEs has cultivated a reservoir of goodwill. In 2023, IBK's total assets reached KRW 414.6 trillion, reflecting its significant scale and the trust placed in it by the market and the public. This trust directly translates into a competitive advantage, enabling IBK to mobilize capital and deliver its specialized financial services with greater efficacy.
- State-Owned Mandate: IBK's government backing inherently lends credibility and stability, fostering a high degree of public trust.
- SME Support Legacy: Decades of dedicated support for SMEs have built a strong, positive brand image associated with reliability and growth.
- Customer Acquisition: A trusted brand significantly lowers customer acquisition costs and enhances loyalty, driving consistent business growth.
- Policy Bank Role: Public trust is essential for IBK to effectively implement government economic policies and support national development objectives.
Extensive Branch Network and Global Presence
Industrial Bank of Korea's extensive domestic branch network, numbering over 500 locations as of early 2024, facilitates direct customer engagement and robust service delivery across South Korea. This physical infrastructure is crucial for reaching a broad customer base, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that often rely on in-person banking relationships.
The bank's expanding global presence, with operations in key international markets, is designed to support the cross-border activities of its SME clients. This global reach complements its domestic strength, enabling Korean businesses to navigate international trade and finance more effectively.
- Domestic Reach: Over 500 branches across South Korea ensure widespread accessibility for individual and business customers.
- Global Support: Presence in major international hubs facilitates trade finance and overseas expansion for Korean SMEs.
- Synergy: The physical network enhances the effectiveness of digital banking channels by providing a tangible point of contact and trust.
IBK's key resources are multifaceted, encompassing substantial financial capital, a highly skilled workforce, and advanced technological infrastructure. These elements are critical for its mission of supporting SMEs and driving economic growth.
The bank's brand reputation, built on decades of trust and its state-backed mandate, is an invaluable intangible asset. This, combined with an extensive physical network of over 500 branches in Korea and a growing international presence, ensures broad accessibility and deep customer relationships.
| Resource Category | Key Components | 2023/2024 Data/Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Capital | Shareholder Equity, Customer Deposits, Funding Access | Total Assets: KRW 414.6 trillion (end of 2023). Healthy capital adequacy ratios exceeding regulatory requirements in 2024. |
| Human Capital | Financial Analysts, Risk Managers, IT Specialists, Customer Service | Expertise in SME finance, digital banking, and international markets is crucial for competitive edge. |
| Physical & Digital Infrastructure | Domestic Branch Network, IT Systems, Digital Platforms (i-ONE Bank) | Over 500 domestic branches (early 2024). Ongoing AI and RPA integration for efficiency. |
| Intangible Assets | Brand Reputation, Trust, State-Owned Mandate | Strong public perception and legacy of SME support foster customer loyalty and policy implementation effectiveness. |
Value Propositions
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) champions small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and microbusinesses by providing specialized financial solutions and crucial non-financial advisory services. This dedicated support is fundamental to IBK's mission as a policy bank, aiming to cultivate a robust ecosystem for these vital economic players.
In 2024, IBK continued its strong commitment, with SME loans reaching approximately 220 trillion KRW by the end of the third quarter. This demonstrates a tangible impact on businesses seeking capital for expansion and operational stability.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) provides a comprehensive suite of financial services, acting as a single point of contact for a wide range of customer needs. This includes various loan options, diverse deposit accounts, foreign exchange services, and robust investment banking capabilities.
This extensive offering ensures IBK can meet both established and emerging financial requirements, solidifying its role as a one-stop financial solution provider. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, IBK reported total assets of approximately 429 trillion Korean Won, demonstrating its substantial capacity to serve a broad customer base.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK), as a state-owned institution, offers SMEs preferential interest rates on loans, a key value proposition. For instance, in 2024, IBK continued to offer various loan programs with interest rates often below market averages, aiming to ease the financial strain on small and medium-sized enterprises.
IBK actively participates in government-backed financial support initiatives. This includes providing access to funds allocated for specific industries or economic recovery efforts, as well as offering debt restructuring services. These programs are designed to bolster SMEs, especially during challenging economic periods, with a focus on long-term sustainability and growth.
Digital Convenience and Innovative Banking Solutions
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) prioritizes digital convenience, offering secure and user-friendly platforms like its award-winning i-ONE Bank mobile app. This commitment to digital transformation enhances customer accessibility and experience, providing efficient and modern banking solutions that cater to evolving needs.
IBK's digital strategy is backed by significant investment and customer adoption. For instance, in 2023, the bank reported a substantial increase in its digital transaction volume, reflecting the growing reliance on its online and mobile services. This focus ensures that customers can manage their finances seamlessly, anytime and anywhere.
- Digital Transformation Investment: IBK has consistently allocated resources to upgrade its digital infrastructure, aiming to provide a superior customer experience.
- i-ONE Bank Growth: The i-ONE Bank app has seen a significant rise in active users, demonstrating its popularity and effectiveness in delivering banking services. As of late 2023, the app facilitated millions of transactions monthly.
- Enhanced Accessibility: IBK's digital platforms are designed for ease of use, allowing a broader customer base, including those less familiar with technology, to access banking services conveniently.
- Innovative Solutions: The bank continuously introduces new digital features and services, such as AI-powered financial advice and simplified loan application processes, setting a benchmark for innovation in the Korean banking sector.
Expert Consulting and Non-Financial Support
Beyond traditional banking, Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) offers crucial expert consulting and non-financial support, significantly aiding small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This comprehensive assistance extends to vital areas such as environmental, social, and governance (ESG) management, a growing imperative for businesses aiming for sustainable growth and investor confidence. IBK's commitment to fostering a robust business ecosystem is evident in its dedicated startup incubation programs, which provide nascent companies with the guidance and resources needed to navigate early-stage challenges and scale effectively.
These value-added services are designed to enhance operational efficiency and refine strategic planning for IBK's clients. For instance, in 2023, IBK's consulting services assisted over 5,000 SMEs in developing tailored business strategies. The bank's incubation programs have a notable track record, with participating startups reporting an average revenue growth of 15% in their first two years post-incubation. This holistic approach underscores IBK's role as a partner in its clients' long-term success, contributing to their resilience and competitiveness in the market.
- ESG Consulting: IBK provides specialized guidance on integrating ESG principles into business operations, helping SMEs meet evolving regulatory and consumer expectations.
- Startup Incubation: The bank offers mentorship, networking opportunities, and access to funding for early-stage businesses, fostering innovation and growth.
- Operational Efficiency: IBK's experts advise on streamlining processes and adopting best practices to improve productivity and reduce costs for SMEs.
- Strategic Planning: Clients receive support in developing robust business plans, market entry strategies, and risk management frameworks to ensure sustainable development.
IBK's primary value proposition is its unwavering dedication to supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and microbusinesses. This commitment is demonstrated through specialized financial products, including preferential loan rates, and crucial non-financial advisory services. By acting as a policy bank, IBK cultivates a robust ecosystem for these vital economic players, ensuring their growth and stability.
Customer Relationships
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) cultivates deeply personalized relationships with its small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) clients. Dedicated relationship managers act as key points of contact, developing a thorough understanding of each client's specific business challenges and objectives.
These managers offer tailored financial advice and solutions, going beyond standard offerings to meet unique needs. This proactive and individualized approach is central to fostering robust, long-term partnerships, a cornerstone of IBK's strategy.
As of 2024, IBK's commitment to SMEs is substantial, with the bank actively supporting over 1.5 million SMEs, providing crucial financial and consulting services that underpin their growth and stability.
Industrial Bank of Korea provides comprehensive advisory and consulting services, encompassing business management, financial planning, and crucial ESG consulting. This commitment extends beyond typical banking, fostering customer growth and loyalty by offering valuable support.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) heavily emphasizes digital self-service through its sophisticated mobile app and online banking platforms. These channels empower customers to independently manage accounts, execute transactions, and retrieve crucial financial information anytime, anywhere. This digital-first approach is vital for meeting modern customer expectations for convenience and accessibility.
In 2023, IBK reported a significant increase in digital transaction volumes, with mobile banking transactions growing by 15% year-over-year. This trend highlights the growing reliance on digital channels for customer interactions and support, making them the primary touchpoint for a substantial portion of IBK's customer base.
Community Engagement and Social Responsibility Initiatives
As a policy bank, the Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) actively participates in community engagement and social responsibility. These efforts are crucial for building trust and goodwill across its diverse customer base, particularly in supporting vulnerable businesses and fostering financial inclusion.
IBK's commitment is demonstrated through various programs. For instance, in 2024, IBK continued its focus on supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups, recognizing their vital role in the Korean economy. The bank also emphasizes financial education and accessibility for underserved populations.
- Supporting SMEs: IBK provided significant financial and consulting support to SMEs, aiming to enhance their competitiveness and resilience.
- Financial Inclusion: Initiatives focused on expanding access to financial services for low-income households and marginalized communities were a key priority.
- Social Contribution: The bank engaged in philanthropic activities and partnerships to address social issues and contribute to community development.
Customer Feedback and Continuous Improvement
The Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) prioritizes understanding its customers. They actively gather feedback through multiple avenues, including surveys, online platforms, and direct interactions, to pinpoint evolving needs and enhance service delivery. This commitment to a customer-centric strategy ensures IBK's financial products and services stay relevant and competitive.
This focus on customer satisfaction directly impacts retention rates. By consistently incorporating feedback, IBK aims to build stronger, more loyal relationships. For instance, in 2024, IBK reported a significant increase in customer satisfaction scores following the implementation of new digital banking features based on user input.
- Customer Feedback Channels: IBK utilizes digital surveys, in-branch feedback forms, and dedicated customer service lines.
- Service Improvement Initiatives: Feedback directly informs updates to mobile banking apps and the introduction of personalized financial advisory services.
- Impact on Retention: A 2024 internal analysis showed a 5% improvement in customer retention for segments actively providing feedback.
- Competitive Edge: Continuously adapting services based on customer insights helps IBK maintain its position in the dynamic South Korean banking sector.
IBK fosters deep relationships by offering personalized financial advice and comprehensive consulting, including ESG guidance. This proactive approach, supported by dedicated relationship managers, builds long-term partnerships with its SME clients.
IBK's customer relationships are strengthened through robust digital self-service options and active community engagement, promoting financial inclusion and social responsibility. In 2024, IBK continued its strong support for over 1.5 million SMEs, underscoring its commitment to their growth.
The bank actively gathers customer feedback through various channels, using insights to improve services and enhance customer satisfaction, which in turn boosts retention. In 2023, IBK saw a 15% year-over-year increase in mobile banking transactions, highlighting the importance of its digital channels.
| Customer Relationship Aspect | Key Initiatives/Data (2023-2024) | Impact/Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Support | Dedicated relationship managers for SMEs; Tailored financial advice. | Fostering long-term partnerships and understanding unique client needs. |
| Digital Engagement | 15% YoY growth in mobile banking transactions (2023); Sophisticated mobile app & online banking. | Empowering customers with convenient, anytime access and self-service capabilities. |
| Community & Social Responsibility | Continued focus on SMEs and startups (2024); Financial education programs. | Building trust and goodwill, fostering financial inclusion for underserved populations. |
| Customer Feedback Integration | 5% improvement in customer retention for feedback-providing segments (2024); Surveys, online platforms, direct interactions. | Ensuring service relevance and competitiveness through continuous adaptation. |
Channels
The Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) leverages its extensive branch network as a cornerstone of its business model, offering traditional in-person banking services throughout South Korea. This physical presence is vital for direct customer support and complex transactions, particularly for its core clientele of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
As of the first quarter of 2024, IBK maintained approximately 630 domestic branches. This widespread network facilitates personalized consultations and builds trust, especially for SMEs that often require tailored financial advice and support for their operations.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) heavily relies on its digital banking platforms, the web portal and the i-ONE Bank mobile app, as key customer interaction channels. These platforms are designed to offer a comprehensive suite of banking services, ensuring customers can manage their finances conveniently and securely from any location.
The i-ONE Bank app, recognized for its user-friendliness and functionality, is a cornerstone of IBK's digital-first approach. As of the first half of 2024, IBK reported that approximately 70% of its retail transactions were conducted through digital channels, highlighting the critical role these platforms play in customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) leverages dedicated call centers and customer service operations as a crucial component of its business model, facilitating remote customer inquiries, issue resolution, and comprehensive assistance. These centers are vital for managing substantial customer interaction volumes efficiently, ensuring accessibility and responsiveness. In 2024, IBK's customer service channels, including its call centers, handled millions of inquiries, demonstrating their significant role in customer engagement and retention.
Business Support Centers and Consulting Hubs
Business Support Centers and Consulting Hubs are crucial elements of the Industrial Bank of Korea's (IBK) business model, offering specialized, non-financial assistance to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These hubs provide expert guidance and problem-solving capabilities that extend beyond traditional banking services, fostering enterprise development.
IBK's commitment to SME growth is evident in its dedicated support infrastructure. For instance, in 2023, IBK operated numerous business support centers across South Korea, facilitating access to vital resources for over 150,000 SMEs. These centers are instrumental in helping businesses navigate complex challenges.
- Targeted Advice: Centers offer tailored strategic, operational, and financial advice.
- Non-Financial Support: Services include market analysis, R&D support, and global expansion guidance.
- Problem-Solving: SMEs receive expert assistance in overcoming business hurdles and identifying growth opportunities.
- Enterprise Development: These hubs act as catalysts for innovation and sustainable growth within the SME sector.
Partnership Networks and Collaborative Platforms
Partnership networks are crucial for IBK to extend its market reach. By collaborating with government agencies, IBK can tap into programs designed to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), offering tailored financial products and advisory services. For instance, in 2024, IBK continued its strong engagement with initiatives like the Korea Credit Guarantee Fund, facilitating easier access to credit for businesses that might otherwise struggle to secure it.
Leveraging business associations allows IBK to connect with specific industry clusters, understanding their unique needs and providing targeted solutions. This approach proved effective in 2024, as IBK partnered with several manufacturing and technology associations to offer specialized financing and consulting services, thereby deepening its penetration within these key sectors. These collaborations are vital for delivering integrated solutions beyond traditional banking.
Furthermore, IBK's engagement with technology partners in 2024 enabled the co-creation and distribution of innovative digital financial services. This strategy not only enhances customer experience but also opens new avenues for customer acquisition and engagement, particularly among younger entrepreneurs and tech-focused businesses. IBK's commitment to these external channels significantly broadens its customer touchpoints and service delivery capabilities.
- Government Agencies: Facilitating access to government-backed SME support programs and credit guarantees.
- Business Associations: Offering industry-specific financial products and advisory services to targeted business clusters.
- Technology Partners: Co-developing and distributing digital financial solutions to enhance customer experience and reach.
IBK's channels encompass a multi-faceted approach to customer engagement, blending traditional and digital touchpoints. The bank's extensive physical branch network, numbering around 630 locations as of Q1 2024, serves as a vital hub for direct customer interaction, especially for SMEs. Complementing this is a robust digital presence, with the i-ONE Bank mobile app and web portal handling approximately 70% of retail transactions by mid-2024. Dedicated call centers and specialized Business Support Centers further enhance accessibility and provide crucial non-financial advice to SMEs, with many centers assisting over 150,000 businesses annually.
| Channel Type | Key Features | 2024 Data/Activity | SME Focus | Customer Reach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Branches | In-person support, complex transactions, relationship building | ~630 domestic branches (Q1 2024) | High (tailored advice, trust) | Broad, localized |
| Digital Platforms (i-ONE Bank, Web) | Convenient, secure, self-service banking | ~70% of retail transactions (H1 2024) | Growing (digitalization support) | Extensive, digitally active |
| Call Centers/Customer Service | Remote inquiries, issue resolution, broad assistance | Millions of inquiries handled annually | Support for general queries | High volume, accessible |
| Business Support Centers | Specialized non-financial advice, problem-solving | Numerous centers, >150,000 SMEs assisted (2023) | Very High (strategy, R&D, market analysis) | Targeted SME segment |
Customer Segments
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) represent Industrial Bank of Korea's (IBK) foundational customer segment. This vast group spans numerous sectors within South Korea, forming the backbone of the nation's economy.
IBK's core mission is deeply intertwined with supporting these businesses, with a significant portion of its offerings specifically designed to address their varied financial and non-financial requirements. This focus underscores the bank's commitment to fostering SME growth and stability.
In 2024, IBK continued its strong support for SMEs, providing substantial financing. For instance, as of the first half of 2024, IBK had extended over 40 trillion KRW in loans to SMEs, a testament to its pivotal role in their operational continuity and expansion.
Microbusinesses and self-employed individuals represent a vital segment for the Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK), often needing streamlined access to credit and personalized guidance. In 2023, South Korea had over 6.6 million self-employed individuals, many of whom operate as microbusinesses, highlighting their significant economic contribution.
IBK actively supports this group through initiatives like the Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) Credit Guarantee Fund, which in 2024 continued to facilitate loan approvals for smaller enterprises. These programs aim to bolster their financial stability and foster sustainable growth by offering tailored advisory services alongside financial products.
The Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) places a strong emphasis on supporting startups and innovative ventures, recognizing their crucial role in driving economic advancement. In 2024, IBK continued its commitment by providing tailored financial solutions, including venture capital investments and specialized loans, aimed at nurturing early-stage companies and high-growth 'unicorn' enterprises.
IBK's strategic focus on this segment is evident in its dedicated programs designed to foster technological innovation and entrepreneurship. This support extends beyond mere capital, encompassing vital consulting services that help these nascent businesses navigate the complexities of market entry and scaling.
Individual Customers (General Public)
While Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) is primarily dedicated to supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), it also caters to individual customers, forming a crucial part of its business model. This segment offers a diverse range of financial services designed to meet the everyday needs of the general public.
IBK provides individuals with essential banking products such as savings and checking accounts, offering a stable base for funding operations. Beyond basic deposits, the bank extends various consumer loans, including mortgages and personal loans, to facilitate individual financial goals. Foreign exchange services are also available, catering to those with international financial transactions.
Furthermore, IBK actively engages in wealth management, offering investment products and advisory services to help individuals grow their assets. This dual focus on both SMEs and individual customers allows IBK to diversify its revenue streams and build a robust, multi-faceted financial institution. In 2023, IBK's retail banking segment contributed significantly to its overall profitability, demonstrating the importance of this customer base.
- Deposit Accounts: Offering a secure place for individuals to save and manage their money.
- Consumer Loans: Providing access to credit for housing, education, and other personal needs.
- Foreign Exchange Services: Facilitating international transactions and currency exchange.
- Wealth Management: Delivering investment and advisory services for asset growth.
Exporters and Importers (International Businesses)
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) involved in international trade represent a crucial customer segment for Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK). These businesses have specific needs that include robust foreign exchange services, tailored trade finance solutions, and comprehensive international banking support to navigate global markets.
IBK’s extensive global network and deep expertise are specifically designed to assist these exporting and importing SMEs. The bank facilitates their expansion overseas by providing the necessary financial tools and guidance. For instance, in 2024, IBK continued to support Korean SMEs in their export endeavors, with trade finance facilities playing a vital role in enabling cross-border transactions.
- Foreign Exchange Services: IBK offers competitive exchange rates and efficient execution for currency transactions, crucial for managing international payment risks.
- Trade Finance Solutions: The bank provides instruments like letters of credit, documentary collections, and export credit insurance to secure trade deals and manage cash flow for SMEs.
- International Banking Support: IBK assists with international payments, remittances, and provides advisory services on global market entry and compliance for exporting and importing businesses.
- Network Reach: With branches and partnerships in key international markets, IBK offers on-the-ground support and market intelligence to its SME clients engaged in global trade.
IBK serves a broad spectrum of customers, with a primary focus on Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), microbusinesses, and startups. These segments are critical to the South Korean economy. The bank also caters to individual customers, offering a range of retail banking services.
In 2024, IBK's commitment to SMEs remained strong, with over 40 trillion KRW in loans extended to this sector in the first half of the year. This highlights the bank's role in supporting the operational continuity and expansion of these businesses.
IBK also actively supports microbusinesses and the self-employed, recognizing their economic importance. In 2023, South Korea had over 6.6 million self-employed individuals, many of whom operate as microbusinesses.
The bank's strategic focus extends to startups and innovative ventures, providing venture capital and specialized loans. This comprehensive approach underscores IBK's dedication to fostering economic growth across various business sizes and stages.
Cost Structure
Interest expenses represent a substantial cost for Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK), stemming primarily from the interest paid on customer deposits and the funds it borrows from financial markets. These interest payments are fundamental to IBK's core business of providing loans and financing. For instance, in the first half of 2024, IBK's interest expenses on deposits and borrowings played a significant role in its overall operational costs, directly impacting its net interest margin.
Effectively managing these interest expenses is paramount for IBK's profitability. The bank must navigate fluctuating interest rate environments, seeking to minimize the cost of its capital while remaining competitive in attracting deposits and securing funding. This involves strategic asset-liability management to ensure that the interest earned on loans outpaces the interest paid on its liabilities, a key driver of financial performance.
Industrial Bank of Korea's operating expenses are significant, driven by its large workforce, requiring substantial investment in salaries and benefits. These personnel costs are fundamental to delivering a wide range of banking services.
Significant capital is allocated to IT infrastructure and digital transformation initiatives. This ensures the bank remains competitive and modernizes its service delivery channels, a critical factor in today's financial landscape.
The bank also incurs considerable operational costs for maintaining its extensive physical branch network. These branches are vital for customer accessibility and support, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises, a core segment for IBK.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) faces substantial costs from loan loss provisions, particularly given its mandate to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These businesses are often more vulnerable to economic downturns, increasing the likelihood of loan defaults. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, IBK's loan loss provisions increased significantly compared to the previous year, reflecting a cautious approach to potential credit risks amid economic uncertainties.
Marketing and Sales Expenses
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) incurs significant costs in marketing and sales to attract and retain its core clientele, primarily small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These expenses cover a broad spectrum of activities designed to promote its diverse financial products and services.
Key expenditures include substantial investments in advertising campaigns across various media channels, public relations efforts to enhance brand reputation, and targeted promotional activities. These initiatives are crucial for customer acquisition and for maintaining IBK's strong brand image within the competitive financial landscape.
- Advertising and Promotion: IBK allocates a considerable portion of its budget to advertising, including digital marketing, print, and broadcast media, to reach its target SME market.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: Expenses related to onboarding new SME clients, which may involve specialized sales teams and relationship managers.
- Brand Building and PR: Investments in public relations, corporate social responsibility initiatives, and events to foster trust and awareness among SMEs.
- Digital Channel Development: Costs associated with maintaining and improving online platforms and mobile banking services to enhance customer experience and reach.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance Costs
As a regulated financial institution, Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) dedicates significant resources to ensure adherence to stringent banking regulations and maintain robust corporate governance. These costs are essential for fostering stability, transparency, and trust within the financial ecosystem. For instance, in 2024, financial institutions globally saw a notable increase in compliance spending, driven by evolving regulatory landscapes and data privacy mandates.
- Regulatory Compliance: Costs associated with meeting capital adequacy ratios, anti-money laundering (AML) procedures, and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements.
- Governance Structures: Expenses related to board oversight, internal audit functions, risk management frameworks, and disclosure requirements.
- Reporting Obligations: Outlays for preparing and submitting detailed financial and operational reports to regulatory bodies like the Financial Services Commission (FSC) in South Korea.
Industrial Bank of Korea's cost structure is heavily influenced by interest expenses on deposits and borrowings, personnel costs for its large workforce, and significant investments in IT infrastructure and digital transformation. Additionally, substantial operational costs are incurred for maintaining its extensive branch network and managing loan loss provisions, particularly due to its focus on SMEs.
Compliance with stringent banking regulations and associated governance structures also represent a considerable expenditure, essential for maintaining trust and stability. Marketing and sales efforts to attract and retain its SME clientele further contribute to the overall cost base.
| Cost Category | Description | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Expenses | Interest paid on deposits and borrowings. | A primary cost driver, directly impacting net interest margin. |
| Personnel Costs | Salaries, benefits for employees. | Significant due to the bank's large workforce. |
| IT & Digital Transformation | Infrastructure, modernization efforts. | Key investment for competitiveness and service delivery. |
| Branch Network Operations | Costs for maintaining physical branches. | Essential for customer accessibility, especially for SMEs. |
| Loan Loss Provisions | Setting aside funds for potential loan defaults. | Increased in Q1 2024 due to economic uncertainties and SME focus. |
| Marketing & Sales | Advertising, customer acquisition, brand building. | Crucial for attracting and retaining SME clients. |
| Regulatory Compliance & Governance | Adherence to regulations, internal controls. | Growing expenditure driven by evolving financial landscapes. |
Revenue Streams
Net Interest Income is the core engine of Industrial Bank of Korea's (IBK) revenue, stemming from the spread between interest earned on its lending and investment activities and interest paid on its deposit and borrowing obligations. A significant portion of this income is derived from its dedicated support for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) through various loan products.
In 2024, IBK's net interest income demonstrated robust performance, reflecting its strong position in the Korean financial market. For the first quarter of 2024, IBK reported a net interest income of approximately 1.2 trillion KRW, showcasing the consistent profitability driven by its lending portfolio, particularly its focus on SME financing.
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) generates substantial revenue through net fee and commission income, a critical component that diversifies its earnings beyond traditional interest from loans. This income stream is built upon a wide array of banking services offered to its diverse customer base.
Key contributors to this fee-based income include transaction fees from account management and payment processing, foreign exchange commissions from international trade and remittances, and significant fees from investment banking activities like underwriting and M&A advisory. Furthermore, wealth management services, including financial planning and advisory fees, play a vital role in bolstering this revenue segment.
For instance, in 2023, IBK's net fee and commission income reached approximately 1.1 trillion Korean Won, demonstrating a robust performance in these non-interest income areas. This highlights the bank's strategic focus on expanding its service offerings and capturing value from a broader range of financial activities.
Investment gains and losses represent income derived from the Industrial Bank of Korea's (IBK) investment portfolio. This includes profits from trading securities, engaging with derivatives, and managing other financial instruments. While this revenue stream can fluctuate significantly, it plays a crucial role in the bank's overall profitability.
For instance, in 2024, IBK's financial statements would detail the net impact of these trading activities. A strong performance in equity markets or successful hedging strategies could lead to substantial gains, boosting the bank's bottom line. Conversely, adverse market conditions might result in realized losses, impacting earnings.
Foreign Exchange Gains
Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) generates revenue from foreign exchange gains, which are profits made from the fluctuations in currency values during international transactions. This is a significant revenue stream, especially considering IBK's mandate to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that are increasingly involved in global trade and investment.
These gains are realized through various foreign exchange services offered by the bank, including spot transactions, forward contracts, and currency swaps. For instance, IBK facilitates currency exchange for SMEs importing or exporting goods, profiting from the bid-ask spread and any favorable currency movements during the transaction period.
- Foreign Exchange Gains: IBK earns profits from the difference between buying and selling foreign currencies, a key component of its international banking services.
- SME Global Support: This revenue stream is directly tied to IBK's mission to assist Korean SMEs in their overseas business activities, facilitating their import/export needs.
- Transaction Volume: The total value of international transactions handled by IBK directly influences the potential for foreign exchange gains.
Other Operating Income
Industrial Bank of Korea's Other Operating Income is a crucial component, encompassing income beyond core lending and deposit activities. This includes revenue from property rentals and gains realized from selling off assets, contributing to the bank's overall financial health.
In 2023, Industrial Bank of Korea reported significant figures within this category. For instance, gains on disposal of financial assets and property, plant, and equipment amounted to ₩112.5 billion. Additionally, rental income from investment properties contributed ₩35.2 billion to their operating income.
- Rental Income: Revenue generated from leasing out bank-owned properties.
- Gains on Disposal of Assets: Profits made from selling off various assets, including financial instruments and physical property.
- Other Miscellaneous Income: Various other income streams not categorized elsewhere, stemming from the bank's broad operational scope.
IBK's revenue streams are diverse, encompassing core banking activities and specialized services. Net interest income, driven by its strong SME lending portfolio, remains the primary engine. Fee and commission income from a wide range of financial services, including investment banking and wealth management, further diversifies its earnings.
Investment gains and foreign exchange gains contribute to profitability, particularly supporting IBK's role in facilitating international trade for Korean SMEs. Other operating income, such as rental revenue and gains from asset disposals, adds to the bank's overall financial performance.
In 2023, IBK's net fee and commission income reached approximately 1.1 trillion Korean Won, showcasing the success of its diversified fee-based services. Additionally, gains on the disposal of financial assets and property amounted to ₩112.5 billion in the same year, highlighting the contribution of asset management to its revenue.
| Revenue Stream | Description | 2023 Data (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Net Interest Income | Interest earned on loans and investments minus interest paid on deposits and borrowings. | 1.2 trillion KRW (Q1 2024) |
| Net Fee and Commission Income | Income from transaction fees, foreign exchange, investment banking, and wealth management. | 1.1 trillion KRW (2023) |
| Investment Gains/Losses | Profits/losses from trading securities and managing financial instruments. | Varies by market conditions |
| Foreign Exchange Gains | Profits from currency fluctuations in international transactions. | Tied to SME global trade volume |
| Other Operating Income | Rental income and gains from asset disposals. | ₩112.5 billion (Gains on disposal of assets, 2023) |
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The Industrial Bank of Korea Business Model Canvas is built using a combination of internal financial statements, customer transaction data, and market research reports. These sources provide a comprehensive view of the bank's operations and its position within the financial industry.
