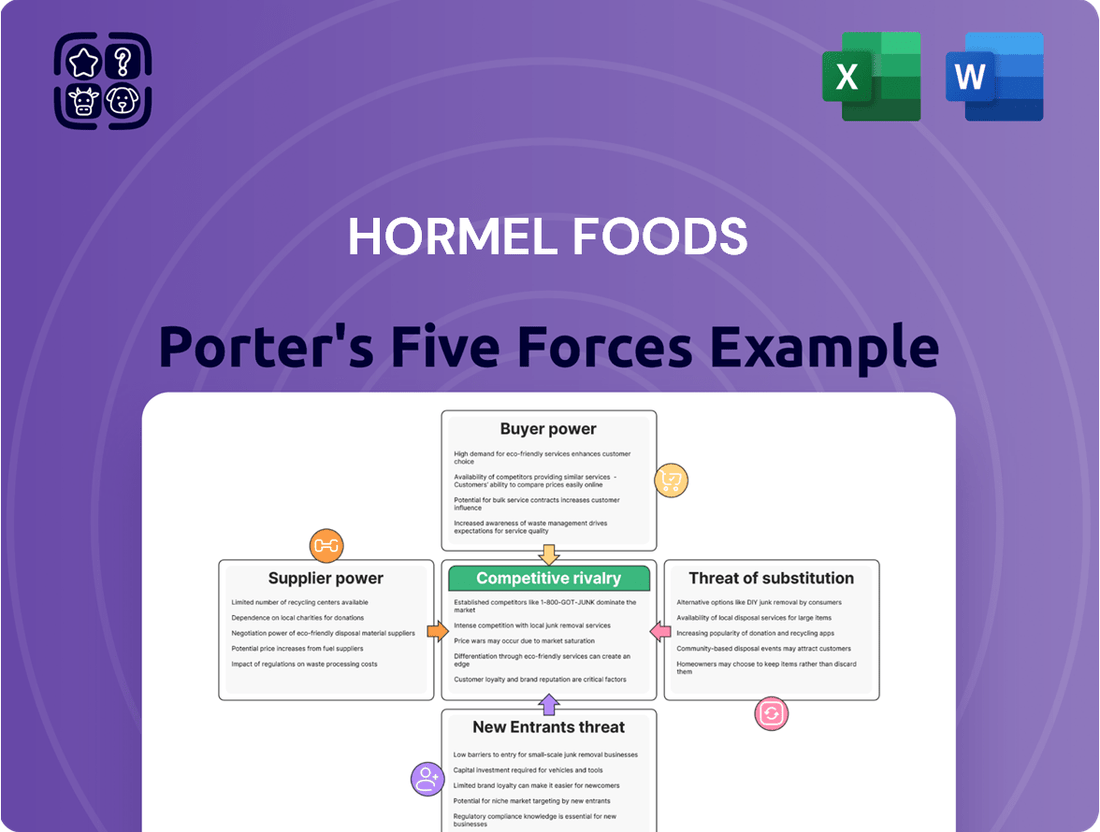
Hormel Foods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hormel Foods Bundle
Hormel Foods operates in a dynamic food industry, where understanding competitive forces is crucial for success. Our analysis reveals moderate bargaining power for buyers and suppliers, while the threat of new entrants is relatively low due to established brands and distribution networks.
The threat of substitutes is a significant factor, as consumers have numerous protein and meal options available. Intense rivalry among existing players, including major food conglomerates, further shapes Hormel's strategic landscape.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Hormel Foods’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers in the meat and food ingredients sector directly affects Hormel Foods' bargaining power. When a few dominant suppliers control essential raw materials like pork, beef, or poultry, they can dictate terms and prices more effectively. This scenario was highlighted in Hormel's Q1 2025 earnings call, where the company cited increased input costs for pork, beef, and nuts as a significant challenge, underscoring the leverage these concentrated suppliers hold.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts the bargaining power of suppliers for Hormel Foods. If Hormel can readily source alternative ingredients, such as different types of proteins or explore plant-based options for certain product lines, the leverage of traditional meat suppliers diminishes. For instance, while Hormel's Spam is iconic, the company also offers a growing portfolio of plant-based products, diversifying its ingredient needs and potentially reducing reliance on specific meat suppliers.
Switching costs for Hormel Foods when changing suppliers can significantly impact negotiations. For instance, if Hormel needs to retool its production lines to accommodate new ingredient specifications or re-establish complex logistics for a different supplier, these expenses directly bolster the supplier's leverage. In 2023, Hormel's cost of goods sold was $7.7 billion, highlighting the scale of their supply chain operations where even minor shifts can incur substantial costs.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into food processing or distribution could significantly enhance their bargaining power. For instance, if a large agricultural cooperative or a major livestock producer decided to process and package their own meat products, they would directly compete with companies like Hormel or become a more formidable negotiating partner.
While this scenario is less probable for a highly diversified food manufacturer such as Hormel Foods, it represents a potential strategic shift that could alter the supply chain dynamics. Such a move would allow suppliers to capture more value downstream, potentially squeezing margins for established food processors.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into food processing or distribution increases their leverage.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: A livestock producer processing their own meat would become a direct competitor or a stronger negotiator.
- Hormel's Diversification: This threat is less pronounced for large, diversified companies like Hormel but remains a theoretical consideration.
Uniqueness of Inputs
The uniqueness or specialization of inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power. While many of Hormel Foods' raw materials, like agricultural commodities, are relatively standardized, the company's diverse product range, which includes branded and specialized items, may depend on certain unique ingredients or proprietary processing techniques from specific suppliers. This can grant those suppliers greater leverage.
For instance, if a particular spice blend, a unique animal breed for a premium product, or a specialized packaging material is sourced from a limited number of providers, those suppliers gain a stronger negotiating position. Hormel's reliance on these specialized inputs, even if a small part of its overall supply chain, can translate into increased costs or supply chain vulnerabilities if not managed carefully.
- Specialized Ingredients: Proprietary flavorings or unique agricultural inputs can create supplier dependence.
- Proprietary Processing: Suppliers offering exclusive or advanced processing techniques for ingredients can command higher prices.
- Limited Supplier Base: For niche products, a concentrated supplier market amplifies individual supplier power.
- Brand Differentiation: Inputs crucial to Hormel's unique product differentiation can give their suppliers more leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hormel Foods is influenced by the concentration of suppliers and the availability of substitute inputs. In 2024, Hormel's reliance on key proteins like pork and beef, which are subject to market volatility and consolidation among producers, means that a few major suppliers can exert significant pricing power. For example, fluctuations in hog prices directly impact Hormel's cost of goods sold, as seen in their ongoing need to manage input cost pressures.
Switching costs for Hormel can also empower suppliers. If a supplier provides specialized ingredients or requires specific processing equipment, the cost and time for Hormel to switch to an alternative can be substantial. This was implicitly acknowledged when Hormel reported its 2024 financial results, noting the operational complexities in adapting to changing ingredient landscapes. The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while less immediate for a company of Hormel's scale, remains a factor that could shift leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Hormel | 2024 Relevance |
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for dominant suppliers | Increased input costs for pork, beef, and nuts cited as challenges. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Reduces supplier power | Growth in plant-based alternatives offers some diversification. |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier leverage | Significant costs associated with retooling production lines. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for stronger supplier negotiation | Less pronounced for Hormel but a theoretical risk. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Hormel Foods' market, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the food industry.
Gain immediate insight into Hormel's competitive landscape with a visual breakdown of each force, streamlining strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Consumer price sensitivity is a significant force, particularly given the economic landscape of 2024. With ongoing inflationary pressures, shoppers are keenly focused on value, often opting for promotions or switching to less expensive alternatives. This heightened price awareness directly impacts Hormel Foods, compelling them to carefully calibrate their pricing to remain competitive and retain their customer base.
The concentration of major retail chains and large foodservice distributors significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. These entities, often operating on a national scale, represent substantial purchasing volumes for Hormel Foods. For instance, in 2023, the top four U.S. grocery retailers accounted for approximately 40% of all grocery sales, a figure that has been steadily increasing due to ongoing consolidation.
This market concentration allows these powerful customers to negotiate favorable pricing, demand extensive promotional support, and dictate terms such as payment schedules and delivery requirements. Their ability to shift substantial business between suppliers means Hormel must remain competitive to retain these crucial relationships.
The sheer volume of choices available to consumers in the food sector significantly amplifies their bargaining power. Hormel faces competition not only from other established meat brands but also from store-brand alternatives and a rapidly expanding market for plant-based proteins.
This abundance of substitutes means customers can easily shift their purchasing habits if Hormel's pricing or product offerings become less attractive. For instance, the plant-based meat market alone saw significant growth, with sales reaching billions in 2024, giving consumers a readily available alternative to traditional meat products.
Low Switching Costs for Consumers
For consumers, the cost of switching from one Hormel product, like bacon or deli meat, to a competitor's offering is typically minimal. This low switching cost significantly enhances their bargaining power. They can easily choose an alternative brand without facing substantial financial penalties or logistical hurdles, putting pressure on Hormel to maintain competitive pricing and product quality.
This dynamic means consumers can readily shift their preferences if they find a better deal or a more appealing product elsewhere. For instance, in the highly competitive U.S. packaged foods market, where Hormel operates, consumers often have a wide array of choices at their fingertips. This forces Hormel to focus on innovation and building strong brand loyalty to retain its customer base.
- Low Switching Costs: Consumers can easily move between brands of bacon, deli meats, and snacks.
- Increased Customer Power: This ease of switching gives consumers more leverage to demand better prices or quality.
- Competitive Pressure: Hormel must continuously innovate and maintain brand appeal to counter this power.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information. Online reviews, price comparison tools, and readily available nutritional data empower consumers, significantly boosting their bargaining power against companies like Hormel Foods. This transparency allows shoppers to make more informed decisions, scrutinizing everything from ingredients to sourcing and pricing, and applying pressure on manufacturers to meet evolving demands.
This heightened awareness means customers can easily compare Hormel's offerings with competitors, demanding better value and quality. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spent approximately 2 hours per week researching products online before making a purchase, a trend that directly impacts brand loyalty and pricing strategies for food manufacturers.
- Informed Choices: Consumers can now easily access detailed product information, including ingredients, nutritional content, and sourcing practices, enabling them to make more discerning purchasing decisions.
- Price Sensitivity: The proliferation of price comparison apps and online deals makes consumers more aware of price variations, increasing their ability to negotiate or switch to more affordable alternatives.
- Brand Accountability: Online platforms and social media amplify customer feedback, allowing consumers to collectively pressure companies like Hormel on issues such as product quality, ethical sourcing, and sustainability.
The bargaining power of Hormel Foods' customers is substantial, driven by several key factors. The concentration of major retail chains, which control significant shelf space, allows them to negotiate favorable terms. Furthermore, the wide availability of substitute products, including plant-based alternatives, and the low cost for consumers to switch brands all contribute to increased customer leverage. This forces Hormel to remain competitive on price and continuously innovate to maintain customer loyalty.
| Factor | Impact on Hormel Foods | Supporting Data (2024 Estimates/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Retailer Concentration | High bargaining power due to large purchase volumes. | Top 4 U.S. grocery retailers account for ~40% of sales. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Consumers can easily switch to alternatives. | Plant-based meat market sales projected to reach $10 billion by 2024. |
| Low Switching Costs | Consumers face minimal barriers to changing brands. | Minimal financial or logistical hurdles for consumers switching food brands. |
| Price Sensitivity | Consumers are highly focused on value due to inflation. | Inflationary pressures continue to drive consumer demand for promotions. |
| Information Access | Empowered consumers make informed decisions. | Average consumer spends ~2 hours/week researching products online. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Hormel Foods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hormel Foods, detailing competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into Hormel's strategic landscape without any placeholders or altered content.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The food and meat products industry is intensely competitive, featuring a broad spectrum of domestic and global participants. Hormel Foods navigates this landscape, facing rivalry from large, established multinational corporations as well as smaller, niche brands across its various business segments.
Hormel's competitive set is diverse, encompassing companies like Tyson Foods, Smithfield Foods, and Perdue Farms in the meat sector, alongside broader food manufacturers such as General Mills and Kraft Heinz, which compete for consumer spending. This broad competition across retail, foodservice, and international markets significantly heightens the rivalry.
The overall growth rate of the food industry directly influences how intensely companies compete. While the global food and beverage market is anticipated to expand, the U.S. packaged food sector, including segments relevant to Hormel Foods, is expected to experience slower growth in 2024 and face challenges leading into 2025. This subdued volume performance in both retail and foodservice channels suggests that companies will likely engage in more aggressive competition to capture market share.
Hormel Foods thrives on product differentiation, leveraging iconic brands such as SPAM, Planters, and Jennie-O to build strong consumer loyalty. This brand equity helps to mitigate direct price wars in many of its product categories.
Despite strong brand recognition, Hormel faces intense competition in numerous segments where product similarity is high. For instance, the salty snack aisle, where Planters competes, is notoriously crowded with numerous brands offering similar products, demanding ongoing investment in marketing and product development to maintain a competitive edge.
In 2023, Hormel's net sales reached $12.3 billion, with a significant portion attributed to its established brands. The company consistently invests in research and development to introduce new flavors, product formats, and healthier options, a strategy essential for standing out in a marketplace where innovation is a key differentiator.
High Fixed Costs and Storage Costs
The food processing industry, including companies like Hormel Foods, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These include investments in manufacturing facilities, sophisticated processing equipment, and extensive supply chain networks, all of which require significant capital outlay. For instance, building and maintaining a modern food processing plant can easily run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars.
Storage costs also add a considerable burden. Perishable goods necessitate specialized warehousing, often with climate control, to prevent spoilage. This ongoing expense contributes to the overall cost structure, especially for companies managing a diverse product portfolio with varying shelf lives. In 2024, Hormel Foods reported significant investments in its operational infrastructure to enhance efficiency and capacity, underscoring the importance of managing these fixed and storage costs effectively.
- High Capital Investment: The food processing sector demands significant upfront investment in plants and machinery, creating a high barrier to entry.
- Storage Expenses: Maintaining inventory, particularly for perishable items, incurs substantial costs related to warehousing and preservation.
- Price Competition Driver: When industry capacity exceeds demand, companies with high fixed costs may engage in aggressive price cutting to cover operational expenses and maximize sales volume.
- Hormel's Operational Focus: In 2024, Hormel continued to optimize its supply chain and manufacturing processes, a strategic imperative driven by the need to manage these inherent cost structures.
Exit Barriers
Hormel Foods faces intense competitive rivalry partly due to high exit barriers. Specialized assets, like their extensive processing plants and sophisticated logistics networks, represent significant sunk costs. For instance, the capital investment required for a modern meat processing facility can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, making it economically unfeasible for many companies to simply shut down operations when facing losses.
These substantial investments, coupled with long-term contracts with suppliers and distributors, trap companies within the industry. Even when a particular segment of the market becomes unprofitable, these fixed commitments and asset specificity prevent firms from easily exiting. This dynamic means that even struggling competitors remain active participants, continuing to vie for market share and putting downward pressure on prices and margins for established players like Hormel.
The inability for underperforming firms to exit cleanly means the number of competitors doesn't naturally shrink during downturns. This sustained level of competition is a key factor in the rivalry Hormel navigates. In 2023, the U.S. meat processing industry, for example, continued to see numerous players, despite some facing margin pressures.
- Specialized Assets: High capital investment in processing plants and equipment creates significant sunk costs.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with suppliers and distributors make it difficult to cease operations quickly.
- Market Stalemate: Unprofitable firms remain in the market, preventing a natural reduction in competitor numbers.
- Intensified Rivalry: The presence of these trapped competitors leads to ongoing price competition and market share battles.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for Hormel Foods, driven by a crowded market with both large corporations and niche players. The U.S. packaged food sector, including Hormel's segments, faces slower growth projections for 2024, intensifying the battle for market share. Companies like Tyson Foods and General Mills are direct competitors, making differentiation through brands like SPAM and Planters crucial.
Hormel's strategy of brand building and innovation helps it stand out, but intense competition persists in categories with similar products. For instance, the salty snack market demands continuous investment to maintain an edge. Hormel's 2023 net sales of $12.3 billion reflect its ability to compete, yet the need for ongoing R&D to introduce new offerings is paramount in this dynamic landscape.
| Competitor Example | Hormel Brand Example | Key Competitive Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Tyson Foods | Jennie-O | Meat sector rivalry |
| General Mills | Hormel Chili | Broader food categories |
| Kraft Heinz | Skippy | Snack and pantry staples |
| Frito-Lay (PepsiCo) | Planters | Salty snacks competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The burgeoning plant-based food market presents a substantial threat of substitution for Hormel Foods. This sector is witnessing impressive growth, with projections indicating continued expansion fueled by consumer shifts towards healthier lifestyles, environmental sustainability, and ethical food choices. For instance, the global plant-based food market was valued at approximately $29.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $162 billion by 2030, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate of over 27%.
Hormel Foods, historically anchored by its extensive meat-based product lines such as SPAM and Jennie-O, faces a direct challenge from these rapidly evolving plant-based alternatives. Companies are innovating with diverse ingredients and product formats, offering consumers viable substitutes that cater to changing dietary preferences and ethical considerations, potentially diverting market share from traditional meat products.
The evolving dietary landscape presents a significant threat of substitutes for Hormel Foods. Trends like the rise of flexitarianism and a growing consumer focus on health and animal welfare are driving demand for plant-based and alternative protein options. For instance, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $6.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, directly impacting traditional meat consumption.
The cost-effectiveness of alternative food options significantly impacts consumer decisions. If plant-based or other novel food products become substantially more affordable or offer superior value compared to Hormel's offerings, the threat of substitutes escalates.
However, recent consumer sentiment suggests a growing dissatisfaction with plant-based meat alternatives, often citing issues with taste and texture. This could temper the immediate threat from these particular substitutes for Hormel Foods.
Innovation in Substitute Products
The threat of substitutes for Hormel Foods is amplified by continuous innovation in alternative food products. Advancements in plant-based meats, dairy alternatives, and other novel food technologies are making these options more appealing and accessible. For example, the plant-based meat market, which saw significant growth, continues to evolve with improved taste and texture, directly challenging traditional meat products. This ongoing development enhances the threat of substitution.
Key innovations impacting Hormel include:
- Plant-based protein advancements: Companies are investing heavily in R&D to mimic the sensory experience of meat, increasing consumer adoption.
- Dairy alternative expansion: A wider variety of oat, almond, and soy-based milks and cheeses offer competitive taste profiles and nutritional benefits.
- Cultivated meat research: While still nascent, the potential for lab-grown meat presents a future disruptive substitute.
Convenience and Accessibility of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Hormel Foods is amplified by the growing convenience and accessibility of alternative food options. Wider retail distribution, including dollar stores and discount grocers, alongside the proliferation of online grocery platforms and meal kit services, means consumers can easily find and purchase substitutes. For instance, the U.S. online grocery market reached an estimated $150 billion in 2024, highlighting this accessibility.
Foodservice channels, from fast-casual restaurants to ghost kitchens, also present readily available substitutes for many of Hormel's core products, like deli meats and prepared meals. As these alternatives become more mainstream and integrated into daily consumer habits, they pose a significant challenge to traditional packaged food manufacturers. This trend is evident in the continued growth of the foodservice industry, which is projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in sales in the U.S. by the end of 2025.
- Wider Retail Distribution: Increased presence in discount and convenience channels offers consumers more accessible substitute options.
- Online Platforms: E-commerce growth provides a vast array of alternative food products, from specialty items to direct-to-consumer brands.
- Foodservice Channels: Restaurants and meal delivery services offer convenient alternatives to home-prepared meals, impacting demand for ingredients and prepared foods.
- Growing Consumer Preferences: Shifts towards plant-based alternatives, fresh ingredients, and unique culinary experiences further expand the substitute landscape.
The threat of substitutes for Hormel Foods is substantial, driven by evolving consumer preferences for plant-based and alternative protein options. The global plant-based food market, valued at approximately $29.7 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $162 billion by 2030, indicating a strong growth trajectory that directly challenges Hormel's traditional meat-centric portfolio.
Innovations in plant-based meats and dairy alternatives are making these substitutes more appealing in taste and texture, further intensifying the competitive landscape. For instance, the plant-based meat market alone is expected to see significant expansion, directly impacting traditional meat consumption patterns.
The increasing accessibility of these substitutes through wider retail distribution and online platforms, coupled with their growing presence in foodservice, means consumers have more convenient choices than ever before. This broad availability, combined with shifts towards healthier and ethically sourced foods, amplifies the threat of substitution for Hormel Foods.
| Substitute Category | Market Value (2023 Est.) | Projected Growth Driver | Impact on Hormel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Foods | $29.7 Billion | Health, sustainability, ethics | Direct competition with meat products |
| Plant-Based Meats | $6.5 Billion | Taste, texture, convenience | Substitution for traditional meat items |
| Dairy Alternatives | Growing rapidly | Health, lactose intolerance, ethics | Competition for dairy-based product lines |
Entrants Threaten
The food manufacturing industry, particularly for large-scale operations like Hormel Foods, demands significant upfront capital. Building and maintaining state-of-the-art processing facilities, establishing robust distribution channels, and funding extensive marketing campaigns all require immense financial resources. For instance, constructing a new food processing plant can easily cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, a substantial hurdle for any aspiring entrant.
Established players like Hormel Foods enjoy significant cost advantages due to economies of scale. In 2023, Hormel's net sales reached $11.5 billion, reflecting a massive operational footprint that allows for lower per-unit production, purchasing, and distribution costs.
Newcomers face a steep uphill battle to match these efficiencies. Without the same volume, they cannot negotiate bulk discounts on raw materials or spread fixed costs like marketing and logistics across as many units, making it challenging to compete on price against Hormel's established cost structure.
Hormel Foods benefits from deeply ingrained brand loyalty, particularly with established products like SPAM and Jennie-O. This loyalty, cultivated over decades, makes it incredibly difficult for newcomers to capture market share without substantial investment in marketing and product development to achieve similar consumer trust and recognition. For instance, in 2023, Hormel's brand equity contributed significantly to its net sales of $12.5 billion, demonstrating the power of its established presence.
Access to Distribution Channels
Securing access to established retail outlets, foodservice distributors, and e-commerce platforms is a significant hurdle for new entrants in the food industry. Hormel Foods, with its long-standing relationships, already benefits from extensive distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, major retailers like Walmart and Kroger continued to consolidate shelf space, making it harder for unknown brands to gain traction.
New companies would find it challenging to secure prime shelf space and market access, especially when negotiating with large, powerful retailers and distributors who prioritize proven sales volumes and established brands. This limited access directly impacts a new entrant's ability to reach consumers effectively.
- Limited Shelf Space: Major retailers often have finite shelf space, prioritizing brands with strong sales history and marketing support, which new entrants typically lack.
- Distribution Agreements: Established food companies like Hormel have long-term contracts with major distributors, creating barriers for new players seeking to enter these channels.
- E-commerce Challenges: While e-commerce offers an alternative, gaining visibility and competitive placement on platforms like Amazon requires significant marketing investment and logistical capabilities that new entrants may struggle to afford.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The food industry, including companies like Hormel Foods, faces significant regulatory hurdles and stringent food safety standards. These requirements, such as those mandated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), demand substantial investment in compliance, quality control, and traceability systems.
Navigating these complex processes can be a major barrier for new entrants. For instance, obtaining necessary certifications, adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs), and ensuring product safety from farm to fork require specialized knowledge and considerable financial resources. This complexity discourages smaller players from entering the market, thereby reducing the threat of new competition.
- Regulatory Burden: New entrants must comply with a vast array of regulations concerning labeling, ingredients, processing, and distribution.
- Food Safety Compliance: Meeting rigorous food safety standards, like HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), involves significant upfront investment and ongoing operational costs.
- Time and Cost: The time and expense associated with achieving and maintaining regulatory compliance can deter potential new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for Hormel Foods is moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for establishing food manufacturing operations and distribution networks. While the industry offers opportunities, the sheer scale of operations and established brand loyalty create significant barriers.
New companies must overcome high upfront costs for facilities and marketing, which can easily run into millions of dollars. For example, in 2023, Hormel's net sales were $11.5 billion, showcasing the immense scale of established players that new entrants struggle to match in terms of cost efficiencies and market reach.
Furthermore, securing prime shelf space in major retail chains, a crucial element for sales, is challenging. In 2024, retailers continued to favor brands with proven sales performance, making it difficult for newcomers to gain visibility and compete effectively against established brands like Hormel's SPAM and Jennie-O.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for manufacturing facilities, R&D, and marketing. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Economies of Scale | Established players like Hormel (2023 net sales: $11.5 billion) benefit from lower per-unit costs. | Difficulty competing on price. |
| Brand Loyalty | Strong consumer trust in brands like SPAM. | Requires substantial marketing investment to build recognition. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to retail and foodservice networks is limited. | Challenges in reaching consumers effectively. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Stringent food safety and labeling standards. | Adds time and cost to market entry. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hormel Foods is built upon comprehensive data from Hormel's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports from firms like IBISWorld and Mintel. We also incorporate publicly available financial data and news releases from competitors to provide a well-rounded view of the competitive landscape.
