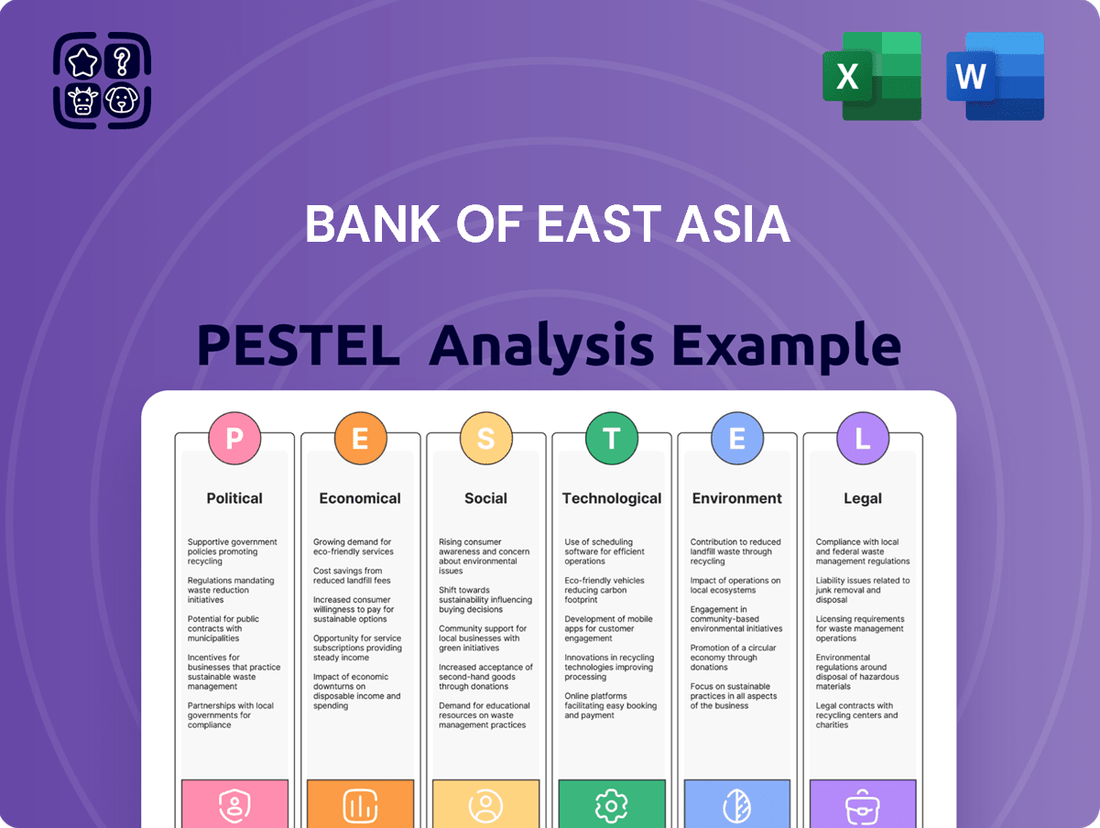
Bank of East Asia PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of East Asia Bundle
Uncover the critical Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting The Bank of East Asia. From shifting geopolitical landscapes to evolving consumer behaviors, understanding these external forces is paramount for strategic planning and competitive advantage. Our expertly crafted PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive overview, highlighting key opportunities and potential challenges.
Gain actionable intelligence on how regulatory changes and economic fluctuations will shape The Bank of East Asia's operations. This detailed report delves into the technological advancements and societal trends that are redefining the banking sector, offering you the foresight needed to adapt and thrive.
Make informed decisions with our in-depth PESTLE analysis, designed to equip investors, strategists, and business leaders with the insights necessary to navigate the complex external environment of The Bank of East Asia. Don't just react to change; anticipate it.
Download the full PESTLE analysis now and arm yourself with the critical understanding of The Bank of East Asia's external landscape. Unlock the insights that will drive your strategy and secure your success in the dynamic financial world.
Political factors
Government policies in both Hong Kong and Mainland China are key drivers for the Bank of East Asia (BEA). For example, Hong Kong's 2024-25 Budget emphasizes digital finance and bond market development, alongside Greater Bay Area financial integration. These initiatives create new avenues for BEA while also introducing evolving regulatory landscapes.
BEA's strategic planning is directly shaped by policies designed to bolster Hong Kong's position as a global financial hub. Measures aimed at improving stock market liquidity and accelerating digital transformation within the financial sector present both challenges and significant opportunities for the bank's growth and operational adjustments.
Escalating geopolitical tensions, especially between the United States and China, pose a significant risk to Bank of East Asia's operations. These tensions directly impact trade flows and overall economic activity within Hong Kong and Mainland China, which are key markets for BEA. For example, the US-China trade war, which saw tariffs imposed on hundreds of billions of dollars worth of goods, can disrupt supply chains and reduce cross-border commerce.
Increased tariffs and ongoing trade disputes can dampen demand for crucial banking services like trade financing. Furthermore, they create heightened pressure on the credit quality of industries heavily exposed to these tariffs, potentially leading to increased non-performing loans for BEA. As of early 2025, the global trade environment remains subject to these persistent uncertainties.
Despite these external challenges, the economic outlook for Mainland China in 2025 suggests that authorities possess policy levers to maintain stable economic growth. The Chinese government has demonstrated a capacity to implement measures to support economic activity, which could partially mitigate the negative impacts of geopolitical friction on BEA's business environment.
The political stability of Hong Kong and Mainland China is a cornerstone for Bank of East Asia's (BEA) operational continuity and maintaining investor trust. These regions are central to BEA's strategic positioning and future growth prospects.
Hong Kong's banking sector demonstrated notable resilience throughout 2024, successfully navigating a complex landscape influenced by US monetary policy shifts and persistent geopolitical uncertainties. However, continued monitoring of these external factors remains essential for sustained stability.
Encouraging policy adjustments within mainland China have injected a sense of renewed optimism for Hong Kong's banking sector towards the close of 2024 and into early 2025. This suggests a potentially more favorable operating environment.
Cross-Border Financial Cooperation
Cross-border financial cooperation, particularly within the Greater Bay Area (GBA), is a significant political driver for Bank of East Asia (BEA). BEA is actively working to expand its Wealth Management Connect (WMC) southbound business, facilitating increased investment and capital movement between mainland China and Hong Kong. This strategic focus not only supports BEA's growth but also reinforces Hong Kong's critical role as a leading offshore RMB business center. As of late 2024, the WMC scheme has seen steady growth in participation and transaction volumes, underscoring the effectiveness of these political initiatives.
This deepening of financial ties is crucial for BEA's strategy.
- GBA Integration: Political emphasis on GBA development fuels BEA's cross-border ambitions.
- Wealth Management Connect: BEA prioritizes expanding southbound WMC to attract mainland investors.
- RMB Hub: Cooperation bolsters Hong Kong's status as a global offshore RMB hub.
- Investment Flows: Initiatives aim to increase cross-boundary investment and fund management opportunities.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) Regulations
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) consistently strengthens its Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) framework. This includes implementing system reforms and technological innovations aimed at combating illicit financial activities. Bank of East Asia (BEA), as a key player in Hong Kong's financial landscape, must rigorously comply with these evolving regulations.
BEA's adherence to these stringent requirements is crucial for maintaining the integrity of Hong Kong's financial system and its global standing. This involves robust customer due diligence (CDD) processes, which include verifying customer identities and understanding their financial activities. Furthermore, enhanced transaction monitoring systems are essential to detect and report suspicious transactions promptly.
The HKMA's proactive approach ensures that financial institutions like BEA are equipped to combat financial crime. For instance, in 2023, the HKMA continued to emphasize the importance of technology in AML/CTF efforts, encouraging banks to leverage advanced analytics and artificial intelligence. BEA's investment in these areas directly supports its compliance obligations.
Failure to comply with AML/CTF regulations can result in significant penalties, including hefty fines and reputational damage. Therefore, BEA's commitment to these standards is not just a regulatory necessity but a strategic imperative for its long-term sustainability and trustworthiness in the international financial market.
- Enhanced Customer Due Diligence (CDD): BEA implements thorough identity verification and risk-based assessments for all customers.
- Transaction Monitoring: The bank utilizes sophisticated systems to scrutinize transactions for suspicious patterns.
- Regulatory Compliance: BEA actively adapts to updated guidelines issued by the HKMA to combat financial crime.
- Reputational Risk Management: Strong AML/CTF practices protect BEA's integrity and international standing.
Political stability in Hong Kong and Mainland China is crucial for Bank of East Asia's (BEA) operations. Government policies focusing on digital finance and Greater Bay Area (GBA) integration, as seen in Hong Kong's 2024-25 Budget, present both opportunities and regulatory challenges for BEA.
Geopolitical tensions, particularly between the US and China, impact trade flows and economic activity, affecting BEA's key markets. Trade disputes can reduce demand for services like trade financing and increase credit risks for affected industries, a concern as of early 2025.
Cross-border financial cooperation within the GBA is a significant political driver, with BEA expanding its Wealth Management Connect southbound business. This initiative, showing steady growth in late 2024, supports BEA's strategy and Hong Kong's role as an offshore RMB hub.
BEA must comply with stringent Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) regulations enforced by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA). This includes robust customer due diligence and transaction monitoring, with the HKMA encouraging technology adoption in these areas, as noted in 2023.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation of the external macro-environmental factors influencing the Bank of East Asia, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions to identify strategic opportunities and threats.
A clear, concise PESTLE analysis for Bank of East Asia that can be easily integrated into strategic planning documents, reducing the time spent on external environmental scanning.
Economic factors
Bank of East Asia anticipates a period of moderate economic expansion for both Chinese Mainland and Hong Kong in 2025. Projections indicate the Mainland's GDP could grow by approximately 4.8%, while Hong Kong is expected to see a growth rate of around 2.5%.
This steady growth trajectory is bolstered by proactive policy measures aimed at stabilizing the Mainland's economy. Concurrently, Hong Kong is benefiting from robust demand in its merchandise trade sector, contributing to its economic outlook.
The banking industry in Hong Kong has shown notable strength, as evidenced by a 4.5% increase in total assets during 2024. This resilience suggests a solid foundation for financial institutions operating within the region, even amidst broader economic uncertainties.
Interest rate fluctuations are a major driver for banks like Bank of East Asia (BEA), directly impacting their net interest margins. For instance, if rates fall, the spread between what banks earn on loans and pay on deposits narrows, potentially reducing profitability.
BEA is anticipating further interest rate cuts in 2025, with the direction of US monetary policy being a critical factor influencing their investment strategy. This expectation stems from global economic trends and potential shifts in central bank actions.
Hong Kong banks, including BEA, are likely to mirror anticipated US rate cuts. This means a gradual reduction in the Hong Kong Dollar (HKD) prime lending rate is probable throughout 2025. Such a move would directly affect the profitability of both lending activities and deposit-taking operations.
The property market in both Hong Kong and Mainland China significantly impacts Bank of East Asia (BEA), influencing its loan books and the overall quality of its assets. Projections suggest Hong Kong's home prices might see a recovery of approximately 5% in 2025.
Mainland China is actively implementing policies to stabilize its real estate sector, though challenges remain, particularly with commercial properties and ongoing subdued demand. Despite these broader market conditions, BEA demonstrated resilience, with its impaired loan ratio holding steady in 2024, indicative of effective risk management practices.
Inflation and Consumer Confidence
Inflation and consumer confidence are critical drivers of economic activity, directly impacting the retail banking and wealth management sectors. The Hong Kong SAR Government projects consumer price inflation to be around 1.5% in 2025. However, the economic landscape in 2024 presented a mixed picture, with high interest rates and subdued domestic consumption being counterbalanced by robust trade demand.
The banking sector is experiencing a resurgence in optimism, partially fueled by supportive policy initiatives from mainland China. These measures are designed to bolster consumer sentiment and, by extension, economic activity. A healthier consumer outlook generally translates to increased spending and investment, benefiting financial institutions.
- Inflation Forecast: Hong Kong SAR Government anticipates consumer price inflation to be 1.5% in 2025.
- 2024 Economic Factors: High interest rates and weak consumption were offset by strong trade demand.
- Sentiment Drivers: Positive policy measures in China are contributing to renewed optimism in the banking sector.
- Impact on Banking: Improved consumer confidence can lead to higher demand for retail banking and wealth management services.
Exchange Rate Volatility
Exchange rate volatility presents a significant factor for Bank of East Asia (BEA). Fluctuations in currency values, especially the Renminbi's movement against the Hong Kong Dollar, can directly influence BEA's international business performance and the profitability reported from its Mainland China operations. For instance, while the Renminbi experienced a roughly 2% depreciation against the Hong Kong Dollar in 2024, BEA China managed to report an increase in its net profit, showcasing a degree of operational resilience amidst these currency shifts.
Broader global exchange rate movements also play a crucial role, affecting the cost and ease of cross-border transactions and influencing international investment flows into and out of the regions where BEA operates. These external currency dynamics can impact BEA's treasury operations and the valuation of its foreign currency assets and liabilities.
- Renminbi Depreciation Impact: The Renminbi's depreciation against the Hong Kong Dollar can reduce the Hong Kong Dollar equivalent of profits earned in Mainland China.
- BEA China's Resilience: Despite a noted 2% Renminbi depreciation in 2024, BEA China's net profit saw an increase, indicating effective management or strong underlying business growth.
- Cross-Border Transaction Costs: Volatile exchange rates can increase the cost and complexity of international payments and remittances for BEA's clients.
- Investment Flow Sensitivity: BEA's investment portfolios, particularly those with international exposure, are subject to gains or losses driven by currency fluctuations.
Economic growth in both Mainland China and Hong Kong is projected to be moderate in 2025, with GDP growth anticipated at around 4.8% and 2.5% respectively. These forecasts are supported by policy measures aimed at economic stabilization in the Mainland and a strong performance in Hong Kong's merchandise trade. The banking sector in Hong Kong demonstrated resilience in 2024, with total assets increasing by 4.5%, indicating a solid financial foundation.
Interest rate movements significantly affect Bank of East Asia's profitability, particularly its net interest margins. Anticipated further interest rate cuts in 2025, influenced by US monetary policy, are expected to lead to a gradual reduction in the Hong Kong Dollar prime lending rate. This shift will directly impact the bank's lending and deposit-taking operations.
The property markets in Hong Kong and Mainland China are key influences on BEA's loan portfolios, with Hong Kong home prices expected to recover by approximately 5% in 2025. While Mainland China implements policies to stabilize its real estate sector, challenges persist. BEA maintained a steady impaired loan ratio in 2024, reflecting effective risk management.
Inflation in Hong Kong is forecast at 1.5% for 2025, according to the Hong Kong SAR Government. Despite past challenges like high interest rates and subdued consumption in 2024, renewed optimism in the banking sector is being fueled by supportive policy initiatives from Mainland China, which aim to boost consumer sentiment and economic activity.
Full Version Awaits
Bank of East Asia PESTLE Analysis
The preview you see here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of The Bank of East Asia delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations and strategic decisions. You'll gain a thorough understanding of the external forces shaping the bank's landscape, enabling informed strategic planning. This detailed report is your direct gateway to actionable insights.
Sociological factors
Customers are increasingly opting for digital banking platforms, valuing the convenience and speed they offer. This shift is evident in the growing usage of mobile apps and online services for everyday transactions. For Bank of East Asia (BEA), this translates into a strategic imperative to enhance its digital offerings to meet evolving customer expectations.
BEA has actively invested in its digital infrastructure, notably revamping its BEA Mobile app and BEA Corporate Online platform. These enhancements have been met with significant customer uptake, demonstrating a positive response to the bank's digital-first approach. This focus aligns with a broader societal trend towards mobile-centric lifestyles and the widespread adoption of digital payment solutions.
Hong Kong's population is aging rapidly, with individuals aged 65 and over projected to make up 30% of the total population by 2041. This demographic trend, coupled with the continued growth of an affluent middle class in both Hong Kong and Mainland China, significantly boosts the demand for sophisticated wealth management services. Bank of East Asia (BEA) is strategically positioned to meet these evolving financial needs.
BEA's commitment to wealth management is evident in its dedicated offerings like SupremeGold and SupremeGold Private Centres. These services are designed to cater to a broad spectrum of customers, from emerging affluent individuals to high-net-worth clients, providing personalized financial advice and investment solutions that align with their life stages and wealth accumulation goals.
Maintaining public trust is absolutely crucial for banks like the Bank of East Asia (BEA). In 2024, for instance, a significant majority of consumers globally indicated that a company's ethical practices heavily influence their purchasing decisions, underscoring the importance of trust.
BEA's dedication to corporate social responsibility (CSR) and sustainable development isn't just a nice-to-have; it's woven into how they do business, directly addressing what society expects from financial institutions. This proactive approach helps build and preserve their reputation.
The bank actively works to be a positive influence in the communities where it operates. By aligning its business strategies with broader societal well-being, BEA aims to foster a symbiotic relationship where stakeholder interests and community benefit go hand-in-hand.
Financial Literacy and Inclusion
The general level of financial literacy significantly impacts how readily people embrace sophisticated financial products and digital banking solutions. Bank of East Asia's (BEA) strategy of offering personalized solutions necessitates a deep understanding of financial literacy across its customer segments in Hong Kong and Mainland China. This insight is crucial for developing relevant product offerings and effective educational campaigns to boost financial inclusion.
Recent data highlights varying financial literacy levels. For instance, a 2023 survey indicated that while a majority of Hong Kong adults possess basic financial knowledge, a substantial portion still struggles with more complex concepts like investment risk. Similarly, in Mainland China, financial literacy is improving, driven by increased access to information, yet a gap persists, particularly in rural areas. BEA's approach must therefore segment its efforts, providing foundational education for some while offering more advanced insights for others.
- Hong Kong SAR: Approximately 60% of Hong Kong adults demonstrate a moderate to high level of financial literacy, according to a 2023 study by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority.
- Mainland China: The People's Bank of China reported in late 2024 that financial literacy scores have risen by 15% over the past five years, with digital financial literacy showing particular growth.
- Digital Adoption: BEA's digital banking services saw a 20% increase in active users in 2024, indicating a growing comfort with technology, but product complexity remains a barrier for some.
- Targeted Initiatives: BEA has launched online modules and workshops in 2025 aimed at improving understanding of investment products and digital security for its customer base.
Workforce Dynamics and Talent Retention
Societal shifts are significantly reshaping the labor landscape for Bank of East Asia (BEA). Employees increasingly prioritize work-life balance and demand greater diversity and inclusion within their workplaces. This necessitates that BEA adapts its talent management approaches to attract and keep skilled individuals. As of 2024, BEA's global workforce stands at approximately 8,000 employees.
Meeting these evolving expectations is vital for BEA to maintain a motivated and competent team. A highly engaged workforce is fundamental to delivering the personalized financial services that customers expect and is also a key driver for the bank's ongoing digital transformation initiatives. Failure to address these workforce dynamics could impact service quality and the pace of innovation.
Key workforce dynamics impacting BEA include:
- Demand for Flexibility: Growing preference for remote or hybrid work arrangements and flexible scheduling.
- Emphasis on DE&I: Increased societal and employee focus on diversity, equity, and inclusion in hiring and workplace culture.
- Continuous Learning: The need for ongoing skill development to keep pace with technological advancements and evolving financial markets.
- Purpose-Driven Work: Employees seeking roles that align with their values and contribute positively to society.
Societal expectations for banks like BEA are evolving, with a strong emphasis on ethical practices and corporate social responsibility. Customers increasingly scrutinize a company's values, making trust a paramount asset. BEA's proactive engagement in CSR initiatives and community support directly addresses these societal demands, bolstering its reputation.
The growing demand for wealth management services, driven by an aging population and an expanding affluent class in Hong Kong and Mainland China, presents a significant opportunity for BEA. The bank's tailored offerings like SupremeGold cater to these diverse needs, reflecting an understanding of demographic shifts.
Financial literacy levels also play a crucial role in customer adoption of digital and complex financial products. BEA's strategic focus on financial education and segmented outreach acknowledges varying literacy levels across its customer base, aiming to enhance financial inclusion.
Workforce expectations are shifting, with employees prioritizing work-life balance and diversity, equity, and inclusion (DE&I). BEA, employing around 8,000 individuals globally as of 2024, must adapt its talent strategies to attract and retain skilled professionals in this competitive landscape.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on BEA | 2024/2025 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Adoption & Convenience | Increased demand for seamless digital banking experiences. | BEA's mobile app active users grew 20% in 2024. |
| Demographics (Aging & Affluence) | Growing demand for wealth management and sophisticated financial products. | Hong Kong's 65+ population to reach 30% by 2041. |
| Ethical Practices & CSR | Importance of public trust and corporate responsibility for brand reputation. | Majority of consumers in 2024 influenced by ethical practices. |
| Financial Literacy | Impacts customer understanding and adoption of financial products. | HK financial literacy moderate-high for ~60%; China literacy up 15% in 5 years (2024). |
| Workforce Expectations (DE&I, Work-Life Balance) | Need for adaptive talent management to attract and retain employees. | BEA employed ~8,000 staff globally in 2024. |
Technological factors
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is heavily invested in digital transformation, integrating FinTech solutions to streamline operations and improve customer interactions. A key initiative is their Global Services Centre (GSC), which now serves as an IT Development & Test Centre specifically for FinTech and AI advancements.
This strategic focus on technological factors, particularly FinTech adoption, is crucial for BEA’s competitive edge. By establishing this dedicated center, the bank aims to equip its various business units with cutting-edge digital tools, thereby fostering innovation and efficiency in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
As digitalization accelerates, cybersecurity threats and data privacy are critical concerns for Bank of East Asia (BEA). BEA must prioritize ongoing investment in strong security infrastructure to safeguard customer information and preserve user confidence.
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) is implementing stricter regulations to counter digital banking fraud. This necessitates that financial institutions like BEA bolster their customer protection mechanisms and anti-fraud technologies.
For instance, in 2024, cybercrime costs globally are projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually, highlighting the significant financial and reputational risks. BEA's proactive stance on cybersecurity is therefore essential for its operational integrity and sustained growth.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively embedding AI and machine learning into its core operations, as demonstrated by its Global Services Centre. This strategic integration aims to significantly boost efficiency and customer experience.
These advanced technologies are instrumental in enhancing fraud detection capabilities, providing superior customer service via sophisticated chatbots, and streamlining internal processes for greater operational agility. For instance, in 2023, financial institutions globally saw a significant reduction in false positives for fraud alerts due to AI, with some reporting improvements of up to 30%.
The adoption of generative AI is particularly gaining momentum within Hong Kong's banking sector. This surge is further fueled by supportive government initiatives designed to foster technological advancement and digital transformation within the financial industry, positioning Hong Kong as a leader in FinTech innovation.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively engaging with blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) to enhance its operations and explore new digital asset opportunities. Hong Kong's financial landscape, particularly its banking sector, is a key area of focus for these advancements. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) launched a Supervisory Incubator for DLT in January 2025, signaling a concerted effort to foster innovation in this space.
BEA’s commitment is further demonstrated by its partnership with IDA to launch an HKD-pegged stablecoin. This initiative includes a trial phase involving a local payment gateway, showcasing BEA's practical application of DLT and its interest in digital asset innovation. This strategic move positions BEA to potentially leverage the efficiency and security benefits offered by these emerging technologies within the Hong Kong market.
The adoption of blockchain and DLT by banks like BEA is driven by several factors:
- Enhanced Efficiency: DLT can streamline processes like cross-border payments and trade finance, reducing settlement times and operational costs.
- Improved Security: The decentralized and cryptographic nature of blockchain offers robust security features, mitigating fraud and enhancing data integrity.
- New Revenue Streams: Stablecoins and other digital asset initiatives can open up new avenues for revenue generation and customer engagement.
- Regulatory Compliance: Early adoption and experimentation with DLT can help banks better understand and prepare for evolving regulatory frameworks surrounding digital assets.
Mobile Banking and Digital Payment Trends
The increasing prevalence of mobile banking and digital payment systems is a key technological influence. Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively responding to this trend, as evidenced by its updated mobile banking application and the introduction of BEA SmarTrade, an application dedicated to stock trading. This strategic focus aims to bolster BEA's digital offerings, anticipating that digital revenue streams will experience more robust growth compared to other banking channels.
Digital transformation continues to reshape the financial landscape, with consumers increasingly favoring convenient, app-based services. BEA's investment in its digital platforms reflects a broader industry movement towards enhancing customer experience through technology. For instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that over 80% of retail transactions in many developed markets will be conducted digitally, a figure that BEA is poised to capitalize on.
The bank's commitment to digital innovation is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and attracting a younger, tech-savvy customer base. BEA SmarTrade, specifically, targets investors looking for seamless mobile access to financial markets. This move aligns with the projected 15% year-over-year growth in the digital wealth management sector through 2025, indicating a significant opportunity for BEA to expand its market share.
- Mobile Banking Adoption: Global mobile banking users are expected to surpass 2.5 billion by 2025.
- Digital Payment Growth: The digital payments market is projected to reach over $15 trillion by 2025.
- BEA's Digital Strategy: BEA SmarTrade aims to tap into the growing demand for mobile investment solutions.
- Revenue Channel Shift: Digital channels are anticipated to drive a larger portion of BEA's future revenue growth.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is significantly integrating AI and machine learning to enhance efficiency and customer service, with financial institutions globally seeing up to a 30% improvement in fraud alert accuracy due to AI in 2023.
The bank is also exploring blockchain and DLT, evidenced by its partnership for an HKD-pegged stablecoin and the HKMA's January 2025 Supervisory Incubator for DLT, aiming for enhanced efficiency and security in operations.
Mobile banking and digital payments are key, with BEA launching BEA SmarTrade to capitalize on the projected 15% year-over-year growth in digital wealth management through 2025.
| Technology Area | BEA Initiative/Focus | Industry Trend/Statistic (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Embedding AI/ML in operations | AI expected to improve fraud detection accuracy by up to 30% |
| Blockchain/DLT | Stablecoin partnership, DLT exploration | HKMA's DLT Incubator launched Jan 2025 |
| Mobile Banking | Updated app, BEA SmarTrade launch | Digital wealth management growth projected at 15% YoY |
Legal factors
The Bank of East Asia (BEA) navigates a complex web of banking regulations, primarily dictated by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC). In 2025, the HKMA is undertaking a thorough self-assessment to verify adherence to the updated Basel Core Principles for Effective Banking Supervision, impacting BEA's operational standards.
Continuous compliance with capital adequacy ratios, liquidity management, and robust risk management frameworks remains a paramount operational focus for BEA. These ongoing requirements are crucial for maintaining financial stability and trust within the banking sector.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) must meticulously adhere to data protection and privacy laws in both Hong Kong and Mainland China. These regulations are fundamental to how BEA handles customer information, influencing everything from its digital banking platforms to its data analytics capabilities. For instance, Hong Kong's Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance (PDPO) sets strict guidelines for data collection and usage, while Mainland China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) imposes even more stringent requirements on data processing and cross-border transfers.
Navigating these diverse legal landscapes presents a significant challenge, particularly as BEA expands its digital services and leverages data for strategic insights. The increasing complexity and stringency of these laws, especially concerning the use of customer data for AI-driven services, act as a considerable hurdle for widespread AI adoption across the Asia-Pacific region, requiring substantial investment in compliance and data governance infrastructure.
Consumer protection laws are crucial for governing how the Bank of East Asia (BEA) markets and delivers its financial products and services. These regulations ensure fair treatment and transparency for customers, a key focus for the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA). For instance, the HKMA's 2025 priorities explicitly highlight investor and consumer protection, particularly concerning product selling practices and transaction processes.
BEA must diligently adhere to these directives, ensuring all its offerings are presented with clarity and fairness. This includes robust disclosure requirements for investments and loans. Failure to comply could result in significant penalties and reputational damage, impacting customer trust and market position.
Anti-Competitive Practices and Market Concentration
Competition laws significantly shape market dynamics and influence Bank of East Asia's (BEA) strategic approach to staying competitive. As a prominent independent local bank, BEA navigates a landscape teeming with both local and international financial institutions. Regulatory bodies actively scrutinize the financial sector for any anti-competitive behaviors, aiming to foster a fair and open marketplace for all participants.
The concentration of market power within the banking sector is a key area of regulatory focus. For instance, in Hong Kong, the banking industry is characterized by the presence of major banking groups, but regulatory frameworks are in place to prevent monopolistic tendencies. This ensures that smaller, independent banks like BEA can still operate and compete effectively. For example, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) is tasked with maintaining the stability and integrity of the financial system, which includes overseeing competition among banks.
- Regulatory Oversight: Competition laws and regulations directly impact how BEA can price its products, form partnerships, and expand its services to avoid being perceived as engaging in anti-competitive practices.
- Market Structure: While BEA is a significant player, the banking sector in its primary markets, particularly Hong Kong, is diverse, with a mix of large conglomerates and smaller specialized institutions, influencing overall market concentration.
- Fair Play Enforcement: Authorities like the HKMA monitor for practices such as price fixing or exclusionary conduct that could stifle competition, ensuring a level playing field.
- Impact on Strategy: BEA's strategies must inherently consider these legal constraints to ensure compliance and maintain its operational license and market reputation.
International Sanctions and Cross-Border Legal Frameworks
As a bank with extensive international operations, The Bank of East Asia (BEA) is deeply impacted by international sanctions and evolving cross-border legal frameworks. Navigating these complex regulations is crucial for maintaining its global business activities and avoiding significant penalties.
Geopolitical tensions directly influence BEA's operations. For instance, ongoing trade disputes, such as those between the United States and China, create intricate legal and compliance hurdles. These tensions can disrupt cross-border trade finance, affecting transactions and investment flows that are vital to the bank's revenue streams.
- Sanctions Compliance: BEA must adhere to sanctions lists imposed by bodies like the UN, OFAC, and EU, which can change frequently. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines, estimated in the billions of dollars for major financial institutions in recent years.
- Cross-Border Regulations: Varying data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations across different jurisdictions require robust compliance systems.
- Trade Finance Impact: Tariffs and sanctions can directly affect the volume and risk profile of trade finance deals, potentially reducing fee income and increasing credit risk exposure.
- Investment Restrictions: Geopolitical factors can lead to restrictions on foreign investment, impacting BEA's ability to facilitate capital flows and advisory services in certain markets.
Legal factors significantly shape BEA's operational landscape, demanding strict adherence to regulations from authorities like the HKMA and CBIRC. For example, the HKMA's 2025 focus includes verifying Basel Core Principles compliance, directly impacting BEA's supervisory standards.
Consumer protection laws are paramount, ensuring fair marketing and transparent product delivery, a key priority for the HKMA in 2025, especially concerning investment and loan disclosures. Competition laws also dictate market behavior, with regulators like the HKMA actively monitoring for anti-competitive practices to ensure a fair playing field within Hong Kong's diverse banking sector.
BEA must also navigate complex international sanctions and cross-border legal frameworks, with geopolitical tensions like US-China trade disputes creating compliance challenges for trade finance and investment flows.
| Regulatory Area | Key Mandate | 2024/2025 Focus/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Banking Supervision | Capital Adequacy, Liquidity Management, Risk Frameworks | HKMA's Basel Core Principles self-assessment (2025) |
| Data Privacy | Customer Information Protection | Compliance with HK PDPO and China's PIPL |
| Consumer Protection | Fair Product Marketing & Transparency | HKMA's 2025 priorities on selling practices |
| Competition Law | Preventing Anti-Competitive Behavior | HKMA oversight on market power and fair play |
| International Sanctions | Adherence to Global Sanctions Lists | Navigating evolving geopolitical tensions and trade disputes |
Environmental factors
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is making significant strides in sustainable finance, actively embedding Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles throughout its business. This commitment positions BEA as a leader in promoting responsible banking practices within its operational framework and investment decision-making.
The bank is dedicated to assisting its clients in achieving their ESG objectives, offering a growing suite of financial products and expert guidance. This includes providing access to various green funds and specialized ESG advisory services designed to meet evolving client needs.
Demonstrating its tangible support for sustainable investments, as of October 2024, BEA features 54 green funds that have received the Securities and Futures Commission stamp. This extensive offering underscores BEA's proactive role in channeling capital towards environmentally and socially conscious enterprises.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively addressing climate change, committing to net-zero financed emissions by 2050. This ambitious goal includes crucial near-term milestones, with plans to measure emissions and establish specific targets for carbon-intensive industries by 2025.
BEA's leadership in sustainability is evident through its pioneering status as the first Hong Kong-headquartered bank to join the Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials. Furthermore, it holds the distinction of being the first Chinese member of the Net-Zero Banking Alliance, underscoring its commitment to global climate action.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively bolstering its green and sustainable finance offerings, introducing products such as green loans, sustainability-linked loans, and social loans. These financial instruments are designed to channel capital towards projects with positive environmental and social impacts.
A key indicator of this strategic direction is BEA's commitment, as highlighted in its 2024-25 Budget welcome statement, to cultivate industries focused on green and innovative technologies. This proactive stance aligns with a broader global trend towards sustainable economic development and investment.
Environmental Reporting and Disclosure Requirements
Regulatory pressures mandating environmental reporting and disclosure are on the rise globally. Bank of East Asia (BEA) proactively addresses this through its annual ESG reports, transparently outlining its advancements in sustainability targets and adherence to established reporting frameworks.
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority's (HKMA) Sustainable Finance Action Agenda sets clear expectations for financial institutions. These include ambitious timelines for achieving net-zero emissions in financed activities by 2050 and in their own operational activities by 2030, underscoring the growing importance of environmental accountability for banks like BEA.
- Increasing Regulatory Scrutiny: Global regulators are intensifying requirements for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures.
- BEA's ESG Reporting: The bank publishes annual ESG reports detailing sustainability progress and compliance with reporting standards.
- HKMA's Net-Zero Targets: The HKMA expects banks to aim for net-zero financed emissions by 2050 and operational emissions by 2030.
Resource Management and Operational Footprint
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively managing its operational environmental footprint, setting a target of net-zero operations by the end of 2030. This commitment extends beyond just financed emissions, focusing on the direct impact of its own business activities. Initiatives are in place to enhance energy efficiency across its widespread network of branches and offices.
These efforts also encompass significant waste reduction programs and a broader strategy for responsible resource management. By the end of 2023, BEA reported a 15% reduction in energy consumption per employee compared to its 2020 baseline, a testament to its ongoing operational efficiency drive.
- Net-Zero Operations Target: Aiming for net-zero operations by year-end 2030.
- Operational Footprint Focus: Addressing energy efficiency, waste reduction, and resource management.
- Progress Indicator: Achieved a 15% reduction in energy consumption per employee by end of 2023 (vs. 2020 baseline).
Environmental factors significantly shape BEA's strategy, driven by increasing regulatory demands for ESG disclosures and a global push towards sustainability. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) mandates net-zero financed emissions by 2050 and operational emissions by 2030, influencing BEA's targets and reporting practices.
BEA is actively addressing climate change, aiming for net-zero financed emissions by 2050 and net-zero operations by 2030, demonstrating a commitment to reducing its environmental impact.
The bank's proactive stance includes a substantial offering of 54 green funds as of October 2024, supported by initiatives like green loans and sustainability-linked loans to channel capital towards eco-friendly projects.
BEA's operational efficiency is also a focus, with a 15% reduction in energy consumption per employee achieved by the end of 2023 compared to a 2020 baseline.
| Environmental Focus Area | BEA Target/Action | Key Metric/Date |
|---|---|---|
| Financed Emissions | Net-Zero Commitment | By 2050 |
| Operational Emissions | Net-Zero Commitment | By 2030 |
| Green Finance Offerings | Green Funds Available | 54 (as of Oct 2024) |
| Operational Efficiency | Energy Consumption Reduction | 15% per employee (by end 2023 vs. 2020) |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Bank of East Asia draws from a robust blend of official financial reports, government policy updates from China and Hong Kong, and reputable economic and market research databases. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental landscapes impacting the bank.
