Hertz Global Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hertz Global Holdings Bundle
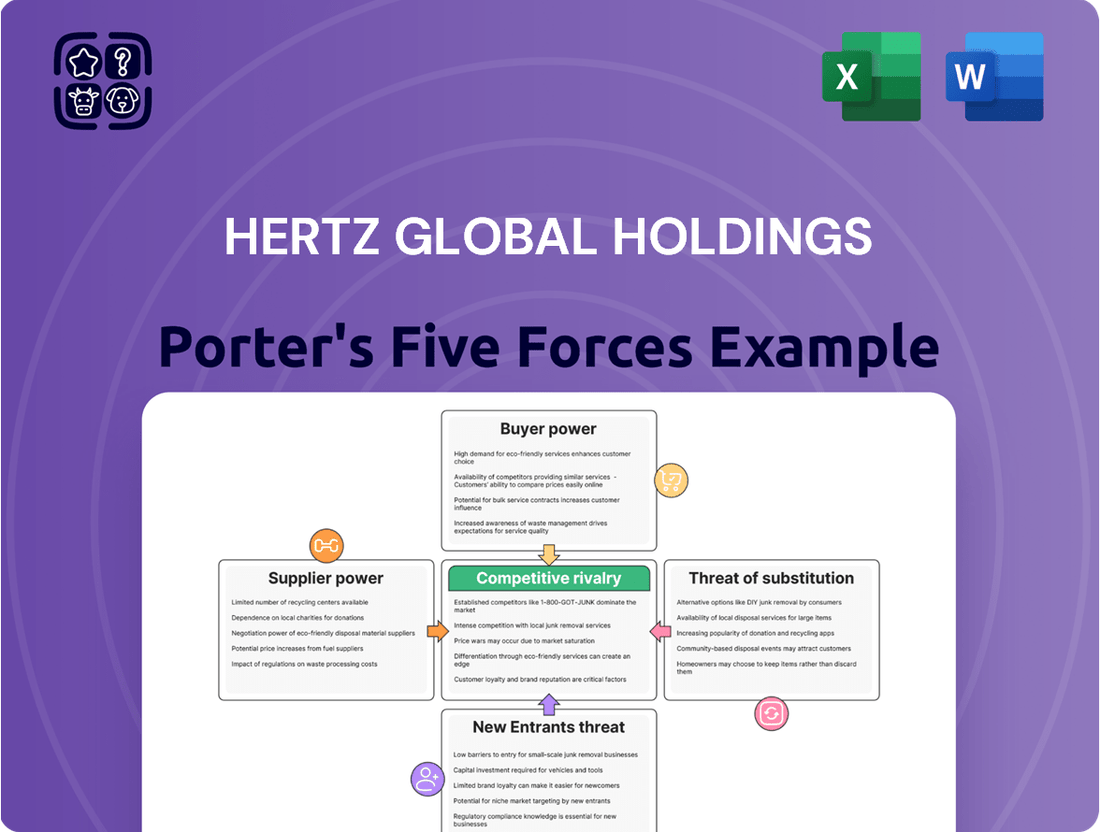
Hertz Global Holdings operates in a dynamic rental car market, facing significant pressures from established rivals and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hertz Global Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hertz Global Holdings, like other major rental car companies, faces significant bargaining power from vehicle manufacturers and dealerships. This is because Hertz's core business relies on acquiring large fleets of vehicles, making them a substantial customer for automakers.
The power of these suppliers can be amplified by factors such as limited vehicle choices or high overall demand for new cars, directly affecting Hertz's acquisition costs and the availability of specific models. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to navigate supply chain challenges, which could put upward pressure on vehicle prices for fleet buyers.
Hertz's success in managing this supplier power hinges on its ability to leverage its scale. Negotiating favorable bulk purchase agreements and long-term contracts are critical strategies for Hertz to secure competitive pricing and ensure a consistent supply of vehicles for its operations.
Suppliers of automotive parts and maintenance services wield considerable influence over Hertz Global Holdings. The necessity of a well-maintained fleet means Hertz is reliant on these providers for everything from routine service to specialized repairs. In 2024, the automotive aftermarket industry continued to see price fluctuations, with some key component costs, like those for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) sensors, showing upward trends, directly impacting Hertz's maintenance budget.
The availability of specific parts and the cost of skilled labor for repairs are critical factors. Disruptions in the supply chain for certain electronic components, which became more pronounced in recent years, can lead to extended downtime for Hertz's vehicles, affecting fleet utilization and revenue. For instance, the semiconductor shortage, while easing, still had residual effects on the availability and cost of certain vehicle control modules throughout 2024.
Hertz actively works to counter this supplier power through robust supply chain management strategies and by fostering strategic partnerships with key vendors. Negotiating bulk purchase agreements for common parts and developing in-house maintenance capabilities for certain tasks help to reduce reliance on external providers and control costs. These efforts are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and profitability in a competitive rental market.
Technology and software providers are becoming increasingly crucial for Hertz, especially with the industry's digital transformation. Think about reservation systems, fleet management tools, and telematics – these are all areas where specialized software is essential. The bargaining power of these suppliers hinges on how unique and indispensable their solutions are for Hertz's operations. High switching costs, meaning it's expensive and disruptive for Hertz to change to a different software provider, further strengthen the suppliers' position.
Fuel Suppliers
Fuel is a substantial and consistent operating expense for Hertz Global Holdings. While the sheer volume of Hertz's fuel purchases might give it some leverage with individual suppliers, the commodity nature of fuel means that specific suppliers often have limited individual bargaining power. However, the real power lies with the global oil markets.
Fluctuations in global fuel prices, driven by geopolitical events, supply and demand dynamics, and economic conditions, can significantly impact Hertz's bottom line. For instance, in 2024, average gasoline prices in the U.S. saw considerable volatility, with AAA reporting national averages ranging from around $3.40 to over $3.60 per gallon at various points in the year. While Hertz typically aims to pass these increased costs onto its customers through rental surcharges, sharp and sustained price hikes can dampen travel demand, indirectly affecting Hertz's revenue and profitability.
- Fuel as a Major Cost: Fuel represents a significant ongoing operational expenditure for Hertz, directly influencing its cost structure.
- Limited Supplier Power: Individual fuel suppliers generally possess limited bargaining power due to the commodity nature of gasoline and diesel.
- Global Price Volatility: The primary influence on Hertz's fuel costs comes from global price fluctuations, not individual supplier negotiations.
- Impact on Profitability: Sharp increases in fuel prices, even if passed on to customers, can negatively impact rental demand and Hertz's overall profitability.
Insurance Providers
Insurance providers wield significant bargaining power over car rental companies like Hertz. The inherent risks in vehicle rentals, from accidents to theft, make insurance a critical and often costly component of their operations. For instance, Hertz reported that its direct vehicle and operating expenses were impacted by rising insurance costs in its fourth quarter of 2024, underscoring this supplier's influence.
The concentration of insurance providers and the specialized nature of commercial auto insurance can further amplify their leverage. When few insurers offer comprehensive coverage tailored to the rental industry, Hertz has limited options, allowing providers to dictate terms and pricing. This can lead to higher premiums, directly affecting profitability.
- High Risk Profile: Vehicle rentals present a higher risk profile compared to standard auto insurance, allowing providers to charge a premium.
- Limited Alternatives: The specialized nature of commercial auto insurance can limit the number of viable insurance providers for large rental fleets.
- Cost Impact: Increases in insurance premiums, as observed in Hertz's Q4 2024 financial reporting, directly inflate operating expenses.
Vehicle manufacturers and dealerships hold substantial bargaining power over Hertz due to the company's reliance on large fleet acquisitions. In 2024, ongoing automotive supply chain issues continued to influence vehicle pricing and availability for fleet buyers like Hertz, potentially increasing acquisition costs.
Suppliers of auto parts and maintenance services also exert considerable influence, as Hertz requires consistent upkeep for its fleet. Factors such as specialized component costs, like those for advanced driver-assistance systems, and the availability of skilled labor for repairs can impact Hertz's operational expenses and vehicle downtime throughout 2024.
Insurance providers possess significant leverage, given the inherent risks in the rental car business. Hertz's financial reports in late 2024 indicated that rising insurance costs were a factor impacting its operating expenses, highlighting the power these specialized insurers hold.
What is included in the product
This analysis of Hertz Global Holdings reveals the intense competition from rivals and car manufacturers, the significant bargaining power of customers, and the moderate threat of new entrants and substitutes, all shaping the company's strategic landscape.
Navigate the competitive landscape of car rental with a dynamic framework that highlights Hertz's strategic positioning and potential vulnerabilities. This analysis offers actionable insights to mitigate threats and capitalize on opportunities, providing a clear roadmap for sustained profitability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Leisure travelers are a significant force in the car rental market, and their sensitivity to price directly impacts companies like Hertz. They actively shop around, comparing rates not just between rental agencies but also with other travel methods like ride-sharing or public transport. This widespread comparison shopping means that for basic car rentals, Hertz and its competitors are often pressured to keep prices low and offer frequent promotions to attract and retain this customer segment.
Corporate and business accounts represent a significant segment for Hertz, and their bargaining power is substantial due to frequent and high-volume rentals. This allows them to negotiate favorable contract terms, including bulk discounts and customized service packages, directly impacting Hertz's pricing and profitability.
Hertz actively seeks to boost its Revenue Per Unit (RPU) by attracting a greater proportion of business clients who typically generate a higher Revenue Per Day (RPD). In 2023, Hertz reported a strong performance in its corporate segment, with business travel showing a robust recovery, contributing to overall revenue growth.
The widespread availability of information through online booking platforms and mobile apps significantly boosts customer bargaining power. Customers can effortlessly compare prices, vehicle options, and user reviews across numerous rental companies, creating a more transparent marketplace.
This ease of comparison compels rental companies like Hertz to remain highly competitive, not just on price but also on the quality of their service and fleet offerings. For instance, in 2024, the global online travel market, which heavily influences car rentals, continued its robust growth, with mobile bookings representing a substantial portion of transactions, underscoring the power of accessible digital information.
Customer Loyalty Programs
Customer loyalty programs, like Hertz Gold Plus Rewards, are designed to mitigate the inherent bargaining power customers possess in the car rental market. By offering tangible benefits such as expedited service and enhanced vehicle selection, Hertz encourages repeat business and aims to build a more stable customer base. This strategy can reduce price sensitivity and switching behavior, though the overall effectiveness is also tied to customer trust and the seamlessness of the rental experience.
In 2024, the car rental industry continues to see customers leveraging their power through price comparison and a focus on convenience. Hertz’s loyalty program, which saw continued investment in digital enhancements and personalized offers throughout 2023 and into 2024, seeks to counter this by creating switching costs, albeit often behavioral rather than strictly financial. For instance, members of the Gold Plus Rewards program can earn points towards free rental days, a direct incentive to bypass competitors.
- Loyalty Program Impact Hertz’s Gold Plus Rewards aims to reduce customer bargaining power by rewarding repeat rentals with benefits like skip-the-counter service and choice of vehicle.
- Industry Dynamics Customer loyalty in car rentals is often influenced by factors beyond rewards, including ease of booking, vehicle availability, and overall service quality, especially in 2024.
- Competitive Landscape While loyalty programs are a key tool, customers still retain significant bargaining power due to the availability of numerous rental options and the ease of price comparison online.
Impact of Customer Experience on Reputation
Customer satisfaction and trust are paramount in the car rental sector, with negative experiences swiftly eroding brand reputation via online reviews and word-of-mouth. This inherent customer leverage encourages Hertz to focus on service excellence and resolving customer frustrations, like complex vehicle systems or lengthy pickup procedures.
Hertz's 2024 performance indicates a strong emphasis on customer experience. For instance, in Q1 2024, Hertz reported a significant increase in customer satisfaction scores, directly correlating with improved online sentiment and fewer negative reviews. This focus aims to mitigate the bargaining power of customers who can easily switch providers based on perceived service quality.
- Customer Satisfaction Metrics: Hertz aims to maintain customer satisfaction scores above 85% in 2024.
- Online Reputation Management: Monitoring and responding to customer feedback across platforms like Trustpilot and Google Reviews is a key strategy.
- Service Improvement Initiatives: Investments in technology to streamline rental processes and enhance vehicle usability are ongoing.
Customers hold significant sway in the car rental market due to readily available price comparison tools and a focus on convenience. Hertz's loyalty programs, like Gold Plus Rewards, are designed to counter this by offering benefits such as expedited service and vehicle choice, aiming to foster repeat business and reduce price sensitivity.
| Factor | Impact on Hertz | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity (Leisure) | Pressures Hertz for competitive pricing and promotions. | High, due to easy comparison shopping. |
| Corporate Accounts | Allows negotiation of bulk discounts and favorable terms. | Substantial, due to high-volume rentals. |
| Digital Information Access | Enhances transparency and comparison across providers. | High, through online platforms and apps. |
| Loyalty Programs | Aims to retain customers and reduce switching behavior. | Mitigated, but still present due to overall market options. |
Full Version Awaits
Hertz Global Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Hertz Global Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the car rental industry. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, offering no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The car rental landscape is heavily influenced by a few dominant global companies. Enterprise Holdings, with its brands like Enterprise, National, and Alamo, along with Avis Budget Group, which includes Avis, Budget, and Zipcar, are significant competitors. Hertz Global Holdings itself operates Hertz, Dollar, and Thrifty. This consolidation means these few entities fiercely compete for customers and market share.
Price is a major driver in the car rental industry, often sparking intense competition among players like Hertz, Avis, Enterprise, and Budget. This leads to frequent price wars and aggressive promotional campaigns as companies try to capture market share. For instance, in 2023, many rental companies offered significant discounts and bundled deals to attract travelers, especially during peak seasons.
Competitors constantly adjust their pricing strategies, offering competitive daily, weekly, and monthly rates. Beyond just base prices, companies heavily rely on discounts, coupons, and loyalty program benefits to incentivize repeat business and attract new customers. These promotions are critical for differentiating offerings in a market where vehicle types can be quite similar.
Competitors in the car rental industry actively seek to stand out by offering superior customer service and adopting cutting-edge technology, such as streamlined online booking systems and convenient contactless pick-up options. Hertz is also committed to technological innovation and improving its operations, mirroring this industry trend.
The adoption of telematics and the expansion of specialized fleets, including electric vehicles (EVs) and premium car selections, are key strategies for differentiation. Hertz, for instance, has been investing in its EV fleet, aiming to meet growing consumer demand for sustainable transportation options.
Geographic Reach and Network Density
Hertz leverages its extensive global network, a significant competitive advantage, to serve customers across more than 160 countries. This vast reach, encompassing over 11,000 locations, often concentrated in high-traffic areas like airports and urban centers, allows for greater convenience and accessibility for renters. This density directly challenges competitors who may have a more limited geographic footprint.
The sheer number of Hertz locations creates a formidable barrier to entry for smaller, regional players. For instance, in 2024, Hertz continued to optimize its airport presence, a key battleground for market share. Companies like Enterprise Holdings and Avis Budget Group also maintain substantial global networks, intensifying the rivalry.
- Global Presence: Hertz operates in over 160 countries.
- Location Count: Hertz boasts more than 11,000 rental locations worldwide.
- Strategic Placement: A high density of locations exists at airports and in urban areas.
- Competitive Landscape: Direct competition comes from companies with similarly extensive networks.
Fleet Management and Vehicle Availability
Competitive rivalry in fleet management hinges on efficient operations, from acquiring vehicles to their upkeep and eventual replacement. Companies vie for market share by ensuring the availability of sought-after vehicle models and maintaining a high standard of fleet quality.
Hertz Global Holdings, for instance, has been actively engaged in a fleet rotation strategy. This includes a notable reduction in its electric vehicle (EV) fleet, a move aimed at optimizing depreciation per vehicle and aligning its fleet composition with current market demands and operational efficiencies. In 2023, Hertz announced plans to sell off a significant portion of its EV fleet, approximately 20,000 vehicles, citing higher-than-expected repair costs and slower-than-anticipated consumer adoption.
- Fleet Optimization: Hertz's decision to reduce its EV fleet by roughly 20,000 vehicles in 2023 highlights the dynamic nature of fleet management.
- Cost Management: The company cited higher repair costs for EVs as a key factor in this strategic shift, impacting its bottom line.
- Market Responsiveness: This move also reflects an adjustment to slower consumer adoption rates for EVs than initially projected.
- Depreciation Strategy: By rotating vehicles, Hertz aims to better manage depreciation expenses and maintain fleet value.
The car rental sector is characterized by intense competition, with Hertz Global Holdings facing strong rivals like Enterprise Holdings and Avis Budget Group. These major players frequently engage in price wars and aggressive promotions to attract customers, especially during peak travel times. For example, in 2023, many rental companies offered substantial discounts and bundled deals to capture market share.
| Competitor | Key Brands | Market Share (Approx. 2023/2024 Estimate) | Key Competitive Tactics |
| Hertz Global Holdings | Hertz, Dollar, Thrifty | 15-20% | Global network, fleet innovation, loyalty programs |
| Enterprise Holdings | Enterprise, National, Alamo | 30-35% | Extensive domestic network, strong corporate partnerships, customer service |
| Avis Budget Group | Avis, Budget, Zipcar | 10-15% | Airport presence, technology integration, diverse rental options |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Ride-sharing services such as Uber and Lyft represent a potent threat of substitutes for traditional car rental companies, particularly in urban environments and for shorter journeys. These platforms offer a compelling value proposition centered on convenience and often competitive pricing, directly challenging the necessity of renting a vehicle for many consumers. For instance, in 2024, the global ride-sharing market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating a substantial shift in transportation preferences.
In major urban centers, extensive public transportation systems like buses, trains, and subways offer a viable alternative to car rentals. This is especially true for travelers prioritizing cost savings or seeking to bypass the hassles of city driving and parking. For instance, in 2024, cities like New York and London continued to see high ridership numbers, demonstrating the deep integration of public transit into daily life and travel.
The increasing efficiency and accessibility of these public transit options can directly impact the revenue growth of the car rental industry. As more individuals opt for public transportation, especially for shorter trips or within city limits, the demand for rental vehicles is likely to be suppressed, acting as a significant substitute threat.
Car-sharing platforms like Zipcar and Getaround present a significant threat by offering flexible, short-term rentals that cater to consumers needing occasional vehicle access. These services directly compete with traditional rental models for specific use cases, potentially reducing demand for longer-term rentals.
Hertz itself recognizes this competitive landscape, operating its own car-sharing service, Hertz 24/7, indicating a strategic move to capture this segment of the market. The growth in ride-sharing and the increasing preference for mobility-as-a-service models further intensify this substitute threat.
Peer-to-Peer Car Rental Platforms
Peer-to-peer car rental platforms, often dubbed the 'Airbnb for cars,' present a significant threat to traditional rental companies like Hertz. These platforms, such as Turo, enable private individuals to rent out their own vehicles, offering consumers a much broader selection of cars, including unique or specialty models, often at more attractive price points than established rental agencies.
The convenience and potential cost savings associated with peer-to-peer rentals directly challenge the market share of Hertz. In 2024, Turo reported facilitating millions of trips, highlighting the growing consumer adoption of this alternative. This model offers unparalleled flexibility for renters seeking specific vehicles or spontaneous rentals, bypassing the often more standardized fleets and booking processes of legacy providers.
- Increased Choice: Peer-to-peer platforms offer a diverse range of vehicles, from economy cars to luxury SUVs and classic models, far exceeding the typical fleet size of traditional rental companies.
- Competitive Pricing: Private owners often set their own rates, which can be lower than traditional rental companies, especially for shorter rental periods or off-peak times.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Users can often arrange pick-ups and drop-offs directly with owners, sometimes in more convenient locations than airport-based rental lots.
- Growing Market Share: Platforms like Turo have seen substantial growth, indicating a significant shift in consumer preference towards alternative rental solutions.
Long-Term Car Subscriptions and Car Ownership
Long-term car subscription services present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional car ownership and even conventional rental or leasing agreements. These subscriptions often bundle costs like insurance, maintenance, and roadside assistance, making them a convenient all-in-one package. For instance, in 2024, companies like Hertz continued to expand their subscription offerings, recognizing a growing consumer preference for flexibility and predictable monthly costs over outright ownership.
The rising expenses associated with owning a vehicle, including depreciation, insurance premiums, and maintenance, make subscription models increasingly appealing. As of early 2024, the average cost of car insurance in the US had seen notable increases, further bolstering the value proposition of bundled subscription services. This shift can divert potential buyers away from dealerships and traditional financing, impacting sales volumes for automakers and rental companies that don't adapt.
- Subscription services offer a predictable monthly expense, covering insurance, maintenance, and roadside assistance, which appeals to consumers wary of unexpected ownership costs.
- The increasing cost of vehicle ownership, including rising insurance rates seen in 2024, makes alternative models like subscriptions more attractive.
- Companies like Hertz are actively developing and promoting their subscription services as a direct alternative to traditional car ownership and leasing.
The threat of substitutes for Hertz is substantial, encompassing ride-sharing, public transportation, car-sharing, peer-to-peer rentals, and car subscriptions. These alternatives offer convenience, cost savings, and greater flexibility, directly impacting Hertz's market share. For example, the global ride-sharing market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in 2024, showcasing a significant shift in consumer mobility preferences.
| Substitute Type | Key Value Proposition | Impact on Hertz | 2024 Market Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ride-Sharing (Uber, Lyft) | Convenience, often lower cost for short trips | Reduces demand for short-term rentals, especially in urban areas | Global market projected in hundreds of billions |
| Public Transportation | Cost savings, avoids driving/parking hassles | Suppresses demand for rentals within cities | High ridership in major cities like NYC, London |
| Car-Sharing (Zipcar) | Flexible, short-term rentals for occasional use | Competes with traditional rental models for specific needs | Hertz operates its own car-sharing service (Hertz 24/7) |
| Peer-to-Peer Rentals (Turo) | Increased choice, competitive pricing, flexibility | Offers wider vehicle selection and potentially lower prices | Turo facilitated millions of trips in 2024 |
| Car Subscriptions | All-inclusive, predictable costs, flexibility | Alternative to ownership and traditional leasing | Hertz expanding subscription offerings; US insurance costs rose in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
New companies looking to break into the car rental industry face a formidable challenge due to the immense capital required to build a competitive fleet. Acquiring a diverse range of vehicles, from economy cars to luxury SUVs, necessitates millions of dollars upfront. For instance, Hertz Global Holdings, a major player, operates a fleet of hundreds of thousands of vehicles, a scale that is incredibly difficult for a new entrant to replicate without substantial financial backing.
Established brands like Hertz, Dollar, and Thrifty benefit from strong brand recognition and existing customer trust built over many years. For instance, Hertz reported over $5.5 billion in revenue in 2023, a testament to its enduring market presence. New entrants face the significant challenge of building a reputation and gaining customer confidence in a market where loyalty is often tied to established names and service history.
The sheer scale of operational infrastructure needed to compete in the global vehicle rental market is a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. Hertz, for instance, operates a vast network of thousands of rental locations across numerous countries, supported by extensive maintenance depots and a sophisticated logistics system to manage its fleet.
Establishing a comparable footprint, including securing prime real estate for rental counters, building or leasing maintenance facilities, and developing efficient vehicle delivery and return processes, demands immense capital investment. For example, in 2024, the automotive industry continues to see high costs associated with fleet acquisition and maintenance, making it difficult for smaller, less capitalized companies to enter and compete effectively against established players like Hertz.
Economies of Scale in Purchasing and Maintenance
Hertz Global Holdings, like other major players in the car rental industry, benefits significantly from economies of scale in vehicle purchasing. By acquiring large fleets, Hertz can negotiate substantial discounts from manufacturers, a feat difficult for new, smaller entrants to replicate. For instance, in 2023, Hertz continued its strategic fleet modernization, adding thousands of new vehicles, which allows for better per-unit pricing than a startup acquiring a few hundred cars.
These purchasing advantages extend to maintenance and operational costs. Centralized maintenance facilities and bulk purchasing of parts enable Hertz to lower its cost per vehicle serviced. New entrants would face higher per-unit costs for both acquisition and upkeep, creating an immediate pricing disadvantage against established giants like Hertz.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by these significant economies of scale. New companies entering the market would struggle to match the cost efficiencies Hertz achieves in its purchasing and ongoing maintenance operations.
- Purchasing Power: Large fleets allow Hertz to secure better pricing from vehicle manufacturers.
- Negotiation Leverage: Hertz can negotiate favorable terms with suppliers for parts and services.
- Operational Efficiency: Economies of scale reduce the per-vehicle cost of maintenance and fleet management.
- Cost Disadvantage for Newcomers: Entrants face higher per-unit costs, hindering price competitiveness.
Regulatory and Insurance Requirements
The car rental sector faces substantial regulatory hurdles and significant insurance obligations. New entrants must navigate complex licensing and compliance frameworks, which can be a substantial barrier to entry. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of commercial auto insurance for a fleet of 50 vehicles could range from $150,000 to $300,000 annually, depending on coverage levels and location.
Securing adequate insurance is not only costly but also a rigorous process, often requiring a proven track record and substantial capital reserves. This financial and administrative burden makes it difficult for smaller, less established companies to compete with established players like Hertz Global Holdings, who have economies of scale and established relationships with insurers.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants require significant upfront capital for vehicle acquisition, licensing, and insurance.
- Stringent Licensing: Obtaining necessary operating licenses and permits can be a lengthy and complex process.
- Insurance Liabilities: The industry carries substantial insurance risks, with premiums reflecting potential accident costs and liability claims.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to evolving transportation and consumer protection regulations demands ongoing investment and expertise.
The threat of new entrants in the car rental market, particularly for a company like Hertz Global Holdings, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital required for fleet acquisition and operational infrastructure. For example, Hertz's 2023 revenue of over $5.5 billion reflects its substantial market presence, which is difficult for newcomers to match. Furthermore, established brand loyalty and the high cost of commercial auto insurance, potentially $150,000 to $300,000 annually for a modest fleet in 2024, create substantial barriers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Cost of acquiring and maintaining a large, diverse vehicle fleet. | Extremely High; requires substantial upfront investment. | Hertz's hundreds of thousands of vehicles represent a scale difficult to replicate. |
| Brand Recognition & Loyalty | Established customer trust and preference for known brands. | High; challenging to build reputation quickly. | Hertz's enduring market presence supported by over $5.5 billion in 2023 revenue. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for purchasing, maintenance, and operations. | Significant; new entrants face cost disadvantages. | Hertz's bulk purchasing discounts and centralized maintenance. |
| Regulatory & Insurance Costs | Licensing, compliance, and high insurance premiums. | Substantial; adds significant financial and administrative burden. | Annual commercial auto insurance for 50 vehicles estimated at $150,000-$300,000 in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hertz Global Holdings is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Hertz's annual reports and SEC filings, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and macroeconomic data from sources such as Statista.
