Hengyi Petrochemical Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hengyi Petrochemical Bundle
Hengyi Petrochemical navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense competition, significant supplier leverage, and the ever-present threat of substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder in the petrochemical sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hengyi Petrochemical’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hengyi Petrochemical's dependence on critical raw materials like paraxylene (PX) for its PTA production and crude oil for its refining activities significantly influences supplier power. The global paraxylene market is expected to grow to 96.40 million tons by 2034, with Asia Pacific, including China, being the leading consumer.
Fluctuations in crude oil prices directly affect the cost of PX, a key feedstock. This price volatility can empower suppliers of these essential materials, as Hengyi Petrochemical faces increased input costs, potentially squeezing profit margins if these costs cannot be passed on to customers.
The market for primary petrochemical feedstocks, such as crude oil and naphtha, is often characterized by a limited number of major global suppliers. This concentration can grant these suppliers considerable bargaining power, allowing them to influence pricing and terms. For Hengyi Petrochemical, this means that securing reliable and cost-effective raw materials is a constant consideration.
Hengyi Petrochemical actively works to manage this supplier concentration risk. By diversifying its supplier base and establishing long-term supply contracts, the company aims to secure stable feedstock availability and favorable pricing. However, even with these strategies, global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical events, or significant shifts in energy markets can still impact feedstock availability and costs, posing ongoing challenges.
Switching suppliers for critical raw materials like paraxylene and crude oil can involve substantial costs for Hengyi Petrochemical. These costs include the re-calibration of manufacturing processes, implementing new quality assurance protocols, and the potential for significant production disruptions during the transition period. For instance, in 2023, Hengyi's reliance on a stable supply chain was evident, with crude oil prices fluctuating significantly, making supplier changes a costly endeavor.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Hengyi Petrochemical's PTA or polyester fiber production represents a significant potential shift in market dynamics. Should key raw material providers make this move, they would transition from being suppliers to direct competitors, inherently boosting their leverage and bargaining power over Hengyi. This scenario, while less frequent in the commodity chemical sector, poses a notable long-term risk.
While direct forward integration by raw material suppliers into PTA or polyester fiber production is not a prevalent strategy in the current petrochemical landscape, the possibility remains a strategic consideration for Hengyi Petrochemical. The financial health and strategic objectives of major upstream players could, in the future, incentivize such a move. For instance, if a major PTA feedstock supplier, like a large-scale naphtha cracker operator, experiences significant margin compression in its core business, it might explore vertical integration as a means to capture more value further down the chain.
- Potential Competitive Landscape Shift: Suppliers integrating forward could directly compete with Hengyi in PTA and polyester fiber markets.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: This integration would grant suppliers greater bargaining power, potentially leading to less favorable terms for Hengyi.
- Long-Term Strategic Threat: While not currently widespread, this remains a potential future risk that requires ongoing monitoring.
- Industry Dynamics: The petrochemical industry's capital-intensive nature and cyclical profitability can influence supplier strategic decisions regarding integration.
Uniqueness of Input
While paraxylene and crude oil are largely commodity chemicals, the bargaining power of suppliers can increase if Hengyi Petrochemical requires specific grades or specialized derivatives with limited alternative sources. For instance, disruptions in the supply of high-purity paraxylene, crucial for PTA production, could significantly impact Hengyi's operations. In 2023, global paraxylene prices fluctuated, with some regional shortages impacting availability and potentially strengthening supplier leverage for specific product types.
Hengyi Petrochemical's strategic approach, including robust supplier relationship management and its significant vertical integration, plays a vital role in mitigating these supplier-specific pressures. By securing long-term contracts and investing in its own refining and petrochemical assets, Hengyi aims to reduce its reliance on external suppliers for critical inputs. This integration allows for greater control over the supply chain, buffering against price volatility and availability issues for key raw materials.
Key considerations regarding the uniqueness of inputs for Hengyi Petrochemical include:
- Niche Petrochemical Feedstocks: While bulk commodities are readily available, specialized catalysts or additives required for certain high-performance polymer production might have a concentrated supplier base, granting those suppliers more leverage.
- Geopolitical Supply Chain Risks: Dependence on crude oil from specific regions can introduce geopolitical risks, potentially limiting supplier options and increasing bargaining power for those unaffected by regional instability.
- Technological Dependencies: If Hengyi relies on proprietary technologies that necessitate specific, uniquely sourced components or intermediates, the suppliers of these specialized items would possess considerable bargaining power.
- Contractual Safeguards: The terms of Hengyi's supply contracts, including volume commitments and pricing mechanisms, are critical in defining the actual bargaining power of its suppliers, especially for less commoditized inputs.
Hengyi Petrochemical's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the availability of critical feedstocks like paraxylene (PX) and crude oil. The global PX market, projected to reach 96.40 million tons by 2034, with Asia Pacific as a key consumer, highlights the importance of securing these inputs. Limited global suppliers for essential petrochemical feedstocks, such as crude oil and naphtha, can grant them significant pricing power, directly impacting Hengyi's input costs and profit margins.
Hengyi actively manages supplier concentration through diversification and long-term contracts to ensure stable feedstock availability and favorable pricing. However, global supply chain disruptions and geopolitical events remain persistent challenges. The cost of switching suppliers for critical materials, involving process recalibration and quality assurance, can be substantial, as seen with crude oil price volatility in 2023.
The potential for raw material suppliers to integrate forward into Hengyi's PTA or polyester fiber production poses a long-term strategic threat, potentially transforming them into direct competitors and increasing their leverage. While not currently widespread, this scenario could be incentivized by margin pressures on upstream players, such as naphtha cracker operators looking to capture more value.
| Factor | Impact on Hengyi Petrochemical | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Feedstock Availability (PX, Crude Oil) | Concentration of suppliers can increase their bargaining power. | Global PX market growth to 96.40 million tons by 2034, with Asia Pacific leading consumption. |
| Input Cost Volatility | Fluctuations in crude oil prices directly affect PX costs, impacting Hengyi's margins. | Crude oil prices experienced significant volatility in 2023. |
| Switching Costs | High costs associated with changing suppliers for critical raw materials. | Process recalibration and quality assurance protocols make supplier changes costly. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential for suppliers to become competitors, increasing their leverage. | Industry dynamics and profitability pressures may incentivize integration. |
What is included in the product
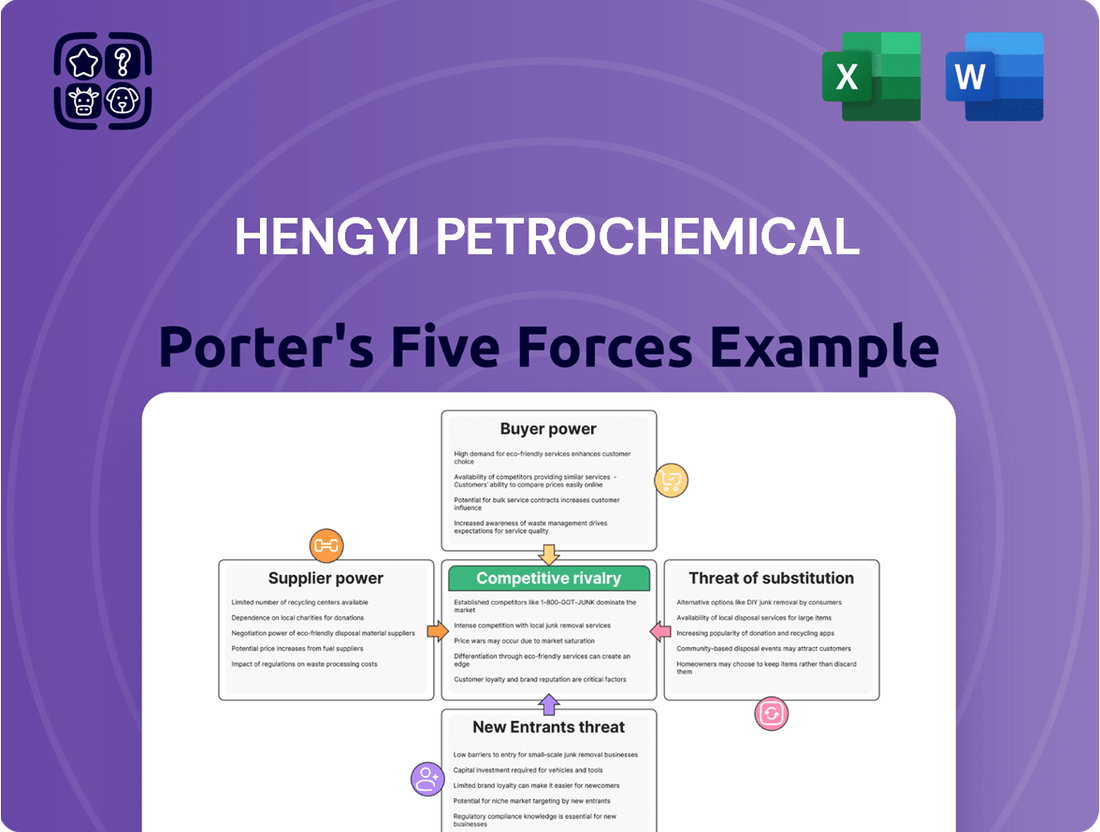
This analysis of Hengyi Petrochemical's competitive landscape reveals the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Hengyi Petrochemical's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making and strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hengyi Petrochemical's customer base is spread across various downstream sectors like textiles, apparel, home furnishings, and packaging. This wide distribution means that individual customers typically don't represent a large chunk of Hengyi's overall sales volume.
Consequently, the bargaining power of any single customer is generally low. Their inability to influence pricing or terms significantly is a key factor in Hengyi's market position.
Hengyi Petrochemical's customers, particularly those in the textile and packaging sectors, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is largely due to intense competition within their own industries, forcing them to seek the lowest possible input costs for polyester fibers and PTA.
This heightened price sensitivity directly impacts Hengyi, as it can lead to downward pressure on the company's product prices and, consequently, its profit margins. This effect is amplified during times of oversupply in the broader petrochemical market, where buyers have more choices and leverage.
The availability of alternatives significantly impacts Hengyi Petrochemical's customer bargaining power. While polyester remains a dominant material, customers can explore options like organic cotton or nylon, especially as sustainability concerns grow. For instance, the global organic cotton market was valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2023, indicating a substantial alternative for textile manufacturers.
Customer Information and Transparency
Increased transparency in the petrochemical industry, particularly regarding pricing and supply chain details, significantly boosts customer bargaining power. This allows buyers to compare offers more readily and push for more favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, global petrochemical prices experienced volatility, giving informed customers leverage to seek discounts.
Despite this trend, Hengyi Petrochemical can mitigate customer power through its specialized product portfolio and by fostering robust, long-term customer relationships. These factors create switching costs and loyalty, enabling Hengyi to retain a degree of pricing control. The company's focus on high-value, differentiated products in 2024 helped it maintain margins even amidst market fluctuations.
- Increased transparency in pricing and supply chain information empowers customers to negotiate better terms, especially during periods of market volatility like seen in 2024.
- Hengyi Petrochemical can counter this by offering specialized, high-value product lines that are less commoditized.
- Cultivating strong, enduring relationships with key clients also enhances customer loyalty and reduces their inclination to switch, thereby preserving Hengyi's pricing power.
Volume of Purchases
The volume of purchases significantly influences customer bargaining power within the petrochemical industry. Large industrial clients, such as textile manufacturers or packaging companies, that buy substantial quantities of PTA (Purified Terephthalic Acid) or polyester fibers can leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate more competitive pricing and favorable contract terms with suppliers like Hengyi Petrochemical.
Hengyi Petrochemical's operational model, characterized by its large-scale production facilities, is strategically designed to cater to these high-volume customers, aiming to achieve economies of scale that can translate into cost efficiencies. This allows Hengyi to potentially offer attractive pricing to its major buyers.
For instance, in 2023, Hengyi Petrochemical reported significant revenue streams, indicating its capacity to serve a broad base of industrial customers. The company's ability to produce millions of tons of polyester and PTA annually positions it as a key supplier capable of meeting the demands of large-scale operations. This scale is a critical factor in its ability to manage customer relationships and pricing dynamics.
Key considerations regarding the volume of purchases include:
- Customer Concentration: A few large customers making up a significant portion of total sales increase their individual bargaining power.
- Volume Discounts: Offering tiered pricing based on purchase volume incentivizes larger orders and can be a point of negotiation.
- Supplier Dependence: If a customer relies heavily on a single supplier for a critical input, their bargaining power might be somewhat limited, but high volume can still be a strong lever.
- Market Share Impact: Securing large, consistent orders from major players contributes significantly to Hengyi's market share and production utilization rates.
Hengyi Petrochemical's customers, particularly large-scale textile and packaging manufacturers, possess considerable bargaining power due to their significant purchase volumes. These major buyers can leverage their substantial orders to negotiate more favorable pricing and contract terms with Hengyi.
The company's ability to meet these high-volume demands, supported by its extensive production capacity, allows it to offer competitive pricing, thereby managing this aspect of customer power. For example, Hengyi's 2023 financial reports indicated substantial sales volumes, underscoring its role as a key supplier capable of satisfying large industrial clients.
While customers' price sensitivity and the availability of alternatives like organic cotton (valued at USD 2.5 billion in 2023) can exert downward price pressure, Hengyi's strategy of offering specialized products and cultivating strong client relationships helps to retain pricing control. Increased market transparency in 2024 further empowers buyers, making Hengyi's focus on differentiation and loyalty crucial.
| Factor | Impact on Hengyi | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase Volume | Hengyi's scale caters to large buyers, enabling competitive pricing. | High volume allows negotiation for better prices and terms. |
| Price Sensitivity | Intense competition in downstream industries drives demand for lower input costs. | Customers actively seek the lowest prices, pressuring Hengyi's margins. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Growing demand for sustainable materials like organic cotton presents options. | Customers can switch to alternatives, reducing reliance on petrochemicals. |
| Market Transparency | Easier access to pricing and supply chain data empowers buyers. | Customers can compare offers and negotiate more effectively, especially during 2024's market volatility. |
Same Document Delivered
Hengyi Petrochemical Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hengyi Petrochemical, detailing the competitive landscape, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products. The insights provided are directly applicable to understanding Hengyi's strategic positioning within the petrochemical industry. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The petrochemical industry, especially in the PTA and polyester fiber sectors, features many large, established companies, particularly in Asia. Hengyi Petrochemical contends with global and regional giants such as Exxon Mobil, Reliance Industries, Shell, Sinopec, and BASF.
While the global polyester fiber market shows promise, the broader petrochemical industry faces a demand slowdown and overcapacity, which naturally fuels more intense rivalry among companies. This environment means players are constantly vying for market share.
The paraxylene market, crucial for producing PTA (a key polyester ingredient), is projected to see a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.59% between 2025 and 2034. This growth, though positive, occurs within a sector already grappling with excess capacity, further intensifying competitive pressures.
PTA and standard polyester fibers are largely commodity products, meaning competition often boils down to price. This intense price-based rivalry is a significant factor for companies like Hengyi Petrochemical.
Hengyi actively works to counter this by focusing on product differentiation. Their strategy includes developing and marketing eco-friendly polyester options and high-value-added fibers, which helps them move away from direct price comparisons with competitors.
For instance, in 2024, the global polyester fiber market, while vast, saw many players heavily reliant on bulk production. Hengyi's investment in specialized, sustainable, and performance-oriented fibers aims to capture higher margins and reduce vulnerability to commodity price fluctuations.
Exit Barriers
The petrochemical industry, including players like Hengyi Petrochemical, faces significant exit barriers due to immense capital investments in plant and equipment. These high fixed costs make it economically unfeasible for companies to simply shut down operations, even when facing losses. For instance, a new ethylene cracker can cost billions of dollars to build, representing a sunk cost that heavily influences strategic decisions.
These substantial exit barriers often contribute to persistent overcapacity within the petrochemical sector. Companies, hesitant to abandon their massive investments, may continue to operate at suboptimal levels, leading to aggressive pricing strategies and reduced profitability for all involved. This reluctance to exit can exacerbate competitive intensity, especially during periods of economic slowdown or declining demand.
- High Capital Intensity: Petrochemical plants require billions in initial investment, creating a significant financial hurdle for exiting the market.
- Specialized Assets: Equipment is often highly specialized and has limited alternative uses, diminishing resale value if a facility is closed.
- Long-Term Commitments: Many operations involve long-term supply contracts and labor agreements that are difficult and costly to terminate.
Cost Structure and Efficiency
Companies that can produce goods or services at a lower cost and operate more efficiently naturally gain an edge over their rivals. This is especially true in the petrochemical industry where scale and integration are key drivers of profitability.
Hengyi Petrochemical's strategy centers on creating cost efficiencies through its vertically integrated model, encompassing refining, processing, and distribution. This integration allows for better control over the supply chain and potential cost savings at various stages.
- Cost Advantage: Lower production costs directly translate to higher profit margins or the ability to offer more competitive pricing, thereby attracting a larger customer base.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes and optimized resource utilization reduce waste and enhance overall productivity, contributing to a stronger financial performance.
- Hengyi's Integration: By controlling multiple stages of the value chain, Hengyi aims to mitigate supply disruptions and capture value at each step, bolstering its competitive positioning.
- 2024 Data Point: While specific 2024 cost structure data for Hengyi is still emerging, the company has historically focused on achieving economies of scale, with its large-scale refining and chemical complexes being central to this strategy. For context, in 2023, Hengyi Petrochemical reported revenue of approximately RMB 129.3 billion, indicating significant operational scale.
Competitive rivalry within the petrochemical sector, particularly for products like PTA and polyester fibers, is intense due to the presence of numerous large-scale global and regional players. Hengyi Petrochemical competes with industry giants such as Sinopec, Reliance Industries, and Exxon Mobil. The market is characterized by overcapacity and a general demand slowdown, forcing companies to aggressively vie for market share, often through price competition.
The paraxylene market, a key precursor for PTA, is expected to grow, but this growth occurs within an already capacity-heavy environment, amplifying competitive pressures. As PTA and standard polyester fibers are commodities, price becomes a primary battleground, impacting profitability for all participants.
Hengyi Petrochemical seeks to mitigate this by focusing on product differentiation, such as developing eco-friendly and high-value-added fibers. This strategy aims to command better margins and reduce reliance on pure price competition, a critical move in the 2024 market landscape where bulk production dominates many segments.
| Competitor | Primary Products | Estimated 2024 Market Position (General) |
|---|---|---|
| Sinopec | Refined products, petrochemicals, synthetic fibers | Leading global player, strong domestic presence in China |
| Reliance Industries | Petrochemicals, refining, textiles | Major integrated player in India, significant global reach |
| Exxon Mobil | Refining, petrochemicals, specialty chemicals | Global energy and chemical giant, broad product portfolio |
| BASF | Chemicals, materials, industrial solutions | World's largest chemical producer, diverse offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Natural fibers such as organic cotton, hemp, and bamboo present a growing threat as substitutes for polyester in the textile and apparel industries. Consumer preference is increasingly shifting towards sustainable and natural materials, fueled by heightened environmental awareness. For instance, the global organic cotton market was valued at approximately USD 10.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong demand for these alternatives.
While polyester dominates many textile applications, other synthetic fibers such as nylon and acrylic present a degree of substitutability. For instance, nylon is often preferred for its superior strength and elasticity in applications like hosiery and activewear. Acrylic fibers can substitute for wool due to their softness and warmth, finding use in sweaters and blankets.
However, polyester's widespread adoption is largely due to its inherent advantages. In 2024, the global polyester fiber market was valued at approximately $100 billion, underscoring its significant market share. This dominance stems from polyester's cost-effectiveness compared to many other synthetics, its excellent durability and wrinkle resistance, and its versatility across a broad range of uses, from apparel to home furnishings and industrial textiles.
The growing availability of bio-based plastics and chemicals, sourced from materials like corn, sugarcane, and algae, presents a substantial long-term threat to traditional petrochemical products. For instance, the global bioplastics market was valued at approximately USD 11.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 30.8 billion by 2028, indicating a strong upward trend in adoption.
Furthermore, recycled polyester, often denoted as rPET, is becoming a direct and more environmentally friendly substitute for virgin polyester, a key product for companies like Hengyi Petrochemical. The demand for recycled textiles is surging, with the global recycled polyester market expected to grow significantly, driven by consumer preference for sustainable fashion and stricter environmental regulations.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are continuously introducing more viable substitutes for petrochemical products. For instance, ongoing research and development in sustainable materials, including next-generation synthetic fibers like protein-based textiles, could lead to more competitive and environmentally friendly alternatives. These innovations have the potential to significantly disrupt the traditional petrochemical-based fiber market, impacting demand for Hengyi Petrochemical's offerings.
The drive for sustainability is a key factor. By 2024, the global market for bio-based plastics, a direct substitute for many petroleum-derived plastics, was projected to reach substantial figures, indicating growing consumer and industry preference for greener options. This trend directly challenges the market share of conventional petrochemical outputs.
- Growing Market for Bio-based Materials: The global bio-based chemicals market is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth through 2025, presenting a direct substitute threat.
- Innovation in Textile Fibers: Developments in biodegradable and recycled synthetic fibers offer alternatives to virgin petrochemical-based textiles.
- Environmental Regulations: Increasing regulatory pressure favoring sustainable materials can accelerate the adoption of substitutes over petrochemical products.
- Consumer Demand Shift: A noticeable trend shows consumers increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly products, driving demand away from traditional petrochemical derivatives.
Shifting Consumer Preferences and Regulations
Growing environmental consciousness is a significant driver, pushing consumers toward greener options and away from traditional petrochemicals. This trend is amplified by increasingly stringent government regulations designed to curb plastic pollution and lower carbon footprints.
These factors collectively intensify the threat of substitution for products derived from petrochemicals. For instance, the global bioplastics market, a direct substitute, is projected to reach approximately $10.7 billion by 2027, up from an estimated $4.5 billion in 2022, indicating a substantial shift.
- Increased consumer demand for sustainable materials: Consumers are actively seeking out products made from recycled content or biodegradable materials.
- Stricter environmental regulations: Governments worldwide are implementing policies to limit single-use plastics and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from manufacturing.
- Growth of alternative materials: The development and adoption of bio-based plastics, recycled polymers, and other sustainable alternatives are directly challenging petrochemical product dominance.
- Impact on petrochemical demand: These shifts can lead to reduced demand for virgin petrochemical feedstocks as industries pivot to more environmentally friendly inputs.
The threat of substitutes for Hengyi Petrochemical's products is multifaceted, stemming from both natural and synthetic alternatives, as well as innovative bio-based materials.
While polyester remains dominant due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility, with the global market valued around $100 billion in 2024, consumer demand is increasingly shifting towards sustainable options. The growing preference for natural fibers like organic cotton, which saw a market value of approximately USD 10.2 billion in 2023, and recycled materials directly challenges petrochemical-based products.
Furthermore, the bioplastics market, a direct substitute for many petroleum-derived plastics, is experiencing robust growth, projected to reach USD 30.8 billion by 2028 from USD 11.7 billion in 2023. This expansion, coupled with advancements in biodegradable synthetics and increasing environmental regulations, intensifies the pressure on traditional petrochemical outputs.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples | Market Context/Growth | Impact on Petrochemicals |
| Natural Fibers | Organic Cotton, Hemp, Bamboo | Global organic cotton market ~USD 10.2 billion (2023); growing consumer preference for sustainability. | Reduces demand for synthetic fibers like polyester in textiles. |
| Other Synthetics | Nylon, Acrylic | Nylon preferred for strength/elasticity; Acrylic substitutes for wool. | Offers performance-driven alternatives in specific applications. |
| Bio-based Materials | Bioplastics (from corn, sugarcane) | Global bioplastics market ~USD 11.7 billion (2023), projected to USD 30.8 billion by 2028. | Directly competes with petroleum-based plastics and chemicals. |
| Recycled Materials | Recycled Polyester (rPET) | Surging demand driven by sustainable fashion and regulations. | Offers a greener alternative to virgin polyester, impacting feedstock demand. |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a large-scale petrochemical enterprise like Hengyi Petrochemical demands substantial capital for advanced refining, PTA, and polyester fiber production facilities. For instance, building a new integrated refining and petrochemical complex can easily cost billions of dollars, making it a formidable hurdle for any new entrant.
These high initial investment requirements create a significant barrier, deterring many potential competitors from entering the market. The sheer scale of funding needed to match existing players' capacities and technological capabilities is often prohibitive.
Existing large-scale petrochemical players, like Sinopec and PetroChina, leverage massive production capacities, allowing them to spread fixed costs over a greater output. This translates to lower per-unit production costs, a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, major integrated refining and petrochemical complexes often boast capacities exceeding 10 million tons per year, a scale that is prohibitively expensive for a new entrant to replicate quickly.
New entrants face the daunting task of achieving comparable cost efficiencies in raw material procurement and logistics. Established companies benefit from bulk purchasing power and optimized supply chains, securing raw materials like crude oil and naphtha at more favorable terms. This cost advantage makes it challenging for smaller, less established entities to compete on price in the global petrochemical market.
The petrochemical sector faces significant regulatory hurdles, particularly concerning environmental compliance. New entrants must contend with complex permitting processes that are both time-consuming and expensive, slowing down market entry. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to strengthen its emissions standards under the Green Deal, requiring substantial upfront investment in cleaner technologies for any new petrochemical facilities.
Access to Raw Materials and Distribution Channels
Newcomers face significant hurdles in securing consistent supplies of essential raw materials like crude oil and paraxylene, which are critical for petrochemical production. Hengyi Petrochemical, for instance, benefits from its established upstream integration and long-term supply agreements, providing a stable and cost-effective feedstock. This access is not easily replicated by new entrants.
Developing a robust and widespread distribution network is another formidable barrier. Hengyi Petrochemical has invested heavily in logistics infrastructure, including storage facilities and transportation capabilities, enabling efficient delivery to a broad customer base. New companies would need substantial capital and time to build comparable networks.
- Raw Material Access: Hengyi Petrochemical's integrated supply chain, extending to crude oil sourcing, significantly reduces its vulnerability to raw material price volatility compared to new, non-integrated players.
- Distribution Network: The company's extensive network of terminals and logistics partnerships across key markets provides a competitive advantage in reaching customers efficiently.
- Capital Investment: Establishing similar levels of raw material access and distribution infrastructure would require billions of dollars in upfront investment for any new entrant.
Technological Expertise and Intellectual Property
The production of PTA and polyester fibers, key products for Hengyi Petrochemical, relies heavily on intricate chemical processes and specialized technology. Newcomers face a steep climb, needing to invest substantially in acquiring or developing this advanced technological know-how. For instance, achieving efficient PTA synthesis often involves proprietary catalyst technologies and precise reaction control, areas where established players like Hengyi have years of operational refinement.
Furthermore, intellectual property rights can act as a significant barrier. Patents covering specific production methods, catalyst formulations, or product enhancements can prevent new entrants from utilizing the most cost-effective or efficient technologies without licensing agreements, which can be costly and difficult to secure. This technological moat is crucial in an industry where efficiency gains directly translate to competitive pricing and profitability.
- Technological Complexity: Manufacturing PTA and polyester requires advanced chemical engineering expertise and specialized equipment.
- Intellectual Property: Existing patents on production processes and catalysts can create significant hurdles for new market entrants.
- R&D Investment: New companies would need substantial investment in research and development to match the technological capabilities of established firms like Hengyi Petrochemical.
The threat of new entrants for Hengyi Petrochemical is relatively low due to immense capital requirements, with new integrated petrochemical complexes costing billions of dollars to establish. For example, building a new refinery and petrochemical facility in 2024 could easily exceed $10 billion. This financial barrier, coupled with the need for advanced technology and established supply chains, deters most potential competitors.
Existing players benefit from economies of scale, with major complexes in 2024 operating at capacities over 10 million tons per year, creating significant cost advantages. New entrants also face challenges securing raw materials at competitive prices and building extensive distribution networks, which require substantial investment and time. Regulatory compliance, particularly environmental standards, adds further complexity and cost for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost for New Entrant (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Building integrated refining and petrochemical facilities | $10 Billion+ |
| Economies of Scale | Matching existing capacities (e.g., 10M+ tons/year) | Prohibitive for initial entry |
| Raw Material Access & Distribution | Establishing secure supply chains and logistics networks | Billions of dollars |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hengyi Petrochemical Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and official filings with regulatory bodies. We supplement this with insights from reputable industry analysis firms and macroeconomic data providers to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
