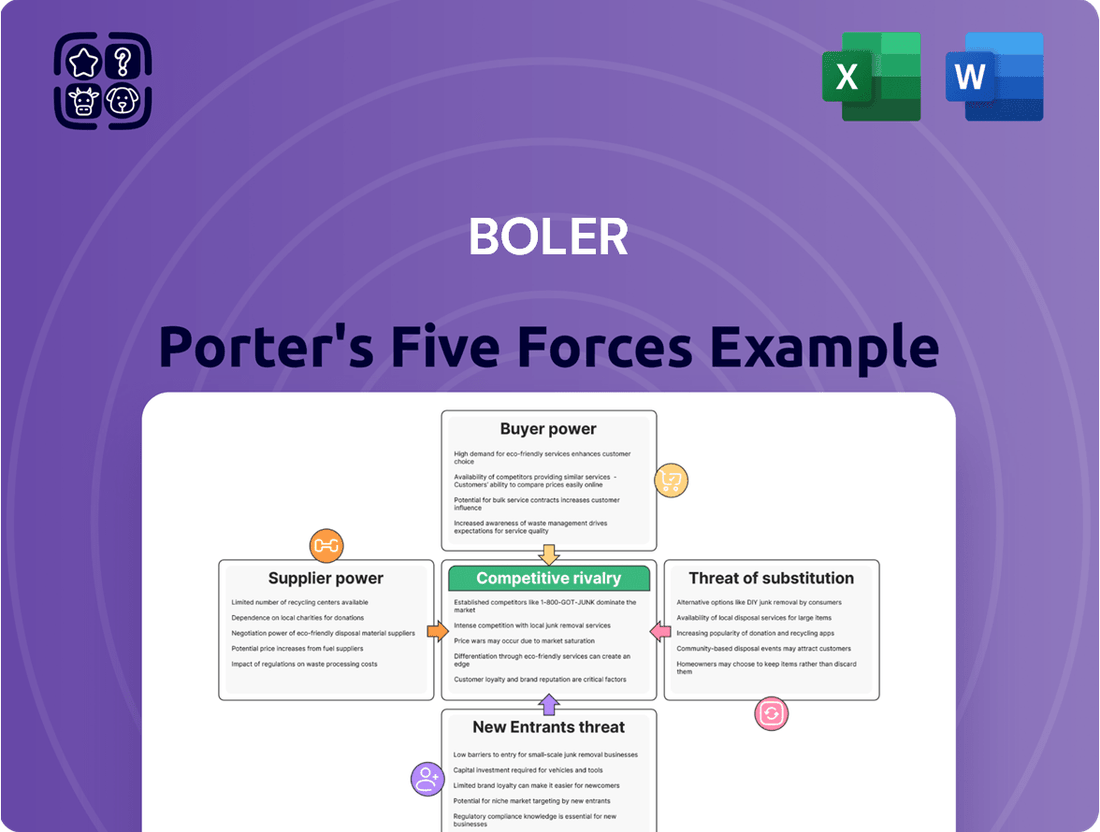
Boler Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Boler Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and Porter's Five Forces provides a powerful framework to dissect industry dynamics. This analysis delves into the forces impacting Boler, revealing the underlying pressures that shape its market. By examining these forces, you can gain a clearer picture of Boler's strategic positioning and potential challenges.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Boler’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical components significantly impacts bargaining power. For instance, if the commercial vehicle suspension market relies on a few specialized manufacturers for advanced materials or unique engineering, these suppliers hold considerable sway over companies like Hendrickson.
This concentration allows them to potentially dictate pricing or supply terms, as Hendrickson may have limited alternatives. In 2024, the automotive supply chain continued to grapple with consolidation in certain high-tech sectors, reinforcing the leverage of concentrated suppliers.
When suppliers offer unique technology, specialized materials, or patented components, their bargaining power significantly increases. For instance, a supplier providing advanced composites essential for lightweighting commercial vehicles, a key trend in the 2024 market aiming for fuel efficiency, would command greater leverage. This is particularly relevant for critical parts like those in advanced suspension systems, such as electronically controlled or air suspension components.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hendrickson is significantly influenced by switching costs. These costs encompass expenses related to retooling manufacturing equipment, re-certifying new components to meet stringent quality standards, or even re-engineering existing designs to accommodate alternative materials or parts. For instance, if a key supplier for Hendrickson's axle components were to increase prices, the cost and time required to switch to a new supplier, including the validation of new parts, could run into millions of dollars and cause significant production delays.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers possess the capability and incentive to move forward and manufacture suspension systems themselves, their bargaining power significantly increases. This threat is more pronounced when suppliers serve a wide range of manufacturers rather than highly specialized niche markets.
For instance, in the automotive sector, a large Tier 1 supplier capable of designing and assembling complete suspension modules could potentially bypass existing manufacturers and sell directly to consumers or other assemblers, thereby capturing a larger portion of the value chain. This forward integration capability forces existing manufacturers to offer more favorable terms to retain their suppliers.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: Suppliers who can integrate forward gain greater control over pricing and distribution channels.
- Market Disruption Potential: Forward integration by suppliers can disrupt existing market structures and competitive dynamics.
- Impact on Component Suppliers: Highly specialized component suppliers are less likely to integrate forward, but broad-based suppliers pose a greater threat.
- Strategic Consideration for Buyers: Manufacturers must assess the forward integration risk from their suppliers when negotiating contracts and developing supply chain strategies.
Importance of Hendrickson to Suppliers
Hendrickson's significance to its suppliers directly impacts the bargaining power of those suppliers. If Hendrickson constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier's leverage is considerably weakened. For instance, in 2024, a supplier heavily reliant on Hendrickson's orders, perhaps accounting for over 30% of their sales, would be hesitant to demand unfavorable terms due to the risk of losing that crucial business.
Conversely, when Hendrickson represents a minor customer for a large, diversified supplier, the supplier's bargaining power increases. Consider a scenario where Hendrickson's purchases make up less than 5% of a major global component manufacturer's total sales. In such a case, the supplier is less dependent on Hendrickson and can more easily dictate terms or prioritize other, larger clients.
- Supplier Dependence: If Hendrickson is a critical revenue source for a supplier, the supplier's bargaining power is reduced.
- Customer Size: A supplier's power is amplified if Hendrickson is a small client relative to the supplier's overall customer base.
- Diversification Impact: Highly diversified suppliers generally hold more power when dealing with individual customers like Hendrickson.
Suppliers gain significant leverage when they are concentrated, offer unique or differentiated products, or when switching costs for buyers are high. In 2024, the automotive sector saw continued supply chain pressures, particularly for specialized electronic components, which amplified supplier power. For instance, a manufacturer needing advanced sensor technology for new vehicle models would face suppliers with substantial bargaining power if only a few companies produced those critical parts.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers also strengthens their position. If a supplier can credibly enter the buyer's market, they gain leverage in negotiations. This was a growing concern in 2024 for some manufacturing segments where suppliers were exploring direct-to-consumer models or acquiring smaller assembly operations.
Conversely, a supplier's power diminishes if the buyer represents a large portion of their sales. In 2024, suppliers heavily reliant on large automotive OEMs, like General Motors or Ford, often had less power than those serving a fragmented customer base. This dynamic means that a supplier's overall customer portfolio significantly shapes their bargaining strength.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High power if few suppliers exist | Limited suppliers for advanced EV battery components |
| Product Differentiation | High power for unique or patented inputs | Specialized materials for lightweighting vehicles |
| Switching Costs | High power if buyer costs to change are high | Retooling for new engine control units |
| Forward Integration Threat | High power if suppliers can enter buyer's market | Suppliers developing their own vehicle assembly capabilities |
| Buyer Dependence on Supplier | Low power if buyer is a large customer | Supplier reliant on orders from major truck manufacturers |
What is included in the product
This analysis examines the five competitive forces impacting Boler: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hendrickson's customer base is heavily concentrated among a few major commercial vehicle original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). These include giants like Daimler, Volvo, PACCAR, and International (Navistar), along with specialized manufacturers such as Peterbilt, Kenworth, and Blue Bird.
This concentration means that these large OEMs often buy in substantial volumes, giving them considerable negotiating power. For instance, PACCAR, a leading manufacturer of heavy-duty trucks, reported net sales of $32.3 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of these customers' operations and their potential to influence pricing and terms.
Customer switching costs for suspension systems in the automotive sector are a key factor influencing the bargaining power of buyers. While original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) might incur expenses like re-engineering vehicle platforms, extensive testing, and validation when changing suppliers, these costs are often offset by the pursuit of competitive advantages.
In 2024, the automotive industry continued its trend of seeking innovation and cost efficiencies, making OEMs more receptive to exploring alternative suppliers, even with incurred switching costs. Long-term contracts do provide some supplier stickiness, but the drive for better performance or lower prices can incentivize OEMs to absorb these transition expenses.
Large commercial vehicle original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) possess the financial clout and technical expertise to explore backward integration for certain suspension components. For example, a major truck manufacturer might assess the cost-effectiveness of producing standard shock absorbers or air springs internally, particularly if they represent a significant portion of their bill of materials. This potential capability directly enhances their bargaining power with existing suppliers like Hendrickson, as they can credibly threaten to bring production in-house, thereby reducing their dependence and potentially driving down supplier prices.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
The price sensitivity of customers significantly impacts the bargaining power they hold. In the commercial vehicle sector, manufacturers are intensely focused on cost efficiency, making them highly attuned to the prices of their component suppliers. This means that even small increases in the cost of parts like suspension systems can create considerable pressure on Hendrickson's pricing strategies and ultimately, its profit margins.
This heightened price sensitivity is a direct consequence of the competitive landscape within the commercial vehicle industry. For instance, in 2024, the global commercial vehicle market experienced ongoing price pressures due to factors such as increased raw material costs and the need for manufacturers to remain competitive. Hendrickson, as a key supplier, must navigate this environment carefully.
- Intense Competition: Commercial vehicle manufacturers face fierce competition, driving a strong focus on cost reduction across their supply chains.
- Margin Squeeze: High customer price sensitivity directly translates into pressure on suppliers like Hendrickson to maintain competitive pricing, potentially impacting their profitability.
- Procurement Decisions: Buyers can leverage their price sensitivity to negotiate better terms, potentially switching suppliers if price points are not met.
- Market Dynamics: The overall health and competitive intensity of the commercial vehicle market in 2024 directly influence the extent of customer price sensitivity.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly impacts the bargaining power of customers. While direct substitutes for specialized components like suspension systems might be few, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) often have a range of alternative technologies and suppliers to consider. This variety inherently limits the power of any single supplier.
For instance, in the heavy-duty truck suspension market, OEMs can opt for different suspension types such as air, mechanical, hydraulic, or even coil and leaf spring systems. Furthermore, multiple reputable suppliers offer solutions within these categories. This broad spectrum of choices empowers OEMs, as they can switch suppliers or technologies if pricing or terms become unfavorable, thus reducing a single supplier's leverage.
- OEMs can select from various suspension technologies like air, mechanical, and hydraulic.
- Multiple suppliers offer similar suspension solutions, increasing customer options.
- This variety reduces the bargaining power of individual suspension system manufacturers.
Customers, particularly large Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in the commercial vehicle sector, wield significant bargaining power. Their substantial order volumes, as evidenced by PACCAR's $32.3 billion in net sales in 2023, allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms.
While switching costs exist, the constant drive for innovation and cost efficiency in 2024 makes OEMs more willing to explore new suppliers, even if it means absorbing transition expenses.
Furthermore, the potential for backward integration, where OEMs might consider producing certain components in-house, serves as a credible threat that amplifies their negotiating leverage.
The intense price sensitivity within the commercial vehicle market, driven by fierce competition and the need for cost reduction, directly pressures suppliers like Hendrickson to maintain competitive pricing, impacting their profit margins.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High | Hendrickson's customer base includes major OEMs like Daimler, Volvo, PACCAR. |
| Customer Order Volume | High | PACCAR's 2023 net sales of $32.3 billion indicate significant purchasing power. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate | OEMs may incur re-engineering costs but are motivated by cost efficiencies. |
| Potential for Backward Integration | High | OEMs can credibly threaten to produce components internally. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Intense competition in the commercial vehicle market drives cost focus. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate | OEMs can choose from various suspension technologies and multiple suppliers. |
Full Version Awaits
Boler Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of your chosen industry. You are viewing the exact document you will receive, ensuring full transparency and no hidden surprises. Once purchased, you'll gain immediate access to this professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global commercial vehicle suspension system market is characterized by moderate concentration. Major players such as Continental AG, ZF Friedrichshafen AG, Tenneco Inc., and Hendrickson USA, LLC command substantial market shares. For instance, Tenneco reported revenues of $8.4 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of these key competitors.
The global commercial vehicle suspension system market is projected to see a healthy compound annual growth rate of 5-6% between 2025 and 2033. This expansion is fueled by a rising need for heavy-duty vehicles and ongoing technological innovations in the sector.
Hendrickson stands out by focusing on technological innovation in its suspension systems, offering advanced solutions like air suspensions and electronically controlled systems. This commitment to cutting-edge technology allows them to differentiate their products from competitors.
This strong product differentiation directly impacts competitive rivalry by lessening the pressure for direct price competition. Companies with unique, high-performing products can often command premium pricing, thereby insulating themselves from the most aggressive price wars that plague more commoditized markets.
For instance, Hendrickson's development of lightweight composite springs not only offers performance benefits but also contributes to fuel efficiency for commercial vehicles, a key selling point that sets them apart. This focus on value-added features, rather than just price, defines their competitive strategy.
Exit Barriers
In the commercial vehicle component manufacturing sector, significant exit barriers often arise from high fixed costs associated with specialized machinery and production facilities. For instance, a plant dedicated to producing complex engine components might require millions in upfront investment, making it economically unviable to simply shut down. This financial commitment means companies are essentially locked into the industry, even when market conditions are unfavorable.
Furthermore, the presence of specialized assets, such as unique tooling or proprietary manufacturing processes, further entrenches companies within the market. These assets have limited alternative uses, meaning their resale value outside the industry is often negligible. Long-term contracts with major vehicle manufacturers also contribute to these barriers, obligating suppliers to continue production and support for extended periods, regardless of immediate profitability.
The consequence of these high exit barriers is a heightened level of competitive rivalry. Companies are compelled to remain active and compete intensely, even during economic downturns or periods of overcapacity. This can lead to price wars and aggressive market share battles as firms strive to maintain operational efficiency and cover their substantial fixed costs. For example, in 2023, the global commercial vehicle market experienced a moderate slowdown, yet many component suppliers continued to operate at high utilization rates to avoid the penalties associated with underutilized, specialized assets.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant capital investment in specialized manufacturing equipment and facilities.
- Specialized Assets: Assets with limited alternative uses, reducing their resale value outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to major clients that necessitate continued operation and supply.
- Intensified Rivalry: Companies remain in the market and compete fiercely, even during industry downturns.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry is intensified as industry players actively pursue strategic partnerships and acquisitions to bolster their capabilities and capture greater market share. This trend indicates a dynamic landscape where companies are consolidating to gain a competitive edge.
For instance, Hendrickson's acquisition of Reyco Granning in 2024 and its subsequent partnership with Voith in 2025 exemplify this consolidation. These moves are designed to enhance product portfolios and expand market reach, signaling a clear drive for market leadership.
- Strategic Alliances: Companies are forming alliances to share resources and technology, thereby improving their competitive positioning.
- Mergers & Acquisitions: The industry is witnessing a wave of consolidation as firms acquire rivals or merge to achieve economies of scale and broader market access.
- Market Share Expansion: These strategic maneuvers are directly aimed at increasing market share and solidifying a company's standing within the sector.
- Product Offering Enhancement: Partnerships and acquisitions often lead to the integration of new technologies and product lines, making offerings more comprehensive and attractive to customers.
Competitive rivalry in the commercial vehicle suspension system market is robust, driven by a moderate industry concentration with key players like Continental AG and ZF Friedrichshafen AG. These firms actively engage in strategic maneuvers such as acquisitions and partnerships, as seen with Hendrickson's moves in 2024 and 2025, to enhance their market position and product offerings. This dynamic environment, characterized by high exit barriers due to substantial fixed costs and specialized assets, compels companies to compete intensely, often leading to price pressures and market share battles even during economic slowdowns.
| Company | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Tenneco Inc. | 8.4 | Product differentiation and innovation |
| ZF Friedrichshafen AG | N/A (Part of larger group) | Technological advancement and market expansion |
| Continental AG | N/A (Part of larger group) | Diversified portfolio and global presence |
| Hendrickson USA, LLC | N/A (Private) | Strategic acquisitions and technological leadership |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While suspension systems are generally essential, alternative designs do exist. Traditional leaf spring and coil spring systems represent a significant competitive force against Hendrickson's advanced air and electronically controlled suspension technologies. For instance, in 2024, the global automotive suspension market, which includes these alternatives, was valued at approximately $35 billion, indicating a substantial existing base for these competing technologies.
Traditional suspension systems, like leaf springs and coil springs, often present a lower upfront cost compared to advanced air or electronically controlled systems. For instance, a basic leaf spring suspension for a light commercial vehicle might cost a few hundred dollars, whereas an adaptive air suspension system for a premium SUV could easily run into thousands. This cost difference is a significant factor for many buyers, especially in price-sensitive market segments.
However, the performance capabilities of these more affordable substitutes are typically less sophisticated. They generally lack the nuanced load-handling adjustments and superior ride comfort that modern air or electronic systems provide. While a traditional system might suffice for basic transportation, it cannot offer the dynamic ride height adjustment or the ability to automatically adapt damping to road conditions, which are increasingly valued features.
The decision between a cheaper, less advanced substitute and a more expensive, feature-rich system hinges on this trade-off between initial investment and long-term performance benefits. For example, in the 2024 automotive market, manufacturers are seeing a growing demand for comfort and technology, pushing the adoption of more advanced suspension solutions despite their higher price points, indicating a shifting perception of value.
Improvements in other vehicle components, like advancements in tire technology and chassis design, can indirectly affect the demand for specific suspension systems. For instance, enhanced tire grip and improved chassis rigidity might lessen the perceived need for highly sophisticated, adaptive suspension features in certain vehicle segments.
These indirect substitutes can alter consumer expectations and the overall driving experience. For example, a vehicle with superior tires and a well-engineered chassis might offer a more comfortable and stable ride, potentially reducing the premium buyers are willing to pay for advanced suspension technology. In 2024, the automotive industry saw significant investments in tire material science and lightweight chassis construction, aiming to improve fuel efficiency and handling without solely relying on complex suspension setups.
Technological Advancements in Non-Suspension Areas
The rise of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies presents a subtle but significant threat of substitutes for traditional suspension systems. As vehicles become more capable of sensing and reacting to their environment, certain functions traditionally handled by sophisticated suspension tuning might be partially replicated by electronic controls and sensor arrays. For instance, active damping systems, while often integrated with suspension, could see their roles partially assumed by advanced traction control and stability management systems that actively adjust power and braking to maintain vehicle composure.
This technological shift could indirectly substitute for certain aspects of suspension performance. Consider the 2024 automotive market, where ADAS features are becoming standard across many vehicle segments. Companies are investing heavily in these areas; for example, NVIDIA’s DRIVE platform, a key enabler of autonomous driving, saw significant revenue growth in 2024, indicating a strong market push towards these technologies. While this doesn't eliminate the need for suspensions, it alters the performance requirements and potentially opens avenues for alternative solutions that reduce reliance on purely mechanical or hydraulic suspension components.
The threat lies in the potential for integrated vehicle dynamics control systems to compensate for less sophisticated suspension setups. As these electronic systems become more advanced and widely adopted, the perceived value of high-performance, complex mechanical suspensions might diminish for certain applications, particularly in mass-market vehicles. This could lead to a shift in demand towards more cost-effective suspension solutions, or even designs that are less reliant on traditional damping and articulation, as the overall vehicle control architecture takes on more of the dynamic management burden.
- ADAS Integration: Advanced driver-assistance systems are increasingly common, with a significant portion of new vehicles in 2024 equipped with at least Level 2 autonomy features.
- Autonomous Driving Investment: Global investment in autonomous vehicle technology is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by the end of the decade, highlighting a strong industry focus.
- Electronic Control Emphasis: The trend is towards vehicles where electronic systems manage ride comfort and handling, potentially reducing the emphasis on purely mechanical suspension sophistication.
Changing Customer Preferences and Regulations
The automotive industry is witnessing a significant shift in consumer demands, with a growing emphasis on enhanced safety, improved fuel efficiency, and superior ride comfort. This evolving preference directly impacts the demand for traditional suspension systems. For instance, by early 2024, electric vehicles (EVs), which often require specialized suspension tuning for battery weight and regenerative braking, represented a substantial portion of new vehicle sales in key markets.
Government regulations are also playing a crucial role in shaping the threat of substitutes. Stricter emissions standards and safety mandates are compelling manufacturers to adopt more advanced technologies. By Q1 2024, many regions had implemented or were in the process of implementing stricter safety regulations, pushing for features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist, which are often integrated with sophisticated suspension systems.
These combined factors are making advanced suspension technologies, such as adaptive damping and air suspension, increasingly attractive alternatives to conventional coil springs and shock absorbers. This trend effectively diminishes the appeal and market share of older, less capable suspension types, thereby reducing the threat they pose.
- Growing demand for EVs: By early 2024, EVs accounted for a notable percentage of new vehicle sales, necessitating specialized suspension.
- Stricter safety regulations: Mandates by Q1 2024 pushed for integrated safety features often linked to advanced suspension.
- Consumer preference shift: Buyers increasingly prioritize safety, fuel efficiency, and ride comfort, favoring modern suspension solutions.
- Technological advancements: Adaptive damping and air suspension are becoming viable substitutes for traditional systems.
The threat of substitutes for advanced suspension systems is significant, primarily from traditional mechanical designs like leaf springs and coil springs. These substitutes are often more affordable, with basic leaf spring systems costing a fraction of advanced air or electronic setups. For example, the global automotive suspension market, including these alternatives, was valued at around $35 billion in 2024, showcasing their widespread use.
While less sophisticated in performance, these traditional systems meet basic transportation needs, making them a viable choice for price-sensitive segments. However, evolving consumer preferences for comfort and technology, as seen in the 2024 market, are driving adoption of more advanced, albeit costlier, suspension solutions.
Indirect substitutes also emerge from advancements in other vehicle components. Enhanced tire technology and chassis design can reduce the perceived need for complex suspension systems. In 2024, substantial investments in tire materials and lightweight chassis construction aimed to improve vehicle dynamics, potentially lessening reliance on advanced suspension alone.
Furthermore, integrated vehicle dynamics control systems, often part of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), can compensate for less sophisticated suspension. As ADAS features become standard, as evidenced by their prevalence in new vehicles by early 2024, the value proposition of complex mechanical suspensions may decrease for mass-market applications.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Context (2024) | Threat Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Mechanical (Leaf/Coil Springs) | Lower upfront cost, simpler design, adequate for basic needs | Significant market share ($35B global market), widely used in cost-sensitive segments | High |
| Improved Chassis/Tire Technology | Enhanced handling and ride comfort through other components | Major investments in material science and lightweight construction | Medium |
| Integrated Vehicle Dynamics Control (ADAS) | Electronic compensation for suspension performance, enhanced safety | Increasingly standard in new vehicles, strong investment in autonomous tech | Medium |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the commercial vehicle suspension manufacturing sector demands significant financial outlay. Companies need to invest heavily in cutting-edge research and development to innovate, alongside establishing robust manufacturing plants equipped with specialized machinery. For instance, a new entrant might need upwards of $50 million to $100 million to set up a basic production line, factoring in tooling and initial inventory.
The cost of building and maintaining a reliable supply chain, crucial for sourcing raw materials and distributing finished products globally, adds another layer of capital intensity. This high upfront investment acts as a powerful deterrent, effectively limiting the number of new players who can realistically enter and compete in this capital-intensive industry.
Established players in the automotive supplier industry, such as Hendrickson, leverage substantial economies of scale. This means they can produce goods at a lower per-unit cost due to high-volume production, bulk purchasing of raw materials, and optimized distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, major automotive suppliers often operate plants with capacities exceeding hundreds of thousands of units annually, allowing them to spread fixed costs over a much larger output.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without the same production volume, they cannot negotiate favorable prices with suppliers or spread their overhead as effectively. This cost disadvantage makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to compete on price with established firms, thereby acting as a deterrent to market entry.
Hendrickson's deep-rooted relationships with major commercial vehicle original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) worldwide present a formidable barrier. New entrants would struggle to gain the trust and secure supply agreements from these critical customers, who prioritize established, reliable suppliers with a proven history of performance.
Product Differentiation and Brand Loyalty
Hendrickson's established legacy and robust reputation for innovation and quality in the heavy-duty transportation sector present a formidable barrier to new competitors. Developing a brand image that resonates with industry demands and delivering uniquely engineered products that adhere to rigorous specifications is a substantial challenge for any newcomer.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the high cost and difficulty associated with achieving product differentiation and cultivating strong brand loyalty. Hendrickson's decades of experience have allowed them to build trust and recognition, making it hard for new players to gain market share without substantial investment in R&D and marketing. For instance, in 2024, the average R&D expenditure for leading automotive component suppliers exceeded 5% of revenue, highlighting the financial commitment required to innovate and differentiate.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants need significant capital to match Hendrickson's technological advancements and manufacturing capabilities.
- Brand Equity: Hendrickson's established brand loyalty, built over many years, is difficult and costly for new companies to replicate.
- Product Complexity: Developing specialized, high-performance components that meet the exacting standards of the heavy-duty market requires deep technical expertise and substantial testing.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating and complying with evolving safety and emissions regulations in the transportation industry adds another layer of complexity and cost for potential new entrants.
Regulatory and Certification Hurdles
The commercial vehicle industry is heavily regulated, with strict standards for safety, emissions, and performance. New companies entering this market must meticulously adhere to these requirements, which often involve lengthy and expensive certification processes. For instance, meeting EPA emissions standards for heavy-duty trucks in the United States can involve significant upfront investment in research and development.
These regulatory and certification hurdles act as a substantial barrier to entry. Newcomers need to demonstrate compliance with complex technical specifications and pass rigorous testing, a process that can delay market entry and drain capital. In 2024, the ongoing evolution of emissions regulations, such as those targeting greenhouse gas reductions, continues to raise the bar for technological innovation and compliance costs.
- Stringent Safety Standards: Regulations like FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards) in the US demand extensive testing and validation for vehicle components and overall design.
- Emissions Compliance: Meeting stringent emissions targets, such as those set by Euro 7 standards in Europe, requires advanced engineering and significant R&D investment.
- Certification Costs: Obtaining necessary certifications can cost millions of dollars, representing a substantial initial investment for any new entrant.
- Technical Expertise: The need for specialized engineering talent to design and certify vehicles adds another layer of difficulty for new players.
The threat of new entrants into the commercial vehicle suspension market is relatively low. Significant capital investment is required for advanced manufacturing and R&D, with new facilities potentially costing tens of millions. Established players benefit from economies of scale, achieving lower per-unit costs that newcomers struggle to match.
Brand equity and strong customer relationships with OEMs represent substantial barriers, as trust and proven performance are paramount. Furthermore, navigating complex regulatory landscapes and obtaining necessary certifications adds considerable cost and time, further deterring new competition.
| Barrier | Description | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in R&D, manufacturing, and supply chains. | Setting up a production line could require $50M-$100M. |
| Economies of Scale | Established players produce at lower per-unit costs due to high volume. | Major suppliers operate plants with capacities over hundreds of thousands of units annually. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Difficulty in securing OEM contracts without a proven track record. | Decades of experience build trust, making it hard for new entrants to gain market share. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with safety and emissions standards involves costly certifications. | Meeting EPA emissions standards can require significant R&D investment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and expert commentary from financial analysts. We also leverage insights from trade publications and company press releases to capture the nuances of competitive dynamics.
