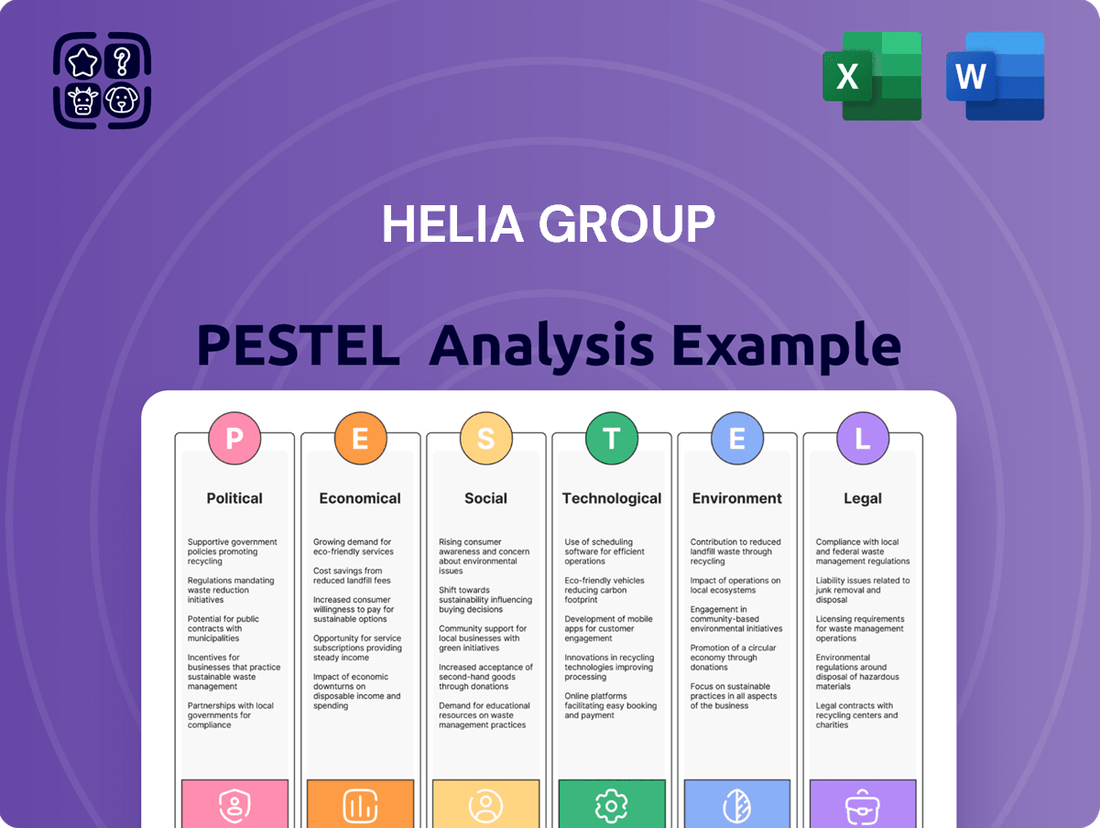
Helia Group PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Helia Group Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping Helia Group's trajectory with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political shifts, economic fluctuations, and technological advancements that are critical to their operations and future growth. Our expert insights will equip you with the knowledge to anticipate challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Don't get left behind – gain a competitive edge by securing the full PESTLE analysis today.
Political factors
Government housing schemes play a significant role in shaping the mortgage market. Initiatives like the First Home Owner Grant (FHOG) and the First Home Loan Deposit Scheme (FHLDS) are designed to assist first-time homebuyers. These programs directly boost demand for mortgages, which in turn can positively affect lenders and related services like Lenders Mortgage Insurance (LMI).
The upcoming 'Help to Buy' scheme, slated to begin accepting applications in late 2025, is particularly noteworthy. This initiative aims to enable low-to-middle income earners to secure home loans with a minimal 2% deposit, crucially without the need for LMI. This could potentially alter market dynamics, impacting Helia's market share within specific buyer demographics.
Helia Group's operations as a Lender's Mortgage Insurer (LMI) in Australia are significantly shaped by the regulatory frameworks established by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC). These bodies ensure the stability of the financial system and protect consumers, directly impacting how banks and other lenders operate and, consequently, their demand for LMI products.
APRA's prudential standards, such as the upcoming APS 117 on Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book (IRRBB), set to be implemented in October 2025, will influence how Authorised Deposit-taking Institutions (ADIs) manage their interest rate exposures. This, in turn, can affect lending appetites and risk assessments for mortgages, potentially altering the volume of business for LMI providers like Helia. Furthermore, APRA's evolving guidance on how ADIs incorporate specific debt types, like Higher Education Loan Program (HELP) debt, into their loan assessments can also indirectly influence the underlying credit risk profile of mortgage portfolios and the need for LMI coverage.
Australia's new mandatory climate-related financial disclosure (CRFD) regime, effective January 1, 2025, significantly impacts large businesses and financial institutions. This legislation mandates annual sustainability reports detailing climate-related risks and opportunities, directly influencing Helia Group's reporting obligations and governance structures.
For entities like Helia, this means a structured approach to quantifying and communicating their environmental impact and strategic responses. The CRFD framework aims to enhance transparency and comparability across industries, encouraging better risk management and investment decisions aligned with climate goals.
The phased introduction of this regime ensures that companies can adapt their systems and processes. By 2027, the majority of Australian entities will be subject to these disclosures, underscoring the broad applicability and importance of climate-related reporting for all major corporations.
Consumer Credit Protection Regulations
The February 2025 introduction of the National Consumer Credit Protection Amendment (Low Cost Credit) Regulations, which reclassified Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) providers, signals a significant governmental push for tighter controls within the consumer credit sector.
This regulatory shift underscores a broader focus on safeguarding consumers and promoting financial system resilience, potentially impacting the credit landscape Helia Group operates within.
While these specific regulations don't directly target Lenders Mortgage Insurance (LMI), they reflect a heightened awareness of consumer credit risks and the government's inclination to intervene to mitigate them.
This evolving regulatory environment necessitates that Helia Group remain vigilant regarding changes that could indirectly affect credit accessibility and associated risk profiles for borrowers.
For instance, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) reported in its 2024 financial stability review that consumer credit growth had moderated, a trend potentially influenced by increased regulatory scrutiny on lending practices.
Political Stability and Policy Certainty
Australia's political landscape generally offers a stable environment for financial services, including Lenders Mortgage Insurance (LMI). This stability translates to a predictable operating framework for companies like Helia. For instance, in the 2023-2024 financial year, Australia maintained a strong sovereign credit rating, reflecting political stability.
However, changes in government policy can significantly impact the LMI sector. Recent discussions and potential policy shifts around housing affordability and lending practices, as seen in the lead-up to and following the 2022 federal election, illustrate this. For example, proposals for a first home buyer scheme or changes to responsible lending regulations could directly influence LMI demand and underwriting. Helia, therefore, must stay attuned to government announcements and legislative proposals, such as those emerging from the Treasury or the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), to adapt its strategies effectively.
- Political Stability: Australia's consistent record of stable governance supports predictable business operations for LMI providers.
- Policy Shifts: Government focus on housing affordability and financial regulation can alter the operating environment for LMI.
- Adaptation Needs: LMI providers must remain agile to respond to evolving policy landscapes.
- Monitoring is Key: Continuous tracking of government policy announcements and legislative changes is crucial for strategic planning.
Australia's political environment generally provides a stable foundation for financial services like LMI, with a strong sovereign credit rating observed through FY2023-2024. However, policy shifts regarding housing affordability and lending practices, particularly those emerging from government initiatives like the upcoming 'Help to Buy' scheme in late 2025, can significantly influence the demand for LMI. Helia Group must remain adaptable to these evolving legislative proposals and regulatory guidance from bodies like APRA and ASIC to effectively manage its strategies.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis of the Helia Group meticulously examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors impacting its operations, providing a comprehensive understanding of the external landscape.
It offers actionable insights and data-driven perspectives to guide strategic decision-making and identify critical opportunities and challenges for the Helia Group.
The Helia Group PESTLE analysis offers a clear and concise version that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions, simplifying complex external factors into actionable insights.
This analysis provides a valuable asset for business consultants creating custom reports for clients, offering a structured framework to identify and address potential market challenges and opportunities.
Economic factors
Interest rate movements are a significant economic lever, with the Reserve Bank of Australia's (RBA) monetary policy directly shaping mortgage costs and, consequently, borrower affordability. This has a direct impact on the housing market, a key sector for Helia Group.
With forecasts pointing towards potential interest rate cuts in 2025 and 2026, a shift is anticipated. These anticipated reductions are expected to bolster buyer confidence and invigorate property demand, potentially leading to an uplift in mortgage lending volumes for Helia.
Inflation also plays a crucial role; persistent high inflation can lead to increased interest rates as central banks attempt to cool the economy. For instance, Australia's inflation rate, while showing signs of moderation, remained a key concern throughout 2024, influencing RBA decisions.
The Australian housing market faced significant affordability challenges in late 2024. High property prices combined with rapidly increasing rental costs pushed affordability to record lows. This environment impacts potential home buyers and the demand for lenders mortgage insurance (LMI).
Looking ahead to early 2025, a slight dip in house prices is anticipated. However, fundamental supply shortages persist, meaning demand will likely continue to outpace the available housing stock. This dynamic creates a complex but still active market for both home ownership and LMI providers.
Consumer credit in Australia hit a record high in May 2025, signaling a significant increase in household borrowing. While overall credit default risk remained steady, a concerning trend emerged in 2024 with heightened risk observed among younger Australians and those with personal loans. This suggests pockets of financial vulnerability within the broader economic landscape.
Helia experienced a rise in new delinquencies during FY24. This increase is directly attributable to escalating mortgage costs and the resultant financial pressures faced by many borrowers. The data indicates that a segment of Australian households is under considerable financial strain, impacting their ability to meet repayment obligations.
Lending Volumes and Loan-to-Value Ratios
Helia Group's gross written premium (GWP) saw a healthy 6% increase in Fiscal Year 2024. This growth was significantly bolstered by an uptick in lending volumes, particularly for loans featuring a loan-to-value (LVR) ratio exceeding 80%.
The company plays a vital role in facilitating these higher LVR loans. By doing so, Helia directly supports aspiring homeowners who might find it challenging to meet traditional, higher deposit requirements, thereby expanding access to homeownership.
This strategic support for higher LVR lending is a key economic driver for Helia. It reflects a market trend where lenders are increasingly comfortable with lower initial equity, and Helia's products are designed to mitigate the associated risks.
- FY24 GWP Growth: 6% increase.
- Key Growth Driver: Higher lending volumes for loans with LVR > 80%.
- Market Impact: Supports homeownership for borrowers with lower deposits.
- Risk Mitigation: Helia's role in insuring higher LVR loans is crucial for market stability.
Economic Growth and Employment Market
A robust employment market and healthy property equity have significantly reduced claims for Helia. In May 2024, Australia's unemployment rate stood at a low 4.0%, indicating strong demand for labor and greater borrower financial stability. This trend directly benefits Helia by minimizing the risk of mortgage defaults.
Sustained economic growth and low unemployment are cornerstones for a stable mortgage market. For instance, Australia's GDP growth for the year ending March 2024 was 1.3%, demonstrating a resilient economy. These conditions bolster borrower capacity to meet mortgage obligations, thereby lowering the incidence of lenders mortgage insurance (LMI) claims.
- Low Unemployment: Australia's unemployment rate remained at 4.0% in May 2024, a key indicator of economic health.
- Economic Resilience: Australia's GDP grew by 1.3% in the year to March 2024, supporting borrower stability.
- Property Equity: High levels of positive equity in property values act as a buffer against potential defaults.
- Reduced Claims: These favorable economic conditions directly translate to lower claim volumes for Helia.
Interest rate movements continue to be a primary economic driver, with the Reserve Bank of Australia's (RBA) monetary policy directly influencing mortgage affordability and, in turn, the housing market. Forecasts suggest potential interest rate cuts in 2025 and 2026, which are expected to boost buyer sentiment and property demand, likely increasing mortgage lending volumes for Helia.
Inflationary pressures remained a concern through 2024, impacting RBA decisions and potentially leading to sustained higher interest rates. The Australian housing market faced significant affordability challenges in late 2024 due to high property prices and rising rents, impacting demand for lenders mortgage insurance (LMI).
Consumer credit reached record levels in May 2025, indicating increased household borrowing, though pockets of financial vulnerability were observed, particularly among younger Australians and those with personal loans. Helia experienced a rise in new delinquencies in FY24, linked to increased mortgage costs and borrower financial strain.
| Economic Factor | Metric | Value/Trend | Implication for Helia |
| Interest Rates | RBA Cash Rate | Anticipated cuts in 2025-2026 | Potential increase in mortgage lending volumes, improved affordability |
| Inflation | CPI (Australia) | Moderating but remains a concern | Influences RBA policy, potentially sustained higher rates |
| Housing Market Affordability | House Prices vs. Income | Record low affordability in late 2024 | Impacts demand for LMI, though supply shortages persist |
| Consumer Credit | Total Household Debt | Record high May 2025 | Increased borrowing, potential for pockets of financial strain |
| Unemployment | Unemployment Rate (Australia) | 4.0% (May 2024) | Low unemployment supports borrower stability, reduces claims |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Helia Group PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis for the Helia Group delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting their operations. It provides a strategic overview of external influences that can shape the company's future success. You'll gain valuable insights into market dynamics and potential challenges or opportunities.
Sociological factors
Australia's population is projected to reach approximately 30.8 million by 2025, a notable increase driven by both natural growth and immigration. High immigration rates, particularly in recent years leading up to 2024, have significantly amplified demand in the housing market, placing considerable pressure on available supply and consequently boosting the need for Lenders Mortgage Insurance (LMI).
Shifting household structures, with more single-person households and smaller family units forming, also play a crucial role. These demographic trends, alongside evolving migration patterns, directly shape the pool of potential homebuyers, influencing the overall demand for LMI products as more individuals seek to enter the property market with less than a 20% deposit.
Despite significant affordability challenges in 2024, the aspiration for home ownership persists among a large segment of Australians. However, heightened financial strain and the extended periods now needed to accumulate a deposit are likely to reshape consumer perspectives on debt and the practicality of securing a home. This shift could directly impact the demand for high Loan-to-Value Ratio (LVR) loans, often requiring Lender's Mortgage Insurance (LMI).
For instance, in early 2024, median house prices in Sydney and Melbourne continued to test record highs, making deposit accumulation a multi-year endeavor for many. This prolonged saving period, coupled with rising interest rates throughout 2023 and into 2024, has amplified concerns about mortgage serviceability and the overall burden of debt. Consequently, a growing number of individuals may reconsider the traditional path to home ownership, exploring alternative housing arrangements or seeking more flexible financing options.
The persistent cost-of-living crisis and elevated interest rates are significantly curtailing borrowing capacity and influencing consumer purchasing decisions. This financial strain is contributing to increased mortgage stress, with observed upticks in new delinquencies suggesting a growing number of borrowers are struggling to meet their loan obligations.
For mortgage lenders and insurers, this trend directly impacts their risk profile, as borrowers' reduced ability to service debt escalates the likelihood of defaults. For instance, in the US, the delinquency rate on prime mortgages saw a slight increase in late 2024, reflecting these broader economic pressures.
Social Wellbeing and Housing Stress
The increasing cost of housing in Australia has led to significant social challenges. Many households are now considered to be in housing stress, meaning they allocate more than 30% of their disposable income to housing costs. This financial pressure can impact overall wellbeing and economic stability.
Helia Group plays a crucial role in mitigating these effects. In the 2023-2024 financial year, the company provided assistance to over 11,000 Australians facing financial hardship, enabling them to remain in their homes through loan deferrals. This demonstrates a direct social impact by providing a safety net during difficult economic times.
- Housing affordability crisis: Over 30% of disposable income spent on housing is a common benchmark for housing stress.
- Helia's support: Assisted over 11,000 Australians in 2023-2024 to avoid home repossession.
- Societal impact: Helia's actions highlight the broader issue of housing security and the need for financial support mechanisms.
- Economic pressure: Rising interest rates and inflation contribute to increased housing costs, exacerbating financial stress for homeowners.
Consumer Trust and Transparency in Financial Services
Consumer trust is a cornerstone for financial institutions like Helia Group. In 2024, a significant percentage of consumers expressed concern over data privacy and ethical business practices within the financial sector, underscoring the need for robust transparency measures.
Helia's commitment to ethical governance and responsible lending directly addresses these concerns. By prioritizing fair practices, the group aims to build and sustain long-term relationships with its customers, which is crucial for market stability and growth.
Initiatives such as transparent climate disclosures, as seen in many leading financial firms' 2024 reports, are becoming increasingly important. These disclosures not only meet regulatory expectations but also resonate with a growing segment of socially conscious investors and consumers.
- Consumer Trust: Studies in 2024 indicated that over 60% of consumers consider transparency a key factor when choosing a financial provider.
- Ethical Governance: Helia's adherence to strict ethical standards is vital for maintaining its reputation and attracting a discerning customer base.
- Responsible Lending: This practice is critical for preventing financial distress among consumers and ensuring the long-term health of the financial system.
- Climate Disclosures: By 2025, a majority of large financial institutions are expected to provide detailed climate-related financial disclosures, reflecting a broader societal shift.
Societal attitudes towards home ownership remain strong, though the path to achieving it is becoming more challenging due to affordability issues. In 2024, many Australians faced extended periods to save for a deposit, with median house prices in major cities like Sydney and Melbourne continuing to climb. This financial pressure highlights the ongoing need for solutions that support aspiring homeowners.
The increasing cost of living and elevated interest rates in 2023-2024 have heightened mortgage stress for many households. This economic strain is reflected in a slight uptick in new mortgage delinquencies, impacting lenders' risk profiles. Helia Group’s role in providing financial assistance, such as loan deferrals to over 11,000 Australians in the 2023-2024 financial year, demonstrates a direct societal impact by helping individuals maintain housing security during tough economic times.
Technological factors
The Australian mortgage lending landscape is rapidly embracing digital solutions, making it easier for consumers to apply for, process, and get approved for home loans through online platforms and mobile applications. This shift is significantly streamlining the entire process.
Helia Group is actively participating in this digital evolution by enhancing its operational efficiency and data management. Key initiatives include the successful integration of new customer APIs and the implementation of a new digital onboarding system, reflecting a commitment to a more digitized customer journey.
In 2024, digital mortgage origination in Australia is expected to continue its upward trend, with a growing percentage of new home loans initiated online, driven by consumer demand for convenience and speed. This digital push is not just about customer experience but also about improving internal workflows and data accuracy for lenders like Helia.
The adoption of AI and machine learning is transforming mortgage brokerage by automating critical processes. AI algorithms are now integral to tasks like document verification, data entry, and credit scoring, significantly reducing processing times. For instance, in 2024, many leading mortgage lenders reported a 20-30% decrease in loan origination cycle times due to AI-driven automation.
Furthermore, AI-powered tools enhance risk assessment capabilities. These systems can more effectively identify potential risks and instances of fraud, leading to more informed and robust lending decisions. This improved accuracy in risk evaluation is a key factor in maintaining portfolio health and minimizing losses, especially in a dynamic economic environment.
Open banking, particularly the expansion of Australia's Consumer Data Right (CDR) in 2025 to encompass non-bank lenders, will significantly enhance data availability for mortgage brokers and lenders. This expansion means more comprehensive financial profiles, leading to more precise loan assessments and the development of personalized credit offerings.
By facilitating access to a wider array of financial information, these open banking initiatives are projected to intensify competition within the lending sector. This increased competition, driven by data-driven insights, will ultimately benefit consumers through more tailored and competitive mortgage solutions.
Cybersecurity and Data Security
Cybersecurity and data security are paramount for financial institutions like Helia Group, especially with the escalating reliance on digital processing and data sharing. Protecting sensitive client information and ensuring data integrity is not just a best practice, but a necessity, necessitating the deployment of sophisticated information security management systems. For instance, the global cost of cybercrime was projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, underscoring the significant financial risk associated with breaches.
Compliance with evolving privacy legislation, such as GDPR or similar regional regulations, further dictates the need for robust data security measures. These regulations impose strict requirements on how personal data is collected, processed, and stored, with substantial penalties for non-compliance. In 2023 alone, data breaches affected an estimated 2.4 billion individuals globally, highlighting the widespread nature of these threats.
- Heightened Regulatory Scrutiny: Financial firms face increasing pressure from regulators to demonstrate strong cybersecurity postures.
- Reputational Risk: A data breach can severely damage customer trust and Helia Group's brand reputation.
- Operational Disruption: Cyberattacks can halt critical business operations, leading to significant financial losses.
- Investment in Advanced Technologies: Continuous investment in AI-driven threat detection, encryption, and secure cloud solutions is vital.
Innovation in Financial Products and Services
Technological advancements are a significant driver in the financial sector, fueling the creation of novel credit products and financing methods. For instance, shared equity models are gaining traction, offering alternative ways for individuals to access capital. This innovation directly impacts how companies like Helia Group can serve its target market.
Helia Group, while primarily focused on low-to-moderate income (LMI) customers, must remain agile in this evolving landscape. Its capacity to integrate with emerging digital platforms and facilitate innovative lending practices adopted by its partners is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in 2024 and beyond. The digital transformation of financial services is accelerating, with FinTech companies introducing new solutions at an unprecedented pace.
Consider the following technological factors:
- Digital Lending Platforms: The proliferation of online loan origination systems and digital marketplaces streamlines the application and approval process, making credit more accessible.
- Data Analytics and AI: Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence are enabling more sophisticated credit scoring models, potentially opening up new customer segments and reducing risk. For example, by mid-2024, many lenders reported increased use of AI in underwriting, leading to faster decision times.
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): While still nascent in widespread credit product innovation, DLT offers potential for secure and transparent record-keeping, which could impact future financing solutions.
- Open Banking Initiatives: Mandates for open banking allow for secure data sharing, enabling third-party providers to develop innovative financial products and services, potentially enhancing Helia’s partner ecosystem.
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the mortgage lending sector, driving efficiency and innovation. The increasing adoption of digital lending platforms and AI in credit assessment, as seen with many lenders reporting 20-30% faster loan origination cycles in 2024 due to AI, are key trends. Furthermore, the expansion of open banking, particularly the Consumer Data Right (CDR) in Australia in 2025, will facilitate greater data sharing, fostering more personalized credit offerings and intensifying competition.
Cybersecurity remains a critical concern, with the global cost of cybercrime projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, underscoring the necessity for robust data protection measures. Helia Group must invest in advanced technologies like AI-driven threat detection to safeguard sensitive client information and maintain operational integrity.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and DLT, while still developing for credit products, offer potential for enhanced security and transparency in future financing solutions. Helia Group's ability to integrate with new digital platforms and support innovative lending practices is vital for its competitive standing in 2024 and beyond.
| Technology Area | Impact on Mortgage Lending | Helia Group Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Lending Platforms | Streamlined applications, faster approvals, increased accessibility. Mid-2024 data shows a significant rise in online mortgage applications. | Enhances operational efficiency and customer onboarding. |
| Data Analytics & AI | Improved credit scoring, faster underwriting decisions, enhanced risk assessment. Lenders reported a 20-30% reduction in origination times in 2024 due to AI. | Enables more accurate risk evaluation and potential for new customer segments. |
| Open Banking (CDR) | Increased data availability, personalized offerings, intensified competition. Expansion to non-bank lenders by 2025. | Facilitates deeper customer insights and potential for partner ecosystem growth. |
| Cybersecurity | Protection of sensitive data, prevention of financial losses. Global cybercrime costs projected at $10.5 trillion by 2025. | Crucial for maintaining trust, brand reputation, and operational continuity. |
Legal factors
Helia Group operates under the watchful eye of the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), a key legal factor shaping its operations. APRA mandates stringent standards for how financial institutions manage themselves, covering crucial areas like governance, capital adequacy, and overall risk management. This oversight is fundamental to maintaining financial stability and protecting policyholders.
A significant development is APRA's Prudential Standard CPS 230 Operational Risk Management, which comes into effect on July 1, 2025. This new standard will require Helia to meticulously identify its most critical business services. Furthermore, the company must assess and demonstrate its capacity to maintain these services even when faced with significant disruptions, a direct push towards enhanced operational resilience.
The National Consumer Credit Protection Act is the bedrock of lending in Australia, mandating responsible lending and robust consumer safeguards. This framework is constantly evolving, as seen with recent changes like the reclassification of Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services.
These amendments are a clear indicator of a more stringent regulatory climate, focusing heavily on suitability assessments for borrowers and imposing caps on various fees. This shift directly affects how credit is offered and managed across the financial sector.
For instance, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) has been actively enforcing responsible lending obligations, with significant penalties for non-compliance. The BNPL sector alone saw a substantial increase in regulatory scrutiny throughout 2023 and into 2024, reflecting a broader trend of enhanced consumer protection in lending.
The Treasury Laws Amendment (Financial Market Infrastructure and Other Measures) Bill 2024, which became law in September 2024, introduces mandatory climate-related financial reporting for large entities starting January 2025. This means Helia Group will need to produce annual sustainability reports alongside its financial statements.
These reports must detail the company's exposure to climate-related risks and the opportunities arising from the transition to a low-carbon economy. For instance, entities will need to report on Scope 1, 2, and potentially Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with international standards.
Compliance with this legislation represents a significant legal and operational shift, requiring robust data collection and governance frameworks. Failure to comply could result in penalties or reputational damage, impacting investor confidence.
Corporate Governance and Shareholder Obligations
Helia's corporate governance structure is designed to meet the standards set by the ASX Corporate Governance Council's Principles and Recommendations, alongside APRA's Prudential Standard CPS 510 Governance. This framework is crucial for maintaining trust and accountability. For instance, in 2024, Helia received a 'first strike' on its remuneration report, indicating significant shareholder dissatisfaction with executive pay practices. This event underscores the need for greater alignment between management compensation and the long-term interests of shareholders.
This shareholder pushback demonstrates the growing influence of investors in shaping corporate behavior and executive remuneration policies. Companies like Helia must actively engage with shareholders to address concerns regarding pay equity and performance metrics. The 'first strike' mechanism, while a warning, signals a potential for more significant shareholder action if governance and remuneration issues are not adequately resolved in future reporting periods.
The implications of such governance challenges extend to regulatory scrutiny and investor confidence. APRA's oversight, particularly through CPS 510, emphasizes the importance of robust governance in financial institutions like Helia. Failure to address shareholder concerns can lead to increased regulatory oversight and a negative impact on the company's valuation and access to capital.
Key aspects of Helia's governance framework include:
- Adherence to ASX Corporate Governance Council Principles and Recommendations.
- Compliance with APRA's Prudential Standard CPS 510 Governance.
- Shareholder engagement on remuneration policies.
- Mitigation of risks associated with 'first strike' warnings on remuneration reports.
Privacy Laws and Data Handling
Helia Group must navigate a complex web of Australian privacy laws, including adherence to the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) and the Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) Scheme. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, impacting both reputation and finances. For instance, the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC) reported investigating numerous data breach notifications in 2023-2024, highlighting the active enforcement of these regulations.
Furthermore, the Critical Infrastructure Act of 2018, with ongoing amendments and implications for 2024-2025, imposes stringent security obligations on entities handling sensitive client data. This legislation is designed to protect essential services and their underlying systems from cyber threats. Helia's robust data handling practices and cybersecurity measures are therefore not merely best practices but legal imperatives.
Maintaining customer trust is paramount, and this trust is directly linked to the perceived security and privacy of their information. By investing in and demonstrating strong data governance, Helia can mitigate legal risks and build a more resilient business model. The financial services sector, in particular, faces heightened scrutiny regarding data protection, making proactive compliance essential for continued operation and growth.
Helia Group operates within a dynamic legal landscape, heavily influenced by APRA's prudential standards and evolving consumer credit regulations. The upcoming CPS 230 standard, effective July 2025, mandates enhanced operational resilience, requiring critical service identification and disruption management plans. The National Consumer Credit Protection Act also continues to evolve, with recent adjustments to BNPL regulations and increased ASIC enforcement on responsible lending, as evidenced by significant penalties issued in 2023-2024.
Environmental factors
Australia's new climate-related financial disclosure regime, starting January 2025, will mandate Helia to detail its climate risks and opportunities. This means Helia must assess and report on how physical impacts, like increased bushfire frequency impacting insured assets, and transition risks, such as shifts in consumer demand away from carbon-intensive products, affect its financial performance.
The upcoming regulations require a comprehensive evaluation of both acute physical risks, such as the economic impact of severe weather events on property values, and chronic physical risks, like rising sea levels affecting coastal infrastructure. Furthermore, transition risks, including policy shifts towards a lower-carbon economy and technological advancements, will necessitate strategic adaptation and transparent reporting from Helia.
For instance, the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters in Australia, with insured losses from major events reaching approximately AUD 1.5 billion in the first half of 2024, underscore the materiality of physical climate risks. Helia will need to quantify its exposure and mitigation strategies to these events as part of its mandatory disclosures.
Climate change is increasingly bringing physical risks like more frequent and intense storms, floods, and wildfires, directly impacting property values. This can significantly affect the collateral supporting mortgages, posing a challenge for lenders. For instance, areas prone to rising sea levels or increased wildfire activity might see a decline in property desirability and market value.
In 2024, the increasing severity of weather events, as documented by organizations like NOAA, highlights the growing financial exposure. LMI providers must meticulously evaluate how these escalating physical risks could impact their entire insurance portfolio. This includes anticipating potential claims arising from lender defaults linked to properties devalued or damaged by climate-related disasters.
The shift towards a low-carbon economy presents significant transition risks for assets and industries. For Helia, this means assessing how evolving climate policies, like carbon pricing mechanisms and stricter emissions standards, could devalue properties or entire sectors within its mortgage portfolio.
Technological advancements in renewable energy and energy efficiency also pose a risk. As greener alternatives become more cost-effective, older, less efficient properties may see a decline in market value, impacting loan collateral for Helia. For instance, the global renewable energy market was valued at approximately USD 1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a rapid shift away from fossil fuel-dependent assets.
Market sentiment and investor preferences are also shifting. Increased demand for sustainable investments could lead to capital flight from carbon-intensive industries, indirectly affecting the financial health of borrowers and the stability of the mortgage market. This trend is evident in the growing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investment landscape, which saw global ESG assets reach an estimated $37.7 trillion in 2024.
ESG Integration in Financial Practices
Environmental factors are increasingly shaping financial practices, with ESG integration becoming a cornerstone of operational strategy. Helia Group, recognizing this global shift, has proactively embedded ESG commitments into its core business. This includes a strong focus on enhancing climate resilience across its operations and maintaining net zero for Scope 1 and 2 carbon emissions, directly aligning with the broader sustainable finance objectives gaining traction worldwide.
The financial sector's embrace of ESG is not merely a trend but a fundamental recalibration of risk and opportunity assessment. For instance, the global sustainable investment market reached an estimated $35.3 trillion in assets under management by early 2024, underscoring the significant capital flowing towards environmentally and socially responsible entities. Helia's strategic alignment with these principles positions it favorably within this evolving landscape.
- Climate Resilience: Helia is actively working to improve its capacity to withstand and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
- Net Zero Emissions: The group has committed to achieving net zero for its direct (Scope 1) and indirect energy (Scope 2) emissions.
- Sustainable Finance Alignment: These efforts directly contribute to the growing global movement towards sustainable financial practices and investment.
- Market Recognition: By integrating ESG, Helia aims to enhance its reputation and attract investors increasingly prioritizing sustainability.
Sustainability Initiatives and Reputation
Helia Group's dedication to sustainability significantly shapes its corporate reputation. By actively assessing and responding to climate change, Helia not only mitigates risks but also uncovers new opportunities, bolstering its image. This proactive approach to environmental stewardship is crucial in today's market.
Transparent reporting on environmental performance is key to building trust with stakeholders. Helia's commitment to clearly communicating its sustainability efforts helps align the company with the growing expectations of investors, customers, and the wider community. This transparency is a cornerstone of its reputation management.
The company's initiatives contribute to a positive brand perception, which can translate into tangible financial benefits. For instance, companies with strong Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) scores often attract more investment capital. As of early 2025, a significant portion of global assets under management are directed towards ESG-compliant investments, highlighting the financial imperative of sustainability.
- Climate Risk Management: Helia's strategy includes detailed analysis of physical and transitional climate risks impacting its operations and supply chains.
- Renewable Energy Adoption: The group aims to increase its reliance on renewable energy sources for its facilities, targeting a 30% renewable energy mix by 2026.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Helia actively engages with environmental NGOs and community groups to foster collaboration and address local environmental concerns.
- ESG Reporting Standards: The company adheres to leading ESG reporting frameworks, such as GRI and SASB, to ensure comprehensive and comparable disclosure of its environmental impact.
Helia Group's environmental strategy is significantly influenced by Australia's upcoming climate-related financial disclosure regime, effective January 2025. This mandates detailed reporting on climate risks and opportunities, impacting how Helia assesses physical risks like increased bushfire frequency and transition risks from shifts in consumer demand. The company is actively enhancing its climate resilience and has committed to net zero for Scope 1 and 2 emissions, aligning with global sustainable finance trends. By integrating ESG, Helia aims to bolster its reputation and attract the growing pool of sustainable investment capital, which reached an estimated $37.7 trillion globally by early 2025.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Helia Group | Data Point/Target |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Disclosure Regime | Mandatory reporting on climate risks and opportunities. | Effective January 2025 |
| Physical Risks (e.g., Bushfires) | Impact on insured assets and property values. | Insured losses from major events in H1 2024: ~AUD 1.5 billion |
| Transition Risks (e.g., Low-Carbon Economy) | Devaluation of carbon-intensive assets within mortgage portfolios. | Global renewable energy market value in 2023: ~USD 1.1 trillion |
| ESG Investment Trend | Increased investor focus on sustainable entities. | Global ESG assets by early 2025: Estimated $37.7 trillion |
| Renewable Energy Adoption | Target for increasing reliance on renewables. | Target: 30% renewable energy mix by 2026 |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis is meticulously constructed using a blend of authoritative public data from government bodies and international organizations, alongside proprietary market research and industry-specific reports. This ensures a comprehensive and accurate understanding of the macro-environmental landscape.
