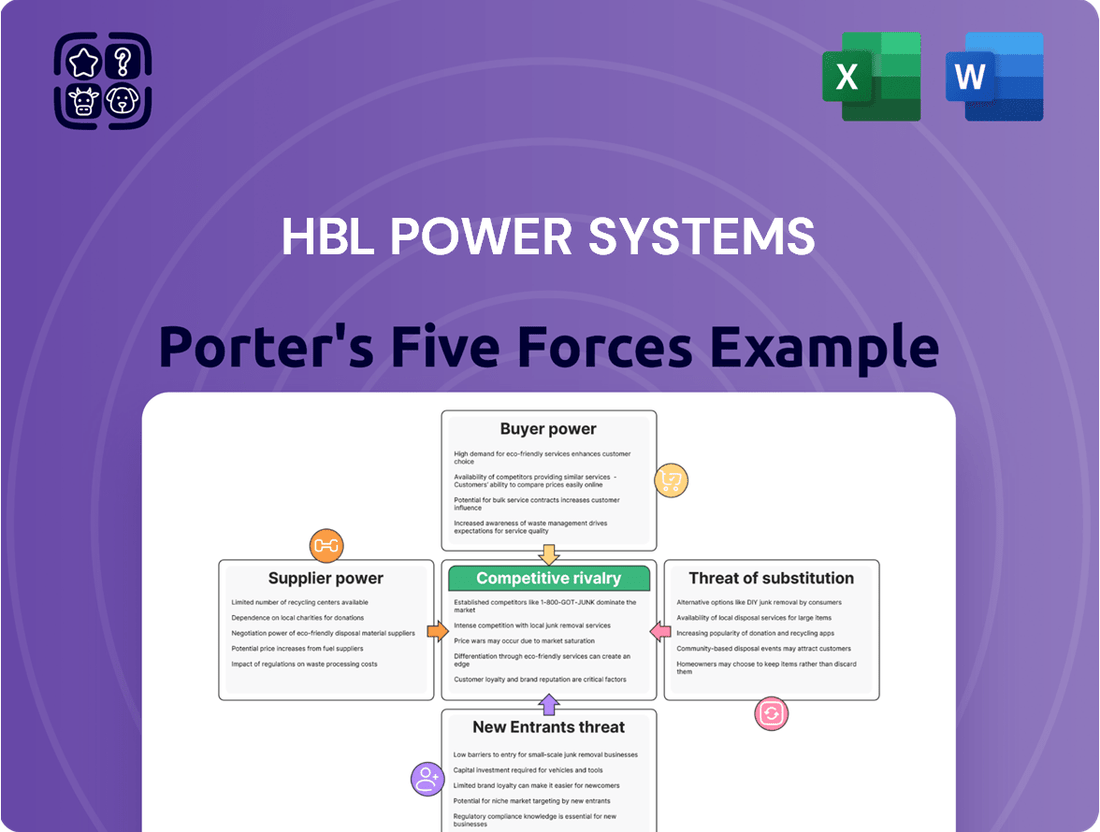
HBL Power Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HBL Power Systems Bundle
HBL Power Systems operates within an industry where buyer bargaining power is moderate, influenced by product differentiation and switching costs. The threat of new entrants is present, but capital requirements and established brand loyalty can act as barriers.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping HBL Power Systems’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
HBL Power Systems, like many in the battery manufacturing sector, depends on specialized inputs such as lithium-ion battery components and sophisticated electronic systems. The concentration of suppliers for these critical materials can significantly influence their bargaining power.
A limited number of manufacturers capable of producing these high-tech components means HBL might face fewer options. If these suppliers are few and far between, or if switching to a new supplier involves substantial costs and time, their leverage naturally increases. For instance, in 2023, global supply chain disruptions highlighted how reliance on a few key regions for battery materials like cobalt and lithium could lead to price volatility, directly impacting manufacturers like HBL.
HBL Power Systems operates in niche markets like defense and railways, often requiring specialized battery components and industrial electronics. The uniqueness of these inputs means suppliers might have a strong hand, especially if these components are proprietary or difficult to source elsewhere. For instance, if HBL needs highly specialized lithium-ion cell chemistries for its defense applications, suppliers offering these specific formulations would possess significant bargaining power.
Furthermore, the switching costs for HBL can be substantial. If a change in supplier necessitates significant re-tooling of manufacturing processes, extensive re-certification for critical applications like defense equipment, or lengthy qualification periods, HBL becomes more reliant on its existing suppliers. This inertia strengthens the supplier's position, as the cost and effort of finding and integrating an alternative supplier can be prohibitive, giving current suppliers leverage in price negotiations.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant concern for HBL Power Systems. If suppliers of crucial battery components or electronic systems develop the capability and motivation to manufacture these products themselves, they could effectively disintermediate HBL. This would allow them to capture more value and exert greater control over the supply chain, potentially bypassing HBL altogether.
This risk is amplified in rapidly evolving sectors, such as advanced battery chemistries. For instance, as the demand for specialized lithium-ion battery components grows, suppliers with the technical expertise and capital could explore producing finished battery packs, directly competing with HBL's core business. This scenario would diminish HBL's bargaining power and necessitate a strategic response to maintain its market position.
Importance of HBL to Suppliers
HBL Power Systems' importance to its suppliers directly influences the suppliers' bargaining power. If HBL represents a substantial portion of a supplier's annual revenue, that supplier might be more inclined to offer favorable terms to HBL to secure continued business. For example, if a key component supplier derives over 20% of its sales from HBL, its leverage to dictate pricing or delivery schedules would likely be diminished.
Conversely, if HBL is a relatively small customer for a particular supplier, the supplier's dependence on HBL's orders is minimal. In such scenarios, the supplier holds greater bargaining power, potentially commanding higher prices or imposing stricter terms, as they can easily substitute HBL's business with other clients. This dynamic is crucial in understanding the negotiation landscape.
- Supplier Dependence: The greater HBL's share of a supplier's revenue, the weaker the supplier's bargaining power.
- HBL's Purchasing Volume: High volume purchases by HBL can solidify its negotiating position.
- Supplier Market Concentration: If few suppliers offer a critical component, HBL’s bargaining power is reduced.
- Alternative Suppliers: The availability of multiple alternative suppliers for HBL strengthens its position.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for HBL Power Systems. If alternative raw materials or components exist, even if they are not exact replacements, it can reduce the leverage held by existing suppliers. This is because HBL could potentially switch to these substitutes, thereby limiting price increases or unfavorable terms from its primary suppliers.
HBL's strategic approach to sourcing plays a crucial role here. For instance, if HBL can secure similar materials from different geographical regions or actively invest in developing in-house alternatives for critical components, it would considerably mitigate the influence of any single supplier. This diversification and internal capability building are key to maintaining a stronger negotiating position.
- Mitigating Supplier Power: The presence of readily available substitute inputs for HBL Power Systems' manufacturing processes directly weakens supplier bargaining power.
- Diversification Strategy: HBL's ability to source comparable materials from multiple regions or develop internal production capabilities for key components reduces reliance on specific suppliers.
- Impact on Costs: A strong position regarding substitute inputs allows HBL to negotiate better pricing and terms, potentially improving its cost structure.
- Example Scenario: If a key chemical component for battery production has viable alternatives sourced from Southeast Asia or can be synthesized internally, the supplier's leverage over HBL diminishes.
The bargaining power of suppliers for HBL Power Systems is moderate, influenced by the specialized nature of its inputs and market concentration. For critical components like advanced lithium-ion cells or specialized electronic modules, HBL faces suppliers with significant leverage due to limited alternatives and high switching costs. For example, in 2023, the global shortage of certain rare earth minerals, essential for high-performance batteries, saw prices surge by up to 30% for some manufacturers, impacting companies like HBL.
HBL's reliance on niche markets, such as defense and railways, often necessitates proprietary or custom-engineered components. Suppliers of these unique items possess considerable power, especially if they hold patents or have established lengthy qualification processes that make switching difficult. The cost and time associated with re-certifying components for defense applications can be substantial, locking HBL into existing supplier relationships.
| Factor | Impact on HBL Power Systems | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized components, reducing HBL's power. | Continued consolidation in the battery materials sector. |
| Switching Costs | Significant due to re-tooling and re-certification needs. | Rising complexity of battery technology increases switching barriers. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Limited for high-performance, niche applications. | Emerging battery chemistries offer potential, but qualification is slow. |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Moderate, especially in rapidly evolving battery tech. | Some component suppliers are exploring battery pack assembly. |
| HBL's Importance to Supplier | Varies; HBL can be a key customer for specialized suppliers. | HBL's diversified customer base can strengthen its overall negotiation stance. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping HBL Power Systems' market, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
HBL Power Systems' Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, actionable framework to navigate competitive pressures, turning complex market dynamics into easily digestible insights for strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
HBL Power Systems operates in sectors such as defense, railways, and telecommunications, which often feature a concentrated customer base, particularly for substantial government tenders. This concentration means that a limited number of significant clients can wield considerable influence over pricing and contract stipulations, potentially impacting HBL's profitability.
For specialized products like railway signaling equipment or defense batteries, switching suppliers can involve high costs for customers. These costs stem from integration complexities, the need for new safety certifications, and existing long-term contracts, all of which significantly reduce the bargaining power of these customers.
HBL Power Systems serves critical sectors like defense and railways, where reliability is paramount. However, even in these areas, customers can exhibit price sensitivity, particularly for substantial orders or when facing tight budgetary controls.
For instance, in 2023, the Indian defense sector saw increased focus on cost-effectiveness in procurement, with a reported 15% increase in budget allocation for indigenization programs, suggesting a drive for value. This necessitates HBL balancing its specialized, high-quality offerings with competitive pricing strategies to secure large contracts.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers is a significant consideration for HBL Power Systems. Large clients, especially those in government or major industrial groups, could potentially explore establishing their own battery or electronics manufacturing facilities if HBL's pricing or product flexibility becomes unsatisfactory. This move, however, is generally a substantial undertaking involving significant capital investment and technical expertise.
For instance, if HBL were to experience a substantial price increase, a large defense contractor might evaluate the feasibility of in-house production. While the exact cost-benefit analysis for such a scenario is complex, the initial outlay for setting up a specialized manufacturing line for batteries or electronic components can easily run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, making it a deterrent for most.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing manufacturing capabilities for batteries or electronics requires immense upfront costs for machinery, facilities, and skilled labor.
- Technical Expertise: Developing proprietary technology and maintaining quality standards in these specialized fields demands significant R&D and operational know-how.
- Economies of Scale: HBL likely benefits from economies of scale in its production, which can be difficult for a single customer to replicate efficiently.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most large customers prefer to concentrate on their primary business functions rather than diverting resources to manufacturing activities that are not central to their operations.
Customer Information and Product Standardization
When customers possess comprehensive knowledge of product costs and have access to easily obtainable, standardized products from various suppliers, their ability to negotiate prices and terms significantly strengthens. This transparency and availability of alternatives empower buyers, allowing them to demand lower prices or better quality. For instance, in industries with commodity products, customer bargaining power is typically high.
However, HBL Power Systems strategically mitigates this by concentrating on engineered and highly customized solutions. This approach inherently reduces the substitutability of their offerings, as each solution is tailored to specific client needs. This specialization means customers are less likely to find direct, off-the-shelf alternatives, thereby diminishing their bargaining leverage.
- Customer Information: Access to detailed cost breakdowns and market pricing information empowers customers.
- Product Standardization: The availability of identical or very similar products from multiple vendors increases customer options.
- HBL's Strategy: HBL's focus on engineered and customized power solutions limits direct product comparability.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Customization reduces the ease with which customers can switch suppliers, thus lowering their bargaining power.
HBL Power Systems faces moderate customer bargaining power, primarily influenced by the concentrated nature of its key clients in sectors like defense and railways. While high switching costs for specialized products like railway signaling equipment do limit buyer leverage, customers can still exert pressure on pricing, especially for large orders. For instance, in 2023, the Indian defense sector's emphasis on cost-effectiveness, with a reported 15% increase in budget allocation for indigenization programs, highlights this price sensitivity. The potential for backward integration by major clients, though requiring substantial capital and expertise, remains a latent threat.
| Factor | HBL's Situation | Impact on Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Key clients in defense, railways, telecom are few but significant. | Moderate to High for large tenders. |
| Switching Costs | High for specialized, integrated systems (e.g., railway signaling). | Lowers customer bargaining power. |
| Price Sensitivity | Present, especially for large volume orders and government budgets. | Increases customer bargaining power. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Possible for large clients, but capital and expertise intensive. | Lowers customer bargaining power due to high barriers. |
| Product Customization | HBL focuses on tailored solutions, reducing direct comparability. | Significantly lowers customer bargaining power. |
Preview Before You Purchase
HBL Power Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive HBL Power Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing a thorough understanding of HBL Power Systems' market dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian battery market is quite crowded, featuring numerous companies vying for market share. Major players like Exide Industries and Amara Raja Batteries are significant competitors, alongside many smaller, specialized firms. This fragmentation means HBL Power Systems faces a highly competitive landscape.
In 2023, the Indian battery market was valued at approximately USD 5.8 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth. Exide Industries, a dominant force, reported revenues of around INR 15,000 crore for the fiscal year ending March 2024. Amara Raja Batteries also showcased strong performance, with revenues nearing INR 10,000 crore in the same period. HBL Power Systems, while a key player, operates within this environment of established giants and numerous other participants.
The Indian battery market is experiencing robust expansion, with projections indicating substantial growth driven by key sectors like electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and the ever-growing telecommunications industry. This expanding market is a significant factor influencing competitive rivalry.
While a high industry growth rate often tempers direct competition as companies focus on capturing market share, it simultaneously acts as a magnet for new entrants and increased investment. This influx of new players can intensify competition, especially in segments where HBL Power Systems operates.
For instance, the Indian EV battery market alone was valued at approximately USD 1.5 billion in 2023 and is forecast to grow at a CAGR of over 30% through 2030, according to various market research reports. This rapid expansion attracts both domestic and international battery manufacturers, creating a dynamic and increasingly competitive landscape for HBL Power Systems.
HBL Power Systems distinguishes itself by offering highly specialized, engineered products and solutions designed for challenging sectors like defense and railways. This focus on niche applications and custom-built systems creates a significant barrier to entry for competitors who may not possess the same technical expertise or manufacturing capabilities. For instance, in the defense sector, HBL's batteries are engineered to meet stringent military specifications, often involving unique performance requirements and extreme environmental resilience, which makes direct substitution difficult.
This strong product differentiation directly impacts competitive rivalry by shifting the focus away from price alone. When customers require specific performance characteristics or reliability for critical applications, they are less likely to switch to a lower-cost alternative that might not meet those exacting standards. In 2023, HBL reported a robust order book, partly driven by its specialized offerings in these sectors, indicating that its differentiation strategy is resonating with key customers and reducing the intensity of price wars.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, like specialized assets or long-term commitments, can trap even unprofitable companies in the market, thereby increasing competition. For HBL Power Systems, its presence in niche segments requiring specialized battery technologies, such as defense and industrial applications, could present such barriers. This means that even if a competitor struggles financially within these specific areas, they might be compelled to continue operations due to the difficulty and cost of exiting.
The nature of HBL's specialized product lines, particularly in areas like defense batteries where contracts can be long-term and require significant upfront investment in research and development and manufacturing capabilities, contributes to these exit barriers. This can lead to a situation where less efficient players remain active, putting sustained pressure on pricing and market share for all participants, including HBL. In 2024, the global defense battery market, a key segment for HBL, is projected to reach approximately USD 15 billion, indicating substantial investment and commitment within this specialized field.
- Specialized Assets: HBL's manufacturing facilities are likely equipped with specialized machinery for producing advanced battery technologies, making it costly to repurpose or sell them.
- Long-Term Contracts: Engagements in sectors like defense often involve multi-year supply agreements, obligating companies to continue production even in less profitable periods.
- Brand Reputation: In niche markets, a strong brand reputation built over time is a significant asset, and exiting could mean forfeiting this hard-earned goodwill.
- Skilled Workforce: Specialized battery manufacturing requires a highly skilled workforce; redundancy or retraining can be a significant cost, acting as an exit barrier.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic importance of the Indian market, especially in crucial areas like defense and railways, significantly fuels competitive rivalry for HBL Power Systems. Competitors recognize the long-term growth potential and are prepared to invest aggressively, potentially accepting lower profit margins to capture market share in these vital sectors.
This intense competition is evident in the battery manufacturing space, where HBL operates. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023-24, the Indian defense sector saw significant capital expenditure, with the Ministry of Defence’s budget allocation for capital procurement reaching ₹1,62,200 crore, a notable increase from the previous year. This creates a strong incentive for battery manufacturers like HBL and its rivals to vie for contracts supplying these growing defense needs.
- Defense Sector Growth: India's defense capital outlay for FY24 was ₹1.62 lakh crore, highlighting the strategic importance and potential for battery suppliers.
- Railway Electrification Push: Continued government focus on railway modernization and electrification presents ongoing opportunities for HBL's specialized battery solutions, attracting competitive interest.
- Market Share Aggression: Competitors are actively seeking to gain a foothold in these lucrative Indian sectors, leading to price-based competition and a drive for innovation.
- Technological Advancement: The demand for advanced battery technologies in defense and railways necessitates continuous R&D, intensifying the competitive landscape as firms strive for technological superiority.
HBL Power Systems faces intense competition within the Indian battery market, characterized by established giants like Exide Industries and Amara Raja Batteries, alongside numerous smaller players. This rivalry is amplified by the market's rapid growth, particularly in sectors like electric vehicles and renewable energy storage, which attracts significant investment and new entrants.
Despite the crowded market, HBL differentiates itself through specialized, engineered products for defense and railways, creating high barriers to entry. This focus on niche applications, supported by strong R&D and custom manufacturing, allows HBL to command premium pricing and reduces direct price competition, as seen in its robust 2023 order book.
However, high exit barriers in these specialized segments can keep less efficient competitors in the market, sustaining pressure on pricing. The strategic importance of India's defense and railway sectors, evidenced by a ₹1.62 lakh crore defense capital outlay in FY24, fuels aggressive competition as firms vie for lucrative contracts.
| Key Competitor | Approximate FY24 Revenue (INR Crore) | Market Focus |
| Exide Industries | 15,000 | Automotive, Industrial, Home UPS |
| Amara Raja Batteries | 10,000 | Automotive, Industrial |
| HBL Power Systems | ~2,000 (FY23) | Defense, Railways, Industrial, Telecom |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for HBL Power Systems is influenced by the price-performance trade-off offered by alternative power storage technologies. While not always direct replacements, these alternatives can present a compelling value proposition to HBL’s customers. For instance, advancements in lithium-ion battery technology, which has seen a significant cost reduction over the past decade, could offer a more attractive price point for certain applications compared to HBL's offerings, especially as the global average selling price for lithium-ion batteries dropped to approximately $130 per kWh in 2023.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives for HBL Power Systems' products is generally low, especially in critical sectors like defense and railways. These industries prioritize proven reliability and performance over marginal cost differences. For instance, the stringent safety and operational demands in railway signaling and defense communication systems mean that even a slight perceived risk with a substitute can deter adoption. HBL's established track record in these areas builds significant customer loyalty.
The threat of substitutes for HBL Power Systems is influenced by the rapid evolution of battery technologies. For instance, advancements in lithium-ion chemistries, like those offering higher energy density or faster charging, could emerge as potent substitutes if they provide a compelling performance or cost advantage that HBL struggles to replicate. The increasing focus on solid-state batteries, with their potential for enhanced safety and longevity, also poses a significant substitute threat.
Alternative Power Sources for Applications
The threat of substitutes for HBL Power Systems is a key consideration, particularly in areas where alternative energy storage or power delivery methods might gain traction. For instance, in telecommunications, while batteries are prevalent, advancements in fuel cell technology or direct improvements to grid stability could offer alternative power solutions. This could reduce reliance on battery backup systems, impacting demand for HBL's offerings.
Considering the broader energy landscape, the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, coupled with advancements in energy storage beyond traditional batteries, presents a potential substitute threat. For applications like remote power or grid stabilization, these integrated renewable solutions might compete with battery-centric approaches. For example, by 2024, the global market for energy storage systems, which includes batteries but also other technologies, was projected to reach significant figures, indicating a dynamic and evolving competitive environment.
HBL Power Systems operates in sectors where technological innovation can rapidly introduce viable substitutes.
- Telecommunications: Fuel cells and improved grid reliability are potential substitutes for battery backup.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Advanced energy storage solutions beyond conventional batteries can substitute traditional power sources.
- Industrial Applications: Emerging power technologies might offer alternatives to existing battery-based systems.
- Market Dynamics: The rapid pace of technological development necessitates continuous innovation to counter substitute threats.
Regulatory or Policy Shifts
Changes in government regulations or policies could significantly impact HBL Power Systems. For instance, a shift towards favoring specific battery chemistries or imposing stricter environmental standards on certain types of batteries could directly influence the demand for HBL's current product offerings. This could, in turn, make alternative battery technologies more attractive, thereby increasing the threat of substitutes.
Consider the evolving regulatory landscape for electric vehicles and energy storage systems. As of early 2024, many governments are actively promoting lithium-ion battery technology due to its performance characteristics and perceived environmental benefits in certain applications. This focus could indirectly disadvantage other battery types that HBL might produce or rely on, pushing consumers and industries towards these government-favored alternatives. For example, subsidies for EV adoption heavily lean towards vehicles utilizing lithium-ion batteries, potentially reducing market share for other battery chemistries.
- Policy Impact: Government incentives and mandates can steer market demand towards specific battery technologies, creating a competitive advantage for substitutes.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations on battery production or disposal could increase costs for existing technologies, making substitutes more appealing.
- Technological Subsidies: Direct or indirect subsidies for emerging battery technologies can accelerate their development and adoption, posing a threat to established players like HBL.
The threat of substitutes for HBL Power Systems is moderate, primarily due to the specialized nature of its core markets like defense and railways, where reliability trumps cost. However, advancements in alternative energy storage, such as improved lithium-ion chemistries and emerging solid-state batteries, present a growing challenge. For instance, the global energy storage market, encompassing various technologies, was projected for significant growth in 2024, indicating a dynamic competitive landscape where substitutes could gain traction if they offer superior performance or cost-effectiveness.
| Technology | Potential Substitute Threat Level | Key Differentiating Factor | 2024 Market Outlook/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion Batteries (Advanced Chemistries) | Moderate to High | Higher energy density, faster charging, cost reduction | Continued market dominance, but innovation is key |
| Solid-State Batteries | Emerging Threat | Enhanced safety, longer lifespan, faster charging | Significant R&D investment, potential for disruption |
| Fuel Cells | Low to Moderate | Longer duration power, specific niche applications | Growing interest in hydrogen economy, niche applications |
| Improved Grid Reliability | Low | Reduced need for backup power in certain sectors | Ongoing infrastructure upgrades |
Entrants Threaten
Entering HBL Power Systems' specialized battery and industrial electronics manufacturing sector demands substantial capital. New players must invest heavily in research and development, advanced manufacturing plants, and precision equipment. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art lithium-ion battery production line can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant hurdle for many potential entrants.
HBL Power Systems benefits significantly from economies of scale, a result of its established production capabilities and years of experience in developing specialized products. This scale allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs, creating a substantial barrier for new companies attempting to enter the market and compete on price from the outset.
New entrants face substantial hurdles in establishing effective distribution channels, particularly in specialized markets. For instance, HBL Power Systems' established relationships with key players in the defense and railway sectors, which often involve lengthy qualification periods and deep-seated trust, present a formidable barrier to entry.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
HBL Power Systems' focus on developing and patenting its own technologies acts as a significant deterrent to new entrants. For instance, their advancements in areas like battery technology, often protected by intellectual property, require substantial upfront investment in research and development for any competitor aiming to match their product capabilities. This proprietary edge means newcomers must either license existing technology or undertake costly, time-consuming innovation to compete effectively.
The threat of new entrants is thus mitigated by HBL's commitment to in-house R&D and its resulting intellectual property portfolio. Developing comparable engineered solutions demands considerable financial resources and technical expertise, creating a high barrier to entry. This strategic emphasis on proprietary technology ensures that potential competitors face a steep challenge in replicating HBL's offerings and market position.
- Proprietary Technology: HBL's in-house developed technologies, often protected by patents, necessitate significant R&D investment from potential new entrants.
- High Entry Costs: Competitors must either license existing technology or invest heavily in innovation to develop comparable proprietary solutions.
- Deterrent Effect: This focus on unique, engineered solutions creates a substantial barrier, discouraging new companies from entering the market.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy significantly impacts the threat of new entrants for HBL Power Systems. Strict regulations and quality standards, particularly in the defense and railway sectors where HBL operates, create substantial barriers. For instance, the defense sector requires extensive certifications and security clearances, making it difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to enter.
Furthermore, government initiatives like 'Make in India' aim to boost domestic manufacturing. While this can create opportunities, it often favors established players like HBL who already possess the necessary infrastructure, expertise, and supply chain relationships. These policies can effectively deter new companies from entering the market by increasing the initial investment and compliance burden.
- High Capital Requirements: Compliance with stringent defense and railway sector regulations necessitates significant upfront investment in specialized facilities and testing equipment, deterring potential new entrants.
- Established Relationships: Government procurement processes often favor companies with a proven track record and established relationships, making it challenging for new players to secure contracts.
- Domestic Manufacturing Push: Initiatives promoting local production, while beneficial for the economy, can also create preferential treatment for existing domestic manufacturers like HBL, increasing the entry barrier for foreign or new domestic competitors.
The threat of new entrants for HBL Power Systems remains relatively low due to significant barriers. These include high capital requirements for specialized manufacturing, established economies of scale, and the need for strong distribution channels. Furthermore, HBL's proprietary technology and the stringent regulatory environment in its key markets, particularly defense, act as substantial deterrents.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing advanced battery and electronics manufacturing facilities, including R&D, requires substantial investment. For example, a modern lithium-ion battery plant can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. | High; discourages smaller or underfunded competitors. |
| Economies of Scale | HBL's existing production volume leads to lower per-unit costs, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price initially. | Moderate to High; new entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies. |
| Distribution Channels | Securing access to specialized markets like defense and railways involves lengthy qualification processes and building trust, which HBL has already achieved. | High; new players face significant hurdles in market penetration. |
| Proprietary Technology & IP | HBL's investment in R&D and patents creates unique product offerings that are costly and time-consuming for competitors to replicate. | High; necessitates significant innovation investment or licensing for newcomers. |
| Government Regulations & Policy | Strict certifications, security clearances in defense, and quality standards in railways, coupled with policies favoring domestic manufacturing, create compliance burdens. | High; increases initial investment and time-to-market for new entrants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our HBL Power Systems Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
