H.B. Fuller Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
H.B. Fuller Bundle
H.B. Fuller navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate to high buyer power, driven by the availability of alternatives and price sensitivity in certain segments. The threat of new entrants is generally moderate, as significant capital investment and specialized knowledge are often required to compete effectively in the adhesives market.
The bargaining power of suppliers for H.B. Fuller can vary depending on the specific raw materials, with some key inputs facing concentrated supply bases. The threat of substitutes is a significant factor, as customers can often find alternative bonding solutions or even redesign products to eliminate the need for adhesives.
Within the adhesives industry, rivalry among existing competitors is intense, characterized by product innovation, pricing strategies, and global reach. This dynamic pressure necessitates continuous adaptation and strategic positioning for H.B. Fuller.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping H.B. Fuller’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
H.B. Fuller, a major player in adhesives and sealants, depends on suppliers for essential components like polymers, resins, and solvents. When these materials come from just a few specialized companies, or if those suppliers hold unique patents for vital ingredients, their leverage increases. This concentration can give suppliers significant bargaining power.
The impact of this supplier power is evident in fluctuating raw material costs. For instance, H.B. Fuller experienced a notable impact on its gross margins during fiscal year 2024 and into the first quarter of 2025 due to these cost volatilities. This trend underscores the direct influence suppliers can exert on the company's profitability.
The cost and complexity H.B. Fuller faces when switching suppliers for its highly specialized chemical inputs are significant. This can involve substantial investment in reformulating existing products, undergoing rigorous requalification processes, and managing potential disruptions to its manufacturing operations, thereby enhancing the bargaining power of its current suppliers.
For instance, in 2024, companies in the specialty chemicals sector often reported R&D expenses ranging from 3% to 7% of revenue, illustrating the investment needed for product development and adaptation, which would be incurred during a supplier switch.
However, H.B. Fuller's strategic focus on supply chain consolidation and ongoing restructuring efforts are designed to streamline operations and potentially reduce reliance on single-source specialized inputs. These initiatives aim to build greater flexibility and mitigate the impact of high switching costs over the long term.
While not a prevalent concern in the specialty chemicals sector, the risk of raw material suppliers moving into adhesive and sealant production could significantly bolster their negotiating leverage over H.B. Fuller. This scenario becomes probable if suppliers possess the requisite technical know-how, established distribution networks, and direct access to end-user markets, enabling them to directly challenge H.B. Fuller's market position.
H.B. Fuller's broad product range and strong, long-standing customer ties currently serve as a mitigating factor against this threat. For instance, in 2024, H.B. Fuller reported a robust revenue stream across various segments, demonstrating its established market presence and customer loyalty, which makes it a less attractive target for supplier integration.
Importance of H.B. Fuller to Suppliers
H.B. Fuller's position as the largest pureplay adhesives company globally means it's a substantial client for many raw material providers. This considerable purchasing volume grants H.B. Fuller some negotiation strength, particularly for common or standardized inputs. In 2023, H.B. Fuller reported net revenue of $3.9 billion, highlighting its significant demand for inputs.
However, the bargaining power dynamic shifts for specialized or proprietary materials. For these critical components, a supplier's unique offering can give them considerable leverage, potentially diminishing H.B. Fuller's volume-based advantage. For instance, if a supplier holds patents on a crucial resin or additive, H.B. Fuller's purchasing power for that specific item is significantly reduced.
- Significant Customer: H.B. Fuller's scale makes it a key account for many suppliers.
- Commodity Inputs: Leverage is higher for standardized raw materials.
- Specialized Inputs: Supplier power increases for unique or patented materials.
- Negotiating Leverage: Volume can offset some supplier power, but not entirely.
Availability of Substitutes for Raw Materials
The availability of substitute raw materials significantly curtails supplier bargaining power. If H.B. Fuller can easily switch to alternative inputs or reformulate its adhesives and sealants, its dependence on any single supplier diminishes. This flexibility allows the company to negotiate better terms or move to a different supplier if prices become unfavorable.
H.B. Fuller's strategic focus on sustainable innovation, including the development and exploration of bio-based and eco-friendly raw materials, directly addresses this factor. By actively seeking out a wider array of input options, the company is building resilience against supply chain disruptions and strengthening its negotiating position. This proactive approach to material sourcing is crucial for maintaining cost competitiveness and operational stability.
- Diversification of Raw Material Sourcing: H.B. Fuller's investment in R&D for alternative materials, such as plant-derived polymers, can reduce reliance on petrochemical-based inputs.
- Product Reformulation Capabilities: The ability to reformulate products using different chemical compositions provides flexibility when specific raw materials become scarce or prohibitively expensive.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Maintaining strong relationships with multiple suppliers across different geographic regions can mitigate the impact of localized supply issues.
- Market Trends in Sustainability: Growing demand for sustainable products encourages innovation in raw material alternatives, further empowering buyers like H.B. Fuller.
H.B. Fuller's bargaining power with its suppliers is a mixed bag, influenced heavily by the type of raw materials it needs. For common inputs, its sheer size as a major adhesive producer, evidenced by its $3.9 billion in net revenue in 2023, gives it considerable negotiation leverage.
However, this leverage diminishes significantly when dealing with specialized or patented materials. For these critical components, suppliers with unique offerings can command higher prices and dictate terms, as H.B. Fuller's ability to switch is limited by high reformulation and requalification costs, which can rival the 3-7% of revenue specialty chemical companies often invest in R&D annually.
The company's efforts in supply chain consolidation and exploring alternative, sustainable materials aim to bolster its position, reducing reliance on single-source suppliers and increasing its flexibility in the face of fluctuating raw material costs, which impacted gross margins in fiscal year 2024.
The bargaining power of suppliers for H.B. Fuller is moderate to high depending on the specificity of the raw material. For commodity chemicals, H.B. Fuller's substantial purchasing volume, reflected in its 2023 net revenue of $3.9 billion, provides significant leverage. However, for specialized polymers or proprietary additives, where suppliers may hold patents or possess unique manufacturing processes, their bargaining power increases substantially, potentially leading to higher costs and reduced flexibility for H.B. Fuller, as seen in margin impacts during fiscal year 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | H.B. Fuller's Position (as of mid-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized inputs | Moderate; relies on a few key suppliers for critical components. |
| Switching Costs for H.B. Fuller | High for specialized inputs | Significant due to reformulation and requalification needs. |
| H.B. Fuller's Purchasing Volume | High for commodity inputs | Strong leverage for standardized materials; $3.9 billion in 2023 revenue. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Lowers supplier power | Increasingly important as H.B. Fuller explores bio-based and alternative materials. |
| Potential for Backward Integration by Suppliers | High threat | Low to moderate; H.B. Fuller's market position and customer ties mitigate this. |
What is included in the product
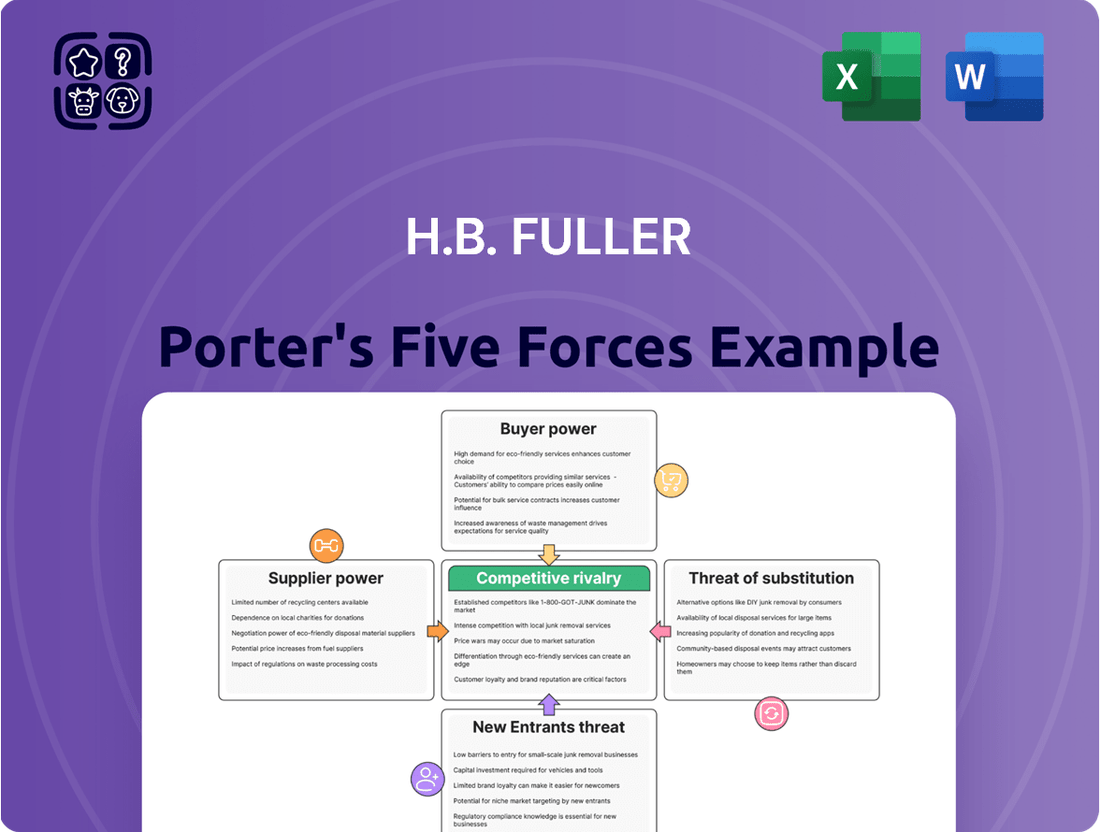
This analysis evaluates the intensity of competition, buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, specifically within H.B. Fuller's adhesive and sealant markets.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
H.B. Fuller's broad industry reach, spanning packaging, hygiene, construction, and electronics across over 140 countries, inherently dilutes individual customer concentration. However, within these diverse segments, large industrial clients and major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) can still exert considerable bargaining power due to the sheer volume of their adhesive and sealant purchases.
For instance, a major automotive OEM requiring substantial quantities of specialized adhesives for vehicle assembly could negotiate favorable terms, impacting H.B. Fuller's pricing and profit margins. This is a common dynamic in business-to-business industries where a few key accounts can represent a significant portion of revenue, giving those customers more leverage.
Customer switching costs for H.B. Fuller can be a significant factor, especially in specialized sectors. For instance, in the automotive industry, adhesives are often deeply integrated into vehicle design and manufacturing processes. Changing suppliers could necessitate costly re-engineering and extensive re-validation of materials, potentially disrupting production lines. For 2023, H.B. Fuller reported approximately $3.2 billion in revenue, indicating a substantial customer base where switching costs play a role in maintaining market share.
H.B. Fuller's product differentiation significantly dampens customer bargaining power. The company focuses on specialized formulations and innovative solutions that directly enhance customer performance, efficiency, and sustainability. This strategic emphasis means customers are less likely to find readily available, interchangeable alternatives that offer the same benefits.
A substantial portion of H.B. Fuller's innovation pipeline, around 60% of its new product development efforts in 2024 and continuing into 2025, is dedicated to improving the sustainability of customer end products. This value-added proposition makes switching costly and less attractive for clients focused on environmental credentials and regulatory compliance.
By offering high-performance, tailored solutions, H.B. Fuller cultivates a strong position that supports pricing power. This was evident in their targeted pricing actions during the second quarter of 2025, indicating that customers value the unique benefits and are less inclined to push for lower prices due to the specialized nature of the offerings.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers backward integrating and producing their own adhesives for H.B. Fuller is generally low. This is primarily because adhesive manufacturing requires substantial capital for specialized equipment and a high degree of technical expertise in chemical formulation and production processes.
Most customers, operating in diverse industries like construction or electronics, find it more strategic to concentrate on their core business operations rather than undertaking the complexities and costs associated with specialty chemical production. For instance, a furniture manufacturer's expertise lies in woodworking and design, not in developing advanced polymer formulations.
However, for very large volume customers with existing chemical production capabilities, the threat, while still modest, could be slightly elevated.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up adhesive manufacturing facilities demands millions in specialized reactors, mixing equipment, and quality control systems.
- Technical Expertise: Formulating adhesives requires deep knowledge of chemistry, rheology, and application-specific performance characteristics.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most customers, including major players in sectors like automotive or packaging, prioritize their primary business activities.
- Economies of Scale: H.B. Fuller benefits from economies of scale in purchasing raw materials and optimizing production, making it difficult for individual customers to match cost-effectiveness.
Importance of H.B. Fuller's Product to Customer's Business
H.B. Fuller's adhesives are frequently vital to the performance and manufacturing processes of its clients. In sectors like automotive and electronics, these adhesives are indispensable for enabling lighter vehicles, integrating advanced battery systems, and ensuring the structural integrity of finished goods. This inherent importance limits customers' ability to switch suppliers based solely on price, thereby dampening their bargaining power.
The criticality of H.B. Fuller's adhesive solutions means that quality and reliability often outweigh cost considerations for customers. For instance, a failure in an adhesive bond in an automotive assembly could lead to significant warranty claims or safety recalls, far exceeding any initial cost savings from a cheaper alternative. This reliance on H.B. Fuller's specialized products strengthens the company's position.
- Adhesives as critical components: H.B. Fuller's products are essential for customer product functionality and manufacturing efficiency.
- Impact on customer end-products: Adhesives influence durability, performance, and assembly in sectors like automotive and electronics.
- Reduced price sensitivity: Customers are less likely to prioritize price over the quality and reliability of crucial adhesive applications.
- Limited customer switching: The specialized nature and critical role of H.B. Fuller's adhesives make it difficult for customers to substitute with lower-cost alternatives without impacting product quality.
While H.B. Fuller serves a broad customer base, the bargaining power of individual customers is generally moderate. This is due to the company's specialization, high switching costs for clients, and the critical nature of its adhesive solutions. For example, the automotive sector, a key market for H.B. Fuller, often faces significant disruption and re-engineering costs if switching adhesive suppliers, thus limiting their leverage.
H.B. Fuller's strategic focus on product differentiation, with approximately 60% of its new product development in 2024 and 2025 aimed at enhancing customer sustainability, further reduces customer price sensitivity. Customers value these tailored, high-performance formulations, as demonstrated by H.B. Fuller's targeted pricing actions in Q2 2025, indicating that product benefits often outweigh price negotiations.
The threat of backward integration by customers is low, as adhesive manufacturing requires substantial capital investment and specialized technical expertise, which most clients prefer not to undertake to maintain focus on their core competencies. However, very large volume customers with existing chemical capabilities might pose a slightly higher, though still modest, threat.
| Factor | Impact on H.B. Fuller's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Moderate | Broad industry reach dilutes individual customer power, though large OEMs can exert influence. |
| Switching Costs | High | Integration into customer processes (e.g., automotive) necessitates costly re-engineering and validation. |
| Product Differentiation & Value-Added Services | Lowers Power | 60% of 2024-2025 NPD focused on customer sustainability, enhancing value and reducing price sensitivity. |
| Criticality of Products | Lowers Power | Adhesives are vital for performance and manufacturing, making quality and reliability paramount over cost. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low | High capital investment and technical expertise required for adhesive production deter most customers. |
Preview Before You Purchase
H.B. Fuller Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact H.B. Fuller Porter's Five Forces Analysis document you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the adhesives industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, all presented in a professionally formatted and ready-to-use file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
H.B. Fuller operates in a highly competitive global market for adhesives, sealants, and specialty chemicals. Key rivals include giants like Henkel, Sika, Arkema, 3M, RPM International, and Eastman Chemical. This diverse competitive landscape presents a significant challenge.
While H.B. Fuller holds the distinction of being the largest pure-play adhesives company, its market position is constantly tested by these formidable competitors. Many of these rivals are large, diversified chemical conglomerates with substantial resources and broad product portfolios, intensifying the competitive rivalry.
The presence of numerous smaller, specialized niche players further fragments the market, adding another layer of competition. These smaller firms often focus on specific applications or technologies, allowing them to carve out distinct market segments and challenge larger players with tailored solutions.
The adhesives market is experiencing growth, fueled by trends such as sustainability, the rise of e-commerce, and the demand for lightweight materials in sectors like automotive. However, H.B. Fuller indicated a tougher period for volume growth in late 2024 and into 2025, especially within consumer goods and packaging.
This slowdown in key segments can heighten competitive rivalry. Companies may aggressively compete for the available business in these slower-growing areas, potentially leading to price pressures and increased marketing efforts to secure market share.
Competitive rivalry in the adhesives market is significantly fueled by product differentiation. Companies actively invest in research and development to create specialized adhesives boasting superior properties like increased strength, quicker curing, and enhanced resistance to environmental factors.
H.B. Fuller exemplifies this focus on innovation, reporting that 22% of its 2024 revenue originated from new products launched within the preceding five years. This demonstrates a clear strategy to stand out from competitors by continuously introducing advanced solutions.
Exit Barriers in the Industry
Exit barriers in the specialty chemicals and adhesives sector are notably substantial, largely driven by the immense capital required for manufacturing plants and highly specialized machinery. These significant fixed costs make it economically challenging for firms to withdraw from the market, even when profitability wanes.
This persistence, even in downturns, contributes to sustained competitive rivalry as companies are reluctant to divest assets. For instance, H.B. Fuller, a major player, operates complex production facilities that represent millions in sunk costs. The specialized nature of adhesive formulations also means that intellectual property and proprietary processes are valuable assets that are difficult to liquidate, further increasing exit costs.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for manufacturing, R&D, and specialized equipment create a financial trap for exiting firms.
- Specialized Assets: Production lines and formulations are often unique to the industry, reducing their resale value outside of it.
- Intellectual Property: Patents and proprietary knowledge represent significant investments that are hard to monetize upon exit.
- Employee Expertise: The need for highly skilled labor and specialized knowledge means that workforce disruption is also a factor in exit decisions.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The adhesives industry, including players like H.B. Fuller, is characterized by substantial investments in manufacturing plants and ongoing research and development. These high fixed costs create a constant need to maximize production output. For instance, in 2023, the global adhesives and sealants market was valued at approximately $70 billion, with significant capital expenditure required to maintain market share and efficiency.
This drive for high capacity utilization often translates into aggressive pricing tactics. When demand softens, companies may lower prices to ensure their facilities are running at optimal levels, thereby capturing sales volume and spreading fixed costs over more units. This can lead to price wars, especially in more commoditized segments of the market, directly intensifying competitive rivalry.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investment in manufacturing infrastructure and R&D in the adhesives sector.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: Companies aim for high production levels to cover fixed costs, influencing operational decisions.
- Aggressive Pricing: Lowering prices to secure sales volume becomes a strategy during periods of reduced demand.
- Intensified Rivalry: The interplay of high fixed costs and the need for utilization fuels a more competitive market environment.
The competitive rivalry within the adhesives market remains intense, driven by a mix of large, diversified players and specialized niche firms. H.B. Fuller, as the largest pure-play adhesives company, faces constant pressure from rivals like Henkel, Sika, and 3M, many of whom possess broader product portfolios and greater financial resources. This dynamic is further amplified by the ongoing pursuit of product differentiation through R&D, with H.B. Fuller reporting that 22% of its 2024 revenue came from new products launched within the last five years. While the market is growing, a slowdown in consumer goods and packaging during late 2024 and into 2025 can escalate price competition as companies vie for market share in these segments.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of direct substitutes for adhesives and sealants is a significant consideration for H.B. Fuller. Alternative joining methods, including mechanical fasteners like screws and rivets, as well as welding, offer different approaches to bonding materials. These substitutes can be particularly appealing in applications where specific performance characteristics are paramount or where traditional methods have long-established infrastructure and expertise.
While adhesives have demonstrably gained ground, replacing traditional fasteners due to their improved performance and often lower overall cost in numerous sectors, the landscape is dynamic. For instance, advancements in lightweight materials and modular designs in industries like automotive and aerospace are sometimes favoring mechanical joining or even eliminating the need for extensive bonding altogether. This ongoing innovation in alternative joining technologies represents a persistent challenge.
The market for industrial adhesives, a key segment for H.B. Fuller, saw substantial growth, with global revenues estimated to reach over $70 billion in 2024. However, the increasing sophistication and cost-competitiveness of mechanical fastening solutions, alongside new material science breakthroughs that reduce reliance on bonding, mean that H.B. Fuller must continually innovate its adhesive offerings to maintain its competitive edge and justify its value proposition against these direct alternatives.
The price-performance trade-off is critical when considering substitutes for H.B. Fuller's adhesives. While mechanical fasteners like screws and rivets might appear cheaper upfront, adhesives frequently provide superior value through benefits such as reduced weight, improved aesthetics, better stress distribution, and enhanced long-term durability. For instance, in the automotive sector, the shift towards lightweighting for fuel efficiency has favored adhesives, which can reduce vehicle weight by up to 10% compared to traditional fasteners.
However, the threat from substitutes escalates if they can match adhesive performance while offering a lower cost or simpler application process. For example, advancements in welding technologies or innovative snap-fit designs could present a more cost-effective alternative in certain assembly operations. If these substitute solutions can deliver comparable structural integrity and longevity at a significantly reduced price point, H.B. Fuller's market position could be challenged.
H.B. Fuller's customers often face significant switching costs when considering alternative bonding methods. These costs can include substantial investments in redesigning products to accommodate different materials or joining techniques, retooling entire production lines to integrate new equipment, and comprehensive retraining of personnel to operate and maintain these new systems. This creates a strong barrier against substitution, particularly in industries dealing with complex assemblies where adhesives are fundamentally embedded within the manufacturing workflow.
Innovation in Substitute Technologies
The threat of substitutes for H.B. Fuller’s adhesive solutions is influenced by ongoing advancements in alternative bonding technologies. Innovations in areas like advanced welding for dissimilar materials or new mechanical fastening methods could present viable alternatives, potentially impacting market share. For instance, advancements in laser welding are making it a more attractive option for joining certain materials traditionally bonded with adhesives.
H.B. Fuller actively counters this threat through its own innovation pipeline. A prime example is their work on debonding-on-demand adhesives for electric vehicle battery packs. This technology not only addresses a critical need for improved recyclability in a rapidly growing market but also reinforces the value proposition of their adhesive solutions in a sector increasingly scrutinized for its environmental impact. This strategic focus on enabling circular economy principles through adhesive technology helps to differentiate their offerings.
The company's commitment to innovation in areas that facilitate disassembly and recycling is crucial. As industries like automotive and electronics prioritize sustainability and end-of-life management, adhesives that enable easier separation of components become more attractive than traditional methods that might permanently fuse materials. This forward-thinking approach positions H.B. Fuller to capture value in evolving market demands where material recovery and reuse are paramount.
The competitive landscape is dynamic, with continuous development in alternative joining methods. However, the inherent advantages of adhesives in specific applications, such as flexibility, weight reduction, and cost-effectiveness, often remain compelling. H.B. Fuller’s ability to innovate within these core strengths, while also developing solutions for emerging challenges like recyclability, is key to managing the threat of substitution.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customer propensity to substitute is a significant factor influencing H.B. Fuller's market position. This willingness to switch is driven by several key elements. For instance, industry trends like lightweighting in the automotive sector, where adhesives replace traditional fasteners, directly impact demand for specific adhesive solutions. By 2024, the global automotive lightweight materials market was projected to reach over $120 billion, highlighting the shift towards materials where advanced bonding is crucial.
Regulatory pressures also play a vital role. As environmental standards tighten, industries are increasingly seeking alternatives to solvent-based adhesives, favoring water-based or hot-melt technologies. This shift creates opportunities for companies offering compliant solutions and pressures those relying on older chemistries. The demand for low-VOC (volatile organic compound) adhesives, for example, has seen steady growth, pushed by regulations in regions like Europe and North America.
Furthermore, evolving design requirements can encourage customers to explore new bonding technologies. As products become more complex or require enhanced performance characteristics, existing adhesive solutions might prove inadequate, leading to a search for substitutes. This dynamic is evident in the electronics industry, where miniaturization and heat dissipation needs demand innovative adhesive formulations. By 2025, the global electronics adhesives market is anticipated to surpass $10 billion, driven by these technological advancements.
- Industry Trends: Lightweighting in automotive fuels demand for advanced adhesives, replacing mechanical fasteners.
- Regulatory Pressures: Stricter environmental regulations promote solvent-free and low-VOC adhesive alternatives.
- Evolving Design: Miniaturization and performance demands in sectors like electronics necessitate new bonding technologies.
- Sustainability Focus: A growing emphasis on sustainable materials and processes encourages exploration of alternative adhesive solutions.
The threat of substitutes for H.B. Fuller's adhesives is managed by understanding customer willingness to switch, which is influenced by industry trends like lightweighting in automotive, regulatory pressures favoring low-VOC adhesives, and evolving product design needs in electronics. For instance, the automotive lightweighting trend, projected to contribute to a global market exceeding $120 billion in 2024, drives demand for advanced bonding solutions.
Innovations in alternative joining methods, such as advanced welding and novel mechanical fasteners, present ongoing challenges. However, H.B. Fuller's strategic focus on developing debonding-on-demand adhesives for electric vehicles and solutions that enhance recyclability helps differentiate its offerings and maintain a competitive edge against these substitutes.
The cost-performance balance remains critical, with adhesives often providing superior long-term value through benefits like weight reduction, which can save up to 10% in vehicle weight compared to traditional fasteners in automotive applications. Despite the potential for substitutes to offer lower upfront costs or simpler application, the comprehensive performance advantages of adhesives, coupled with customer switching costs, create significant barriers.
The market for industrial adhesives is robust, with global revenues estimated to exceed $70 billion in 2024. H.B. Fuller's continued investment in research and development, particularly in areas supporting sustainability and circular economy principles, is essential for navigating the evolving threat of substitutes and reinforcing the value of its adhesive technologies.
Entrants Threaten
The specialty chemicals and adhesives sector, including companies like H.B. Fuller, demands significant upfront investment. Entry requires substantial capital for robust research and development to innovate new formulations, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and specialized production equipment. Establishing a comprehensive global distribution and sales network also adds to these considerable capital needs.
These high capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, deterring potential new competitors from easily entering the market. For instance, the construction of a new, modern chemical manufacturing facility can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, not including the ongoing investment in R&D and market penetration.
Established players like H.B. Fuller leverage considerable economies of scale, particularly in raw material sourcing. For instance, in 2023, H.B. Fuller reported over $3.2 billion in net revenue, suggesting significant purchasing power that allows for bulk discounts on chemicals and resins.
This scale translates directly into lower per-unit production costs. New entrants would find it challenging to match these efficiencies, as they would likely face higher initial costs for materials and may not achieve the same production volumes to spread fixed costs effectively.
Furthermore, H.B. Fuller's investment in research and development, supported by its revenue base, creates another barrier. Their ability to fund ongoing innovation and product development at a substantial scale, potentially millions of dollars annually, is difficult for newcomers to replicate.
Consequently, new entrants are at a distinct cost disadvantage. They would need to absorb higher operating expenses, making it harder to compete on price against incumbents who benefit from decades of optimized operations and market presence.
Brand loyalty and significant customer switching costs, particularly within demanding industrial adhesive applications, erect formidable barriers for emerging competitors. Newcomers face the challenge of convincing established clients to abandon reliable, performance-tested solutions. This reluctance stems from the inherent risks of compromising product efficacy or introducing costly disruptions to ongoing manufacturing operations. For instance, in the automotive sector, a switch in adhesive supplier might necessitate extensive re-qualification and testing, a process that can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars and delay product launches, making H.B. Fuller's established relationships a powerful deterrent.
Access to Distribution Channels
New companies entering the adhesives market face significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution networks. H.B. Fuller's robust global infrastructure, reaching customers in over 140 countries, represents a formidable barrier that new entrants would struggle to match in terms of both scale and efficiency.
The ability to leverage existing distribution channels, which often involve complex logistics and strong customer relationships built over years, provides incumbents like H.B. Fuller with a substantial competitive advantage. For instance, H.B. Fuller's extensive network allows for timely product delivery and localized support, critical factors in the adhesives industry where application-specific needs and quick turnaround times are common.
- Limited Reach: New entrants often lack the capital and established relationships to build a comparable global distribution network quickly.
- Logistical Complexity: Managing a global supply chain for adhesives requires specialized expertise and significant investment in infrastructure.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing distributors often have strong ties with customers, making it difficult for new suppliers to gain shelf space or preferred supplier status.
- Cost Disadvantage: Without the economies of scale afforded by broad distribution, new entrants face higher per-unit distribution costs.
Regulatory and Environmental Barriers
The specialty chemicals sector, where H.B. Fuller operates, faces significant hurdles for newcomers due to rigorous regulatory frameworks. These regulations cover a wide range of concerns, including environmental protection, workplace safety, and product specific certifications. For instance, compliance with standards like REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) in Europe and volatile organic compound (VOC) limits is not only complex but also demands substantial capital outlay and specialized knowledge.
These compliance costs act as a formidable barrier to entry. New companies must invest heavily in research and development to ensure their products meet these stringent standards, alongside establishing robust safety protocols and obtaining necessary certifications. This financial and technical commitment can deter many potential competitors from entering the market, thereby protecting established players like H.B. Fuller from immediate new threats.
In 2024, the global chemical industry continued to grapple with evolving environmental legislation. For example, stricter emissions standards and waste management requirements necessitate ongoing investment in cleaner production technologies. Companies failing to meet these benchmarks face penalties and reputational damage, further emphasizing the capital intensity of adhering to regulatory demands.
- Environmental Regulations: Stringent rules on emissions, waste disposal, and hazardous materials management increase operational costs.
- Product Safety & Certifications: Meeting standards for toxicity, flammability, and end-use application safety requires extensive testing and validation.
- Global Compliance Complexity: Navigating diverse regulatory landscapes across different countries adds significant operational and legal overhead.
- R&D Investment for Compliance: Developing compliant formulations and manufacturing processes demands considerable financial resources and technical expertise.
The threat of new entrants in the specialty chemicals and adhesives market, where H.B. Fuller operates, is generally low due to substantial barriers. These include high capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents, strong customer loyalty and switching costs, and complex regulatory compliance. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing investment in sustainable chemical production and compliance with evolving environmental laws, such as stricter VOC limits, continue to raise the cost of entry. These factors collectively protect established players from significant new competition.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our H.B. Fuller Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including H.B. Fuller's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld and Statista. This blend of company-specific financial disclosures and broad industry data ensures a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
