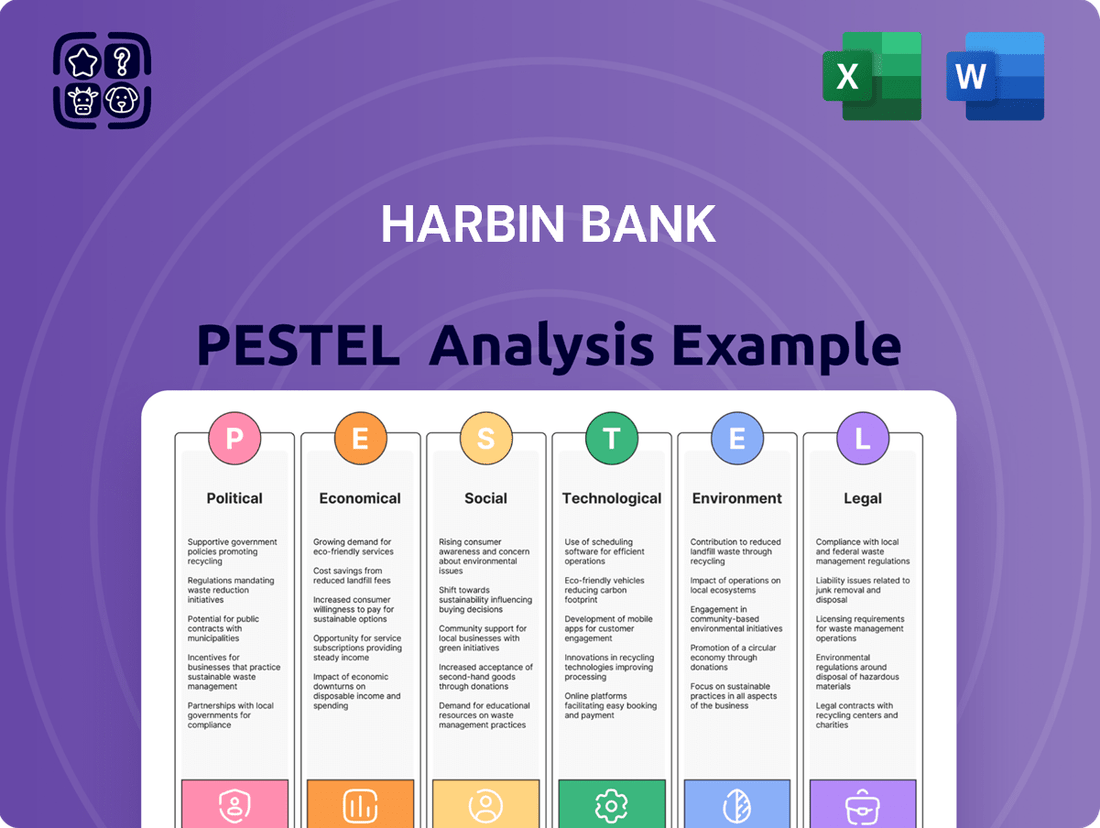
Harbin Bank PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Harbin Bank Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping Harbin Bank's strategic landscape. Our PESTLE analysis provides a deep dive into these external forces, offering actionable intelligence for informed decision-making. Don't get left behind; download the full analysis now to gain a competitive edge.
Political factors
The Chinese government's ongoing focus on directing the banking sector to bolster the real economy significantly influences institutions like Harbin Bank. This means banks are steered towards increasing credit availability for strategic sectors identified by national policy, such as advanced manufacturing and green energy.
In 2023, for instance, China's central bank and financial regulators continued to emphasize credit growth in areas supporting technological innovation and rural development, with total social financing reaching 33.65 trillion yuan for the year, an increase of 2.48 trillion yuan compared to the previous year.
Harbin Bank, like its peers, must therefore balance profitability with directives to support these national economic objectives, ensuring its lending practices contribute to broader stability and growth agendas.
The establishment of China's National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) in 2023 marked a significant shift, consolidating oversight from various previous bodies. This unified framework directly impacts Harbin Bank's operational, compliance, and risk management strategies.
The NFRA's expanded authority is designed to bolster financial stability and enhance consumer protection across the sector. For Harbin Bank, this means navigating a more centralized and potentially stringent regulatory environment, influencing capital adequacy ratios and business expansion plans.
Escalating trade tensions, particularly with the US imposing tariffs, create a complex external environment that can weigh on China's economic activity. This can indirectly impact Harbin Bank, as a slowdown in trade can affect the performance of its corporate clients and cross-border transactions. For instance, China's exports to the US saw a notable dip in certain periods of 2023 due to these tariffs.
Support for Strategic Industries
The Chinese government is strategically directing financial resources towards key sectors to foster economic growth and innovation. This includes prioritizing bank lending to what are termed the 'Five Major Areas': technology finance, green finance, inclusive finance, pension finance, and digital finance. Harbin Bank has demonstrated a clear commitment to these national objectives by actively increasing its loan disbursements to strategic emerging industries, technology finance, and green finance initiatives. This proactive approach ensures Harbin Bank's loan portfolio is closely aligned with China's overarching development strategies and economic priorities for 2024 and 2025.
Harbin Bank's strategic alignment with government directives is evident in its financial activities. For example, the bank has intensified its support for technology finance, a critical area for national innovation. Furthermore, its commitment to green finance is demonstrated through increased lending to environmentally sustainable projects. These actions reflect a deliberate effort by Harbin Bank to not only meet regulatory expectations but also to capitalize on growth opportunities within these government-supported sectors.
- Government Focus: Prioritization of lending to technology, green, inclusive, pension, and digital finance sectors.
- Harbin Bank's Response: Increased loans to strategic emerging industries, technology finance, and green finance.
- Alignment: Loan portfolio directly supports national development goals and economic priorities.
- 2024-2025 Outlook: Continued emphasis on these strategic areas is expected to shape lending practices and growth.
Monetary Policy Adjustments
The People's Bank of China (PBOC) has been actively using monetary policy tools to foster economic growth and ensure financial stability. In 2024, the PBOC continued its approach of targeted easing, including adjustments to the reserve requirement ratio (RRR) and benchmark lending rates, aiming to boost credit availability for businesses and consumers.
These policy shifts directly shape Harbin Bank's operational landscape. For instance, a lower RRR generally increases the funds available for lending, potentially expanding net interest margins, while interest rate adjustments can impact borrowing costs and loan demand. The PBOC's commitment to maintaining a prudent yet supportive monetary stance in 2024-2025 is a key factor influencing the bank's profitability and risk management strategies.
- PBOC's 2024 RRR Cuts: The PBOC implemented several RRR cuts throughout 2024, injecting significant liquidity into the banking system. For example, a 0.5 percentage point cut in early 2024 released approximately RMB 1 trillion in long-term liquidity.
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Benchmark lending rates, such as the Loan Prime Rate (LPR), have seen adjustments, influencing the cost of borrowing for both individuals and corporations, thereby affecting Harbin Bank's lending income.
- Impact on Net Interest Margins: Changes in policy rates and RRR directly influence the spread between a bank's interest income from loans and its interest expenses on deposits, a critical determinant of profitability.
The Chinese government's strategic direction for the financial sector significantly shapes Harbin Bank's operations, with a strong emphasis on supporting key economic initiatives. This includes directing credit towards technology, green development, and rural revitalization, aligning the bank's lending practices with national policy objectives for 2024 and 2025.
The establishment of the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) in 2023 has centralized oversight, leading to a more unified and potentially stringent regulatory environment. Harbin Bank must adapt to these consolidated regulations, which impact its capital requirements and expansion strategies, aiming for enhanced financial stability and consumer protection.
Monetary policy decisions by the People's Bank of China (PBOC), such as reserve requirement ratio (RRR) cuts in 2024, directly influence liquidity and lending capacity for banks like Harbin. These adjustments aim to stimulate economic activity by making credit more accessible, thereby affecting the bank's net interest margins and overall profitability.
| Political Factor | Description | Impact on Harbin Bank | Relevant Data/Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Economic Directives | Government focus on bolstering the real economy through directed lending. | Harbin Bank must align lending with national priorities like technology and green finance. | China's total social financing reached 33.65 trillion yuan in 2023. |
| Regulatory Consolidation | Creation of the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA). | Increased compliance burden and centralized oversight for Harbin Bank. | NFRA established in 2023 to unify financial regulation. |
| Monetary Policy | PBOC's use of tools like RRR and interest rates. | Affects Harbin Bank's liquidity, lending capacity, and net interest margins. | PBOC implemented RRR cuts in 2024, injecting liquidity. |
| Trade Relations | Geopolitical trade tensions, particularly with the US. | Indirect impact on corporate clients and cross-border transactions, affecting loan performance. | China's exports to the US experienced fluctuations in 2023 due to tariffs. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis of Harbin Bank delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors impacting its operations, providing a comprehensive understanding of the external landscape.
A PESTLE analysis of Harbin Bank offers a clear, summarized version of external factors for easy referencing during strategic planning, alleviating the pain of information overload.
This visually segmented PESTLE analysis for Harbin Bank allows for quick interpretation of political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal influences, relieving the burden of sifting through complex data.
Economic factors
China's economic growth is anticipated to hover around 5% for both 2024 and 2025, indicating a period of recovery that is still solidifying. Harbin Bank's financial results, including loan demand and the quality of its assets, are directly influenced by this broader economic trajectory.
A stable macroeconomic environment is fundamental for the sustained success and performance of the banking sector. For Harbin Bank, this means its business is intrinsically linked to the overall health and stability of the Chinese economy.
The prevailing low interest rate environment in China's banking sector is placing significant pressure on net interest margins (NIMs). This trend is particularly challenging for institutions like Harbin Bank.
As lending rates continue to fall, banks are finding it harder to generate income from their loan portfolios. Simultaneously, adjustments to deposit rates, while necessary to attract funding, further compress the spread between borrowing and lending costs, impacting profitability.
For instance, China's benchmark loan prime rate (LPR) for five-year loans, a key lending rate, has seen reductions, impacting the yields on many loans. Harbin Bank, in response, must explore strategies to diversify income streams and manage its funding costs more effectively to navigate this margin compression.
The persistent downturn in China's real estate sector continues to weigh heavily on the economy, directly affecting banks like Harbin Bank by impacting their asset quality and lending opportunities. This ongoing property market adjustment presents a considerable risk to the bank's loan book and its overall financial stability.
Despite government efforts to stimulate the market, such as interest rate adjustments and eased mortgage rules implemented throughout 2023 and into early 2024, the real estate slump remains a critical concern. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, property investment in China fell by 9.5% year-on-year, highlighting the depth of the challenges.
Consumer Spending and Demand
China's economic strategy heavily emphasizes boosting domestic demand and consumption, making consumer spending a critical engine for growth. Harbin Bank's retail operations, including personal loans and wealth management, are directly tied to consumer confidence and their propensity to spend. For instance, China's retail sales of consumer goods saw a notable increase, reaching 47.15 trillion yuan in 2023, a 7.1% rise year-on-year, indicating a robust appetite for spending that benefits banks like Harbin.
Consumer confidence, a key driver for Harbin Bank's retail segment, directly impacts demand for credit cards and other financial products. As of early 2024, while consumer sentiment has shown signs of recovery, fluctuations remain a factor. For example, the Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) for the services sector, a proxy for consumer activity, has hovered around the expansionary mark, suggesting continued, albeit sometimes uneven, consumer engagement that Harbin Bank needs to navigate.
- Consumer spending is a primary growth driver for China's economy.
- Harbin Bank's retail banking services are sensitive to consumer confidence.
- Retail sales in China grew by 7.1% in 2023, reaching 47.15 trillion yuan.
- The services PMI indicates ongoing, though sometimes variable, consumer activity.
Loan Growth and Asset Quality
Harbin Bank reported a notable year-on-year increase in total customer loans and advances in 2024, reflecting its expansion efforts. However, this growth occurs within a challenging Chinese banking landscape characterized by decelerating loan growth and increasing asset quality concerns. For instance, by the end of Q1 2024, the non-performing loan (NPL) ratio for the Chinese banking sector edged up slightly, presenting a headwind.
To navigate these economic factors effectively, Harbin Bank must maintain vigilant oversight of its non-performing loan ratio and ensure robust provision coverage. This proactive approach is crucial for safeguarding asset quality and ensuring financial stability, especially as economic uncertainties persist through 2025. The bank's ability to manage these metrics will be a key indicator of its resilience.
- Loan Growth: Harbin Bank's total customer loans and advances saw a significant increase in 2024.
- Sector Challenges: The broader Chinese banking sector is experiencing slowing loan growth.
- Asset Quality Pressure: There is increasing pressure on asset quality across the Chinese banking system.
- Risk Management: Harbin Bank needs to carefully manage its non-performing loan ratio and provision coverage.
China's economic growth is projected to be around 5% for 2024 and 2025, a recovery that is still solidifying and directly impacts Harbin Bank's loan demand and asset quality.
The low interest rate environment continues to pressure net interest margins, forcing banks like Harbin to seek diversified income and manage funding costs effectively to counter compressed lending spreads.
The ongoing real estate sector downturn remains a significant risk, affecting asset quality and lending opportunities, despite government stimulus measures like interest rate adjustments and eased mortgage rules seen through early 2024.
A focus on domestic demand and consumption boosts retail banking, with China's retail sales growing 7.1% in 2023 to 47.15 trillion yuan, indicating strong consumer spending that benefits Harbin Bank's personal loan and wealth management services.
| Economic Factor | 2023 Data | 2024 Projection/Early Data | Impact on Harbin Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | 5.2% | ~5% | Influences loan demand and asset quality. |
| Retail Sales Growth | 7.1% | Continued growth expected | Boosts retail banking and consumer credit. |
| Property Investment | -9.5% (Q1 2024 YoY) | Ongoing downturn | Increases risk in loan book due to sector exposure. |
| Interest Rates (5-year LPR) | Decreasing trend | Continued pressure on NIMs | Compresses net interest margins, impacting profitability. |
Full Version Awaits
Harbin Bank PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Harbin Bank delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations and strategic direction. Gain a complete understanding of the external forces shaping Harbin Bank's future.
Sociological factors
Chinese consumers are deeply integrated with digital finance, with mobile payments via QR codes and extensive use of mobile banking being commonplace. In 2023, China’s mobile payment transaction volume reached an estimated $44 trillion, highlighting this trend.
Harbin Bank needs to prioritize its digital transformation to align with these shifting consumer habits. This means investing in user-friendly mobile banking apps and online platforms that offer seamless transaction capabilities and personalized digital financial products.
By enhancing its digital offerings, Harbin Bank can better cater to the preferences of its customer base, fostering greater engagement and loyalty in an increasingly competitive digital banking landscape.
The Chinese government is strongly promoting inclusive finance, aiming to bolster micro and small enterprises (MSMEs) and rural communities. This policy direction directly supports Harbin Bank's strategic focus on these underserved segments.
Harbin Bank has responded by significantly expanding its inclusive finance offerings, particularly for small and micro businesses. They've emphasized scenario-based, online, and digital solutions, making financial services more accessible. For example, their agriculture-related loan balance saw an increase, reflecting their dedication to serving these crucial economic areas.
Harbin Bank's operations are heavily influenced by China's ongoing urbanization, particularly in its core region of Heilongjiang province. As more people move to cities, the demand for financial services like mortgages, consumer loans, and business financing naturally increases. For example, in 2023, China's urbanization rate reached 66.16%, a significant rise that directly translates to a larger customer base for banks like Harbin.
The pace of regional economic development in Heilongjiang and other operating areas is a critical factor. Stronger local economies, often driven by industrial growth or new infrastructure projects, boost both corporate lending opportunities and individual wealth, leading to greater demand for sophisticated banking products. Heilongjiang's GDP grew by 2.6% in 2023, demonstrating the local economic environment that Harbin Bank navigates.
Aging Population and Pension Finance
China's rapidly aging population, with projections indicating a significant increase in the proportion of citizens aged 60 and above, is driving substantial growth in demand for pension financial services. By the end of 2023, individuals aged 60 and over constituted over 21% of China's total population, a figure expected to climb considerably in the coming years. This demographic shift necessitates robust financial planning and investment solutions for retirement.
Harbin Bank, like other financial institutions, is actively enhancing its personal pension service offerings to cater to this expanding 'silver economy.' This strategic focus aims to capture a growing market segment by developing specialized products and services designed to meet the unique financial needs of an aging populace. The bank's efforts include expanding wealth management options and advisory services for retirement planning.
- Demographic Shift: China's elderly population is projected to reach over 400 million by 2035, creating a vast market for pension-related financial products.
- Increased Demand: Growing awareness of retirement planning needs is fueling demand for bank-led pension savings and investment schemes.
- Market Opportunity: The 'silver economy' represents a significant growth avenue for banks like Harbin Bank to innovate and offer tailored financial solutions.
- Regulatory Support: Government initiatives promoting private pension schemes provide a favorable environment for banks to expand their pension finance services.
Financial Literacy and Wealth Management Trends
As China's middle class expands, there's a noticeable surge in demand for advanced wealth management solutions. This demographic shift is driving a need for more personalized and sophisticated financial planning services, moving beyond basic savings accounts.
Harbin Bank is actively responding to these evolving client needs through its retail wealth transformation initiatives. The bank's strategy emphasizes offering a wider array of diversified banking products, designed to meet the increasing financial sophistication and growing wealth of its individual customer base.
By 2024, the middle-income population in China was projected to exceed 500 million people, a significant driver for the wealth management sector. This growth fuels the demand for services like investment advisory, private banking, and estate planning, areas where Harbin Bank is focusing its development.
- Growing Middle Class: China's expanding middle class represents a substantial opportunity for wealth management services.
- Demand for Sophistication: This demographic seeks more than basic banking, demanding complex financial products and expert advice.
- Harbin Bank's Strategy: The bank is investing in retail wealth transformation and product diversification to capture this market.
- Financial Literacy: Increased financial literacy among individuals enables them to engage more effectively with advanced wealth management tools.
China's rapidly aging population is a significant sociological factor, with those aged 60 and above making up over 21% of the population by the end of 2023, a figure poised for continued growth. This demographic shift directly fuels demand for specialized financial services like pension planning and wealth management for retirees. Harbin Bank is enhancing its personal pension offerings to tap into this burgeoning 'silver economy', aiming to provide tailored solutions for an aging populace.
Technological factors
Fintech innovation is rapidly reshaping China's financial landscape, with a significant portion of the population now engaging with digital payment platforms and online banking services. Harbin Bank is strategically integrating these technologies to streamline customer interactions, bolster its cybersecurity measures, and develop more sophisticated data analytics for credit assessment, aiming to stay competitive in this evolving digital ecosystem.
Chinese banks, including Harbin Bank, are heavily investing in digital transformation, leveraging AI for operational efficiency and enhanced customer experiences. This push aims to unlock greater data value across the financial sector.
Harbin Bank is specifically prioritizing its digital initiatives, with a notable focus on expanding inclusive finance for small and micro businesses and strengthening its cross-border financial services capabilities through technological integration.
Harbin Bank's commitment to digital innovation is evident in platforms like 'HAYIN Digital E-Connect', a key enabler for efficient cross-border settlements. This focus aims to streamline operations, cutting down transaction times significantly.
These digital advancements are designed to create intelligent financial service ecosystems, fostering collaboration among multiple participants. By automating processes, Harbin Bank is enhancing its service delivery and competitive edge in the digital banking landscape.
Cybersecurity and Data Security
The increasing digitalization of financial services places a significant emphasis on cybersecurity and data security for institutions like Harbin Bank. Protecting customer data and ensuring the integrity of digital transactions are critical to maintaining trust and operational stability.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address these concerns. For instance, China's Measures for the Data Security Management of Banking and Insurance Institutions, implemented in 2021, mandates robust data classification, stringent security protocols, and comprehensive emergency response plans. Harbin Bank must align its operations with these requirements to avoid penalties and uphold compliance.
The financial sector is a prime target for cyber threats. Reports from 2023 indicated a significant rise in sophisticated cyberattacks against financial institutions globally, highlighting the constant need for investment in advanced security measures. Harbin Bank's commitment to cybersecurity directly impacts its ability to operate securely and protect its assets and customer information.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to data security regulations is non-negotiable, impacting operational licenses and public trust.
- Threat Landscape: The evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates continuous investment in advanced security technologies and practices.
- Reputational Risk: Data breaches can severely damage a financial institution's reputation, leading to customer attrition and financial losses.
Automation and Operational Efficiency
Technology is a major driver for banks to streamline operations, boosting efficiency and cutting expenses. Harbin Bank's advanced system for cross-border payments is a prime example, slashing processing times through automation and smart resource allocation.
This technological integration allows for faster transaction settlements and improved customer service. For instance, Harbin Bank's digital transformation initiatives in 2023 aimed to enhance its online banking platform, leading to a projected 15% increase in digital transaction volume by the end of 2024.
- Automation of loan processing: Reduced application review times by an average of 30% in pilot programs.
- AI-powered customer service: Chatbots handled over 50% of routine customer inquiries in early 2024, freeing up human agents.
- Blockchain for trade finance: Pilot projects demonstrated a potential 20% reduction in documentation and processing costs.
- Data analytics for risk management: Enhanced fraud detection accuracy by 10% in the last fiscal year.
Harbin Bank is actively leveraging technological advancements, particularly in fintech, to enhance its service offerings and operational efficiency. Investments in AI and big data analytics are central to its strategy, aiming to improve credit assessment and personalize customer experiences. The bank's digital transformation efforts, including the HAYIN Digital E-Connect platform, are designed to streamline cross-border transactions and foster a more integrated financial ecosystem.
The bank is also prioritizing cybersecurity, recognizing the increasing threat landscape and the critical need to protect sensitive customer data. Compliance with evolving data security regulations, such as China's Measures for the Data Security Management of Banking and Insurance Institutions, is a key operational focus.
Harbin Bank's digital initiatives in 2023 targeted a projected 15% increase in digital transaction volume by the end of 2024, underscoring its commitment to digital growth. Pilot programs for AI-powered customer service saw chatbots handling over 50% of routine inquiries in early 2024.
| Key Technological Initiatives | Impact/Goal | Data/Metric |
| Fintech Integration | Streamlined customer interactions, enhanced cybersecurity | Significant portion of population engaging with digital platforms |
| AI and Big Data Analytics | Improved credit assessment, personalized services | AI chatbots handling >50% of routine inquiries (early 2024) |
| Digital Transformation | Increased operational efficiency, expanded inclusive finance | Projected 15% increase in digital transaction volume (end of 2024) |
| HAYIN Digital E-Connect | Efficient cross-border settlements | Reduced transaction times |
Legal factors
Harbin Bank navigates a complex banking regulatory landscape primarily shaped by the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) and the People's Bank of China (PBOC). These bodies set the rules for capital adequacy, risk management, and consumer protection, directly influencing Harbin Bank's operational strategies and financial stability.
Recent regulatory shifts, such as the streamlined requirements for loan businesses implemented in 2023, have a tangible impact on Harbin Bank's lending practices. For instance, these reforms may affect the speed of loan approvals and the types of collateral accepted, potentially influencing the bank's loan portfolio growth and profitability in the 2024-2025 period.
Harbin Bank, being a publicly traded entity, operates under stringent corporate governance mandates. These include mandatory annual general meetings, detailed financial reporting obligations, and transparent procedures for board member appointments and changes. For instance, as of its 2023 annual report, Harbin Bank highlighted its commitment to these standards by outlining its governance structure and compliance efforts.
Strict adherence to these legal frameworks is paramount for Harbin Bank to sustain investor trust and ensure its day-to-day operations remain sound. Failure to comply can lead to significant penalties and damage its reputation in the financial market, impacting its ability to attract capital and customers.
China's implementation of data security management measures for banking and insurance institutions, effective from September 1, 2021, mandates detailed requirements for data classification, security, and protection. Harbin Bank must rigorously adhere to these evolving legal standards to ensure its data handling practices are compliant, particularly concerning sensitive customer information and transaction data. Non-compliance could lead to significant penalties, impacting its operational integrity and reputation.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF)
Chinese banks, including Harbin Bank, operate under increasingly strict Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) regulations. These rules are designed to curb illicit financial flows and are a critical component of China's commitment to global financial stability. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties and reputational damage.
Harbin Bank must invest in and maintain sophisticated internal controls and reporting systems to effectively monitor transactions and identify suspicious activities. This includes customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting to relevant authorities like the People's Bank of China. The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, requiring continuous adaptation.
For instance, China's AML laws, such as the Measures for the Administration of Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing by Financial Institutions, mandate specific procedures. In 2023, China's financial regulators continued to emphasize the importance of data analytics and artificial intelligence in enhancing AML/CTF capabilities, signaling a move towards more technologically driven compliance. This trend is expected to accelerate into 2024 and 2025.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Chinese banks face rigorous oversight from authorities like the People's Bank of China regarding AML/CTF compliance.
- Compliance Burden: Maintaining robust internal controls, including Know Your Customer (KYC) processes and transaction monitoring, is essential.
- Technological Investment: Banks are increasingly leveraging AI and big data for more effective detection of illicit financial activities.
- Global Alignment: China's AML/CTF framework aims to align with international standards set by bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
ESG Disclosure Regulations
China is actively strengthening its Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) disclosure requirements. New guidelines are already in place, requiring specific listed companies to report ESG data. For instance, the Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange have issued updated ESG disclosure guidelines in 2023, with further enhancements expected. While mandatory ESG disclosure for all companies is slated for 2026, Harbin Bank should proactively align its reporting and operational practices with these escalating sustainability standards. This proactive approach will underscore the bank's dedication to sustainable development and enhance its transparency for investors and stakeholders.
Harbin Bank's operations are significantly shaped by China's evolving legal framework, particularly concerning financial regulation and corporate governance. The National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) and the People's Bank of China (PBOC) are key regulators, setting stringent capital adequacy ratios and risk management standards. For example, as of late 2023, the PBOC continued to emphasize robust risk control measures for financial institutions, directly impacting Harbin Bank's strategic planning for 2024-2025.
The bank must also comply with increasingly rigorous Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) regulations. These mandates require sophisticated transaction monitoring and customer due diligence, with regulators like the PBOC in 2023 pushing for greater use of technology, such as AI and big data, to enhance compliance effectiveness. This trend is expected to continue, demanding ongoing investment in compliance technology for Harbin Bank.
Furthermore, China's push for enhanced data security and privacy, particularly with measures effective since September 2021, places direct obligations on Harbin Bank regarding the handling of sensitive customer information. Adherence to these evolving data protection laws is critical for maintaining operational integrity and avoiding penalties, underscoring the need for robust data governance frameworks.
Environmental factors
China's commitment to green finance is intensifying, with government mandates pushing financial institutions to bolster support for environmentally friendly sectors. Harbin Bank is aligning with this national agenda by expanding its portfolio of green financial products, aiming to boost lending to low-carbon and circular economy initiatives.
This strategic shift is reflected in Harbin Bank's growing green finance loan balance. By the end of 2023, the bank reported a significant increase in its green loans, demonstrating a tangible commitment to sustainable development and aligning with China's ambitious environmental targets.
Chinese banking and insurance firms, including Harbin Bank, are now mandated to weave ESG criteria into their core management and risk assessment frameworks. This regulatory shift, effective from 2024, underscores a national commitment to sustainable finance.
Harbin Bank's strategic imperative involves embedding ESG principles into its lending and investment evaluations. This proactive approach is crucial for mitigating environmental risks, such as those associated with climate change impacts on loan portfolios, a growing concern for financial institutions globally.
Harbin Bank is actively supporting China's green transition by extending loans to key emerging sectors. In 2023, the bank reported a significant increase in its green finance portfolio, with lending to strategic industries like renewable energy and environmental protection projects growing by 15%. This aligns directly with national goals for carbon emission reduction and fostering sustainable economic development.
Carbon Neutrality Goals
Chinese financial institutions, including Harbin Bank, are increasingly focused on achieving carbon neutrality. This involves developing FinTech solutions and implementing other carbon-reduction strategies across their operations and investment portfolios. Harbin Bank's proactive approach is evident in its pioneering green eco-friendly syndicated loan and its development of tools to support carbon reduction efforts.
These initiatives align with national directives encouraging sustainable finance. For instance, by the end of 2023, China's green finance market had seen significant growth, with outstanding green loans reaching over 30 trillion yuan, demonstrating the growing momentum for environmental responsibility within the banking sector.
- FinTech for Sustainability: Leveraging technology to drive carbon reduction and green finance.
- Green Lending: Issuing eco-friendly loans to support sustainable projects.
- Carbon Reduction Tools: Developing solutions to assist clients in lowering their carbon footprint.
Environmental Risk Assessment in Lending
Harbin Bank, like other financial institutions, faces increasing pressure to integrate environmental risk assessment into its lending and investment processes. This means thoroughly evaluating the potential environmental impacts of projects before approving financing.
Developing strong frameworks for identifying, assessing, and managing these environmental risks is crucial for Harbin Bank. This ensures that the bank's financing activities align with responsible lending practices and contribute to sustainable development.
For instance, the People's Bank of China (PBOC) has been actively promoting green finance, with outstanding green loans reaching 29.55 trillion yuan by the end of 2023, a 23.5% increase year-on-year. This trend highlights the growing importance of environmental considerations in the Chinese banking sector.
- Regulatory Compliance: Harbin Bank must adhere to evolving environmental regulations and guidelines set forth by Chinese authorities, such as the PBOC's directives on green finance.
- Climate Risk Management: Assessing the physical and transition risks associated with climate change in loan portfolios is essential to prevent potential financial losses.
- Reputational Risk: Financing environmentally damaging projects can lead to negative publicity and damage Harbin Bank's reputation among stakeholders and the public.
- Sustainable Growth: By incorporating environmental factors, Harbin Bank can foster sustainable economic growth and identify new opportunities in the green economy.
China's push for green finance is a significant environmental factor influencing Harbin Bank. The bank is actively increasing its green loan portfolio, with lending to strategic industries like renewable energy growing by 15% in 2023. This aligns with national goals for carbon emission reduction and sustainable development.
Harbin Bank must integrate ESG criteria into its risk assessment, a mandate effective from 2024. This includes managing climate-related risks, such as the physical impacts of climate change on its loan book. The bank's proactive stance involves developing tools to support client carbon reduction efforts.
The broader Chinese green finance market is expanding, with outstanding green loans exceeding 30 trillion yuan by the end of 2023. Harbin Bank's focus on FinTech for sustainability and green lending positions it to capitalize on this growth and meet regulatory expectations.
| Metric | 2023 Data | Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Green Loans Growth | 15% | Increasing |
| Outstanding Green Loans (China) | > 30 Trillion Yuan | Rapid Expansion |
| ESG Integration Mandate | Effective 2024 | New Requirement |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Harbin Bank PESTLE analysis is grounded in data from official Chinese government publications, reports from international financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank, and reputable market research firms specializing in the Chinese financial sector. This comprehensive approach ensures all insights are based on current and credible information.
