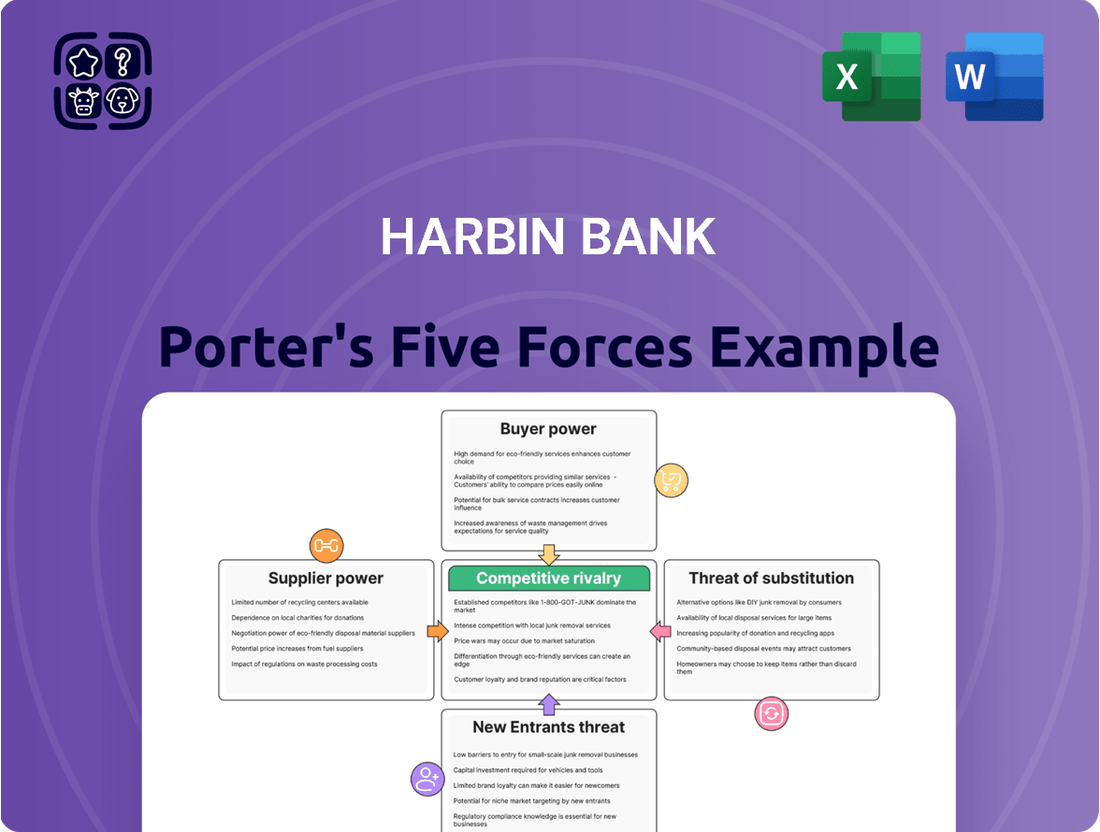
Harbin Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Harbin Bank Bundle
Harbin Bank faces significant competitive forces, including the bargaining power of buyers and the threat of substitute products. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Harbin Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Depositors, particularly large corporate and institutional clients, wield considerable influence over Harbin Bank by providing its core funding through deposits. In 2023, the total deposit balance for Chinese commercial banks reached approximately 257 trillion yuan, highlighting the sheer volume of funds available. The ease with which these depositors can move their money to other financial institutions or investment options directly impacts Harbin Bank's need to offer competitive interest rates and appealing services to secure and retain their capital.
Technology providers, especially those offering core banking systems, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure, hold considerable sway over banks like Harbin Bank. Their leverage is significant because these specialized systems are crucial for smooth operations and delivering excellent customer experiences. For instance, the global market for core banking software was valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a concentrated supplier base for essential services.
The substantial costs associated with switching these critical technology platforms mean Harbin Bank has limited flexibility. This dependence can translate into higher expenses if providers decide to raise prices or if service quality deteriorates, directly impacting the bank's operational efficiency and profitability.
The availability of highly skilled professionals in crucial areas such as risk management, fintech, data analytics, and compliance significantly influences Harbin Bank's operational effectiveness. A scarcity of this specialized talent can lead to elevated labor expenses and heightened recruitment difficulties.
This situation directly translates into increased bargaining power for skilled employees, who can demand higher salaries and more attractive benefits, particularly within the highly competitive financial sector. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning specialists in banking saw a notable surge, with average salaries for these roles increasing by an estimated 15-20% year-over-year in many major financial hubs.
Interbank Market Dynamics
Harbin Bank relies on the interbank market for a portion of its funding. The cost of this funding, determined by interest rates and terms, is significantly shaped by overall market liquidity and the monetary policies set by authorities like the People's Bank of China. For instance, in early 2024, interbank rates saw fluctuations influenced by the central bank's liquidity management operations, directly impacting Harbin Bank's borrowing costs.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the interbank market is evident when liquidity conditions tighten. During periods of reduced liquidity, other financial institutions, acting as suppliers of funds, can command higher interest rates. Harbin Bank's creditworthiness also plays a crucial role; a weaker perception can lead to less favorable terms from interbank lenders, effectively increasing the cost of its funding from these sources.
- Interbank Funding Dependence: Harbin Bank utilizes the interbank market to secure a portion of its operational funds.
- Market Influence on Costs: Interest rates and terms in this market are directly influenced by liquidity levels and central bank policies, as seen in 2024's dynamic monetary environment.
- Supplier Power Indicators: Tightening interbank liquidity or a perceived weakening of Harbin Bank's credit standing can lead to increased borrowing costs, reflecting greater supplier power.
Regulatory and Compliance Bodies
While not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, regulatory and compliance bodies wield significant influence over Harbin Bank. For instance, the People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) dictate critical operational parameters. These include capital adequacy ratios, liquidity requirements, and the overall standards for banking operations.
The impact of these regulatory mandates is substantial. Harbin Bank, like all financial institutions, faces considerable compliance costs associated with meeting these evolving requirements. These costs directly affect profitability and can constrain the bank's strategic flexibility and operational choices.
- Regulatory Authority: The PBOC and CBIRC set the rules for China's banking sector.
- Key Requirements: Capital adequacy, liquidity ratios, and operational standards are crucial.
- Cost of Compliance: Adhering to regulations incurs significant expenses for Harbin Bank.
- Operational Impact: Evolving regulations can limit strategic freedom and affect profitability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Harbin Bank is moderate. While depositors and interbank lenders hold some sway, the bank's access to a broad funding base and established relationships with technology providers helps to mitigate extreme supplier leverage.
Harbin Bank's reliance on technology providers for core systems and cybersecurity presents a key area of supplier influence. The specialized nature of these services and the high costs associated with switching platforms mean these suppliers can command favorable terms. For example, the global market for core banking software was valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023, indicating a concentrated supplier landscape for essential banking infrastructure.
Depositors, particularly large corporate and institutional clients, also exert influence by providing the bank's core funding. The ease with which these depositors can shift funds to alternative investments or institutions necessitates competitive interest rates and services from Harbin Bank. In 2023, total deposits for Chinese commercial banks neared 257 trillion yuan, underscoring the significant capital at stake.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on Harbin Bank |
| Depositors (Large) | Moderate to High | Ease of switching funds, availability of alternative investments, deposit size | Influences interest rates offered, need for competitive services |
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, Cybersecurity) | High | Specialized nature of services, high switching costs, limited number of providers | Can lead to higher costs, potential for service disruptions if terms are unfavorable |
| Interbank Lenders | Moderate | Market liquidity, Harbin Bank's creditworthiness, central bank policies | Affects borrowing costs and availability of short-term funding |
| Skilled Labor (Fintech, Risk, Compliance) | Moderate to High | Scarcity of specialized talent, high demand in the financial sector | Drives up labor costs, impacts recruitment efficiency |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Harbin Bank's competitive environment highlights the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual representation of each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Retail depositors at Harbin Bank wield significant bargaining power, largely due to the increasing ease of switching financial institutions. Digital banking platforms and the proliferation of diverse financial products mean customers can readily compare and move their funds, a trend amplified by widespread internet access. For instance, in 2024, mobile banking adoption in China continued its upward trajectory, with reports indicating over 80% of banking customers utilizing mobile channels for transactions, making account switching more seamless than ever.
To counter this, Harbin Bank must focus on retaining these crucial retail depositors by offering compelling deposit rates that remain competitive within the market. Furthermore, investing in user-friendly digital services and prioritizing an exceptional customer experience are paramount. The collective deposits from individual customers represent a vital funding source for the bank, and failing to meet their expectations could lead to significant outflows, impacting Harbin Bank's liquidity and lending capacity.
Harbin Bank's corporate clients, particularly large enterprises, wield significant bargaining power. These sophisticated clients often have substantial transaction volumes and considerable borrowing needs, allowing them to negotiate for more favorable terms. For instance, in 2023, major Chinese banks saw corporate loan growth of around 10-12%, indicating strong demand from these clients who can leverage their importance to secure better rates and services.
This leverage enables corporate clients to demand tailored financial solutions, such as customized hedging strategies or specialized trade finance products. They can also exert pressure on loan pricing, pushing for lower interest rates or reduced fees. The ability of these clients to maintain relationships with multiple banking institutions further amplifies their bargaining position, compelling Harbin Bank to offer competitive packages to retain their business.
Borrowers, both individuals and businesses, are keenly aware of interest rates and loan conditions. This price sensitivity is a significant factor influencing their choices.
In the current financial landscape, where multiple banks offer similar lending products, customers have the power to shop around and compare. This ease of comparison puts pressure on institutions like Harbin Bank to offer attractive rates and terms.
For instance, in 2024, the average prime lending rate in China, a benchmark for many loans, hovered around 3.95% to 4.35%. Harbin Bank, to remain competitive, needs to align its offerings within this range, which can impact its profitability by narrowing its net interest margin.
Digital Service Expectations
Customers today demand effortless digital interactions, from intuitive mobile banking apps to swift online transactions. Harbin Bank's capacity to deliver these advanced digital services is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty and satisfaction.
The increasing sophistication of digital offerings from competitors means that a lag in innovation can push customers towards more technologically adept financial institutions. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of banking transactions globally occurred through digital channels, highlighting this trend.
- Digital Adoption: A substantial percentage of banking customers, particularly younger demographics, prefer digital channels for most of their banking needs.
- Competitive Pressure: Banks that fail to offer competitive digital features risk losing market share to fintech companies and digitally advanced traditional banks.
- Customer Retention: Meeting evolving digital expectations is no longer a differentiator but a baseline requirement for retaining customers in the current financial landscape.
Wealth Management Clients' Demands
Wealth management clients, particularly high-net-worth individuals, wield significant bargaining power. They demand highly personalized advice, a broad spectrum of investment products, and demonstrably strong returns. In 2024, the global wealth management market saw continued client demand for tailored solutions, with assets under management reaching trillions of dollars, underscoring the clients' leverage.
These sophisticated investors can readily shift their assets to competitors if Harbin Bank fails to meet their exacting investment objectives and service expectations. This ease of switching, coupled with the high value of their portfolios, amplifies their influence. For instance, reports from late 2023 indicated that client retention in wealth management is heavily dependent on service quality and performance, with a notable percentage of clients considering a switch if dissatisfied.
- High client expectations for personalized service and strong investment returns.
- Significant leverage due to the ease of moving assets to alternative providers.
- The substantial value of assets managed by high-net-worth individuals amplifies their bargaining power.
Retail depositors at Harbin Bank possess considerable bargaining power, primarily driven by the increasing ease of switching financial institutions. Digital banking platforms and a wide array of financial products allow customers to readily compare and move their funds, a trend bolstered by ubiquitous internet access. In 2024, mobile banking adoption in China continued to rise, with over 80% of banking customers utilizing mobile channels for transactions, making account switching more seamless than ever.
Harbin Bank must focus on retaining these vital retail depositors by offering competitive deposit rates and investing in user-friendly digital services. Failing to meet customer expectations could lead to significant deposit outflows, impacting the bank's liquidity and lending capacity.
Corporate clients, especially large enterprises, hold significant bargaining power due to their substantial transaction volumes and borrowing needs. This allows them to negotiate for more favorable terms, such as lower interest rates or reduced fees. In 2023, major Chinese banks experienced corporate loan growth of approximately 10-12%, reflecting strong demand from clients who can leverage their importance to secure better deals.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Harbin Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Depositors | Ease of switching, digital banking adoption | Pressure on deposit rates, need for superior digital experience |
| Corporate Clients | Transaction volume, borrowing needs, multiple banking relationships | Negotiation for lower loan pricing and tailored services |
| Borrowers (Individuals & Businesses) | Price sensitivity, availability of comparable products | Need for competitive interest rates and loan terms |
| Wealth Management Clients | High expectations for personalized service, investment performance, ease of asset transfer | Demand for specialized products and high-quality advisory services |
Full Version Awaits
Harbin Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Harbin Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, providing a fully formatted and ready-to-use strategic assessment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Harbin Bank contends with formidable competition from China's major state-owned commercial banks, including ICBC, CCB, Bank of China, and ABC. These giants boast extensive nationwide branch networks and deeply entrenched customer relationships, often bolstered by significant government support.
These larger institutions benefit from substantial economies of scale, enabling them to offer a wider array of financial products and services, which inherently puts pressure on regional players like Harbin Bank.
Joint-stock commercial banks like China Merchants Bank and CITIC Bank present a formidable competitive challenge to Harbin Bank. These institutions are known for their agility and a strong focus on market responsiveness, particularly in the retail and corporate banking sectors. Their ability to quickly adapt to market demands and customer preferences puts pressure on Harbin Bank to maintain its own competitive edge.
These agile competitors are often at the forefront of digital innovation, consistently introducing new services and product enhancements. For Harbin Bank, this means a continuous need to invest in and upgrade its digital capabilities to avoid falling behind. For instance, in 2023, China Merchants Bank reported a net profit of 149.0 billion yuan, showcasing its strong financial performance and capacity for innovation, which directly impacts the competitive landscape for regional banks.
Harbin Bank faces intense competition from a multitude of city commercial banks and rural commercial banks operating within its core geographical areas. This localized rivalry is particularly pronounced in the crucial segments of deposit gathering and lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These regional players often leverage deep-rooted community relationships and an intimate knowledge of local market dynamics to their advantage.
Product and Service Differentiation
The Chinese banking landscape, including Harbin Bank, often experiences a high degree of product and service similarity. This homogenization intensifies competition, frequently pushing banks towards price-driven strategies for core offerings. For instance, interest rate differentials on standard savings accounts or basic loans can become a primary battleground.
To counter this, Harbin Bank needs to actively pursue differentiation. This could involve developing specialized financial products tailored to specific customer segments, such as innovative lending solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or targeted financing programs for the agricultural sector. A superior customer experience, characterized by efficient service and personalized advice, also serves as a crucial differentiator.
- Product Homogenization: Many basic banking products in China, like savings accounts and standard loans, are very similar across institutions, leading to intense price competition.
- Differentiation Strategies: Harbin Bank can stand out by offering specialized services, such as tailored solutions for small businesses or agricultural clients, and by focusing on an enhanced customer experience.
- Market Focus: Targeting niche markets, like specific industries or demographic groups, allows banks to build expertise and offer more relevant products, thereby reducing direct comparison with competitors offering broader services.
Digital Transformation Race
Harbin Bank, like all financial institutions, is deeply entrenched in a digital transformation race. This means a constant push to offer cutting-edge mobile banking, seamless online payment solutions, and increasingly, AI-powered customer service and analytical tools. The effectiveness and speed of adopting these digital advancements are critical battlegrounds for market share and customer loyalty.
The intensity of this rivalry is underscored by industry-wide investment trends. For instance, in 2023, global banks collectively invested billions in digital transformation initiatives, with a significant portion allocated to enhancing customer-facing digital platforms and backend infrastructure. Harbin Bank's own strategic investments in areas like cloud computing and data analytics are directly influencing its capacity to vie with both established banking giants and agile fintech newcomers.
- Digital Adoption Metrics: In 2024, leading banks reported mobile banking adoption rates exceeding 70% among their retail customer base.
- Fintech Investment: Global fintech funding in the first half of 2024 reached over $50 billion, highlighting the rapid innovation and competition from non-traditional players.
- AI in Banking: By the end of 2024, an estimated 60% of customer service interactions in major banks were projected to be handled by AI-powered chatbots or virtual assistants.
- Cybersecurity Spending: Financial institutions are expected to increase cybersecurity spending by 10-15% in 2024 to protect digital assets and customer data amidst escalating threats.
Harbin Bank faces intense competition from large state-owned banks, agile joint-stock banks, and numerous regional players, all vying for market share. This rivalry is amplified by product homogenization, forcing banks to compete on price for basic services.
Digital transformation is a key battleground, with banks investing heavily in mobile banking, AI, and cybersecurity. In 2024, leading banks saw mobile adoption rates over 70%, while global fintech funding exceeded $50 billion in the first half of the year, underscoring the rapid pace of innovation and competition.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on Harbin Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Major State-Owned Banks (e.g., ICBC, CCB) | Extensive networks, deep customer relationships, government support, economies of scale | Significant pressure on market share and pricing due to scale and resources |
| Joint-Stock Banks (e.g., China Merchants Bank) | Agility, market responsiveness, digital innovation, strong retail/corporate focus | Requires continuous investment in digital capabilities and product development to stay competitive |
| City/Rural Commercial Banks | Local market knowledge, strong community ties, focus on SMEs | Intense localized competition for deposits and SME lending |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech payment platforms like Alipay and WeChat Pay are strong substitutes for Harbin Bank's traditional payment services. These digital wallets offer unparalleled convenience and speed, often integrating with daily life services, which directly challenges the need for conventional banking transactions. In 2023, mobile payments accounted for over 80% of all transactions in China, highlighting the significant shift away from traditional methods.
Online lending and peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for Harbin Bank. These platforms offer alternative avenues for both individuals and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to secure financing, often bypassing the more traditional banking system. While the P2P lending landscape in China has seen substantial regulatory shifts, operational online lending platforms persist as viable competitors.
These digital channels frequently boast quicker loan approval processes and more adaptable terms compared to conventional banks, directly challenging Harbin Bank's market share. For instance, by mid-2024, the digital lending market continued to expand, with many fintech platforms offering streamlined application and disbursement cycles that appeal to borrowers seeking speed and convenience.
Large corporations increasingly bypass traditional banking by directly accessing capital markets. In 2024, China's bond market saw significant activity, with corporate bond issuance reaching trillions of yuan, offering companies an alternative to bank loans for raising capital. This trend directly substitutes for services offered by banks like Harbin Bank, as companies can now tap into a broader investor base for their funding needs.
Wealth Management and Investment Firms
Non-bank financial institutions present a significant threat of substitution for Harbin Bank's wealth management and investment services. Asset management companies, trust companies, and independent wealth advisors compete directly by offering diverse investment products and tailored wealth management solutions.
These substitutes often provide a broader spectrum of investment opportunities, attracting capital that might otherwise flow into traditional banking products like deposits or bank-managed investment funds. For instance, by mid-2024, the global asset management industry was managing trillions of dollars, with many firms specializing in niche or alternative investments that banks may not readily offer.
- Competition from Asset Managers: Firms like BlackRock and Vanguard, with their extensive ETF and mutual fund offerings, directly compete for investor capital.
- Rise of Robo-Advisors: Digital platforms provide low-cost, algorithm-driven investment advice and portfolio management, appealing to a growing segment of investors.
- Independent Wealth Advisors: These professionals offer personalized financial planning and investment strategies, often building strong client relationships that can divert business from banks.
- Alternative Investment Platforms: Fintech companies are increasingly offering access to alternative assets like private equity, real estate, and cryptocurrencies, further diversifying investment choices away from traditional banks.
Shadow Banking Activities
Despite ongoing regulatory efforts, informal lending networks and various shadow banking operations continue to function as viable substitutes for conventional bank financing. These channels often cater to individuals and businesses that find it difficult to secure credit through traditional banking channels, thereby capturing a segment of the market that Harbin Bank might otherwise serve.
These alternative credit sources, while carrying inherent risks, can attract significant borrower demand, presenting a direct challenge to Harbin Bank's core lending operations. For instance, reports from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) in late 2023 highlighted the persistent growth in non-bank financial intermediation globally, indicating a substantial pool of capital operating outside traditional regulatory perimeters.
The appeal of these substitutes often lies in their perceived flexibility and speed, which can be particularly attractive to borrowers facing urgent funding needs. This creates a competitive pressure that Harbin Bank must actively manage to retain its market share in lending.
Key aspects of these substitute activities include:
- Peer-to-peer lending platforms: Offering direct lending between individuals or businesses, often with less stringent credit checks.
- Fintech lending solutions: Utilizing technology to streamline loan applications and approvals, sometimes bypassing traditional banking infrastructure.
- Informal credit groups: Community-based lending circles that provide accessible, albeit often unregulated, funding.
- Securitization of non-traditional assets: Packaging and selling loans or other financial assets that may not meet traditional bank collateral standards.
The threat of substitutes for Harbin Bank is substantial, primarily from digital payment platforms and online lending services. These alternatives offer convenience and speed that traditional banking struggles to match. For example, by early 2024, over 80% of transactions in China were conducted via mobile payments, underscoring the shift away from traditional banking methods.
Online lending platforms and direct access to capital markets by corporations also serve as significant substitutes. These channels provide faster, more flexible financing options, bypassing conventional bank loans. In 2024, corporate bond issuance in China reached trillions of yuan, illustrating companies' ability to secure funding outside the banking system.
Wealth management and investment services face substitution from asset managers, robo-advisors, and alternative investment platforms. These entities offer diverse products and personalized advice, attracting capital that might otherwise be managed by banks. The global asset management industry, managing trillions by mid-2024, highlights the breadth of these competing services.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Harbin Bank | Key Characteristics | Market Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Payment Platforms | Directly competes with traditional payment services | Convenience, speed, integration with daily life | Mobile payments exceeded 80% of transactions in China (2023) |
| Online Lending & P2P Platforms | Offers alternative financing for individuals and SMEs | Faster approval, flexible terms, bypasses traditional banking | Continued expansion of digital lending market (mid-2024) |
| Capital Markets Access | Substitutes for corporate lending | Direct access to investor capital, large-scale funding | Trillions of yuan in corporate bond issuance (2024) |
| Asset Managers & Robo-Advisors | Competes for wealth management and investment capital | Diverse products, lower fees, personalized advice | Global AUM in trillions, with significant growth in digital advisory services |
Entrants Threaten
The Chinese banking sector is a prime example of high regulatory barriers deterring new entrants. Substantial capital requirements, often in the billions of yuan, are mandated by bodies like the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), now the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA). Securing the necessary licenses involves a rigorous and lengthy approval process, making it incredibly challenging for new players to even begin operations. For instance, in 2024, the NFRA continued to emphasize stringent capital adequacy ratios and risk management frameworks, further solidifying these entry hurdles.
Establishing a commercial bank, like Harbin Bank, requires a colossal amount of capital. We're talking about significant investments needed for physical infrastructure, cutting-edge technology systems, and critically, meeting stringent capital adequacy ratios mandated by regulators. For example, in 2024, the average minimum capital requirement for a new bank in many developed economies can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
This substantial financial barrier acts as a powerful deterrent for most potential new entrants. Only those organizations or individuals possessing exceptionally deep financial resources can even contemplate entering the banking sector, effectively limiting the pool of new competitors.
Established banks like Harbin Bank possess significant brand recognition and deep-seated customer trust, essential commodities in the financial services industry. This existing loyalty acts as a formidable barrier, as new entrants must undertake substantial marketing and reputation-building efforts, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive.
Network Effects and Customer Loyalty
Network effects and customer loyalty are significant barriers for new entrants in the banking sector, especially for institutions like Harbin Bank. Established banks benefit from extensive physical branch networks and ATM accessibility, which foster strong customer relationships. For instance, by the end of 2023, Harbin Bank operated a substantial number of branches and service outlets across China, providing a tangible advantage in customer reach and convenience that new digital-only banks struggle to replicate quickly.
Customer loyalty, cultivated over years of service and trust, further solidifies the position of incumbent banks. While digital banking offers convenience, the ingrained habits and perceived security of traditional banking relationships are not easily swayed. This loyalty translates into a sticky customer base that new entrants find challenging and costly to attract, requiring substantial incentives or unique value propositions to gain traction.
- Incumbent Advantage: Established banks leverage wide-reaching branch and ATM networks, creating convenience and accessibility that new entrants must overcome.
- Customer Stickiness: Years of building trust and relationships result in a loyal customer base, making it difficult for new players to acquire market share.
- Digital vs. Physical: While digital banking is growing, the established physical presence of banks like Harbin Bank still holds significant sway with a large segment of the population.
- Acquisition Costs: Attracting customers away from established institutions requires considerable investment in marketing, promotions, and superior service offerings.
Technological and Talent Acquisition Challenges
New entrants into the banking sector, particularly those aiming to compete with established players like Harbin Bank, face significant hurdles in developing and maintaining advanced technological capabilities. Building a robust IT infrastructure, essential for modern digital banking services, requires substantial upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. For instance, the global IT spending in the banking sector was projected to reach over $250 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of investment required.
Furthermore, the acquisition of specialized talent is a major challenge. Banks increasingly need professionals skilled in areas such as cybersecurity, data analytics, and artificial intelligence to remain competitive and secure. The competition for these highly sought-after individuals is intense, driving up recruitment costs and making it difficult for new entrants to assemble a capable team. In 2023, the average salary for a senior data scientist in the financial services industry in China, for example, could range from ¥400,000 to ¥700,000 annually, a significant cost for a new business.
- High IT Infrastructure Costs: Developing and maintaining cutting-edge banking technology demands significant capital investment, often running into billions of dollars for global institutions.
- Talent Acquisition Competition: Attracting and retaining top-tier talent in cybersecurity, AI, and data analytics is a fierce battle, with high salary expectations and limited supply.
- Regulatory Compliance Burden: New entrants must also navigate complex and evolving regulatory landscapes, which often necessitate further technological investment and specialized expertise.
The threat of new entrants in the Chinese banking sector, including for institutions like Harbin Bank, is significantly mitigated by substantial regulatory and capital barriers. These include high minimum capital requirements, often in the billions of yuan, and a rigorous licensing process overseen by bodies like the NFRA. For instance, in 2024, the NFRA continued to emphasize stringent capital adequacy ratios, making it exceptionally difficult for new players to gain a foothold.
Established banks benefit from strong brand recognition and deep customer loyalty, cultivated over years of service. This existing trust acts as a formidable hurdle, as new entrants must invest heavily in marketing and reputation building to attract customers away from incumbents like Harbin Bank, which by the end of 2023 operated a substantial network of branches and service outlets across China.
The substantial investment required for advanced IT infrastructure and the intense competition for specialized talent in areas like cybersecurity and AI also deter new entrants. Global IT spending in banking was projected to exceed $250 billion in 2024, illustrating the scale of technological investment needed, while high salaries for data scientists in China, potentially ¥400,000-¥700,000 annually in 2023, add to these costs.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory & Capital | High minimum capital requirements and complex licensing processes. | Severely limits the number of potential new entrants. | NFRA emphasizes stringent capital adequacy ratios. |
| Brand & Loyalty | Established trust and customer relationships. | Makes customer acquisition costly and time-consuming. | Harbin Bank's extensive branch network (end of 2023). |
| Technology & Talent | High costs for IT infrastructure and competition for skilled professionals. | Requires significant upfront investment and ongoing expense. | Global banking IT spending >$250B (2024); Data scientist salaries ¥400k-¥700k (2023). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Harbin Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Harbin Bank's annual reports and financial statements, alongside industry-specific reports from financial research firms and government economic data for China.
