Hansae Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hansae Bundle
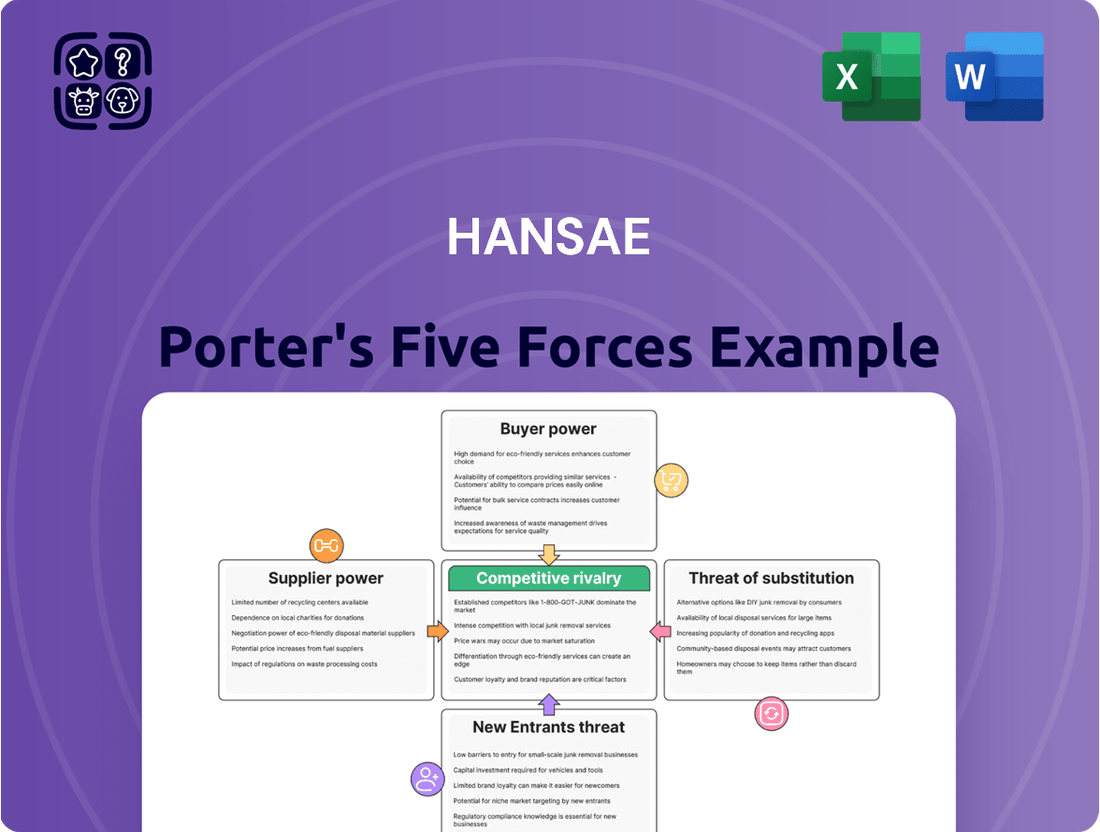
Porter's Five Forces Analysis offers a powerful lens to understand the competitive landscape surrounding Hansae.
By examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry, we can uncover critical insights into Hansae's market position.
This framework illuminates the external pressures that shape profitability and strategic decision-making within Hansae's industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hansae’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants.
Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hansae's primary raw materials, including cotton and various synthetic textiles, are sourced from a highly fragmented global supplier base. As of 2024, the textile raw material market is characterized by numerous producers worldwide, significantly diluting the bargaining power of any single supplier. This wide dispersion allows Hansae to easily switch between suppliers, preventing any one entity from dictating prices or terms. Such fragmentation ensures competitive procurement conditions for Hansae's extensive production needs.
For an apparel manufacturer of Hansae's scale, the costs linked to changing fabric suppliers are notably low. While some adjustments for quality assurance and logistics might occur, these are not prohibitive enough to lock Hansae into unfavorable contracts. Hansae's extensive global footprint, including production facilities across countries like Vietnam and Indonesia, significantly boosts its flexibility to source from a diverse pool of suppliers. This geographic diversification, a key aspect of their 2024 operational strategy, reduces supplier leverage. Therefore, the bargaining power of Hansae's suppliers is diminished due to the ease of switching.
The fabrics and other inputs Hansae uses for mass-market apparel are largely standardized globally, with the textile market valued at over $1 trillion in 2024. While variations in quality exist, fundamental materials like cotton, polyester, and basic dyes are not unique or patented. This lack of differentiation significantly reduces Hansae's dependence on specific suppliers. Consequently, suppliers find their bargaining power weakened due to the readily available alternatives for these generic components.
Potential for Forward Integration is Low
Raw material suppliers, such as cotton growers or textile mills, rarely forward integrate into global apparel manufacturing. This is largely due to the substantial capital investment required for production facilities and the specialized design expertise needed for garment creation. Building relationships with major global brands, a critical component for success, also presents a significant hurdle. Therefore, these suppliers do not represent a credible threat of becoming direct competitors to Hansae in 2024, limiting their bargaining power.
- Global textile and apparel manufacturing capital expenditure reached approximately $35 billion in 2023.
- Developing a competitive apparel design team requires significant investment in talent and technology.
- Establishing deep, long-term relationships with major brands typically takes several years.
- The operational complexities of apparel production differ vastly from raw material supply.
Hansae's Large Purchase Volumes
As a major global apparel manufacturer, Hansae purchases raw materials in very large quantities, giving it considerable leverage over its suppliers. With annual revenues exceeding $1.2 billion USD in 2023, Hansae's significant order volume ensures it holds strong bargaining power. Suppliers are often highly dependent on large-volume clients like Hansae for a substantial portion of their revenue, making them more accommodating to Hansae's terms and pricing demands. This scale allows Hansae to negotiate favorable conditions, impacting its cost structure positively through 2024.
- Hansae's large-scale procurement secures preferential pricing.
- Suppliers rely heavily on Hansae's substantial orders.
- This dependence leads to more flexible supplier terms for Hansae.
- Hansae's purchasing power enhances its operational efficiency.
Hansae faces low supplier bargaining power due to a highly fragmented global textile market, valued over $1 trillion in 2024, offering numerous producers and standardized raw materials. Its low switching costs and significant purchasing volume, with 2023 revenues exceeding $1.2 billion, further diminish supplier leverage. Suppliers rarely forward integrate into apparel manufacturing, ensuring Hansae maintains strong control over procurement terms. This market structure, prominent in 2024, benefits Hansae's cost efficiency.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | 2024 Data Point | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | Lowers supplier leverage | Global textile market: >$1 trillion | ||
| Switching Costs | Enables Hansae flexibility | Apparel supplier change cost: Low | ||
| Hansae's Purchase Volume | Increases buyer leverage | Hansae 2023 Revenue: $1.2B+ USD |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the five competitive forces impacting Hansae, including new entrants, buyer and supplier power, substitutes, and existing rivals, to understand industry profitability and strategic positioning.
Instantly identify and neutralize competitive threats with a visual breakdown of supplier power, buyer bargaining, and substitute product impact.
Effortlessly assess new market entry barriers and the intensity of rivalry, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hansae relies on a concentrated base of powerful global customers such as GAP, H&M, and Nike. This high buyer concentration means these major brands wield significant bargaining power over Hansae. The potential loss of even one key client, like a major retailer whose orders might represent a substantial portion of Hansae's 2024 revenue, could severely impact financial performance. This dynamic grants customers substantial leverage in pricing and contract negotiations, influencing Hansae's profitability and operational strategy.
The OEM/ODM apparel manufacturing industry is intensely competitive, with many manufacturers operating in low-cost regions like Vietnam and Bangladesh. This widespread availability means Hansae's customers face relatively low costs when considering a switch to another supplier. For example, Bangladesh's apparel exports continued robust growth into 2024, highlighting the ample alternative options. This ease of transitioning significantly strengthens the bargaining power of buyers, as they can readily seek more favorable terms elsewhere.
The apparel industry, particularly the segments Hansae's major customers operate in, faces intense price competition, pushing brands and retailers to minimize costs. This pressure is directly transferred to manufacturers like Hansae, making their customers highly sensitive to pricing. For instance, apparel import prices into the US, a key market for Hansae's customers, saw a decline of approximately 3% in Q1 2024 compared to the previous year, reflecting this persistent downward cost pressure. Such market conditions mean customers rigorously scrutinize Hansae's quotes, demanding competitive pricing to maintain their own profitability and market share.
Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of backward integration significantly enhances customer bargaining power for Hansae. While not always feasible for every brand, major apparel customers, particularly those with substantial financial resources and operational scale like Nike or H&M, possess the capability to consider establishing their own manufacturing facilities. This possibility, however remote for some, provides them with considerable leverage in negotiations over pricing and terms with manufacturers such as Hansae.
This dynamic means Hansae must remain competitive and efficient to retain these key clients, especially as global apparel manufacturing investments continue to evolve in 2024.
- Large brands, like those generating billions in annual revenue, have the capital for self-manufacturing.
- The potential for in-house production gives customers significant negotiation leverage.
- Hansae must offer competitive pricing and quality to mitigate this threat.
Product Standardization
While Hansae provides ODM services, a substantial portion of its business operates under the OEM model, where manufacturing follows client-specific designs. In this OEM framework, products are largely standardized from a production standpoint, as buyers dictate specifications. This standardization diminishes Hansae's differentiation from competitors, strengthening customer bargaining power. For example, Hansae's 2024 sales forecast reflects ongoing reliance on major OEM contracts.
- Hansae's OEM revenue share remained significant, influencing customer leverage.
- Industry trends in 2024 show increasing buyer demands for cost efficiency in standardized apparel.
- Customers can easily switch suppliers for basic manufacturing needs, impacting Hansae's pricing power.
- Global apparel manufacturing capacity in 2024 continues to support buyer options.
Hansae faces strong customer bargaining power due to its reliance on a concentrated base of major global brands. These key clients, whose orders significantly contribute to Hansae's 2024 revenue, benefit from low switching costs as many alternative manufacturers exist in regions like Bangladesh. The threat of backward integration and the standardized nature of OEM production further enhance their leverage over pricing and terms.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Concentration | High leverage | Major brands dominate Hansae's sales |
| Low Switching Costs | Easy supplier change | Growing apparel export options globally |
| Backward Integration Threat | Negotiation leverage | Large brands have capital for self-production |
What You See Is What You Get
Hansae Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hansae will equip you with a deep understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. Each force is thoroughly examined to provide actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global apparel manufacturing industry is highly fragmented, with a vast number of players, particularly concentrated in Asia. Hansae faces intense competition from numerous large OEM/ODM manufacturers operating in countries like Vietnam, Bangladesh, and China. This expansive competitive landscape means that Hansae must continually innovate and maintain cost efficiency to retain its market position. The sheer volume of competitors, estimated to be hundreds of thousands of firms globally in 2024, intensifies rivalry and pressure on pricing and lead times for apparel orders.
In the OEM apparel segment, products are manufactured precisely to client brand specifications, leading to inherently low differentiation among competing manufacturers like Hansae. This lack of unique product features intensifies rivalry, as firms primarily compete on price, quality, and delivery speed. For instance, in 2024, the highly commoditized nature of basic apparel production means manufacturers constantly vie for contracts, with pricing often being the decisive factor for many large retailers. This dynamic ensures fierce competition for market share.
Major apparel brands and retailers, who are key customers in this industry, face remarkably low costs when considering a switch between manufacturers. This ease of transitioning encourages intense competition among global manufacturers like Hansae, all vying fiercely to retain their prominent clients. For instance, in 2024, the highly fragmented global apparel manufacturing market continues to see brands readily shift suppliers based on factors like pricing, lead times, or sustainability compliance. This ability for buyers to effortlessly switch suppliers significantly fuels the competitive rivalry among producers, pushing companies to constantly optimize their offerings.
High Strategic Stakes
For apparel manufacturers like Hansae, securing contracts with major global brands is of high strategic importance, often dictating market position and profitability. These agreements involve substantial volumes, crucial for achieving economies of scale and operational efficiency. The fierce competition to win and retain these key customers, whose orders can represent a significant portion of a manufacturer's revenue, drives aggressive rivalry within the industry. For instance, Hansae's reliance on large global clients, contributing to its reported 2023 net sales of approximately KRW 1.9 trillion, underscores these high stakes.
- Global apparel market value is projected to reach over USD 2 trillion by 2024.
- Major brands like Nike and H&M contribute billions in revenue, translating to large production orders.
- Securing contracts allows manufacturers to leverage production capacities and optimize supply chains.
- The pursuit of long-term partnerships reduces vulnerability to market fluctuations.
Price-Based Competition
Due to factors like low product differentiation in standard apparel manufacturing and minimal switching costs for buyers, the competitive landscape for Hansae is often marked by intense price-based rivalry. Manufacturers face constant pressure to offer the most competitive pricing to secure and retain large orders, which significantly strains profit margins and intensifies competition. For example, in 2024, global apparel manufacturers continue to navigate a market where buyers frequently seek the lowest cost per unit, leading to widespread price wars and downward pressure on sourcing prices.
- Price elasticity is high, with buyers prioritizing cost efficiency.
- Commoditization of basic apparel items fuels aggressive pricing strategies.
- Profit margins for manufacturers can be as low as 3-5% on commodity goods.
- The need for economies of scale drives volume-based competition.
Hansae faces fierce competitive rivalry in the highly fragmented global apparel manufacturing industry, estimated to have hundreds of thousands of firms in 2024. Low product differentiation in OEM apparel and minimal switching costs for major brands intensify price-based competition. This dynamic pressures profit margins, often as low as 3-5% for commodity goods, as manufacturers vie for large contracts. Securing these key client relationships is crucial for market position.
| Metric | 2024 Data | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Global Apparel Market Value | > USD 2 Trillion | Attracts many competitors |
| Manufacturer Profit Margins (Commodity) | 3-5% | Drives aggressive pricing |
| Hansae 2023 Net Sales | KRW 1.9 Trillion | Highlights competition for large orders |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A potential substitute for Hansae's outsourced production is for apparel brands to manage manufacturing in-house. While many brands shifted away from this model to reduce costs, a renewed focus on supply chain resilience and quality control, especially after 2024's market dynamics, could prompt a return to vertical integration. This strategic shift would directly substitute Hansae's services. Brands might invest in their own facilities to gain more direct oversight. This represents a tangible threat to outsourcing providers.
The growing trend of nearshoring and reshoring presents a significant substitute threat to Hansae’s traditional supply chain model. As brands increasingly prioritize supply chain resilience and speed-to-market, moving manufacturing closer to home markets directly competes with Hansae's operations in distant regions. While Hansae has strategically expanded into Central America, a substantial shift by US and European buyers towards domestic or very near-shore production could impact demand. For instance, reports in 2024 indicate a continued emphasis on diversification and regionalization in textile sourcing, challenging reliance on single-country or far-shore hubs.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing and advanced automation in apparel manufacturing could eventually substitute traditional mass production. While mass-market apparel adoption is in early stages, the global 3D printing market is projected to exceed $44 billion in 2024, indicating significant growth. This shift enables localized, on-demand manufacturing, disrupting the current OEM/ODM model. Such advancements reduce reliance on large-scale, centralized manufacturing facilities, potentially altering the industry landscape for companies like Hansae.
Direct Sourcing from Smaller, Local Factories
Smaller, niche brands increasingly bypass large manufacturers like Hansae, opting for direct sourcing from local factories. This offers greater flexibility and quicker turnaround times for smaller production runs, particularly for fashion brands needing rapid adjustments. While Hansae excels in large-scale orders, this localized approach represents an alternative for a growing segment of the market seeking agility. The global market for local production is expanding, with a 2024 survey indicating a 15% increase in brands exploring nearshoring or reshoring options.
- Direct sourcing from local factories offers quicker lead times, often reducing delivery from months to weeks.
- This model suits brands focusing on limited editions or hyper-responsive fashion cycles.
- Local sourcing reduces shipping costs and carbon footprint, appealing to sustainability-focused consumers.
- The global textile and apparel market saw a 5% rise in localized production efforts in 2024.
Second-hand and Rental Markets
The rise of second-hand and apparel rental markets presents a notable substitute threat to new garment manufacturers like Hansae. Driven by increasing consumer awareness regarding sustainability and a desire for circular fashion, these models can significantly reduce the overall demand for newly produced apparel. The global second-hand apparel market, for instance, is projected to reach $350 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.7% from 2023 to 2027, indicating a substantial shift in purchasing habits.
- The global second-hand apparel market reached approximately $177 billion in 2024.
- Apparel rental services are expanding, with platforms reporting increased user engagement in 2024.
- Consumer surveys in 2024 indicate over 40% of shoppers consider second-hand options before buying new.
- This trend directly impacts the volume of new orders for large-scale manufacturers such as Hansae.
Hansae faces significant substitution threats from apparel brands opting for in-house production or nearshoring, driven by supply chain resilience. Emerging technologies like 3D printing enable localized, on-demand manufacturing, disrupting traditional models. The rise of second-hand and rental markets also reduces demand for new garments, impacting Hansae's core business. These shifts challenge Hansae's reliance on large-scale, far-shore manufacturing.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Trend | Impact on Hansae |
|---|---|---|
| In-house/Nearshoring | 15% rise in brands exploring nearshoring | Reduced demand for outsourced, far-shore production |
| 3D Printing/Automation | Global 3D printing market >$44B | Potential for localized, on-demand manufacturing |
| Second-hand/Rental | Second-hand market ~$177B | Decreased overall demand for new apparel orders |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a globally competitive apparel manufacturing operation, like Hansae's, demands substantial capital outlays for modern factories, advanced machinery, and cutting-edge technology. Building a diversified network of production facilities across multiple countries, a key Hansae strategy, represents an immense financial barrier. For new entrants aiming to match Hansae's scale, which includes facilities in Vietnam, Indonesia, and Nicaragua, this presents a significant hurdle. Such an endeavor in 2024 could require initial investments easily exceeding hundreds of millions of USD. This high capital requirement makes it incredibly difficult for new companies to enter and effectively compete at a similar global scale.
Large, established manufacturers like Hansae Co., Ltd. benefit significantly from economies of scale, making new entry challenging. With 2023 consolidated revenues around KRW 1.94 trillion, Hansae leverages its massive purchasing power to secure raw materials at lower costs. This scale allows for highly efficient factory operations, exemplified by their global production network. New entrants would struggle to match these formidable cost advantages, hindering their ability to compete effectively on price in the apparel manufacturing market.
Hansae's deep, long-standing relationships with major global apparel brands significantly deter new entrants. These connections, built on a proven track record of quality and reliability, mean clients like Gap and H&M, who contributed substantially to Hansae's 2024 sales, prefer established partners. A new competitor would struggle immensely to gain trust and secure contracts, given the high switching costs and the extensive lead times required to meet the stringent demands of such large-scale buyers. This formidable barrier makes it exceptionally difficult for any newcomer to truly compete.
Complex Global Supply Chain Management
Operating a global network, like Hansae's 2024 operations spanning Vietnam, Indonesia, and Myanmar, demands navigating intricate logistics, diverse trade regulations, and varying labor laws. Established players possess sophisticated supply chain management capabilities, built over decades, which are difficult for newcomers to replicate. A new entrant would face a substantial learning curve and significant capital investment to match this operational complexity, impacting their ability to compete on cost and efficiency.
- Global apparel supply chains involve over 150 stages from raw material to retail, increasing complexity.
- Hansae's 2024 global production network includes over 20 facilities across multiple countries.
- Navigating trade agreements like CPTPP or RCEP requires deep expertise in compliance and duties.
- Logistics costs, a significant barrier, can represent 5-10% of total product cost in global apparel.
Access to Low-Cost Labor
Access to low-cost labor is crucial for the apparel manufacturing industry, yet new entrants face substantial hurdles. Establishing operations in key low-cost manufacturing hubs, like Vietnam or Indonesia, demands significant experience and local market insight. In 2024, countries like Bangladesh continue to offer competitive wages, with average monthly garment worker wages often below 200 USD, but building a skilled and productive workforce there requires deep operational knowledge. New companies often struggle to replicate the established supply chains and labor management efficiency of incumbents like Hansae, which benefits from years of experience in these regions.
- In 2024, apparel manufacturing hubs like Vietnam and Bangladesh remain primary sources of low-cost labor.
- Navigating labor laws and cultural nuances in these countries poses a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Establishing a large, stable workforce requires substantial investment in training and infrastructure.
- Experienced firms leverage long-standing relationships with local labor pools, a competitive edge.
New entrants face substantial hurdles due to Hansae's immense capital requirements for global facilities, with initial investments easily exceeding hundreds of millions of USD in 2024. The company's deep relationships with major brands, crucial for its 2024 sales, create high switching costs and deter competition. Furthermore, Hansae's economies of scale, stemming from its KRW 1.94 trillion 2023 revenues, allow for cost advantages difficult for newcomers to replicate.
| Barrier Type | Hansae's Advantage | 2024 Impact for New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Global network of 20+ facilities | Multi-hundred million USD investment for similar scale |
| Economies of Scale | KRW 1.94 trillion (2023) revenue | Difficulty matching cost efficiency and raw material pricing |
| Brand Relationships | Long-standing ties with Gap, H&M | High switching costs, limited access to major clients |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from diverse sources such as company annual reports, industry-specific market research, government economic data, and financial analyst reports to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
