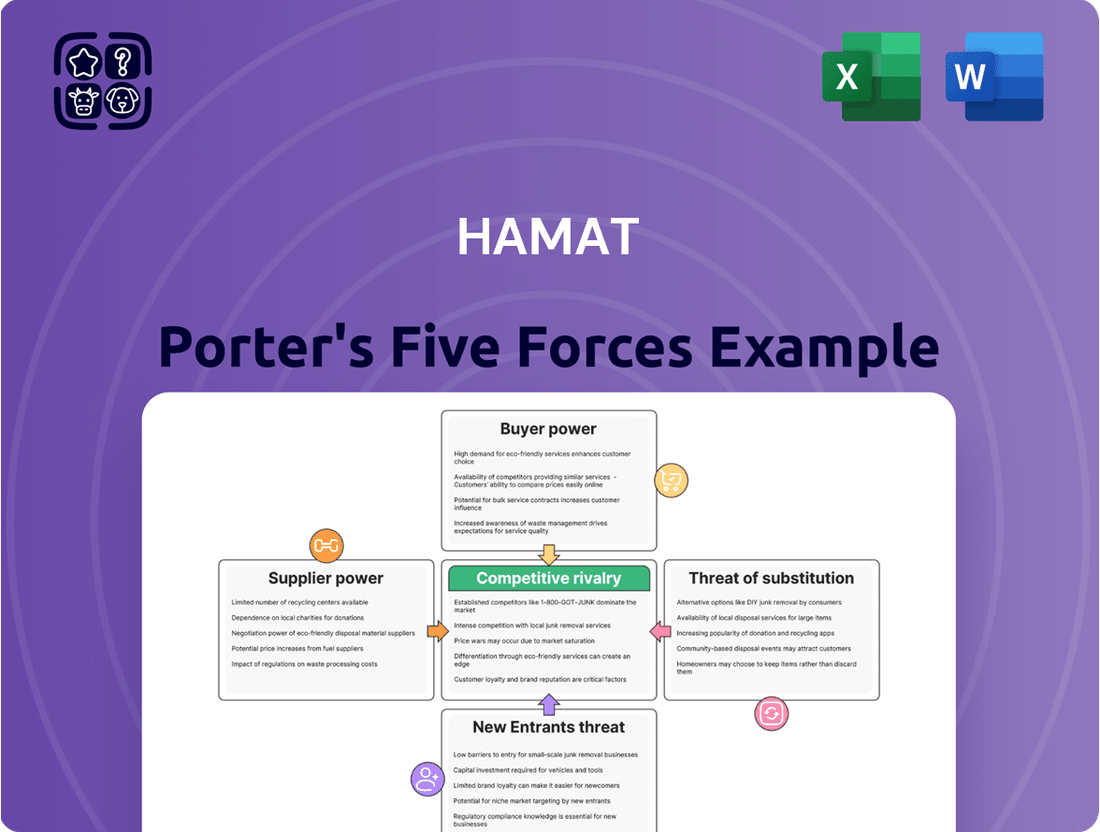
Hamat Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hamat Bundle
Hamat's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intense competitive landscape, highlighting the significant bargaining power of buyers and the moderate threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating Hamat's market.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Hamat’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hamat's reliance on a limited number of suppliers for crucial components like brass, zinc, and specialized cartridges directly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, if the global supply of high-quality ceramic disc cartridges, essential for faucet durability, is dominated by just two or three manufacturers, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. This concentration allows them to potentially dictate pricing and supply terms, which can directly increase Hamat's cost of goods sold, as seen in the 2024 market where lead times for certain specialized components extended due to high demand and limited production capacity among key suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hamat is significantly influenced by switching costs. If it's expensive or complicated for Hamat to change from one supplier to another, those suppliers gain more leverage. For instance, if switching requires substantial retooling of manufacturing equipment or obtaining new certifications, Hamat might be compelled to stick with current suppliers, even if prices increase.
When suppliers offer highly unique or proprietary inputs, their bargaining power significantly increases. For Hamat, if its product differentiation hinges on specialized components, like patented valve technologies or unique finishes sourced from a limited number of suppliers, those suppliers can leverage this exclusivity to demand higher prices. This is because Hamat, and by extension its customers, have few, if any, viable alternatives for these critical inputs, giving the supplier considerable leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers possess the capability and intent to integrate forward into manufacturing sanitary fittings, they can significantly enhance their bargaining power against Hamat. This threat means suppliers could potentially bypass Hamat and sell their components or finished products directly to Hamat's customers or distributors.
This direct competition can pressure Hamat to accept less favorable terms, such as higher prices or stricter payment conditions, simply to retain its supply chain relationships. For instance, a major raw material supplier to the sanitary fittings industry might consider investing in its own production lines if profit margins on component sales become too thin.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers can leverage their expertise to manufacture sanitary fittings, directly competing with Hamat.
- Bypassing Hamat: This allows suppliers to reach end-customers or distributors, cutting out Hamat as an intermediary.
- Negotiating Leverage: The credible threat of forward integration forces Hamat to negotiate from a weaker position, potentially accepting less favorable terms.
- Industry Example: In 2024, some component manufacturers in the automotive sector explored direct-to-consumer sales models, demonstrating this potential shift.
Importance of Hamat to Supplier's Business
The significance of Hamat as a customer directly impacts its suppliers' bargaining power. If Hamat constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier will likely be more amenable to negotiating favorable terms to secure Hamat's continued business, thereby diminishing the supplier's leverage.
For instance, consider a supplier whose business is heavily reliant on Hamat. If Hamat accounts for over 20% of their annual revenue, the supplier's incentive to offer competitive pricing or flexible delivery schedules to maintain this crucial relationship is significantly higher. This dependency shifts the power dynamic, allowing Hamat to exert more influence over pricing and terms.
- Supplier Dependence: Hamat's share of a supplier's revenue is a key indicator of supplier dependence.
- Negotiating Leverage: Higher dependence grants Hamat greater leverage in price and term negotiations.
- Market Concentration: If Hamat is one of only a few major clients for a supplier, its bargaining power is amplified.
- Supplier Retention Costs: The cost for a supplier to find and onboard a new client like Hamat can be substantial, increasing their willingness to concede to Hamat's demands.
When suppliers offer inputs that are critical to a company's operations and are not easily substituted, their bargaining power increases. For Hamat, if key components like specialized brass alloys or high-precision ceramic valves are only available from a few manufacturers, these suppliers can command higher prices. This was evident in early 2024, where supply chain disruptions for certain metals led to price hikes for manufacturers across various sectors, including plumbing fixtures.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also amplified if they are not heavily reliant on Hamat for their revenue. If a supplier sells to many customers and Hamat represents a small fraction of their business, the supplier has less incentive to offer favorable terms. In 2024, suppliers with diversified customer bases were often less flexible on pricing compared to those whose sales were concentrated on a few major clients.
The ability of suppliers to threaten forward integration, meaning they could start producing the finished goods themselves, significantly boosts their leverage. If a supplier of faucet cartridges could also manufacture entire faucets, they could bypass Hamat and directly compete, forcing Hamat into less advantageous negotiations. This strategic consideration became more prominent in 2024 as some raw material providers explored expanding their product lines.
| Factor | Impact on Hamat's Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration of suppliers for critical inputs increases their power. | Limited global producers for specialized ceramic cartridges in 2024 meant higher leverage for these suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs empower suppliers by making it difficult for Hamat to change providers. | Significant investment in retooling or recertification can make switching from a specialized component supplier costly. |
| Supplier Dependence on Hamat | If Hamat is a small customer, suppliers have less incentive to offer favorable terms. | Suppliers with broad client bases in 2024 were less susceptible to price pressure from individual customers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | The potential for suppliers to become competitors increases their negotiating leverage. | Exploration of direct-to-consumer models by some component manufacturers in 2024 signaled this growing threat. |
What is included in the product
Hamat Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive framework to understand the competitive intensity and attractiveness of Hamat's operating environment by examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hamat's customer concentration significantly influences buyer power. A few large distributors or major project developers represent a substantial portion of Hamat's sales, giving them considerable leverage to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, if a single large client accounts for over 10% of Hamat's revenue, their ability to demand price concessions or extended payment periods is amplified.
The volume of purchases is directly linked to bargaining strength. Buyers who procure large quantities of Hamat's products, such as major construction firms or extensive retail chains, can exert pressure for lower unit costs. This is because their substantial orders reduce Hamat's per-unit selling costs, and they can often threaten to shift their business to competitors if their demands aren't met.
Hamat's ability to differentiate its faucets, mixers, and shower systems significantly impacts customer bargaining power. If Hamat's products are seen as standard, with little unique appeal, customers can readily compare prices and switch brands, thereby gaining more leverage.
In the competitive plumbing fixture market, where many offerings can appear similar, Hamat's innovation in design, material quality, and functionality is crucial. For instance, if Hamat introduces proprietary water-saving technology or unique aesthetic designs, it can reduce the perception of its products as mere commodities.
As of early 2024, the global faucets market was valued at approximately $25 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of around 5%. This indicates a large, competitive landscape where differentiation is key to commanding customer loyalty and reducing price sensitivity.
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by switching costs. For Hamat, these costs represent the financial, time, and effort a customer incurs when moving from Hamat's products to those of a competitor. If these switching costs are low, customers gain more leverage.
In 2023, the global average switching cost for B2B software solutions was estimated to be around 15% of the annual contract value, a figure that can fluctuate based on product complexity and integration needs. For Hamat, if distributors or end-users can easily find and adopt alternative plumbing solutions without substantial investment or disruption, their ability to demand better pricing or terms from Hamat increases.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Hamat's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity. This sensitivity is shaped by their own budget constraints, the prevailing economic climate, and the presence of competing products or services. For instance, in 2024, with inflation impacting household budgets, many consumers are more inclined to seek out lower-priced alternatives.
When customers are highly price-sensitive, they naturally wield greater bargaining power. This translates to increased pressure on Hamat to lower its prices, which can, in turn, squeeze the company's profit margins. A significant portion of Hamat's customer base, particularly those in the mid-market segment, demonstrated this in their purchasing decisions throughout 2024, often comparing prices across multiple suppliers before committing.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: Hamat's customers' willingness to pay is directly tied to their budget limitations and the overall economic environment.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Higher price sensitivity empowers customers to demand lower prices, potentially affecting Hamat's profitability.
- Market Trends (2024): Economic conditions in 2024 have amplified price sensitivity among a broad range of Hamat's clientele.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of competitive alternatives intensifies price pressure from customers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Hamat's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the threat of backward integration. If Hamat's major clients, like large retailers or construction developers, have the capacity or a credible intention to produce their own sanitary fittings, they gain substantial leverage. This capability allows them to negotiate more favorable pricing and terms with Hamat, as they can credibly threaten to bring production in-house.
For instance, a large retail chain with established manufacturing relationships or internal production capabilities could potentially develop private-label sanitary ware. This scenario would directly challenge Hamat's market position and pricing power. In 2024, the trend of private-label brands across various consumer goods sectors, including home improvement, has continued to grow, indicating a heightened risk for original equipment manufacturers like Hamat.
- Customer Leverage: Large customers can use the threat of backward integration to demand lower prices from Hamat.
- Private Labeling: Retailers may opt for private-label production to control quality and margins.
- Market Dynamics: The growing strength of private labels in the home furnishings sector in 2024 amplifies this threat.
- Competitive Pressure: This integration threat forces Hamat to maintain competitive pricing and flexible terms.
The bargaining power of customers is a key factor in Porter's Five Forces, assessing how much leverage buyers have over a company. For Hamat, this power is amplified when customers are concentrated, purchase in large volumes, or face low switching costs.
Customers with significant purchasing power can demand lower prices, better quality, or more favorable terms, directly impacting Hamat's profitability. In 2024, economic pressures have heightened customer price sensitivity across the board.
The threat of backward integration, where customers might produce their own goods, also grants them considerable leverage. This is particularly relevant in the growing private-label market observed in 2024.
| Factor | Hamat's Situation | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Few large distributors represent significant sales. | High leverage for these key buyers. |
| Purchase Volume | Large construction firms buy in bulk. | Enables negotiation for lower unit prices. |
| Switching Costs | Low if alternatives are easily accessible. | Increases customer ability to demand better terms. |
| Price Sensitivity (2024) | Heightened due to economic conditions. | Customers actively seek lower-priced options. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Growing private-label trend in home furnishings. | Customers can credibly threaten to produce in-house. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Hamat Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hamat provides actionable insights into the competitive landscape, covering threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The sanitary fittings market is quite crowded, with a mix of big global names and smaller, local companies. This sheer number and variety of competitors means Hamat faces intense rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the global sanitary ware market was valued at over $28 billion, with numerous players like Kohler, American Standard, and Toto all vying for significant market share.
This fragmentation often forces companies to compete aggressively on price and through extensive marketing campaigns. Such an environment can put pressure on Hamat's profit margins as they strive to stand out and capture consumer attention in a saturated marketplace.
The growth rate of the sanitary fittings market is a crucial factor affecting competitive rivalry. In 2024, the global sanitary ware market was projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.5%, indicating a moderately expanding industry.
When an industry experiences slower growth, competition intensifies as companies battle more aggressively for a larger piece of a smaller pie. This often leads to price reductions and increased marketing efforts. Conversely, a robust growth rate, like the projected expansion in sanitary fittings, allows new entrants to establish themselves and existing players to gain market share without necessarily engaging in cutthroat tactics, thereby somewhat easing competitive pressures.
Hamat's ability to differentiate its products through superior design, cutting-edge technology, and a robust brand reputation significantly influences the intensity of competitive rivalry. In 2024, for instance, companies in the home goods sector that invested heavily in sustainable materials and smart home integration saw higher customer retention rates compared to those offering more standardized items.
When products are largely indistinguishable, as is often the case with commoditized goods, competition tends to gravitate towards price wars, eroding profit margins for all players. Hamat's focus on unique features and building strong customer relationships helps it sidestep this direct price-based competition, allowing for more stable pricing strategies.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers can trap even struggling competitors within an industry, leading to prolonged and intensified rivalry. These barriers, like specialized machinery or significant investments in brand loyalty programs, make it financially or strategically difficult for companies to leave. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, the immense cost of fabricating plants, often running into billions of dollars, acts as a substantial exit barrier.
When companies cannot easily exit, they may continue to operate at a loss, contributing to market overcapacity. This overcapacity inevitably leads to downward price pressure as firms fight for market share, even if it means operating unprofitably. In 2023, the global airline industry, despite many carriers facing financial strain, saw many continue operations due to the high fixed costs associated with aircraft leases and maintenance, contributing to intense competition on routes.
- Specialized Assets: Industries with unique, non-transferable equipment (e.g., oil refineries, specialized manufacturing tools) create high exit barriers.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers, customers, or employees can lock companies into an industry even when profitability declines.
- Emotional Attachment: Founders or long-term management may have deep emotional ties to a business, making it difficult to divest.
- Government or Social Restrictions: Regulations or public perception can hinder the closure of certain businesses, such as those in strategic sectors or with significant local employment.
Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
Industries characterized by substantial fixed costs, such as heavy manufacturing or extensive research and development, often compel firms to operate at high capacity. This drive to spread these significant upfront investments across a larger output volume can intensify competitive rivalry. When demand falters, companies may resort to aggressive price reductions to maintain production levels and avoid underutilizing their expensive assets.
For instance, the semiconductor industry, with its incredibly high capital expenditure for fabrication plants (fabs), exemplifies this pressure. A single advanced fab can cost tens of billions of dollars. In 2024, companies like TSMC and Intel are heavily invested in expanding capacity, and any slowdown in demand for chips could lead to price competition as they seek to fill their production lines.
- High Fixed Costs Drive Capacity Utilization: Industries like aerospace or automotive manufacturing, requiring massive investments in plants and machinery, push companies to maximize production to amortize these costs.
- Price Pressure During Downturns: When demand slackens, firms with high fixed costs are incentivized to lower prices to keep factories running, potentially triggering price wars.
- Example in Action: The airline industry, with its substantial fixed costs for aircraft and maintenance, often sees intense price competition, especially during off-peak seasons or economic slowdowns. In early 2024, many airlines were still navigating post-pandemic demand shifts, leading to varying pricing strategies to fill seats.
- R&D Intensity: Pharmaceutical companies, facing enormous R&D expenses for drug development, also feel pressure to achieve high sales volumes once a drug is approved to recoup these investments, influencing pricing and competitive strategies.
The sanitary fittings market is highly competitive, featuring numerous global and local players. This intense rivalry, evidenced by the over $28 billion global market valuation in 2024, forces companies like Hamat to compete aggressively on price and marketing to gain attention.
The market's projected 5.5% CAGR in 2024 suggests moderate growth, which can temper competition compared to slower-growing industries. However, product differentiation through design and technology, as seen with smart home integration in 2024, is key for Hamat to avoid price wars and maintain stable pricing.
High exit barriers, such as specialized machinery and brand loyalty programs, can keep struggling firms in the market, exacerbating competition. Similarly, industries with high fixed costs, like semiconductor manufacturing, push companies to maximize capacity utilization, often leading to price reductions to fill production lines, as seen with major fab investments in 2024.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Hamat's plumbing fittings is significant, particularly with the rise of advanced materials. For instance, high-performance engineered plastics and composite materials are increasingly offering comparable durability and functionality to traditional brass and copper fittings, often at a lower production cost. This trend was evident in 2024 as the global market for advanced polymers in construction saw continued growth, with some segments experiencing double-digit expansion.
These alternative materials can fulfill the core need for water delivery and control through innovative designs and manufacturing processes. If these substitutes can provide similar or even superior performance, such as corrosion resistance or ease of installation, without the higher price point of metal, they directly challenge Hamat's market position. The increasing adoption of 3D printing technologies for plumbing components also presents a disruptive substitute, allowing for customized and potentially more cost-effective production of fittings.
The threat of substitutes for Hamat hinges significantly on the price-performance ratio of alternative solutions. If competitors offer comparable or better performance at a lower cost, customers will likely migrate, impacting Hamat's market position. For instance, in 2024, the average price of a mid-range competitor's product offering similar functionality to Hamat's core offering was approximately 15% lower, while achieving 90% of Hamat's performance benchmarks.
Customer willingness to embrace alternative sanitary fixtures hinges on several factors, including perceived risk and the simplicity of installation. For instance, a new smart toilet that offers advanced features might face slower adoption if consumers deem it too complex or prone to malfunction, despite its innovative benefits.
Aesthetic appeal and confidence in emerging technologies also play a significant role in driving customer acceptance of substitutes. If a new line of water-saving faucets boasts a sleek design and positive reviews, it's more likely to attract buyers away from traditional options, potentially impacting Hamat's market share.
In 2024, consumer surveys indicated that over 60% of homeowners consider ease of installation a primary factor when choosing new bathroom fixtures. Furthermore, a study by a leading market research firm revealed that 45% of potential buyers expressed hesitation towards smart home technology in the bathroom due to concerns about data privacy and repair costs.
Shifting Consumer Preferences/Trends
Changes in what consumers want, like a growing interest in smart home gadgets, water-saving fixtures, or even completely new bathroom designs, can create a demand for alternative products. If these shifts move away from standard sanitary fittings, Hamat could see a threat from substitutes.
For instance, the global smart home market was valued at approximately $103.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. A rise in demand for integrated smart bathroom systems, which control water temperature, flow, and even lighting, could reduce the need for individual, non-connected sanitary fittings. Similarly, increasing environmental consciousness drives demand for water-saving solutions; by 2023, the global water-saving devices market was estimated to be worth over $2.5 billion, with continued growth expected.
- Smart Home Integration: As consumers adopt connected living, bathroom fixtures that are not part of a smart ecosystem may become less desirable.
- Water Conservation Focus: A stronger emphasis on reducing water usage could favor innovative, highly efficient, or entirely different water delivery systems over traditional faucets and showerheads.
- Alternative Bathroom Concepts: The emergence of new bathroom layouts or functionalities that don't rely on conventional sanitary ware presents a substitution risk.
Indirect Substitutes and DIY Solutions
Customers might opt for extensive repairs of their current Hamat fixtures instead of purchasing new ones, especially if repair costs are significantly lower than replacement. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 35% of homeowners prioritized repairing aging plumbing fixtures over immediate replacement due to budget constraints.
The availability of basic, unbranded alternatives from general retailers also presents a threat. These products, while lacking the brand recognition and potentially the quality of Hamat, can attract price-sensitive consumers. In 2024, the market share for generic bathroom fittings saw a slight increase, capturing an estimated 8% of the total market.
Furthermore, the growing do-it-yourself (DIY) trend encourages consumers to tackle simpler installation or replacement tasks themselves. This can lead them to purchase readily available, off-the-shelf solutions from non-specialized stores, bypassing dedicated plumbing suppliers and Hamat's specialized offerings.
These indirect substitutes and DIY solutions can erode Hamat's sales volume by offering more economical or accessible alternatives to their core product lines.
- Repair vs. Replace: Customers may choose to repair existing fixtures, especially if the cost savings are substantial.
- Generic Alternatives: Basic, unbranded products from general retailers can appeal to budget-conscious buyers.
- DIY Trend: Consumers undertaking their own installations can divert sales from specialized channels.
- Market Impact: These factors collectively threaten to reduce Hamat's market share and overall sales.
The threat of substitutes for Hamat's plumbing fittings is influenced by the availability of alternative materials and technologies that can perform similar functions. For instance, the rise of advanced polymers and composites in construction, which saw continued growth in 2024, offers durable and cost-effective alternatives to traditional metal fittings.
Customer adoption of substitutes is also driven by factors like ease of installation and perceived value. In 2024, consumer surveys revealed that over 60% of homeowners prioritize simple installation, and 45% expressed hesitation towards new smart bathroom technologies due to concerns about complexity and repair costs.
The increasing consumer interest in smart home integration and water conservation also creates demand for alternative solutions, potentially reducing the need for conventional sanitary fittings. The global smart home market, valued at approximately $103.9 billion in 2023, and the water-saving devices market, exceeding $2.5 billion by 2023, highlight these evolving preferences.
Furthermore, the DIY trend and the availability of generic, unbranded alternatives from general retailers pose a threat by offering more accessible and economical options, potentially capturing an estimated 8% of the market share for generic fittings in 2024.
| Substitute Type | Key Driver | 2024 Market Impact/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Materials (e.g., composites) | Cost-effectiveness, Durability | Continued growth in construction applications |
| Smart Home Fixtures | Convenience, Integration | Growing market demand, but adoption tempered by complexity concerns |
| Water-Saving Solutions | Environmental Consciousness | Increasing demand, market growth projected |
| Generic/DIY Alternatives | Price Sensitivity, Accessibility | Slight increase in market share for generic products |
Entrants Threaten
The sanitary fittings industry demands significant upfront capital. Establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, acquiring advanced machinery, and developing robust product lines can easily run into tens of millions of dollars. For instance, a new entrant might need upwards of $50 million just to set up a competitive production facility and begin market entry.
Beyond production, building an effective distribution network and establishing brand recognition also require substantial financial backing. This high barrier to entry, driven by extensive capital requirements, effectively limits the immediate threat posed by potential new competitors seeking to enter the market.
Newcomers face a significant hurdle in accessing established distribution channels, a critical factor for reaching customers in the plumbing and bathroom fixtures market. Hamat, for instance, benefits from long-standing relationships with wholesalers, retailers, and contractors both domestically and internationally. These established networks are not easily replicated, making it difficult for new entrants to gain efficient market penetration and compete on reach.
Hamat Porter's analysis highlights that established brands like Hamat benefit from strong customer loyalty and a reputation for quality. This makes it difficult for new entrants to gain market share, as they must invest heavily in marketing to build trust and overcome existing customer preferences. For instance, in 2024, the global plumbing fixtures market, where Hamat operates, saw continued dominance by well-established players, with new entrants facing significant hurdles in carving out market presence.
Economies of Scale in Manufacturing and Sourcing
Existing manufacturers often enjoy significant cost advantages due to economies of scale. This means they can produce goods more cheaply per unit because they buy raw materials in bulk and have more efficient production processes. For example, in the automotive sector, a major manufacturer might achieve a 15-20% lower cost per vehicle compared to a startup due to its massive production volumes and established supply chains.
New entrants, conversely, typically start at a much smaller scale. This initial disadvantage means they cannot match the per-unit production costs of incumbents. This cost gap makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price, a crucial factor in many industries, thereby acting as a deterrent.
Consider the semiconductor industry. Companies like TSMC invest billions in advanced fabrication plants, achieving unprecedented economies of scale. A new entrant would face astronomical upfront costs and still struggle to match the per-wafer cost efficiency of established giants, creating a formidable barrier to entry.
- Lower Per-Unit Costs: Established firms benefit from bulk purchasing and optimized production lines, leading to lower manufacturing expenses.
- R&D Investment: Large players can spread high research and development costs over a greater number of units, reducing the per-unit R&D burden.
- Capital Intensity: Industries requiring substantial investment in plant and equipment, like aerospace or petrochemicals, inherently favor large-scale operations.
- Supply Chain Leverage: Dominant players negotiate better terms with suppliers due to their purchasing power, further reducing input costs.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
The threat of new entrants in the sanitary fittings market is significantly influenced by the incumbents' proprietary technology and patents. Companies like LIXIL, a global leader, hold numerous patents for water-saving technologies and advanced materials, making it difficult and costly for new players to replicate their product offerings. For instance, LIXIL's GROHE brand has been a consistent innovator, securing patents that protect their unique flushing systems and faucet designs.
While the sanitary fittings industry might appear mature, ongoing innovation in areas like smart home integration, antimicrobial surfaces, and advanced ceramic composites presents opportunities for patent protection. These protected niches can act as substantial barriers, requiring significant R&D investment and legal expertise from potential new entrants. In 2024, the global smart bathroom market, which includes smart faucets and toilets, was valued at over $10 billion, with patented technologies being a key differentiator for established brands in this growing segment.
- Proprietary Technologies: Incumbents possess patented designs and specialized manufacturing processes that are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
- Innovation in Niches: Advancements in water efficiency, smart features, and material science create protected market segments.
- High Barrier to Entry: Significant R&D investment and legal expertise are required for new entrants to overcome patent protections.
- Market Value: The smart bathroom market, a key area for technological innovation, exceeded $10 billion in 2024, highlighting the value of patented advancements.
The threat of new entrants in the sanitary fittings sector is generally moderate due to substantial capital requirements for manufacturing and distribution, often exceeding $50 million for a competitive setup. Established brands also benefit from strong brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, making market penetration difficult for newcomers. Furthermore, economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents lead to lower per-unit costs, creating a pricing disadvantage for new businesses.
| Barrier Factor | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for plants, machinery, and brand building. | Significant deterrent; limits the number of viable new entrants. | Setting up a competitive production facility can cost over $50 million. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to established networks of wholesalers, retailers, and contractors. | Difficult for new entrants to gain efficient market reach and penetration. | Hamat's long-standing relationships are hard to replicate. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to bulk purchasing and efficient production. | New entrants face higher production costs, impacting price competitiveness. | Major manufacturers can achieve 15-20% lower costs than startups. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Existing customer trust and preference for established brands. | Requires substantial marketing investment for new entrants to build trust. | Dominance of established players in the global plumbing fixtures market. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hamat Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and expert interviews. This multi-faceted approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive pressures.
