Halozyme Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Halozyme Bundle
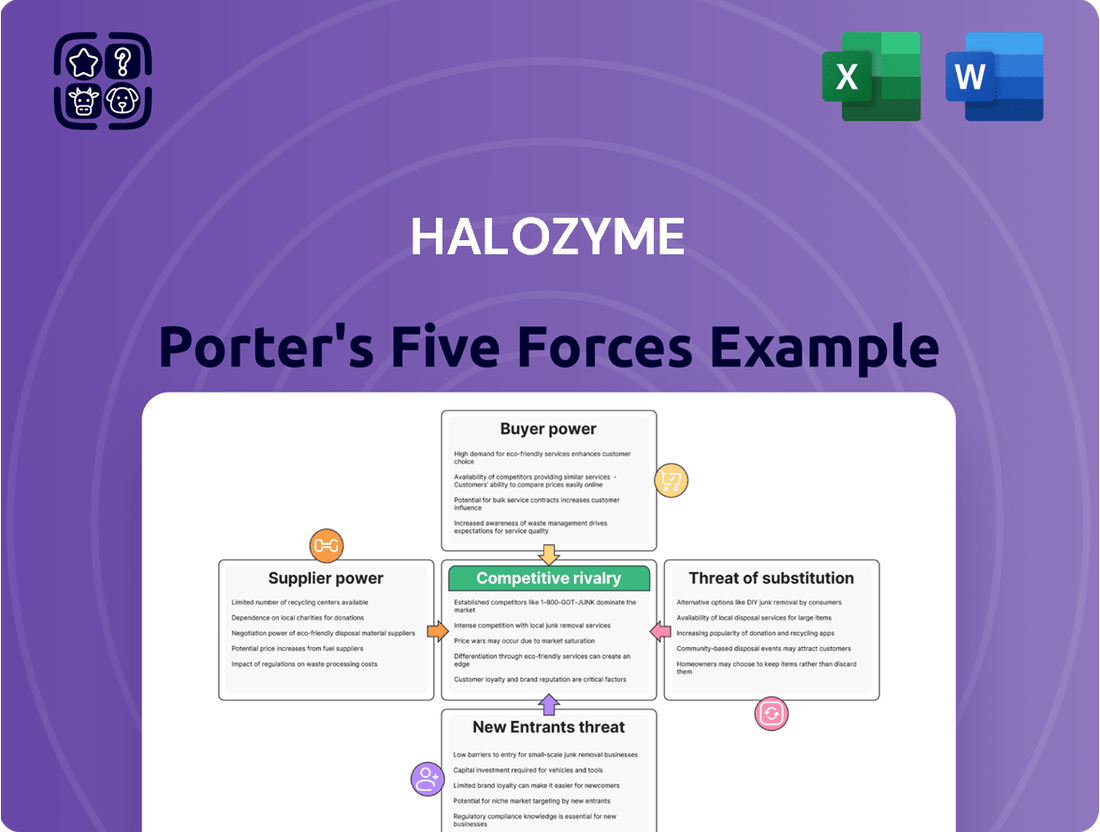
Halozyme's competitive landscape is shaped by significant forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the intense rivalry within the biotech sector. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
The threat of new entrants is moderate, as high R&D costs and regulatory hurdles present barriers, yet innovative technologies can disrupt established players.
Supplier power, particularly for specialized enzymes and manufacturing capabilities, can influence Halozyme's operational costs and flexibility.
The threat of substitutes, while not immediately pressing, requires continuous innovation to maintain market advantage and demonstrate the unique value of their drug delivery platform.
Intense rivalry among pharmaceutical companies and drug delivery solution providers necessitates a deep understanding of market positioning and differentiation.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Halozyme’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Halozyme's ENHANZE technology hinges on its exclusive recombinant human hyaluronidase (rHuPH20) enzyme. This specialized enzyme is a unique and essential input, making alternative suppliers for this precise component virtually nonexistent.
The company's control over the manufacturing and supply chain of rHuPH20 grants it substantial influence over its production processes and licensing agreements. This proprietary aspect significantly bolsters Halozyme's bargaining power with potential partners and customers who require this specific technology.
The production of biopharmaceuticals like Halozyme's rHuPH20 hinges on highly specialized raw materials and cell culture media. The limited availability and exacting quality demands for these components grant certain suppliers significant bargaining power.
Stringent regulatory standards within the pharmaceutical sector further amplify this supplier leverage, as only approved, high-quality inputs are permissible. This necessity underscores the importance of supply chain resilience and strategic diversification for companies like Halozyme.
Halozyme's reliance on specialized manufacturing equipment and potential contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) means that providers of these high-tech solutions can wield significant bargaining power. If the equipment or services are highly specialized and difficult to substitute, suppliers gain leverage. This is particularly true if switching costs are substantial for Halozyme, considering the rigorous validation and regulatory hurdles involved in changing manufacturing processes.
Intellectual Property and Licensing
While Halozyme Therapeutics licenses its patented ENHANZE® drug delivery technology to pharmaceutical partners, its own ability to innovate and operate could be influenced by its reliance on intellectual property licensed from third parties. If Halozyme requires crucial, specialized technology or patents from a limited number of suppliers for its research, development, or manufacturing, those suppliers would possess significant bargaining power. This could manifest in higher licensing fees or more restrictive terms, impacting Halozyme's operational costs and strategic flexibility.
Consider the scenario where Halozyme depends on a specific enzyme or a unique chemical synthesis process that is patented and exclusively controlled by a single entity. In such cases, this sole supplier could dictate terms, potentially increasing costs if demand for the ENHANZE® technology grows substantially. For instance, if a critical component for ENHANZE® formulation is sourced from a company holding a dominant patent, that company's leverage is high, directly affecting Halozyme's ability to scale production efficiently.
- Reliance on Critical Third-Party IP: If Halozyme's innovation or manufacturing processes depend on foundational intellectual property licensed from a few key providers, these licensors gain significant leverage.
- Impact of Licensing Fees: Higher licensing costs for essential external IP can directly impact Halozyme's profitability and the overall cost structure of its ENHANZE® platform.
- Limited Supplier Options: A scarcity of alternative suppliers for critical patented technologies amplifies the bargaining power of existing licensors.
- Strategic Flexibility Constraints: Dependence on third-party IP can limit Halozyme's strategic options, potentially restricting its ability to adapt or expand its technology without renegotiating favorable terms.
Skilled Labor and Expertise
The biopharmaceutical industry, where Halozyme operates, relies heavily on highly specialized scientific and technical expertise. This includes professionals in areas like protein engineering, formulation science, clinical trial management, and regulatory affairs. The demand for these niche skills often outstrips the available supply, creating a situation where skilled labor possesses considerable bargaining power.
This scarcity directly impacts Halozyme by potentially driving up labor costs. Companies compete fiercely for top talent, leading to higher salaries, more attractive benefits packages, and increased retention efforts. For instance, in 2024, the median salary for a senior protein scientist in the biotech sector could easily exceed $150,000 annually, reflecting the demand. Halozyme must factor these costs into its operational budget and R&D investments.
- High Demand for Niche Expertise: Fields like enzyme engineering and bioconjugation are critical for Halozyme's ENHANZE technology, and the pool of experienced professionals is limited.
- Talent Retention Challenges: Competitors actively recruit specialized talent, forcing companies like Halozyme to offer competitive compensation and career development opportunities to retain key personnel.
- Impact on Project Timelines: Delays in securing essential scientific talent can slow down research, development, and clinical trial phases, potentially affecting market entry and revenue generation.
- Wage Inflation in Specialized Roles: The intense competition for skilled scientists and engineers in biopharma contributed to an estimated 5-8% year-over-year wage inflation for these roles in 2024.
Halozyme's primary dependence on its proprietary rHuPH20 enzyme, a component with virtually no direct substitutes, grants it significant leverage over its customers and partners. This exclusivity means that companies seeking to utilize the ENHANZE technology must engage with Halozyme, strengthening its position.
The limited number of suppliers for critical raw materials and specialized equipment in biopharmaceutical manufacturing also empowers these suppliers. Halozyme's need for high-quality, regulatory-compliant inputs means it must work with approved vendors, giving those vendors considerable bargaining power.
Similarly, the scarcity of highly specialized scientific and technical talent in the biopharma sector, particularly in fields like enzyme engineering, allows skilled professionals to command higher compensation and favorable terms. This competition for talent, which saw an estimated 5-8% wage inflation for specialized roles in 2024, directly impacts Halozyme's operational costs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Halozyme is amplified by the industry's stringent regulatory environment and the highly specialized nature of its technology and the inputs required.
What is included in the product
This analysis uncovers the key drivers of competition within Halozyme's biotechnology sector, evaluating the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Streamline competitive assessment with a visual overview of Halozyme's market position, simplifying complex strategic pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Halozyme's primary customers are large pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms. These companies incorporate Halozyme's ENHANZE® drug delivery technology into their own specialized medications.
The integration process involves substantial investment. Once a drug is co-formulated with ENHANZE® and successfully navigates rigorous clinical trials and regulatory approvals, the costs associated with switching to an alternative technology become prohibitively high.
This significant upfront investment in development, regulatory submissions, and market launch creates a formidable barrier for customers seeking to change suppliers. For instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market can exceed $2 billion, making the ENHANZE® component a relatively small, but critically integrated, part of that massive expenditure.
Consequently, the bargaining power of these customers is considerably weakened because of these exceptionally high switching costs.
Several of Halozyme's partnered products, including blockbuster therapies like DARZALEX SC, Phesgo, and VYVGART Hytrulo, command significant market share within their therapeutic categories. The success of these drugs, amplified by the subcutaneous delivery facilitated by Halozyme's ENHANZE technology, creates a strong incentive for these major pharmaceutical clients to maintain their partnerships. This substantial market presence, however, also grants these large customers a degree of bargaining power in ongoing negotiations with Halozyme.
Customers seeking to enhance subcutaneous delivery of biologics face a limited landscape of readily available, commercially proven alternatives to Halozyme's ENHANZE technology. While other drug delivery methods exist, ENHANZE's ability to enable large-volume subcutaneous injections, thereby reducing treatment burden and improving patient experience, sets it apart. This unique value proposition for frequently high-volume infusions means that pharmaceutical companies have few immediately comparable solutions offering the same efficacy and patient benefits.
Concentration of Major Pharma Partners
Halozyme's bargaining power of customers is influenced by its concentration of major pharmaceutical and biotechnology partners. Companies like Roche, Takeda, Pfizer, Janssen, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and argenx represent a significant portion of Halozyme's clientele.
The reliance on this relatively small group of major players means that any disruption with one or two of these key partners could have a substantial impact on Halozyme's revenue streams. This concentration grants these large customers considerable leverage in negotiations.
For instance, if a major partner decides to reduce its reliance on Halozyme's technology or renegotiates terms unfavorably, it could significantly affect Halozyme's financial performance. This dynamic underscores the importance of maintaining strong relationships and providing consistent value to these core clients.
- Key Partners: Halozyme's technology is licensed to prominent companies such as Roche, Takeda, Pfizer, Janssen, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and argenx.
- Revenue Impact: The loss of a major partner or a significant contract dispute could materially impact Halozyme's revenue, increasing customer bargaining power.
- Concentration Risk: While diverse partnerships are sought, the reliance on a few large entities creates a degree of vulnerability and empowers those major customers.
Royalty-Based Revenue Model
Halozyme's royalty-based revenue model means its customers, primarily pharmaceutical companies licensing its ENHANZE® drug delivery technology, hold significant bargaining power. This is because Halozyme's income is directly tied to the sales volume of these partner products. If a partner faces challenges in marketing or sales execution, it directly impacts Halozyme's royalty payments, giving the partner leverage.
This dependency creates an indirect influence for customers. For example, if a partner believes a higher royalty rate is unsustainable for their product's profitability, they can exert pressure through negotiations, potentially impacting Halozyme's future revenue streams. In 2023, Halozyme reported royalty and milestone revenues of approximately $800 million, highlighting the direct correlation between partner sales and Halozyme's financial performance.
- Customer Dependence: Halozyme's revenue is primarily derived from royalties and milestones, making its financial success contingent on its partners' product sales.
- Sales Strategy Influence: Partners' marketing and sales strategies directly affect Halozyme's income, granting them indirect control over revenue generation.
- Negotiating Leverage: Challenges in partner sales can be used as leverage in royalty rate negotiations, impacting Halozyme's financial outlook.
- Revenue Correlation: Halozyme's 2023 royalty and milestone revenue of around $800 million underscores the direct link between partner commercial success and Halozyme's earnings.
Halozyme's customers, primarily large pharmaceutical companies, possess significant bargaining power due to the high switching costs associated with its ENHANZE® drug delivery technology. Once a drug is co-formulated and approved, the immense investment in clinical trials and regulatory processes makes it extremely difficult and costly to change suppliers. For instance, bringing a new drug to market can cost over $2 billion, with ENHANZE® being a critical, integrated component.
The concentration of Halozyme's business among a few major pharmaceutical partners also amplifies customer leverage. Companies like Roche, Pfizer, and AbbVie represent a substantial portion of Halozyme's revenue, meaning any negotiation pressure from these key clients carries significant weight. This reliance creates a vulnerability for Halozyme, empowering its major customers.
Furthermore, Halozyme's royalty-based revenue model directly links its income to its partners' product sales. If a partner's sales falter, Halozyme's royalty payments decrease, giving the partner leverage in royalty rate negotiations. Halozyme's 2023 royalty and milestone revenue of approximately $800 million underscores this direct financial dependency.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Halozyme |
| Major Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Firms | High Switching Costs (R&D, regulatory) | Weakens customer power due to investment lock-in |
| Concentration of Key Partners (e.g., Roche, Pfizer) | Increases customer power due to revenue reliance | |
| Royalty-Based Revenue Model | Increases customer power via influence on sales performance |
Full Version Awaits
Halozyme Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview offers a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Halozyme, detailing the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier bargaining, threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes for Halozyme. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, enabling you to leverage its detailed strategic assessment. No mockups, no samples – the Halozyme Porter's Five Forces analysis you see here is precisely what you’ll be able to download after payment, ready for your immediate strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Halozyme Therapeutics thrives in a specialized niche within the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on enhancing drug delivery through its proprietary ENHANZE® technology. This enzyme-based platform, utilizing rHuPH20, allows for the subcutaneous administration of drugs typically given intravenously, offering a significant advantage in patient convenience and potentially reducing healthcare system burdens. The company's market position is further strengthened by its highly differentiated offering, which directly addresses unmet needs in drug administration for various therapeutic areas.
This high degree of specialization inherently limits the number of direct competitors capable of replicating Halozyme's core technology. While other companies may offer general drug delivery systems, few possess the specific enzymatic expertise and approved applications that ENHANZE® provides. This focused approach means competitive rivalry is less about broad market share battles and more about the specific therapeutic indications where Halozyme's technology can be applied and partnered.
In 2024, Halozyme continued to expand its partnerships, demonstrating the value and differentiation of ENHANZE®. For example, collaborations with major pharmaceutical companies are crucial for market penetration. The company's revenue growth, often driven by these partnerships and royalty streams, underscores the market's acceptance of its specialized solution. This specialization reduces direct head-to-head competition from companies offering similar enzymatic drug delivery enhancements.
While Halozyme Therapeutics is a prominent player in the hyaluronidase market with its ENHANZE drug delivery technology, it's not the only one. Companies like Amphastar Pharmaceuticals are also active in this space, developing and marketing hyaluronidase products.
Furthermore, the strategic landscape includes players like Alteogen, which has notably partnered with MSD (Merck & Co.) for its hyaluronidase technology. This indicates a growing interest and investment in hyaluronidase solutions by major pharmaceutical entities.
This presence of other developers signifies direct competition, particularly for therapeutic applications where enhanced drug delivery is crucial. For instance, in 2023, the global hyaluronidase market was valued at approximately $1.7 billion and is projected to grow significantly, attracting more participants.
However, Halozyme's established partnerships, strong intellectual property portfolio, and extensive clinical data provide a substantial competitive moat, even as new entrants emerge in this dynamic market.
The drug delivery market is a hotbed of innovation, with companies constantly pushing the boundaries. Think nanotechnology, microneedles, and other cutting-edge systems designed to get medications into the body more effectively. This relentless pursuit of better delivery methods means that companies have to stay ahead of the curve or risk falling behind.
This intense focus on research and development means that companies like Halozyme are locked in a fierce race. Those that can develop and patent novel drug delivery technologies gain a significant competitive advantage. For instance, advancements in subcutaneous drug delivery, a key area for Halozyme, have seen significant investment and patent filings globally throughout 2023 and early 2024 as companies vie for market share.
Strategic Partnerships and Pipeline Expansion
Halozyme's strategic partnerships and pipeline expansion directly influence competitive rivalry. By forging agreements for its ENHANZE drug delivery technology, Halozyme enables partners to develop new subcutaneous formulations for existing blockbuster drugs. This can intensify competition within therapeutic areas where these reformulated drugs gain market share, for example, in oncology where many of its partners operate. The commercial success of these partnerships, such as those with large pharmaceutical companies, directly impacts the competitive dynamics of the drugs delivered via Halozyme's platform. For instance, in 2023, Halozyme reported approximately $700 million in total revenue, a significant portion of which is tied to royalty and milestone payments from these collaborations.
The landscape of competitive rivalry is indirectly shaped by Halozyme's focus on expanding its pipeline through new clinical trials and securing auto-injector partnerships. These efforts aim to broaden the application of its technology across various therapeutic classes. As more pharmaceutical companies leverage ENHANZE, the rivalry among these companies for market dominance in their respective fields can escalate. Halozyme's revenue in 2024 is projected to grow, underscoring the increasing adoption and impact of its technology on partner product competitiveness. This growth is fueled by an expanding pipeline of partnered products expected to launch in the coming years, further intensifying the competitive pressures faced by both Halozyme's partners and their rivals.
The success of Halozyme's strategy is intrinsically linked to the commercial performance of its partners' products. These products frequently compete in highly saturated and dynamic therapeutic areas, such as oncology and immunology, where rivalries are particularly fierce. For example, Halozyme has partnerships with companies like Roche and Bristol Myers Squibb, both major players in oncology. The ability of these partners to successfully launch and market subcutaneous versions of their drugs, facilitated by ENHANZE, can disrupt established treatment paradigms and heighten competition. This makes the competitive rivalry an indirect but crucial factor for Halozyme's own market position and revenue generation.
The expansion of Halozyme's pipeline and its auto-injector partnerships are key drivers of competitive intensity. As more companies integrate Halozyme's ENHANZE technology into their drug development, the market becomes more crowded with innovative delivery methods. This can lead to increased price competition and a greater need for differentiation among pharmaceutical companies. In 2024, with several key partners expected to advance their ENHANZE-enabled products through late-stage clinical trials and potential approvals, the impact on competitive rivalry is set to increase significantly.
Intellectual Property Disputes
Intellectual property disputes are a significant factor in competitive rivalry, particularly for companies like Halozyme Therapeutics. These disputes often center on patented technologies that provide a competitive edge, such as Halozyme's ENHANZE drug delivery technology. The value of these proprietary platforms can lead to intense legal battles when competitors are perceived to be infringing on existing patents.
A prime example of this dynamic is Halozyme's patent infringement lawsuit filed against Merck. This legal action specifically targeted Merck's use of its own hyaluronidase technology, which Halozyme alleged infringed upon its patents related to its proprietary MDASE™ technology. The case underscores how critical intellectual property is in the pharmaceutical sector, where innovative drug delivery systems can significantly impact market share and profitability.
The outcome of such litigation can have substantial financial and strategic implications. For instance, a favorable ruling can reinforce a company's market position and potentially lead to significant licensing revenue or damages. Conversely, an unfavorable outcome can weaken a company's competitive standing and necessitate costly redesigns of its products or delivery methods.
- Halozyme's ENHANZE technology is a key proprietary asset, enabling subcutaneous administration of biologic drugs.
- Patent infringement lawsuits, like the one against Merck, highlight the high stakes involved in protecting these valuable intellectual assets.
- The contested nature of drug delivery technologies means that legal challenges are an inherent part of the competitive landscape.
- Financial impacts from IP disputes can range from significant legal costs to substantial licensing fees or damages awarded.
Competitive rivalry in the drug delivery sector, where Halozyme operates, is intense due to the constant drive for innovation. Companies like Amphastar Pharmaceuticals and Alteogen are developing their own hyaluronidase technologies, directly challenging Halozyme's market position. This competition is amplified by major pharmaceutical firms actively seeking advanced delivery systems.
Intellectual property is a critical battleground, as seen in Halozyme's patent dispute with Merck over hyaluronidase technology. Such legal actions underscore the significant financial and strategic implications of protecting proprietary drug delivery platforms. The value of these innovations means legal challenges are an intrinsic element of the competitive environment.
The growing market for hyaluronidase, valued at approximately $1.7 billion in 2023, attracts new entrants and intensifies rivalry. Halozyme's strategic partnerships, like those with Roche and Bristol Myers Squibb, are vital for its revenue, with approximately $700 million in total revenue reported in 2023, largely from these collaborations.
| Competitor | Technology Focus | Key Partnerships/Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Amphastar Pharmaceuticals | Hyaluronidase products | Marketing and development of hyaluronidase |
| Alteogen | Hyaluronidase technology | Partnership with MSD (Merck & Co.) |
| Merck | Hyaluronidase technology | Subject of patent infringement litigation with Halozyme |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for Halozyme's ENHANZE® technology is traditional intravenous (IV) infusions. This method is commonly used for biologics, which often necessitate substantial drug volumes.
While IV infusions are a proven delivery method, they typically demand clinical settings and extended administration periods. This inherent inconvenience makes subcutaneous delivery, like that enabled by ENHANZE®, a more appealing option for patients when feasible.
The market for biologics administered intravenously is substantial. For example, in 2024, the global biologics market was projected to reach over $600 billion, with a significant portion still relying on IV administration.
Beyond hyaluronidase, alternative subcutaneous drug delivery methods are emerging that could act as substitutes. These include high-volume auto-injectors and on-body delivery systems (OBDS), which may bypass the need for permeation enhancers like ENHANZE®. These technologies focus on convenience and patient self-administration, offering a different pathway to achieving similar delivery goals.
Pharmaceutical firms are actively exploring alternative drug formulations that bypass the need for hyaluronidase. For example, advancements in nanoparticle or liposomal delivery systems might enable subcutaneous administration of biologics without enzymatic assistance, directly impacting demand for Halozyme's ENHANZE technology.
Companies may also opt for different excipients to improve drug solubility and viscosity, reducing the inherent need for technologies that enhance drug absorption. This focus on internal formulation improvements presents a significant threat by potentially diminishing the reliance on external drug delivery enhancement platforms.
The increasing sophistication in drug development means that by 2024, more therapies could be engineered for easier subcutaneous delivery. This internal innovation by pharmaceutical giants is a direct substitute for the value proposition offered by Halozyme's proprietary enzyme technology, posing a competitive challenge.
Oral or Transdermal Delivery Systems
While injectable therapies remain dominant for many biologics, advancements in alternative delivery systems pose a potential long-term threat. Oral drug delivery, utilizing technologies like microjet systems, is increasingly being researched for complex molecules. For instance, early-stage research in 2024 continues to explore encapsulation techniques to protect biologics from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Transdermal patches, particularly those employing microneedle technology, also offer a non-invasive alternative to injections. Studies published in early 2024 highlight the potential of microneedles to create transient pathways for larger molecules to penetrate the skin barrier.
These emerging technologies, if they mature to effectively deliver complex biologics, could significantly impact the market by offering patient-friendly administration routes.
This could lead to a shift in patient preference and payer reimbursement strategies, potentially reducing reliance on existing injectable platforms.
Gene and Cell Therapies
Emerging therapeutic modalities such as gene and cell therapies present a significant threat of substitution for traditional biologics. While these advanced treatments often necessitate specialized delivery systems, their growing efficacy and adoption could reshape the treatment paradigms for various diseases. For instance, advancements in CAR T-cell therapy have shown remarkable results in certain hematological malignancies, potentially reducing the reliance on conventional antibody-based treatments in those specific indications.
If gene and cell therapies become more broadly accessible and proven effective across a wider range of conditions, they could indirectly substitute for diseases currently managed by ENHANZE®-enabled drugs. Consider the potential for gene therapy to offer a one-time cure for inherited disorders, thereby eliminating the need for chronic biologic treatments that ENHANZE® might facilitate. The market for gene therapies is projected for substantial growth, with estimates suggesting it could reach tens of billions of dollars annually in the coming years, indicating a tangible shift in treatment options.
- Growing Investment: Venture capital funding for gene and cell therapy companies has seen significant increases, with billions invested annually, signaling strong market confidence and accelerated development.
- Regulatory Approvals: The number of approved gene and cell therapies has steadily climbed, demonstrating the increasing viability and acceptance of these modalities by regulatory bodies worldwide.
- Disease Scope Expansion: Research is actively exploring the application of these therapies beyond rare genetic diseases to more common conditions, including certain cancers and autoimmune disorders, potentially broadening their substitutive impact.
- Cost-Effectiveness Debate: While initial costs are high, the long-term cost-effectiveness of curative gene therapies is being increasingly evaluated against the lifetime costs of managing chronic diseases with biologics.
While traditional intravenous (IV) infusions remain a primary substitute, the threat is compounded by emerging subcutaneous delivery technologies that could bypass the need for enhancers like ENHANZE®. These include advanced auto-injectors and on-body delivery systems, which focus on patient convenience and self-administration, directly competing with the value proposition of ENHANZE®.
Furthermore, pharmaceutical companies are developing alternative drug formulations, such as nanoparticle or liposomal systems, designed for subcutaneous delivery without enzymatic assistance. This internal innovation by drug developers poses a significant threat by potentially reducing the reliance on external drug delivery enhancement platforms.
The growing sophistication in drug development means that by 2024, more therapies are being engineered for easier subcutaneous delivery, directly challenging Halozyme's technology. For instance, oral delivery systems and microneedle patches are also being researched for complex biologics, offering non-invasive alternatives that could shift patient and payer preferences away from injectable solutions.
The rise of gene and cell therapies presents a significant long-term substitution threat. As these advanced treatments become more accessible and effective for a wider range of diseases, they could reduce the overall demand for chronic biologic treatments, many of which utilize ENHANZE® for administration.
| Delivery Method | Key Features | Potential Impact on ENHANZE® |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional IV Infusion | Proven, high drug volume capacity, clinical setting required | Established but less convenient than subcutaneous |
| Advanced Auto-Injectors/OBDS | Patient convenience, self-administration | Direct substitute for subcutaneous delivery, may not require enhancers |
| Nanoparticle/Liposomal Systems | Enhanced stability, potential for intrinsic subcutaneous delivery | Bypasses need for enzymatic enhancers |
| Oral Drug Delivery (emerging) | Non-invasive, high patient preference | Long-term threat if efficacy challenges are overcome |
| Microneedle Patches | Non-invasive, transient skin pathways | Alternative for subcutaneous delivery of larger molecules |
| Gene & Cell Therapies | Curative potential, disease-specific applications | Indirect substitute by reducing need for chronic biologics |
Entrants Threaten
The biopharmaceutical sector, particularly in pioneering new drug delivery systems like those Halozyme operates within, demands massive upfront investment in research and development. For instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market has been estimated to be well over $2 billion, with development timelines often spanning 10 to 15 years.
These extensive R&D costs, coupled with the rigorous and protracted phases of clinical trials, present a formidable financial barrier to entry for potential new competitors. A successful product launch requires not only scientific innovation but also significant capital to navigate these complex and expensive stages.
The sheer scale of investment needed to even begin the process of developing and testing novel drug delivery technologies effectively deters many smaller or less capitalized entities from entering this highly specialized market.
Bringing a new drug delivery technology to market, especially one designed for use with various therapeutic compounds, presents significant challenges due to extensive regulatory hurdles and protracted approval processes. For instance, entities seeking to introduce novel delivery systems must meticulously satisfy requirements from bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a process that can take years and involve substantial investment.
The necessity for comprehensive data, including robust safety profiles and extensive clinical validation, acts as a formidable barrier to entry for potential new competitors in this specialized field. These stringent data requirements mean that any new entrant must commit considerable resources to research and development, ensuring their technology meets the highest standards of efficacy and patient safety before it can even be considered for market approval.
In 2024, the landscape for pharmaceutical innovation continues to emphasize patient safety and therapeutic efficacy, meaning regulatory bodies are unlikely to relax these stringent requirements for new drug delivery platforms. Companies like Halozyme, which have already established their technologies and navigated these complex pathways, possess a distinct advantage over emerging players who are just beginning the arduous journey through regulatory review.
Halozyme's strong intellectual property protection, particularly its patents for rHuPH20 and ENHANZE technology, acts as a significant deterrent to new entrants. These patents, covering the enzyme itself, its various formulations, and how it's used, create a substantial hurdle. Without licensing agreements, which would be costly, competitors would find it extremely challenging to legally offer similar drug delivery solutions. This robust IP landscape effectively shields Halozyme from direct imitation, making the threat of new entrants relatively low in this specific technological domain.
Established Partnerships and Commercial Validation
Halozyme's robust network of established, long-term licensing agreements with major pharmaceutical giants, including collaborations with companies like Pfizer and Roche, significantly raises the barrier to entry for potential new competitors. These partnerships are not merely agreements; they represent commercially validated endorsements of Halozyme's technology, providing a significant competitive moat. New entrants would struggle to replicate this level of trust and market penetration, which is crucial for widespread adoption of drug delivery technologies. For instance, by 2024, Halozyme's ENHANZE technology was incorporated into numerous blockbuster drugs, demonstrating its commercial viability and the deep integration within the existing pharmaceutical ecosystem.
The established partnerships act as a powerful deterrent, creating a network effect that benefits Halozyme. Companies that already utilize ENHANZE have little incentive to switch to an unproven alternative, and new entrants would find it exceedingly difficult to secure similar high-profile collaborations. This existing market penetration means new entrants lack the critical commercial validation and proven track record necessary to gain traction against Halozyme's established market position.
- Established Licensing Agreements: Halozyme boasts long-standing licensing deals with leading global pharmaceutical companies.
- Commercial Validation: These partnerships signify market acceptance and proven efficacy of Halozyme's technology.
- Network Effect: Existing customer base creates a strong advantage, making it harder for newcomers to penetrate the market.
- High Bar for Entry: New entrants face significant challenges in replicating Halozyme's established trust and market access.
Need for Specialized Manufacturing and Expertise
The development and production of recombinant enzymes, such as Halozyme's rHuPH20, demand highly specialized manufacturing processes and rigorous quality control systems. New companies entering this space would need substantial investment to establish these sophisticated facilities. For instance, biopharmaceutical manufacturing can involve billions in capital expenditure to meet stringent regulatory standards.
Furthermore, acquiring and retaining the necessary scientific and technical expertise is a significant hurdle. This includes specialized knowledge in molecular biology, protein engineering, and bioprocessing. The talent pool for such niche skills is limited, making it difficult and costly for new entrants to build an experienced team. This expertise is crucial for ensuring product efficacy and safety, directly impacting market competitiveness.
- Specialized Manufacturing: Biologics manufacturing facilities can cost upwards of $100 million to over $1 billion to build and equip, reflecting the complexity and regulatory demands.
- Technical Expertise: The recruitment and retention of highly skilled personnel in bioprocessing and regulatory affairs can represent a significant portion of operational costs for biotechnology firms.
- Quality Control: Implementing robust Quality Management Systems (QMS) compliant with FDA and EMA regulations requires dedicated resources and specialized personnel, adding to the barrier.
- Intellectual Property: Navigating and respecting existing patents related to enzyme technology and drug delivery systems adds another layer of complexity and potential legal expense for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Halozyme is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements, particularly in research and development, with average drug development costs exceeding $2 billion.
Rigorous regulatory hurdles, demanding years of testing and substantial investment for approvals from bodies like the FDA, further deter potential competitors.
Halozyme's strong patent portfolio for its ENHANZE technology and its extensive network of licensing agreements with major pharmaceutical companies, established through years of commercial validation by 2024, create a formidable barrier.
These established relationships and the resulting network effect mean new entrants face immense challenges in gaining market access and trust against Halozyme's deeply integrated position.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D and clinical trial costs (>$2 billion per drug). | Deters smaller or less capitalized entities. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Lengthy FDA/EMA approval processes (years). | Requires significant time and financial commitment. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents on rHuPH20 and ENHANZE technology. | Prevents direct imitation without costly licensing. |
| Existing Partnerships | Long-term licensing deals with major pharma (e.g., Pfizer, Roche). | Creates a network effect and commercial validation advantage. |
| Specialized Manufacturing & Expertise | Need for specialized bioprocessing facilities and talent. | Requires substantial investment and niche skill acquisition. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Halozyme leverages data from SEC filings, investor relations reports, and industry-specific market research to understand competitive dynamics. We also incorporate insights from clinical trial databases and pharmaceutical trade publications to assess the threat of new entrants and substitute products.
