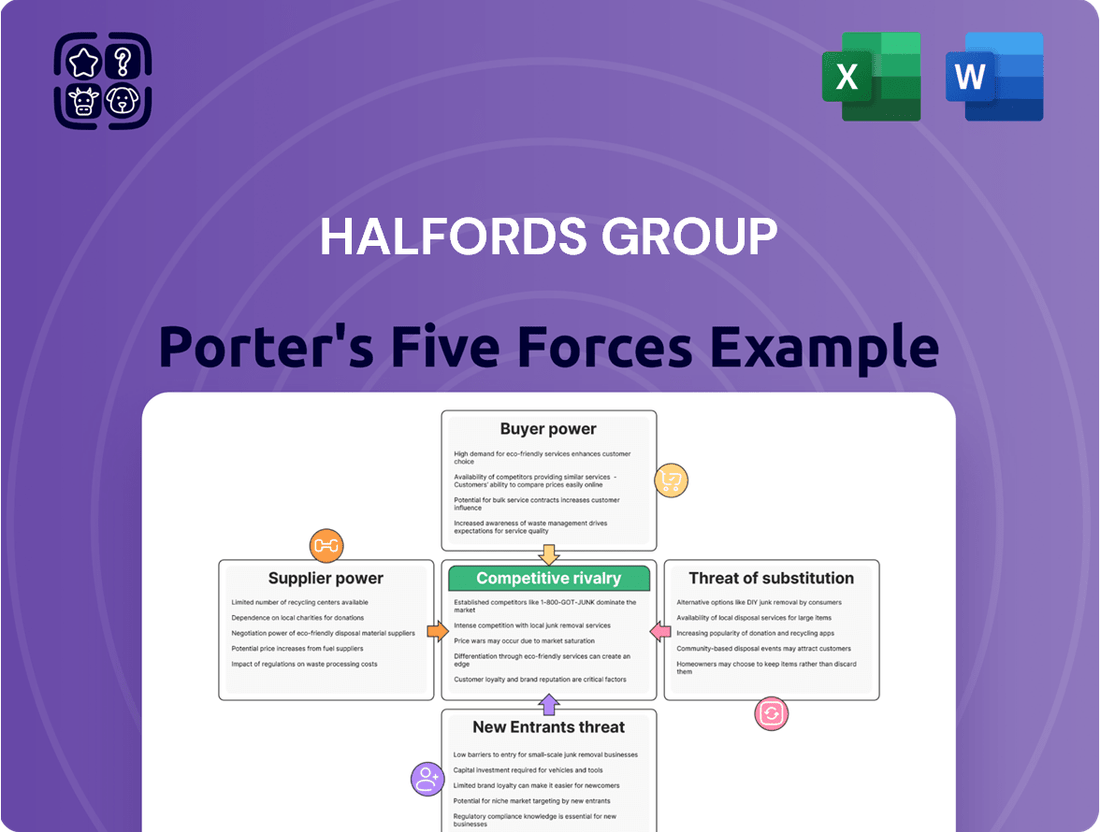
Halfords Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Halfords Group Bundle
Halfords Group navigates a competitive retail landscape where supplier power is moderate, and the threat of new entrants is somewhat limited by brand recognition and capital investment. However, intense rivalry among existing players and the growing influence of online retailers present significant challenges.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Halfords Group’s industry—from buyer power to the threat of substitutes. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Halfords Group is significantly influenced by supplier concentration and specialization. When a few suppliers dominate specific product categories, such as high-end bicycle brands or advanced automotive diagnostic tools, their ability to dictate terms to Halfords increases. This concentration means Halfords may have fewer alternatives, making it harder to negotiate favorable pricing or delivery schedules.
For instance, if Halfords relies heavily on a limited number of premium bicycle manufacturers for its popular cycling range, these suppliers can leverage their market position. Similarly, specialized automotive parts or diagnostic equipment sourced from a small number of highly technical providers can grant those suppliers considerable leverage. In 2023, the automotive aftermarket sector saw continued demand for specialized diagnostic tools, with key providers maintaining strong pricing power due to the complexity and proprietary nature of their offerings.
Halfords can mitigate this supplier power by diversifying its supplier base and developing its own private label products. By sourcing from a wider array of vendors or creating in-house brands, the company reduces its dependence on any single supplier. This strategy allows for greater flexibility in pricing, product development, and supply chain management, ultimately strengthening Halfords' negotiating position.
For Halfords, significant switching costs for certain suppliers can indeed bolster their bargaining power. If Halfords needs to invest heavily in retooling its operations or re-certifying new products to work with a different supplier, especially for specialized workshop equipment or critical IT systems, this creates a strong dependency. These costs make it financially prohibitive to switch, thereby giving the incumbent supplier more leverage in negotiations.
The uniqueness of supplier offerings significantly influences bargaining power. When suppliers provide specialized, patented, or highly differentiated products, like exclusive bicycle models or proprietary car parts, their leverage increases. Halfords may find itself with few viable alternatives for these unique items, potentially leading to less favorable purchasing terms.
Conversely, for more standardized or commoditized products, the bargaining power of suppliers diminishes considerably. In 2024, the automotive aftermarket, a key sector for Halfords, saw continued availability of many standardized parts from multiple manufacturers, keeping supplier price pressure relatively low for these items.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers can significantly bolster their bargaining power against Halfords. If a key supplier, such as a major automotive parts manufacturer or a prominent bicycle brand, were to establish its own retail outlets or service centers, it could directly compete with Halfords. This move would potentially limit Halfords' product sourcing options or force them to accept less favorable terms.
For Halfords, this particular threat appears to be relatively low across its diverse supplier base. The complexity and capital investment required to establish a nationwide retail or service network are substantial barriers for most individual suppliers. For instance, while a large tire manufacturer could potentially open service bays, replicating Halfords' extensive retail footprint and brand recognition is a considerable challenge.
- Low Threat of Forward Integration: Most of Halfords' suppliers, especially those providing specialized automotive parts or bicycle components, lack the scale and resources to establish competing retail or service operations.
- Capital Intensive Nature: Building a retail and service infrastructure comparable to Halfords requires significant capital expenditure, making it an unlikely strategy for most suppliers.
- Brand and Distribution Focus: Suppliers typically focus on manufacturing and wholesale distribution, rather than direct-to-consumer retail, which is Halfords' core competency.
Importance of Halfords to Suppliers
The significance of Halfords as a customer directly impacts its suppliers' bargaining power. If Halfords constitutes a large segment of a supplier's total sales, that supplier is likely to be more accommodating with pricing and contract terms to secure Halfords' continued business. For instance, in 2023, Halfords Group reported revenues of £1.3 billion, indicating a substantial purchasing volume that can be leveraged in negotiations.
Conversely, if Halfords represents only a small fraction of a supplier's revenue stream, the supplier will have less incentive to concede on terms, as losing Halfords' business would not significantly impact their overall financial performance. This dynamic means that suppliers catering to a broader customer base might hold more leverage when dealing with Halfords.
- Halfords' Revenue Contribution: The percentage of a supplier's revenue derived from Halfords is a key determinant of supplier bargaining power.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers heavily reliant on Halfords are more susceptible to Halfords' demands.
- Market Position of Suppliers: Suppliers with strong market positions and diverse customer portfolios can exert greater influence.
- Halfords' Purchasing Volume: The sheer scale of Halfords' procurement, evidenced by its £1.3 billion revenue in 2023, provides a strong negotiating position.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Halfords Group is influenced by several key factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, and the uniqueness of their offerings. When suppliers are few and specialized, or when switching to alternatives involves significant costs for Halfords, their leverage increases. Conversely, a diverse supplier base for standardized products generally reduces supplier power.
In 2024, the automotive aftermarket continued to see competitive pricing for many standardized parts due to multiple manufacturers. However, specialized components, like advanced diagnostic tools or specific branded bicycle parts, still grant considerable pricing power to their respective suppliers. Halfords' strategy of developing private label brands and diversifying its supplier base aims to mitigate this inherent supplier leverage.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into retail or service operations is generally low for Halfords, given the substantial capital and brand recognition required to compete. However, the significant purchasing volume of Halfords, evidenced by its £1.3 billion revenue in 2023, provides a strong counter-leveraging position against many of its suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Halfords' Supplier Power | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration & Specialization | Increases Supplier Power | Reliance on few premium bicycle brands or specialized diagnostic tool providers. |
| Switching Costs | Increases Supplier Power | Costs associated with retooling or re-certifying for new suppliers, especially for workshop equipment. |
| Uniqueness of Offerings | Increases Supplier Power | Exclusive bicycle models or proprietary car parts with few alternatives. |
| Availability of Substitutes (Standardized Goods) | Decreases Supplier Power | Multiple manufacturers for standardized automotive parts in 2024 kept price pressure low. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low Impact | High capital and brand barriers for suppliers to establish competing retail/service networks. |
| Halfords' Significance as a Customer | Decreases Supplier Power | £1.3 billion revenue in 2023 indicates substantial purchasing volume, strengthening negotiation leverage. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Halfords Group examines the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes within the automotive aftermarket and cycling sectors.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats by clearly visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces impacting Halfords Group.
Customers Bargaining Power
Halfords' customers, especially for routine motoring and cycling needs, are quite sensitive to price. This is largely because there are so many other options available, and it's incredibly easy to compare prices online. For example, in the UK automotive aftermarket, online retailers often offer significant discounts, putting pressure on brick-and-mortar stores like Halfords.
This price sensitivity means Halfords must keep its prices competitive to attract and retain shoppers. This constant need to match or beat competitor pricing can squeeze profit margins. In 2023, Halfords reported a revenue of £1.5 billion, but managing these price pressures is key to maintaining profitability.
To counter this, Halfords emphasizes its value beyond just price. Offering convenience, such as accessible store locations and quick service options like its "WeFit" service, and providing expert advice from trained staff are vital. These elements help differentiate Halfords and make its offerings more appealing than just the lowest price tag.
Customers of Halfords Group face a significant bargaining power due to the abundant availability of substitutes and alternatives for both their product offerings and services. For automotive parts and accessories, consumers can readily turn to online giants like Amazon and eBay, as well as numerous supermarket chains that increasingly stock car care items. This wide accessibility means Halfords must remain competitive on price and product selection to retain its customer base.
The ease with which customers can switch between providers further bolsters their bargaining power. For automotive servicing and repairs, independent garages and even main dealerships often present comparable or superior alternatives. With minimal switching costs, customers are empowered to seek out the best combination of price, quality, and convenience, forcing Halfords to consistently deliver value and excellent service to avoid customer attrition. In 2024, the online retail sector continued its dominance, with e-commerce sales in the UK automotive aftermarket projected to grow by 8-10%, highlighting the pressure on brick-and-mortar retailers like Halfords.
The internet has dramatically shifted the bargaining power of customers for companies like Halfords Group. With readily available information on product features, prices, and service reviews across numerous competitors, customers are far more informed than ever before. This transparency empowers them to easily compare offerings and negotiate for better value, putting pressure on Halfords to maintain competitive pricing and superior service quality to keep their business.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
For a significant portion of its offerings, Halfords Group customers encounter very low costs or effort when deciding to switch to a competitor. This ease of transition empowers them considerably in their purchasing choices.
For instance, a consumer can readily purchase car accessories from a local supermarket or a large online retailer, or opt for vehicle servicing at an independent garage rather than a Halfords Autocentre. This broad availability of alternatives means customers aren't locked into specific providers.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily shift between providers for car parts, accessories, and servicing without incurring significant financial penalties or time investment.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of numerous alternative suppliers, including online retailers and independent garages, intensifies competition and reinforces customer bargaining power.
- Price Sensitivity: With readily available substitutes, customers are more likely to compare prices and seek the best deals, putting pressure on Halfords' pricing strategies.
Volume of Purchases by Customers
While individual purchases from the general public are typically small and infrequent, the sheer scale of Halfords' customer base means the collective volume is significant. This broad customer base generally dilutes the bargaining power of any single retail customer, as they represent a negligible portion of overall revenue.
However, the situation shifts for Halfords Autocentres, particularly concerning fleet services. Larger corporate clients or fleet operators, due to the consistent and substantial business they provide, can indeed exert more influence and potentially negotiate more favorable terms.
For instance, in the 2024 financial year, Halfords reported a total revenue of £1,570.6 million. This vast revenue stream is built upon millions of individual transactions, underscoring the dispersed nature of power among its retail customers.
- Customer Volume: Millions of individual transactions contribute to Halfords' substantial revenue base.
- Individual Customer Power: Limited due to small purchase sizes and infrequent buying habits.
- Fleet Services Impact: Larger fleet clients in Autocentres can wield more significant bargaining power.
- Revenue Context: Halfords' £1,570.6 million revenue in FY24 highlights the dispersed nature of retail customer influence.
Halfords' customers possess considerable bargaining power, primarily driven by low switching costs and the widespread availability of substitutes for both products and services. The ease with which consumers can access alternative suppliers for car parts, accessories, and maintenance, such as online retailers and independent garages, forces Halfords to remain highly competitive on price and service quality.
| Factor | Impact on Halfords | Evidence/Example |
| Low Switching Costs | High customer bargaining power | Customers can easily switch between Halfords and online retailers or independent garages for parts and servicing. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High customer bargaining power | Online giants (Amazon, eBay) and supermarkets offer car care items; independent garages provide alternatives for servicing. |
| Price Sensitivity | High customer bargaining power | Customers readily compare prices online, pressuring Halfords to offer competitive pricing. UK automotive aftermarket online sales projected to grow 8-10% in 2024. |
| Information Transparency | High customer bargaining power | Customers are well-informed about product features, prices, and reviews, enabling better negotiation. |
Same Document Delivered
Halfords Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Halfords Group, offering a detailed examination of industry competitiveness. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights without any alterations or missing sections. You can be confident that this professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Halfords faces intense competition from a broad spectrum of rivals. This includes major online players like Amazon, large supermarket chains with automotive sections, and numerous independent specialist retailers. The automotive services sector is equally crowded, featuring national garage networks and franchised car dealerships.
This diversity means Halfords must contend with different competitive strategies simultaneously. For instance, online retailers often compete on price and convenience, while independent garages may focus on specialized services or local customer relationships. In 2023, the UK automotive aftermarket saw continued growth, indicating a dynamic market where differentiation is key.
The UK automotive aftermarket and cycling retail sectors are generally considered mature, suggesting a moderate to slow overall industry growth rate. This maturity means companies like Halfords often focus on gaining market share rather than simply capitalizing on broad market expansion.
In such mature environments, competitive rivalry intensifies. Businesses may engage in more aggressive pricing strategies and increased marketing expenditure to attract and retain customers. For instance, in 2023, the UK automotive aftermarket saw continued price sensitivity among consumers, impacting margins for many players.
However, pockets of higher growth exist within these mature markets. Emerging areas such as electric bike (e-bike) sales and the servicing of electric vehicles (EVs) present opportunities for companies to offset slower growth in traditional segments. The e-bike market, in particular, demonstrated robust growth in 2023, with sales increasing by over 15% year-on-year.
While Halfords offers a wide array of automotive and cycling products, a significant portion faces intense price-based competition due to their commoditized nature. This means that simply having a product on the shelf isn't enough; the real battleground is often on price.
Halfords strives to differentiate itself through several key avenues. Expert advice from staff, particularly within their Autocentres, provides a valuable service that generic online retailers struggle to replicate. Exclusive product lines also help carve out a unique offering.
Convenience plays a major role in their strategy. Services like in-store fitting for car parts or bike maintenance, coupled with an extensive network of physical stores across the UK, offer a tangible advantage. For example, Halfords' Autocentres performed over 1.5 million MOTs in the year to March 2024, highlighting the scale of their service operations.
Companies that can effectively differentiate, like Halfords aims to do through service and convenience, are better positioned to attract and retain customers. This allows them to potentially command premium pricing and foster stronger brand loyalty, mitigating the impact of pure price wars.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers, such as significant fixed assets like stores and workshops, specialized equipment, and long-term lease commitments, can trap unprofitable competitors in the market. This situation intensifies rivalry, often leading to prolonged price wars and industry overcapacity.
For Halfords, its substantial physical footprint, comprising numerous retail stores and service centers, acts as a considerable exit barrier. This extensive network represents a significant investment that is difficult and costly to divest, potentially keeping even underperforming rivals in the competitive arena.
- Extensive Store Network: As of early 2024, Halfords operated approximately 340 stores across the UK and Ireland, representing a considerable fixed asset base.
- Specialized Equipment: The automotive services sector requires specialized tools and diagnostic equipment, which are costly to acquire and difficult to repurpose, increasing exit costs.
- Lease Commitments: Many retail and service locations are subject to long-term lease agreements, obligating companies to continue payments even if operations become unprofitable.
Competitive Strategies Employed
Competitive rivalry within the automotive aftermarket and cycling sectors is intense, driven by aggressive pricing, extensive promotional campaigns, and a continuous push for product innovation. Competitors are also heavily investing in enhancing customer service and expanding their digital footprints to capture market share.
Halfords' strategy, particularly its focus on expanding its Motoring Services through its Autocentres, is a direct response to these competitive pressures. This move aims to differentiate Halfords by offering a more comprehensive service proposition beyond just parts and accessories.
- Aggressive Pricing: Competitors often engage in price wars, forcing Halfords to carefully manage its pricing strategies to remain competitive while maintaining profitability.
- Promotional Activities: Frequent sales, discounts, and loyalty programs are common tactics used by rivals to attract and retain customers, necessitating similar or more compelling offers from Halfords.
- Product Innovation: The rapid development of new automotive technologies and cycling equipment requires Halfords to stay abreast of these trends and invest in its own product development or sourcing to offer up-to-date solutions.
- Digital Transformation: Competitors are enhancing their online platforms and e-commerce capabilities, pushing Halfords to improve its digital customer experience and omnichannel offerings.
Competitive rivalry for Halfords is fierce due to a fragmented market encompassing online giants, supermarkets, and specialist independent retailers. This broad competition forces Halfords to navigate diverse strategies, from aggressive pricing by online sellers to specialized service offerings from local garages.
The UK automotive aftermarket and cycling sectors are mature, meaning companies like Halfords primarily battle for market share rather than relying on overall market expansion. This often translates into price-sensitive consumer behavior, as seen in 2023, which puts pressure on margins.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Tactics | Halfords' Response/Challenge |
| Online Retailers (e.g., Amazon) | Price, Convenience, Wide Selection | Price competition, emphasis on in-store expertise and service. |
| Supermarkets (Automotive Sections) | Price, Convenience for basic items | Focus on specialized automotive parts and services. |
| Independent Specialists | Niche Expertise, Local Relationships | Leveraging brand recognition, extensive store network, and comprehensive service offerings. |
| National Garage Networks | Service Quality, Pricing | Differentiating through integrated retail and service (Autocentres), loyalty programs. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of public transportation and ride-sharing services poses a significant threat to Halfords' motoring segment. As more individuals opt for alternatives like Uber, Bolt, or enhanced public transit networks, the fundamental need for personal car ownership, and consequently its associated maintenance and parts, diminishes. This trend, particularly strong in urban areas, directly erodes demand for Halfords' core product and service offerings.
The threat of substitutes for traditional bicycles, particularly for short journeys, is significant. Alternatives like walking and e-scooters are increasingly popular, driven by convenience and growing environmental awareness. For instance, the e-scooter market saw substantial growth, with global sales reaching an estimated $30 billion in 2023, indicating a clear shift in consumer preference for micro-mobility solutions.
While Halfords does offer e-scooters, a broader societal move towards these alternatives could directly impact its core bicycle sales segment. This trend is further amplified by health consciousness and a desire for sustainable transport options, which may lead consumers to opt for e-scooters or even simply walking for shorter commutes, bypassing traditional cycling altogether.
The threat of substitutes for Halfords' Autocentres is significant due to the rise of DIY repairs and maintenance. Online tutorials, diagnostic tools, and easily available parts empower consumers to tackle simpler car and bike tasks themselves, directly substituting for professional services and some retail products. For instance, the increasing popularity of YouTube channels dedicated to car maintenance, with millions of views on videos demonstrating oil changes or brake pad replacements, highlights this trend.
Durability of Products and Components
The increasing durability of vehicle components poses a significant threat of substitutes for Halfords Group. As cars and their parts become more reliable and last longer, the need for frequent replacements and repairs diminishes. This directly impacts Halfords' autocentre services and aftermarket product sales.
For instance, advancements in engine technology and materials science mean that components like spark plugs or brake pads may now have significantly extended service lives compared to a decade ago. This trend reduces the recurring revenue stream from routine maintenance and part replacements, a core part of Halfords' business model.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations leading to longer-lasting vehicle parts directly substitute for Halfords' replacement parts and repair services.
- Reduced Maintenance Frequency: Improved vehicle reliability means customers require fewer visits to autocentres, impacting service revenue.
- Consumer Savings: Durable products offer consumers cost savings over time, potentially leading them to defer or forgo aftermarket purchases.
Digital Services and Information
The rise of digital services presents a significant threat to traditional automotive retail and service providers like Halfords. Online platforms now offer readily accessible car diagnostics, maintenance scheduling, and even virtual consultations, diminishing the customer's reliance on physical stores for initial assessments and information gathering. This shift in customer behavior, driven by convenience and often lower perceived costs, can erode the need for in-person interactions at traditional service centers.
For instance, a growing number of consumers are utilizing mobile apps for basic vehicle health checks and to source parts. This trend is supported by data showing a substantial increase in online automotive parts sales. In 2024, the global online automotive aftermarket was projected to reach over $100 billion, indicating a strong preference for digital channels.
- Digital Diagnostics: Apps and online tools can provide initial fault code readings, reducing the need for a visit to a mechanic for basic checks.
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon and eBay offer a vast selection of car parts, often at competitive prices, directly to consumers.
- Maintenance Reminders: Digital services can send automated reminders for servicing, bypassing traditional dealership or service center communication channels.
- Information Access: Online forums and video tutorials empower consumers with knowledge, enabling them to perform simple maintenance tasks themselves, thereby reducing service demand.
The threat of substitutes for Halfords' cycling segment is amplified by the growing popularity of electric bikes and micro-mobility solutions. While Halfords does sell e-bikes, a significant shift towards these alternatives, especially for commuting, could reduce demand for traditional pedal cycles. For example, e-bike sales in the UK saw a substantial increase, with reports indicating growth of over 20% year-on-year leading into 2024.
Furthermore, the increasing availability of affordable, high-quality used bicycles also acts as a substitute. This trend allows consumers to access cycling at a lower price point, potentially bypassing the need for new purchases from retailers like Halfords. The used market's accessibility, particularly for casual riders, presents a direct substitution for new bike sales.
| Substitute Category | Impact on Halfords | Examples | Market Trend (as of 2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ride-Sharing & Public Transport | Reduces demand for car maintenance and parts | Uber, Bolt, enhanced bus/train networks | Continued growth, especially in urban areas |
| E-Scooters & Walking | Threatens traditional bicycle sales | Electric scooters, pedestrian travel | E-scooter market valued globally at ~$30 billion (2023), strong growth |
| DIY Car Maintenance | Decreases demand for Autocentres services | Online tutorials, accessible parts | High viewership for DIY auto repair videos |
| Durable Vehicle Parts | Lowers frequency of replacement needs | Longer-lasting engine components, tires | Advancements in materials science |
| Online Automotive Marketplaces | Offers direct consumer access to parts and diagnostics | Amazon, eBay, specialized auto parts sites | Global online automotive aftermarket projected over $100 billion (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive retail and service sector, where Halfords operates, presents a significant capital barrier to entry. Establishing a national network of physical stores and service centers, as Halfords does, demands considerable upfront investment in real estate, fitting out workshops with specialized tools and diagnostic equipment, and stocking a wide range of parts and accessories. For instance, a new competitor aiming for a similar scale would likely need to spend hundreds of millions of pounds just to acquire and equip a comparable number of locations.
Halfords benefits from decades of building a recognizable brand, fostering a degree of customer loyalty. New competitors would face substantial marketing costs and a lengthy period to achieve similar levels of trust and awareness. This established brand equity is a formidable barrier, especially for the Autocentres division where customer confidence is crucial for service uptake.
New companies entering the automotive and cycling retail space often face significant hurdles in securing reliable supply chains and favorable terms with manufacturers. For instance, establishing a robust distribution network comparable to Halfords, which has a long-standing presence and significant purchasing power, requires substantial upfront investment and time. In 2024, the automotive parts market alone was valued at over $800 billion globally, highlighting the scale of operations required to gain traction.
Halfords leverages its established relationships with suppliers and its considerable economies of scale to negotiate better prices and ensure product availability. This gives them a competitive edge over newcomers who might struggle to match these purchasing efficiencies. Without a similarly strong supply network, new entrants may find it difficult to compete on cost or consistently meet customer demand for a wide range of products.
Regulatory and Licensing Requirements
The automotive service sector, especially areas like MOT testing and vehicle repairs, is heavily regulated. New businesses must navigate complex compliance, obtain specific certifications, and secure necessary licenses. For instance, in the UK, mechanics performing MOTs need to be accredited by the Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency (DVSA), a process that requires demonstrated competence and adherence to strict standards.
These regulatory hurdles significantly increase the initial investment and operational complexity for potential new entrants. The time and resources required to meet these stringent requirements act as a substantial barrier, deterring many from entering the market and thereby protecting established players like Halfords Group.
Meeting these requirements ensures a baseline of professionalism and safety within the industry.
- DVSA Accreditation: Mechanics must be certified by the DVSA to conduct MOT tests.
- Complex Compliance: Navigating environmental regulations and safety standards adds to operational costs.
- Time-Consuming Processes: Obtaining and maintaining licenses and certifications requires ongoing effort.
Economies of Scale and Experience
Halfords leverages significant economies of scale across its operations. In 2023, its revenue reached £1.37 billion, allowing for substantial purchasing power and optimized marketing spend. New entrants would struggle to match these cost efficiencies, facing higher per-unit costs until they achieve comparable market penetration.
The company's extensive network of over 300 retail stores and 600 service centers, as of early 2024, creates a formidable barrier. This established infrastructure provides operational efficiencies that are difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly or cost-effectively. The accumulated experience in managing logistics, inventory, and customer service across such a broad footprint is a key differentiator.
- Economies of Scale: Halfords' large purchasing volume leads to lower input costs compared to smaller competitors.
- Marketing Efficiency: A larger customer base allows for more cost-effective national marketing campaigns.
- Operational Expertise: Decades of experience in retail and automotive services translate to streamlined processes and reduced waste.
- Network Advantage: The sheer number of locations provides convenience and brand visibility that new entrants lack.
The threat of new entrants for Halfords Group is moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements for establishing a physical presence and the need for brand recognition in the automotive and cycling retail sectors. While the market offers opportunities, the cost of building a comparable network of stores and service centers, coupled with the expense of marketing to gain customer trust, acts as a significant deterrent.
New competitors face considerable challenges in replicating Halfords' established supply chain and economies of scale. Securing favorable terms with manufacturers and building a robust distribution network requires significant investment and time, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost or product availability. The global automotive parts market's valuation in 2024, exceeding $800 billion, underscores the scale needed to achieve competitive purchasing power.
Regulatory compliance, particularly in automotive servicing like MOT testing, presents another hurdle. Obtaining necessary certifications and adhering to stringent standards, such as DVSA accreditation for mechanics in the UK, adds complexity and cost for new entrants. These barriers collectively limit the ease with which new players can enter and effectively challenge Halfords' market position.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing a national network of stores and service centers, including real estate, equipment, and inventory. | High; requires hundreds of millions in investment for comparable scale. |
| Brand Loyalty & Marketing Costs | Building brand recognition, trust, and customer loyalty takes time and significant marketing expenditure. | High; decades of brand building are difficult to replicate quickly. |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | Securing reliable supply chains and favorable terms with manufacturers, plus establishing a distribution network. | High; requires substantial upfront investment and time to match Halfords' purchasing power. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex regulations, obtaining certifications, and securing licenses, especially for service operations. | Moderate to High; adds complexity, cost, and time to market entry. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Halfords Group leverages data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and competitor financial filings. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific market research reports and automotive trade publications to assess competitive dynamics.
