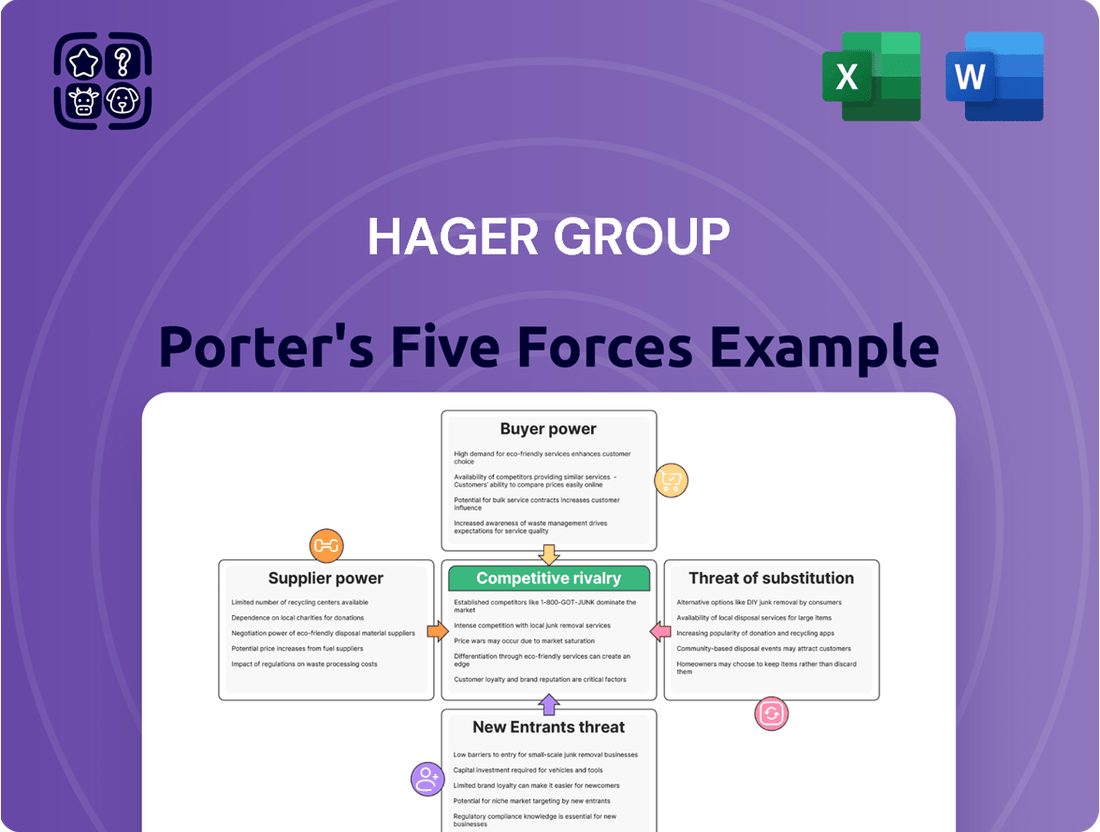
Hager Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hager Group Bundle
The Hager Group operates within a dynamic market, facing significant pressures from rivals and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any strategic decision.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Hager Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical components, such as semiconductors and specialized plastics, presents a significant challenge for Hager Group. When only a handful of suppliers provide these essential materials, their bargaining power escalates, potentially driving up procurement costs and creating vulnerabilities in the supply chain. For instance, the global semiconductor shortage experienced in 2021-2022 demonstrated how limited supply can lead to substantial price increases and production delays across various industries, including electrical equipment manufacturing.
High switching costs significantly bolster the bargaining power of suppliers to Hager Group. If Hager faces substantial expenses or operational disruptions when changing to a new supplier, such as those associated with specialized tooling or intricate integration with existing systems, the current suppliers gain leverage. For instance, if a key component requires custom molds that are expensive to replicate, the supplier holding those molds can command higher prices.
The uniqueness of inputs is a significant factor in supplier bargaining power. When suppliers offer proprietary technologies or highly specialized components, their leverage increases. For Hager Group, if a critical component is difficult to source elsewhere or has few viable substitutes, the supplier can dictate terms, impacting Hager's costs and flexibility.
Hager Group's commitment to innovation and developing integrated electrical and building management systems often necessitates the use of unique or advanced inputs. This reliance on specialized materials or technologies can strengthen the bargaining position of the suppliers providing them, as alternatives may not meet the required performance or integration standards.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Hager Group's business, meaning they start manufacturing electrical installation products themselves, would significantly boost their bargaining power. While this is generally a low risk in the complex electrical equipment sector, it could become a factor if suppliers control truly unique or foundational technologies.
For instance, a supplier of a highly specialized semiconductor component crucial for Hager's smart home systems might consider direct manufacturing. This would allow them to capture more value and potentially compete with Hager directly. However, the substantial capital investment and established brand recognition of companies like Hager make this a difficult strategy for most suppliers to execute successfully.
- Low Likelihood: The high capital requirements and technical expertise needed to compete in Hager Group's established market segments limit the feasibility of supplier forward integration.
- Niche Technology Risk: A credible threat could emerge from suppliers of critical, proprietary components where their technological advantage is substantial and easily transferable to finished product manufacturing.
- Industry Dynamics: The electrical installation industry is characterized by strong brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, which suppliers would need to overcome to effectively compete.
Importance of Volume to Supplier
Hager Group's substantial purchasing volume directly influences its suppliers' willingness to offer competitive pricing and favorable terms. When a significant portion of a supplier's annual revenue is tied to Hager Group, they are naturally incentivized to maintain this relationship through negotiation. This leverage can translate into better payment terms, lower unit costs, and even customized product development. For instance, if Hager Group accounts for over 15% of a key component manufacturer's sales, that supplier will likely prioritize Hager's needs to secure their own financial stability.
- Hager Group's significant order volumes can make suppliers more amenable to price concessions.
- A supplier's reliance on Hager Group for a large percentage of their revenue strengthens Hager's bargaining position.
- This dependence can lead to suppliers offering preferential treatment, including better credit terms or priority delivery.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hager Group is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, and the uniqueness of inputs. When few suppliers dominate the market for critical components, their ability to dictate terms increases, potentially impacting Hager's costs and supply chain stability. For example, the semiconductor shortage in 2021-2022 saw significant price hikes due to limited availability.
High switching costs for Hager Group, such as those associated with specialized tooling or system integration, empower suppliers by making it expensive and disruptive to change providers. This leverage allows suppliers to maintain higher prices. Similarly, the use of proprietary technologies or unique components by Hager can strengthen supplier positions, as viable alternatives may be scarce or non-existent.
| Factor | Impact on Hager Group | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage | Limited number of semiconductor manufacturers worldwide. |
| Switching Costs | Strengthens supplier position | Costs of retooling or re-qualifying new specialized components. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Enhances supplier pricing power | Proprietary smart home system components. |
| Hager's Purchasing Volume | Reduces supplier leverage | Hager's significant orders can lead to price concessions. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Hager Group, offering strategic insights into its industry position.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual representation of market power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
The concentration of buyers significantly influences Hager Group's bargaining power. While Hager serves a broad range of customers, from individual homeowners to large industrial clients, the latter can exert considerable influence. For instance, major electrical wholesalers or large-scale construction developers who purchase in significant volumes can negotiate more favorable terms due to their concentrated purchasing power.
In 2024, the construction industry, a key market for Hager, saw varied regional performance. Europe, a significant market for Hager, experienced moderate growth in new building projects. This environment means that large developers in these regions, representing a concentrated buyer segment, hold a stronger hand when negotiating prices and contract terms with suppliers like Hager Group.
Low switching costs for customers in the electrical installation products market significantly boost their bargaining power. If customers can easily switch to competitors like Schneider Electric or Legrand without incurring substantial costs or facing operational disruptions, Hager Group must remain highly competitive on price and product quality. For instance, a simple product swap for standard circuit breakers presents minimal friction.
However, the landscape shifts when integrated solutions are involved. For example, a customer invested in Hager's building automation systems, which often involve proprietary software and hardware interdependencies, would face higher switching costs. This integration makes it more complex and expensive to move to a competitor, thereby reducing the customer's bargaining power. Data from 2024 suggests that the market for smart home and building automation solutions is growing rapidly, indicating a trend towards increased integration and potentially higher switching costs in specific segments.
Hager Group's emphasis on product differentiation significantly shapes customer bargaining power. When Hager offers highly unique solutions, perhaps in advanced energy management or sophisticated smart home integration, customers find fewer direct substitutes. This distinctiveness, often built on innovation and superior quality, inherently reduces their leverage to demand lower prices, as they are seeking specific, valuable functionalities.
Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of customers integrating backward to produce their own electrical components is generally low for most of Hager Group's business segments. This is because the scale and complexity of manufacturing electrical distribution systems and building automation solutions require significant investment and specialized expertise. For instance, the global electrical equipment market, valued at approximately $800 billion in 2023, demonstrates the substantial capital required for efficient production.
While very large industrial clients might explore in-house solutions for highly specialized or critical components, this is an uncommon strategy for standard electrical installations. The cost-effectiveness and reliability of sourcing from established manufacturers like Hager, which benefits from economies of scale and continuous R&D, typically outweigh the benefits of backward integration for most customers.
- Low Threat: Most customers lack the necessary scale and technical expertise for backward integration in electrical component manufacturing.
- Economies of Scale: Hager's production volume provides cost advantages that are difficult for individual customers to replicate.
- Specialized Needs Exception: Extremely large industrial clients might consider in-house production for very niche requirements, though this remains rare.
- Market Dynamics: The high capital investment and specialized knowledge needed to compete in the electrical component market deter most customers from backward integration.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customer price sensitivity for Hager Group's offerings is a key determinant of their bargaining power. This sensitivity is directly tied to how much Hager's products contribute to a customer's overall project expenses and the customer's own financial standing. For instance, in highly competitive segments of the electrical infrastructure market, where multiple suppliers offer similar solutions, customers naturally become more attuned to pricing, thereby amplifying their ability to negotiate favorable terms.
The broader economic climate also plays a significant role. In 2024, with ongoing inflationary pressures and fluctuating material costs, customers are increasingly evaluating the total cost of ownership. This means that while initial price is important, the long-term operational costs and energy efficiency benefits offered by Hager's solutions can become a more compelling factor. For example, if Hager's energy-efficient products can demonstrably reduce a building's energy bills by, say, 15-20% annually, customers may be willing to accept a higher upfront cost, thus reducing their price sensitivity and, consequently, their bargaining power.
- Cost Contribution: The proportion of Hager's product cost within a larger construction or renovation project.
- Customer Financial Health: The ability of the customer to absorb price increases versus their need to seek the lowest cost option.
- Market Competition: The availability of comparable products from other manufacturers directly impacts customer price leverage.
- Energy Efficiency Value Proposition: Hager's ability to quantify and deliver long-term savings can offset initial price concerns for customers in 2024.
The bargaining power of Hager Group's customers is a significant factor, influenced by buyer concentration, switching costs, and price sensitivity. Large customers, particularly in the construction sector, can leverage their volume to negotiate better terms. For instance, major electrical wholesalers in Europe, a key market for Hager, often secure preferential pricing due to their substantial purchasing power, especially as new building projects saw moderate growth in the region during 2024.
Low switching costs for standard electrical installation products empower customers to easily opt for competitors, forcing Hager to maintain competitive pricing and quality. However, Hager's integrated solutions, like building automation systems, increase customer switching costs by creating interdependencies, thus reducing buyer leverage. The growing market for smart home solutions in 2024 further highlights this trend towards integration.
Hager's product differentiation, particularly in advanced energy management, can mitigate customer bargaining power by offering unique value propositions. While backward integration is generally a low threat due to high capital and expertise requirements, customers' price sensitivity is heightened in competitive market segments. The overall economic climate in 2024, marked by inflation, also makes customers more cost-conscious, although Hager's energy-efficient offerings can offset initial price concerns.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Hager Group Context |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Concentration | High for large buyers | Major wholesalers and developers can negotiate favorable terms. |
| Switching Costs | Low for standard products, High for integrated solutions | Easy to switch standard components; difficult to replace building automation systems. |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies with product contribution and competition | High in competitive segments; reduced by long-term savings from energy-efficient products. |
| Product Differentiation | Lowers bargaining power | Unique solutions in smart home and energy management reduce customer leverage. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Hager Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview provides a comprehensive overview of the Hager Group's Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document you are viewing is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering no surprises or placeholders. This thorough examination will equip you with actionable insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the Hager Group's industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The electrical installation market is quite crowded, featuring several major global players like Siemens, Schneider Electric, Eaton, ABB, and Honeywell. These large companies compete fiercely with many smaller, regional, and specialized firms. This dynamic creates a highly competitive environment for Hager Group.
The growth rate within Hager Group's operating sectors significantly shapes competitive rivalry. Markets experiencing robust expansion, like smart homes and building automation, generally see less intense competition. For instance, the smart home market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.05% between 2025 and 2035, while building automation is expected to expand at 11.5% from 2024 to 2025. These high growth rates create ample room for all participants to capture market share, thereby tempering the urge for aggressive competitive actions.
The degree to which competitors distinguish their products significantly influences the intensity of rivalry. When products are largely interchangeable, like basic commodities, competition often devolves into a price war. Hager Group actively works to counteract this by emphasizing innovation, a commitment to sustainability in its electrical installation systems, and the development of comprehensive, integrated solutions for buildings.
This strategic focus on differentiation allows Hager to move beyond simple price comparisons. For instance, Hager's investment in smart building technology and energy management systems provides distinct value propositions not found in more standardized offerings. In 2024, the electrical installation market continues to see demand for smart and sustainable solutions, a trend Hager is well-positioned to capitalize on through its differentiated product portfolio, thereby mitigating direct price-based competition.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can significantly impact competitive rivalry within the electrical manufacturing sector, where Hager Group operates. When companies face substantial costs or difficulties in leaving the market, they are often forced to continue operations even when facing low profitability. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition as firms fight for market share rather than exiting.
For businesses like Hager Group, these barriers often stem from considerable investments in specialized assets, such as advanced manufacturing equipment and dedicated production lines. The electrical manufacturing industry, in particular, is characterized by high capital intensity. For instance, the global electrical equipment market was valued at approximately USD 780 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating substantial ongoing investment in fixed assets. These specialized assets are not easily repurposed or sold, making divestment costly.
Furthermore, established supply chains and long-term contracts with suppliers and customers can also act as significant exit barriers. Breaking these commitments often incurs penalties or reputational damage, further trapping companies in the market. The intricate nature of these relationships, built over years, makes a clean exit challenging. This situation can intensify price competition and reduce overall industry profitability as firms struggle to recoup their investments.
- Specialized Assets: High capital expenditure on manufacturing plants and machinery in electrical manufacturing makes exiting difficult.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing agreements with suppliers and customers create obligations that are costly to terminate.
- Industry Inertia: Companies may remain in a low-profit market due to the difficulty of selling specialized assets or fulfilling contractual obligations.
- Intensified Rivalry: The presence of high exit barriers forces companies to compete more aggressively for market share, potentially leading to price wars.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic stakes for competitors in the electrical equipment and building technology sector are incredibly high, fueling intense rivalry. Companies are not just vying for immediate sales but are making significant investments to capture future market share, especially in rapidly evolving areas. For instance, the push towards smart building technologies and the integration of renewable energy sources means that establishing early leadership in these domains can lock in customers and create significant long-term advantages. This competition is evident in the substantial R&D spending by major players; in 2023, for example, industry leaders were reportedly increasing their innovation budgets by as much as 10-15% to stay ahead of the curve.
Aggressive competition is also driven by the desire for technological supremacy and the securing of crucial client partnerships. In markets where Hager Group operates, such as commercial real estate and infrastructure development, a single large contract can represent millions in revenue and set a precedent for future business. Companies are therefore willing to compete fiercely on price, performance, and innovation to win these key accounts. This dynamic is particularly pronounced as new regulations and sustainability mandates, like those aimed at improving energy efficiency in buildings, create new market opportunities that all players are eager to capitalize on.
- High R&D Investment: Competitors are significantly increasing research and development budgets, with some projecting a 10-15% rise in 2023 for innovation in smart building and renewable energy solutions.
- Market Share Capture: Aggressive strategies are employed to gain a dominant position in emerging technology segments, aiming to secure long-term customer loyalty.
- Technological Leadership: Companies are investing heavily to achieve and maintain a competitive edge through cutting-edge product development and proprietary solutions.
- Key Customer Relationships: Securing major contracts with large developers and infrastructure projects is a critical battleground, with significant financial and strategic implications.
The electrical installation market is highly competitive, featuring numerous global and regional players. Hager Group faces intense rivalry from established giants like Siemens and Schneider Electric, as well as specialized smaller firms. This crowded landscape means companies must constantly innovate and differentiate to stand out.
Growth in sectors like smart homes, with a projected 2025-2035 CAGR of 9.05%, and building automation, expected to grow at 11.5% from 2024-2025, tempers rivalry by offering ample room for expansion. However, when products are similar, competition can shift to price, making differentiation through innovation, sustainability, and integrated solutions, like Hager's smart building technologies, crucial for mitigating direct price wars in 2024.
High exit barriers, such as significant investments in specialized manufacturing assets within the capital-intensive electrical equipment market (valued at approximately USD 780 billion in 2023), coupled with long-term contracts, trap firms in the market. This often intensifies rivalry as companies fight for survival rather than exiting, potentially leading to price wars and reduced profitability.
| Factor | Impact on Hager Group | Evidence/Example |
| Number of Competitors | High Rivalry | Presence of global players (Siemens, Schneider Electric) and numerous regional/specialized firms. |
| Industry Growth Rate | Moderate Rivalry (in high-growth segments) | Smart home market CAGR 9.05% (2025-2035); Building automation CAGR 11.5% (2024-2025). |
| Product Differentiation | Mitigated Rivalry (through innovation) | Hager's focus on sustainability, smart technologies, and integrated solutions contrasts with undifferentiated offerings. |
| Exit Barriers | Intensified Rivalry | High capital expenditure in electrical manufacturing (USD 780 billion market in 2023) and long-term contracts make exiting costly. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Hager Group stems from alternative solutions that meet similar customer needs through different methods. For instance, in the energy sector, direct solar power for specific applications can bypass traditional grid infrastructure, offering an alternative to electrical distribution systems. Similarly, non-electrical solutions for building functions, like mechanical ventilation instead of electrical HVAC, represent another form of substitution.
The appeal of substitute products for Hager Group hinges significantly on their price-performance ratio. When alternatives provide comparable or superior functionality at a more attractive price point, the threat they pose escalates considerably.
For example, advancements in wireless automation technologies present a viable substitute for traditional wired electrical installations, potentially offering cost savings and easier deployment. Similarly, innovations in building materials, such as high-efficiency insulation, can reduce the demand for extensive heating and cooling systems, thereby impacting Hager's core offerings.
In 2024, the global market for smart home automation, a key area where substitutes are emerging, was projected to reach over $150 billion, indicating a strong consumer interest in alternative solutions that offer convenience and potential cost efficiencies.
Customer willingness to switch to alternative solutions for electrical installations and smart home technology is a key factor. This willingness is shaped by how aware customers are of these alternatives, the perceived risks involved in switching, and how easy it is to make the change. For instance, as smart home devices become more intuitive and affordable, consumers may find it easier to adopt them, potentially bypassing traditional electrical solutions.
The increasing availability and affordability of user-friendly smart home and energy management systems directly impacts customer propensity to substitute. For example, by mid-2024, the global smart home market was projected to reach over $150 billion, indicating a growing customer interest in integrated, easily managed solutions. This trend suggests that customers might increasingly opt for comprehensive smart systems over individual, less integrated electrical components.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Rapid technological advancements in substitute industries present a considerable threat to Hager Group's established market position. Innovations in areas like advanced battery storage solutions and decentralized microgrid technologies are actively reducing the traditional reliance on centralized energy distribution networks. This shift directly challenges Hager's core business model, which is heavily invested in the infrastructure for distributing electrical energy.
The increasing efficiency and decreasing costs of renewable energy generation, coupled with sophisticated energy management systems, are creating viable alternatives to conventional grid-based power. For instance, the global renewable energy sector saw significant growth, with solar power installations alone increasing by an estimated 30% in 2023 compared to the previous year, according to the International Energy Agency. This trend empowers consumers and businesses to generate and manage their own energy, potentially bypassing traditional distributors.
- Technological Disruption: Innovations in energy storage and microgrids offer alternatives to centralized distribution.
- Market Shift: Decentralized energy solutions reduce dependence on traditional grid infrastructure.
- Renewable Energy Growth: Increased efficiency and lower costs of renewables accelerate the adoption of alternative energy sources.
- Consumer Empowerment: Advanced energy management systems allow for greater self-sufficiency, impacting demand for traditional distribution services.
Regulatory and Environmental Factors
Regulatory shifts and environmental policies significantly impact the threat of substitutes for companies like Hager Group. For instance, mandates promoting energy efficiency or the adoption of specific green technologies can directly encourage alternatives to conventional electrical systems. In 2024, many governments continued to roll out ambitious renewable energy targets, with the International Energy Agency reporting a substantial increase in global renewable capacity additions, potentially accelerating the adoption of off-grid or decentralized power solutions.
Government incentives play a crucial role in making these substitutes more competitive. Subsidies for solar installations or tax credits for electric vehicle charging infrastructure, common in 2024, can lower the upfront cost of alternative solutions. This makes them more attractive compared to traditional electrical grid components, thereby increasing the threat of substitution.
- Regulatory Push: Environmental mandates, such as stricter emissions standards or building codes requiring higher energy efficiency, can favor substitute technologies.
- Incentive Landscape: Government subsidies and tax breaks for renewable energy sources and electric mobility directly reduce the cost-competitiveness of alternatives.
- Market Shift: By 2024, a growing consumer and corporate demand for sustainable solutions, often driven by regulatory pressures and incentives, was observed across key markets.
The threat of substitutes for Hager Group is significant, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. Alternatives like smart home systems and decentralized energy solutions directly challenge traditional electrical infrastructure. The appeal of these substitutes is often tied to their price-performance ratio and ease of adoption.
In 2024, the global smart home market was projected to exceed $150 billion, highlighting strong consumer interest in integrated, convenient alternatives. Furthermore, the increasing efficiency and decreasing costs of renewable energy sources, such as solar power, empower consumers to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on grid-based distribution systems. For example, solar installations saw substantial growth in 2023, with an estimated 30% increase year-over-year, according to the IEA, making self-sufficiency more attainable.
| Substitute Category | Key Drivers | Impact on Hager |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Home Automation | Convenience, energy efficiency, integrated control | Potential reduction in demand for traditional wiring and components |
| Decentralized Energy Solutions (Microgrids, Battery Storage) | Energy independence, resilience, cost savings | Challenges traditional grid infrastructure sales |
| Renewable Energy Generation (Solar, Wind) | Environmental concerns, cost competitiveness, government incentives | Reduced reliance on grid-supplied electricity, impacting distribution equipment |
| Non-Electrical Building Systems | Energy efficiency mandates, alternative technologies | Impacts demand for electrical HVAC and lighting solutions |
Entrants Threaten
Significant economies of scale in manufacturing and distribution of electrical installation products create a substantial barrier for new companies trying to enter the market. Hager Group, as a well-established player, leverages its extensive production facilities and sophisticated global logistics network. This allows them to achieve considerable cost advantages per unit, making it difficult for smaller, newer entrants to compete on price.
For instance, in 2023, Hager Group reported a revenue of approximately €3.7 billion, reflecting the scale of its operations and market presence. This scale translates into lower per-unit production costs due to bulk purchasing of raw materials and optimized manufacturing processes. New entrants would need to invest heavily to reach a comparable production volume and efficiency, a hurdle that deters many potential competitors.
The electrical installation and building technology sectors demand significant upfront capital for research and development, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and building robust distribution channels. This financial hurdle naturally limits the number of new players that can realistically enter the market.
Hager Group's consistent investment in innovation and production capabilities, evidenced by their ongoing expansion and upgrades to manufacturing plants, underscores the capital-intensive nature of this industry. For instance, in 2023, Hager Group reported significant investments in modernizing its production lines to enhance efficiency and product quality, a typical characteristic of established firms navigating high capital requirements.
Newcomers face a significant hurdle in accessing established distribution channels, such as wholesalers and contractor networks, which are vital for reaching end customers in the electrical installation materials market. Hager Group's extensive and long-standing relationships with these intermediaries act as a formidable barrier, making it difficult and costly for new entrants to gain comparable market penetration. For instance, in 2024, the electrical wholesale sector in Europe continued to consolidate, with major players reporting strong revenue growth, further solidifying their importance and making access more challenging for unestablished brands.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
Hager Group benefits from a strong brand identity and deeply ingrained customer loyalty, cultivated through decades of delivering quality and reliable electrical installation systems. This established reputation acts as a significant barrier to entry for newcomers, as potential customers are often hesitant to switch from a trusted brand. For instance, Hager's consistent performance in product durability and customer service, which has been a hallmark since its founding in 1955, fosters a sticky customer base.
The difficulty for new entrants is further amplified by Hager Group's extensive distribution network and established relationships with installers and specifiers. Building comparable trust and market penetration would require substantial investment and time. In 2024, Hager Group continued to invest in brand building and customer engagement, reinforcing its market position against potential disruptors.
New competitors face the challenge of replicating Hager's long-standing commitment to innovation and customer support. This includes:
- Brand Recognition: Hager is a recognized name in electrical installations globally.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customers are less likely to switch due to perceived risk with unknown brands.
- Reputation for Quality: Years of reliable product performance build significant trust.
- Established Distribution Channels: Access to markets is already secured, unlike new entrants.
Proprietary Product Technology and Expertise
Hager Group's commitment to innovation in energy distribution, building automation, and security systems has resulted in proprietary product technologies. This deep well of accumulated expertise makes it challenging for new competitors to quickly develop comparable offerings. The company actively protects its innovations through patents and a strong emphasis on continuous research and development, effectively raising the barrier to entry.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by Hager Group's significant investment in R&D, which fuels its proprietary technology. For instance, in 2023, Hager Group reported a significant portion of its revenue being reinvested into innovation, aiming to stay ahead in areas like smart home technology and sustainable energy solutions. This focus creates a technological moat that new players would find difficult and costly to overcome.
- Proprietary Technology: Hager Group develops unique solutions in energy management and building automation, making replication difficult.
- Patents and Expertise: The company's patent portfolio and specialized knowledge act as significant deterrents to new market entrants.
- R&D Investment: Continuous investment in research and development ensures Hager Group maintains a technological edge, increasing the cost and time for competitors to catch up.
The threat of new entrants for Hager Group is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, coupled with established brand loyalty and distribution networks, make market entry challenging. Hager's scale, evidenced by its 2023 revenue of approximately €3.7 billion, allows for cost advantages that new players struggle to match.
Access to established distribution channels, crucial for reaching customers in the electrical installation market, is a major hurdle. In 2024, the consolidation within the European electrical wholesale sector further solidified the position of major players, making it harder for new brands to gain traction. Hager's long-standing relationships in these channels are a key deterrent.
Hager Group's proprietary technology, protected by patents and bolstered by continuous R&D investment, creates a technological moat. For example, their focus on smart home technology and sustainable solutions, supported by significant R&D reinvestment in 2023, means new entrants face substantial costs and time to develop comparable offerings.
| Barrier Type | Hager Group's Advantage | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Economies of Scale | Large production volume, cost efficiencies | High cost to achieve comparable unit costs |
| Capital Requirements | Extensive R&D and manufacturing facilities | Significant upfront investment needed |
| Distribution Channels | Established relationships with wholesalers | Difficult and costly to gain market access |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Decades of quality and trust | Hesitancy for customers to switch |
| Proprietary Technology | Patented innovations, strong R&D | Replication is costly and time-consuming |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hager Group is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Hager's official annual reports, investor presentations, and press releases. This is complemented by industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial information providers to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
