Guttman Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Guttman Holdings Bundle
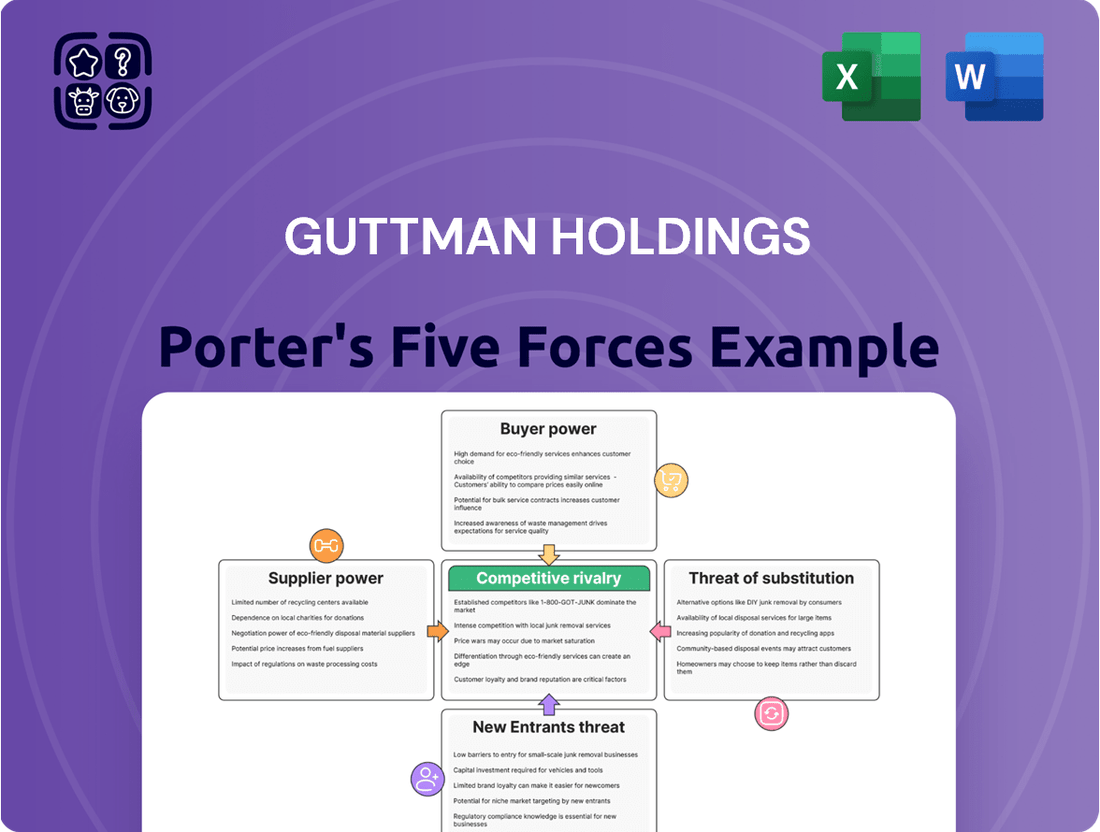
Guttman Holdings operates within a dynamic market, influenced by several key competitive forces. Understanding the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers is crucial for navigating its industry landscape. The threat of new entrants and the intensity of rivalry among existing players significantly shape Guttman Holdings's strategic options.
Furthermore, the constant pressure from substitute products and services demands continuous innovation and adaptation from Guttman Holdings. This intricate web of forces dictates profitability and market positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Guttman Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Guttman Energy's primary suppliers are crude oil producers and refiners, whose leverage is closely tied to global oil price fluctuations and geopolitical events. For instance, in early 2024, Brent crude oil prices averaged around $80 per barrel, a figure sensitive to supply disruptions.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified when the market experiences supply shortages or when a few dominant producers control a significant portion of the output. If Guttman Energy faces a situation where alternative suppliers are scarce or less reliable, the existing suppliers can command higher prices.
Looking ahead to 2025, projections suggest a potential increase in global oil supply, which could, in theory, temper supplier power. However, ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly in oil-producing regions, remain a significant wildcard that can quickly shift the balance, leading to price spikes and increased supplier leverage.
The refining industry is seeing significant shifts, with forecasts indicating a reduction in capacity over the next ten years as the world moves towards cleaner energy sources. This anticipated capacity contraction could create tighter markets for specific refined products, thereby bolstering the bargaining power of refiners. For example, in 2024, the global refining capacity is projected to see a net increase of only around 0.5 million barrels per day, a stark contrast to previous years, reflecting this structural change.
Transportation and logistics providers wield significant bargaining power, particularly as operational costs in 2025 climb due to elevated fuel prices, labor demands, and infrastructure investments. For distributors like Guttman, these escalating costs directly impact their bottom line.
The ongoing supply chain disruptions and a persistent shortage of truck drivers exacerbate this situation, allowing logistics firms to command higher rates. This increased leverage for suppliers means Guttman faces a more challenging cost environment for moving its goods.
Supplier Power 4
Guttman Energy's reliance on suppliers for biofuels and alternative fuels is growing due to sustainability mandates. The specialized nature of these products means fewer suppliers can meet Guttman's needs, potentially increasing supplier leverage. For instance, the global biofuels market was projected to reach approximately $200 billion by 2024, indicating a significant and specialized supply chain. This concentration of specialized suppliers grants them considerable bargaining power.
The pricing and availability of these cleaner-burning fuels directly impact Guttman's operational costs and ability to meet environmental regulations. Suppliers in this niche market can dictate terms, especially if Guttman cannot easily switch to alternative fuel sources or if their production capacity is limited. In 2024, the demand for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), a key alternative, saw significant growth, potentially tightening supply for other biofuel sectors.
- Increased Dependence: Guttman's commitment to cleaner fuels elevates its dependence on a narrower supplier base.
- Specialized Products: The unique nature of biofuels and alternative fuels limits the number of viable suppliers.
- Market Growth: The expanding market for sustainable fuels, projected to exceed $200 billion globally by 2024, can lead to supply constraints.
- Pricing Power: Suppliers can leverage their position to influence pricing and contract terms for Guttman Energy.
Supplier Power 5
Consolidation in the refining and transportation sectors presents a significant threat to Guttman Holdings by potentially reducing the number of available fuel suppliers. This scarcity could embolden remaining suppliers, granting them increased leverage in negotiations with fuel distributors like Guttman. For instance, in 2024, several smaller regional fuel transporters were acquired by larger national carriers, a trend that could continue, concentrating market power. This dynamic means suppliers might dictate terms more forcefully, impacting Guttman's procurement costs and operational flexibility.
To counter this rising supplier power, Guttman Holdings must prioritize strategic partnerships and long-term contracts. These agreements can lock in favorable pricing and supply volumes, providing a buffer against market volatility and supplier opportunism. By securing dedicated supply channels, Guttman can reduce its reliance on the spot market, where price fluctuations are more pronounced. Furthermore, exploring diversified sourcing options, even if they involve slightly higher initial costs, can build resilience against any single supplier’s increased bargaining strength.
- Industry Consolidation: Increased mergers and acquisitions in the fuel supply chain can lead to fewer, more powerful suppliers.
- Supplier Leverage: Reduced competition among suppliers translates to greater ability to dictate terms and prices.
- Risk Mitigation: Guttman must proactively seek strategic alliances and multi-year supply agreements.
- Diversification: Exploring multiple sourcing avenues is critical to avoid over-reliance on any single supplier.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Guttman Holdings is considerable, particularly with crude oil producers and refiners whose leverage is tied to global price volatility. In early 2024, Brent crude averaged about $80 per barrel, a figure susceptible to supply disruptions.
This power intensifies during supply shortages or when a few dominant producers control output. Reduced refining capacity, projected to decrease by 0.5 million barrels per day globally in 2024, further bolsters refiner leverage.
Additionally, rising costs for transportation and logistics, driven by fuel prices and labor shortages, empower these service providers. The growing demand for specialized biofuels, a market valued at approximately $200 billion by 2024, also concentrates power among a limited number of suppliers, impacting Guttman's operational costs and regulatory compliance.
| Supplier Segment | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on Guttman Holdings | Relevant 2024/2025 Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude Oil Producers | Global supply/demand, geopolitical stability | Price volatility, supply availability | Brent crude averaged ~$80/barrel in early 2024. Potential supply increase in 2025, but geopolitical risks remain. |
| Refiners | Refining capacity, product demand | Availability and cost of refined fuels | Global refining capacity projected net increase of ~0.5 million bpd in 2024. Anticipated capacity contraction over next decade. |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fuel costs, labor availability, infrastructure | Increased costs for distribution, reduced flexibility | Elevated fuel prices and truck driver shortages in 2024/2025. |
| Biofuels & Alternative Fuels | Specialization, sustainability mandates, market growth | Limited supplier options, potential for dictated terms | Biofuels market projected to reach ~$200 billion by 2024. Strong growth in sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) demand in 2024. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Guttman Holdings' specific industry position.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive five forces dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Guttman Energy's customer base, comprising commercial, industrial, and government entities, wields considerable bargaining power. These buyers often procure energy in substantial volumes, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms and volume discounts. For instance, in 2024, major industrial consumers continued to leverage competitive bidding processes to secure the most advantageous energy contracts, driving down per-unit costs for large-scale purchases.
Buyers' increasing demand for real-time visibility and digital procurement tools significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This allows them to easily compare Guttman Holdings' offerings against competitors, fostering a more competitive pricing environment. For instance, in 2024, the global e-procurement market was valued at approximately $15.5 billion, reflecting the widespread adoption of digital tools that empower buyers.
Flexible fulfillment models further enhance customer leverage. As buyers can readily switch between providers offering diverse delivery and service options, Guttman Holdings faces pressure to adapt its operations. Companies that offer transparent data and agile solutions are better positioned to retain these empowered customers, as they can directly demonstrate value and responsiveness.
Customers increasingly hold sway when they can easily switch suppliers or when their purchase represents a significant portion of a supplier's revenue. In 2024, as the demand for sustainable practices intensifies, Guttman Holdings' customers are showing a greater preference for distributors providing eco-friendly fuel alternatives and detailed emission reports. This growing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors empowers buyers to negotiate better pricing or service agreements by leveraging their purchasing power for greener solutions.
Buyer Power 4
Customers in the wholesale fuel market, including Guttman Holdings, face numerous choices from various distributors and even integrated oil companies. This abundance of options significantly strengthens their bargaining power, as they can readily switch suppliers if pricing or service levels are not competitive. For instance, in 2024, the global wholesale fuel market saw continued price volatility, driven by geopolitical events and supply chain dynamics, further empowering buyers to seek the best available terms.
The wholesale fuel sector is known for its high degree of competition, a factor that directly benefits customers. With many players vying for market share, buyers can leverage this environment to negotiate more favorable pricing and contract conditions. Reports from late 2023 and early 2024 indicated that while demand remained robust, the number of independent distributors had grown in several key regions, intensifying competition and giving customers more leverage.
- Customer Choice: Access to multiple wholesale fuel distributors and integrated oil companies provides customers with readily available alternatives.
- Competitive Landscape: The wholesale fuel market is characterized by intense competition among suppliers, which naturally shifts power towards buyers.
- Price Sensitivity: Fluctuations in fuel prices, common in 2024, increase customer focus on cost and their willingness to switch for better deals.
- Switching Costs: While some switching costs exist, the availability of numerous suppliers generally keeps these costs manageable for buyers.
Buyer Power 5
For fleet operators and industrial clients, fuel quality assurance and reliable, just-in-time delivery are crucial. These customers possess significant leverage, capable of dictating terms by demanding stringent quality standards and imposing penalties on distributors for any deviations or delays. This directly impacts Guttman's ability to differentiate its services.
The bargaining power of customers in the fuel distribution sector is a significant factor for Guttman Holdings.
- Customer Concentration: A few large fleet operators or industrial clients can represent a substantial portion of Guttman's revenue, giving them considerable negotiating power.
- Switching Costs: While switching fuel suppliers might involve some administrative effort, the potential cost savings or improved service reliability can incentivize customers to change.
- Information Availability: Customers often have access to market pricing and competitor offerings, enabling them to negotiate more effectively for better terms.
- Threat of Backward Integration: In some industrial sectors, large customers might consider investing in their own fuel storage and delivery infrastructure if they perceive they can achieve better cost control and reliability, thereby reducing their reliance on distributors like Guttman.
Guttman Holdings' customers, particularly large commercial and industrial buyers, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchase volumes and the competitive nature of the energy market. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, especially when they can easily access information on market rates and competitor offerings. For instance, in 2024, the increasing adoption of digital procurement platforms further amplified this power by facilitating easier comparison shopping and supplier switching.
The trend towards sustainability also empowers customers, as they increasingly demand eco-friendly fuel alternatives and transparent emission reporting. This focus on ESG factors allows buyers to negotiate better deals by leveraging their preference for greener solutions, putting pressure on suppliers like Guttman Holdings to adapt their offerings and demonstrate environmental responsibility.
| Factor | Impact on Guttman Holdings | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Volume | High volume buyers can demand discounts. | Major industrial consumers secured favorable contracts through competitive bidding in 2024. |
| Information Availability | Easy access to market pricing enhances negotiation. | Digital procurement tools and market data access increased buyer leverage in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower customers to change suppliers. | The abundance of wholesale fuel distributors in 2024 kept switching costs manageable. |
| ESG Demands | Customers leverage demand for sustainable options. | Growing preference for eco-friendly fuels in 2024 enabled customers to negotiate better terms. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Guttman Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version of Guttman Holdings' Porter's Five Forces Analysis—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This comprehensive report delves into the competitive landscape, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry within Guttman Holdings' industry. Understand the strategic implications of each force to make informed business decisions. This is your complete, ready-to-use analysis file, professionally formatted and ready for your needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The wholesale petroleum distribution market, especially in North America, is quite mature and has been around for a long time. This maturity means there are a lot of companies already in the game, making competition really tough. Guttman Energy, which has been operating since 1931, faces this challenge head-on, competing with many rivals who also have deep roots in the industry.
Competitive rivalry within the distribution sector is notably intense, exacerbated by rising operational expenses. For instance, fuel prices, a significant cost driver, saw a surge in late 2023 and early 2024, impacting transportation budgets. This pressure, combined with increasing labor costs and the burden of stringent regulatory compliance, forces distributors to compete aggressively on price to maintain market share.
To navigate this challenging environment, distributors are actively seeking operational efficiencies. This includes optimizing logistics, investing in technology for better inventory management, and exploring cost-saving measures in warehousing and delivery. For Guttman Holdings, maintaining a competitive edge requires a sharp focus on these cost-reduction strategies to offset the margin squeeze.
The competitive rivalry within the energy sector is intensifying as traditional fuel distributors increasingly diversify into renewable energy and biofuels. This shift creates new battlegrounds for market share, forcing established players to innovate and expand their product portfolios to include cleaner energy solutions. For instance, in 2024, global investment in renewable energy reached record highs, pushing companies like Guttman Holdings to reassess their strategies. This diversification strategy directly impacts competitive dynamics, as companies vie for leadership in emerging green energy markets.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry within the energy distribution sector is intensifying, driven by strategic consolidation. For instance, Guttman Holdings' acquisition of Weaver Energy in late 2024 exemplifies a trend where larger entities are absorbing smaller competitors to broaden their market presence and diversify service portfolios. This move, alongside similar industry-wide M&A activities, directly heightens pressure on distributors that haven't achieved similar scale or integration.
This consolidation is not just about size; it's about creating more formidable, end-to-end service providers. Companies like Guttman, post-acquisition, can offer a more comprehensive suite of products and logistics, making it harder for independent distributors to compete on price, efficiency, or service breadth. The market is clearly shifting towards fewer, larger players with greater operational leverage.
- Increased Market Power: Acquisitions allow firms to gain a larger share of the market, potentially leading to greater pricing influence.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiencies: Merging operations often leads to cost savings through economies of scale and optimized supply chains.
- Broader Service Offerings: Consolidating companies can integrate complementary services, providing a more attractive one-stop solution for customers.
- Heightened Barriers to Entry: The presence of larger, more integrated competitors can make it more challenging for new or smaller businesses to enter and thrive.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Competitive rivalry within Guttman Holdings' industry is intensifying, particularly as technological advancements reshape operational landscapes. Companies are increasingly leveraging AI-driven platforms for sophisticated demand forecasting and streamlined supply chain optimization, creating significant competitive differentiators.
Those firms that proactively invest in and effectively deploy these advanced technologies are positioning themselves to capture a distinct advantage in both operational efficiency and the quality of their customer service. This technological arms race means that lagging behind on innovation can quickly translate to a loss of market share.
For instance, in 2024, the global AI in supply chain market was valued at approximately $5.2 billion and is projected to grow substantially, highlighting the widespread adoption and impact of these tools. Companies like Guttman Holdings must continually assess their technological investments to remain competitive.
- AI Adoption: Critical for demand forecasting and supply chain efficiency.
- Competitive Edge: Gained through investment in advanced technologies.
- Market Growth: The AI in supply chain market saw significant growth in 2024.
- Strategic Imperative: Continuous technological investment is crucial for staying ahead.
Competitive rivalry in the wholesale petroleum distribution market is fierce due to industry maturity and increasing operational costs. For Guttman Holdings, this means navigating a landscape where price competition is paramount, especially with rising fuel and labor expenses. Strategic consolidation, like Guttman's acquisition of Weaver Energy in late 2024, further intensifies this rivalry by creating larger, more integrated players.
| Factor | Impact on Guttman Holdings | Industry Trend (2024) |
| Market Maturity | High competition, price sensitivity | Mature North American market |
| Operational Costs | Margin pressure from fuel/labor increases | Fuel prices up late 2023/early 2024 |
| Consolidation | Increased pressure from larger rivals | Guttman acquired Weaver Energy (late 2024) |
| Technological Adoption | Need for AI/automation for efficiency | AI in supply chain market valued at ~$5.2B in 2024 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for Guttman Holdings stems from the accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the transportation sector. This shift directly erodes the demand for the gasoline and diesel fuels that are central to Guttman's business. While the impact is most pronounced at the retail level, it casts a long shadow over the long-term prospects for wholesale distributors that supply fuel to commercial fleets, potentially reducing their market share.
The threat of substitutes for Guttman Holdings' core oil and gas business is significant and growing. Alternative energy sources such as natural gas, biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel, and increasingly, hydrogen, are becoming more competitive and widely adopted. This shift is fueled by mounting environmental concerns, governmental policies promoting cleaner energy, and advancements in technology making these alternatives more efficient and cost-effective. For instance, global investment in renewable energy sources reached an estimated $500 billion in 2023, highlighting the accelerating transition away from traditional fossil fuels.
Guttman Energy itself recognizes this evolving landscape. The company's strategic move to establish Guttman Renewables is a direct acknowledgment of this substitute threat. This initiative signals a proactive approach to diversify its energy portfolio and capture opportunities in emerging clean energy markets. By investing in and developing renewable energy capabilities, Guttman Holdings aims to mitigate the impact of declining demand for its traditional products and position itself for future growth in a changing energy sector.
The threat of substitutes for Guttman Energy's products is significant. For instance, advancements in energy efficiency are directly impacting fuel demand. In 2024, global efforts to decarbonize are pushing industries to adopt more efficient technologies. This means less energy is needed for the same output, directly reducing the market for traditional energy sources.
Businesses are increasingly investing in upgrades that lead to substantial energy savings. Consider the commercial building sector, where retrofitting for better insulation and HVAC systems can cut energy consumption by up to 30%. This directly erodes the need for the fuels Guttman Energy supplies, presenting a clear challenge to its market position.
4
The rise of sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) presents a significant long-term threat to Guttman Holdings' aviation fuel segment. As SAF technology matures and adoption increases, demand for traditional jet fuel could decline, impacting revenue streams. For instance, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) projects that SAF could account for 65% of all aviation fuel used by 2050, highlighting the scale of this potential shift.
Guttman's diversified business model acts as a crucial buffer against this substitute threat. By operating across various energy sectors, including traditional fuels, renewables, and potentially petrochemicals, the company can offset potential downturns in any single market. This diversification strategy spreads risk and allows Guttman to adapt more readily to evolving energy landscapes.
- SAF Market Growth: The SAF market is projected to grow substantially, with estimates suggesting it could reach tens of billions of dollars annually by the late 2020s and early 2030s.
- Guttman's Diversification: Guttman's presence in renewable energy projects, such as solar and wind farms, provides an alternative revenue stream less susceptible to jet fuel demand fluctuations.
- Adaptation Potential: Guttman's strategic investments in research and development could position it to capitalize on the SAF market, potentially becoming a producer or distributor of these sustainable alternatives.
- Geopolitical Factors: Government incentives and mandates supporting SAF production and usage will play a key role in accelerating its adoption and, consequently, influencing the threat level to traditional jet fuel markets.
5
Policy shifts and increasingly stringent environmental regulations favoring cleaner energy sources are accelerating the adoption of substitutes for traditional petroleum products. This trend is making it harder for companies heavily invested in fossil fuels. For instance, in 2024, government incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) continued to grow, with many nations setting ambitious targets for EV adoption and internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle phase-outs. This regulatory push directly encourages consumers and businesses to explore and embrace alternatives.
The growing availability and improving performance of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, present a significant threat. As these technologies become more cost-competitive, they directly substitute for energy derived from petroleum. By mid-2024, the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for new utility-scale solar PV projects had fallen significantly, often making it cheaper than new fossil fuel power generation in many regions. This economic advantage further drives the substitution away from petroleum.
- Government mandates and subsidies for renewable energy projects are increasing globally.
- Advancements in battery technology are making electric vehicles a more viable and attractive substitute for gasoline-powered cars.
- Companies are investing heavily in research and development for alternative fuels and energy storage solutions.
- Consumer awareness and preference for sustainable products are influencing purchasing decisions, favoring substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Guttman Holdings is substantial, driven by the global energy transition. Alternative energy sources like solar, wind, and battery storage are becoming increasingly cost-competitive, directly challenging the demand for fossil fuels. For instance, by mid-2024, the levelized cost of electricity from new utility-scale solar PV projects often made it cheaper than new fossil fuel power generation in many regions, accelerating this substitution trend.
The accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a primary substitute threat, directly impacting gasoline and diesel fuel demand. Furthermore, sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are gaining traction, with projections suggesting they could represent a significant portion of aviation fuel by 2050, posing a long-term risk to Guttman's aviation fuel segment.
Companies are actively investing in energy efficiency and alternative technologies, further reducing reliance on traditional energy. This includes advancements in battery technology, making EVs more viable, and corporate commitments to renewable energy procurement. For example, many large corporations have set ambitious targets for sourcing 100% renewable electricity, directly diverting demand from fossil fuel suppliers like Guttman.
| Substitute Energy Source | 2023 Global Investment (Estimate) | Projected Impact on Fossil Fuel Demand | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind) | $500 billion | Significant reduction in demand for electricity generation from fossil fuels | Cost competitiveness, government incentives, environmental concerns |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Varies by region, but significant growth | Direct reduction in gasoline and diesel consumption | Government mandates, improving battery technology, consumer preference |
| Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) | Growing market, tens of billions by late 2020s | Potential decline in demand for traditional jet fuel | Technological advancements, regulatory support, airline commitments |
| Energy Efficiency Measures | Integral part of corporate and government strategies | Reduced overall energy consumption, impacting all fossil fuel segments | Cost savings, regulatory requirements, corporate sustainability goals |
Entrants Threaten
The wholesale petroleum distribution sector presents a formidable barrier to new companies looking to enter. Significant capital is absolutely essential to establish the necessary infrastructure, which includes vast storage tanks, a dedicated fleet of transport vehicles, and broad, efficient distribution channels. For instance, building a single modern fuel terminal can cost tens of millions of dollars, a substantial hurdle for any newcomer.
Stringent regulatory requirements and significant environmental compliance costs act as major deterrents for potential new entrants in the fuel handling and distribution sector. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for obtaining necessary operational licenses and permits within the energy sector globally ranged from tens of thousands to several hundred thousand dollars, depending on the jurisdiction and scale of operation. This financial barrier, coupled with the complexity of navigating safety and environmental standards, makes entry exceedingly challenging.
The capital-intensive nature of establishing fuel storage facilities, transportation networks, and ensuring adherence to strict safety protocols, such as those mandated by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) for fuel bunkering, requires substantial upfront investment. In 2024, the estimated cost for a new, compliant fuel depot could easily exceed $50 million, a sum prohibitive for many aspiring competitors. Furthermore, the ongoing operational expenses for maintaining these high standards add another layer of difficulty, effectively limiting the threat of new entrants.
Established players like Guttman Energy benefit from strong, long-standing relationships with both suppliers and commercial/industrial customers. For instance, in 2024, major oil refiners continued to prioritize existing contracts, making it challenging for newcomers to secure reliable, cost-effective supply chains.
New entrants would struggle to build comparable trust and supply agreements, especially given the capital-intensive nature of the energy sector. Securing stable feedstock and distribution networks requires significant upfront investment and proven reliability, barriers that Guttman Energy has already overcome.
Threat of New Entrants 4
The threat of new entrants for Guttman Holdings in the fuel industry is moderately high, primarily due to the intricate nature of fuel supply chain management. This complexity encompasses not only the physical movement of fuel but also sophisticated risk management, dynamic pricing strategies, and constant logistics optimization. Newcomers would require substantial capital and specialized knowledge to navigate these challenges effectively.
Establishing a competitive presence necessitates significant investment in both skilled personnel and cutting-edge technology. For instance, companies entering the market must contend with global commodity price volatility, which in 2024 continued to be influenced by geopolitical events and supply-demand imbalances. Building robust relationships with suppliers and distributors also presents a formidable barrier.
Key barriers to entry include:
- Capital Requirements: Significant upfront investment is needed for infrastructure, transportation fleets, storage facilities, and regulatory compliance.
- Industry Expertise: Deep understanding of fuel markets, regulatory landscapes, and operational intricacies is crucial for success.
- Brand Loyalty and Relationships: Established players benefit from existing customer relationships and supplier agreements, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate.
- Economies of Scale: Larger companies often achieve lower per-unit costs in procurement and distribution, making it challenging for smaller, new entities to compete on price.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants into Guttman Holdings' wholesale petroleum distribution market is currently moderate, influenced by several factors. A significant trend impacting this is the global energy transition. For instance, the International Energy Agency reported in 2024 that renewable energy sources accounted for over 30% of global electricity generation, a figure projected to climb steadily. This declining demand for traditional fossil fuels in certain sectors, particularly transportation and power generation, makes the wholesale petroleum distribution market less appealing for new investors solely focused on conventional products.
Several barriers to entry exist, but some are being eroded. High capital requirements for storage facilities, transportation fleets, and regulatory compliance remain substantial hurdles. However, the increasing availability of specialized third-party logistics providers and the potential for digital platforms to streamline operations could lower these initial investment costs for agile new players. For example, by mid-2024, several startups were exploring blockchain-based supply chain solutions in the energy sector, aiming to reduce operational overhead.
Guttman Holdings benefits from established relationships with suppliers and customers, offering a significant competitive advantage. New entrants would struggle to replicate these deep-seated networks and the trust built over years of operation. Despite this, market consolidation and the potential for private equity firms to acquire smaller, struggling distributors could introduce new, well-capitalized entities into the market. The financial landscape in 2024 saw significant M&A activity in the energy services sector, indicating potential for such strategic acquisitions.
The regulatory environment also plays a crucial role. Strict environmental regulations and licensing requirements for handling petroleum products create a high barrier. However, as the market shifts, new regulations favoring alternative fuels or carbon capture technologies could emerge, potentially creating opportunities for new entrants focused on these evolving areas rather than traditional distribution.
- Declining Demand: The global shift towards renewables, with solar and wind capacity expanding significantly in 2024, reduces the long-term attractiveness of traditional fuel distribution for new entrants.
- Capital Intensity: While high, the cost of entry for infrastructure like storage tanks and pipelines might be partially mitigated by the rise of shared logistics and technological solutions.
- Established Networks: Guttman Holdings' existing supplier and customer relationships are a strong defense, making it difficult for newcomers to gain immediate market share.
- Regulatory Landscape: Stringent environmental and safety regulations remain a significant deterrent, though future regulatory changes could open doors for niche players.
The threat of new entrants into Guttman Holdings' wholesale petroleum distribution sector is currently moderate. High capital requirements for infrastructure, such as storage terminals costing upwards of $50 million in 2024, and stringent regulatory compliance, with licensing fees ranging from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars globally, remain significant deterrents.
However, emerging trends like the increasing adoption of shared logistics and digital platforms could potentially lower initial investment barriers for new players. For instance, in 2024, startups explored blockchain solutions to streamline energy supply chains, aiming to reduce operational overhead.
| Barrier | Description | 2024 Impact/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing infrastructure (storage, transport) | New fuel depot estimated cost: $50M+ |
| Regulatory Compliance | Licenses, safety, environmental standards | License fees: $10K - $100K+ globally |
| Established Relationships | Supplier and customer networks | Refiners prioritized existing contracts in 2024 |
| Industry Expertise | Market knowledge, risk management | Navigating price volatility influenced by geopolitics |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Guttman Holdings leverages data from annual reports, financial statements, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of competitive forces.
