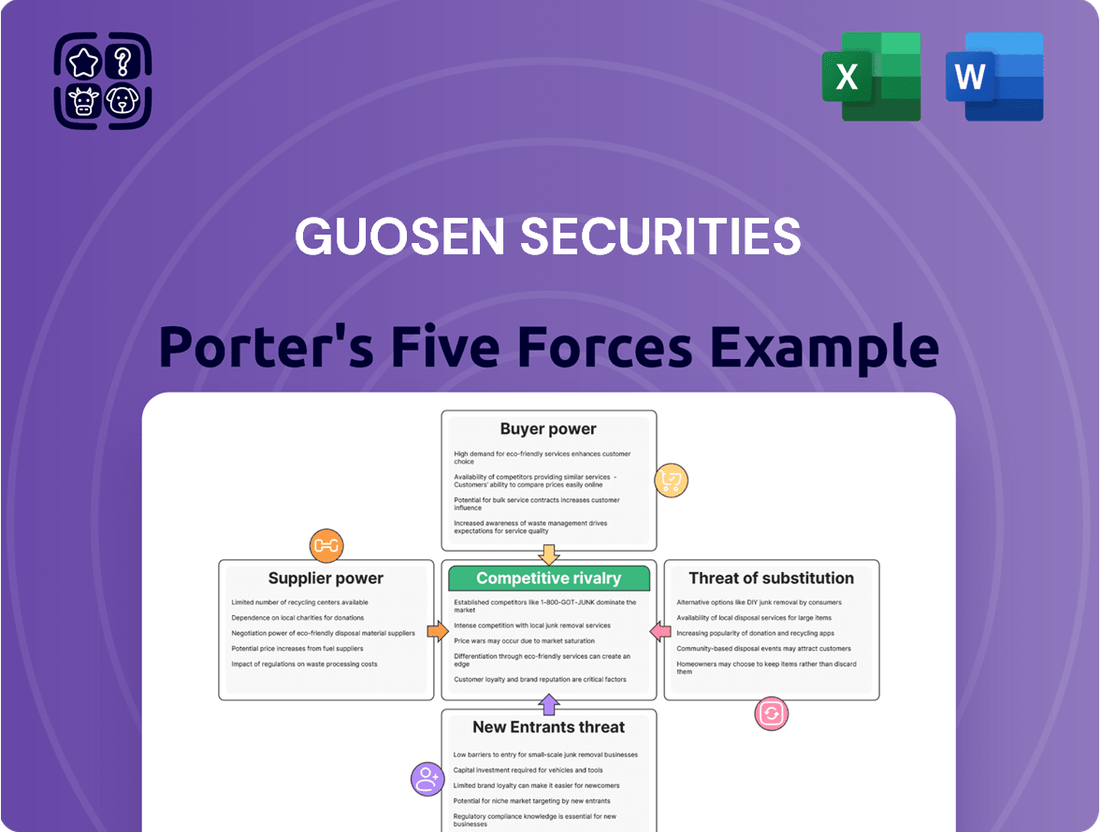
Guosen Securities Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Guosen Securities Bundle
Guosen Securities operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing intense competition and evolving regulatory pressures. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, and substitute products is crucial for navigating this market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Guosen Securities’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Guosen Securities, like many financial firms, depends heavily on technology and data suppliers for its operations, from trading platforms to market analytics. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be significant, particularly for those offering specialized, cutting-edge solutions such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, which are vital for competitive advantage.
The financial industry's push towards digital transformation and AI integration is amplifying the leverage of technology providers. For instance, the global market for AI in financial services was projected to reach over $25 billion by 2024, highlighting the critical demand for these advanced capabilities and the resulting supplier influence.
The financial services sector, especially investment banking and asset management, relies on skilled professionals like financial analysts, traders, and investment bankers. The limited availability of top talent in niche fields grants these individuals substantial leverage regarding salary and benefits.
Guosen Securities must actively recruit and retain these experts to preserve its competitive advantage in the market.
Guosen Securities' reliance on regulatory and compliance service providers, especially those specializing in China's complex financial rules, grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. The need for expert legal counsel and advanced RegTech solutions to navigate evolving regulations, such as those impacting data privacy and anti-money laundering, means Guosen must engage with specialized firms. For instance, the increasing focus on cybersecurity and fintech regulation in China necessitates partnerships with providers offering robust compliance frameworks, a trend that continued to strengthen through 2024.
Office Space and Infrastructure Providers
Guosen Securities, as a major player in financial services, has a significant need for office space and robust IT infrastructure. This creates a dynamic where suppliers of these essential services can exert some influence. For instance, while generic office leases might offer ample choice, the specialized data centers and secure network providers critical for financial operations often have more leverage due to the stringent requirements and limited number of qualified vendors.
The bargaining power of office space and infrastructure providers for Guosen Securities is generally considered moderate. While the sheer scale of Guosen's operations means they are a significant customer, the availability of multiple providers for standard office facilities can temper supplier power. However, for highly specialized infrastructure like secure data centers and advanced network solutions, the bargaining power of these niche providers can increase, especially given the critical nature of these services to Guosen's business continuity and security.
- Specialized Infrastructure Needs: Financial services firms like Guosen Securities require high levels of security, uptime, and data processing capabilities from their IT infrastructure providers, potentially increasing supplier bargaining power.
- Geographic Reach: Guosen's extensive network across China necessitates relationships with numerous local infrastructure providers, diversifying reliance but also potentially creating dependencies on regional suppliers.
- Market Dynamics for Office Space: The general office real estate market in China, particularly in major financial hubs, can offer competitive leasing options, which might limit the bargaining power of landlords for standard office spaces.
- Vendor Concentration in Niche Markets: In the realm of specialized data centers and cybersecurity solutions, a smaller pool of highly capable providers may lead to greater bargaining power for those suppliers.
Market Information and Research Vendors
Market information and research vendors hold significant bargaining power over Guosen Securities. Access to accurate, timely market data and proprietary research reports is crucial for Guosen's investment and advisory offerings, particularly for its institutional clientele. For instance, in 2024, the global market for financial data and analytics was estimated to be worth over $35 billion, with a few dominant players controlling a substantial share of this market, indicating their leverage.
These vendors often possess unique datasets and analytical tools that are difficult for Guosen to replicate internally. The cost of subscribing to premium data feeds and research from these established providers can be substantial, directly impacting Guosen's operational expenses. The reliance on these specialized services means that price increases or changes in service terms from these vendors can significantly affect Guosen's competitive edge and profitability.
- High concentration of vendors: A few key providers dominate the market for specialized financial data and research.
- Proprietary data and analytics: Vendors offer unique information and tools not readily available elsewhere.
- Switching costs: Migrating data systems and retraining staff can be costly and time-consuming for Guosen.
- Impact on service quality: The quality and timeliness of vendor data directly influence Guosen's client services.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Guosen Securities is a critical factor, particularly concerning technology and specialized data providers. Firms like Guosen rely heavily on these external entities for everything from trading platforms to advanced analytics, which are essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the fast-paced financial markets. The increasing demand for AI and big data solutions in finance, a market projected to exceed $25 billion by 2024, underscores the leverage these specialized suppliers possess.
Furthermore, the concentration of vendors in niche areas, such as proprietary financial data and sophisticated research, amplifies their influence. Guosen Securities' dependence on these unique datasets and analytical tools, which are difficult to replicate internally, means that price adjustments or changes in service terms from these providers can have a substantial impact on the firm's operational costs and its ability to serve clients effectively. The high switching costs associated with migrating data systems and retraining personnel further solidify the suppliers' advantageous position.
| Supplier Category | Key Dependencies for Guosen | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors | Illustrative 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology & Data Providers | Trading platforms, AI/Big Data analytics, market data feeds | Vendor concentration, proprietary technology, high switching costs | Global AI in financial services market projected over $25 billion |
| Talent Providers (Recruiters/Agencies) | Skilled financial analysts, traders, investment bankers | Scarcity of top talent in niche fields, high demand | N/A (Talent is not a direct supplier in the same vein as data) |
| Regulatory & Compliance Services | Legal counsel, RegTech solutions, compliance frameworks | Complexity of regulations, specialization of providers | Increased focus on cybersecurity and fintech regulation in China |
| Infrastructure Providers | Data centers, secure network solutions | Specialized requirements (security, uptime), limited qualified vendors | N/A (Specific data on infrastructure provider concentration not readily available) |
What is included in the product
Guosen Securities' Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the competitive intensity, buyer power, and threat of substitutes impacting its market position.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces specific to Guosen Securities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual retail investors, especially those with smaller portfolios, typically possess limited bargaining power. Their influence is constrained by smaller transaction volumes and a reliance on the standardized services offered by brokerage firms. However, the intense competition within the brokerage sector allows these investors to readily switch providers based on factors like fees, service quality, and platform usability.
Guosen Securities, by serving a substantial base of individual clients in China, faces a dynamic environment where customer retention is key. While individual investors may not wield significant power on their own, their collective ability to move assets in a competitive landscape means firms must continually offer attractive terms and robust services to maintain their loyalty.
High-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) wield significant bargaining power, particularly when seeking bespoke wealth management and investment advisory services. Their demand for customized strategies, competitive fees, and exclusive investment opportunities means Guosen Securities must cater to their specific needs to retain their business.
Institutional clients like corporations and investment funds wield considerable influence over Guosen Securities. Their substantial trading volumes and demand for complex services, including underwriting and asset management, give them leverage to negotiate favorable terms and specialized offerings. In 2024, Guosen Securities reported significant revenue streams from its institutional business, underscoring the importance of these relationships.
Corporate Issuers (for Investment Banking)
Corporate issuers seeking investment banking services, such as IPOs or M&A advisory, typically wield moderate to high bargaining power. This stems from the ability to select from a diverse pool of investment banks, often prioritizing those with proven track records, strong industry reputations, and competitive fee structures. For instance, in 2024, many companies were able to negotiate lower underwriting fees due to increased competition among global and domestic investment banks.
The landscape is further shaped by government-led efforts to foster robust domestic investment banking capabilities. China's ongoing drive to cultivate world-class financial institutions, as evidenced by the continued growth and expansion of firms like Guosen Securities, is expected to intensify competition. This increased competition among investment banks vying for mandates naturally enhances the bargaining leverage of corporate clients.
- Issuer Choice: Companies can choose from numerous investment banks, influencing pricing and service quality.
- Reputation & Track Record: Issuers often select banks based on past successes and industry standing.
- Competitive Landscape: Government support for domestic investment banks increases competition, benefiting issuers.
- Fee Negotiation: Issuers can leverage competition to negotiate more favorable underwriting and advisory fees.
Accessibility and Digital Platforms
The proliferation of online brokerage platforms and fintech innovations significantly enhances customer access to financial information and simplifies provider switching. This digital shift directly amplifies customer bargaining power.
In China's financial landscape, major technology companies are at the forefront of digital finance, presenting a competitive hurdle for established firms like Guosen Securities. These platforms often provide more user-friendly interfaces and competitively priced services, further concentrating power in the hands of the customer.
- Increased Information Access: Customers can easily compare fees, services, and investment options across multiple providers online.
- Ease of Switching: Digital platforms reduce the friction and cost associated with moving assets from one brokerage to another.
- Fintech Disruptors: Companies like Ant Group and Tencent's WeChat Pay are integrating financial services, offering convenient and often lower-cost alternatives.
- Competitive Pressure: The availability of these digital alternatives forces traditional firms to innovate and improve their offerings to retain clients.
The bargaining power of customers for Guosen Securities is multifaceted, influenced by investor type and the evolving digital landscape. While individual retail investors have limited individual power, their collective ability to switch providers in a competitive market compels firms to offer value. Conversely, high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients possess significant leverage due to the scale and complexity of services they demand, allowing them to negotiate terms and specialized offerings.
The rise of fintech and online platforms has dramatically increased customer bargaining power by enhancing information access and simplifying the process of switching providers. This digital transformation forces traditional firms like Guosen Securities to continually innovate and improve their services to remain competitive and retain their client base.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Retail Investors | Low to Moderate | Transaction volume, ease of switching, competitive fee structures |
| High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIs) | High | Demand for bespoke services, fee negotiation, exclusive opportunities |
| Institutional Clients | Very High | Trading volume, demand for complex services, negotiation of specialized offerings |
| Corporate Issuers (Investment Banking) | Moderate to High | Choice of investment banks, bank reputation, competitive fee negotiation |
What You See Is What You Get
Guosen Securities Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Guosen Securities details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Chinese securities market is notably crowded, with more than 140 companies actively competing. This high number of players means Guosen Securities faces intense rivalry, pushing firms to differentiate through competitive pricing, enhanced service offerings, and robust underwriting capabilities.
The Chinese government is actively pushing for mergers and acquisitions within the securities industry, a move designed to foster fewer, larger, and more globally competitive investment banks by 2035. This strategic consolidation aims to elevate the sector's overall strength and international standing.
While this consolidation may reduce the total number of securities firms, it paradoxically intensifies competition among the surviving giants. These larger entities are now locked in a fierce battle for market share and global influence, driving a more concentrated, high-stakes rivalry.
Price-based competition is a significant force within China's securities industry, intensifying rivalry among firms like Guosen Securities. This aggressive pricing, especially in areas like brokerage commissions and initial public offering (IPO) underwriting fees, can put substantial pressure on profitability across the board. For instance, some Chinese investment banks have been observed offering exceptionally low underwriting fees, sometimes as low as 1% or even less, to win mandates, a clear signal of this fierce price war.
Service Differentiation and Innovation
Guosen Securities differentiates itself by focusing on innovation and a broad spectrum of financial services. This includes adopting advanced technologies like AI and big data to offer personalized client experiences and strengthen risk management. The firm is also actively developing new financial products to meet evolving market demands.
In 2024, Guosen Securities continued to emphasize its comprehensive financial service offerings. A key strategic direction for the company involves integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles into its core business operations, aiming to attract socially conscious investors and align with global sustainability trends. This strategic move positions Guosen to capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable finance solutions.
- Service Differentiation: Guosen Securities leverages technological advancements and a diverse product suite to set itself apart in the competitive financial landscape.
- Innovation Focus: The company actively explores and implements AI and big data analytics for enhanced client services and improved risk assessment capabilities.
- ESG Integration: Guosen Securities is committed to embedding ESG principles into its business model, reflecting a forward-looking approach to financial services.
Market Volatility and Regulatory Environment
The Chinese stock market's inherent volatility, characterized by significant price swings, directly fuels intense competition among securities firms like Guosen. During periods of heightened market turbulence, such as the sharp corrections seen in early 2024, trading volumes often contract, diminishing revenue opportunities for all players and forcing them to compete more aggressively for a smaller pool of business.
Ongoing regulatory shifts in China's financial sector also play a crucial role in shaping competitive rivalry. For instance, new regulations introduced in 2024 aimed at curbing excessive speculation and improving market transparency, while beneficial for long-term stability, can temporarily disrupt business models and necessitate rapid adaptation, creating winners and losers among brokerage houses based on their agility.
- Market Volatility Impact: In Q1 2024, the Shanghai Composite Index experienced fluctuations, leading to an average daily turnover of approximately RMB 700 billion, a figure that can shrink during downturns, intensifying competition for commission-based revenues.
- Regulatory Reshaping: New rules implemented in 2024 regarding capital requirements for brokerages and restrictions on certain high-risk trading activities have forced firms to re-evaluate their strategies and product offerings, altering the competitive landscape.
- Intensified Fight for Share: As regulatory pressures and market uncertainty increase, firms are more keenly focused on retaining existing clients and attracting new ones, leading to heightened competition in areas like research quality and client service to capture market share.
The competitive rivalry within China's securities sector is exceptionally high, driven by over 140 active firms, including Guosen Securities. This intense competition compels companies to differentiate through pricing, service, and underwriting prowess, with underwriting fees sometimes dipping below 1% in 2024, highlighting aggressive price wars.
Government-backed consolidation efforts, aiming for larger, globally competitive banks by 2035, paradoxically intensify rivalry among the remaining major players. Guosen Securities counters this by focusing on innovation, leveraging AI and big data, and integrating ESG principles into its operations, as seen in its 2024 strategic focus.
| Metric | Guosen Securities (Example) | Industry Average (China) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | 1 | 140+ | High rivalry due to market saturation |
| Average IPO Underwriting Fee (2024 Estimate) | ~1.5% | ~1.0% - 1.2% | Intensifies price competition |
| Focus on ESG Integration | High (Strategic Priority) | Growing but varied | Differentiator for attracting specific investor segments |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Individuals increasingly bypass traditional securities markets by directly investing in assets like real estate or commodities. In 2024, the global real estate market continued to see significant individual investment, with many seeking tangible assets outside of stock portfolios. This direct approach reduces the need for securities firms, impacting their service demand.
Traditional commercial banks present a significant threat of substitutes for certain services offered by securities firms. These banks provide a broad spectrum of financial products, such as savings and checking accounts, various types of loans, and wealth management solutions. For instance, a retail investor looking for investment opportunities might find suitable alternatives within a bank's offerings, like mutual funds or managed accounts, directly competing with similar products from securities firms.
While banks and securities firms often work in tandem, for specific client requirements, banking products can act as a direct substitute. Consider a small business needing capital; while a securities firm might facilitate a bond issuance, a commercial bank's term loan can serve the same purpose, albeit through a different mechanism. In 2024, the banking sector continued to be a dominant force in financial intermediation, with total assets of U.S. commercial banks reaching over $23 trillion, indicating their substantial capacity to absorb demand that might otherwise flow to securities firms.
Fintech platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat of substitution for Guosen Securities. These digital disruptors offer automated, low-cost investment management and financial advice, directly challenging the traditional human-led brokerage and advisory services that form a core part of Guosen's business model. For instance, by mid-2024, the global robo-advisory market was projected to exceed $3.5 trillion in assets under management, indicating a substantial shift in consumer preference towards these more accessible and affordable alternatives.
The impact is particularly pronounced in markets where large technology firms, or Bigtechs, have entered the financial services arena. In China, for example, companies like Ant Group and Tencent have leveraged their massive user bases and advanced technological capabilities to offer a wide array of financial products and services, including wealth management and investment platforms. This has significantly disrupted the landscape for established financial institutions, forcing them to adapt or risk losing market share to these agile, tech-native competitors.
Alternative Financing Channels
Alternative financing channels present a significant threat to Guosen Securities' traditional investment banking services. For corporations, options like direct lending, private equity placements, and crowdfunding can bypass the need for initial public offerings (IPOs) or traditional bond underwriting. This diversification of capital access means fewer companies might turn to investment banks for these core services.
The evolving Chinese financial landscape further amplifies this threat. As of early 2024, direct financing levels in China have shown increasing stability, indicating a growing comfort and capacity for companies to raise funds outside of conventional bank intermediation. This trend directly impacts the demand for underwriting services, potentially reducing fee income for firms like Guosen Securities.
- Direct Lending: Offers corporations faster access to capital without the extensive regulatory hurdles of public markets.
- Private Equity: Provides significant capital injections and strategic guidance, often preferred by growth-stage companies.
- Crowdfunding: Democratizes fundraising, allowing businesses to tap into a broad base of individual investors.
- Impact on Underwriting: The rise of these channels can diminish the market share and profitability of traditional IPO and bond underwriting services.
Self-Directed Online Trading Platforms
Self-directed online trading platforms represent a significant threat of substitution for traditional brokerage services. These platforms empower individual investors to manage their own portfolios, bypassing the need for full-service brokers. This trend has been accelerating, with many users finding these digital tools more cost-effective and convenient for executing trades and accessing market data.
The increasing sophistication of these platforms allows for complex order types and real-time analytics, mirroring capabilities once exclusive to professional traders. This accessibility democratizes investment, shifting power dynamics and reducing reliance on intermediaries for basic trading functions. For instance, by late 2023, many retail investors were actively using commission-free trading apps, a stark contrast to the fee structures of a decade prior.
The threat is amplified by the continuous innovation in user experience and the integration of advanced financial tools. This leads to:
- Lower Transaction Costs: Many platforms offer commission-free trades, significantly reducing the expense for active traders.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Mobile apps and intuitive web interfaces make trading accessible from anywhere, anytime.
- Direct Market Access: Investors can bypass traditional advisory layers, making quicker decisions and executing trades directly.
- Data and Research Tools: Sophisticated platforms provide real-time market data, charting tools, and research reports, enabling informed self-directed decisions.
The rise of alternative investment avenues, such as direct real estate or commodity investments, presents a substitute for traditional securities. Many individuals in 2024 continued to allocate capital to tangible assets, reducing their reliance on stock markets and, by extension, securities firms like Guosen.
Fintech platforms and robo-advisors are increasingly offering automated, low-cost investment management, directly competing with Guosen's advisory services. By mid-2024, the global robo-advisory market was projected to manage over $3.5 trillion, highlighting a significant shift towards these digital alternatives.
Alternative financing channels, including direct lending and private equity, allow companies to bypass traditional investment banking services like IPOs and bond underwriting. China's financial landscape, with increasing direct financing levels as of early 2024, reflects this trend, potentially impacting Guosen's deal origination and fee income.
| Substitute Channel | Impact on Guosen Securities | Key Data/Trend (2024) |
| Direct Real Estate/Commodity Investment | Reduced demand for traditional securities brokerage. | Continued strong individual investment in tangible assets. |
| Fintech & Robo-Advisors | Competition for wealth management and advisory services. | Global robo-advisory market projected to exceed $3.5 trillion in AUM. |
| Alternative Financing (Direct Lending, PE) | Lower demand for IPOs and bond underwriting. | Increasing stability in China's direct financing levels. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Guosen Securities is significantly mitigated by high regulatory barriers within China's financial services sector. Obtaining the necessary licenses and demonstrating substantial capital reserves, as mandated by bodies like the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), presents a formidable challenge for aspiring firms. This stringent oversight, coupled with the need for robust compliance infrastructure, makes establishing a foothold exceptionally difficult.
Building a full-service financial institution like Guosen Securities, encompassing brokerage, investment banking, and asset management, necessitates immense upfront capital. For instance, in 2023, the total assets of the Chinese securities industry exceeded 16 trillion RMB, highlighting the scale of investment required. This significant financial hurdle deters many aspiring firms from entering the market.
Established brand reputation and trust act as a significant barrier to new entrants in the securities industry. Guosen Securities, with three decades of operation, has cultivated strong brand recognition and client loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Building this level of credibility and an extensive network in a market where trust is paramount requires substantial time and investment, posing a considerable hurdle for potential competitors.
Technological Investment and Expertise
Developing and maintaining cutting-edge financial technology, such as AI-driven analytics and robust trading platforms, demands substantial and continuous capital outlay. For instance, in 2024, major financial institutions are projected to invest billions in digital transformation initiatives, with a significant portion allocated to technology infrastructure and talent acquisition. This high barrier to entry deters many potential new players.
New entrants would need to demonstrate a significant technological leap to even approach the capabilities of established firms. This includes not only the initial development but also the ongoing maintenance and upgrades required to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Without this, their offerings would likely be perceived as outdated.
Consider the specialized expertise required: data scientists, cybersecurity professionals, and blockchain developers are in high demand and command premium salaries. A new entrant must assemble a team with this advanced knowledge, adding considerably to their operational costs and making it difficult to match the innovation pace of incumbents.
- High Capital Expenditure: Significant investment needed for advanced trading platforms and AI.
- Specialized Talent Acquisition: High demand and cost for data scientists and cybersecurity experts.
- Continuous Innovation: Ongoing R&D essential to remain competitive against established tech investments.
Intense Competition from Incumbents
New entrants into the Chinese securities market, like Guosen Securities operates within, would immediately confront fierce competition from established domestic firms. This market, while fragmented, is also undergoing consolidation, meaning newcomers would face a crowded field of players, including large state-backed entities and other significant brokerages.
The existing competitive landscape is already intense, making it a considerable challenge for any new firm to carve out a significant market share. For instance, as of the end of 2023, China had over 140 licensed securities firms, with the top 10 accounting for a substantial portion of market share in key areas like underwriting and brokerage.
- Market Share Concentration: The top 10 securities firms in China held approximately 50% of the total brokerage market share in 2023, indicating a high degree of concentration.
- Capital Requirements: Establishing a securities firm in China requires significant capital, with minimum registered capital requirements often exceeding RMB 1 billion, creating a high barrier to entry.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating China's complex and evolving financial regulations, overseen by bodies like the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), presents a substantial challenge for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Guosen Securities is low due to substantial capital requirements, stringent regulatory approvals from bodies like the CSRC, and the need for significant technological investment. For instance, in 2023, the total assets of the Chinese securities industry surpassed 16 trillion RMB, underscoring the immense financial scale required to compete effectively. Furthermore, established brand loyalty and the high cost of acquiring specialized talent in areas like AI and cybersecurity present significant hurdles for newcomers.
The existing competitive landscape in China's securities market is already intense, with over 140 licensed firms as of late 2023. The top 10 firms alone controlled a significant market share, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Requirements | Strict licensing and compliance mandated by CSRC. | High; significant time and resources needed for approval. |
| Capital Investment | Massive upfront capital for operations and technology. | High; deters firms lacking substantial funding. |
| Brand & Trust | Established reputation and client networks of incumbents. | High; difficult for newcomers to build credibility. |
| Technology & Talent | Need for advanced platforms and specialized expertise. | High; requires continuous, costly R&D and recruitment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Guosen Securities Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data, including financial reports, industry-specific research, and market intelligence from leading financial data providers, to offer a robust assessment of the competitive landscape.
