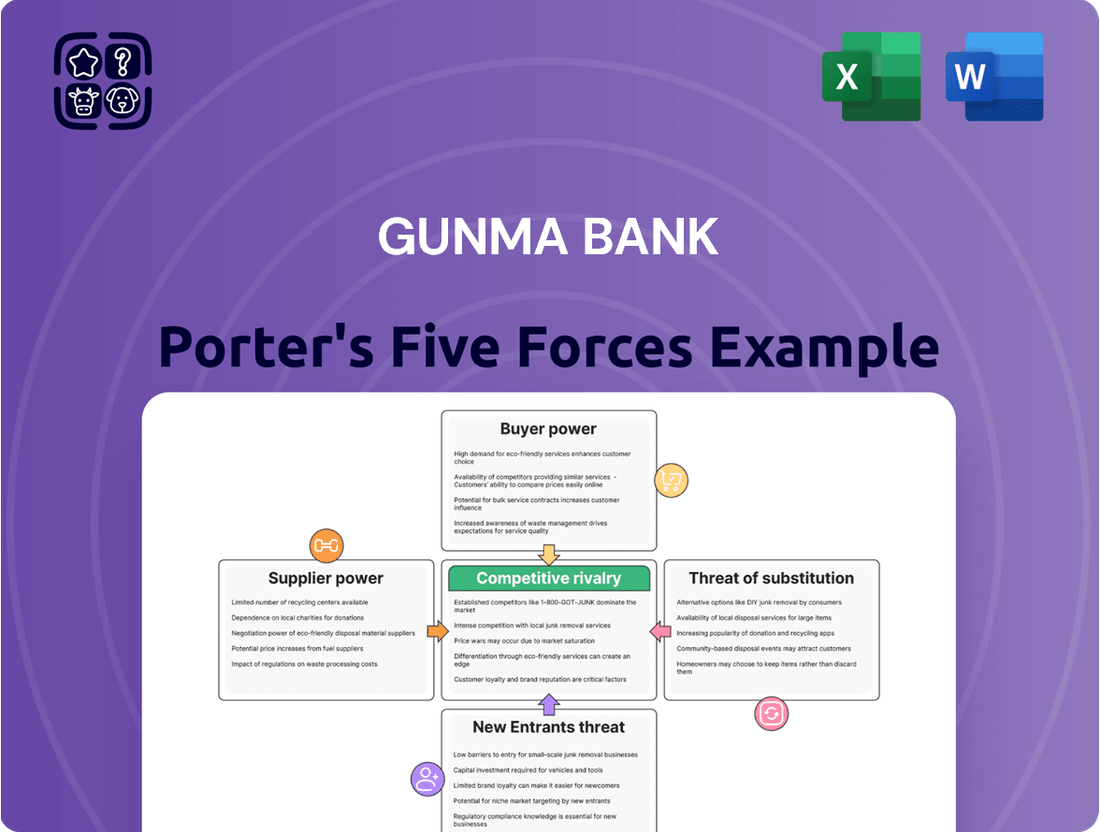
Gunma Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gunma Bank Bundle
Gunma Bank operates in a dynamic banking landscape, where understanding the intensity of industry competition is paramount. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intricate interplay of forces like buyer bargaining power and the threat of new entrants, directly impacting Gunma Bank's strategic positioning. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Gunma Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
For Gunma Bank, the primary inputs are customer deposits and investor capital, meaning suppliers are largely the general public and capital markets. The Bank of Japan's monetary policy significantly influences the cost of these funds. In Q4 2024, the BOJ's policy rate remained at 0.25%, but projections suggest a potential rise to 0.5% by 2025, which would increase borrowing costs for banks like Gunma.
As Gunma Bank, like many Japanese regional banks, pushes forward with digital transformation, the influence of technology and infrastructure providers is on the rise. These suppliers, offering everything from core banking software to cloud computing and cybersecurity, are becoming increasingly vital to the bank's operational efficiency and competitive edge.
In 2024, the banking sector's reliance on these tech partners is undeniable. For instance, global spending on financial technology (FinTech) solutions was projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant investment in these areas. Gunma Bank's strategic focus on digital initiatives means that the bargaining power of these technology vendors, who can dictate terms based on the uniqueness and necessity of their offerings, is substantial.
Skilled human capital, particularly in digital finance, AI, and robust risk management, acts as a crucial supplier for banks like Gunma Bank. The intense competition for these specialized skills significantly impacts a bank's ability to innovate and maintain operational efficiency.
In Japan, the banking sector faces a growing deficit in IT and digital talent. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of Japanese financial institutions reported difficulties in recruiting personnel with advanced digital skills, directly affecting their capacity to implement new technologies and services.
Gunma Bank's success in attracting and retaining top-tier talent in these critical areas directly influences its competitive edge. The bargaining power of these skilled individuals, therefore, is substantial, as their expertise is indispensable for the bank's future growth and technological advancement.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Services
Regulatory bodies, like Japan's Financial Services Agency (FSA), exert considerable influence as suppliers by granting operating licenses and dictating compliance standards. Banks must constantly adapt to new rules, such as those concerning digital innovation and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, which can significantly increase operational expenses.
These regulatory demands translate into tangible costs. For instance, in 2024, Japanese banks, including Gunma Bank, are expected to dedicate substantial resources to cybersecurity enhancements and data privacy compliance, driven by stricter data protection laws. The ongoing digital transformation initiatives within the banking sector also necessitate investment in new technologies and training to meet regulatory expectations for secure and efficient online services.
- Increased Compliance Costs: Banks face rising expenses for adhering to evolving financial regulations, including those related to digital assets and anti-money laundering (AML) measures.
- FSA Oversight: The Financial Services Agency (FSA) in Japan plays a critical role in setting operational standards and enforcing compliance, directly impacting bank operations.
- Digital Transformation Demands: Regulations often mandate specific security protocols and customer protection measures for digital banking services, adding to implementation costs.
Interbank Market and Funding Sources
While customer deposits form the bedrock of Gunma Bank's funding, its reliance on interbank markets and other wholesale sources is significant. These alternative funding channels, crucial for liquidity management and meeting lending demands, can expose the bank to the volatility of broader financial conditions. For instance, in early 2024, the Bank of Japan's monetary policy shifts, including the gradual move away from negative interest rates, directly impacted the cost of funds in these wholesale markets, influencing Gunma Bank's overall cost of funding.
The bargaining power of suppliers in this context relates to the institutions and markets providing these wholesale funds. Factors such as the overall liquidity in the Japanese financial system, the Bank of Japan's quantitative easing or tightening measures, and the creditworthiness of other financial institutions directly influence the availability and pricing of these funds. For example, if interbank liquidity tightens, as it can during periods of financial stress, the cost of borrowing for banks like Gunma Bank will inevitably rise, increasing the bargaining power of the lenders.
- Interbank Market Dependence: Gunma Bank, like many regional banks, utilizes the interbank market to manage short-term liquidity needs beyond its deposit base.
- Wholesale Funding Costs: The cost of these wholesale funds is sensitive to market conditions and central bank policy, directly impacting profitability.
- BOJ Influence: Bank of Japan's monetary policy decisions, such as interest rate adjustments or changes in asset purchases, significantly shape the pricing and availability of funds in these markets.
- Supplier Power Dynamics: The bargaining power of suppliers (providers of wholesale funds) increases when overall market liquidity is constrained or when demand for funds is high.
Gunma Bank's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by its reliance on customer deposits and capital markets. The Bank of Japan's monetary policy, such as its policy rate, directly impacts the cost of funds. Technology providers are gaining influence due to the bank's digital transformation, with global FinTech spending projected to exceed $300 billion in 2024, underscoring the importance of these vendors.
Skilled labor, especially in digital finance and risk management, acts as a crucial supplier, with over 60% of Japanese financial institutions reporting difficulty in recruiting digital talent in 2024. Regulatory bodies like the FSA also hold significant power, imposing compliance costs related to digital innovation and ESG criteria, with Japanese banks investing heavily in cybersecurity and data privacy in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Key Influences | 2024 Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|
| Depositors/Capital Markets | Bank of Japan Monetary Policy, Market Liquidity | BOJ Policy Rate: 0.25% (Q4 2024), potential 0.5% by 2025 |
| Technology Providers | Digital Transformation Needs, Software/Cloud Services | Global FinTech Spending: >$300 billion (2024 projection) |
| Skilled Human Capital | Demand for Digital/AI/Risk Management Expertise | 60%+ Japanese FIs reporting digital talent recruitment difficulty (2024) |
| Regulatory Bodies (FSA) | Compliance Standards, Digital Security, Data Privacy | Increased investment in cybersecurity & data privacy by Japanese banks (2024) |
What is included in the product
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to Gunma Bank, dissecting the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its strategic positioning.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Gunma Bank's industry landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual customers, particularly in today's economic climate, are highly attuned to interest rates and bank fees. For instance, in early 2024, many retail customers were actively comparing deposit rates across institutions, seeking the best yields for their savings. This heightened awareness puts pressure on banks like Gunma Bank to offer competitive rates and transparent fee structures to retain and attract depositors.
Furthermore, the growing interest in alternative investments such as mutual funds and real estate, driven by the pursuit of higher returns, signifies a shift in customer behavior. As of the first quarter of 2024, data showed a notable uptick in retail investment flows into these sectors, suggesting customers are less tethered to traditional banking products if better opportunities exist elsewhere. This trend compels banks to innovate their product suites, perhaps by offering more attractive savings accounts or tailored investment solutions, to maintain customer loyalty and bargaining power.
Corporate clients, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) within Gunma Prefecture, increasingly seek financial institutions that offer specialized, customized solutions and expert advice. Their ability to negotiate favorable terms is amplified when they maintain relationships with several banks or if a particular bank's offerings, like trade finance, fall short of their unique operational requirements, particularly when facing global export headwinds.
Customers in Japan are increasingly expecting highly convenient digital and mobile banking solutions. This shift is driven by the growing availability of sophisticated fintech services.
The proliferation of digital banks and fintech innovators in Japan significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. These alternatives offer seamless experiences in payments, lending, and wealth management, making it easier for customers to switch if traditional banks like Gunma Bank lag in digital offerings.
For instance, by the end of 2023, Japan's digital payment market was projected to reach ¥123.5 trillion, indicating a strong consumer preference for digital transactions. This trend underscores the pressure on established banks to enhance their digital platforms to retain and attract customers.
Local Market Concentration and Relationships
Gunma Bank's strong presence within its home region fosters deep local relationships, which can translate into significant customer loyalty. This localized approach means customers often feel a personal connection to the bank, making them less likely to switch. For instance, in 2023, Gunma Bank reported a customer base heavily concentrated in the Gunma Prefecture, underscoring the importance of these regional ties.
However, this loyalty can be tested if competitors, particularly larger national banks or agile digital-only banks, present more compelling local offerings. These rivals might leverage economies of scale or innovative technology to provide superior rates or services specifically tailored to the Gunma market. A prime example is the increasing competition from fintech companies that offer streamlined digital banking experiences, potentially attracting customers who prioritize convenience and competitive pricing over established local relationships.
- Local Focus: Gunma Bank's strategy emphasizes building strong relationships within its primary operating region, fostering customer loyalty.
- Competitive Threats: National banks and digital challengers can erode this loyalty by offering more attractive local solutions or superior digital services.
- Customer Loyalty Factors: Loyalty is influenced by the perceived value and convenience offered by both incumbent and new market entrants.
Aging Population and Financial Literacy
Japan's aging population, representing a significant portion of Gunma Bank's customer base, often exhibits lower financial literacy and a preference for traditional banking methods. This demographic's specific needs, such as simpler transaction processes and accessible in-person support, directly influence the bank's service offerings and customer acquisition strategies.
As of 2024, over 30% of Japan's population is aged 65 or older, a trend that continues to grow. This segment may be less inclined to adopt digital banking solutions, potentially limiting the bank's ability to streamline operations and reduce costs through technology. Consequently, Gunma Bank must balance digital innovation with the continued provision of traditional, personalized services to retain this crucial customer group.
- Aging Demographic: Over 30% of Japan's population is projected to be 65+ in 2024, a key customer segment.
- Financial Literacy Gap: This group may require more tailored financial education and simpler product offerings.
- Service Adaptation: Banks must invest in accessible branches and customer support alongside digital channels.
- Customer Retention: Meeting the unique needs of older customers is vital for Gunma Bank's stability.
Customers' bargaining power at Gunma Bank is significant, driven by increased price sensitivity and the availability of alternatives. In early 2024, customers actively sought better deposit rates, pressuring banks like Gunma to offer competitive yields. The growing appeal of investments beyond traditional banking, such as mutual funds, further highlights this power as customers explore higher returns elsewhere.
Digitalization amplifies this trend, with fintech and digital banks offering seamless experiences that challenge traditional institutions. Japan's digital payment market, projected to reach ¥123.5 trillion by the end of 2023, underscores a strong consumer preference for digital convenience, forcing banks to enhance their online platforms.
While Gunma Bank benefits from strong local relationships, this loyalty can be tested by national banks and digital challengers offering superior local or digital solutions. For instance, the increasing competition from fintech companies providing streamlined digital banking experiences pressures established banks to match convenience and competitive pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Gunma Bank | Customer Action |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on interest rates and fees | Seeking higher yields, comparing offers |
| Alternative Investments | Reduced reliance on traditional banking products | Shifting funds to mutual funds, real estate |
| Digitalization & Fintech | Need for enhanced digital platforms | Switching to digital banks for convenience |
| Local Relationships vs. Competition | Loyalty can be eroded by better offers | Evaluating national banks and digital challengers |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Gunma Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Gunma Bank, detailing the industry's competitive landscape. You're looking at the actual document, which meticulously breaks down the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Gunma Bank contends with formidable rivals in the form of Japan's major megabanks, including Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG), Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group (SMFG), and Mizuho Financial Group. These giants possess substantially greater financial resources, a wider array of financial products and services, and are making significant investments in digital innovation. For instance, as of early 2024, MUFG reported total assets exceeding ¥330 trillion, dwarfing regional banks like Gunma Bank, which had total assets around ¥9 trillion as of March 2024. This disparity in scale allows megabanks to absorb greater technological development costs and offer more competitive pricing.
The Japanese banking sector is densely populated with regional banks, creating intense localized competition for both customer deposits and loan opportunities. This fragmented market means Gunma Bank faces numerous rivals vying for the same financial business within its operating regions.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by ongoing consolidation within the regional banking industry. Notably, Gunma Bank itself is actively pursuing a business integration through a memorandum of understanding with Daishi Hokuetsu Financial Group, underscoring the dynamic and evolving nature of competition it navigates.
The emergence of digital-only banks and innovative fintech companies is significantly ramping up competitive rivalry for traditional institutions like Gunma Bank. These agile players, such as Rakuten Bank and SBI Sumishin Net Bank in Japan, are capturing market share by offering streamlined digital payment solutions, accessible online lending platforms, and user-friendly investment services. In 2023, Japan's digital banking sector saw continued growth, with fintech adoption rates rising, putting pressure on established banks to enhance their digital offerings to remain competitive.
Low-Interest-Rate Environment and Profitability Pressures
Japan's prolonged period of low interest rates has significantly squeezed banks like Gunma Bank, directly impacting their net interest margins. This financial pressure compels institutions to diversify revenue streams, often by focusing on fee-generating services and streamlining operations to maintain profitability.
The intense competition in this low-yield landscape means banks are constantly battling for a larger slice of a shrinking profit pie. This environment fuels aggressive strategies as each institution strives to capture market share and offset the margin compression.
- Net Interest Margin Pressure: Historically, Japanese banks have seen net interest margins hover around 0.5% to 1%, a stark contrast to higher rates seen elsewhere.
- Shift to Fee Income: This necessitates a greater reliance on non-interest income sources, such as commissions from financial products and transaction fees.
- Operational Efficiency Drive: Banks are investing in technology and process improvements to reduce costs and enhance productivity.
- Intensified Competition: The struggle for profitability exacerbates rivalry among domestic banks and increasingly, regional financial institutions.
Demographic Challenges and Shrinking Domestic Market
Japan's demographic headwinds present a significant challenge for Gunma Bank. The nation's declining and aging population directly translates to a shrinking domestic market, dampening overall consumption and, crucially, loan demand. This is particularly acute for regional banks heavily reliant on local economic activity.
The intensified competition for a diminishing customer base forces banks like Gunma to seek greater efficiencies and explore avenues for strategic diversification. In 2024, Japan's birth rate continued its downward trend, with preliminary data suggesting a further decrease from the 758,631 births recorded in 2023. This ongoing demographic shift exacerbates the pressure on traditional banking models.
- Shrinking Consumer Base: A declining birthrate and an aging population reduce the pool of potential borrowers and depositors.
- Reduced Loan Demand: Fewer young people entering the workforce and a generally aging population can lead to lower overall demand for loans, impacting revenue streams.
- Increased Competition: With fewer customers available, regional banks face fiercer competition for market share, potentially driving down interest margins.
- Necessity for Diversification: To counter these trends, banks must explore new revenue streams beyond traditional lending, such as wealth management or fee-based services.
Gunma Bank faces intense rivalry from larger megabanks like MUFG, which boast significantly greater resources and digital investment capacity, as evidenced by MUFG's ¥330 trillion in total assets compared to Gunma Bank's ¥9 trillion as of March 2024. The regional banking sector is also highly fragmented, with numerous local competitors vying for the same customers and loan opportunities. Furthermore, the rise of agile fintechs and digital-only banks, such as Rakuten Bank, is increasing pressure on traditional players to innovate their digital offerings.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Gunma Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Megabanks (e.g., MUFG) | Vast financial resources, broad product range, heavy digital investment | Superior ability to absorb costs, offer competitive pricing, and drive digital innovation |
| Other Regional Banks | Numerous local competitors | Intense competition for deposits and loans within operating regions |
| Fintech & Digital Banks | Agile, user-friendly digital platforms, streamlined services | Capturing market share, forcing traditional banks to accelerate digital transformation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of digital payment platforms and e-wallets like PayPay and LINE Pay presents a substantial threat of substitution for traditional banking services in Japan. These services are increasingly preferred for everyday transactions, offering a streamlined and often quicker alternative to conventional methods. By mid-2024, Japan's digital payment market was experiencing robust growth, with user penetration rates for mobile payments exceeding 60% in major urban areas, indicating a clear shift in consumer behavior away from traditional bank-centric transactions.
Non-bank direct lending and peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms present a significant threat of substitution for Gunma Bank. These alternatives offer quicker loan approvals and more flexible terms, particularly appealing to small businesses and individuals who may find traditional banking processes cumbersome. For instance, the UK P2P lending market saw significant growth, with platforms facilitating billions in loans, demonstrating a clear alternative for borrowers.
Customers are increasingly looking beyond traditional bank deposits for better returns, especially when interest rates are low. In 2024, we've seen a significant move towards alternative investments like mutual funds, ETFs, and direct real estate investments, with global assets under management in alternative investments projected to reach $22.1 trillion by 2026, according to Preqin. This shift directly impacts banks' ability to retain deposit bases, forcing them to compete with a wider array of wealth management solutions.
The proliferation of user-friendly investment platforms and robo-advisors further lowers the barrier to entry for alternative investments, making them more accessible to a broader range of individuals. For instance, the global robo-advisor market was valued at approximately $3.1 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially. This accessibility means Gunma Bank faces a growing threat from non-bank financial institutions and fintech companies offering sophisticated wealth management services, often with lower fees.
Consequently, banks like Gunma Bank must enhance their advisory capabilities and product offerings to retain customers. Simply offering deposit accounts is no longer sufficient when individuals can easily access diversified portfolios and potentially higher yields through other channels. The need to provide value-added services, such as personalized financial planning and investment guidance, becomes paramount to counter the threat of substitutes.
Crowdfunding and Alternative Funding Sources
Crowdfunding and alternative funding sources present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional bank loans, including those offered by Gunma Bank. These platforms allow businesses to access capital from a wide array of individual and institutional investors, often bypassing the stringent requirements of conventional banking. For instance, by mid-2024, the global crowdfunding market was projected to reach over $300 billion, demonstrating its growing capacity to fund businesses of all sizes.
These alternative channels provide a viable substitute by democratizing access to capital. Businesses can leverage platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo for project-based funding or explore peer-to-peer lending services for more general operational capital. The ease of access and speed of deployment can make these options particularly attractive, especially for startups and small to medium-sized enterprises that might struggle with traditional loan approvals.
The increasing sophistication and regulatory clarity surrounding alternative finance further solidify their position as substitutes. By 2024, many countries have established frameworks to govern crowdfunding and P2P lending, building investor confidence and expanding the pool of available funds. This trend suggests that businesses will continue to diversify their funding strategies away from solely relying on banks.
Key aspects of this threat include:
- Diversified Capital Access: Businesses can tap into a global network of investors, reducing reliance on a single financial institution.
- Faster Funding Cycles: Alternative platforms often offer quicker approval and disbursement processes compared to traditional loans.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: Startups and smaller businesses may find it easier to secure funding through crowdfunding or P2P lending.
- Increased Investor Participation: The growth of alternative finance has broadened the investor base, providing more capital options for businesses.
Emergence of Embedded Finance
The rise of embedded finance presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. This trend integrates financial products directly into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce sites or ride-sharing apps. For instance, a customer can secure a loan or make a payment without ever needing to visit a bank's website or app.
This seamless integration means consumers can access financial solutions at the point of need, directly within their everyday activities. This bypasses the traditional banking channel, reducing customer reliance on banks for basic financial transactions and lending. By 2024, the global embedded finance market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating its rapid growth and disruptive potential.
- Seamless Integration: Financial services are now part of user journeys on non-financial platforms.
- Reduced Bank Interaction: Customers can access loans, payments, and insurance without directly engaging with a bank.
- Market Growth: The embedded finance sector experienced substantial growth through 2024, indicating increasing adoption.
- Customer Convenience: This model prioritizes convenience, offering financial products at the point of sale or service.
The threat of substitutes for Gunma Bank is amplified by the growing accessibility of alternative investment vehicles and wealth management tools. As of 2024, global assets in alternative investments are projected to reach $22.1 trillion by 2026, indicating a significant shift away from traditional bank deposits for yield. Robo-advisors, valued at approximately $3.1 billion in 2023, further democratize sophisticated investment strategies, often at lower costs, directly challenging banks' traditional roles.
Digital payment platforms and non-bank lending services represent substantial substitutes, offering convenience and speed for everyday transactions and business financing. Japan's digital payment market, with user penetration exceeding 60% in urban areas by mid-2024, highlights a clear consumer preference shift. Similarly, the global crowdfunding market, projected to surpass $300 billion by mid-2024, provides businesses with accessible capital alternatives.
Embedded finance, integrating financial services into non-financial platforms, further erodes traditional banking engagement. This trend, with the global embedded finance market projected to reach hundreds of billions by 2024, allows customers to access loans and payments at their point of need, bypassing banks entirely.
| Threat of Substitution | Description | 2024 Market Data/Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments & E-wallets | Streamlined, faster alternatives for everyday transactions. | User penetration >60% in Japanese urban areas (mid-2024). |
| Non-Bank Lending & P2P Platforms | Quicker loan approvals and flexible terms for businesses and individuals. | UK P2P market facilitated billions in loans. |
| Alternative Investments (Funds, ETFs, Real Estate) | Higher potential returns compared to traditional bank deposits. | Global AUM in alternatives projected to reach $22.1T by 2026. |
| Robo-Advisors | Accessible, lower-fee wealth management services. | Global robo-advisor market valued at ~$3.1B (2023). |
| Crowdfunding & Alternative Funding | Bypasses traditional requirements for business capital. | Global crowdfunding market projected to exceed $300B (mid-2024). |
| Embedded Finance | Financial products integrated into non-financial platforms. | Global market projected to reach hundreds of billions (2024). |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector in Japan, overseen by the Financial Services Agency (FSA), presents substantial regulatory hurdles for potential new entrants. Strict licensing procedures and rigorous capital adequacy ratios, such as the Basel III framework, demand significant upfront investment and compliance expertise, effectively deterring many new traditional banking operations.
The threat of new entrants for Gunma Bank is moderate, largely due to high capital intensity. Launching a new banking operation demands significant upfront investment in regulatory compliance, robust IT infrastructure, and a physical or digital presence, easily running into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, establishing a fully digital bank still requires substantial expenditure on cybersecurity and user experience platforms.
Existing institutions like Gunma Bank leverage considerable economies of scale. This means they can spread their fixed costs over a larger customer base and transaction volume, leading to lower average costs per service. New entrants would struggle to match these cost efficiencies initially, making it challenging to offer competitive pricing on loans and deposits from the outset.
Established regional banks like Gunma Bank benefit from deep-rooted brand recognition and customer trust, cultivated over years of service. For instance, Gunma Bank’s strong local presence and history in the Gunma prefecture foster a sense of reliability that new entrants struggle to replicate. This established trust is a significant barrier, as financial institutions rely heavily on customer confidence for deposits and lending.
Access to Funding and Deposit Bases
New entrants in the banking sector, particularly in regions like Gunma, face significant hurdles in establishing a competitive funding structure. Attracting a substantial and stable deposit base, the lifeblood of traditional banking, is a formidable challenge when competing against established institutions with deep-rooted customer loyalty and extensive existing deposit pools. For instance, as of early 2024, major Japanese banks, including those with a strong presence in regional markets, generally maintained significantly higher total deposits compared to newly formed financial entities. This disparity directly impacts a new bank's ability to fund its lending activities and operational growth.
The established financial infrastructure and customer relationships of incumbent banks like Gunma Bank create a substantial barrier. These existing players have cultivated trust and convenience over years, making it difficult for newcomers to siphon off market share.
- Established Deposit Advantage: Incumbent banks, such as Gunma Bank, benefit from a large and loyal customer base that provides a consistent and cost-effective source of funding through deposits.
- Funding Cost Disparity: New entrants often face higher initial costs to attract deposits, potentially leading to a disadvantage in interest rate competitiveness for loans compared to established banks.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Securing necessary capital and licenses to operate a banking institution is a complex and resource-intensive process, further deterring potential new entrants.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Decades of operation build brand recognition and trust, which are critical for attracting and retaining depositors, a factor new banks must overcome.
Fintech Companies and Digital Banking Licenses
The threat of new entrants for traditional banks like Gunma Bank is evolving. While establishing a full-service bank remains capital-intensive and heavily regulated, fintech companies are finding ways to enter specific market segments. These entrants often leverage specialized digital banking licenses or strategic partnerships to offer niche services.
Japan's government is actively encouraging fintech innovation, which is fostering the emergence of new digital banks. For instance, in 2023, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) continued its focus on digital transformation within the financial sector. These new players can bypass some of the legacy infrastructure costs of traditional banks.
- Fintech Entry: Fintechs can enter by obtaining specific digital banking licenses or partnering with existing institutions.
- Government Support: Japan's government actively promotes fintech development, lowering barriers for new digital banks.
- Market Segmentation: New entrants often target specific, profitable segments of the banking market rather than competing across the board.
The threat of new entrants for Gunma Bank remains moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and stringent regulatory frameworks in Japan's banking sector. Establishing a new bank necessitates substantial investment in technology, compliance, and obtaining licenses, which can easily reach hundreds of millions of dollars, as seen with the capital needs for digital banking initiatives.
While traditional banking faces high entry barriers, the rise of fintech companies presents a more nuanced threat. These agile players can target specific market niches, often by partnering with existing institutions or obtaining specialized digital licenses, thereby circumventing some of the legacy infrastructure costs faced by established banks.
Gunma Bank benefits from established economies of scale and strong brand recognition, which new entrants find difficult to match. For instance, as of early 2024, major Japanese banks typically held significantly larger deposit bases than emerging financial entities, providing a cost advantage in funding.
The Japanese government's support for fintech innovation, exemplified by the FSA's focus on digital transformation in 2023, is creating pathways for new digital banks. These newcomers can leverage technology to offer specialized services, potentially disrupting traditional banking models by focusing on customer segments underserved by incumbents.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Gunma Bank is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including the bank's annual reports, financial statements, and disclosures from regulatory bodies. We also incorporate industry-specific research from financial publications and market analysis firms to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
