Grupo Catalana Occidente Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Grupo Catalana Occidente Bundle
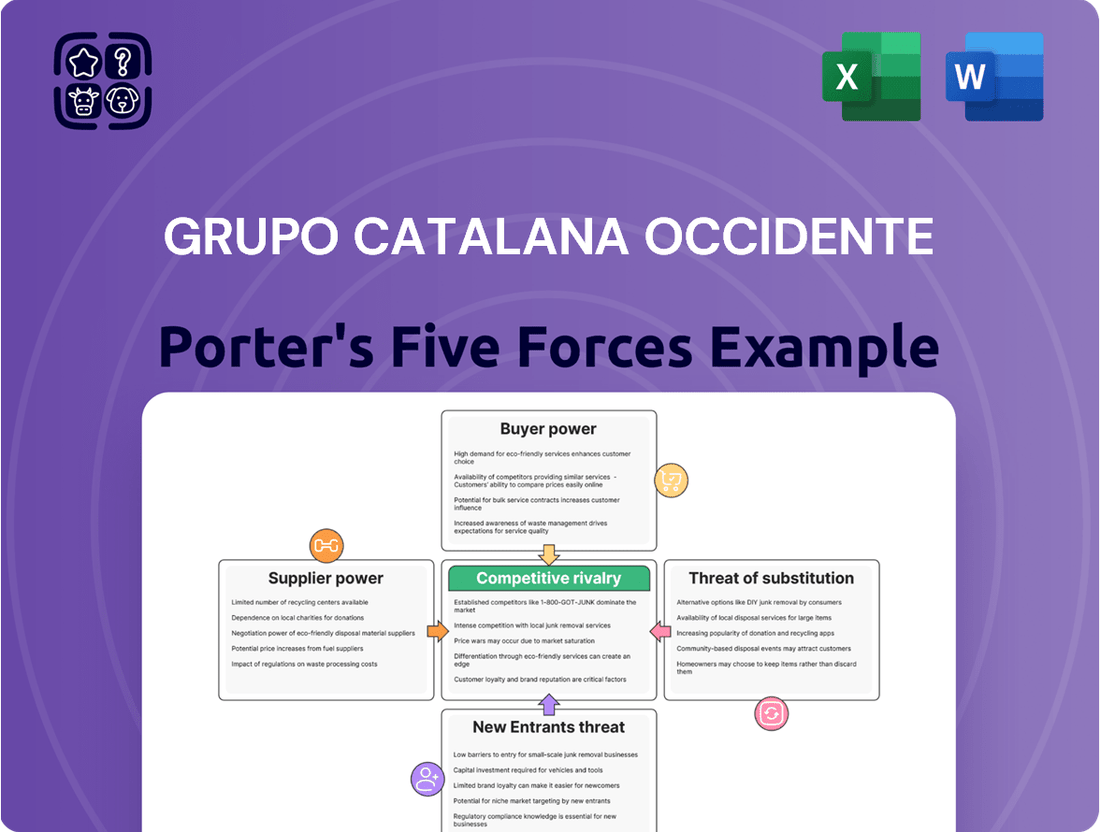
Grupo Catalana Occidente navigates a competitive insurance landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and intense rivalry among existing players. The threat of substitutes, while present, is somewhat mitigated by the specialized nature of insurance products.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Grupo Catalana Occidente’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) and other insurers depend on reinsurers for risk management and capital relief. The reinsurance market, particularly in 2024, has seen sustained high pricing, making risk transfer more expensive for primary insurers like GCO.
Despite rising reinsurance costs, European insurers, including GCO, generally maintain strong capital positions. For instance, GCO reported a robust solvency ratio, which helps them absorb some of the increased supplier costs and lessens the bargaining power of reinsurers.
The insurance sector's embrace of advanced technologies like AI and data analytics is significant. Grupo Catalana Occidente's (GCO) investment in AI and robotics for its Atradius subsidiary exemplifies this trend, underscoring a growing dependence on specialized tech providers. These vendors, particularly those offering unique or mission-critical solutions for efficiency and customer experience, can wield considerable bargaining power.
Grupo Catalana Occidente's reliance on highly skilled actuaries, underwriters, IT experts, and specialized sales teams significantly influences supplier power. These professionals are the backbone of delivering complex risk management solutions.
The increasing demand for data scientists and AI specialists within the insurance industry, a trend clearly visible in 2024, grants these individuals considerable leverage regarding salaries and benefits. Insurers are actively competing for this specialized talent.
Attracting and retaining this crucial human capital remains a paramount strategic objective for Grupo Catalana Occidente, directly impacting operational efficiency and innovation in a competitive market.
Capital Providers and Financial Markets
Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) benefits from a robust financial standing and high solvency, yet its access to capital markets remains crucial for funding strategic initiatives like acquisitions and maintaining regulatory capital requirements. The current interest rate environment, which has seen increases, is actually proving beneficial for insurers' investment returns.
Capital providers, including financial institutions and bondholders, wield influence through their decisions on the cost and availability of funding. This dynamic directly impacts GCO's financial strategy and its capacity for expansion. For instance, in 2023, GCO reported a solvency ratio of 214%, demonstrating its strong capital base, which can positively influence its borrowing costs.
- Cost of Capital: Higher interest rates in 2024 generally increase the cost of debt financing, potentially impacting GCO's expansion plans if not offset by strong investment returns.
- Investor Confidence: Strong investor confidence, often reflected in credit ratings, can lower borrowing costs and improve access to capital, a factor GCO actively manages.
- Regulatory Capital: Maintaining adequate capital buffers, as mandated by Solvency II, requires continuous access to capital markets to ensure compliance and financial stability.
Service Providers for Claims
For traditional insurance lines, Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) relies on a network of service providers for claims management, including repair shops, medical facilities, and legal professionals. The widespread availability and competition among many of these providers typically reduce their individual ability to dictate terms. However, providers offering highly specialized or in-demand services may indeed wield more influence over costs.
Inflationary trends can significantly affect the operational expenses of these service providers, potentially leading to increased costs for GCO. For instance, rising labor costs in the automotive repair sector or increased medical supply prices can directly translate to higher claims payouts for GCO. In 2024, the automotive repair industry, a key service provider for property and casualty insurance, continued to grapple with elevated parts costs, with some component prices seeing increases of 5-10% year-over-year due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand.
- Fragmented Provider Landscape: The majority of service providers for claims handling are numerous and operate in a competitive environment, limiting individual bargaining power.
- Specialization and Demand: Providers with unique expertise or those facing high demand for their services can exert greater influence on pricing.
- Inflationary Impact: Rising costs for labor and materials in sectors like automotive repair and healthcare directly impact the expenses incurred by insurers like GCO.
- 2024 Cost Pressures: Specific sectors, such as auto repair, experienced notable cost increases in 2024, affecting claims handling expenses.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) is a multifaceted consideration, influenced by reinsurers, technology providers, specialized talent, and claims service providers. While GCO's strong financial health, evidenced by a 214% solvency ratio in 2023, offers some buffer against cost increases, the specialized nature of certain inputs grants suppliers leverage.
The increasing reliance on AI and data science talent, with demand surging in 2024, positions these professionals as powerful suppliers of critical human capital. Similarly, specialized technology providers offering unique solutions for efficiency can command higher prices, as seen with GCO's investments in AI for its Atradius subsidiary. Even in traditional claims management, providers with unique expertise or those facing high demand can influence costs, a trend exacerbated by inflationary pressures in sectors like automotive repair, which saw 5-10% increases in parts costs in 2024.
| Supplier Type | Influence Factors | Impact on GCO | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Risk transfer costs, capital relief | Increased cost of risk management | Sustained high pricing |
| Tech Providers (AI/Data) | Specialized solutions, mission-criticality | Higher costs for advanced capabilities | Growing demand for AI specialists |
| Specialized Talent (Actuaries, Data Scientists) | Scarcity, in-demand skills | Increased labor costs, competition for talent | High demand for data scientists |
| Claims Service Providers (e.g., Auto Repair) | Specialization, demand, inflation | Potential for higher claims expenses | Elevated parts costs (5-10% increase) |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products impacting Grupo Catalana Occidente's insurance market position.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces, enabling rapid identification of key challenges for Grupo Catalana Occidente.
Easily adapt the analysis to reflect shifts in supplier power or the threat of substitutes, providing a dynamic tool for proactive strategy adjustment.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers today, both individuals and businesses, possess unprecedented access to information about insurance products, pricing, and service quality. Online aggregators and digital platforms have made it incredibly easy to compare offerings from various providers. This surge in information transparency significantly boosts the bargaining power of customers.
With the ability to readily compare policies and prices, customers can negotiate more effectively for better terms and personalized solutions. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spent several hours researching insurance options online before making a purchase, indicating a strong reliance on accessible data to inform their decisions. This empowers them to demand more competitive pricing and superior service from insurers like Grupo Catalana Occidente.
Modern consumers and businesses increasingly demand digital convenience and personalized interactions. For Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO), this means investing heavily in digital platforms that allow for seamless policy management and efficient claims processing via mobile devices. Failure to meet these expectations, such as slow response times or a lack of personalized digital tools, can directly lead to customers seeking alternatives, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Customers are increasingly sensitive to price, especially with rising premiums for essential insurance like car insurance. In 2024, many consumers are actively comparing quotes from different providers to find more affordable options. This trend directly amplifies their bargaining power, as they are more inclined to switch if they find a better deal elsewhere.
Large Corporate and Institutional Clients
For specialized services like credit insurance offered by Grupo Catalana Occidente's subsidiary Atradius, large corporate and institutional clients wield considerable bargaining power. This stems from the substantial volume of business they can bring, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms and pricing. In 2024, the global credit insurance market continued to see strong demand, with major corporations increasingly relying on these solutions to mitigate trade credit risks, further amplifying their negotiating leverage.
Grupo Catalana Occidente's strategy emphasizes fostering strong relationships with these key clients by providing robust support in managing trade risks. This focus on client success is crucial for maintaining high customer retention rates, acknowledging the significant impact these large accounts have on the company's overall performance. For instance, Atradius reported a solid performance in its corporate segment throughout 2024, underscoring the value of these partnerships.
- High Volume Business: Large clients can commit to significant premium volumes, making their business highly sought after.
- Negotiation Leverage: Their ability to switch providers or self-insure, though costly, grants them considerable power to negotiate pricing and service level agreements.
- Strategic Importance: Maintaining these relationships is vital for GCO's market share and revenue stability in its specialized insurance lines.
- Risk Management Focus: GCO's success with these clients is tied to its effectiveness in helping them manage complex trade credit exposures.
Availability of Multiple Providers
The Spanish insurance market, a key arena for Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO), is quite competitive. With many companies offering a wide array of insurance products, from home and car to life and health, customers have plenty of options. This abundance of choice naturally shifts power towards the consumer.
This situation means customers can easily compare prices and coverage from different insurers. If they feel they aren't getting the best deal or service, switching providers is a straightforward process. For GCO, this translates into a constant need to focus on customer loyalty and delivering superior value to stand out in a crowded marketplace.
- Market Saturation: The Spanish insurance sector is mature, with numerous established and emerging players.
- Customer Choice: A wide range of providers across various insurance lines (property, casualty, life, health) empowers customers.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can readily compare premiums and benefits, leading to increased price sensitivity.
- Retention Challenge: GCO faces a significant challenge in retaining customers due to the ease with which they can switch providers.
The bargaining power of customers for Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) is significantly elevated due to increased market transparency and a wide array of choices. In 2024, the digital landscape continued to empower consumers, with online aggregators facilitating easy comparison of insurance products and pricing, forcing insurers like GCO to offer competitive rates and superior service to retain business.
Large corporate clients, particularly in specialized areas like credit insurance through GCO's subsidiary Atradius, hold substantial bargaining power. Their ability to commit to high premium volumes and their potential to switch providers or explore self-insurance options means they can negotiate favorable terms. For instance, Atradius's strong performance in its corporate segment in 2024 highlights the critical importance of managing these high-value relationships effectively.
The competitive nature of the Spanish insurance market further amplifies customer bargaining power. With numerous providers offering diverse products, customers can readily switch for better deals, making customer loyalty a paramount challenge for GCO. This necessitates a continuous focus on delivering exceptional value and personalized experiences to mitigate churn.
| Factor | Impact on GCO | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Information Access | Increased customer knowledge and comparison ability. | Consumers spent an average of 4 hours researching insurance in 2024. |
| Market Competition | Amplifies price sensitivity and ease of switching. | Spanish insurance market characterized by numerous providers across all segments. |
| Digitalization Demand | Need for seamless online interaction and personalized service. | Growing consumer preference for mobile-first policy management and claims. |
| Corporate Client Leverage | Significant negotiation power for large accounts. | Major corporations increasingly use credit insurance, enhancing their leverage. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Grupo Catalana Occidente Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Grupo Catalana Occidente Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. You'll gain a thorough understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the insurance sector. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file; what you're previewing is precisely what you get.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Spanish insurance market is indeed mature, meaning growth is slower and competition is fierce. This maturity, coupled with a fragmented landscape, means there are many insurance companies vying for customers, with no single entity dominating the scene.
Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) itself is the seventh largest insurance group in Spain. This ranking underscores the fragmented nature of the market, as it implies that the top players, including GCO, hold relatively smaller market shares compared to a more consolidated industry.
This intense rivalry forces companies like GCO to constantly innovate and compete on price, service, and product offerings to capture and retain market share across all insurance segments.
Competitive rivalry in the insurance sector is intensifying, driven by a strong focus on digital transformation and operational efficiency. Many players are channeling significant resources into cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and automation. This strategic push aims to not only boost internal processes but also to elevate customer interactions and expedite claims handling, a crucial differentiator in the market.
Grupo Catalana Occidente's (GCO) own commitment to these digital advancements, especially within its Atradius division, is paramount. Rival insurers are equally aggressive in adopting technology to carve out unique market positions and attract customers. For instance, in 2024, the global insurance sector saw continued heavy investment in insurtech, with funding rounds supporting companies focused on AI-driven underwriting and personalized customer journeys, highlighting the industry-wide race to leverage digital capabilities.
The insurance sector, including players like Grupo Catalana Occidente, grapples with persistent pricing pressures, exacerbated by claims inflation, especially in motor and home insurance. This dynamic forces insurers to tread a fine line between offering competitive rates and safeguarding profitability. For instance, in 2024, many European insurers reported rising claims costs impacting their combined ratios, making it harder to maintain healthy profit margins.
This inflationary environment directly challenges insurers' ability to maintain profitability, as increased claims payouts can quickly erode underwriting gains. Grupo Catalana Occidente, like its peers, must meticulously manage its expenses and risk exposure to offset these rising costs. The ability to control operational expenditures and effectively price risk becomes a critical differentiator in this competitive landscape.
Product Differentiation Challenges
In many established insurance markets, distinguishing products is a real hurdle. Many policies are shaped by the same external risks and government rules, making true uniqueness scarce. This forces companies like Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) to compete more on how well they serve customers, what they charge, and how easily people can access their products. For instance, in 2024, the Spanish non-life insurance sector, where GCO is a major player, saw premiums grow, but this often came with intense price competition.
GCO's approach to tackle this challenge involves creating comprehensive and integrated service packages. The idea is to offer a more complete solution rather than just a single product. This strategy aims to build customer loyalty by providing a broader value proposition.
- Limited Differentiation in Traditional Lines: Many insurance products are standardized due to regulatory frameworks and the nature of insured risks, pushing competition towards non-product factors.
- Focus on Service and Distribution: With similar product features, competition intensifies on customer service quality, pricing strategies, and the effectiveness of distribution networks.
- GCO's Integrated Service Strategy: Grupo Catalana Occidente aims to stand out by offering bundled and holistic insurance solutions, enhancing customer value beyond individual policy features.
Strategic Acquisitions and Consolidation
The insurance market, particularly in Spain where Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) operates, is quite mature. This maturity means that established companies like GCO often look to mergers and acquisitions (M&A) as a primary avenue for growth, rather than solely relying on organic expansion. This strategic move allows them to gain market share and operational efficiencies.
GCO has actively engaged in inorganic growth. A notable example is its acquisition of Mémora, a significant player in the funeral services sector, which demonstrates a clear strategy of consolidation. This approach isn't limited to one segment; GCO continually evaluates opportunities across various business lines to strengthen its position and diversify its offerings.
This trend of strategic acquisitions significantly reshapes the competitive landscape. As larger entities consolidate, the market structure shifts, often leading to fewer, but larger, players. This intensifies the rivalry among these dominant companies, as they compete for market dominance through further M&A or by leveraging their expanded scale and resources.
- Market Maturity Drives M&A: In mature markets, growth often stems from acquiring competitors rather than organic expansion.
- GCO's Inorganic Growth: Grupo Catalana Occidente has pursued strategic acquisitions, such as its significant investment in the Mémora funeral business, to expand its reach.
- Consolidation Alters Competition: Such consolidation trends lead to fewer, larger players, intensifying rivalry and potentially changing market dynamics.
The Spanish insurance market is characterized by intense competitive rivalry, with Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO) being the seventh-largest player. This fragmented landscape means companies must differentiate through innovation, service, and pricing to capture market share. The ongoing digital transformation, with significant investments in AI and automation by various insurers, further fuels this rivalry, as seen in the global insurtech funding in 2024.
Pricing pressures are a constant challenge, exacerbated by rising claims inflation, particularly in motor and home insurance, impacting profitability. For example, many European insurers in 2024 reported increased claims costs affecting their combined ratios. This necessitates meticulous expense management and risk pricing for companies like GCO to maintain healthy margins.
Limited product differentiation in traditional lines forces competition onto service quality and distribution networks, with GCO focusing on integrated service packages to enhance customer value. Furthermore, market maturity drives mergers and acquisitions; GCO's acquisition of Mémora exemplifies this trend, leading to market consolidation and intensified rivalry among larger entities.
| Metric | 2023 (Approximate) | 2024 (Estimated/Early Data) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spanish Insurance Market Growth | Low single digits | Continued low single digits | Intensifies competition for market share |
| Digital Investment (Insurtech) | Significant | Increased investment in AI/automation | Drives innovation and efficiency race |
| Claims Inflation (Motor/Home) | Elevated | Persistent pressure | Pressures pricing and profitability |
| M&A Activity | Moderate | Ongoing strategic acquisitions | Consolidates market, intensifies rivalry among larger players |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large corporations and institutions often explore self-insurance or alternative risk transfer methods like captives or risk retention groups as substitutes for conventional insurance. These strategies offer greater control over risk exposure and can lead to cost savings, particularly for recurring or predictable losses. For instance, in 2024, the global captive insurance market continued to expand, demonstrating a growing appetite for these alternative risk financing solutions.
Government-backed schemes and social security programs can present a threat of substitutes for certain insurance products. In Spain, for instance, while public healthcare exists, a growing demand for private health insurance, noted in 2024, indicates that public options may not fully satisfy all consumer needs, potentially limiting their substitutive power in this segment.
The growing sophistication of risk prevention and mitigation services, fueled by advancements in data analytics and the Internet of Things (IoT), presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional insurance providers like Grupo Catalana Occidente. These technological leaps empower customers to proactively manage and reduce their risk exposure, potentially diminishing their reliance on comprehensive insurance policies.
For instance, the increasing adoption of IoT devices in homes and businesses allows for real-time monitoring and early detection of potential hazards, such as water leaks or faulty wiring. This capability can lead customers to invest more in these preventive measures, thereby reducing their overall risk profile. In 2024, the global IoT market was valued at over $200 billion, with a significant portion dedicated to security and safety applications, indicating a strong trend towards proactive risk management.
Consequently, customers may opt for insurance policies with higher deductibles or even choose to self-insure for certain risks, as their confidence in their preventive strategies grows. This shift from a focus on indemnification after an event to prevention before an event directly challenges the core value proposition of many insurance products.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance Models
Emerging peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance models, where groups of individuals or businesses pool premiums to cover each other's losses, pose a potential threat to traditional insurers like Grupo Catalana Occidente. These models offer an alternative, often appealing to specific customer segments looking for increased transparency and potentially reduced costs.
While P2P insurance is still a developing market, its growth could impact market share. For instance, in 2023, the global insurtech market, which encompasses P2P platforms, was valued at approximately $20 billion, with projections indicating significant expansion. This suggests a growing appetite for alternative insurance solutions.
- Niche Appeal: P2P models can attract customers dissatisfied with traditional insurance pricing or transparency.
- Cost Savings Potential: By cutting out intermediaries, P2P platforms may offer lower premiums.
- Technological Advancement: Innovations in blockchain and smart contracts could further enhance P2P insurance efficiency and trust.
- Regulatory Landscape: Evolving regulations will play a crucial role in the scalability and mainstream adoption of P2P insurance.
Embedded Insurance Solutions
The rise of embedded insurance solutions presents a significant threat. This model seamlessly integrates coverage into product or service purchases, like travel insurance offered during flight booking. For instance, in 2024, the embedded insurance market continued its robust expansion, with projections indicating it could reach hundreds of billions of dollars globally in the coming years, directly competing with traditional, standalone policies by offering unparalleled convenience.
This convenience-driven approach can divert customers from traditional insurance providers. By bundling insurance at the point of sale, these solutions simplify the customer journey and can be perceived as a more integrated and cost-effective option. This bypasses established distribution networks and directly influences consumer purchasing decisions, potentially eroding market share for companies relying on traditional sales channels.
Key aspects of this threat include:
- Convenience: Insurance is offered at the exact moment of need or purchase.
- Reduced Friction: Eliminates the need for separate applications or research.
- Partnership Models: Insurers collaborate with non-insurance companies to embed products.
- Data Utilization: Leverages customer data from the primary purchase to tailor offers.
The threat of substitutes for Grupo Catalana Occidente is multifaceted, encompassing alternative risk management strategies and evolving customer preferences. These substitutes can reduce the demand for traditional insurance products by offering comparable protection or risk mitigation at potentially lower costs or with greater convenience.
Self-insurance, captive insurance, and risk retention groups offer greater control and potential cost savings, particularly for businesses with predictable loss patterns. The global captive insurance market's continued expansion in 2024 underscores this trend. Similarly, government-backed schemes, while not always a perfect substitute, can influence demand for private insurance, as seen with the ongoing demand for private health insurance in Spain in 2024 despite public healthcare availability.
Technological advancements, such as IoT devices for risk prevention and the rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance models, also present significant threats. The over $200 billion global IoT market in 2024, with a focus on safety applications, highlights a shift towards proactive risk management. P2P insurance, part of the growing $20 billion global insurtech market in 2023, offers alternative, potentially more transparent and cost-effective solutions.
Embedded insurance, seamlessly integrated into other purchases, is another potent substitute, offering unparalleled convenience. This model, experiencing robust expansion in 2024 and projected to reach hundreds of billions globally, bypasses traditional distribution channels by offering insurance at the point of need, directly impacting consumer purchasing decisions and potentially eroding market share for companies like Grupo Catalana Occidente.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Traditional Insurance | 2024/2023 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Risk Transfer | Self-insurance, Captives, Risk Retention Groups | Reduced demand for conventional policies, greater control for customers | Global captive insurance market continued expansion |
| Government/Social Schemes | Public healthcare, social security | Can limit demand for private alternatives, but often doesn't fully satisfy all needs | Growing demand for private health insurance in Spain (2024) |
| Risk Prevention Technology | IoT devices, data analytics | Diminishes reliance on insurance by reducing risk exposure | Global IoT market valued over $200 billion (2024) |
| Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance | Direct pooling of premiums, transparency | Potential market share erosion, appeals to specific customer segments | Global insurtech market valued approx. $20 billion (2023) |
| Embedded Insurance | Integrated into product/service purchases | Bypasses traditional channels, offers convenience, diverts customers | Projected to reach hundreds of billions globally (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
High capital requirements present a formidable barrier for new companies looking to enter the insurance and reinsurance sectors in Spain and across Europe. For example, to operate in life, credit, surety, civil liability, or reinsurance, a new entity must possess a minimum capital of EUR 9,015,000. This substantial financial hurdle significantly restricts the pool of potential new competitors, thereby protecting existing players like Grupo Catalana Occidente.
The insurance sector, including operations in Spain, is characterized by a stringent regulatory framework. Entities like Spain's Dirección General de Seguros y Fondos de Pensiones (DGSFP) impose rigorous licensing procedures, substantial solvency requirements, and continuous compliance mandates. This complex web of regulations presents a significant barrier to entry, demanding considerable time and financial investment from potential new competitors seeking authorization for various insurance lines.
Grupo Catalana Occidente, like many established insurers, operates in a sector where trust is paramount. Their long history has cultivated significant brand recognition and customer loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2023, the Spanish insurance market saw continued consolidation, with established players like Catalana Occidente maintaining strong market shares, underscoring the enduring value of brand equity.
Insurtech Disruption and Niche Entry
While the insurance industry traditionally boasts high barriers to entry, the rise of Insurtech firms presents a significant threat. These companies utilize technology to bypass established channels, offering innovative, digital-first products or focusing on underserved market segments. For Grupo Catalana Occidente (GCO), this means potential erosion of market share in specific areas.
Insurtechs are not necessarily aiming to replicate GCO's entire product portfolio. Instead, they often target lucrative niches where they can offer a superior digital experience or more specialized coverage. For instance, a digital-first approach to car insurance or highly personalized health insurance plans can attract customers away from traditional providers.
- Insurtech Investment Growth: Global Insurtech funding reached $10.6 billion in 2023, indicating significant capital flowing into new entrants.
- Digital Adoption in Insurance: By early 2024, over 60% of insurance customers expressed a preference for digital channels for policy management and claims.
- Niche Market Penetration: Insurtechs focusing on specific segments like travel insurance or pet insurance have seen rapid growth, demonstrating the viability of targeted disruption.
Potential Entry of Big Tech Companies
The potential entry of major technology companies represents a significant long-term threat to Grupo Catalana Occidente. These tech giants, such as Amazon and Google, possess immense customer bases, sophisticated data analytics, and substantial financial reserves.
While direct entry into core insurance underwriting might be unlikely, their involvement could disrupt traditional models. They could easily penetrate distribution channels or claims processing, or even offer embedded insurance products seamlessly integrated into their existing platforms. For instance, Amazon's vast e-commerce network could offer tailored insurance at the point of sale for various goods, bypassing conventional insurance agent networks.
- Vast Customer Reach: Companies like Google have billions of users globally, offering unparalleled access to potential insurance customers.
- Data Analytics Prowess: Advanced AI and machine learning capabilities allow for highly personalized risk assessment and product development.
- Financial Muscle: The significant capital available to Big Tech firms enables aggressive market entry and investment in new technologies.
- Platform Integration: Leveraging existing digital ecosystems, they can offer insurance as a value-added service, potentially reducing customer acquisition costs for traditional insurers.
While high capital and regulatory hurdles traditionally limit new entrants, the evolving landscape presents challenges. Insurtechs, fueled by significant investment, are increasingly disrupting niche markets with digital-first solutions, as evidenced by $10.6 billion in global Insurtech funding in 2023. Furthermore, the potential entry of tech giants with vast customer bases and data analytics capabilities poses a long-term threat, as they could leverage existing platforms to offer embedded insurance products.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Minimum capital needed to operate in insurance sectors. | High barrier, limiting the number of potential competitors. | EUR 9,015,000 minimum capital for various insurance lines in Spain. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Licensing, solvency, and ongoing compliance mandates. | Demands significant time and financial investment. | Stringent oversight by bodies like Spain's DGSFP. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established reputation and customer relationships. | Difficult for newcomers to gain market share. | Continued market consolidation in 2023, with established players retaining strong shares. |
| Insurtech Disruption | Digital-first offerings and niche market focus. | Potential erosion of market share in specific segments. | $10.6 billion in global Insurtech funding in 2023; over 60% of customers prefer digital channels by early 2024. |
| Big Tech Entry | Leveraging customer bases, data, and financial power. | Potential for disruptive distribution or embedded insurance. | Billions of users for companies like Google; advanced AI for personalized risk assessment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Grupo Catalana Occidente is built upon comprehensive data from the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and official press releases. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and data from financial information providers to capture the competitive landscape.
