Grocery Outlet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Grocery Outlet Bundle
Grocery Outlet's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals a compelling picture of its competitive landscape, highlighting how buyer power and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its market. Understanding these forces is crucial for anyone looking to grasp Grocery Outlet's unique position in the retail sector.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Grocery Outlet’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Grocery Outlet's diverse supplier network, encompassing around 1,200 manufacturers and distributors, is a key factor in mitigating supplier bargaining power. This broad base of suppliers ensures that the company is not overly reliant on any single source for its inventory. For instance, in 2023, Grocery Outlet reported sourcing from a vast number of vendors, preventing any one from dictating terms.
Grocery Outlet's opportunistic buying model significantly reduces supplier bargaining power. By actively seeking surplus and near-dated inventory, often at discounts of 40-70%, Grocery Outlet creates a situation where suppliers are eager to sell to avoid waste and associated costs.
This strategy allows Grocery Outlet to secure deals, sometimes achieving up to 75% off standard retail prices, effectively dictating terms due to suppliers' need to clear excess stock. The company's ability to absorb large quantities of these discounted goods further strengthens its negotiating position.
Grocery Outlet benefits from a strong foundation of supplier loyalty, with an average relationship duration of 7.3 years. This longevity is further underscored by a remarkable 68% repeat supplier rate, indicating a consistent and reliable partnership. These stable relationships can mitigate some supplier power, as suppliers are less likely to disrupt a valuable and ongoing sales channel.
While long-term relationships can sometimes empower suppliers, Grocery Outlet's business model is inherently opportunistic. Suppliers engage with Grocery Outlet primarily to move distressed or overstocked inventory, creating a symbiotic relationship built on mutual benefit rather than dependence. This dynamic means suppliers are less inclined to leverage their position, as they gain a consistent outlet for goods that might otherwise be difficult to sell.
Mitigation of Single-Source Dependency
Grocery Outlet effectively mitigates the bargaining power of suppliers by strategically avoiding single-source dependency. A key tactic is ensuring no single supplier contributes more than 5% of their total merchandise inventory, a practice that significantly diversifies their supply chain.
This diversification across numerous product categories not only reduces reliance on any one entity but also bolsters Grocery Outlet's negotiation leverage. By spreading their purchasing power, they remain less vulnerable to price hikes or supply disruptions from individual suppliers.
- Supplier Diversification: No single supplier represents over 5% of total inventory.
- Category Breadth: Sourcing from a wide array of product categories.
- Negotiation Strength: Enhanced ability to negotiate favorable terms due to reduced dependency.
- Risk Reduction: Minimized vulnerability to supplier-specific price increases or disruptions.
Private Label Program Expansion
Grocery Outlet's strategic expansion of its private label program, marked by the introduction of over 180 new SKUs in 2024, significantly bolsters its bargaining power with suppliers. This move allows the company to decrease its dependence on national brand manufacturers for key product categories, thereby gaining greater leverage over pricing, supply chain management, and product specifications.
The development of proprietary brands empowers Grocery Outlet to offer customers compelling, high-quality alternatives that often come at a more attractive price point. This strengthens the company's position by providing a differentiated product offering and reducing the inherent risk associated with relying solely on external suppliers for its merchandise.
- Private Label Expansion: Over 180 new SKUs added in 2024.
- Reduced Supplier Reliance: Decreased dependence on national brands for staple items.
- Enhanced Control: Greater influence over pricing, supply, and product attributes.
- Customer Value: Offering high-quality, affordable alternatives.
Grocery Outlet's supplier bargaining power is considerably low due to its diverse sourcing strategy and opportunistic buying model. By working with approximately 1,200 manufacturers and distributors, the company avoids over-reliance on any single supplier, ensuring no one vendor accounts for more than 5% of its inventory. This broad network, coupled with a 7.3-year average supplier relationship and a 68% repeat supplier rate, fosters stability while maintaining leverage.
| Metric | Value | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
| Number of Suppliers | ~1,200 | Lowers power, reduces dependency |
| Max Supplier Inventory % | < 5% | Lowers power, diversifies risk |
| Average Supplier Relationship | 7.3 years | Can slightly increase power, but offset by opportunistic model |
| Repeat Supplier Rate | 68% | Indicates stable partnerships, but suppliers are eager to sell excess |
| Opportunistic Buying Discount | 40-75% | Significantly lowers power, suppliers need to move stock |
What is included in the product
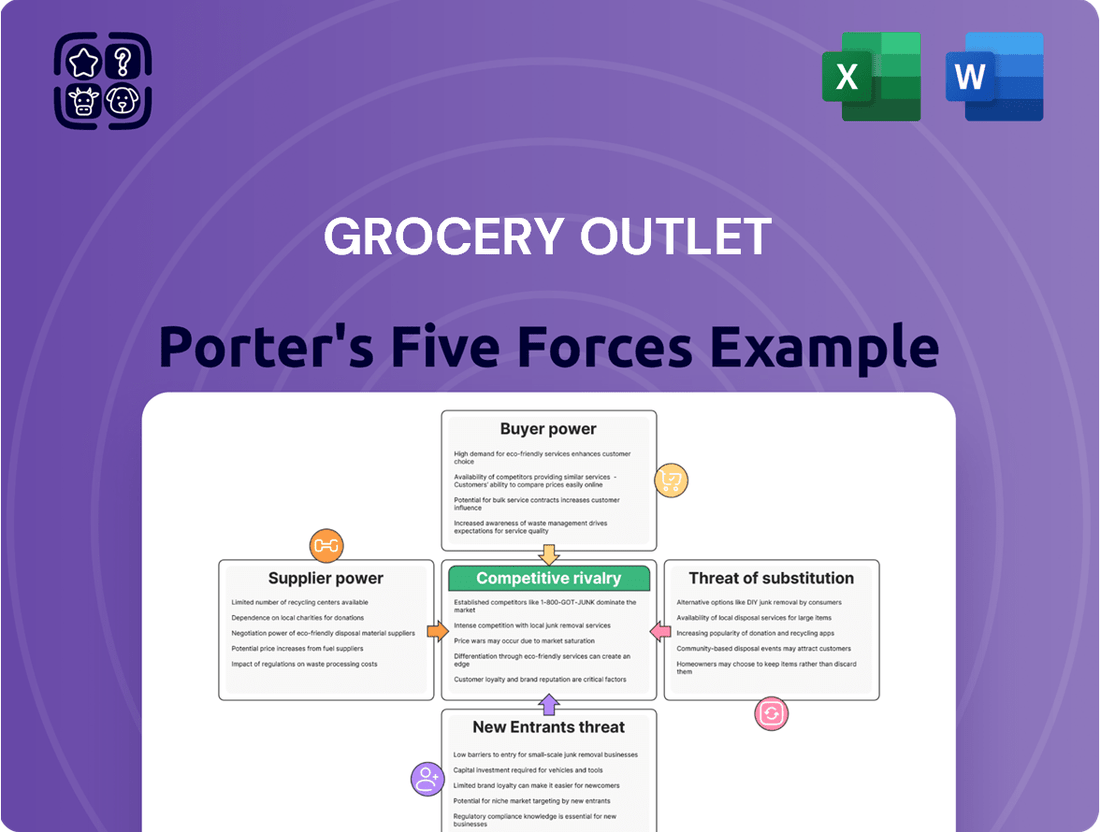
This analysis dissects Grocery Outlet's competitive landscape by examining supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrant threats, substitute product availability, and the intensity of rivalry within the discount grocery sector.
Effortlessly assess competitive pressures by visualizing threat levels for each of Porter's Five Forces, enabling swift identification of Grocery Outlet's key pain points.
Customers Bargaining Power
Grocery Outlet's customers are very focused on price, drawn in by the potential for substantial savings, often 40-70% less than conventional supermarkets and around 20% cheaper than other discount chains. This price sensitivity means customers hold significant leverage, readily switching if they feel they aren't getting the best deal.
The unique 'treasure hunt' aspect of Grocery Outlet, with its ever-changing inventory and surprising deals, definitely keeps customers coming back. This excitement, however, also gives shoppers more power. They are actively hunting for those "WOW!" moments and are willing to visit multiple locations to snag the best bargains, making them less dependent on any single store's predictable offerings.
Grocery Outlet benefits from a strong base of repeat customers, with 1.6 million individuals shopping with them multiple times in 2023. Their loyalty program, which encompasses 47% of their total customer base, underscores this dedication. This loyalty is cultivated through consistent deep discounts and a distinctive shopping atmosphere, encouraging customers to return.
Despite this loyalty, customers retain significant bargaining power. The grocery market is highly competitive, with numerous alternatives available, including online grocery services and a growing number of discount retailers. This accessibility means customers can easily switch providers if they find better prices or a more convenient shopping experience elsewhere.
Accessibility of Alternatives
Grocery Outlet's customers possess significant bargaining power due to the wide array of readily available alternatives. Traditional supermarkets, other discount grocers such as Aldi and Lidl, and the burgeoning online grocery sector all provide consumers with numerous choices. This accessibility means customers can easily compare prices and product offerings, forcing retailers to remain competitive.
The ease with which customers can switch between these grocery options, particularly with the rise of digital platforms, further amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, online grocery sales continued their upward trajectory, with platforms like Instacart and Amazon Fresh offering convenient alternatives that often highlight competitive pricing and delivery options. This makes it simple for shoppers to move to a competitor if they perceive better value elsewhere.
- Wide Availability of Alternatives: Customers can choose from traditional supermarkets, discount grocers, and online platforms.
- Ease of Switching: Digital platforms and competitive pricing make it simple for customers to change their grocery provider.
- Impact on Pricing: The availability of alternatives pressures retailers like Grocery Outlet to maintain competitive pricing strategies.
- 2024 Market Trends: Continued growth in online grocery sales in 2024 underscores the increasing options available to consumers.
Impact of Economic Conditions
In periods of economic uncertainty, such as the elevated food prices experienced in 2024, consumers become even more focused on value. This heightened sensitivity to price significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers, particularly at discount retailers like Grocery Outlet. As shoppers actively seek to stretch their budgets, they become more discerning and responsive to competitive pricing strategies and promotional offers.
This trend is a critical consideration for Grocery Outlet. With consumers actively seeking ways to maximize their purchasing power, they are more likely to switch to or favor retailers that consistently offer lower prices. For instance, in 2024, inflation impacted household budgets, driving demand for value-oriented grocery options.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Consumers are more likely to compare prices and switch retailers based on cost savings.
- Demand for Promotions: Shoppers actively seek out discounts, coupons, and loyalty programs to reduce their grocery bills.
- Focus on Essential Goods: During economic downturns, consumers prioritize essential food items, making price a paramount factor in purchasing decisions.
Grocery Outlet's customers wield considerable power due to the highly competitive grocery landscape. Shoppers can easily find alternatives, from traditional supermarkets to other discount chains and a growing online grocery sector. This accessibility means customers are not tied to any single retailer and can readily switch if better prices or value are found elsewhere, a trend amplified in 2024 with continued growth in online grocery sales.
| Factor | Impact on Grocery Outlet | Customer Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Forces competitive pricing strategies. | Actively seeks the lowest prices, willing to switch for savings. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Limits pricing power. | Can easily compare and choose from numerous grocery providers. |
| "Treasure Hunt" Aspect | Creates engagement but also shopper independence. | Motivated to visit multiple stores for perceived best deals. |
| Economic Conditions (2024) | Increases focus on value and budget stretching. | Prioritizes essential goods and seeks maximum purchasing power. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Grocery Outlet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Grocery Outlet's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive assessment will equip you with a deep understanding of the strategic forces shaping Grocery Outlet's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The grocery retail landscape, particularly within the discount sector, is fiercely competitive, with price serving as the central arena for rivalry. Grocery Outlet faces direct competition from other extreme-value grocers such as Aldi and Lidl, alongside traditional supermarkets and online retailers that aggressively price their products. This constant price pressure forces competitors to frequently adjust their pricing strategies and promotional offers to capture and keep customers who are highly sensitive to cost.
Grocery Outlet's opportunistic buying and unique 'treasure hunt' shopping experience significantly differentiate it from traditional supermarkets, thereby lessening direct rivalry focused on consistent product assortment. This strategy allows them to offer deep discounts by purchasing surplus and closeout inventory, a model distinct from competitors who rely on predictable supply chains.
While Grocery Outlet thrives on surprise and value, other players like Aldi and Lidl also compete on price with their private-label focused, no-frills formats. Furthermore, specialty grocers and even online retailers are increasingly carving out niches by offering curated selections or unique value propositions, intensifying the competitive landscape based on overall customer perception and specific offerings.
The grocery sector is experiencing robust expansion, with discount and specialty grocers leading the charge. This dynamic environment fuels intense competition as companies battle for dominance.
Grocery Outlet's strategic expansion, notably its 2024 acquisition of United Grocery Outlet, significantly heightens competitive rivalry. This move not only broadens its market presence but also intensifies the struggle for market share, particularly as businesses encroach upon each other's established territories.
Private Label Offerings
The grocery industry's growing emphasis on private label brands, a trend embraced by Grocery Outlet with its own expanding program, significantly fuels competitive rivalry. These store-brand offerings present consumers with more affordable alternatives to national brands, directly challenging rivals on price and potentially siphoning market share from established names.
This dynamic is largely a response to heightened consumer demand for value, particularly evident in recent economic conditions. For instance, in 2023, private label sales in the U.S. grocery market reached approximately $200 billion, accounting for over 20% of total sales, demonstrating their significant impact on the competitive landscape.
- Increased Private Label Penetration: Retailers are actively expanding their private label portfolios to capture price-sensitive shoppers.
- Price Competition: Private labels enable retailers to offer lower price points, directly impacting the sales of national brands.
- Consumer Demand for Value: Economic pressures have amplified consumer preference for affordable, store-brand options.
- Erosion of National Brand Share: The success of private labels can lead to a decline in market share for national brand manufacturers sold by competitors.
Omnichannel and Technology Investments
The grocery sector's competitive rivalry is intensifying due to significant investments in omnichannel capabilities, e-commerce, and broader technology adoption. Grocery Outlet is actively upgrading its inventory and financial reporting systems, a move mirrored by competitors who are simultaneously enhancing their digital storefronts, expanding delivery options, and integrating advanced in-store technologies to elevate customer experiences and streamline operations. This ongoing technological advancement creates a dynamic environment where retailers must continuously innovate to remain competitive.
This technological arms race is a key driver of competitive pressure. For instance, in 2024, many major grocery chains continued to invest heavily in their mobile apps and online ordering platforms. Walmart, a significant player, reported continued growth in its e-commerce sales, driven by its grocery pickup and delivery services, which puts pressure on all other retailers, including discounters like Grocery Outlet, to match these conveniences.
Retailers are focusing on several key areas:
- E-commerce Growth: Continued expansion of online ordering, curbside pickup, and home delivery services.
- In-store Technology: Implementation of self-checkout options, digital signage, and improved point-of-sale systems.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging customer data for personalized promotions and optimized inventory management.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Investing in technology to improve forecasting, reduce waste, and ensure product availability.
Competitive rivalry in the grocery sector remains intense, driven by price, private label expansion, and technological advancements. Grocery Outlet's unique model of opportunistic buying helps it stand out, but it still contends with direct competitors like Aldi and Lidl, as well as traditional and online grocers. The acquisition of United Grocery Outlet in 2024 further amplified this rivalry by expanding Grocery Outlet's footprint.
The push for private label brands, a strategy Grocery Outlet employs, directly challenges national brands and appeals to value-conscious consumers. In 2023, private label sales in the U.S. grocery market exceeded $200 billion, representing over 20% of total sales, underscoring their competitive significance.
Furthermore, investments in omnichannel capabilities and e-commerce are escalating competition. Major players like Walmart continue to bolster their online grocery services, pressuring all retailers, including Grocery Outlet, to enhance their digital offerings and in-store technologies to maintain customer engagement and operational efficiency.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Tactics | Impact on Grocery Outlet |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme-Value Grocers (e.g., Aldi, Lidl) | Price leadership, private label focus, no-frills format | Direct price pressure, competition for value-seeking customers |
| Traditional Supermarkets | Broad assortment, loyalty programs, evolving private labels | Competition on convenience and perceived quality, potential loss of market share to private labels |
| Online Retailers & E-commerce Platforms | Convenience, delivery options, curated selections | Pressure to develop robust omnichannel strategies, competition for digitally-engaged consumers |
| Specialty Grocers | Niche products, unique value propositions, customer experience | Competition for specific customer segments, differentiation through specialized offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional supermarkets and hypermarkets represent a significant substitute for Grocery Outlet's business model. These stores offer a comprehensive selection of grocery items, catering to a broader range of consumer needs beyond just discounted products. While Grocery Outlet thrives on opportunistic purchasing and lower price points, consumers may opt for conventional supermarkets when they prioritize convenience, a consistent product assortment, or the ability to fulfill all their shopping needs in a single trip, even at a higher cost.
Other discount grocers, including Aldi and Lidl, along with dollar stores, present a significant threat of substitution. These retailers also compete on price, offering consumers budget-friendly alternatives. For instance, Aldi's expansion in 2024, with plans to open hundreds of new stores, directly challenges Grocery Outlet's market share by providing similar value propositions.
The rise of online grocery platforms like Amazon Fresh and Instacart poses a substantial threat of substitutes for traditional grocery retailers. These services provide unparalleled convenience, often matching or beating in-store prices, and deliver directly to consumers' doors. The online grocery market is expected to continue its rapid expansion, with projections indicating significant growth in 2024 and 2025, signaling a clear consumer preference shift towards digital shopping channels.
Foodservice and Dining Out
The threat of substitutes for the grocery sector, including Grocery Outlet, is significant, primarily stemming from the foodservice and dining-out industry. Consumers can easily opt for restaurant meals, takeout, or prepared foods from delis and convenience stores as alternatives to preparing meals at home using groceries.
While grocery inflation has moderated, data from 2024 suggests a widening gap in consumer spending between dining out and grocery shopping. For instance, reports indicate that consumer spending on food away from home has continued to grow, even as grocery spending growth has slowed, signaling a shift in consumer preference towards convenience and prepared options.
- Dining Out vs. Groceries: Consumers increasingly choose prepared meals and restaurant experiences over home cooking.
- Spending Trends: In 2024, the divergence in spending growth between foodservice and grocery sectors highlights this substitution.
- Convenience Factor: The convenience offered by restaurants and prepared foods presents a strong alternative to traditional grocery shopping.
- Broad Industry Impact: This substitution threat impacts the entire grocery retail landscape, challenging traditional business models.
Farmers' Markets and Specialty Food Stores
Farmers' markets and specialty food stores present a threat of substitutes for Grocery Outlet, particularly for consumers seeking fresh, locally sourced, or unique food items. While these alternatives often don't compete on price, they cater to specific consumer preferences for quality and experience. For instance, the organic food market in the US was valued at approximately $24.8 billion in 2023, indicating a significant segment of consumers willing to pay a premium for perceived higher quality or ethical sourcing, which specialty stores and farmers' markets often emphasize.
These substitutes can siphon off demand from Grocery Outlet, especially for categories like fresh produce, artisanal cheeses, or baked goods. Consumers might visit these venues for specific high-value items, even if they continue to purchase staples from discounters. Data from the USDA in 2023 showed that direct-to-consumer food sales, which include farmers' markets, reached over $3.7 billion, highlighting the continued relevance of these channels.
- Farmers' markets and specialty stores offer alternatives for consumers prioritizing freshness and unique products.
- These substitutes often compete on quality and experience rather than price, appealing to a specific consumer segment.
- The growing organic food market, valued at nearly $25 billion in 2023, demonstrates consumer willingness to pay more for perceived quality, benefiting these alternative channels.
- Direct-to-consumer food sales, including farmers' markets, exceeded $3.7 billion in 2023, indicating their persistent market share.
The threat of substitutes for Grocery Outlet is multifaceted, encompassing traditional supermarkets, other discount grocers, online platforms, and even the foodservice industry. These alternatives offer varying degrees of convenience, selection, and price points, directly impacting consumer choices.
In 2024, the continued expansion of discounters like Aldi, aiming for hundreds of new locations, intensifies price competition. Simultaneously, the robust growth of online grocery services, projected to see significant gains through 2025, highlights a consumer shift towards digital convenience, often matched with competitive pricing.
The foodservice sector also presents a considerable substitute, with consumer spending on dining out outpacing grocery spending growth in 2024. This trend underscores a preference for prepared meals and convenience over home cooking, directly impacting the demand for traditional grocery items.
| Substitute Type | Key Differentiator | 2024/2025 Relevance |
| Traditional Supermarkets | Broad selection, convenience | Consistent consumer reliance |
| Discount Grocers (e.g., Aldi) | Price | Aggressive expansion in 2024 |
| Online Grocery Platforms | Convenience, delivery | Projected significant growth |
| Foodservice/Dining Out | Prepared meals, convenience | Outpacing grocery spending growth in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The grocery retail sector, especially for businesses with physical stores, demands significant upfront capital. This includes costs for acquiring or leasing property, stocking a wide variety of inventory, and setting up essential operational infrastructure like refrigeration and checkout systems.
For instance, Grocery Outlet's own expansion efforts highlight this barrier, with estimates suggesting that opening a new store requires an initial investment ranging from $2.5 million to $3.5 million. Such substantial financial requirements act as a considerable deterrent for many aspiring new competitors looking to enter the market.
Grocery Outlet's success hinges on its unique opportunistic buying model, which is built upon deep-rooted relationships with a wide array of suppliers and specialized sourcing expertise. This allows them to consistently acquire overstock and closeout merchandise at significantly reduced prices. For instance, in 2023, Grocery Outlet reported sourcing from thousands of suppliers, a testament to their extensive network.
Newcomers would face a formidable challenge in replicating these intricate supply chain connections and the nuanced ability to consistently source such diverse inventory. Building and maintaining these relationships takes considerable time and effort, presenting a substantial barrier to entry for potential competitors looking to disrupt Grocery Outlet's established sourcing advantage.
Grocery Outlet has cultivated significant brand recognition and a dedicated customer following, primarily due to its unique 'treasure hunt' shopping experience and unwavering commitment to value. This loyalty is a substantial barrier to new entrants.
As of 2023, Grocery Outlet reported a robust customer retention rate of 68%, underscoring the stickiness of its customer relationships. Furthermore, its loyalty program boasts 1.2 million active members, demonstrating a deep engagement with its core shopper base.
Consequently, any new competitor entering the market would face the daunting task of matching Grocery Outlet's established brand awareness and earning similar levels of consumer trust, requiring substantial investment in marketing and customer acquisition efforts.
Independent Operator Model
Grocery Outlet's reliance on independent owner-operators (IOs) creates a significant barrier to entry. This decentralized structure, where IOs manage individual stores, fosters strong local market understanding and a highly motivated, entrepreneurial workforce. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Grocery Outlet operated over 440 stores, each with its own dedicated IO.
Replicating this unique operational model presents a substantial challenge for potential new entrants. It requires not only capital investment but also the complex task of attracting, vetting, and effectively training a diverse network of independent business owners who are committed to the company's discount grocery strategy.
The success of the independent operator model is directly tied to Grocery Outlet's ability to maintain consistent quality and brand standards across its decentralized network. This requires robust support systems and ongoing training, which are costly and time-consuming for any new competitor to establish.
- Decentralized Operations: Grocery Outlet's model leverages independent owner-operators (IOs), fostering localized appeal and entrepreneurial commitment.
- Human Capital Challenge: Attracting, training, and retaining a network of qualified independent operators is a significant hurdle for new entrants.
- Operational Complexity: Replicating the infrastructure and support systems needed for a decentralized operator model requires substantial investment and expertise.
Intense Competition from Existing Players
The grocery sector is already a crowded arena, with major national chains, regional players, and numerous discount grocers vying for market share. This saturation means any new entrant would immediately face formidable opposition from established businesses that benefit from significant market presence, economies of scale, and loyal customer loyalty.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. grocery market continued to be dominated by giants like Walmart, Kroger, and Costco, which collectively held a substantial portion of the overall sales. Grocery Outlet itself, while operating on a unique model, competes directly with these and other regional supermarket chains, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
- High Market Saturation: The U.S. grocery market is already densely populated with established retailers.
- Economies of Scale: Existing large players enjoy cost advantages due to their size and purchasing power.
- Customer Loyalty: Entrenched competitors have built strong relationships and brand recognition with consumers.
- Barriers to Entry: Significant capital investment is required to establish a physical presence and supply chain, further deterring new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Grocery Outlet is moderate. Significant capital is needed for physical stores and inventory, with new store openings estimated between $2.5 million to $3.5 million. Grocery Outlet's established supplier relationships and sourcing expertise, built over years and involving thousands of suppliers in 2023, are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
The company's strong brand recognition and a loyal customer base, evidenced by a 68% customer retention rate in 2023 and 1.2 million active loyalty program members, also pose a barrier. Furthermore, replicating Grocery Outlet's unique independent owner-operator model, with over 440 stores operated by dedicated IOs as of Q1 2024, presents a complex operational and human capital challenge.
The existing market saturation, with dominant players like Walmart and Kroger in 2024, means new entrants face immediate competition from businesses with established scale and loyalty.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for property, inventory, and infrastructure. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Supplier Relationships | Deeply embedded network and sourcing expertise. | Difficult to match pricing and product diversity. |
| Brand Loyalty | Strong customer following and unique shopping experience. | Challenging to attract and retain customers. |
| Operational Model | Independent owner-operator structure. | Complex to replicate and manage effectively. |
| Market Saturation | Crowded retail landscape with established giants. | Intense competition from incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Grocery Outlet leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and trade publications to understand competitive dynamics.
