Grammer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Grammer Bundle
Grammer's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier bargaining, and the threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the industry's dynamics.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Grammer’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Grammer’s reliance on suppliers for specialized materials like advanced plastics, metals, and sustainable fabrics for its seating and interior components is a key factor in supplier bargaining power. The automotive industry's push for lightweighting and smart surfaces in 2024 means suppliers with unique technological capabilities in these areas hold significant leverage. If Grammer cannot easily substitute these specialized suppliers, their power increases.
Grammer's bargaining power with suppliers can be significantly impacted by the concentration of suppliers in specific automotive segments. For instance, if only a few companies can produce highly specialized, critical components, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This is particularly true if these suppliers hold unique certifications or face exceptionally high demand, limiting Grammer's ability to negotiate favorable pricing or terms. In 2024, the automotive industry continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions, with lead times for certain semiconductors and advanced materials extending, often due to the limited number of manufacturers capable of producing them. This situation directly amplifies the bargaining power of these concentrated suppliers, potentially driving up input costs for companies like Grammer.
The costs associated with switching suppliers for Grammer are substantial, including expenses for re-tooling production lines, obtaining new certifications for materials, and managing potential production downtime. These significant switching costs limit Grammer's ability to easily change suppliers, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of its existing suppliers.
Supplier's Importance to Grammer
Grammer's position as a significant customer for its suppliers is undeniable, particularly given its global reach and expertise in automotive interiors and commercial vehicle seating. This makes Grammer an important account for many in its supply chain.
However, the bargaining power of suppliers hinges on their dependence on Grammer. If Grammer represents a small fraction of a supplier's total sales, that supplier has less incentive to offer concessions, thus gaining leverage. For instance, if a key component supplier derives only 5% of its revenue from Grammer, it can demand higher prices or less favorable terms.
Conversely, if Grammer is a cornerstone of a supplier's business, accounting for a substantial portion of their revenue, the supplier is more likely to negotiate favorable terms to secure and maintain that business. This dynamic can lead to cost savings for Grammer if it strategically consolidates its purchasing power with key suppliers.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which a supplier relies on Grammer for revenue significantly impacts their bargaining power.
- Grammer's Purchasing Volume: High purchase volumes can give Grammer leverage, but only if it represents a large portion of the supplier's sales.
- Industry Concentration: If the supplier serves a niche market with few alternatives for Grammer, their bargaining power increases.
- Switching Costs: High costs for Grammer to switch suppliers further empower those suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Grammer's business is generally low, especially for raw material providers. However, specialized component manufacturers could potentially move into producing more complex assemblies or even finished products, directly competing with Grammer. This risk is largely contained by the substantial capital needed and the established relationships Grammer has with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in its target sectors.
This latent threat encourages Grammer to cultivate robust supplier partnerships and consistently offer competitive products. For instance, in the automotive sector, where Grammer is a significant player, the cost of developing and certifying new components to meet stringent OEM standards is a major barrier to entry for potential forward-integrating suppliers. In 2024, the automotive industry continued to emphasize supplier consolidation and long-term partnerships, making it less likely for component suppliers to undertake such a significant strategic shift.
- Specialized component suppliers possess the technical capability for forward integration.
- High capital investment and established OEM relationships act as significant deterrents.
- Grammer's focus on strong supplier relations mitigates this threat.
- The automotive industry's trend towards supplier consolidation in 2024 further limits this risk.
Suppliers wield significant power when they provide essential, specialized inputs that are difficult for Grammer to substitute. This leverage is amplified if there are few suppliers for these critical components, as seen with advanced materials or unique technological solutions in the automotive sector. In 2024, the ongoing demand for lightweighting and smart surfaces in vehicles meant suppliers with these capabilities held substantial sway, potentially increasing Grammer's input costs.
Grammer's ability to negotiate with suppliers is also influenced by the concentration of suppliers in specific market niches. When only a handful of companies can produce crucial parts, those suppliers gain considerable leverage, especially if they possess unique certifications or face high demand, limiting Grammer's options. The persistent supply chain disruptions in 2024, particularly for semiconductors and specialized materials with extended lead times, directly bolstered the bargaining power of these concentrated suppliers.
High switching costs for Grammer, including retooling and new certifications, inherently strengthen the bargaining power of its existing suppliers. Conversely, a supplier's dependence on Grammer for a significant portion of its revenue can reduce its leverage. For instance, if Grammer accounts for only a small percentage of a supplier's sales, that supplier has less incentive to offer favorable terms.
What is included in the product
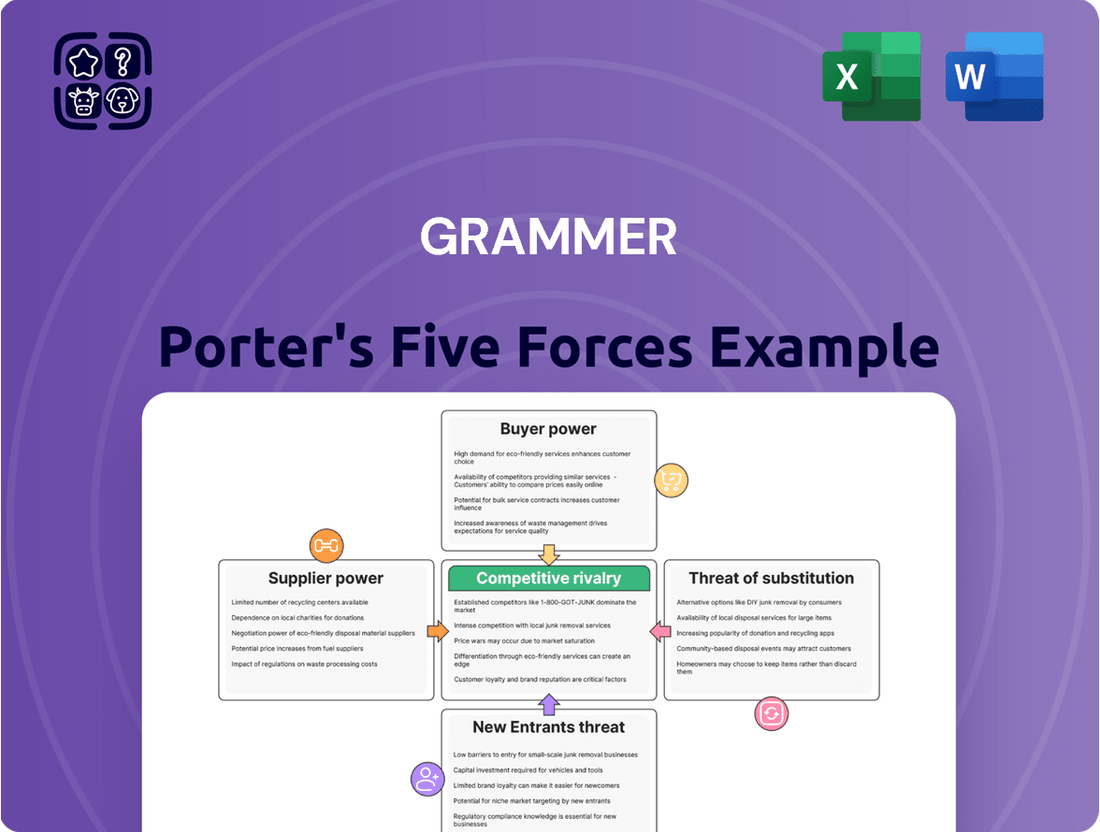
Grammer's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, making strategic adjustments straightforward.
Customers Bargaining Power
Grammer's customer base is highly concentrated, primarily consisting of major global automotive and commercial vehicle Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). These large-scale buyers, such as Volkswagen Group or Daimler Truck, wield substantial purchasing power due to their significant order volumes. This concentration inherently strengthens their bargaining position.
The sheer scale of these OEMs allows them to negotiate favorable terms, impacting Grammer's pricing, quality expectations, and delivery schedules. For instance, a single OEM contract can represent a substantial portion of Grammer's revenue, giving that customer significant leverage in discussions.
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) often purchase components and systems in substantial volumes, making them significant contributors to Grammer's overall revenue. For instance, in 2023, Grammer's top ten customers accounted for a considerable percentage of its sales, highlighting the concentration of its customer base. This high volume inherently grants these large customers considerable bargaining power.
Grammer's reliance on securing and retaining these large OEM contracts means that these customers can exert significant leverage. The potential loss of a major OEM client, due to price negotiations or alternative supplier arrangements, could have a material impact on Grammer's financial performance and profitability.
Grammer operates within a competitive landscape featuring significant players like Adient, Lear, Forvia, and Commercial Vehicle Group. This robust market presence of alternative suppliers directly empowers Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), Grammer's primary customers.
The availability of multiple strong competitors means OEMs possess considerable leverage. They can readily shift their business to another supplier if Grammer's pricing, product quality, or service levels fail to meet their expectations, or if competitors offer more attractive terms.
For instance, the automotive seating market, a key area for Grammer, saw significant consolidation and strategic realignments among suppliers in recent years. This ongoing market dynamism underscores the OEMs' ability to find alternative sourcing options, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Customers' Price Sensitivity
Customers in the automotive and commercial vehicle sectors exhibit significant price sensitivity, a trend amplified by prevailing economic conditions and geopolitical instability. This means Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are perpetually focused on cost reduction, creating substantial pricing pressure on suppliers like Grammer.
This intense customer demand for competitive pricing directly affects Grammer's ability to maintain healthy profit margins. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry faced ongoing supply chain challenges and fluctuating raw material costs, forcing OEMs to scrutinize every component's price point.
- Price Sensitivity: Automotive and commercial vehicle customers are highly cost-conscious.
- OEM Cost Optimization: OEMs actively seek to reduce expenses, translating to supplier pricing pressure.
- Margin Impact: High customer price sensitivity directly squeezes Grammer's profitability.
- 2024 Context: Economic uncertainty and supply chain issues intensified cost scrutiny in the automotive sector.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large automotive and commercial vehicle original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) often have the financial clout and technical expertise to consider producing certain interior components or seating systems themselves. This capability, even if not fully realized, puts pressure on suppliers like Grammer.
The mere possibility of OEMs bringing production in-house acts as a significant check on suppliers' pricing power. This underlying threat directly enhances the bargaining leverage that Grammer's major clients hold.
- Customer Bargaining Power: The threat of backward integration by major automotive OEMs is a key factor influencing Grammer's customer bargaining power.
- Financial & Technical Capacity: Large OEMs possess substantial financial resources and the necessary technical know-how to potentially manufacture interior components internally.
- Deterrent Effect: This latent threat discourages suppliers from imposing excessively high prices, thereby strengthening the customers' negotiating position.
- Supplier Pricing Influence: The potential for in-house production limits how much Grammer can increase prices without risking a shift in customer sourcing strategies.
Grammer's customer bargaining power is significantly influenced by the concentration of its buyer base, primarily large automotive and commercial vehicle OEMs like Volkswagen and Daimler Truck. These major clients, due to their substantial order volumes, wield considerable leverage in negotiations, impacting pricing and terms. For example, in 2023, Grammer's top ten customers represented a significant portion of its sales, underscoring the power these large buyers hold.
The competitive landscape, featuring alternative suppliers such as Adient and Lear, further empowers these OEMs. If Grammer fails to meet expectations on price, quality, or service, customers can easily switch, a scenario amplified by market dynamics like consolidation in the automotive seating sector. This availability of choices directly enhances customer leverage.
Price sensitivity among automotive customers is high, a trend exacerbated by economic conditions and supply chain issues prevalent in 2024, forcing OEMs to scrutinize costs. This pressure on Grammer's margins is substantial, as customers actively seek cost reductions on every component.
Furthermore, the potential for OEMs to bring certain component production in-house acts as a deterrent against excessive pricing by suppliers like Grammer, strengthening the customers' negotiating position.
| Customer Factor | Impact on Grammer | Supporting Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High Bargaining Power | Top 10 customers accounted for a significant portion of 2023 sales. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increased Leverage | Presence of major competitors like Adient, Lear, Forvia. |
| Price Sensitivity | Margin Pressure | Intensified cost scrutiny in 2024 automotive sector due to economic factors. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Limits Pricing Power | Potential for OEMs to produce components internally. |
Same Document Delivered
Grammer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive intensity and attractiveness of an industry. You'll gain insights into the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This document is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, providing a robust framework for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The automotive interior components and commercial vehicle seating sectors are populated by numerous robust global competitors. Major players like Adient, Lear Corporation, Forvia, and Commercial Vehicle Group, alongside Grammer, vie intensely for original equipment manufacturer (OEM) contracts. This highly competitive environment demands constant innovation and aggressive pricing strategies from all participants, including Grammer.
Moderate industry growth rates, such as the 3.0-6.7% CAGR projected for the automotive interior components market between 2024 and 2033, often intensify competitive rivalry. This limited expansion means companies must actively battle for existing customers rather than simply capturing new ones emerging from market growth.
For instance, the commercial vehicle seat market anticipates a 4.4-4.63% growth from 2025 to 2034. In such an environment, companies are more likely to engage in price competition and increase marketing efforts to differentiate themselves and gain a larger slice of the pie.
Grammer, a key player in automotive interior components and seating systems, faces intense competitive rivalry stemming from high fixed costs and substantial capacity. The manufacturing process demands significant capital outlay for advanced machinery, expansive facilities, and ongoing research and development. This substantial investment necessitates high capacity utilization to spread costs and achieve profitability, creating a constant pressure to maintain production volumes.
This drive for scale can ignite aggressive pricing strategies and fierce competition as companies vie for new orders, particularly when market demand softens. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry experienced fluctuations in production, intensifying the need for suppliers like Grammer to secure contracts to keep their production lines running efficiently and absorb their considerable fixed expenses.
Product Differentiation and Innovation
Competitive rivalry at Grammer is intensified by more than just price; product differentiation plays a critical role. Companies like Grammer emphasize ergonomics, comfort, safety, and the integration of new technologies in their seating solutions. For instance, Grammer's development of advanced suspension systems and integrated heating/cooling aims to set their products apart.
Rivals are also heavily investing in research and development to introduce innovative features. These advancements include smart surfaces that adapt to user needs, the use of lightweight yet durable materials to improve efficiency, and enhanced connectivity options for integrated digital experiences. The capacity to consistently innovate and deliver superior or unique solutions is paramount for securing and sustaining a competitive advantage in this market.
The industry saw significant R&D spending. For example, a major competitor in the automotive seating sector reported a 15% increase in R&D investment in 2024, specifically targeting lightweight materials and smart features. This highlights the ongoing race to differentiate through technological advancement and user-centric design.
- Ergonomics and Comfort: Key differentiators in seating solutions.
- Technological Integration: Smart surfaces and connectivity are becoming standard expectations.
- R&D Investment: Competitors are increasing spending to gain an edge.
- Material Innovation: Lightweight and advanced materials are crucial for performance and efficiency.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly influence competitive rivalry. For instance, in the semiconductor manufacturing industry, the immense capital investment required for fabrication plants, often exceeding billions of dollars, along with highly specialized assets like lithography machines, makes exiting the market incredibly difficult. Companies are often locked into these investments for years, even if profitability wanes.
These substantial sunk costs mean that firms are reluctant to shut down operations, even when facing financial distress. This persistence can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition as struggling players continue to vie for market share. In 2024, the global semiconductor market, despite its cyclical nature, continued to see companies investing heavily in advanced nodes, reinforcing these high exit barriers.
Furthermore, long-term contracts with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) can further entrench companies, making it challenging to divest or cease operations without significant penalties. This creates a scenario where even less profitable entities remain active participants, contributing to a more aggressive and sustained competitive landscape.
- High Capital Investment: Semiconductor fabrication plants can cost upwards of $20 billion, creating a massive financial hurdle for new entrants and a significant disincentive for exiting firms.
- Specialized Assets: Equipment like extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines are unique, costly, and have limited resale value outside the semiconductor industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Agreements with major tech companies for chip supply often span several years, obligating manufacturers to continue production.
- Sustained Rivalry: The inability to easily exit means that even firms with declining profitability may continue to operate, intensifying competition for all players in the market.
Competitive rivalry in the automotive interior and commercial vehicle seating sectors is fierce due to a concentrated market with many strong global players. Companies like Adient, Lear Corporation, and Forvia, alongside Grammer, are constantly vying for OEM contracts, leading to aggressive pricing and a continuous need for innovation to stand out.
The moderate growth projected for these markets, such as the 3.0-6.7% CAGR for automotive interiors from 2024-2033, means companies must fight harder for existing business rather than relying on market expansion. This dynamic is further fueled by high fixed costs associated with advanced manufacturing, pushing firms to maintain high capacity utilization and secure orders to cover expenses.
Differentiation through product features like ergonomics, comfort, safety, and technology integration is critical. For instance, Grammer's focus on advanced suspension systems and smart features aims to capture market share. Competitors are also boosting R&D, with one major player increasing investment by 15% in 2024 for lightweight materials and smart features, underscoring the importance of technological advancement.
High exit barriers, such as the substantial capital investment in specialized manufacturing equipment and long-term OEM contracts, keep companies invested even during downturns, prolonging intense competition. For example, the semiconductor industry's need for billions in fabrication plants and unique machinery like EUV lithography machines exemplifies these barriers, forcing firms to remain active participants and intensifying rivalry.
| Competitor | Key Focus Areas | Example Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Adient | Seating systems, ergonomics | Advanced lumbar support systems |
| Lear Corporation | Interior components, electrification | Integrated thermal management in seating |
| Forvia | Interior, lighting, seating | Smart surfaces and connectivity |
| Grammer | Automotive interiors, commercial vehicle seating | Enhanced suspension systems, integrated heating/cooling |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for interior components is significant, particularly from alternative designs and emerging technologies. For example, the increasing integration of large touchscreens and advanced digital interfaces in vehicles could diminish the demand for traditional physical buttons and controls. This trend was evident in 2024, with many automakers showcasing interiors heavily reliant on digital displays, potentially reducing the need for components like switchgear and manual climate controls.
While direct substitutes for complete seating systems are scarce, advancements in seating technology present a potential threat. Innovations like seats with integrated advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) or novel ergonomic designs could disrupt the market. For instance, the growing trend towards autonomous driving might encourage entirely new interior cabin designs, moving away from conventional driver and passenger seating arrangements.
The long-term shift towards shared mobility and autonomous vehicles presents a significant threat of substitution for Grammer. As private car ownership potentially declines in favor of ride-sharing services, the demand for highly personalized and premium interior components, a core offering for Grammer, could diminish. For instance, by 2024, ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft continue to gain traction in urban centers, with Uber reporting over 130 million monthly active users globally in Q1 2024.
If vehicles are predominantly used for short, shared trips, the focus for interior design will likely pivot from individual comfort and customization to robust durability and essential functionality. This could mean a reduced market for Grammer's specialized seating and interior systems, as simpler, more utilitarian solutions become the norm. The economic advantage of shared fleets prioritizing longevity over luxury directly challenges the value proposition of Grammer's higher-end products.
Non-Traditional Materials and Manufacturing Processes
The automotive sector's embrace of non-traditional materials and innovative manufacturing processes presents a significant threat of substitution for companies like Grammer. As the industry increasingly looks towards sustainable options and advanced composites for interior components, a swift adoption of entirely new material compositions or production methods by competitors or new market entrants could render Grammer's current capabilities and supply chains less competitive.
For instance, the push for lightweighting in vehicles, a key driver for new materials, saw the global automotive lightweight materials market valued at approximately USD 75 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. If a competitor were to master the production of a highly cost-effective and performant composite material for seating structures, for example, it could directly substitute Grammer's current offerings.
- Emerging Material Technologies: Competitors might leverage breakthroughs in areas like bio-based polymers or advanced recycled composites, offering comparable or superior performance at a lower cost.
- Disruptive Manufacturing: Innovations such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) for complex interior parts could allow new players to bypass traditional tooling and assembly costs, creating a substitution threat.
- Supply Chain Agility: Companies with more agile and diversified supply chains for these novel materials would be better positioned to capitalize on these trends, potentially displacing those reliant on established, but potentially less adaptable, networks.
Price-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The willingness of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to adopt substitute interior or seating technologies hinges critically on the price-performance trade-off. If an alternative solution provides substantial cost reductions or demonstrably superior features, such as enhanced safety, reduced weight, or better system integration, at a similar or lower price, the threat posed by substitutes escalates significantly.
Grammer needs to maintain a relentless focus on innovation and cost optimization. This ensures its product offerings remain competitive when measured against the performance and cost profiles of potential substitute solutions available in the market. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry saw continued pressure on material costs, with some suppliers exploring advanced composites to reduce vehicle weight, a direct challenge to traditional seating materials.
- Price-Performance Balance: OEMs evaluate substitutes based on whether they offer comparable or better features for less cost.
- Innovation Imperative: Grammer must innovate to provide superior value, justifying its pricing against alternatives.
- Cost Structure Optimization: Efficient cost management is key to maintaining competitiveness against emerging substitute technologies.
- Market Dynamics: The automotive sector's 2024 focus on lightweighting and sustainability creates opportunities for new materials that could substitute traditional seating components.
The threat of substitutes for interior components is significant, driven by evolving automotive designs and new technologies. For example, the rise of large touchscreens in 2024 vehicles is reducing the need for traditional physical controls. This shift means components like switchgear face substitution from digital interfaces.
While direct substitutes for entire seating systems are limited, advancements in seating technology pose a threat. Innovations like integrated driver-assistance systems or new ergonomic designs could disrupt the market, especially with autonomous driving potentially reshaping cabin layouts.
The increasing adoption of shared mobility and autonomous vehicles by 2024 presents a substantial substitution threat to Grammer. As private car ownership potentially declines in favor of ride-sharing, the demand for personalized, premium interior components could decrease, impacting Grammer's core offerings.
If vehicles are primarily used for short, shared trips, interior design will likely prioritize durability and functionality over individual comfort. This shift could favor simpler, more utilitarian solutions, potentially reducing the market for Grammer's specialized seating and interior systems.
The automotive industry's embrace of non-traditional materials and advanced manufacturing processes creates a substitution threat for Grammer. Competitors adopting new materials or production methods could render Grammer's current capabilities less competitive.
The global automotive lightweight materials market was valued at approximately USD 75 billion in 2023, highlighting the drive for new materials that could substitute traditional seating components.
| Substitution Area | Example Substitute | Impact on Grammer | 2024 Trend Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | Large Touchscreens/Digital Interfaces | Reduced demand for physical buttons, switchgear | Widespread OEM adoption |
| Seating Technology | Integrated ADAS, Novel Ergonomic Designs | Potential shift in seating requirements | Growing interest in autonomous vehicle interiors |
| Vehicle Usage Model | Shared Mobility/Autonomous Vehicles | Lower demand for personalized interiors | Increasing urban ride-sharing penetration |
| Materials | Advanced Composites, Bio-based Polymers | Challenge to traditional material suppliers | Focus on lightweighting and sustainability |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive interior components and seating systems sector, where Grammer operates, presents a formidable threat of new entrants due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, acquiring sophisticated machinery, and investing heavily in research and development demand billions of dollars. For instance, setting up a new automotive seating plant with advanced robotics and automation can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a significant hurdle for aspiring competitors.
These substantial upfront investments are essential to meet the stringent quality standards and production volumes demanded by global original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). New entrants must also contend with the need for significant working capital to manage inventory and supply chain operations. In 2024, the average capital expenditure for a new automotive manufacturing facility, even for specialized components, often exceeds $500 million, making it a highly capital-intensive industry.
Grammer, as an established player in the automotive supply industry, benefits immensely from economies of scale. In 2024, its substantial production volumes allow for lower per-unit costs in manufacturing and procurement, a significant barrier for any newcomer.
The experience curve effect also plays a crucial role; Grammer’s decades of accumulated knowledge in design, engineering, and efficient manufacturing processes translate into superior product quality and cost-effectiveness. New entrants would find it challenging and costly to replicate this deep-seated expertise and achieve comparable operational efficiencies in the short to medium term.
Grammer's deep-rooted relationships with major automotive and commercial vehicle OEMs represent a formidable barrier to new entrants. These established connections, often spanning decades, are cemented by a proven track record of quality, reliability, and adherence to stringent industry standards. For instance, in 2024, leading OEMs continued to prioritize suppliers with a demonstrated history of consistent performance and robust supply chain management, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to penetrate these trusted partnerships.
Stringent Regulatory and Certification Requirements
The automotive and commercial vehicle sectors are heavily regulated, demanding strict adherence to safety, quality, and environmental standards. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to enforce stringent emissions standards for new vehicles, requiring manufacturers to invest heavily in advanced technologies and rigorous testing protocols. Navigating these complex, evolving regulations and obtaining necessary certifications represents a substantial financial and operational hurdle for any potential new competitor.
These compliance requirements translate into significant upfront capital expenditure. New entrants must allocate substantial resources towards establishing robust testing facilities, implementing comprehensive quality management systems, and ensuring their products meet all mandated specifications. This can easily run into millions of dollars, making it a formidable barrier to entry. For example, developing a new vehicle platform compliant with 2024 safety standards, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), requires extensive research and development, simulation, and physical testing.
The time and expertise needed to understand and successfully implement these regulatory frameworks are also considerable. New players must not only invest financially but also build internal capabilities or outsource expertise to manage the intricate compliance processes. This can delay market entry and increase initial operating costs, effectively deterring those without established infrastructure and deep industry knowledge.
- Regulatory Complexity: Automotive industries face intricate safety (e.g., NHTSA standards), emissions (e.g., EPA standards), and manufacturing quality (e.g., ISO certifications) requirements.
- Capital Investment: Compliance necessitates significant spending on testing equipment, R&D for cleaner technologies, and quality control systems, often totaling hundreds of millions for new vehicle platforms.
- Time and Expertise: Successfully navigating these regulations requires specialized knowledge and can add years to product development cycles, increasing the cost and risk for new entrants.
- Market Entry Barrier: The combined financial and operational demands of regulatory compliance create a substantial barrier, protecting incumbent firms with established compliance infrastructure.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Grammer's significant investment in research and development, evidenced by its substantial R&D spending which has consistently represented a notable percentage of its revenue, creates a formidable barrier. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to allocate significant resources towards developing next-generation seating solutions, aiming to further solidify its technological lead. This focus on proprietary technology and patents means new entrants face the daunting task of either replicating Grammer's advanced innovations or acquiring expensive licenses.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by Grammer's established intellectual property portfolio. Holding numerous patents across its core product lines, particularly in areas like advanced suspension systems and integrated safety features, makes it difficult and costly for newcomers to offer comparable products. Developing equivalent technologies would require substantial time and capital investment, a hurdle that deters many potential competitors.
Grammer's specialized know-how in areas such as material science and ergonomic design also acts as a barrier. This deep expertise, cultivated over years of experience and product development, is not easily replicated. Potential entrants would struggle to match the performance, durability, and user comfort that Grammer consistently delivers, requiring them to undertake extensive and costly research and development to catch up.
The high cost associated with developing or licensing proprietary technology presents a significant deterrent. New companies entering the market would need to either invest heavily in their own innovation pipeline or negotiate licensing agreements, both of which represent substantial financial outlays. This capital intensity makes the sector less attractive to smaller, less-resourced entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the automotive interior components sector is significantly lowered by the immense capital required for manufacturing and technology. For example, establishing a new automotive seating plant in 2024, equipped with advanced robotics, could easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars. Furthermore, the need for substantial working capital to manage supply chains and inventory adds another layer of financial burden, making it a highly capital-intensive industry.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and government economic indicators. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive pressures.
