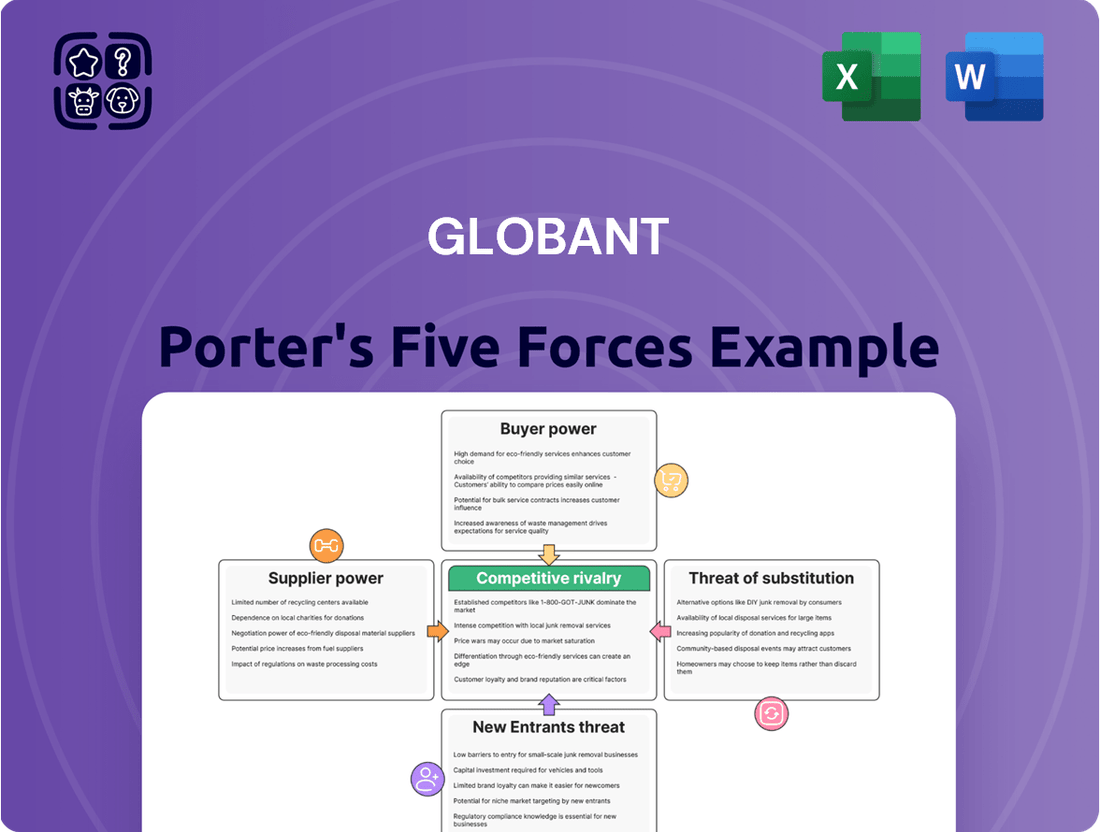
Globant Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Globant Bundle
Globant navigates a dynamic tech landscape where buyer power and the threat of substitutes are significant considerations. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis dives deep into the competitive intensity, supplier leverage, and barriers to entry impacting Globant. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Globant's reliance on specialized tech talent, particularly in areas like AI and cloud computing, means that skilled professionals hold considerable sway. This high demand directly translates into increased bargaining power for these individuals, impacting Globant's operational costs.
In 2024, the global shortage of cybersecurity experts, a key area for tech services, saw average salaries rise by 15-20% year-over-year according to industry reports. This upward pressure on wages for specialized skills is a direct manifestation of supplier bargaining power impacting companies like Globant.
Globant, like many tech service companies, relies on key technology providers for its operations. For instance, major cloud infrastructure players such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are critical. In 2024, the cloud computing market continued its robust growth, with AWS holding a significant market share, demonstrating the leverage these providers possess. This reliance means Globant's costs and service delivery can be influenced by the pricing and service terms of these foundational technology partners.
When Globant requires highly specialized tools or components for cutting-edge digital transformation projects, the limited number of vendors offering these niche solutions can significantly amplify their bargaining power. This scarcity means Globant may face higher costs or less favorable contract terms for essential, advanced technologies. For instance, in areas like specialized AI development platforms or unique cybersecurity solutions, only a handful of providers might exist, giving them considerable leverage.
Low Switching Costs for Talent
While highly skilled IT professionals certainly hold significant bargaining power due to high demand, the actual costs for these individuals to switch employers are quite low. This ease of transition in the competitive tech job market means companies like Globant face a constant need to offer competitive packages to keep their best people. For instance, in 2024, the average tech employee tenure in the US hovered around 2.8 years, highlighting the fluidity of the workforce.
This low switching cost directly impacts Globant's operational expenses. To combat talent attrition, the company must continually invest in more than just salary; this includes robust benefits, professional development opportunities, and a positive work environment. Failure to do so can lead to increased recruitment costs and project delays, directly affecting profitability.
- Low Individual Switching Costs: IT professionals can move between companies with minimal financial or logistical hurdles.
- Retention Investment: Globant needs to spend on competitive compensation, benefits, and culture to keep talent.
- Impact on Operational Expenses: High turnover necessitates ongoing investment in recruitment and training, increasing costs.
Strategic Partnerships Mitigate Power
Globant's strategic partnerships, like its collaboration with Google Cloud, can significantly lessen the bargaining power of technology suppliers. These alliances often secure preferential access to essential platforms and tools, fostering collaborative development and potentially leading to more advantageous pricing structures. For instance, in 2024, Globant continued to deepen its relationship with major cloud providers, which is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in digital transformation services.
These crucial alliances ensure Globant's access to the latest technological advancements and platforms, which are vital for delivering innovative solutions to its clients. By integrating deeply with key suppliers, Globant can influence product roadmaps and secure resources, thereby reducing the suppliers' leverage.
- Strategic Alliances: Globant's partnerships with leading technology firms, including cloud service providers and software developers, are key to managing supplier power.
- Preferential Access: These collaborations often guarantee early access to new technologies and beta programs, giving Globant a competitive advantage.
- Collaborative Development: Working closely with suppliers allows for co-creation of solutions, aligning supplier offerings with Globant's specific needs and reducing reliance on off-the-shelf products.
- Favorable Pricing: Long-term, deep partnerships can result in volume discounts and customized pricing models, directly impacting cost efficiency.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Globant is moderate, primarily influenced by the specialized nature of the talent and technology it requires. While individual tech professionals have low switching costs, the scarcity of highly skilled individuals in areas like AI and cloud computing in 2024, evidenced by salary increases of 15-20% for cybersecurity experts, grants them leverage. Similarly, key technology providers such as AWS and Google Cloud, with their dominant market positions in 2024, possess significant influence over pricing and service terms.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Globant | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Tech Talent | High Demand, Low Switching Costs | Increased wage pressure, retention investment | 15-20% salary rise for cybersecurity experts |
| Key Technology Providers (e.g., Cloud) | Market Dominance, Criticality of Services | Influence on pricing and service terms | AWS continued robust growth in cloud market |
| Niche Technology Vendors | Limited Number of Providers | Higher costs, less favorable contract terms | Scarcity in specialized AI platforms |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Globant's competitive environment by examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, offering strategic insights into its market position.
Globant's Porter's Five Forces analysis offers a streamlined, visual approach to understanding competitive pressures, allowing for swift identification of strategic opportunities and threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
Globant's customer base includes major global players such as Google, Electronic Arts, and Santander. This diverse and significant client portfolio grants these large enterprises substantial bargaining power.
These clients, often leaders in their respective industries, possess a deep understanding of the digital transformation landscape. This knowledge allows them to negotiate effectively, pushing for competitive pricing and demanding the highest standards of service delivery from Globant.
The digital transformation sector, where Globant operates, is intensely competitive. This means clients often find it relatively easy to switch between service providers. In fact, industry surveys from 2024 indicated that a substantial portion of clients actively evaluated changing their digital transformation partners, highlighting the low switching costs.
These low switching costs directly empower customers, giving them significant leverage. It means Globant must consistently provide exceptional value and cutting-edge innovation to keep its clients satisfied and loyal. If clients can move to a competitor without much difficulty or expense, they will, putting pressure on Globant to perform at its best.
Clients are increasingly focused on tangible results and return on investment (ROI) for digital transformation initiatives. This means they're less inclined to pay solely for hours worked and more interested in performance-based pricing, directly linking fees to measurable outcomes. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of businesses now prioritize vendors who can demonstrate clear ROI and offer outcome-based contracts for technology services.
This demand for accountability significantly strengthens the bargaining power of Globant's customers. They can leverage their ability to measure success and negotiate terms that reflect the actual business value delivered. Companies are more likely to scrutinize project success metrics, pushing Globant to prove its effectiveness and justify its pricing structures beyond simple time and materials.
In-house Capabilities and Multi-vendor Strategies
Many large enterprises are increasingly building out their in-house digital expertise, a trend that directly impacts the bargaining power of customers. For instance, a 2024 survey by Gartner indicated that over 60% of CIOs planned to increase investment in internal digital transformation capabilities. This allows clients to bring core competencies in-house, reducing their reliance on external providers like Globant.
Furthermore, the adoption of multi-vendor procurement strategies by these enterprises significantly shifts the negotiation dynamic. By diversifying their service providers, clients can pit different agencies against each other, fostering competition that drives down costs and improves service levels. This strategic move inherently strengthens the customer's position.
- In-house Capability Growth: Enterprises are investing heavily in internal digital skills, with a significant portion of CIOs prioritizing this in 2024.
- Multi-vendor Adoption: A growing number of large organizations are engaging multiple vendors to manage their digital needs, creating a more competitive landscape.
- Reduced Dependence: By internalizing expertise and diversifying suppliers, clients lessen their dependence on any single provider, enhancing their leverage.
- Negotiation Power Boost: The combination of in-house skills and multi-vendor strategies directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers when negotiating with IT service firms.
Globant's Customer Concentration
While Globant serves a vast customer base exceeding 1,000 clients, a significant portion of its revenue stems from its largest accounts. In the fourth quarter of 2024, its top customer alone contributed 9.1% to the company's revenue. This concentration means that these key clients hold considerable bargaining power.
The influence of these major clients is further amplified by the fact that the top ten customers collectively account for nearly one-third of Globant's total revenues. This dependency on a select group of large clients can grant them leverage in price negotiations and contract terms, as Globant has a vested interest in retaining their business.
- Customer Concentration: Top customer represents 9.1% of Q4 2024 revenue.
- Revenue Dependence: Top ten customers account for nearly one-third of total revenue.
- Negotiating Leverage: Concentration empowers large clients in bargaining.
Globant's large client base, including major players like Google and Santander, grants these enterprises significant bargaining power. Their deep understanding of digital transformation allows them to negotiate effectively, demanding competitive pricing and high service standards.
Clients' ability to easily switch providers due to low switching costs in the competitive digital transformation sector empowers them. This forces Globant to consistently deliver exceptional value to retain clients, as evidenced by industry surveys in 2024 showing a substantial portion of clients evaluating provider changes.
The increasing focus on tangible results and ROI by clients, with over 60% prioritizing outcome-based contracts in 2024, further strengthens their negotiating position. They can leverage their ability to measure success to negotiate terms reflecting actual business value delivered.
Enterprises building in-house digital expertise, with over 60% of CIOs planning increased investment in 2024, reduces reliance on external firms like Globant. Coupled with multi-vendor strategies, this significantly enhances customer leverage in negotiations.
Globant's revenue concentration, where its top customer contributed 9.1% in Q4 2024 and the top ten accounted for nearly a third of revenue, amplifies the bargaining power of these key clients. This dependency gives them considerable leverage in price and contract term negotiations.
| Factor | Impact on Globant | Supporting Data (2024) |
| Client Size & Knowledge | High Bargaining Power | Major clients like Google, Santander |
| Switching Costs | Low for Clients | Significant client evaluation of changing providers |
| Focus on ROI | Increased Negotiation Leverage | Over 60% prioritize outcome-based contracts |
| In-house Capabilities | Reduced Client Dependence | Over 60% of CIOs increasing internal digital investment |
| Customer Concentration | Amplified Client Leverage | Top customer: 9.1% revenue; Top 10: ~33% revenue |
Full Version Awaits
Globant Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Globant Porter's Five Forces Analysis, demonstrating the exact document you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholders. You're looking at the actual, professionally written analysis, which will be available for instant download and use the moment your transaction is complete. No mockups or samples; the document you see here is precisely the deliverable, fully formatted and ready for your strategic needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The digital transformation and IT services market is incredibly crowded, with a vast number of global and regional companies vying for business. This includes giants like Accenture, Capgemini, IBM, and Deloitte, alongside many specialized firms. This intense competition means companies like Globant must constantly innovate and differentiate themselves to capture and maintain market share.
The digital transformation market is booming, with projections indicating it will surpass $2 trillion by 2025. This rapid expansion naturally draws in new entrants and intensifies the efforts of established players. Consequently, competitive rivalry is high as companies battle for market share in this lucrative and growing sector.
Globant carves out its competitive edge through a distinct focus on being digitally native and its deep-seated expertise in artificial intelligence. This specialization is further bolstered by its industry-specific 'Studios,' allowing for tailored solutions. For instance, as of early 2024, Globant's revenue grew by 10.9% year-over-year, reaching $1.7 billion in Q1 2024, showcasing the demand for its specialized services.
However, the IT services landscape is intensely competitive, with many rivals also pouring significant resources into AI development and niche market offerings. This necessitates that Globant, and others like Accenture and Tata Consultancy Services, constantly innovate and clearly articulate their unique value propositions to maintain market leadership and attract clients seeking cutting-edge digital transformation.
Pressure on Pricing and Margins
The IT services sector is characterized by fierce competition, which directly impacts pricing and profit margins. With many providers vying for business and clients often having significant leverage, companies are compelled to offer competitive rates, sometimes at the expense of higher profitability.
Globant, like its peers, navigates this environment by balancing aggressive pricing strategies with the need to maintain healthy margins. This delicate act is crucial for sustained growth and investment in innovation. For instance, in 2023, the global IT services market was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, showcasing the scale of competition and the pressure to capture market share.
- Intense Competition: A crowded marketplace with numerous global and regional IT service providers.
- Customer Bargaining Power: Clients, especially large enterprises, can negotiate favorable terms due to the availability of alternatives.
- Price Sensitivity: Clients often prioritize cost-effectiveness, leading to downward pressure on service fees.
- Margin Squeeze: The combination of competition and customer power can compress profit margins, requiring efficient operations and value differentiation.
Acquisition as a Growth Strategy
Competitive rivalry in the IT services sector is notably high, with mergers and acquisitions frequently used as a key growth strategy. Companies actively pursue acquisitions to broaden their service offerings, secure specialized talent, and expand their market reach, a trend that has been particularly pronounced in recent years. For instance, in 2023, the IT services sector saw significant M&A activity, with major players acquiring smaller firms to enhance their capabilities in areas like cloud, AI, and cybersecurity.
This ongoing consolidation signifies a mature market where firms are constantly seeking to strengthen their competitive standing. The drive to acquire is fueled by the need to stay ahead of technological shifts and client demands. This dynamic intensifies rivalry as companies either absorb competitors or are themselves absorbed, leading to a more concentrated, yet fiercely contested, industry landscape.
- Increased M&A Activity: The IT services industry consistently witnesses mergers and acquisitions as companies aim to expand their service portfolios and market presence.
- Talent Acquisition: Acquisitions are often driven by the strategic need to acquire skilled talent, particularly in high-demand areas like artificial intelligence and cloud computing.
- Market Share Consolidation: Ongoing M&A activity leads to market share consolidation, intensifying competition among the remaining larger players.
- Capability Expansion: Companies acquire businesses to gain access to new technologies, intellectual property, and complementary services, thereby enhancing their overall competitive offering.
The competitive rivalry within the digital transformation and IT services market is exceptionally fierce. Globant faces numerous global and regional players, including giants like Accenture and IBM, all vying for market share in a sector projected to exceed $2 trillion by 2025.
This intense competition forces companies to constantly innovate and differentiate. Globant's focus on being digitally native and its AI expertise, along with specialized 'Studios,' helps it stand out. However, rivals are also heavily investing in AI, intensifying the need for clear value propositions.
The market's growth attracts new entrants and intensifies efforts of established players, leading to price sensitivity and margin pressures. Companies like Globant must balance competitive pricing with the need for healthy margins, a challenge underscored by the global IT services market's approximate $1.3 trillion valuation in 2023.
Mergers and acquisitions are a common strategy for growth, further consolidating the market and intensifying rivalry. Companies acquire others to expand service offerings, gain talent in areas like AI, and increase market presence, a trend observed throughout 2023.
| Company | Approx. 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Competitors | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Globant | ~6.0 | Accenture, Capgemini, IBM, TCS | Digital Native, AI, Industry Studios |
| Accenture | ~64.9 | Globant, Capgemini, IBM, Deloitte | Digital Transformation, Cloud, AI, Strategy |
| Capgemini | ~23.0 | Globant, Accenture, IBM, TCS | Digital Transformation, Cloud, AI, Engineering |
| IBM | ~62.0 | Globant, Accenture, Capgemini, TCS | Hybrid Cloud, AI, Consulting, Software |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Clients increasingly possess the capability to develop or enhance their internal IT and digital transformation teams. This growing in-house expertise directly reduces their dependence on external service providers such as Globant. For instance, many large enterprises are making significant investments in building internal digital capabilities, aiming to manage ongoing strategic initiatives and routine operational tasks without relying on third-party consultants.
The rise of off-the-shelf software and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for Globant's custom development and consulting services. Businesses can increasingly opt for readily available, often more affordable, solutions to meet their digital needs, bypassing the requirement for bespoke development. This trend is amplified by the growth of low-code/no-code tools, which further democratize software creation.
For instance, the global SaaS market was projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, demonstrating the widespread adoption of these alternative solutions. Companies can leverage platforms like Salesforce for CRM, Workday for HR, or Shopify for e-commerce, thereby reducing their reliance on custom-built systems or extensive digital transformation consulting. This accessibility means that many functionalities previously requiring specialized development can now be acquired through subscription-based services.
The proliferation of freelance networks and the broader gig economy presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional consulting services like those offered by Globant. These platforms, such as Upwork and Fiverr, directly connect businesses with a vast pool of digital talent, including specialized consultants and developers. This allows companies to bypass larger agencies and engage individual experts for specific tasks, often at a more competitive price point.
In 2024, the freelance economy continued its rapid expansion. For instance, reports indicated that the global gig economy was projected to reach over $455 billion, showcasing the sheer scale of this alternative. Businesses are increasingly leveraging these platforms to source talent for everything from software development to marketing strategy, directly impacting the demand for the comprehensive, often more expensive, service packages offered by firms like Globant.
Generic Consulting Firms and System Integrators
While Globant excels in digital reinvention, traditional management consulting firms and large system integrators pose a significant threat. These established players, even those not solely focused on digital, can offer comparable digital transformation advisory and implementation services. Clients might favor these familiar entities, particularly if they already have established relationships and trust.
The threat is amplified by the fact that many of these firms have been actively acquiring digital capabilities and talent. For instance, in 2024, major consulting groups continued to invest heavily in their digital and cloud practices, aiming to capture a larger share of the digital transformation market. This makes them direct competitors for Globant’s core offerings.
- Broad Service Offerings: Traditional firms often provide a wider range of services beyond digital, appealing to clients seeking a single vendor for multiple needs.
- Established Client Relationships: Existing partnerships can lead clients to choose familiar system integrators for digital projects, even if a specialist like Globant might offer more tailored expertise.
- Acquisition of Digital Capabilities: Major consulting players are actively expanding their digital service portfolios through acquisitions and internal development, directly challenging Globant's market position.
Automation and AI-driven Tools
Advanced automation and AI-driven tools present a significant threat of substitution for traditional consulting services. These technologies allow companies to automate routine tasks and gain insights previously requiring external expertise. For instance, AI-powered analytics platforms can now perform data analysis and generate reports, reducing the need for human analysts.
The increasing sophistication of AI means that many services once exclusive to consultants are becoming accessible through internal tools. This trend is particularly evident in areas like market research, process optimization, and even basic strategy formulation. By 2024, the global AI market was valued at over $200 billion, with significant growth projected as more businesses integrate these capabilities.
- Automation of routine tasks: AI can handle data entry, report generation, and customer service inquiries, reducing reliance on human resources.
- AI-powered analytics: Sophisticated algorithms can identify trends, predict outcomes, and offer strategic recommendations, bypassing traditional analytical consultancies.
- Cost-effectiveness: Internal AI tools often represent a one-time or subscription cost, which can be more economical than ongoing consulting fees.
- Scalability: AI solutions can be scaled up or down easily to meet changing business needs, offering greater flexibility than hiring external consultants.
Clients are increasingly building internal digital capabilities, reducing reliance on external providers like Globant. This trend is fueled by significant investments in in-house IT and digital transformation teams to manage ongoing initiatives and operational tasks.
Off-the-shelf software and SaaS platforms offer a compelling alternative to custom development, with the global SaaS market projected to exceed $300 billion in 2024. Tools like Salesforce and Shopify enable businesses to acquire functionalities without extensive consulting.
The gig economy, with platforms like Upwork and Fiverr, provides direct access to specialized talent, allowing companies to bypass larger agencies. The global freelance economy was projected to surpass $455 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of this substitute.
Traditional management consulting firms and system integrators are expanding their digital service offerings, directly competing with Globant. These established players, with existing client relationships and broad service portfolios, are actively acquiring digital capabilities.
Advanced automation and AI-driven tools are also substituting consulting services. The global AI market, valued at over $200 billion in 2024, enables companies to automate tasks and gain insights, reducing the need for external expertise.
| Type of Substitute | Market Size/Growth (2024 Projections) | Impact on Globant |
|---|---|---|
| In-house IT Teams | Significant enterprise investment | Reduced demand for external development/consulting |
| SaaS Platforms | >$300 Billion (Global SaaS Market) | Substitution for custom solutions |
| Freelance/Gig Economy | >$455 Billion (Global Gig Economy) | Competition for talent and project outsourcing |
| Traditional Consulting Firms | Continued investment in digital practices | Direct competition for digital transformation projects |
| AI & Automation Tools | >$200 Billion (Global AI Market) | Automation of tasks previously requiring consultants |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a global digital services firm like Globant, which offers comprehensive solutions from initial strategy to complex engineering, demands substantial capital. This includes investments in technology infrastructure, research and development, and building a widespread operational presence. For instance, in 2024, major digital transformation projects often involve budgets in the tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Beyond financial resources, a deep well of specialized expertise is crucial. This encompasses a wide range of skills, from AI and machine learning to cybersecurity and cloud computing. Attracting and retaining top-tier talent in these competitive fields requires robust HR strategies and significant compensation, further increasing the cost of entry. Globant's success is built on its ability to cultivate this talent pool, a feat difficult for nascent companies to replicate quickly.
The sheer scale of talent required to deliver end-to-end digital solutions globally presents another formidable barrier. A new entrant would need to recruit, train, and manage thousands of highly skilled professionals across multiple geographies. This operational complexity, coupled with the need for a strong brand reputation to win large contracts, makes it exceptionally challenging for smaller, less established companies to compete effectively with established players in the digital services market.
Globant's strong brand reputation, acknowledged as a fast-growing IT firm and a frontrunner in AI, presents a substantial barrier. Newcomers must invest heavily to cultivate similar trust and credibility, especially when aiming for Globant's established base of major global clients.
Access to specialized talent acts as a significant hurdle for new companies looking to enter Globant's market. Attracting and keeping the right people with skills in technology, design, and AI is tough and costly, making it hard for newcomers to get a foothold.
Globant's workforce, which surpassed 31,000 employees, known as Globers, by the end of 2023, provides a substantial competitive edge. This large pool of experienced professionals is not something new entrants can easily or quickly build, presenting a considerable barrier to entry.
Niche Players and AI-Native Startups
The digital economy, fueled by advancements in artificial intelligence, is fostering the rise of specialized, AI-native consultancies and boutique firms. These agile players often operate with significantly lower overheads and possess flexible business models, enabling them to swiftly adapt to market demands.
These niche competitors can effectively target specific market segments or introduce disruptive, technology-driven solutions. By doing so, they pose a considerable threat to established firms by effectively lowering the cost and barriers to entry in certain specialized areas of the consulting market.
- AI-Native Startups: Companies focused solely on AI solutions, often with lean operations.
- Lower Overheads: Reduced infrastructure and staffing costs compared to larger, traditional consultancies.
- Targeted Expertise: Deep specialization in specific AI applications or industries.
- Disruptive Potential: Ability to offer innovative, technology-first solutions that challenge existing market norms.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Methodologies
Globant's development of proprietary platforms, such as Globant Enterprise AI (GEAI), and its specialized 'Studios' model create a barrier to entry. These unique assets require significant investment in research and development for new competitors to replicate or surpass. For instance, in 2023, Globant reported R&D expenses of $317.4 million, highlighting the commitment needed to build such intellectual property.
New entrants face the challenge of developing their own innovative methodologies and intellectual property to compete effectively. This process demands substantial R&D investment and considerable time, making it difficult for newcomers to quickly challenge Globant's established technological advantages. The company's focus on specialized digital transformation services further entrenches its market position.
- Proprietary Platforms: Globant's GEAI and 'Studios' model are key differentiators.
- R&D Investment: New entrants need significant capital for similar innovation, mirroring Globant's 2023 R&D spend of $317.4 million.
- Methodology Development: Creating unique service delivery frameworks is crucial for competitive entry.
- Time to Market: Replicating Globant's IP and expertise is a time-consuming endeavor for potential rivals.
The threat of new entrants in Globant's market is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and the need for specialized talent. While agile, AI-native startups can emerge with lower overheads, they often lack the scale and established reputation to compete for large-scale, end-to-end digital transformation projects. Globant's significant investment in R&D, exemplified by its $317.4 million spend in 2023, and its workforce exceeding 31,000 employees by the end of 2023, create substantial barriers to entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (Globant) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for technology, R&D, and global operations. | Significant hurdle for smaller firms. | Major digital projects in 2024 often cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Specialized Talent | Need for deep expertise in AI, cloud, cybersecurity, etc. | Difficult and costly to acquire and retain talent. | Globant's workforce of over 31,000 professionals (end of 2023). |
| Brand Reputation & Scale | Established trust and ability to manage large global contracts. | New entrants struggle to build credibility quickly. | Globant recognized as a fast-growing IT firm and AI frontrunner. |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary platforms and unique methodologies. | Requires substantial R&D to replicate or surpass. | Globant's 2023 R&D expenses: $317.4 million. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Globant Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, integrating insights from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and expert analyst commentary to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
