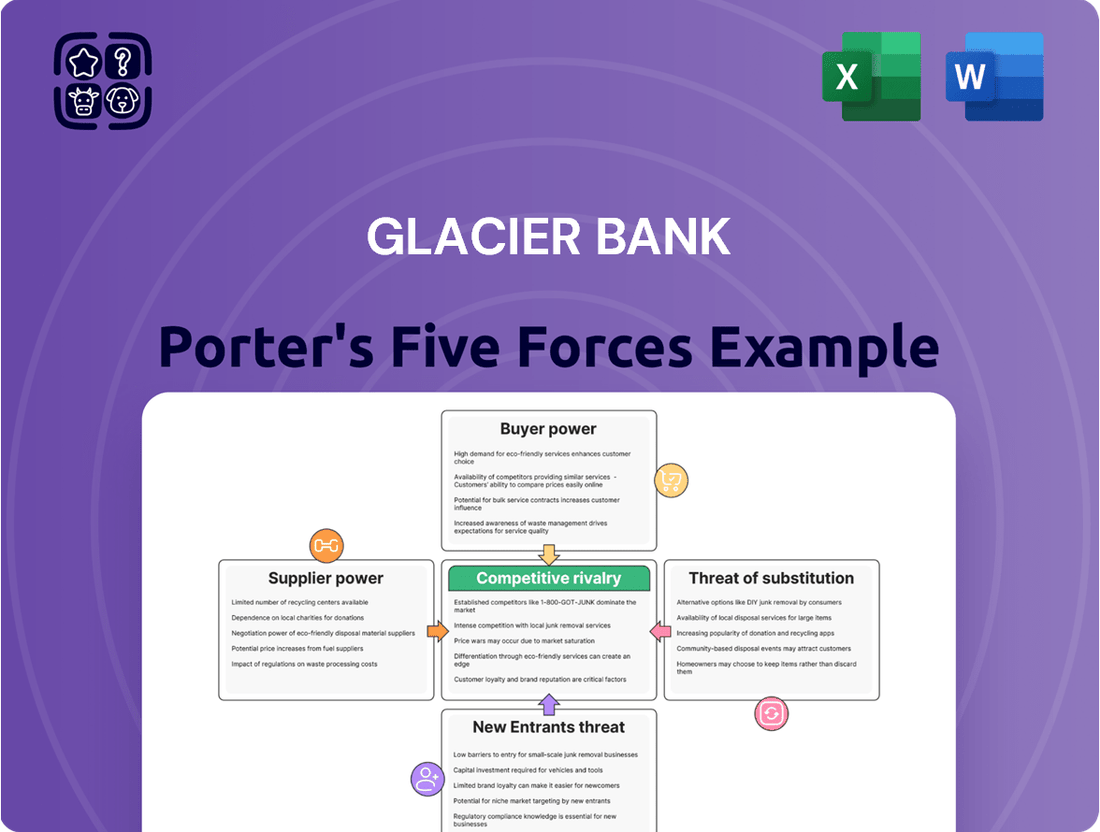
Glacier Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Glacier Bank Bundle
Glacier Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, where understanding the intensity of competitive rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic success. This brief overview highlights the core pressures shaping their market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Glacier Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Glacier Bancorp, like any bank, needs access to capital. This comes from customer deposits, which are a primary source, and also from borrowing in wholesale markets. The easier and cheaper it is for Glacier to get these funds, the less power its "suppliers" of capital have over it.
In 2024, deposits remain a cornerstone of bank funding. For instance, a stable and growing deposit base, often built on strong customer relationships, means Glacier isn't as dependent on potentially more expensive and volatile sources like brokered deposits or Federal Home Loan Bank advances. This diversification strengthens Glacier's hand.
Technology and software providers are increasingly vital for banks like Glacier Bancorp, offering everything from core banking systems to advanced cybersecurity and data analytics. The power these suppliers hold hinges on how unique and essential their solutions are, how difficult and costly it would be for Glacier Bancorp to switch to another provider, and how many other options are out there.
For instance, specialized AI-driven fraud detection software, if highly effective and difficult to replicate, could give its provider significant leverage. Conversely, if Glacier Bancorp can readily find multiple vendors for standard cloud storage or general-purpose analytics tools, supplier power in those areas would be lower.
The banking sector, including institutions like Glacier Bank, heavily relies on human capital, demanding expertise in finance, risk management, technology, and customer service. The availability of these skilled professionals, coupled with their wage expectations and the competitive environment for talent acquisition and retention, directly impacts labor's bargaining power as a supplier.
In 2024, a notable trend has been the increasing demand for cybersecurity and data analytics professionals within banking, often leading to higher salary expectations for these specialized roles. This scarcity of specific skills can significantly amplify the bargaining power of skilled labor, forcing banks to offer competitive compensation and benefits to attract and keep top talent.
Regulatory and Compliance Services
The banking sector, including Glacier Bancorp, operates under a stringent regulatory environment, making legal and compliance service providers powerful suppliers. Their specialized knowledge in areas like data privacy, anti-money laundering (AML), and evolving financial reporting standards grants them significant leverage. For instance, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) continuously updates its guidance, requiring banks to adapt their compliance programs, often necessitating external expertise.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified by the critical nature of their services; failure to comply can result in substantial fines and reputational damage. In 2024, the global regulatory compliance market was valued at over $50 billion, reflecting the significant demand and specialized nature of these services. The cost and effectiveness of these outsourced compliance solutions directly impact Glacier Bancorp's operational efficiency and risk management.
- Specialized Expertise: Suppliers possess niche knowledge in complex financial regulations.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing new compliance systems can be costly and time-consuming.
- Regulatory Dependence: Banks rely on external experts to navigate ever-changing legal landscapes.
- Market Concentration: A limited number of highly reputable firms may dominate specific compliance niches.
Information and Data Providers
Information and data providers hold significant sway over banks like Glacier Bank. Access to accurate, up-to-the-minute financial data, market insights, and credit reports is absolutely critical for everything a bank does, from assessing risk to making smart strategic moves. Suppliers such as major credit bureaus and providers of financial data terminals can leverage their position, especially if their data is unique or indispensable.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified by the essential nature of their offerings. For instance, services like those provided by Experian or Moody's Analytics are not easily replicated. In 2024, the demand for sophisticated data analytics tools continues to grow, giving these specialized providers more leverage.
- Criticality of Data: Banks rely heavily on data providers for market intelligence and creditworthiness assessments.
- Exclusivity and Integration: The uniqueness of data and a bank's ability to integrate it efficiently influence supplier power.
- Market Trends: The increasing reliance on advanced analytics in 2024 strengthens the bargaining position of data suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Glacier Bancorp is influenced by several factors, including the availability of capital, the uniqueness of technology solutions, the scarcity of skilled labor, and the critical nature of regulatory and data services. In 2024, deposit growth remains a key strength for banks, reducing reliance on external funding. However, specialized technology and compliance expertise can grant significant leverage to their providers.
The banking sector's reliance on specialized talent, particularly in areas like cybersecurity, has intensified in 2024, leading to increased wage demands. Similarly, regulatory compliance providers wield considerable power due to the complexity of financial laws and the high cost of non-compliance, with the global compliance market exceeding $50 billion in 2024. Data providers also hold strong positions, as banks depend on their unique insights for critical decision-making, a trend amplified by the growing demand for advanced analytics.
| Factor | Impact on Glacier Bancorp | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
| Capital Providers (Deposits) | Lower bargaining power with strong deposit base. | Stable deposit growth reduces reliance on wholesale funding. |
| Technology Providers | Higher power for unique/essential solutions; lower for commoditized ones. | Increasing demand for specialized AI and cybersecurity tools. |
| Skilled Labor | Significant power for in-demand roles (e.g., cybersecurity). | Higher salary expectations for specialized banking professionals. |
| Regulatory Compliance Services | High power due to complexity and non-compliance costs. | Global compliance market valued over $50 billion in 2024. |
| Information & Data Providers | High power for unique, integrated, and critical data. | Growing reliance on advanced analytics strengthens their position. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Glacier Bank, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics, simplifying complex strategic challenges.
Customers Bargaining Power
Glacier Bancorp's diverse customer base, encompassing individuals, small to medium-sized businesses, and public entities, influences customer bargaining power. While individual customers typically wield low power due to the small scale of their transactions and the standardized offerings in banking, larger commercial clients and public entities can exert more influence. For instance, in 2024, Glacier Bancorp reported a significant portion of its deposits coming from commercial relationships, suggesting these larger clients have a notable ability to negotiate terms on deposits and loans, thereby increasing their bargaining leverage.
Customers today have a vast array of banking options readily available, from large national institutions and other regional players to credit unions and digital-only banks. This abundance of choice significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. If a customer finds better rates, superior service, or more convenient digital tools elsewhere, they can readily switch providers. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. saw continued growth in digital banking adoption, with approximately 75% of consumers using mobile banking apps, making switching even easier.
Customers, particularly those looking for deposit accounts or loans, exhibit significant price sensitivity, closely monitoring interest rates and fees. This sensitivity intensifies in a competitive banking landscape, compelling Glacier Bancorp to maintain competitive pricing to attract and retain clients.
The Federal Reserve's monetary policy, including its benchmark interest rate decisions, directly impacts customer behavior. For instance, as of mid-2024, the Federal Funds Rate has remained elevated, influencing deposit yields and loan origination costs, thereby shaping customer expectations and their willingness to switch providers based on rate differentials.
Digital Banking Expectations
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by evolving digital banking expectations. The widespread adoption of digital-first banking and innovative fintech solutions means customers now anticipate a highly convenient, rapid, and smooth online experience. This shift means banks must offer 24/7 service availability, robust mobile applications, and streamlined digital processes for everything from opening accounts to applying for loans.
Failure to meet these heightened digital demands can lead to customer attrition. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers would consider switching banks if their digital experience was subpar. Glacier Bank, like its peers, faces pressure to invest in and upgrade its digital platforms to retain and attract customers in this competitive landscape.
- Digital Channel Preference: A significant portion of banking transactions, estimated to be over 70% by early 2024, are now conducted through digital channels, highlighting customer preference for online and mobile banking.
- Fintech Competition: The rise of fintech companies offering specialized, user-friendly digital services puts pressure on traditional banks to match or exceed these offerings.
- Customer Loyalty Drivers: Convenience and ease of use in digital interactions are increasingly becoming key drivers of customer loyalty, directly impacting a bank's ability to retain its customer base.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching banks, while requiring some administrative effort like updating direct deposits and automatic payments, generally doesn't present insurmountable hurdles for most retail customers. The increasing sophistication of digital banking tools, designed to streamline account transfers and information migration, further lowers these barriers. For instance, many neobanks and traditional banks alike offer automated switch kits, simplifying the process for customers looking to move their accounts.
This relative ease of transition empowers customers, as they can readily shift their business to competitors offering better rates, services, or customer experiences. For example, a customer dissatisfied with Glacier Bank's fees could easily compare offerings from other institutions and initiate a switch, potentially within days, using online portals. This flexibility significantly enhances the bargaining power of the average consumer.
However, this dynamic shifts for more complex commercial banking relationships. For businesses with integrated treasury management systems, specialized loan agreements, or significant operational reliance on a particular bank's infrastructure, the switching costs can be substantially higher. These embedded costs, often involving system reconfigurations, contract renegotiations, and potential disruptions to cash flow, can create stickiness, reducing customer bargaining power in those specific instances.
The overall impact on bargaining power is therefore nuanced:
- Retail Customer Switching: Generally low switching costs due to digital tools and ease of fund transfer.
- Digital Facilitation: Banks actively developing tools to simplify account switching for customers.
- Commercial Relationships: Higher switching costs for businesses due to integrated systems and complex agreements.
- Impact on Power: Lower costs for retail customers increase their bargaining power, while higher costs for commercial clients decrease theirs.
Glacier Bancorp's customers possess considerable bargaining power, largely due to the highly competitive banking landscape and the ease with which consumers can switch providers. The increasing prevalence of digital banking, with over 70% of transactions conducted online or via mobile by early 2024, means customers expect seamless, convenient experiences. If these expectations aren't met, or if better rates are available elsewhere, customers can readily move their business, especially given that many banks now offer tools to simplify account transfers.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Continued growth in digital banking adoption; ~75% of consumers using mobile banking apps. |
| Switching Costs (Retail) | Low | Digital tools simplify account transfers and information migration. |
| Digital Expectations | High | Over 60% of consumers would switch banks for a subpar digital experience. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Customers closely monitor interest rates and fees, especially for deposits and loans. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Glacier Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Glacier Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is precisely what you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into threats and opportunities. You're looking at the actual, professionally formatted analysis, ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Glacier Bancorp navigates a banking environment populated by a significant number of competitors. This includes a vast array of regional banks, larger national institutions, and numerous credit unions, all actively seeking to capture market share.
The sheer volume of these players, regardless of their size, creates a highly competitive atmosphere. Each entity is constantly working to attract and retain customers, leading to intensified rivalry across the sector.
While some regional banks have experienced positive momentum, the banking industry as a whole continues to be characterized by robust competition. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the U.S. banking industry reported total assets exceeding $23 trillion, underscoring the scale and competitive nature of the market.
The growth rate of the banking sector significantly shapes competitive rivalry for Glacier Bancorp. In 2023, the U.S. banking industry saw moderate growth, with net income for all commercial banks increasing by 1.7% year-over-year, according to the FDIC. This pace suggests a generally stable competitive environment, though specific regional variations within Glacier Bancorp's operating areas could present more intense competition if those areas are experiencing slower economic expansion.
Regions with slower market growth often force banks to fight harder for a limited customer base. This can manifest as aggressive pricing on loans and deposits or heightened spending on advertising and new product development. Conversely, in markets experiencing robust economic expansion, such as certain areas in the Mountain West where Glacier Bancorp has a presence, the availability of new customers and business opportunities can temper the need for direct, cutthroat competition among incumbent banks.
Product and service differentiation in banking is often subtle, as core offerings like checking accounts and standard loans are largely similar across institutions. Competition frequently hinges on pricing, such as interest rates and fees, alongside the quality of customer service and the accessibility of physical branches. Glacier Bancorp aims to stand out by emphasizing its community-centric approach and specializing in commercial real estate and construction financing, areas where tailored expertise can be a key differentiator.
Regulatory Environment and M&A Activity
The regulatory environment significantly shapes competitive rivalry in banking. For instance, changes in capital requirements or lending standards can favor larger institutions with greater resources to adapt, potentially intensifying competition for smaller banks. In 2024, discussions around potential adjustments to bank capital rules continue, which could influence how banks compete and invest.
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are a key mechanism through which the regulatory landscape influences rivalry. Increased M&A activity, often spurred by regulatory pressures or opportunities, can lead to a more concentrated market. This consolidation can create larger, more dominant players, thereby altering the competitive dynamics for remaining independent banks. The trend towards regional bank consolidation, observed in recent years, is expected to persist, potentially reshaping market share and competitive intensity.
- Regulatory Changes: Evolving regulations can create advantages for some banks over others, impacting competitive positioning.
- M&A Drivers: Regulatory shifts and the pursuit of scale are key drivers of consolidation in the banking sector.
- Competitive Landscape Alteration: Increased M&A activity can lead to fewer, but larger, competitors, intensifying rivalry.
- 2024 Trends: Anticipated adjustments to bank capital rules and ongoing regional M&A activity are notable factors in 2024.
Technological Advancements and Fintech Integration
The banking sector is experiencing heightened rivalry due to rapid technological advancements, especially in fintech. Glacier Bancorp, like its peers, faces pressure to invest heavily in digital transformation to keep pace with nimble fintech firms that are disrupting traditional services like payments and lending. For instance, the global fintech market size was valued at approximately $112.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating the scale of this competitive force.
- Fintech Disruption: Agile fintech companies are offering innovative, often lower-cost, digital solutions across various banking functions.
- Digital Transformation Imperative: Traditional banks must invest in technology to remain competitive and meet evolving customer expectations for seamless digital experiences.
- Collaboration as a Strategy: Partnerships between established banks and fintechs are emerging as a key competitive strategy, blending traditional trust with technological innovation.
The competitive rivalry for Glacier Bancorp is intense, fueled by a diverse range of financial institutions. This includes large national banks, numerous regional players, and credit unions, all vying for customer deposits and loan business. The sheer number of these competitors means that market share gains often come at the expense of rivals, leading to aggressive strategies in pricing and service offerings.
Technological innovation, particularly from fintech companies, further escalates this rivalry. These agile firms are challenging traditional banking models with digital-first solutions, forcing established players like Glacier Bancorp to accelerate their own digital transformations. The global fintech market's projected growth underscores the ongoing pressure to adapt and innovate.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Actions | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| National Banks | Broad product offerings, extensive branch networks, significant marketing budgets | Set industry standards, exert pricing pressure |
| Regional Banks | Community focus, tailored services, competitive loan rates | Direct competition in local markets, often with similar customer bases |
| Credit Unions | Member-centric approach, often lower fees and better rates on deposits/loans | Attract specific customer segments, particularly those with shared affiliations |
| Fintech Companies | Digital-native platforms, specialized services (payments, lending), lower overhead | Disrupt traditional models, drive digital innovation, introduce new competitive pressures |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies present a substantial threat of substitution for Glacier Bank, particularly through digital payment platforms. These platforms, such as Venmo and Zelle (which partners with many banks), allow for quick, often fee-free money transfers, directly competing with traditional wire transfers and account-to-account payments offered by banks.
The rise of mobile payment apps and digital wallets further erodes traditional banking's dominance in transaction services. For instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that over 80% of consumers in developed markets will utilize mobile payment solutions for at least some of their purchases, a trend that bypasses traditional bank infrastructure for everyday transactions.
Beyond payments, peer-to-peer lending platforms and online investment services offer alternative avenues for borrowing and wealth management, diverting customers and revenue streams from established financial institutions like Glacier Bank. These digital alternatives often boast lower overheads, translating into more competitive rates and fees for consumers.
Beyond traditional bank loans, businesses and individuals can access capital through various alternative lending sources. These include online lenders, private equity firms, crowdfunding platforms, and credit unions. For instance, the online lending market saw significant growth, with small business loan origination through fintech lenders reaching an estimated $20 billion in 2024, offering a direct substitute for Glacier Bancorp's services.
These alternatives can offer more flexible terms or faster approvals, particularly for specific types of loans. For example, some fintech platforms provide loan decisions within minutes, a stark contrast to traditional bank processing times, thereby substituting for Glacier Bancorp's lending options.
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets, while still emerging for widespread use in daily transactions, pose a potential long-term threat to traditional banking services. As these technologies mature and gain broader acceptance, they could offer alternative methods for value storage, fund transfers, and transactional activities. For instance, by mid-2024, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies fluctuated significantly but remained in the trillions, indicating substantial investor interest and a growing ecosystem.
This evolving landscape could diminish customer reliance on conventional deposit accounts and established payment networks. The increasing development of stablecoins, pegged to fiat currencies, further strengthens their potential as a substitute for traditional monetary functions. By 2024, several countries were actively exploring or piloting central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), signaling a significant shift in how digital value might be managed and transacted.
In-house Financial Management by Businesses
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), is growing. Many SMBs are finding that in-house financial management solutions are becoming increasingly viable alternatives for certain functions. For instance, payroll processing and basic treasury management, once exclusively the domain of banks, can now be efficiently handled using readily available accounting software or specialized business management platforms. This shift doesn't eliminate the need for banks entirely, as lending and deposit services remain crucial, but it does reduce reliance on banks for these specific transactional needs.
In 2024, the adoption of cloud-based accounting software by SMBs continued its upward trajectory. Reports indicate that over 60% of SMBs in developed economies were utilizing such software, which often includes integrated payroll and basic treasury functions. This trend directly impacts the revenue streams banks derive from these services. For example, while specific market share data for banks losing payroll processing to in-house solutions is not readily available, the broader trend suggests a significant portion of the estimated $100 billion global payroll services market is now accessible to software providers and internal IT departments.
- Growing adoption of accounting software: Over 60% of SMBs in developed economies used cloud-based accounting software in 2024, often with built-in payroll and treasury features.
- Reduced reliance on banks: SMBs can now manage payroll and basic treasury functions internally, lessening their dependence on traditional banking services for these tasks.
- Impact on bank revenue: This shift presents a substitute threat to banks’ fee-based income from transactional services, though core lending and deposit services remain essential.
- Competitive landscape evolution: Fintech companies and software providers are increasingly offering integrated financial management tools that directly compete with bank offerings for SMBs.
Non-Bank Investment Vehicles
Customers seeking to grow their savings have a vast array of alternatives beyond traditional bank deposit accounts, presenting a significant threat of substitution for Glacier Bank. These non-bank investment vehicles, such as money market funds, individual stocks, bonds, and diversified mutual funds, often promise higher yields compared to standard savings or checking accounts. For instance, by mid-2024, the average yield on a money market fund was hovering around 4.5%, significantly outpacing typical bank savings account rates.
The sheer breadth of the investment market means customers can tailor their risk tolerance and return expectations precisely. While Glacier Bank might offer some investment products through its wealth management division, the broader financial landscape provides a much more extensive menu of options. This accessibility to alternative investment avenues, particularly for individuals looking for growth beyond simple capital preservation, directly siphons potential deposits away from traditional banking services.
- Money Market Funds: Offered yields around 4.5% in mid-2024, providing a liquid alternative to bank deposits.
- Bonds: Government and corporate bonds offer varying levels of risk and return, attracting investors seeking income.
- Stocks and Mutual Funds: Provide potential for higher capital appreciation, appealing to growth-oriented savers.
- Alternative Investments: Real estate investment trusts (REITs) and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer further diversification and return potential.
The threat of substitutes for Glacier Bank is significant, with fintech and digital platforms offering faster, often cheaper alternatives for payments and money transfers. By the end of 2024, over 80% of consumers in developed markets are expected to use mobile payment solutions, bypassing traditional banking infrastructure for daily transactions.
Peer-to-peer lending and online investment services provide alternative avenues for borrowing and wealth management, diverting customers and revenue. For instance, small business loan origination through fintech lenders was projected to reach $20 billion in 2024, directly competing with Glacier Bancorp's lending services.
Beyond payments, businesses and individuals can access capital through online lenders, private equity, crowdfunding, and credit unions, often with faster approvals and more flexible terms. Cryptocurrencies and digital assets, while still evolving, represent a potential long-term threat for value storage and fund transfers, with a global market capitalization in the trillions by mid-2024.
For small and medium-sized businesses, in-house financial management solutions, like cloud-based accounting software with integrated payroll, are becoming viable substitutes for certain banking functions. In 2024, over 60% of SMBs in developed economies used such software, impacting bank revenue from transactional services.
| Substitute Area | Example | 2024 Data/Trend | Impact on Glacier Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payments & Transfers | Digital Wallets, P2P Apps | >80% consumer adoption of mobile payments in developed markets. | Reduced transaction fees, customer migration. |
| Lending | Fintech Lenders, Crowdfunding | $20B projected SMB loan origination via fintech lenders. | Loss of loan origination revenue, competitive pressure on rates. |
| Wealth Management | Money Market Funds, Stocks, Bonds | Money market fund yields ~4.5% (mid-2024). | Diversion of deposits, reduced fee income from advisory services. |
| Business Services | Accounting Software (Payroll) | >60% SMBs using cloud accounting software. | Erosion of fee-based income from payroll and treasury services. |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like Glacier Bank, faces substantial regulatory barriers. Establishing a new bank requires navigating a complex charter application process, which can be lengthy and demanding. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain a national bank charter in the U.S. remained a significant hurdle, often extending over a year, coupled with rigorous compliance checks.
Furthermore, significant capital requirements act as a powerful deterrent for potential new entrants. Regulators mandate substantial minimum capital reserves to ensure stability and protect depositors. In 2024, many jurisdictions, including the U.S., maintained or even increased these capital adequacy ratios, with Tier 1 capital requirements for larger banks often exceeding 10% of risk-weighted assets, making it prohibitively expensive for many to enter the market.
Existing banks, including Glacier Bancorp, leverage decades of established brand recognition and deep customer trust. For instance, Glacier Bancorp's long-standing presence in its communities fosters a sense of reliability that new players struggle to replicate quickly. This loyalty means customers are less likely to switch to an unfamiliar institution, even with competitive offerings.
Established banks like Glacier Bancorp benefit from significant economies of scale. This means they can spread costs like technology infrastructure and marketing across a larger customer base, making them more cost-efficient than smaller, newer competitors. For instance, in 2024, major banks reported operating leverage gains as transaction volumes increased.
Network effects further solidify the position of incumbent banks. Glacier Bancorp's extensive branch and ATM network provides convenience that new entrants struggle to match. This widespread accessibility creates a powerful advantage, as customers prefer banks with readily available physical touchpoints, a trend that remained prevalent throughout 2024.
Access to Funding and Deposit Bases
New banks often face significant hurdles in building a robust and cost-effective deposit base, a foundational element for their lending operations. Established institutions like Glacier Bank benefit from long-standing customer loyalty and a broad, diversified deposit portfolio, which typically offers lower funding costs.
In contrast, new entrants may initially depend on more expensive wholesale funding markets to finance their activities. This reliance on pricier funding sources can place them at a distinct competitive disadvantage compared to incumbents with access to cheaper, retail deposits. For instance, as of late 2023, the average interest rate on savings accounts at large banks hovered around 0.35%, while wholesale funding rates could be considerably higher, reflecting market volatility and perceived risk.
- Deposit Base Challenge New entrants struggle to attract stable, low-cost deposits essential for lending.
- Established Advantage Incumbents possess existing customer relationships and diversified, cheaper deposit funding.
- Funding Cost Disparity New banks may initially rely on more expensive wholesale funding, impacting profitability.
Fintech Startups and Niche Players
Fintech startups are a significant threat, as they can bypass some of the stringent regulations faced by established banks by focusing on specialized, often digital-first, services. These nimble companies can target specific customer needs or market segments, offering streamlined digital experiences that traditional banks may struggle to replicate quickly.
While not always directly competing as full-service banks, these niche players can erode market share in areas like payments, lending, or wealth management. For example, by mid-2024, neobanks and digital payment platforms continued to attract substantial customer bases, particularly among younger demographics, demonstrating the appeal of their specialized offerings.
- Digital-first offerings: Fintechs often excel in user experience and speed, attracting customers who prioritize convenience.
- Niche market focus: Many startups target underserved segments or specific product lines, avoiding direct, head-on competition with large banks initially.
- Lower overheads: Digital-only models typically have lower operational costs compared to brick-and-mortar banks, allowing for competitive pricing.
- Rapid innovation: Fintechs can adapt and deploy new technologies much faster than traditional institutions, responding quickly to market changes.
The threat of new entrants for Glacier Bank is generally considered moderate due to significant barriers. However, the rise of agile fintech companies presents a more dynamic challenge, capable of disrupting specific banking services with innovative, digital-first approaches. These new players often leverage lower operational costs and rapid technological adoption to gain traction.
| Barrier Category | Description | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex charter applications and strict compliance requirements. | Average U.S. national bank charter process often exceeded one year. |
| Capital Requirements | Mandatory minimum capital reserves for stability. | Tier 1 capital requirements for large banks frequently remained above 10% of risk-weighted assets. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established customer relationships and community presence. | Incumbents like Glacier Bancorp benefit from decades of built trust. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost efficiencies from larger operations and customer bases. | Major banks saw operating leverage gains in 2024 due to increased transaction volumes. |
| Network Effects | Extensive branch and ATM networks offering convenience. | Widespread physical accessibility remained a key customer preference in 2024. |
| Fintech Disruption | Digital-first services targeting niche markets. | Neobanks and digital payment platforms continued to attract younger demographics mid-2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Glacier Bank is built upon a foundation of credible data, including the bank's annual reports, regulatory filings with the FDIC, and industry-specific research from financial institutions and market analysis firms.
