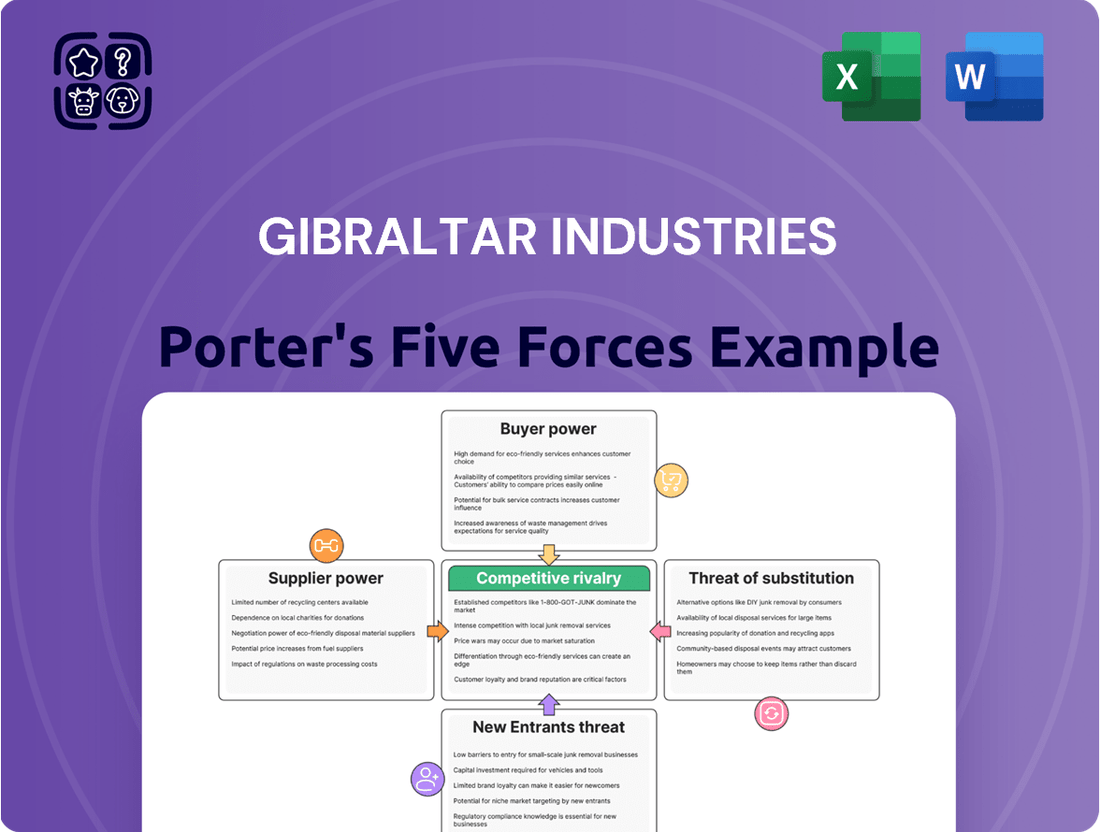
Gibraltar Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gibraltar Industries Bundle
Gibraltar Industries faces moderate buyer power due to fragmented customer bases across its diverse product lines, but intense competition from established players and new entrants significantly pressures pricing. The threat of substitutes is also a key consideration, particularly in its modular building and traditional construction segments.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Gibraltar Industries’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration significantly shapes the bargaining power of those providing materials to Gibraltar Industries. For instance, if a limited number of steel producers supply the majority of the raw steel needed for Gibraltar's fabricated metal products, those few suppliers hold considerable sway over pricing and delivery schedules. In 2023, global steel prices experienced volatility, indicating the potential leverage concentrated suppliers can wield.
Gibraltar Industries faces significant switching costs, which directly bolster the bargaining power of its suppliers. If Gibraltar were to change suppliers, it would likely incur substantial expenses related to retooling its manufacturing processes to accommodate new materials or specifications. For instance, in 2023, capital expenditures for Gibraltar Industries were $138.7 million, illustrating the investment in its operational infrastructure.
Furthermore, the need to requalify new materials and potentially disrupt existing supply chains adds layers of complexity and cost. These disruptions can lead to production delays and increased operational expenses, making a switch from an established supplier a costly endeavor. This financial and operational burden strengthens the leverage suppliers hold over Gibraltar.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for Gibraltar Industries. If readily available alternatives exist for the raw materials or components Gibraltar uses, such as different types of steel or alternative manufacturing processes, then suppliers have less leverage to demand higher prices or impose unfavorable terms. This is because Gibraltar could more easily switch to another supplier or adopt a different input, reducing reliance on any single source.
Uniqueness of Supplier Offerings
Gibraltar Industries' suppliers can wield significant bargaining power when their offerings are highly unique or proprietary. This is particularly true for components crucial to specialized products like their solar racking systems or advanced building materials. For instance, a supplier providing a patented fastening mechanism for solar panels, essential for the system's structural integrity and efficiency, would have considerable leverage.
When these unique inputs are indispensable to Gibraltar's product performance or drive innovation, suppliers can often dictate higher prices. This situation was evident in early 2024 when certain specialty steel alloys, vital for high-strength, lightweight construction components, saw price increases due to limited global producers and strong demand. This directly impacted input costs for manufacturers like Gibraltar.
- Supplier Differentiation: Suppliers offering patented or highly specialized materials for Gibraltar's product lines, such as advanced coatings or unique metal alloys, possess stronger negotiation positions.
- Essential Inputs: If a supplier's product is critical to the performance, durability, or innovation of Gibraltar's end products, like specialized fasteners for solar racking, their bargaining power increases.
- Limited Alternatives: The absence of readily available substitutes for a supplier's unique offering means Gibraltar has fewer options, thereby enhancing the supplier's ability to influence terms and pricing.
- Impact on Costs: In 2024, for example, supply chain disruptions for certain high-performance polymers used in building products led to price hikes by key suppliers, directly affecting Gibraltar's cost of goods sold.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Gibraltar Industries' markets, essentially becoming competitors by manufacturing or distributing similar products, directly enhances their bargaining power. This potential competition can pressure Gibraltar to accept less favorable terms, such as higher prices or stricter payment schedules, to maintain a stable supply chain and avoid direct rivalry with entities that currently supply their raw materials or components.
For instance, if a key supplier of fabricated metal products were to start selling directly to Gibraltar's end customers, it would fundamentally alter the competitive landscape. This move would not only increase the supplier's leverage but also force Gibraltar to consider its own competitive strategies more carefully.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into manufacturing or distribution creates direct competition for Gibraltar.
- Increased Bargaining Power: This integration allows suppliers to dictate terms more aggressively.
- Impact on Gibraltar: Gibraltar may face higher costs or less favorable contract conditions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Gibraltar Industries is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, and the availability of substitutes. When a few suppliers dominate the market for essential raw materials, they can exert significant pricing power. For example, in 2023, Gibraltar's capital expenditures of $138.7 million highlight the investment in its operations, suggesting that changing suppliers could involve substantial costs and disruptions.
Gibraltar's reliance on specialized or proprietary components also strengthens supplier leverage. If a supplier provides unique materials critical to product performance, like patented fasteners for solar racking, they can command higher prices. This was observed in early 2024 with price increases for specialty steel alloys due to limited producers and high demand, directly impacting input costs for manufacturers.
| Factor | Impact on Gibraltar | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Higher leverage for suppliers | Limited number of steel producers for fabricated metal products |
| Switching Costs | Increased supplier power | Gibraltar's 2023 CapEx: $138.7 million (indicates infrastructure investment) |
| Supplier Differentiation | Stronger negotiation position | Patented fasteners for solar racking systems |
| Essential Inputs | Increased supplier leverage | Specialty steel alloys vital for construction components (price hikes in early 2024) |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Gibraltar Industries reveals the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing a strategic understanding of its competitive environment.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, helping Gibraltar Industries pinpoint and alleviate strategic pain points.
Customers Bargaining Power
Gibraltar Industries' customer bargaining power is significantly shaped by customer concentration and the sheer volume of their purchases. For instance, major home improvement retailers like Home Depot or Lowe's, which represent substantial sales volumes, can leverage their purchasing power to negotiate more competitive pricing and favorable contract terms. This concentration means a few key clients can exert considerable influence over Gibraltar's pricing and product development strategies.
Gibraltar Industries' customers possess significant bargaining power when switching costs are low. For instance, if a builder can easily source comparable building components or solar racking systems from multiple suppliers without incurring substantial costs or disruptions, they are more empowered to negotiate favorable pricing or demand better terms from Gibraltar. This ease of transition directly translates into leverage for the customer.
Customer price sensitivity is a major factor in their ability to negotiate. In industries like building materials, where many products are similar, customers tend to focus heavily on price. This puts pressure on companies like Gibraltar Industries to keep their prices competitive to win business.
For Gibraltar Industries, this means that if competitors offer similar products at lower prices, customers will likely switch. This was evident in 2024, where rising input costs pressured margins, and customers in sectors like residential construction showed a heightened sensitivity to price increases, demanding more favorable terms.
Availability of Substitute Products
The availability of substitute products significantly influences customer bargaining power. If customers can readily find comparable building components, solar racking systems, or mail solutions from other manufacturers, their leverage to negotiate better terms with Gibraltar Industries increases. This is particularly true in markets where product differentiation is low.
For instance, in the construction sector, a wide array of suppliers offer similar metal building components, making it easier for contractors to switch if Gibraltar's pricing or terms are unfavorable. Similarly, the burgeoning solar energy market has seen numerous companies enter the solar racking space, providing ample alternatives for installers and developers. In 2024, the competitive landscape for building materials saw an estimated 15% increase in the number of new entrants offering comparable products, directly impacting pricing power.
- Increased competition in building materials: The market for metal building components is highly competitive, with numerous domestic and international suppliers offering similar products.
- Growth of alternative solar racking solutions: The solar industry’s rapid expansion has led to a proliferation of solar racking system providers, many with innovative or cost-effective designs.
- Availability of mail and security solutions: The mail and security solutions market also presents various alternatives, from traditional postal solutions to advanced digital communication and secure delivery systems.
- Impact on pricing and terms: The ease with which customers can switch to alternatives directly translates into higher bargaining power, pressuring Gibraltar to offer competitive pricing and favorable contract terms.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers integrating backward, meaning they start producing their own building materials or components, significantly boosts their bargaining power against Gibraltar Industries. This capability allows them to dictate terms and pricing more effectively, as they can reduce their reliance on external suppliers like Gibraltar.
For instance, large construction conglomerates or major renewable energy developers, if they possess the in-house expertise and capital to manufacture certain products currently sourced from Gibraltar, can leverage this potential to negotiate better deals. This puts pressure on Gibraltar to remain competitive in both price and quality.
- Backward Integration Threat: Customers may develop the capacity to produce Gibraltar's products internally, increasing their leverage.
- Impact on Pricing: This capability empowers customers to demand lower prices or more favorable terms from Gibraltar.
- Competitive Pressure: Gibraltar faces pressure to maintain competitive pricing and product quality to deter customer backward integration.
Gibraltar Industries faces substantial customer bargaining power due to market concentration and customer price sensitivity. Major retailers and large-scale developers, representing significant sales volumes, can negotiate favorable pricing and terms, especially when switching costs are low and substitutes are readily available. In 2024, the competitive landscape saw a notable increase in alternative suppliers, intensifying this pressure on Gibraltar.
| Factor | Impact on Gibraltar | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for large customers | Major retailers represent significant sales volumes. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower customers | Easy sourcing of comparable components from multiple suppliers. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers focus on price, especially in construction | Heightened sensitivity to price increases in residential construction. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases customer negotiation power | Estimated 15% increase in comparable product entrants in building materials. |
Full Version Awaits
Gibraltar Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Porter's Five Forces analysis for Gibraltar Industries you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It delves into the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This comprehensive document is ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape for Gibraltar Industries is shaped by a mix of numerous smaller players and a few larger, more established entities across its key markets. In the residential segment, for instance, the presence of many regional and local manufacturers intensifies rivalry, as these smaller firms often compete on price and localized service.
In contrast, the renewable energy and infrastructure sectors feature a more concentrated group of larger competitors, some of whom possess significant scale and capital. For example, companies like Nucor in steel fabrication, a key input for infrastructure projects, operate at a much larger scale than many of Gibraltar's direct competitors in specific niche markets.
Gibraltar Industries' revenue in 2023 was $1.49 billion, indicating it is a substantial player but still operates in markets where its size relative to some giants in adjacent industries, like large steel producers, can influence competitive dynamics. The intensity of rivalry is therefore a dynamic factor, varying by market segment and the specific capabilities of its rivals.
The growth rate of the industries Gibraltar Industries operates in significantly influences competitive rivalry. In mature or slower-growing markets, companies often engage in more aggressive competition for market share, which can lead to price wars and reduced profitability. Conversely, rapidly expanding industries can accommodate growth for all participants, lessening the intensity of direct competition as firms focus on capturing new demand.
Gibraltar's exposure to the solar industry highlights this dynamic. While the solar sector has experienced substantial growth, it has also been subject to market fluctuations and evolving government policies. For instance, in 2024, the global solar market continued its upward trajectory, with installations projected to reach new highs, yet this growth is accompanied by intense competition from established players and new entrants alike, particularly in utility-scale projects.
The degree to which Gibraltar Industries' products stand out from competitors significantly impacts rivalry. When products are largely interchangeable, like basic construction materials, price wars become more common. For instance, in the pre-engineered steel buildings market, where many players offer similar designs, price is often a primary deciding factor.
Gibraltar Industries' strategic emphasis on efficiency, safety, and sustainability offers a potential avenue for differentiation. By highlighting superior product performance, reduced environmental impact, or enhanced safety features, Gibraltar can carve out a niche. This approach can lessen direct price comparisons and foster customer loyalty, even in competitive segments.
In 2024, the construction materials sector, a key area for Gibraltar, continued to see varied demand. While some segments experienced robust growth, others faced pressure from oversupply, intensifying the need for clear product differentiation to mitigate intense competitive rivalry.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the building and construction sector can significantly fuel competitive rivalry. When it's difficult or costly for companies to leave the market, they often remain even when facing low profitability. This persistence can lead to prolonged periods of intense price competition and market overcapacity, as firms fight for a shrinking or stagnant profit pool.
These barriers include specialized assets that are hard to repurpose, significant contractual obligations, and the emotional or reputational costs associated with shutting down operations. For instance, in 2024, many construction firms continued to operate despite tighter margins, partly due to existing long-term contracts and the difficulty in divesting specialized heavy machinery.
- Specialized Assets: Difficulty in selling or redeploying industry-specific equipment and facilities.
- Contractual Commitments: Existing projects and supply agreements that must be fulfilled.
- Management Discretion: Reluctance to close down operations due to employee welfare or reputational concerns.
- Governmental or Regulatory Constraints: Licenses or permits that are difficult to transfer or abandon.
Market Diversity
Gibraltar Industries navigates a landscape where competitive rivalry is shaped by its presence in distinct sectors like residential, renewable energy, infrastructure, and industrial markets. These diverse operational arenas present varying levels of competitive intensity, often influenced by specialized demands and the presence of numerous niche competitors.
For instance, in the residential construction segment, Gibraltar faces competition from a broad range of manufacturers and distributors, where product differentiation and cost efficiency are key. Conversely, the renewable energy sector, particularly solar, might see rivalry among specialized component providers and installers, with innovation and project execution capabilities being critical differentiators. In 2023, the North American solar installation market, a key area for renewable energy components, saw significant growth, indicating a dynamic competitive environment.
- Residential Market: High competition from numerous players focusing on cost and product variety.
- Renewable Energy: Intense rivalry among specialized component suppliers, driven by technological advancements.
- Infrastructure & Industrial: Competition may be more project-specific, with fewer but larger players in certain segments.
- Market Fragmentation: The diversity of markets means Gibraltar encounters different competitive forces, requiring tailored strategies for each segment.
Gibraltar Industries operates in markets with varying degrees of competitive rivalry, from fragmented residential sectors with many small players to more concentrated infrastructure and renewable energy segments. The intensity is often driven by industry growth rates, product differentiation, and high exit barriers, which can keep less profitable firms in the market. For example, in 2024, the construction materials sector saw intense competition due to oversupply in certain areas, pushing companies to focus on differentiation.
The company's revenue of $1.49 billion in 2023 places it as a significant player, but it still contends with larger entities in adjacent markets like steel production. In the solar industry, a growth area for Gibraltar, competition is fierce among specialized suppliers and installers, with technological advancements being a key battleground. The North American solar installation market's growth in 2023 underscored this dynamic competitive environment.
Product interchangeability, especially in areas like pre-engineered steel buildings, often leads to price-based competition. Gibraltar's strategy to differentiate through efficiency, safety, and sustainability aims to mitigate this. High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and contractual commitments, can further intensify rivalry by keeping firms active even with reduced profitability, a trend observed in 2024 for many construction firms facing tighter margins.
| Market Segment | Key Competitive Factors | Gibraltar's Position Indicator (2023 Revenue) |
| Residential Construction | Price, Product Variety, Local Service | Substantial, but faces many regional players |
| Renewable Energy (Solar) | Technology, Project Execution, Scale | Growing presence in a dynamic, competitive sector |
| Infrastructure & Industrial | Scale, Capital, Project Specific Capabilities | Competes with larger, established players in certain niches |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Gibraltar Industries' products is present due to alternative materials and technologies that can meet similar customer needs. For example, in their building products segment, advanced plastics or composite materials could potentially replace traditional metal components, offering different performance characteristics or cost advantages.
In the renewable energy sector, while Gibraltar provides steel for solar racking systems, alternative mounting solutions or even different energy generation technologies could emerge as substitutes. The company's 2023 revenue was $1.4 billion, and understanding these evolving alternatives is crucial for maintaining market share.
The threat of substitutes for Gibraltar Industries hinges significantly on the relative price and performance of alternatives. If competitors offer similar products or services at a lower cost, or with enhanced features, customers may find them more appealing. For instance, in the modular data center market, while Gibraltar offers robust solutions, the emergence of more cost-effective, pre-fabricated units from agile competitors could divert demand if their price-to-performance ratio proves superior.
Customer willingness to adopt substitute products is a significant factor in assessing the threat of substitutes for Gibraltar Industries. This willingness is shaped by elements like brand loyalty, the perceived risk associated with switching, and the overall ease of making that transition. For example, in the solar racking market, a move towards alternative mounting technologies or the adoption of integrated solar solutions could represent a viable substitute.
Evolution of Renewable Energy Solutions
The threat of substitutes in the renewable energy sector is significant, particularly for companies like Gibraltar Industries that focus on solar racking systems. Rapid technological advancements are constantly introducing new energy generation and storage solutions. These innovations could diminish the demand for traditional solar racking, presenting a direct substitute threat.
For instance, the burgeoning field of advanced battery storage systems, coupled with the increasing efficiency of integrated solar panel designs, might reduce the need for separate, robust racking structures in certain applications. By 2024, the global energy storage market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the rapid growth and innovation in this area. This growth fuels the development of alternative energy delivery and integration methods that bypass traditional component reliance.
- Emerging Energy Storage Technologies: Innovations in battery chemistry and grid-scale storage solutions offer alternatives to distributed solar generation reliant on racking.
- Integrated Solar Solutions: Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and other aesthetically driven solar designs can reduce or eliminate the need for conventional racking.
- Advancements in Energy Transmission: Improved grid infrastructure and direct energy transfer methods could lessen the reliance on localized, rack-mounted generation.
- Policy and Market Shifts: Government incentives and evolving consumer preferences towards diverse renewable sources can accelerate the adoption of non-racking dependent energy solutions.
Shift in Construction Methods
Innovations in construction, like modular building and 3D-printed homes, present a significant threat to traditional building component manufacturers such as Gibraltar Industries. These new methods can streamline construction processes and potentially lower costs, directly impacting the demand for Gibraltar's existing product lines in both residential and infrastructure sectors. For instance, the global 3D printing construction market was valued at approximately $1.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a tangible shift in building practices.
These evolving construction techniques act as substitutes by offering alternative ways to achieve the final building outcome. If modular or pre-fabricated components become more cost-effective and widely adopted, they could displace the need for many of the materials and systems Gibraltar currently supplies. This substitution risk is amplified as these technologies mature and gain broader market acceptance, potentially altering the competitive landscape significantly.
The threat of substitutes is particularly relevant for Gibraltar in markets where speed and cost efficiency are paramount. For example, in the affordable housing sector, the adoption of pre-fabricated or 3D-printed solutions could accelerate, directly impacting demand for traditional materials. In 2024, the construction industry continues to explore these efficiencies, with significant investment flowing into proptech and innovative building solutions.
- Modular Construction: Offers faster build times and reduced on-site labor, potentially decreasing reliance on traditional on-site assembly components.
- 3D Printing: Enables rapid creation of building elements, potentially substituting for pre-cast concrete or other manufactured components.
- Pre-fabricated Solutions: Systems like pre-engineered metal buildings or panelized wall systems can offer quicker assembly, impacting demand for site-built structures.
- Material Innovation: Development of new, lighter, or more sustainable building materials could also serve as substitutes for traditional offerings.
The threat of substitutes remains a key consideration for Gibraltar Industries, particularly as alternative materials and technologies gain traction. In the building products segment, advancements in composites or high-performance plastics could offer competitive alternatives to traditional metal components, influencing material choices based on cost and performance. Gibraltar's 2023 revenue of $1.4 billion underscores the scale of its operations and the potential impact of these substitutions.
In the renewable energy sector, while Gibraltar supplies steel for solar racking, innovations in energy storage and integrated solar solutions present significant substitute threats. For example, advancements in battery technology and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) could reduce the need for separate racking systems. The global energy storage market, projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2024, highlights the rapid pace of innovation in this area, potentially shifting demand away from traditional solar infrastructure components.
Furthermore, the construction industry's embrace of modular building and 3D printing offers alternative methods that can streamline processes and lower costs, directly impacting demand for Gibraltar's conventional building materials. The global 3D printing construction market, valued at approximately $1.6 billion in 2023, demonstrates a tangible shift towards these innovative building practices, posing a direct substitution risk.
| Threat Category | Specific Substitute Examples | Potential Impact on Gibraltar | Key Drivers |
| Building Products | Advanced composites, high-performance plastics | Reduced demand for metal components, price pressure | Cost-effectiveness, enhanced performance characteristics |
| Renewable Energy | Integrated solar solutions (BIPV), advanced battery storage | Decreased need for solar racking systems | Technological innovation, aesthetic integration, energy independence |
| Construction Methods | Modular construction, 3D printing | Lower demand for traditional on-site building materials | Speed of construction, cost reduction, labor efficiency |
Entrants Threaten
The building and construction, and renewable energy sectors, where Gibraltar Industries operates, demand substantial upfront capital. Establishing manufacturing plants, robust distribution channels, and advanced research and development facilities requires significant financial commitment, often running into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, setting up a new solar panel manufacturing line can easily cost upwards of $50 million, not including ongoing operational expenses.
Gibraltar's existing, well-established infrastructure, built over years of operation, presents a considerable barrier to entry. New competitors would need to replicate this extensive network of production sites, warehouses, and logistics, a feat that demands immense capital and time. This is particularly true in the fragmented construction materials market, where economies of scale are crucial for profitability.
Gibraltar Industries, a significant player in its markets, likely leverages substantial economies of scale. This means their large production volumes allow for lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, raw material purchasing, and logistics. For instance, in 2023, the company reported net sales of $1.5 billion, indicating a considerable operational footprint that new entrants would find challenging to replicate.
New companies entering Gibraltar's sectors would face a steep uphill battle to achieve comparable cost efficiencies. Without the same scale, their initial production costs would be higher, making it difficult to compete on price with an established entity like Gibraltar. This cost disadvantage acts as a significant barrier, deterring potential new competitors from entering the market.
Securing access to established distribution channels, like relationships with major retailers, wholesalers, and contractors, is a significant hurdle for new entrants in Gibraltar Industries' markets. Building these crucial connections takes time and substantial investment, often requiring proven track records and extensive networks.
For instance, in the building products sector, where Gibraltar operates, established players often have long-standing agreements with key distributors. Newcomers would struggle to replicate these established relationships, making it difficult to get their products to market efficiently. In 2024, the average lead time for securing new distribution agreements in the construction materials industry was reported to be between 6 to 12 months, highlighting the time commitment involved.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
Gibraltar Industries has cultivated strong brand loyalty and established deep customer relationships across its various segments, a significant barrier for potential new entrants. These established connections, built over years of reliable service and product quality, mean newcomers must undertake substantial marketing and sales efforts to even begin to compete. For instance, in the U.S. construction materials market, where Gibraltar operates, brand recognition plays a crucial role in purchasing decisions, and displacing incumbent trust requires considerable investment and time.
The cost of overcoming Gibraltar's entrenched brand loyalty is a major deterrent. New companies entering markets like engineered products or infrastructure solutions would face the challenge of not only matching product offerings but also convincing customers to switch from trusted, long-standing suppliers. This necessitates significant expenditure on advertising, promotional activities, and building a robust sales force, directly impacting the profitability of new ventures in the short to medium term.
- Brand Loyalty: Gibraltar's established reputation makes it difficult for new players to gain market share.
- Customer Relationships: Long-term ties with existing customers create switching costs for buyers.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants must commit significant capital to marketing and sales to build credibility.
- Market Entry Costs: Overcoming brand preference requires substantial resources, increasing the threat of new entrants.
Regulatory Hurdles and Permits
The building and construction, as well as the renewable energy sectors, where Gibraltar Industries operates, are characterized by significant regulatory hurdles. New entrants face a complex web of certifications, permits, and compliance requirements that can be both time-consuming and expensive to navigate.
These regulatory barriers act as a substantial deterrent to new companies entering the market. For instance, obtaining necessary permits for construction projects or renewable energy installations can take months, if not years, and often involves substantial legal and consulting fees. This lengthy and costly process can significantly delay market entry, making it less attractive for potential competitors.
- Complex Permitting: Navigating local, state, and federal regulations for building and renewable energy projects requires specialized knowledge and resources.
- Certification Requirements: Companies must meet stringent quality and safety standards, often requiring third-party certifications that add to upfront costs.
- Cost of Compliance: The financial investment in understanding and adhering to these regulations can be a major barrier, especially for smaller, emerging businesses.
- Time Delays: The extended timelines associated with regulatory approvals can impact a new entrant's ability to gain market traction quickly.
The threat of new entrants for Gibraltar Industries is generally considered low. High capital requirements for manufacturing and distribution, coupled with established economies of scale that lower per-unit costs, create significant financial barriers. For example, Gibraltar's 2023 net sales of $1.5 billion underscore the scale new competitors would need to match.
Furthermore, Gibraltar benefits from strong brand loyalty and established distribution networks, making it challenging for newcomers to gain traction. In 2024, securing new distribution agreements in the construction materials sector averaged 6-12 months, illustrating the time and effort required to build comparable market access.
Regulatory hurdles in the building and renewable energy sectors also deter new entrants. Obtaining necessary certifications and permits can be a lengthy and costly process, adding to the overall market entry expenses for any aspiring competitor.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Gibraltar Industries is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial data from SEC filings, investor relations reports, and annual reports. This is supplemented by industry-specific market research from reputable sources like IBISWorld and trade publications to capture competitive dynamics.
