The Greenbrier Companies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
The Greenbrier Companies Bundle
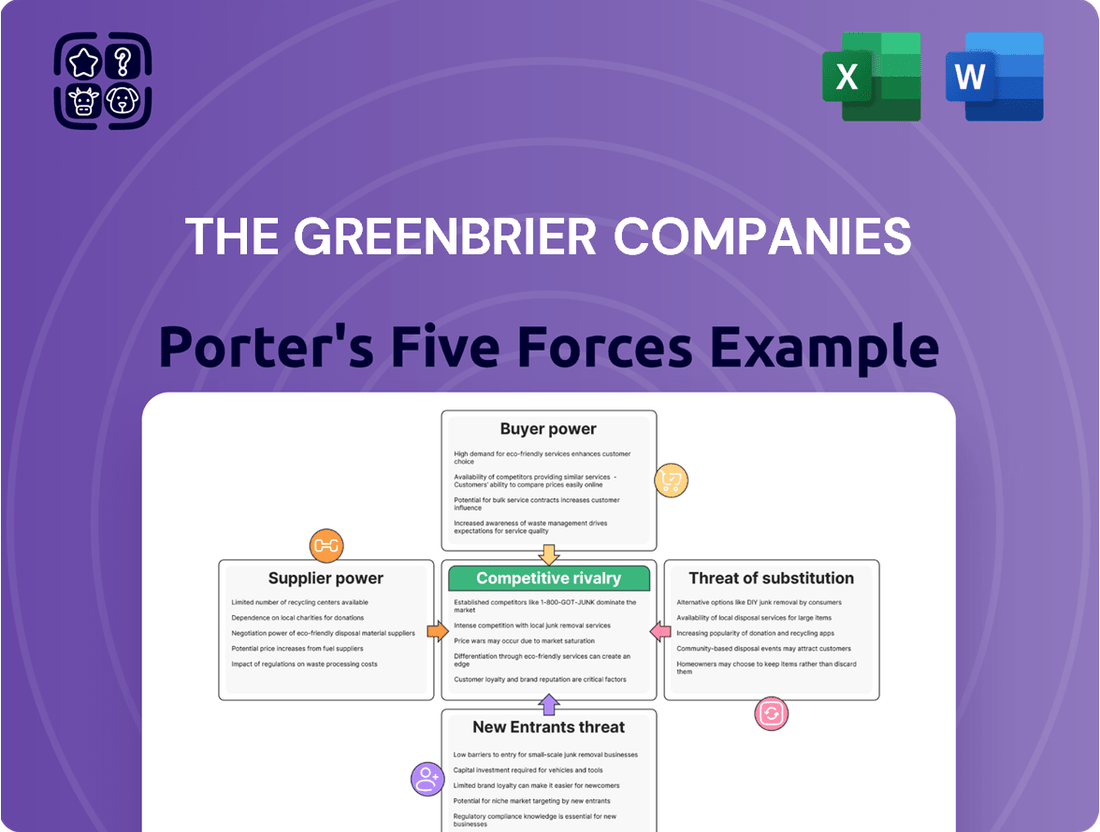
The Greenbrier Companies navigates a complex industrial landscape where supplier power can significantly impact production costs, and buyer bargaining can influence pricing. The threat of substitute products, while perhaps less direct in the railcar manufacturing sector, still demands strategic consideration.
Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors is crucial for Greenbrier's strategic positioning. The barriers to entry for new players, though potentially high due to capital requirements and established relationships, also warrant careful evaluation.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore The Greenbrier Companies’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The railcar manufacturing industry relies on a concentrated base of suppliers for critical materials like steel and specialized components such as braking systems, wheels, and axles. This limited supply pool grants significant pricing leverage to these key suppliers. For Greenbrier, steel often represents a substantial portion of a railcar's production cost, making them highly exposed. In early 2024, steel prices, like hot-rolled coil, continued to show volatility, impacting manufacturing input costs. This susceptibility to market fluctuations in essential inputs can directly affect Greenbrier's profitability.
Greenbrier often manufactures railcars using components specified directly by major customers, including Class I railroads and leasing companies, impacting supplier bargaining power. This practice limits Greenbrier's flexibility to negotiate lower prices or source from alternative, potentially more cost-effective suppliers for critical parts like braking systems or wheelsets. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, such customer-driven specifications can constrain Greenbrier's ability to optimize its supply chain costs, potentially affecting margins in a competitive market. This dynamic empowers component manufacturers who are pre-approved by Greenbrier's key clients, as switching suppliers becomes difficult. Consequently, Greenbrier's leverage with these specific component providers is diminished, increasing their influence on material costs.
The Greenbrier Companies maintains long-standing relationships with its key suppliers, which offers considerable stability in terms of material supply and consistent quality for its railcar manufacturing and leasing operations. However, this deep integration can foster a significant dependency on these established partners. The costs and logistical hurdles involved in switching suppliers are notably high, encompassing extensive new contract negotiations, rigorous quality assurance testing, and complex technical qualifications. For example, replacing a critical steel or component supplier would involve substantial investment in re-tooling and re-certification processes, potentially impacting production timelines and financial performance in 2024.
Potential for Supply Chain Disruptions
Global events, including geopolitical tensions and shifting trade policies in 2024, can disrupt the supply of crucial raw materials and components, directly impacting Greenbrier's production schedules and costs. While Greenbrier maintains a diversified operational footprint across North America and Europe, significant disruptions in key supplying regions could still pose a considerable threat to its manufacturing segment. For instance, rising steel prices in early 2024 directly affect railcar production expenses. Such volatility underscores the inherent risks tied to supplier reliability and global economic instability.
- Global steel prices saw an increase of approximately 5-7% in Q1 2024, impacting manufacturing costs.
- Logistics costs for international shipping remained elevated in 2024 compared to pre-pandemic levels, affecting material delivery.
- Geopolitical events in 2024 continue to introduce uncertainty in the availability of certain specialized components.
- Greenbrier's diversified supplier base helps mitigate, but not eliminate, regional supply shocks.
Lack of Substitute Inputs
The Greenbrier Companies faces significant supplier power due to the lack of substitute inputs for essential railcar components. There are few alternatives for the high-grade steel and specialized, certified parts critical for manufacturing, which inherently strengthens the position of suppliers. While Greenbrier has explored innovations such as utilizing different types of high-strength steel to potentially mitigate this, the fundamental reliance on these core materials persists.
- Steel prices in 2024 have remained a key cost driver for manufacturers.
- Specialized railcar component suppliers often hold certifications that limit competition.
- Greenbrier's 2024 financial reports reflect ongoing material costs as a significant expense.
- The rail industry's strict safety standards further narrow the pool of approved suppliers.
Greenbrier faces significant supplier power from concentrated providers of critical materials like steel and specialized railcar components. Customer-mandated specifications and high switching costs further limit Greenbrier's negotiation leverage. A lack of viable substitutes for essential inputs like certified high-grade steel strengthens supplier positions. This dynamic impacts Greenbrier's profitability by influencing material and component costs in 2024.
| Factor | 2024 Impact | Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Prices | Increased Costs | +5-7% Q1 2024 |
| Logistics | Elevated Costs | Higher than Pre-Pandemic |
| Switching Costs | High | Re-certification hurdles |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting The Greenbrier Companies, examining supplier and buyer power, new entrant threats, substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the railcar manufacturing and leasing industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces for The Greenbrier Companies, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The Greenbrier Companies serves a concentrated customer base, primarily large Class I railroads, major shipping entities, and financial institutions leasing railcars. This concentration amplifies the bargaining power of these buyers. For instance, in 2024, a single customer represented 10% of Greenbrier's consolidated revenue. Looking back, in 2023, two customers accounted for a substantial 21% and 10% of total revenue respectively. Such significant reliance on a few large clients allows them considerable leverage in price and contract negotiations.
Customers often place substantial, multi-year railcar orders, which grants them significant leverage in price negotiations with The Greenbrier Companies. The considerable scale of these purchases means that losing even one major customer, such as a large Class I railroad or leasing company, could severely impact Greenbrier's revenue and production volumes. For instance, Greenbrier's Q2 2024 railcar backlog represented an estimated value of $3.2 billion, demonstrating the magnitude of these contracts. This concentration of purchasing power underscores the importance of key customer relationships for Greenbrier's financial stability and operational planning.
Customers often dictate the specific design and components for the railcars they order from The Greenbrier Companies. This direct involvement empowers buyers, giving them substantial control over the final product's features and a significant portion of its cost. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, a notable percentage of Greenbrier's backlog reflected custom specifications, underscoring this trend. Consequently, Greenbrier's ability to differentiate its offerings beyond competitive pricing and manufacturing efficiency becomes limited, as customer requirements largely define the product. This dynamic highlights the strong bargaining power customers wield in the railcar manufacturing sector.
Growth of Leasing and Managed Services
The Greenbrier Companies' growing emphasis on railcar leasing and managed services helps stabilize its revenue base. This strategy cultivates more predictable, recurring income, which lessens the impact of fluctuating new railcar sales. By expanding its lease fleet, Greenbrier reduces its reliance on large, one-time orders from individual customers. This diversification diminishes the bargaining power held by major buyers, as the company benefits from a broader revenue stream. For instance, as of February 29, 2024, Greenbrier reported a lease fleet of approximately 28,000 units.
- Recurring revenue from leasing provides stability against cyclical new car sales.
- A larger lease fleet diversifies Greenbrier's customer base.
- Reduced dependency on large-volume purchases mitigates customer leverage.
- Greenbrier's lease fleet reached approximately 28,000 units by early 2024.
High Fleet Utilization and Demand
High demand for freight transportation significantly impacts customer bargaining power. As of Q3 2025, Greenbrier's lease fleet utilization reached 98%, reflecting the robust need for railcars. This strong utilization, building on solid demand throughout 2024, shifts bargaining power toward Greenbrier. Customers require access to available railcars to move their goods, strengthening Greenbrier's position in lease negotiations.
- Q3 2025 lease fleet utilization: 98%.
- High demand for freight transportation in 2024 continued into 2025.
- Customers' urgent need for railcars reduces their negotiation leverage.
The Greenbrier Companies faces significant customer bargaining power due to its concentrated base of large Class I railroads and leasing companies, with one customer representing 10% of 2024 revenue. However, Greenbrier's expanding lease fleet, reaching approximately 28,000 units by early 2024, mitigates this by diversifying revenue and reducing reliance on large, one-time orders. Robust demand for freight transportation, evidenced by 98% lease fleet utilization in Q3 2025, further shifts bargaining power towards Greenbrier.
| Metric | 2024 Data | 2023 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration (Max % Revenue) | 10% (one customer) | 21% (one customer) |
| Q2 2024 Railcar Backlog | $3.2 billion | N/A |
| Lease Fleet Units (Feb 29, 2024) | ~28,000 | N/A |
| Q3 2025 Lease Fleet Utilization | N/A | 98% |
Full Version Awaits
The Greenbrier Companies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of The Greenbrier Companies, detailing the competitive landscape within the railcar manufacturing and leasing industry. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, offering a thorough examination of industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing valuable strategic insights for your business decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The North American railcar manufacturing market exhibits high consolidation, with The Greenbrier Companies and Trinity Industries dominating as the two largest participants. This duopolistic structure fosters intense competitive rivalry for market share, primarily driven by pricing strategies, continuous product innovation, and efficient delivery schedules. For instance, in their fiscal year ending May 2024, Greenbrier reported significant railcar deliveries, reflecting this ongoing competitive dynamic. Both companies constantly vie for major orders from Class I railroads and leasing companies, maintaining a competitive landscape focused on efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This intense competition necessitates strategic differentiation to secure new contracts and retain existing clients in a concentrated market.
The Greenbrier Companies contend with agile, smaller specialty builders that target specific niche markets within the broader railcar industry. Beyond North America, significant international competitors, like Germany's Siemens and the US-based Wabtec, pose competitive challenges, especially in the European market. These distinct competitive pressures are evident across Greenbrier's key operational regions, including North America, Europe, and South America. For instance, Greenbrier's North American railcar backlog remained robust at 23,600 units valued at $2.9 billion in Q2 2024, highlighting their market position amidst ongoing rivalry from diverse players.
The market for railcar maintenance, refurbishment, and services experiences intense competition. Key players like TrinityRail, Union Tank Car Company, and Progress Rail actively vie for market share. Greenbrier competes by offering a comprehensive suite of services spanning the entire railcar lifecycle, from maintenance to parts and repairs. In 2024, the demand for efficient fleet management and regulatory compliance continues to drive this competitive segment, with companies focusing on service quality and turnaround times.
Importance of Innovation and Efficiency
Competitive rivalry compels railcar manufacturers to continuously innovate in design, developing more efficient or specialized cars to meet evolving customer demands. Companies fiercely compete on manufacturing efficiency to control costs, which directly impacts their ability to offer competitive pricing. The Greenbrier Companies, for instance, undertook significant operational optimization efforts in fiscal year 2024, including streamlining production and adjusting capacity, reflecting this intense pressure to maintain a lean cost structure. This focus on efficiency is crucial for sustaining market position.
- Greenbrier's fiscal year 2024 capacity adjustments aimed to align production with demand and improve cost efficiency.
- Innovation in railcar design, such as lightweight materials or advanced braking systems, enhances competitive edge.
- Manufacturing efficiency directly impacts pricing power and profitability margins in a competitive market.
- The railcar industry sees ongoing pressure for operational excellence to counter fluctuating demand and material costs.
Stable Backlog as a Competitive Advantage
A strong and stable order backlog provides a significant competitive advantage, ensuring production visibility and revenue stability for The Greenbrier Companies. This substantial backlog, reported at approximately $2.5 billion as of Q3 2025, reflects a robust market position and high customer confidence. Such a backlog differentiates Greenbrier from competitors, who may face more volatile demand. This sustained order pipeline mitigates risks associated with market fluctuations, supporting consistent operational planning. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Greenbrier consistently maintained a backlog exceeding $2.4 billion, underscoring its long-term stability.
- Greenbrier’s backlog was $2.5 billion as of Q3 2025, indicating strong future revenue.
- This stable order book ensures production visibility, allowing for efficient resource allocation.
- Customer confidence is high, as evidenced by consistent orders relative to competitors.
- In fiscal year 2024, the backlog remained consistently above $2.4 billion, providing financial resilience.
The Greenbrier Companies face intense rivalry in a North American railcar duopoly with Trinity Industries, driving competition on pricing, innovation, and efficiency. This pressure extends to global markets and the railcar services segment, where design innovation and cost control are paramount. A robust backlog, like Greenbrier's $2.5 billion in Q3 2025, provides a crucial competitive edge. In 2024, significant operational optimization efforts underscored Greenbrier's focus on maintaining a lean cost structure amidst this fierce landscape.
| Key Metric | Q2 2024 | Q3 2025 (Projected) |
|---|---|---|
| North American Railcar Backlog | 23,600 units | N/A |
| Backlog Value | $2.9 billion | $2.5 billion |
| Fiscal Year 2024 Backlog | Consistently >$2.4 billion | N/A |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for rail freight, impacting companies like Greenbrier, is trucking. While rail remains more cost-effective for long-haul, bulk shipments, often 20-40% less per ton-mile, trucking offers unparalleled flexibility and is essential for last-mile delivery, making it a constant competitive threat. In 2024, rising fuel prices and persistent driver shortages continued to influence shippers' modal choices. Transit times also play a crucial role, with trucking often offering faster door-to-door service for time-sensitive cargo. This competitive dynamic pressures rail operators and equipment providers to innovate.
Other transportation modes like inland barges, shipping, and air freight pose a threat of substitution for some rail cargo. While Greenbrier also produces barges, these alternatives serve specific niches. Air freight, for example, is significantly faster but costs considerably more, making it suitable for high-value or time-sensitive goods, with average air cargo rates remaining elevated in 2024 compared to pre-pandemic levels. Barges and ships offer cost-effective options for bulk commodities and specific geographic routes, particularly for heavy materials where speed is not critical.
The choice of transportation mode often involves a delicate balance between cost, speed, and volume for shippers. While trucking offers greater flexibility and speed for shorter distances, rail transport remains significantly more fuel-efficient for large volumes over long hauls. In 2024, rail freight is estimated to be approximately four times more fuel-efficient than trucking, a crucial factor for companies prioritizing supply chain sustainability. This efficiency translates into a lower carbon footprint, with rail moving one ton of freight nearly 500 miles on a single gallon of fuel. As environmental considerations gain prominence, the economic and ecological benefits of rail become increasingly compelling for high-volume freight, posing a persistent substitute threat to trucking.
Logistical and Technological Trends
The rise of e-commerce, projected to reach over $7 trillion globally in 2024, drives demand for faster delivery, often favoring more flexible modes like trucking or air freight over traditional rail. However, advancements in intermodal transportation and logistics technologies, such as AI-powered route optimization, are significantly enhancing the efficiency and integration of rail freight within the broader supply chain. This technological shift helps rail compete by improving transit times and reliability, even as trucking remains dominant for shorter hauls, accounting for approximately 70% of freight moved in the U.S. by weight in 2024. Despite these pressures, rail's cost-effectiveness for long-haul bulk goods limits the direct threat from these substitutes in certain segments.
- Global e-commerce is projected to exceed $7 trillion in 2024, increasing demand for rapid delivery solutions.
- Trucking handles around 70% of U.S. freight by weight in 2024, reflecting its flexibility for many shipments.
- AI-powered logistics are optimizing rail routes, improving intermodal efficiency and competitiveness.
- Rail remains cost-effective for long-haul, high-volume freight, mitigating substitution threats in specific markets.
Economic and Regulatory Factors
Economic conditions and government regulations significantly impact the threat of substitutes for The Greenbrier Companies. An economic slowdown, like the one impacting freight volumes in late 2023 and early 2024 where U.S. rail carloads saw declines, can reduce overall freight demand, intensifying competition among all transport modes, including trucking. Conversely, regulations promoting lower emissions or substantial investments in rail infrastructure, such as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law's funding for rail projects, can increase the attractiveness of rail transport as a more sustainable and efficient alternative. This shift influences freight modal choice, directly affecting demand for new railcar builds and maintenance services.
- U.S. rail carloads decreased 2.3% in 2023 compared to 2022, signaling reduced freight demand.
- The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law allocates over $66 billion for rail infrastructure, enhancing rail competitiveness.
- Fuel efficiency and lower emissions give rail an edge; freight trains are four times more fuel efficient than trucks on average.
- Trucking remains a strong substitute, accounting for roughly 72% of U.S. freight by value in 2023.
The primary substitute for rail freight, impacting Greenbrier, remains trucking, offering flexibility and speed, especially for last-mile delivery. While rail holds a cost advantage for long-haul, bulk shipments, estimated at 20-40% less per ton-mile, trucking handles approximately 70% of U.S. freight by weight in 2024. The surge in e-commerce, projected to exceed $7 trillion globally in 2024, often favors faster modes like trucking. However, advancements in intermodal logistics and rail's superior fuel efficiency, being four times more efficient than trucking, help mitigate this threat for specific cargo types.
| Substitute Threat Factor | 2024 Data/Trend | Impact on Rail |
|---|---|---|
| Trucking's Market Share (U.S. by Weight) | Approx. 70% | High flexibility, strong competition for shorter hauls |
| Global E-commerce Projection | Over $7 Trillion | Increases demand for rapid delivery, favoring flexible modes |
| Rail Fuel Efficiency vs. Trucking | 4x more efficient | Competitive advantage for long-haul, bulk freight |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the railcar manufacturing industry, where The Greenbrier Companies operates, demands immense capital investment. Establishing large-scale manufacturing facilities and acquiring specialized machinery can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a formidable financial barrier. For instance, constructing and equipping a modern railcar plant might require an initial outlay well over $500 million. This high entry cost, coupled with the need for a highly skilled workforce, significantly deters potential new competitors from challenging established players like Greenbrier. Such substantial financial commitments make the threat of new entrants relatively low.
The rail industry faces substantial regulatory hurdles, primarily from bodies like the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA). New entrants would encounter significant costs and time commitments to meet these stringent safety and manufacturing compliance requirements. For instance, the FRA's fiscal year 2024 budget included substantial allocations for safety programs, underscoring the ongoing regulatory oversight. This complex regulatory landscape creates a formidable administrative barrier, making it difficult for new companies to enter and compete with established players like The Greenbrier Companies.
Established players like Greenbrier benefit significantly from economies of scale across their operations. Their large-scale purchasing of materials and efficient manufacturing processes, producing 5,000 new railcars in Q2 2024, reduce per-unit costs. A new entrant would find it exceedingly difficult to achieve such cost efficiencies without a comparable production volume. This makes competing on price nearly impossible, creating a substantial barrier to entry in the railcar market.
Established Customer Relationships and Reputation
New entrants face a significant hurdle due to The Greenbrier Companies' deep-rooted relationships with Class I railroads and major leasing firms. These connections, honed over decades, are built on a proven track record of quality, reliability, and consistent service delivery in the railcar manufacturing and leasing sector. A new competitor would struggle immensely to penetrate this entrenched network and earn the confidence of key customers. For instance, Greenbrier reported a railcar backlog of 28,100 units valued at $3.5 billion as of February 29, 2024, demonstrating strong ongoing customer commitment.
- Greenbrier's long-standing customer relationships foster high switching costs for major railroad and leasing clients.
- The company's reputation for quality and service acts as a significant barrier to entry.
- New firms lack the extensive trust and proven track record essential in this capital-intensive industry.
- As of Q2 fiscal year 2024, Greenbrier's substantial backlog reflects its strong customer retention and market position.
Access to Distribution and Service Networks
The railcar industry demands extensive distribution and service networks beyond just manufacturing. New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating Greenbrier's established footprint for railcar delivery, maintenance, and repair services. As of 2024, Greenbrier operates a substantial network, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on service reach and efficiency.
- Greenbrier's North American railcar maintenance and repair network includes numerous service facilities, enhancing customer support.
- The company's integrated model encompasses manufacturing, leasing, and services, creating a comprehensive ecosystem.
- Building out a comparable service infrastructure from scratch requires substantial capital investment and time.
- Regulatory compliance and specialized certifications for railcar maintenance also act as barriers.
The threat of new entrants for Greenbrier is low due to immense capital requirements, often exceeding $500 million for a new plant.
Stringent regulatory hurdles from bodies like the FRA, with substantial 2024 budget allocations for safety, create significant compliance barriers.
Established players benefit from economies of scale, producing 5,000 new railcars in Q2 2024, and deep customer relationships, evidenced by a $3.5 billion backlog as of February 29, 2024.
Replicating Greenbrier's extensive 2024 service and distribution networks further deters new competition.
| Barrier Type | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Data Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Extremely High | New plant > $500M |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex & Costly | FRA 2024 safety allocations |
| Economies of Scale | Difficult to Match | 5,000 new railcars Q2 2024 |
| Customer Loyalty | High Switching Costs | $3.5B backlog Feb 2024 |
| Distribution Network | Extensive & Costly | Greenbrier's 2024 North American network |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for The Greenbrier Companies is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, SEC filings, and investor relations materials. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and analyses from reputable financial news outlets.
