Cubic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cubic Bundle
Understanding Cubic's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces reveals the intense rivalry, the power of buyers, and the potential threat of new entrants. This analysis highlights how supplier power and the availability of substitutes shape Cubic's strategic options.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cubic’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Wuhan Cubic Optoelectronics' reliance on specialized raw materials and optoelectronic components, like infrared sources and detectors for its NDIR technology, can foster dependency on a select group of suppliers. This specialization means fewer alternatives are available, giving these suppliers more sway.
The broader optical components industry grapples with significant challenges, including supply chain disruptions and a scarcity of skilled professionals. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor shortage continued to impact component availability, potentially extending lead times and increasing costs for manufacturers like Cubic.
Rising raw material costs are a significant factor impacting the bargaining power of suppliers in the electronics industry. For companies like Cubic, which rely on a steady supply of components, escalating prices for essential materials, often influenced by global supply chain disruptions and currency fluctuations, can directly squeeze profit margins. For instance, in early 2024, the price of certain semiconductors saw notable increases due to high demand and limited production capacity, directly affecting the cost of goods for electronics manufacturers.
If Cubic relies on highly specialized or proprietary components for its advanced gas sensors, the cost and time involved in transitioning to new suppliers can be substantial. This situation significantly bolsters the bargaining power of those suppliers. For instance, the intricate fabrication and unique packaging methods required for advanced optoelectronic components, critical for Cubic's sensor technology, create these elevated switching costs.
Consolidation Among Component Suppliers
The electronics component distribution landscape is seeing increased consolidation. This trend, where some suppliers are merging or acquiring competitors, directly impacts manufacturers like Cubic. It means fewer options for sourcing critical parts, which in turn strengthens the bargaining power of the remaining, larger distributors.
This consolidation raises the barrier to entry and participation within the supply chain. Companies that cannot scale or adapt to these changes may find it difficult to secure reliable component sources, potentially impacting their production capabilities and cost structures.
- Market Consolidation: The electronics component distribution market has seen significant M&A activity. For instance, in 2023, Avnet acquired Too Much Information, Inc. (TMI), a move aimed at expanding its reach in the industrial and aerospace markets.
- Supplier Power: As the number of independent distributors shrinks, the remaining entities can command better terms, potentially increasing costs for buyers like Cubic.
- Increased Thresholds: For manufacturers to maintain access to essential components, they may need to work with larger, more established distributors, or invest in developing direct relationships with original component manufacturers.
Technological Advancements by Suppliers
Suppliers pushing the envelope with innovations in core NDIR (Non-Dispersive Infrared) components or related sensor technologies can significantly shift the balance of power. If these advancements offer Cubic substantial performance gains or cost savings, suppliers gain leverage to dictate terms, especially concerning pricing and supply agreements. For instance, a supplier developing a next-generation NDIR sensor with 15% greater accuracy or a 20% reduction in manufacturing cost could command premium pricing or preferential contract terms.
Furthermore, technological leaps in miniaturization and energy efficiency from component manufacturers directly impact Cubic's product development roadmap. Suppliers achieving breakthroughs that enable smaller, more power-efficient sensors could allow Cubic to design more compact and longer-lasting devices, potentially opening new market segments. Consider a scenario where a supplier's new sensor module is 30% smaller and consumes 25% less power, enabling Cubic to create handheld devices with extended battery life.
- Supplier Innovation in NDIR: Suppliers developing advanced NDIR components with enhanced accuracy or reduced manufacturing costs can increase their bargaining power.
- Impact on Cubic's Costs: Significant performance improvements or cost efficiencies from suppliers may lead to higher prices or stricter contract terms for Cubic.
- Miniaturization and Energy Efficiency: Supplier advancements in making sensors smaller and more power-efficient enable Cubic to innovate in product design, potentially creating competitive advantages.
- Strategic Importance of Supplier Tech: Cubic's reliance on cutting-edge sensor technology from suppliers means that supplier technological prowess directly influences Cubic's ability to compete.
Suppliers of specialized NDIR components and raw materials hold significant power over Wuhan Cubic Optoelectronics. This power is amplified when few alternative suppliers exist, or when switching costs are high due to proprietary technology or complex integration. For instance, in 2024, the continued global demand for advanced semiconductors, coupled with production constraints, meant that suppliers of these critical components could dictate terms more readily.
Market consolidation among component distributors further concentrates supplier power. As fewer distributors remain, they can leverage their market share to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially increasing costs for buyers like Cubic. The acquisition of smaller distributors by larger entities, a trend observed throughout 2023 and continuing into 2024, exemplifies this shift, reducing sourcing options and strengthening the bargaining position of the remaining large players.
Technological innovation from suppliers also enhances their leverage. If a supplier develops a component offering substantial performance improvements, such as increased accuracy or reduced energy consumption, they can command premium pricing or stricter contract terms. For example, a supplier offering a next-generation NDIR sensor with a 15% accuracy improvement could significantly influence Cubic's cost structure and product development, as demonstrated by ongoing advancements in sensor miniaturization and power efficiency throughout 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example/Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Specialization & Few Alternatives | High | Limited suppliers for highly specific infrared detectors used in NDIR technology. |
| Switching Costs | High | Significant R&D and integration effort required to change suppliers for proprietary sensor components. |
| Market Consolidation | Increasing | Acquisitions like Avnet's purchase of TMI in late 2023 reduce distributor options for manufacturers. |
| Supplier Innovation (e.g., NDIR Tech) | High | New sensors with improved accuracy (e.g., 15% gain) or reduced cost can command premium pricing. |
| Raw Material Cost Escalation | High | Semiconductor price increases in early 2024 due to demand and capacity limits directly impact component costs. |
What is included in the product
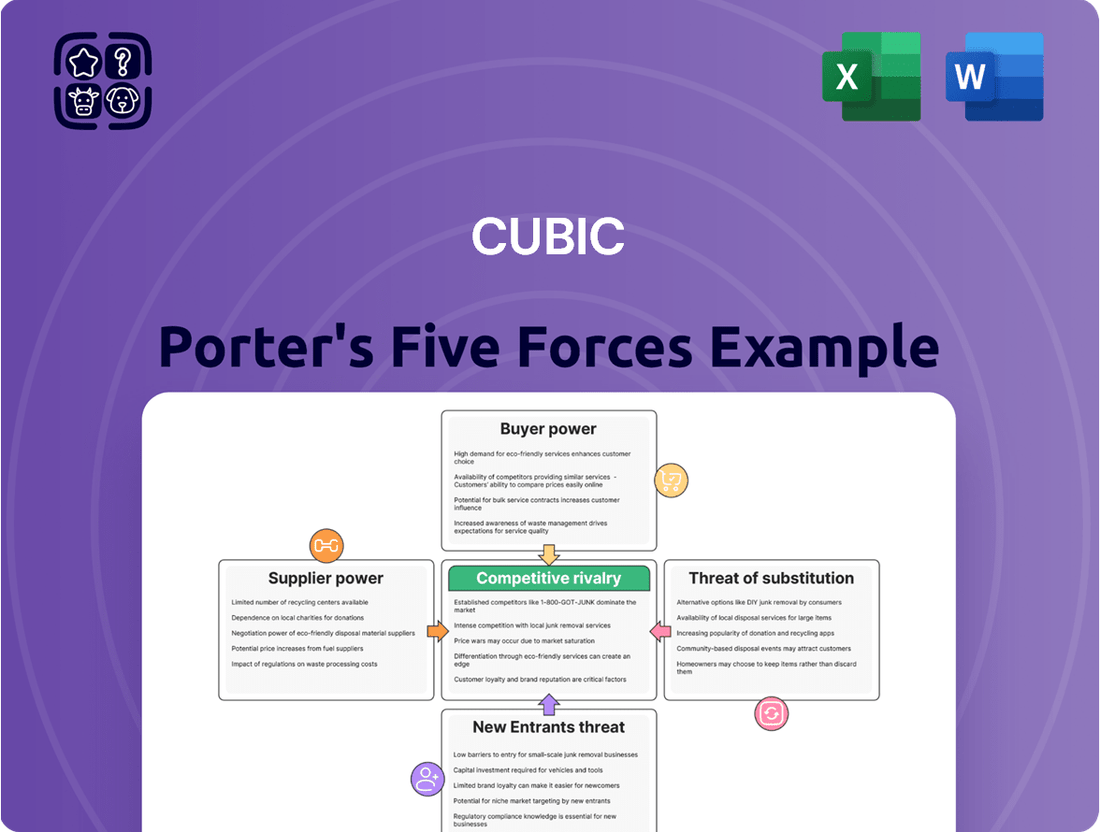
Cubic's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential within its operating markets, examining threats from new entrants, substitute products, buyer and supplier power, and existing rivalry.
Uncover hidden competitive threats and opportunities with a visual, interactive breakdown of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cubic Corporation’s broad reach across diverse industries like HVAC, industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and smart agriculture significantly dilutes the bargaining power of its customers. This wide market penetration means that no single industry segment holds a disproportionate sway over Cubic’s revenue streams. For instance, in 2023, Cubic reported revenue segments spread across transportation, defense, and public transit, showcasing this diversification.
In sectors like industrial safety and environmental monitoring, customer demand is heavily shaped by stringent government regulations. For instance, compliance mandates for gas detection equipment mean businesses must purchase these products regardless of price fluctuations, thereby reducing their bargaining leverage.
This regulatory necessity significantly limits customers' ability to push for lower prices. Companies operating in these fields are less sensitive to price changes when the product is essential for meeting legal obligations and ensuring worker safety, a key factor in the industrial safety equipment market which saw global sales exceeding $50 billion in 2024.
In critical sectors such as industrial safety and environmental monitoring, the precision and dependability of gas detection systems are non-negotiable. Lives and substantial assets depend on accurate readings, meaning performance trumps minor cost savings for buyers.
This intense focus on reliability significantly curtails the bargaining power of customers. When the cost of failure is exceptionally high, such as in preventing toxic gas leaks in a chemical plant, buyers are less likely to switch suppliers based solely on price, as demonstrated by the stringent certification requirements for safety equipment in the oil and gas industry.
Market Growth in Key Application Areas
The bargaining power of customers is generally lower in markets experiencing significant growth. For instance, the global gas sensor market was projected to reach USD 6.3 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% through 2030. Similarly, the NDIR sensor market is anticipated to grow substantially, driven by applications in environmental monitoring and industrial safety. This robust demand means customers are often more focused on securing a reliable supply of these critical components rather than aggressively negotiating prices.
In the rapidly expanding smart agriculture sensor market, which saw significant investment and innovation in 2024, the dynamic also favors suppliers. As new technologies emerge and adoption rates increase, customers are eager to integrate these solutions to improve efficiency and yield. This heightened demand, coupled with the specialized nature of many sensor technologies, often translates to less customer leverage in price discussions.
- Gas Sensor Market Growth: Projected to reach USD 6.3 billion in 2024 with a 7.5% CAGR through 2030.
- NDIR Sensor Market Expansion: Driven by environmental monitoring and industrial safety needs.
- Smart Agriculture Sensor Adoption: Increased investment and demand in 2024 for efficiency improvements.
- Supplier Leverage: Robust demand in these growing sectors typically reduces customer bargaining power, as securing supply becomes a priority over price.
Customer Focus on Integrated Solutions
Customers are increasingly demanding integrated solutions that combine hardware, software, and services, particularly those incorporating IoT connectivity and predictive analytics. This shift means that a provider offering a comprehensive, end-to-end offering can reduce a customer's reliance on multiple vendors, thereby lessening their ability to negotiate on price alone. For example, if Cubic can bundle its transit payment systems with real-time passenger information displays and predictive maintenance for infrastructure, it creates a more sticky solution.
The bargaining power of customers is influenced by their focus on integrated solutions. As customers seek more sophisticated, connected systems, their ability to pit vendors against each other based solely on price diminishes if one vendor can offer a superior, all-in-one package. This trend is evident across many sectors where customers value reduced complexity and enhanced operational efficiency. For instance, in the smart city infrastructure space, clients are looking for unified platforms rather than disparate components.
- Customer demand for integrated solutions is rising, with a focus on IoT and data analytics.
- Providers offering comprehensive, end-to-end packages can reduce customer price sensitivity.
- Cubic's ability to deliver integrated smart transit solutions can enhance its position against price-focused competition.
Cubic's diverse product portfolio and presence across multiple industries, including transportation and defense, inherently limits the bargaining power of any single customer group. This diversification, as evidenced by Cubic's 2023 revenue distribution across various sectors, prevents any one segment from dictating terms. Furthermore, in critical areas like industrial safety, where regulatory compliance is paramount, customers have less room to negotiate on price.
The high cost of failure in sectors like industrial safety, where accurate gas detection is vital, significantly reduces customer price sensitivity. Buyers prioritize reliability over minor cost savings, as seen in the stringent certification demands within the oil and gas industry. This focus on performance, coupled with the robust growth of markets like gas sensors, which was projected at USD 6.3 billion in 2024, further empowers suppliers like Cubic by ensuring consistent demand for essential, high-quality products.
| Market Segment | 2024 Market Size (USD Billion) | Projected CAGR (2024-2030) | Customer Bargaining Power Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Sensors | 6.3 | 7.5% | Low (due to regulatory needs & high reliability demand) |
| Industrial Safety Equipment | 50+ (Global) | Moderate (driven by safety compliance) | Moderate (price is a factor, but safety is paramount) |
| Smart Agriculture Sensors | Growing | High (driven by tech adoption & efficiency) | Low (eagerness for new tech limits price negotiation) |
Same Document Delivered
Cubic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Cubic Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape for the company. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted document immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes. No placeholders or sample content, just the actionable insights you need.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global gas sensor market is characterized by a high degree of competitive rivalry, with numerous established global players vying for market share. Key industry participants include giants like Honeywell, Siemens, ABB, and Figaro Engineering, each offering a broad spectrum of gas detection solutions.
This intense competition, driven by a multitude of vendors, leads to pressure on pricing and necessitates continuous innovation to differentiate products and services. For instance, Honeywell, a major player, reported revenues of approximately $36.7 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of operations in this sector.
Competitive rivalry in the sensor technology sector is fierce, driven by continuous product innovation. Companies are heavily investing in research and development to integrate cutting-edge advancements like miniaturization, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI) into their offerings. This relentless pursuit of technological superiority means that new and improved sensor solutions are constantly emerging, pushing the boundaries of workplace safety and efficiency.
For example, the global market for industrial sensors, a key area for workplace safety, was projected to reach approximately $27.5 billion in 2024, with continued growth expected. This robust market size fuels intense competition as firms strive to capture market share through differentiated and superior product features. Companies like Honeywell and Siemens are at the forefront, frequently launching updated product lines that incorporate enhanced data analytics and predictive maintenance capabilities, directly impacting workplace safety protocols.
The robust growth in sectors like gas sensors, NDIR technology, and smart agriculture sensors is a double-edged sword for companies like Cubic. While this expansion can support numerous participants, it simultaneously acts as a magnet for substantial investment and new competitors. This influx inevitably escalates the intensity of rivalry, making it harder for established players to maintain market share and profitability.
Asia-Pacific, Cubic's primary operational theater, exemplifies this trend. This region is experiencing particularly rapid market expansion, which is drawing in both domestic and international players. For instance, the global smart agriculture market was valued at approximately $15.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $32.4 billion by 2030, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate of over 11%. This high growth environment in Cubic's backyard means increased pressure from a widening array of competitors.
Product Differentiation Through NDIR Technology
Cubic's focus on Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) technology provides a significant competitive edge. This specialization allows for sensors with superior accuracy and extended operational life, often outperforming other sensing methods. For instance, NDIR sensors are inherently more resistant to chemical interference, a common issue with alternative technologies.
This technological differentiation allows Cubic to stand out in a market where many competitors may rely on less advanced or more susceptible sensing principles. The inherent advantages of NDIR, such as its robustness and precision, enable Cubic to command a premium or secure market share in applications demanding high reliability.
- NDIR Technology Advantages: High accuracy, long lifespan, resistance to chemical poisoning.
- Competitive Impact: Differentiates Cubic from rivals using alternative, potentially less robust, sensing methods.
- Market Positioning: Enables Cubic to target applications requiring high-reliability gas sensing solutions.
Strategic Importance of Industrial Safety and Environmental Monitoring
The critical need for gas sensors in industrial safety, environmental monitoring, and regulatory compliance fuels intense competition among companies. These businesses fiercely vie for contracts within these essential sectors, understanding the high stakes involved.
Competitors differentiate themselves by offering reliable and certified solutions that meet stringent industry standards, a non-negotiable requirement for clients. For instance, in 2024, the global industrial safety market, which heavily relies on such monitoring technology, was projected to reach over $60 billion, highlighting the significant financial incentives driving this rivalry.
- Market Share Battles: Companies like Honeywell, 3M, and MSA Safety actively compete for dominance in the industrial safety sensor market, which saw significant contract awards throughout 2024.
- Technological Advancement Race: Innovation in sensor accuracy, durability, and data transmission capabilities is a key battleground, with R&D investments playing a crucial role in securing competitive advantage.
- Regulatory Compliance as a Differentiator: Firms that can consistently demonstrate adherence to evolving environmental and safety regulations, such as those from the EPA or OSHA, gain a distinct edge in securing long-term contracts.
- Price Sensitivity and Value Proposition: While reliability is paramount, competitive pricing and the overall value proposition, including support and integration services, are critical factors influencing customer choices in this high-demand sector.
Competitive rivalry in the gas sensor market is intense, driven by a large number of established global players and the constant pursuit of innovation. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous investment in research and development to stay ahead, as seen with companies like Honeywell and Siemens heavily investing in advanced technologies.
The significant market size, with the global industrial sensors market projected to reach approximately $27.5 billion in 2024, fuels this fierce competition. Companies differentiate themselves through technological superiority, such as Cubic's focus on NDIR technology, offering higher accuracy and reliability compared to alternative sensing methods.
This rivalry extends to critical sectors like industrial safety, where reliable and certified solutions are paramount. The global industrial safety market, a key area for gas sensors, was projected to exceed $60 billion in 2024, underscoring the high stakes and intense competition for contracts and market share.
| Key Players | 2023 Revenue (approx.) | Key Differentiators |
| Honeywell | $36.7 billion | Broad spectrum of solutions, IoT integration |
| Siemens | N/A (Part of larger conglomerate) | Advanced analytics, predictive maintenance |
| ABB | N/A (Part of larger conglomerate) | Automation and digitalization focus |
| Figaro Engineering | N/A (Specialized sensor manufacturer) | High-performance sensor components |
| Cubic | N/A (Focus on specific technologies) | NDIR technology, high accuracy, durability |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Beyond NDIR, a range of alternative gas sensing technologies like electrochemical, metal oxide semiconductor (MOX), photoionization detectors (PID), and catalytic sensors offer viable solutions for similar applications. For instance, the global electrochemical gas sensor market was valued at approximately USD 1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a robust substitute market.
These diverse technologies can fulfill comparable functions, presenting a tangible threat of substitution for NDIR sensors across various industries, including environmental monitoring, industrial safety, and automotive emissions control.
New and emerging sensor technologies represent a significant threat of substitution for traditional NDIR solutions. Innovations like printed sensors, acoustic gas sensors, quantum sensors, and biodegradable sensors are entering the market with potentially different form factors, cost structures, and performance capabilities. For instance, the global printed electronics market is projected to reach $11.8 billion by 2026, indicating a growing acceptance of alternative manufacturing methods that could extend to sensor production.
These advancements could lead to the displacement of NDIR sensors in various applications if they offer a compelling value proposition. Biodegradable sensors, for example, could appeal to environmentally conscious markets, while quantum sensors might provide unparalleled accuracy in specialized fields. The accessibility and cost-effectiveness of these emerging technologies will be key determinants in their ability to capture market share from established NDIR solutions.
While Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) sensors are known for their precision and durability, alternative technologies present a cost-performance trade-off. Some substitutes may offer a lower entry price or unique benefits for niche applications, prompting customers to explore these options.
However, the landscape is shifting. Innovations in MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology are driving down the manufacturing costs of NDIR chips, making them increasingly competitive. For instance, by 2024, the average cost of a MEMS-based NDIR sensor module has seen a notable decrease, making NDIR a more accessible solution across various industries.
Multi-gas Detection and Integrated Systems
The emergence of multi-gas detection sensors and integrated systems presents a significant threat of substitution for single-gas NDIR sensors. These advanced solutions allow for simultaneous monitoring of various gases, offering a more comprehensive and potentially cost-effective approach for users who previously relied on multiple single-gas units.
Customers increasingly seek integrated solutions that consolidate monitoring functions. For instance, smart building management systems or advanced industrial safety platforms can incorporate multi-gas detection capabilities, reducing the need for standalone NDIR sensors. This trend is driven by a desire for simplified data management and a holistic view of environmental conditions.
- Technological Advancements: Development of sophisticated sensors capable of detecting multiple gases concurrently.
- Integrated Systems: Smart building and industrial safety platforms incorporating multi-gas monitoring.
- Customer Preference: Growing demand for comprehensive solutions offering broader monitoring capabilities.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Potential for consolidated monitoring to be more economical than purchasing multiple single-gas sensors.
Non-Sensor Based Monitoring Methods
While sensor-based monitoring is becoming the norm, some sectors still utilize less precise or manual methods as substitutes. This is particularly true in industries with lower regulatory oversight or tighter budgets, where the cost-benefit analysis favors simpler approaches. For instance, some agricultural operations might still rely on visual inspections rather than sophisticated soil moisture sensors, despite the inherent limitations in accuracy.
The trend, however, is a clear shift towards more accurate and automated detection systems. This is driven by the desire for better data quality and operational efficiency. For example, in 2024, the global industrial automation market, which heavily relies on advanced monitoring, was projected to reach over $200 billion, indicating a strong demand for sophisticated solutions that often supersede manual checks.
- Manual inspections: Still viable in low-cost or unregulated environments, but increasingly replaced by technology.
- Older, less precise technologies: May persist in niche applications where high accuracy is not paramount.
- Cost sensitivity: A key driver for the continued use of some non-sensor based methods, especially for smaller businesses.
- Trend towards automation: The market shows a strong preference for advanced, sensor-driven monitoring for improved data and efficiency.
The threat of substitutes for NDIR sensors is significant, driven by a diverse range of alternative technologies. Electrochemical sensors, valued at approximately USD 1.5 billion in 2023, offer comparable functions in environmental and industrial safety. Emerging technologies like printed sensors, with the global market projected at $11.8 billion by 2026, also pose a substitution risk due to potential cost and form factor advantages.
Furthermore, integrated multi-gas detection systems are increasingly replacing standalone NDIR sensors, offering consolidated monitoring and simplified data management. While manual inspections persist in some lower-cost sectors, the overarching trend favors automated, sensor-driven solutions for improved data quality and operational efficiency, as evidenced by the over $200 billion global industrial automation market in 2024.
| Substitute Technology | 2023 Market Value (Approx.) | Projected Market Value | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical Sensors | USD 1.5 billion | Significant Growth | Cost-effectiveness, specific gas detection |
| Printed Sensors | N/A | USD 11.8 billion by 2026 | Potential for low-cost manufacturing, flexible form factors |
| Integrated Multi-Gas Systems | N/A | Growing Adoption | Consolidated monitoring, simplified data management |
Entrants Threaten
Developing and manufacturing advanced gas sensors, particularly those employing sophisticated optical technologies like Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR), demands significant upfront capital. Companies must invest heavily in research and development to innovate and refine sensor accuracy and lifespan. For instance, the global NDIR sensor market, projected to reach over $1.5 billion by 2028, highlights the substantial R&D and manufacturing infrastructure needed to compete effectively.
Cubic's robust intellectual property, encompassing over 100 patents in gas sensing technologies like NDIR, ultrasonic, and MEMS, presents a formidable barrier to entry. This extensive patent portfolio effectively deters new competitors aiming to replicate Cubic's advanced technological capabilities without facing infringement risks.
Stringent regulatory and certification hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the gas sensor and analyzer market. For instance, compliance with international safety standards like UL 60335-2-40 is mandatory for industrial safety and environmental monitoring applications. Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes requires substantial investment in time and resources, creating a high barrier to entry for new companies.
Need for Established Supply Chains and Distribution Networks
New entrants would struggle to replicate Cubic's established supply chains for specialized electronic components and its extensive distribution and service networks. These networks are crucial for reaching diverse markets such as HVAC, industrial safety, and smart agriculture, where Cubic has a strong presence.
The electronics industry, in general, continues to grapple with supply chain disruptions. For instance, in early 2024, semiconductor shortages, though easing from previous years, still impacted lead times for certain critical components, making it difficult for newcomers to secure reliable and timely supply.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Building and managing the intricate global supply chains required for Cubic's product lines, which often involve specialized and high-performance electronic parts, presents a significant barrier.
- Distribution Network Costs: Establishing a comparable distribution and service infrastructure across multiple industries and geographies would require substantial upfront investment and time, a hurdle for most new entrants.
- Supplier Relationships: Cubic's long-standing relationships with key suppliers provide it with preferential pricing and access to critical materials, advantages that are difficult for new players to match.
- Logistical Expertise: Efficiently managing the logistics of delivering and servicing complex electronic systems across various demanding environments requires deep operational expertise that new entrants would need to develop from scratch.
Brand Reputation and Customer Trust
The threat of new entrants for Cubic is significantly mitigated by the immense value placed on brand reputation and customer trust, particularly in sectors where precision and reliability are non-negotiable. Cubic has cultivated decades of trust, making it a go-to provider for mission-critical systems. For instance, in defense or aerospace, switching costs are extremely high due to rigorous testing and certification processes, which new entrants cannot easily replicate.
Newcomers face a steep uphill battle in establishing the kind of credibility that Cubic enjoys. Large industrial and governmental clients, who represent a substantial portion of Cubic's revenue, are inherently risk-averse. They prioritize proven track records over unproven innovations, making it challenging for new companies to penetrate these lucrative markets. This established trust acts as a powerful barrier, protecting Cubic's market position.
- Brand Reputation: Cubic's long-standing commitment to quality and performance has built a reservoir of trust.
- Customer Trust: In high-stakes industries, reliability is paramount, favoring established players like Cubic.
- Switching Costs: The rigorous qualification and integration processes for Cubic's solutions create high barriers for clients to switch.
- Market Penetration Difficulty: New entrants struggle to gain traction with risk-averse, large-scale clients who value proven solutions.
The threat of new entrants for Cubic is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, exemplified by the over $1.5 billion projected NDIR sensor market by 2028. Cubic's extensive patent portfolio, exceeding 100 patents, further deters potential competitors. Navigating complex regulatory environments and establishing robust supply chains and distribution networks also pose significant challenges for newcomers, making market entry difficult.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D and manufacturing. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Intellectual Property | Over 100 patents in gas sensing technologies. | Legal risks and replication difficulty. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with safety standards (e.g., UL 60335-2-40). | Time-consuming and costly compliance. |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | Established networks and supplier relationships. | Difficult to match Cubic's reach and access. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Decades of proven reliability in critical sectors. | High switching costs for established clients. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including detailed financial statements, industry-specific market research reports from firms like Gartner and Forrester, and public company filings such as 10-K reports.
