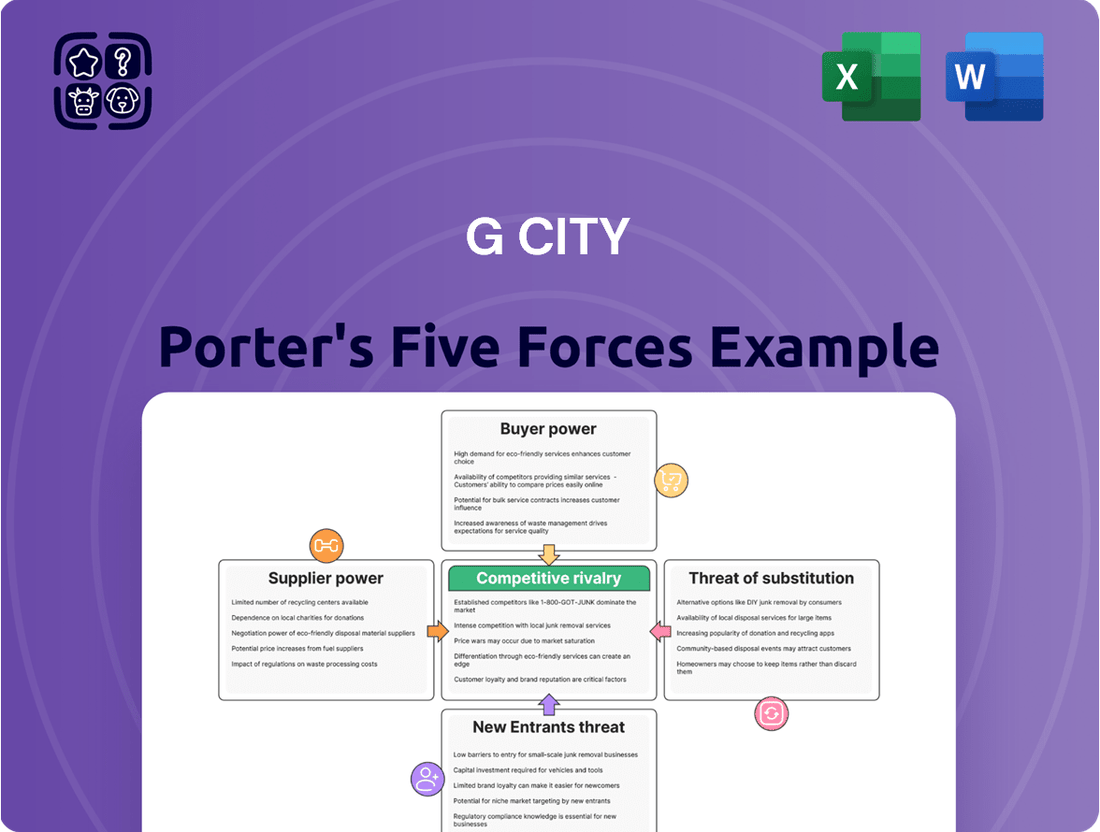
G City Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
G City Bundle
G City's competitive landscape is shaped by intense rivalry and the significant bargaining power of its buyers. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping G City’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The scarcity of prime urban land parcels across G City Porter's key markets in Europe, Israel, and North America significantly bolsters the bargaining power of landowners. These sellers hold considerable leverage due to the unique, often irreplaceable, characteristics of each site, including its specific location, prevailing zoning regulations, and the presence or absence of existing infrastructure.
This limited availability of suitable sites restricts G City Porter's alternative options, thereby amplifying the negotiating strength of property owners. The direct impact of land cost and its overall availability is a critical determinant of project feasibility and, consequently, the potential profitability of G City Porter's developments.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the construction sector, particularly for materials like steel and concrete, and for skilled labor, significantly impacts developers such as G City. In 2024, ongoing supply chain volatility and inflationary pressures continued to affect material costs; for instance, steel prices experienced fluctuations, and the demand for specialized construction labor remained high, leading to increased wages for skilled trades.
These factors can extend project timelines and inflate overall expenses for G City, effectively granting suppliers more leverage. For example, a shortage of certified project managers or a sudden spike in lumber prices can force developers to accept less favorable terms. Mitigating this power often involves securing long-term supply agreements or forging strategic alliances with key material providers and labor unions.
Financing institutions, including banks and private equity firms, wield considerable power over G City Porter. The cost and availability of capital for its development and acquisition projects are directly influenced by factors like prevailing interest rates and credit market liquidity. For instance, in early 2024, the Federal Reserve maintained its benchmark interest rate, impacting borrowing costs for real estate developers.
Lenders' perception of risk in real estate investments significantly shapes the terms of financing. A strong financial position and a diverse funding strategy for G City Porter can mitigate this supplier power. The ability to secure favorable loan terms or access alternative funding sources is crucial for managing these costs.
Technology and Service Providers
The bargaining power of technology and service providers for G City Porter is significant, particularly for specialized components like advanced building management systems and smart city infrastructure. As G City focuses on integrated urban environments, reliance on cutting-edge solutions from firms offering proprietary technologies can amplify supplier leverage. For instance, a provider of a unique AI-driven traffic management system, crucial for G City's operational efficiency, could command higher prices if few alternatives exist. In 2024, the global smart city market was valued at over $500 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of around 12%, indicating strong demand for these specialized services.
This reliance on sophisticated suppliers, including architectural design and property management software firms, can lead to vendor lock-in. If G City Porter invests heavily in a particular software ecosystem, switching costs can be substantial, thereby strengthening the supplier's position. The need for unique expertise in areas like sustainable urban planning or advanced cybersecurity further bolsters the bargaining power of these specialized service providers.
- Increased reliance on proprietary smart city technologies for G City Porter.
- Potential for vendor lock-in with specialized software and infrastructure providers.
- High demand in the growing smart city market (over $500 billion in 2024) empowers key technology suppliers.
- Unique expertise in areas like sustainable design enhances supplier bargaining power.
Regulatory and Permitting Authorities
Regulatory and permitting authorities, while not traditional suppliers, wield substantial power over G City Porter's operations. Their control over zoning laws, essential permits, environmental impact assessments, and building standards can significantly influence project timelines and overall development costs. For instance, in 2024, the average time for obtaining building permits in major metropolitan areas saw an increase, with some regions experiencing delays of up to 6-12 months for complex projects, directly impacting G City's ability to launch new developments efficiently.
These governmental bodies act as gatekeepers, and their requirements can effectively dictate the feasibility and profitability of G City's projects. Changes in environmental regulations, for example, might necessitate costly redesigns or halt construction altogether. The need to navigate these intricate regulatory landscapes demands specialized expertise and considerable resources, adding another layer of complexity to G City's strategic planning and operational execution.
The bargaining power of these authorities is evident in several key areas:
- Zoning and Land Use: Authorities determine where and what type of development can occur, limiting available land and influencing project scope.
- Permitting Processes: The speed and stringency of permit approvals directly impact project schedules and incur associated costs.
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with evolving environmental standards, such as emissions or waste management, can require significant investment and affect project viability.
- Building Codes and Safety Standards: Adherence to these codes ensures safety but also dictates construction methods and material choices, influencing costs.
Suppliers of raw materials and skilled labor hold significant sway over G City Porter. In 2024, persistent supply chain disruptions and inflation kept material costs elevated, with steel prices fluctuating and a strong demand for experienced construction workers driving up wages. This dynamic can prolong project schedules and increase overall development expenses, giving suppliers more leverage.
For instance, a scarcity of certified project managers or a sudden surge in lumber prices could compel developers like G City to accept less favorable terms. To counter this, G City might pursue long-term supply contracts or establish strategic partnerships with key material providers and labor organizations.
| Supplier Type | 2024 Impact Factors | G City Porter's Leverage Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Suppliers (Steel, Concrete, Lumber) | Supply chain volatility, inflationary pressures, fluctuating commodity prices | Long-term supply agreements, strategic alliances with providers |
| Skilled Labor Providers | High demand for specialized trades, increased wage pressures | Partnerships with labor unions, workforce development programs |
| Financing Institutions | Interest rate environment, credit market liquidity, lender risk perception | Strong financial position, diverse funding strategies, securing favorable loan terms |
| Technology & Service Providers (Smart City Tech) | Reliance on proprietary solutions, vendor lock-in potential, growing smart city market (>$500B in 2024) | Diversifying technology partners, negotiating flexible contracts, exploring open-source solutions |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously dissects the competitive forces impacting G City, revealing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers, specifically necessity-based retail tenants within G City's portfolio, is a nuanced factor. While many smaller, independent tenants possess limited leverage, larger anchor tenants or well-established national brands can wield considerable influence. These key players are crucial for driving foot traffic and ensuring consistent occupancy, giving them a stronger hand in lease negotiations. For instance, a major grocery chain or a popular pharmacy, vital for a shopping center's appeal, can often negotiate more favorable rental rates or lease terms due to their guaranteed customer draw and the potential cost of their relocation for G City.
The bargaining power of residential tenants within G City's developments is generally moderate, influenced heavily by local market conditions. In areas experiencing high demand and limited housing supply, such as prime urban centers where G City often operates, tenants have fewer alternatives, thus reducing their negotiating leverage. For instance, in 2024, major metropolitan areas like New York City saw vacancy rates dip below 3%, giving landlords more pricing power.
Large institutional investors, such as pension funds and sovereign wealth funds, wield considerable bargaining power when acquiring G City's completed properties or entire portfolios. These sophisticated entities possess substantial capital, extensive market expertise, and numerous alternative investment options, enabling them to negotiate for competitive pricing and advantageous terms. For instance, in 2024, global real estate investment by institutional investors reached an estimated $1.5 trillion, highlighting their significant market presence and influence.
Their capacity to execute large-scale transactions swiftly can be a key advantage, as G City may prioritize efficient divestitures of its developed assets. The sheer volume of capital these investors can deploy means they can demand thorough due diligence and favorable contract clauses, directly impacting G City's profitability and deal structure.
Competitive Market Options for Tenants
The bargaining power of customers, specifically tenants, is significantly influenced by the availability of competitive market options. In 2024, the retail and residential property markets in many urban centers, including those where G City operates, showed a robust supply of comparable units. For instance, reports from major real estate analytics firms indicated an average vacancy rate of 5.5% for retail spaces and 4.2% for residential units across key metropolitan areas in the first half of 2024. This ample supply directly translates to tenants having more choices, empowering them to negotiate lease terms or seek out properties with more favorable pricing and amenities.
G City's strategic approach focuses on differentiating its properties to counter this customer power. By developing integrated urban environments that offer unique amenities, lifestyle features, and a strong sense of community, G City aims to reduce the perception of its properties as easily substitutable. This strategy is crucial in markets where tenants can readily find similar square footage or location benefits from competitors. For example, G City's recent developments have incorporated features like extensive green spaces, co-working facilities, and curated retail experiences, which are designed to foster loyalty and diminish the tenant's inclination to switch based solely on price.
The ability of tenants to bargain is directly correlated with the ease of finding alternatives. In 2024, the ease of switching was amplified by digital platforms that provide comprehensive listings and transparent pricing for rental properties. This accessibility means that a tenant can quickly compare G City's offerings against numerous other options. Therefore, G City's success in mitigating customer bargaining power hinges on its ability to create distinct value propositions that go beyond mere physical space, fostering a sticky customer base through superior experience and community engagement.
- High Availability of Substitutes: In 2024, the market offered numerous comparable retail and residential properties, increasing tenant choice and negotiation leverage.
- G City's Differentiation Strategy: Integrated urban environments with unique amenities and community appeal aim to reduce perceived substitutability and tenant bargaining power.
- Impact of Digital Platforms: Online real estate portals in 2024 made it easier for tenants to compare options, thereby enhancing their ability to negotiate or switch.
- Value Beyond Space: G City's focus on experience and community is key to retaining tenants and mitigating the inherent bargaining power of customers in competitive markets.
Economic Conditions and Consumer Spending
Economic conditions significantly shape the bargaining power of G City's customers. During periods of economic slowdown, such as the projected slowdown in global growth for 2024, consumer spending tightens. This directly impacts retail tenants who may face reduced sales, increasing their leverage to negotiate lower rents or seek concessions from property owners like G City. For instance, if consumer confidence dips, retailers are more likely to demand favorable lease terms.
Residential tenants also see their bargaining power rise when economic conditions are unfavorable. High inflation, as seen in many regions throughout 2023 and continuing into 2024, erodes purchasing power. When household budgets are strained, tenants become more sensitive to rent increases, potentially leading to higher turnover or demands for rent freezes, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
G City's strategy to focus on 'necessity-based' retail, such as grocery stores and pharmacies, offers a degree of insulation. However, even these sectors are not entirely immune to broader economic pressures. For example, while food demand is relatively stable, discretionary spending within grocery stores can still decline, affecting the overall financial health of these tenants and their ability to absorb rent increases.
- Consumer Confidence: In early 2024, many economic forecasts indicated a cautious consumer sentiment, a direct consequence of persistent inflation and interest rate hikes in the preceding years.
- Retail Sales Performance: While specific G City retail tenant data isn't publicly available, broader retail sales growth in 2023 showed signs of deceleration compared to the post-pandemic rebound, highlighting potential pressure on retailers.
- Inflationary Impact: Inflation rates in major economies in 2023 averaged around 5-7%, significantly impacting household disposable income and thus rent affordability for residential tenants.
- Vacancy Rates: While specific G City figures are proprietary, the retail sector nationally has experienced fluctuating vacancy rates, with economic downturns historically correlating with increased availability of retail space.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly tenants, is a significant force within G City's operational landscape. In 2024, the availability of numerous comparable retail and residential properties across urban centers amplified tenant choice and their negotiation leverage. G City counters this by developing integrated urban environments with unique amenities and community appeal to reduce perceived substitutability.
Digital platforms in 2024 further empowered tenants by simplifying the comparison of rental options, thereby enhancing their ability to negotiate or switch properties. Consequently, G City's strategy to foster tenant loyalty relies on creating distinct value propositions that extend beyond mere physical space, emphasizing superior experience and community engagement.
| Customer Segment | 2024 Market Condition Impact | Tenant Bargaining Power Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Tenants | High availability of substitutes; digital listing transparency | Increased leverage to negotiate lease terms and pricing. |
| Residential Tenants | Moderate to high demand in prime urban centers; digital listing transparency | Generally moderate, but increased by readily available alternatives. |
| Institutional Investors | Significant capital deployment ($1.5 trillion globally in 2024 real estate) | High, due to substantial capital, market expertise, and alternative investment options. |
Preview Before You Purchase
G City Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete G City Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of G City. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global real estate market is incredibly fragmented, meaning G City contends with a vast number of competitors. This includes local builders, regional players, and other international developers, all vying for the same opportunities. For instance, in 2024, the sheer volume of real estate transactions globally, involving millions of properties, highlights this widespread participation.
Within any given urban market, G City faces fierce competition for prime land, desirable tenants, and opportunities to sell its assets. The market is populated by a diverse range of entities, from massive publicly traded Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) to smaller, privately held development firms. This broad spectrum of competitors ensures that no single entity can establish a dominant position across all real estate sectors or geographic regions.
Competitive rivalry in mixed-use urban development is intense, with G City facing off against established real estate giants and opportunistic private equity firms. These players vie for prime urban locations, often leading to aggressive bidding wars for development sites. For instance, in 2024, major urban regeneration projects saw land acquisition costs escalate by an average of 15% in key metropolitan areas, directly impacting development margins.
Attracting and retaining high-caliber tenants is another critical battleground. Companies like Brookfield Properties and Simon Property Group, with their extensive retail and office portfolios, often leverage existing tenant relationships to secure anchor tenants in new mixed-use developments. This competition forces developers to offer compelling incentives and unique tenant experiences, impacting leasing costs and overall project profitability.
Achieving optimal asset valuations is paramount, as competitors aim to outperform through superior design, innovative sustainability features, and curated tenant mixes. In 2024, mixed-use properties with strong ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) credentials achieved an average cap rate compression of 25 basis points compared to similar assets lacking these features, highlighting the importance of differentiation in a crowded market.
Real estate developers like G City face intense competition for capital, crucial for both funding new projects and attracting institutional buyers for finished properties. This means competing for attractive loan terms from banks and vying for the attention of large investors, such as pension funds and sovereign wealth funds, who have numerous investment options. In 2024, global real estate investment volume saw fluctuations, with certain markets experiencing increased competition for prime assets and development finance.
Securing this capital hinges on a developer's ability to showcase strong financial performance, a promising development pipeline, and solid risk management practices. For instance, demonstrating a track record of delivering projects on time and within budget, coupled with clear exit strategies, becomes paramount. This directly impacts a company's capacity to secure the necessary funding and achieve profitable sales, intensifying the rivalry among well-capitalized and strategically sound real estate entities.
Geographic and Local Market Specifics
Competitive rivalry for G City is intensely localized, meaning that even a global player encounters distinct competitors in different urban centers. For instance, in Europe, Israel, and North America, G City must contend with a unique set of local developers in each city or sub-market. These local entities often possess superior market insights, existing community ties, and potentially more streamlined regulatory navigation.
This granular competitive landscape necessitates that G City tailor its operational strategies, marketing efforts, and tenant engagement models to the specific dynamics of each locale. A one-size-fits-all approach is unlikely to succeed. Understanding these local nuances is paramount for effective competition.
- Localized Competition: G City faces distinct competitors in each city and sub-market across Europe, Israel, and North America.
- Local Developer Advantages: Local competitors often leverage deep market knowledge, established relationships, and faster approval processes.
- Strategic Adaptation: G City must customize its strategies for tenant preferences and regulatory environments in each specific market.
Innovation and Differentiation in Urban Environments
Competitive rivalry in urban environments is intensely driven by innovation and differentiation. Developers like G City Porter are constantly challenged to integrate cutting-edge sustainable features, smart building technologies, and unique architectural designs to capture tenant and investor interest. This ongoing pursuit of novelty is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
For instance, in 2024, the commercial real estate sector saw a significant push towards incorporating advanced sustainability metrics. Buildings achieving LEED Platinum certification, a benchmark for green building, are increasingly commanding higher rents. This trend highlights how differentiation through eco-friendly practices directly impacts market attractiveness and G City Porter's ability to retain its competitive standing.
The focus extends beyond physical attributes to curated tenant experiences. Offering integrated community events, specialized amenities, and responsive property management can significantly differentiate a development. Competitors are actively investing in these areas, making it imperative for G City Porter to continually enhance its offerings to avoid losing market share.
- Sustainable Features: Developers are prioritizing LEED and BREEAM certifications, with a growing demand for net-zero energy buildings.
- Smart Building Technology: Integration of IoT for energy management, security, and tenant convenience is becoming standard.
- Tenant Experience: Amenities like co-working spaces, fitness centers, and community engagement programs are key differentiators.
- Architectural Design: Unique and aesthetically pleasing designs attract premium tenants and investors, setting properties apart in crowded urban landscapes.
Competitive rivalry for G City is fierce, driven by a multitude of players from local developers to global REITs, all vying for prime locations and tenants. This fragmented market sees intense bidding for development sites, with land acquisition costs in major urban areas rising by approximately 15% in 2024. Differentiation through sustainability, such as LEED certifications, is critical, with such properties achieving an average cap rate compression of 25 basis points in 2024, indicating a strong market preference.
The competition extends to attracting and retaining tenants, where established players leverage existing relationships. Developers must offer compelling incentives and unique experiences, impacting leasing costs. Furthermore, securing capital is a battleground, with developers needing to demonstrate strong financial performance and robust risk management to attract investors and favorable loan terms, especially amidst fluctuating global real estate investment volumes in 2024.
| Competitive Factor | 2024 Impact/Trend | G City Porter's Response |
|---|---|---|
| Land Acquisition Costs | Up ~15% in key urban areas | Strategic site selection, joint ventures |
| Tenant Attraction | Demand for unique experiences & amenities | Focus on integrated community features, flexible spaces |
| Capital Access | Increased scrutiny on financial performance | Emphasis on strong development pipeline, ESG credentials |
| Sustainability Demand | LEED-certified properties command higher rents | Prioritizing green building certifications and net-zero goals |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The persistent expansion of e-commerce presents a substantial substitute threat to G City's essential retail properties. As more consumers opt for online purchasing across various categories, the need for physical retail locations, even for necessities, may diminish. This shift could lead to reduced customer traffic and tenant interest, consequently impacting rental revenue and property values.
While necessity-based retail exhibits a degree of resilience against online competition, a pronounced change in consumer habits could still exert pressure. For instance, in 2024, global e-commerce sales were projected to reach over $6.3 trillion, highlighting the significant market share captured by online channels. This trend necessitates G City's strategy of developing urban centers with mixed-use properties designed to offer unique experiences that online retail cannot easily replicate.
The increasing prevalence of remote and hybrid work models presents a significant threat to G City Porter's portfolio, especially its mixed-use developments. As more companies embrace flexible work arrangements, the demand for traditional office spaces diminishes, potentially impacting the need for residential properties situated near central business districts. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 60% of U.S. employees prefer a hybrid work model, a trend that directly affects commuter patterns and urban center vitality.
This shift away from daily commuting could reduce the appeal and necessity of urban living, thereby influencing the long-term viability of certain mixed-use components within G City's holdings. If fewer people are drawn to city centers for work, the foot traffic and economic activity that support retail and residential spaces may decline, creating a substitute for the traditional urban lifestyle G City Porter often caters to.
Alternative housing models present a significant threat by offering different value propositions than traditional rentals. Co-living spaces, for instance, gained considerable traction, with the global co-living market projected to reach $17.7 billion by 2025, according to some industry estimates, appealing to younger demographics seeking community and affordability.
Purpose-built student accommodation (PBSA) also diverts demand, especially in university cities where G City might operate. In the UK alone, the PBSA sector saw significant investment, with student numbers remaining robust, indicating continued demand for specialized housing.
Furthermore, a societal shift towards suburbanization, potentially accelerated by remote work trends observed through 2024, could reduce the demand for urban rental units. This demographic movement offers alternative lifestyle choices that may be perceived as more affordable or desirable by a segment of the population.
Alternative Investment Vehicles
The threat of substitutes for G City's real estate investments is significant, as investors have a wide array of alternative avenues to deploy capital. These include traditional financial markets like stocks and bonds, as well as more specialized options such as private equity and venture capital. For instance, as of late 2023, the S&P 500 had seen substantial gains, potentially drawing investor interest away from real estate.
The attractiveness of these substitutes often hinges on perceived risk-adjusted returns and liquidity. If alternative investments offer a more compelling proposition, it can directly impact G City's capacity to attract capital and influence the valuation of its property portfolio. This is particularly relevant when considering the broader economic climate, where interest rate changes can make fixed-income investments more appealing.
Here are some key alternative investment considerations:
- Bonds: In early 2024, yields on U.S. Treasury bonds have remained competitive, offering a relatively safe haven for investors seeking income.
- Stocks: The equity market, while volatile, can offer higher growth potential, with sectors like technology experiencing strong performance in recent periods.
- Private Equity: This asset class provides exposure to non-publicly traded companies, often with the promise of higher returns but typically with lower liquidity.
- Other Real Estate Investments: Investors might opt for Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) or direct investments in other property types or geographic locations, which can serve as substitutes for G City's specific offerings.
Shifting Urban Planning Paradigms
Shifting urban planning paradigms pose a significant threat to G City's mixed-use urban center model. Emerging trends favoring decentralized development or hyper-local community hubs could reduce demand for large, integrated urban properties. This necessitates a re-evaluation of the core value proposition of traditional urban centers in light of evolving societal preferences.
For instance, the rise of remote work, accelerated by events in 2020 and continuing through 2024, has lessened the daily reliance on centralized business districts for many. Data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics in early 2024 indicated that approximately 28% of the workforce was working remotely full-time. This trend directly challenges the necessity of dense, mixed-use urban cores for a substantial portion of the population.
- Decentralization Trend: Increased adoption of suburban and rural living, driven by affordability and quality of life preferences, offers an alternative to dense urban environments.
- Hyper-local Focus: The growing emphasis on self-sufficient neighborhood hubs, offering amenities and services within walking or short-distance commuting, can substitute the need for travel to a central urban core.
- Technological Integration: Advancements in virtual collaboration tools and e-commerce continue to erode the traditional advantages of physical proximity for work and retail.
- Green Space Prioritization: Urban planning initiatives increasingly prioritize green spaces and lower-density living, potentially diverting investment and appeal away from traditional, high-density urban centers.
The threat of substitutes for G City's real estate assets is multifaceted, encompassing alternative investment vehicles and evolving lifestyle preferences. Financial markets, particularly equities and bonds, present a direct substitute for real estate capital. For example, in early 2024, competitive yields on U.S. Treasury bonds offered a compelling alternative for income-seeking investors, potentially drawing funds away from property investments.
Furthermore, changing consumer behaviors and urban planning trends create substitute offerings for G City's core real estate products. The rise of e-commerce, projected to exceed $6.3 trillion in global sales for 2024, directly substitutes for physical retail spaces. Similarly, the increasing adoption of hybrid and remote work, with around 28% of the U.S. workforce working remotely full-time in early 2024, reduces the demand for traditional office and related urban residential properties.
Alternative housing models like co-living, with a market projected to reach $17.7 billion by 2025, and purpose-built student accommodation offer distinct value propositions that divert demand from conventional rental units. These substitutes cater to specific demographic needs and preferences, impacting G City's traditional revenue streams.
| Substitute Category | Example | 2024 Data/Projection | Impact on G City | Key Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Investments | U.S. Treasury Bonds | Competitive yields in early 2024 | Capital diversion from real estate | Risk-adjusted returns, safety |
| E-commerce | Online Retail Platforms | Global sales projected over $6.3 trillion | Reduced demand for physical retail | Convenience, price |
| Work Models | Remote/Hybrid Work | 28% of U.S. workforce remote full-time (early 2024) | Lower demand for office/urban residential | Flexibility, work-life balance |
| Housing Models | Co-living Spaces | Market projected to reach $17.7 billion by 2025 | Reduced demand for traditional rentals | Affordability, community |
Entrants Threaten
The urban real estate development and ownership market, particularly for large-scale, mixed-use projects like those undertaken by G City, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Acquiring prime land in desirable urban locations alone can cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. For instance, major downtown land parcels in cities like New York or London can command prices exceeding $500 million.
Beyond land acquisition, the financing of construction for such extensive developments, often encompassing residential, commercial, and retail spaces, necessitates substantial debt and equity. Projects of G City's magnitude can easily require upwards of $1 billion in total investment. This immense financial hurdle significantly limits the pool of potential new competitors, as only well-capitalized firms or those with strong access to global financial markets can realistically consider entering this space, thereby protecting incumbent players.
The intricate web of regulations and permitting processes presents a formidable barrier to entry in G City's real estate market. For instance, in 2024, the average time to secure building permits in major metropolitan areas often stretched over six months, with some complex projects exceeding a year. Newcomers often struggle with the sheer volume of paperwork, zoning variances, and environmental impact assessments, which can significantly inflate initial development costs and timelines.
Established players like G City possess the institutional knowledge and dedicated legal teams to efficiently manage these complexities. This existing expertise allows them to anticipate regulatory changes and navigate the approval pathways more smoothly than nascent competitors. In 2023, reports indicated that navigating these compliance requirements could add as much as 15-20% to a new development's overall budget.
Consequently, the steep learning curve and the substantial upfront investment in legal and consulting services required to understand and comply with these regulations act as a significant deterrent. This regulatory environment effectively favors incumbents who have already invested in building the necessary infrastructure and relationships to manage these processes effectively, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants.
Land scarcity in prime urban centers, G City's operational hubs, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. Acquiring strategically located land parcels is exceptionally difficult and costly. For instance, in 2024, prime commercial land prices in major global cities like New York and London saw continued increases, with some areas experiencing year-over-year growth exceeding 10%, making it prohibitively expensive for new players to compete for desirable sites.
Established developers, including G City, often hold significant land banks or have long-standing relationships with landowners and brokers. These established networks and existing ownerships create a substantial barrier, as new entrants struggle to secure the necessary land at competitive prices. This limited access to prime real estate restricts their ability to develop projects that can effectively challenge G City's market position.
Brand Reputation and Tenant Relationships
The threat of new entrants for G City Porter is significantly mitigated by its established brand reputation and deeply entrenched tenant relationships. New players face the considerable challenge of replicating the trust and loyalty G City has built over years with its retail and residential occupants. For instance, in 2024, major mixed-use developments often cite strong tenant retention rates, sometimes exceeding 90%, as a key competitive advantage, a benchmark difficult for newcomers to immediately achieve.
New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing and offer substantial incentives to attract and retain high-quality tenants, a process that is both costly and time-consuming. G City’s proven track record in successful property management and development makes it a preferred partner, securing its occupancy rates and long-term financial stability against nascent competition.
- Brand Equity: G City's established name recognition provides a significant barrier to entry, as new developers struggle to build comparable market trust.
- Tenant Loyalty: Years of reliable service and attractive leasing terms have fostered strong relationships with key tenants, ensuring high occupancy.
- Operational Expertise: G City's proven success in property management and development offers a compelling advantage over less experienced new entrants.
- Market Penetration Costs: Newcomers would face substantial costs for marketing, tenant acquisition, and potentially offering lower initial rents to gain market share.
Specialized Expertise and Operational Scale
Developing and managing large-scale, mixed-use urban properties demands highly specialized expertise. This includes intricate knowledge of urban planning, sophisticated architectural design, complex construction logistics, and nuanced leasing and marketing strategies. For instance, navigating the regulatory landscape for a new development in a major European city like Berlin in 2024 requires deep understanding of local zoning laws and environmental impact assessments, a process that can take years to master.
New entrants often find it challenging to replicate the integrated operational scale and deep institutional knowledge that established players like G City possess. G City's ability to efficiently manage a diverse portfolio across multiple countries, from securing financing to ongoing asset management, is a significant barrier. In 2024, the average time for a new developer to secure all necessary permits for a large urban regeneration project in a Tier 1 city can exceed 36 months, highlighting the entrenched advantage of experienced firms.
The complexity of managing a diverse portfolio across multiple countries, coupled with the need for efficient operational processes, presents a significant barrier to entry for less experienced or smaller firms. Building this level of expertise, honed through years of project execution and market cycles, is not easily replicated. For example, G City's success in integrating sustainable building practices across its global portfolio by 2024, which involved extensive R&D and supply chain development, demonstrates this accumulated advantage.
Key barriers related to specialized expertise and operational scale include:
- Deep understanding of urban planning and zoning regulations: Navigating diverse and often complex local government requirements.
- Sophisticated financial structuring and capital access: Securing the substantial funding required for large-scale developments.
- Integrated supply chain and construction management: Optimizing project delivery and cost control across multiple sites.
- Long-term asset management and tenant relations: Maintaining property value and occupancy rates in competitive markets.
The threat of new entrants for G City is significantly low due to the immense capital requirements for large-scale urban real estate development. Acquiring prime land in major cities can cost hundreds of millions, and total project financing often exceeds $1 billion, limiting competition to only well-capitalized firms.
Regulatory hurdles and permitting processes also act as substantial barriers, with new projects in 2024 often facing over six months for permits, and compliance costs potentially adding 15-20% to budgets. G City's established expertise and legal teams navigate these complexities more efficiently than newcomers.
Land scarcity in prime urban centers, with prices in cities like New York and London increasing by over 10% year-over-year in 2024, further restricts new entrants. G City's existing land banks and strong relationships with landowners create a significant advantage in securing desirable sites.
Furthermore, G City's strong brand reputation and established tenant relationships, demonstrated by tenant retention rates often exceeding 90% in 2024, make it difficult for new players to attract and retain high-quality occupants without substantial investment in marketing and incentives.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Supporting Data (2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High cost of land acquisition and project financing. | Severely limits the number of potential competitors. | Major land parcels can exceed $500 million; total project costs can surpass $1 billion. |
| Regulatory & Permitting | Complex and time-consuming approval processes. | Increases upfront costs, timelines, and requires specialized knowledge. | Permit acquisition can take over six months; compliance costs add 15-20% to development budgets. |
| Land Scarcity | Limited availability of prime urban locations. | Makes securing competitive sites difficult and expensive. | Prime land prices in global cities saw over 10% year-over-year growth. |
| Brand & Tenant Relationships | Established reputation and loyal tenant base. | New entrants struggle to build trust and secure occupancy. | High tenant retention rates (often >90%) are a key advantage for incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data sources, including detailed financial reports from publicly traded companies, in-depth market research from leading industry analysts, and official government statistics. This ensures a robust understanding of competitive intensity and market dynamics.
