F.W. Webb Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
F.W. Webb Bundle
F.W. Webb navigates a complex market, influenced by powerful suppliers and intense rivalry among distributors. Understanding these pressures is crucial for any player in the wholesale plumbing, HVAC, and building materials sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping F.W. Webb’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The wholesale distribution sector, especially for specialized goods like plumbing and HVAC equipment, frequently depends on a smaller group of dominant manufacturers for critical parts. This concentration means suppliers can wield considerable influence, particularly if they provide unique or essential products.
For a company like F.W. Webb, a concentrated supplier base can translate into significant bargaining power for those suppliers. If only a few manufacturers produce the specialized components Webb needs, those suppliers can dictate terms and pricing more effectively. For instance, in 2024, the HVAC market saw continued consolidation among major equipment manufacturers, potentially increasing their leverage over distributors.
Strong, established relationships with suppliers are vital for wholesale distributors like F.W. Webb. These partnerships ensure consistent product availability and favorable terms, which are critical for maintaining operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
F.W. Webb's extensive network and long-standing presence in the Northeast can be a significant asset, potentially offering suppliers a valuable and reliable distribution channel. This can give Webb some leverage, especially with manufacturers seeking broad market reach.
However, the bargaining power of suppliers remains a key consideration. If a supplier's products are essential and they have limited alternative distributors of comparable scale to F.W. Webb, their ability to dictate terms, such as pricing or minimum order quantities, can be substantial.
For F.W. Webb, the costs associated with switching suppliers can be considerable. These expenses include the effort to rebuild established supply chains, the administrative burden of renegotiating contracts and terms, and the potential for product compatibility challenges with existing systems. Furthermore, staff may require retraining to effectively manage new product lines, adding another layer of cost and disruption.
These substantial switching costs inherently strengthen the bargaining power of F.W. Webb's current suppliers. The significant disruption and financial outlay required to transition to a new supplier make it less feasible for F.W. Webb to easily change their sources. For example, the ongoing industry-wide shift to new refrigerants in the HVAC sector presents a scenario where switching suppliers for these critical components could incur substantial costs and operational complexities.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for companies like F.W. Webb. If F.W. Webb can easily find similar products from multiple manufacturers or readily available generic alternatives, the power of any single supplier is reduced. This is because F.W. Webb has more options and can switch suppliers if prices become too high or terms are unfavorable.
For instance, if F.W. Webb sources common plumbing fixtures, the market likely offers numerous brands and manufacturers producing comparable items. This abundance of choice dilutes the power of any one fixture supplier. In 2024, the global plumbing fixtures market was valued at approximately $130 billion, with a significant portion comprised of standardized products, indicating a competitive supplier landscape for many of F.W. Webb's needs.
- Availability of substitutes: If F.W. Webb can easily source comparable products from multiple suppliers, the bargaining power of any single supplier is weakened.
- Impact of generic alternatives: The presence of generic or unbranded alternatives further diminishes supplier leverage, allowing F.W. Webb to negotiate better terms.
- Specialized vs. standard products: Supplier power is higher for highly specialized or proprietary components where substitutes are scarce, potentially increasing costs for F.W. Webb.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
If suppliers can easily bypass distributors like F.W. Webb and sell directly to contractors or end-users, their bargaining power significantly increases. This capability, known as forward integration, allows them to capture more of the value chain.
This trend is particularly noticeable in the wholesale distribution sector. Manufacturers are increasingly exploring direct-to-consumer (DTC) models, which can disrupt traditional distribution channels and empower suppliers.
For instance, in 2024, many manufacturers in the building materials sector reported exploring or implementing DTC strategies to enhance margins and customer relationships. This directly challenges the role of intermediaries like F.W. Webb.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: Suppliers capable of forward integration can exert greater pressure on distributors regarding pricing and terms.
- Disintermediation Risk: Distributors face the risk of being cut out of the sales process as suppliers establish direct customer channels.
- Industry Shift: The wholesale distribution industry is witnessing a gradual shift where manufacturers are actively seeking direct sales avenues.
- Competitive Threat: The ability of suppliers to integrate forward presents a significant competitive threat, impacting distributor profitability and market share.
Suppliers hold significant sway when they provide unique, essential products with few alternatives, allowing them to dictate terms and pricing. F.W. Webb faces this reality, especially with specialized HVAC components where manufacturer consolidation in 2024 increased supplier leverage. The substantial costs and operational complexities associated with switching suppliers, such as navigating new refrigerant standards, further solidify existing supplier power.
| Factor | Impact on F.W. Webb | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Supplier Concentration | Higher power for fewer suppliers | HVAC market consolidation continued |
| Switching Costs | Reduces Webb's ability to change suppliers | High costs for new refrigerant adoption |
| Availability of Substitutes | Weakens supplier power for common items | Plumbing fixtures market valued at ~$130B, with many standard products |
| Forward Integration Risk | Suppliers selling directly to customers | Building material manufacturers exploring DTC models |
What is included in the product
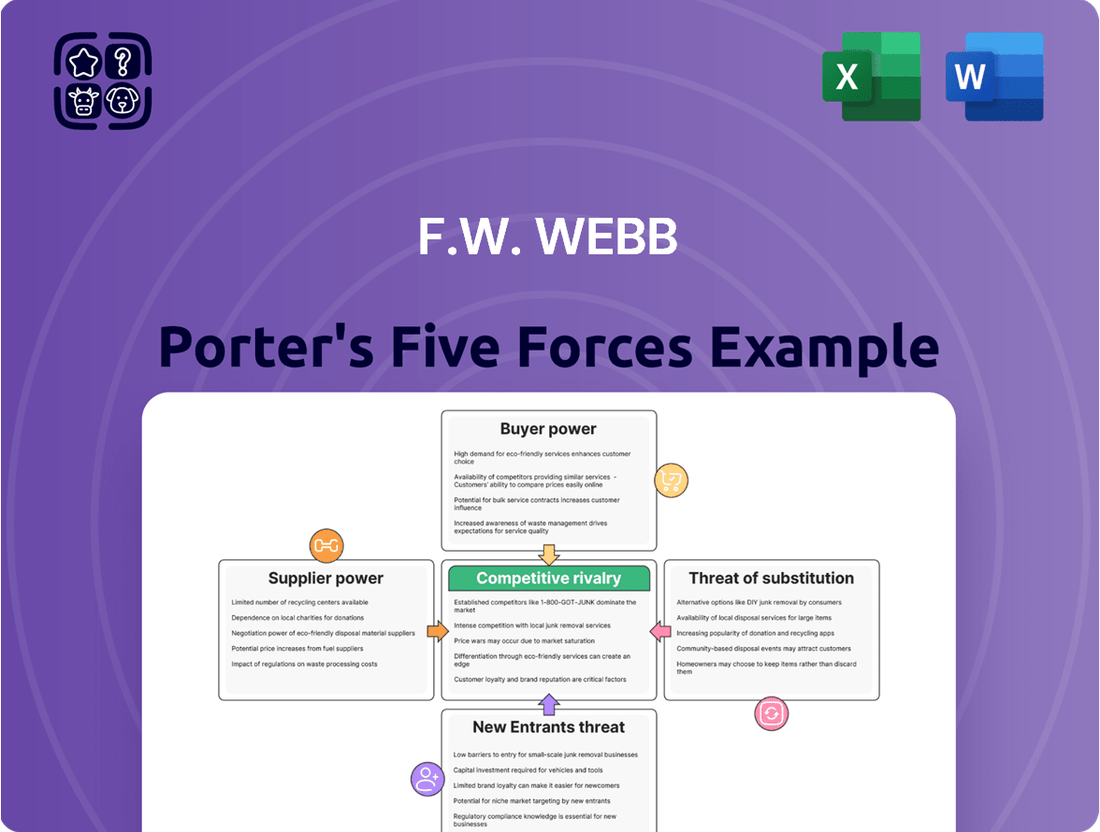
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting F.W. Webb, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces dashboard, allowing for immediate strategic assessment and targeted pain point relief.
Customers Bargaining Power
F.W. Webb's diverse customer base, encompassing contractors, engineers, and facility managers, inherently dilutes individual customer bargaining power. This broad reach across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors means the company isn't overly dependent on any single client or small group, providing a buffer against concentrated demands. For instance, in 2024, F.W. Webb continued to serve thousands of unique customer accounts, a testament to its wide market penetration.
While the overall customer base is diverse, F.W. Webb's strong regional focus on the Northeastern United States could lead to a higher concentration of certain customer segments within that geographic area. This might slightly increase the bargaining power of larger, established customers within specific Northeastern markets, though the company's extensive product lines and services still offer significant leverage.
Contractors in the construction and maintenance sectors, a key customer base for F.W. Webb, frequently operate with slim profit margins. This financial reality makes them acutely sensitive to price fluctuations, directly impacting their purchasing decisions.
The wholesale distribution landscape F.W. Webb navigates is highly competitive. This intense rivalry among distributors often translates into price wars, empowering customers to demand lower prices and thus increasing their bargaining power.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. construction industry faced ongoing challenges with material cost inflation, with some key inputs seeing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year. This economic pressure on contractors intensifies their focus on procurement costs, making price a paramount factor in their supplier selection.
For F.W. Webb's customers, the effort involved in switching distributors, like setting up new accounts or learning new product lines, can be a hurdle. If the products they buy are very similar across different suppliers, these costs are minimal, making it easy for customers to switch to a competitor with a better deal. For instance, in the plumbing supply sector, if F.W. Webb primarily deals in widely available, standardized fittings, customers might not face significant barriers to switching.
Customer's Ability to Backward Integrate
Customers, particularly substantial contractors and facility managers, possess the potential to backward integrate. This means they might explore acquiring products directly from manufacturers or even establishing their own inventory systems, effectively cutting out intermediaries like F.W. Webb.
While this strategy is less feasible for smaller clientele, larger customers can leverage this capability as a bargaining chip. They might threaten to bypass distributors if the offered terms and pricing are not sufficiently attractive, thereby increasing their negotiating power.
F.W. Webb counters this threat by emphasizing its value-added services and a comprehensive product selection. These offerings are designed to retain customer loyalty and demonstrate that direct sourcing may not always be the most efficient or cost-effective option.
- Potential for backward integration by large customers: Some major contractors, managing significant project volumes, might find it economically viable to source directly from manufacturers, bypassing distributors.
- Leveraging direct sourcing as a negotiation tactic: The mere possibility of customers shifting to direct purchasing can empower them to demand better pricing or terms from F.W. Webb.
- F.W. Webb's mitigation strategies: The company's extensive product catalog and specialized services, such as technical support and logistics, are key to deterring customers from pursuing backward integration.
Availability of Information and Comparison
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, thanks to the digital age. Online platforms and review sites mean they can easily research products, compare prices across numerous vendors, and understand competitor offerings. This transparency significantly shifts the balance of power towards the buyer.
For instance, in 2024, a significant majority of consumers reported using online resources to research purchases before making a decision. This readily available data allows them to identify the best value, forcing businesses like F.W. Webb to remain competitive not just on price but also on service and product quality to retain customers.
- Informed Decisions: Customers can now easily compare features, specifications, and pricing from multiple suppliers, making informed choices.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased transparency leads to greater price sensitivity, pressuring distributors to offer competitive rates.
- Service Expectations: Beyond price, customers can research and compare service levels, delivery times, and return policies, raising overall expectations.
- Digital Reach: The widespread availability of online comparison tools means even small businesses face scrutiny from a global customer base.
F.W. Webb's customers, especially those in price-sensitive sectors like construction, wield considerable bargaining power. The competitive wholesale distribution market, marked by potential price wars, compels distributors to offer competitive rates. In 2024, the construction industry's struggle with material cost inflation further amplified customer focus on procurement expenses, increasing their leverage with suppliers like F.W. Webb.
The ease with which customers can switch suppliers, particularly for standardized products, reduces their switching costs and enhances their bargaining power. Furthermore, the digital age has equipped customers with extensive information, enabling easy price and service comparisons, thus intensifying pressure on F.W. Webb to maintain competitive offerings.
| Factor | Impact on F.W. Webb | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Price Sensitivity | High | Construction material cost inflation impacting contractor margins. |
| Switching Costs | Low for standardized products | Ease of switching for common plumbing or HVAC components. |
| Information Availability | High | Widespread online research and price comparison by customers. |
| Potential for Backward Integration | Moderate for large customers | Large contractors may explore direct sourcing from manufacturers. |
Preview Before You Purchase
F.W. Webb Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact F.W. Webb Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual, professionally written document, which details the competitive landscape for F.W. Webb. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, fully formatted file, ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The wholesale distribution market for plumbing, heating, HVAC, and industrial PVF in the Northeast is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation. This means F.W. Webb operates within an environment populated by a multitude of regional and local players, in addition to larger, more established companies.
Key competitors like Hajoca and Winsupply actively compete across various segments, including HVACR and broader industrial supply. This dense competitive landscape fuels intense rivalry as businesses constantly strive to capture and maintain market share.
The growth rate within the construction and related sectors in the Northeast is a key driver of competitive rivalry for companies like F.W. Webb. A robust market generally softens competition as there's ample business for everyone. However, a decelerating or uneven growth environment intensifies the battle for market share.
Looking ahead to 2025, the Northeast construction landscape presents a mixed picture. While commercial construction is anticipated to experience growth, other vital segments such as multi-family housing and government-funded projects are projected to contract. This divergence means that companies will likely face heightened competition as they vie for a smaller pool of opportunities in the declining sectors.
In wholesale distribution, products often become commodities, sparking fierce price wars. F.W. Webb combats this by offering an extensive product selection across various specialty markets, distinguishing itself beyond just price. For instance, their commitment to specialized product lines, such as HVAC or plumbing, allows them to cater to specific industry needs, a key differentiator.
The company's strategy extends to providing valuable support services, including training centers and customer showrooms. These offerings create a sticky customer base, reducing the temptation for clients to switch solely based on price. In 2024, F.W. Webb's continued investment in these value-added services underscores their importance in a market where differentiation is paramount for sustained competitive advantage.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity
Wholesale distribution, like that undertaken by F.W. Webb, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These include expenses for large warehouses, sophisticated logistics networks, and maintaining significant inventory levels. These high overheads create pressure to operate at or near full capacity.
When demand softens, companies with high fixed costs often resort to aggressive pricing to keep their operations running efficiently and cover these costs. This can lead to price wars, intensifying competition among rivals. F.W. Webb's ongoing investments in expanding and modernizing its facilities, such as its recent development projects, indicate a strategic effort to leverage economies of scale and improve operational efficiency, thereby managing these high fixed costs.
- High Fixed Costs: Warehousing, logistics, and inventory management represent significant capital outlays for wholesale distributors.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: Companies are incentivized to maintain high operating levels to spread fixed costs, leading to competitive pricing.
- F.W. Webb's Investment Strategy: Recent facility expansions and upgrades by F.W. Webb aim to enhance efficiency and cost optimization in a high fixed-cost environment.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are actively reshaping the competitive landscape within the plumbing and HVAC distribution sector. F.W. Webb's own strategic acquisitions demonstrate a clear industry trend towards consolidation. For instance, in 2023, F.W. Webb acquired several smaller regional distributors, expanding its footprint and product offerings, a move mirrored by many of its competitors.
This consolidation can lead to a market dominated by fewer, larger entities. These consolidated players often wield greater purchasing power and market influence, potentially intensifying rivalry for the remaining independent distributors or smaller chains. The increased scale can also enable these larger firms to invest more heavily in technology, logistics, and customer service, further differentiating them from smaller competitors.
- Industry Consolidation: M&A activity is a significant driver of change, leading to fewer, larger competitors.
- F.W. Webb's Strategy: The company's own acquisition history highlights its participation in this consolidation trend.
- Impact on Rivalry: Consolidation can increase the market power of dominant players, intensifying competition for others.
- Shifting Dynamics: New competitive dynamics emerge as larger, consolidated entities leverage their scale and resources.
Competitive rivalry within F.W. Webb's wholesale distribution market is fierce due to a fragmented industry structure and numerous regional players. Intense competition is further fueled by the commoditization of products, leading to price wars, and the pressure to maintain high capacity utilization given substantial fixed costs. F.W. Webb differentiates itself through extensive product selection and value-added services like training and showrooms, mitigating price-based competition.
The wholesale distribution sector for plumbing, heating, and HVAC in the Northeast is highly fragmented, with F.W. Webb facing numerous regional and local competitors. This intense rivalry is exacerbated by the tendency for products to become commodities, often resulting in price wars. F.W. Webb counters this by offering a broad product range and specialized support services, aiming to build customer loyalty beyond price alone.
The competitive landscape is also shaped by industry consolidation driven by mergers and acquisitions. F.W. Webb's own strategic acquisitions, such as those in 2023, reflect this trend, leading to fewer, larger competitors with greater market influence and resources. This consolidation intensifies rivalry, forcing remaining players to adapt through efficiency and superior customer value.
| Key Competitor | Primary Market Focus | Competitive Strategy Highlight |
|---|---|---|
| Hajoca | Plumbing, HVAC, Industrial PVF | Extensive branch network, localized service |
| Winsupply | Plumbing, HVAC, Industrial PVF | Local entrepreneurship, diverse product lines |
| Ferguson Enterprises | Plumbing, HVAC, Waterworks, Fire Protection | Broad product offering, strong e-commerce presence |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for F.W. Webb arises when its customers, especially those with substantial purchasing power, choose to bypass distributors and procure goods directly from manufacturers. This direct-to-manufacturer sourcing model is a growing concern for wholesale distributors across various sectors.
In 2024, the trend of customers seeking direct relationships with producers intensified, driven by a desire for better pricing and more control over their supply chains. For instance, large construction firms or industrial clients might find it economically advantageous to negotiate bulk deals directly with plumbing or HVAC equipment manufacturers, thereby cutting out the intermediary distribution layer.
The burgeoning growth of online retailers and e-commerce platforms, including those specifically catering to plumbing, HVAC, and industrial supplies, poses a significant threat of substitutes for traditional distributors like F.W. Webb. These digital marketplaces often provide a wider selection and can achieve lower overheads, translating into more competitive pricing for consumers. For instance, in 2024, the global e-commerce market was projected to reach over $6.3 trillion, a testament to its increasing dominance and ability to attract customers seeking convenience and value.
Technological advancements continuously introduce substitute solutions that can diminish the demand for F.W. Webb Porter's traditional plumbing and HVAC components. For instance, the burgeoning smart home market offers integrated systems that may reduce the need for individual, conventional fixtures. In 2024, the global smart home market was valued at approximately $138.9 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, suggesting a growing preference for connected solutions.
New construction methods and energy-efficient systems also present significant substitution threats. Innovations in building insulation, prefabrication, and advanced climate control technologies can lessen reliance on certain types of piping or traditional heating and cooling units. The global green building market, valued at over $1.7 trillion in 2023, highlights a strong market push towards sustainable and potentially less component-intensive building practices.
Furthermore, regulatory shifts, such as the mandated transition to low Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants in HVAC systems, exemplify a technology-driven substitution. This change necessitates new equipment and refrigerants, potentially impacting the market share of existing product lines and requiring adaptation from manufacturers and distributors like F.W. Webb Porter.
DIY Market and Smaller Retailers
While F.W. Webb primarily targets professional contractors, the increasing accessibility of plumbing and HVAC supplies through large home improvement retailers like Home Depot and Lowe's poses an indirect threat. These big-box stores cater to a growing DIY segment, offering a range of products that can substitute for F.W. Webb's offerings, especially for less complex or specialized items. This trend can dilute demand for certain product categories within F.W. Webb's broader market.
The DIY market, fueled by online tutorials and accessible retail channels, directly competes for consumer spending on home repair and improvement projects. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. home improvement market was valued at over $500 billion, with a significant portion attributed to DIY projects. This expansion means more consumers might bypass traditional distributors for readily available, albeit sometimes lower-tier, products.
- DIY Market Growth: The U.S. DIY home improvement market continues to expand, with consumers increasingly undertaking their own projects.
- Big-Box Retailer Competition: Major retailers offer a wide array of plumbing and HVAC products, serving as accessible alternatives for consumers.
- Indirect Substitution: Less specialized items are particularly vulnerable to substitution from these channels, potentially impacting F.W. Webb's sales volume in those areas.
- Showroom Strategy: F.W. Webb's retail showrooms may help to mitigate this threat by offering a direct-to-consumer experience that can compete with DIY channels.
Refurbishment and Repair over Replacement
Customers are increasingly choosing to repair rather than replace their existing systems, driven by economic pressures and a growing emphasis on sustainability. This trend directly impacts F.W. Webb by potentially reducing the demand for new products and components they distribute, thereby affecting sales volumes.
The HVAC sector exemplifies this shift, with a noticeable move towards repair services over outright system replacements, a direct consequence of economic considerations. For example, in 2024, consumer spending on home repairs and maintenance saw a significant uptick, with many homeowners prioritizing extending the life of their current appliances, including HVAC units, over the capital outlay for new ones.
- Economic Incentives Drive Repair: Higher costs for new equipment and installation encourage customers to invest in repairs, making older systems economically viable for longer.
- Sustainability Focus: Environmental consciousness is pushing consumers and businesses towards repair and refurbishment as a more sustainable alternative to discarding and replacing functional equipment.
- Impact on Distribution: This preference for repair can decrease the overall sales volume of new units and associated components that F.W. Webb distributes, necessitating a strategic adjustment in inventory and sales focus.
- Industry Trend: The HVAC industry, a key sector for F.W. Webb, has reported a growing preference for repair, with service providers noting a substantial increase in repair requests compared to replacement inquiries throughout 2024.
The threat of substitutes for F.W. Webb is multifaceted, encompassing direct sourcing by large customers, the rise of e-commerce, and technological innovations that offer alternative solutions. Furthermore, the growing DIY market and a consumer preference for repairing existing systems over purchasing new ones also represent significant substitution pressures.
These substitutes can erode F.W. Webb's market share by offering lower prices, greater convenience, or entirely different product functionalities. For example, the increasing adoption of smart home technology in 2024, valued at approximately $138.9 billion, directly competes with traditional component sales.
The shift towards repair over replacement, particularly in the HVAC sector, means fewer new units are sold, impacting distributors like F.W. Webb. This trend, evident throughout 2024, highlights a strategic challenge for businesses reliant on new product sales.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by large home improvement retailers, which serve as accessible substitutes for less specialized plumbing and HVAC needs, particularly for the growing DIY consumer base.
| Threat of Substitutes | Description | 2024 Data/Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Sourcing | Customers bypassing distributors to buy directly from manufacturers. | Intensified trend driven by pricing and supply chain control desires. |
| E-commerce & Online Retailers | Digital marketplaces offering wider selection and competitive pricing. | Global e-commerce projected over $6.3 trillion, indicating significant customer migration. |
| Technological Advancements (e.g., Smart Home) | New integrated systems reducing demand for traditional components. | Smart home market valued at ~$138.9 billion, showing growing preference for connected solutions. |
| New Construction Methods & Energy Efficiency | Innovations lessening reliance on certain traditional components. | Global green building market over $1.7 trillion (2023), indicating a push for sustainable, potentially less component-intensive building. |
| DIY Market & Big-Box Retailers | Accessible retail channels for consumers undertaking their own projects. | U.S. home improvement market >$500 billion (2024), with a substantial DIY segment. |
| Repair Over Replacement | Consumer preference for extending the life of existing systems. | Significant uptick in home repair spending in 2024, with HVAC sector showing increased repair vs. replacement requests. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the wholesale distribution sector for plumbing, heating, HVAC, and industrial pipe, valves, and fittings (PVF) demands significant upfront capital. Newcomers must invest heavily in stocking a wide array of products, establishing robust warehousing facilities, and building efficient logistics networks to compete effectively.
Consider F.W. Webb's operational footprint: over 100 locations spread across nine states, showcasing the sheer scale of infrastructure needed. This extensive physical presence and inventory commitment represent a formidable financial hurdle, effectively deterring many potential new entrants from challenging established players.
Established relationships and strong brand loyalty act as significant barriers to new entrants in the wholesale plumbing and HVAC supply market. F.W. Webb, with its 150-year history, has cultivated deep, trust-based connections with both suppliers and a broad customer base. These long-standing partnerships are difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate, requiring substantial investment in building reliability and service reputation.
Large distributors like F.W. Webb leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. This allows them to negotiate better prices from manufacturers due to high-volume purchasing, optimize inventory holding costs through efficient management systems, and spread fixed distribution expenses over a larger operational base. For instance, in 2024, major plumbing and HVAC distributors reported operating margins that benefited from these scale advantages.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without the established volume, they cannot command the same purchasing power, leading to higher per-unit costs for inventory. This makes it exceedingly difficult for them to compete on price with established players who benefit from lower cost of goods sold and more efficient logistics.
Furthermore, the ability to offer a comprehensive and readily available inventory is a critical advantage for companies like F.W. Webb. Their scale enables them to stock a vast array of products, meeting diverse customer needs immediately. New competitors would find it prohibitively expensive to build a comparable inventory breadth, further weakening their competitive position against established, large-scale distributors.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The distribution of specialized products like HVAC refrigerants and industrial piping, valves, and fittings (PVF) presents significant regulatory and compliance hurdles for potential new entrants. Navigating complex industry standards, obtaining necessary certifications, and adhering to evolving environmental regulations, such as those surrounding new HVAC refrigerants, demands substantial expertise and investment. These barriers can deter new companies from entering the market, thereby reducing the threat of new competition.
For instance, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continues to phase down hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) under the AIM Act, requiring distributors to handle refrigerants with lower global warming potential. This transition necessitates updated training for staff and potentially new infrastructure to manage these substances safely and compliantly. By 2024, the demand for these lower-GWP refrigerants is expected to significantly increase, creating a knowledge and compliance gap that new entrants must bridge.
- Complex Certifications: Distributors often need specific certifications for handling hazardous or regulated materials, which can take years and significant capital to acquire.
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with environmental laws, such as those governing refrigerant reclamation and disposal, adds operational complexity and cost.
- Product Knowledge: Understanding and adhering to technical specifications and safety standards for products like industrial PVF is critical and requires specialized training.
- Evolving Standards: The constant evolution of regulations, like the shift in HVAC refrigerants, requires continuous adaptation and investment in compliance.
Talent and Expertise Shortages
The wholesale distribution sector, especially for technical goods like HVAC and plumbing, relies heavily on employees possessing specialized product knowledge and industry experience. This need for expertise creates a significant barrier for potential new competitors. Finding and keeping individuals with these specific skills is a challenge, as the trades face ongoing labor shortages.
For instance, data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics in 2024 indicates a continuing demand for skilled tradespeople, with projected growth in areas like HVAC technicians. New entrants would face substantial hurdles in attracting and training a qualified workforce to match the established expertise of companies like F.W. Webb. This difficulty in acquiring necessary talent directly impacts their ability to compete effectively on service and product knowledge.
- Skilled Workforce Requirement: Technical wholesale distribution demands deep product and industry understanding.
- Labor Shortage Impact: Persistent gaps in skilled trades make recruitment difficult for new entrants.
- Competitive Disadvantage: New companies struggle to match the expertise of established players.
The threat of new entrants in the wholesale distribution of plumbing, HVAC, and industrial PVF is significantly low due to substantial capital requirements for inventory, warehousing, and logistics. F.W. Webb's extensive network of over 100 locations across nine states exemplifies the scale of investment needed, making it difficult for newcomers to match this infrastructure. Furthermore, established customer loyalty and deep supplier relationships, built over decades, present a formidable challenge for new players seeking to gain market traction. The ability of large distributors to achieve economies of scale in purchasing and operations also creates a cost advantage that new entrants struggle to overcome, impacting their ability to compete on price.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in inventory, warehousing, and logistics. | Significant financial hurdle, limiting entry for undercapitalized firms. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Established trust with suppliers and customers. | Difficult and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume purchasing and operations. | New entrants face higher costs, making price competition challenging. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex environmental and safety standards. | Requires specialized expertise and investment, deterring new entrants. |
| Skilled Workforce | Need for specialized product knowledge and industry experience. | Labor shortages and training costs create a competitive disadvantage for new entrants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for F.W. Webb leverages data from industry-specific trade publications, company financial reports, and market research databases. We also incorporate insights from competitor websites and public announcements to understand the competitive landscape.
