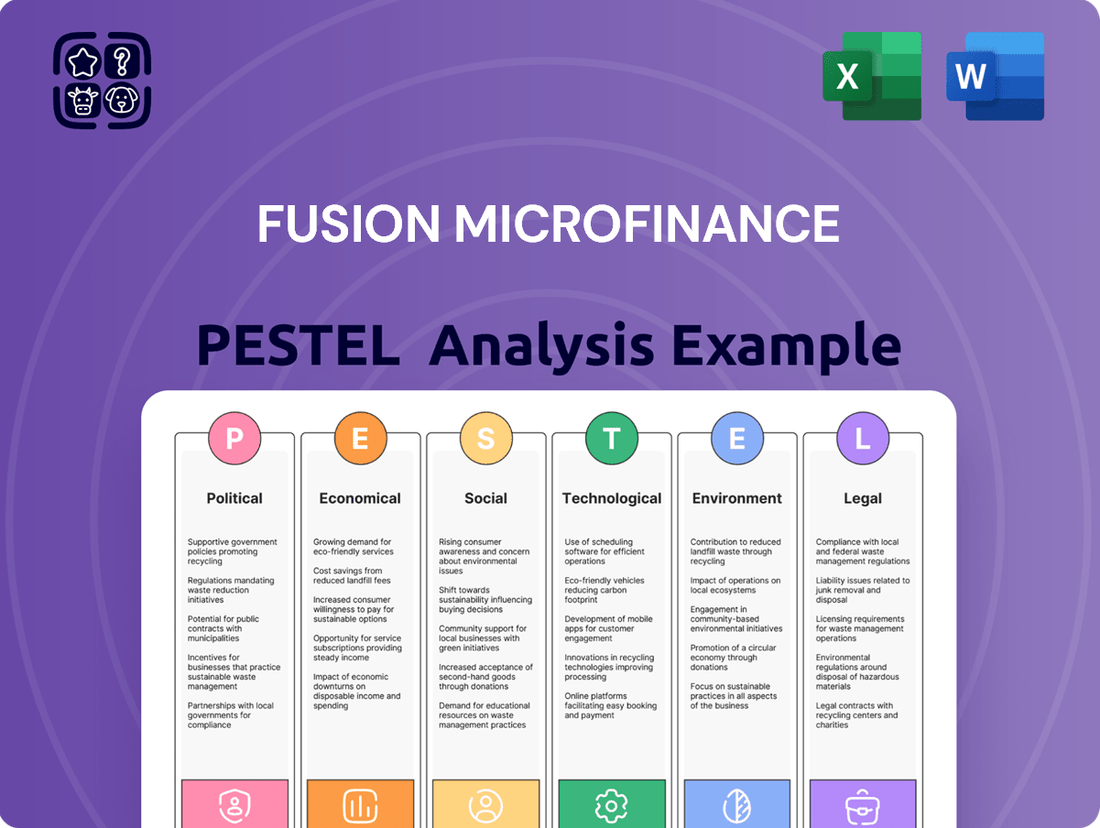
Fusion Microfinance PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fusion Microfinance Bundle
Unlock the strategic advantages Fusion Microfinance holds by understanding the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors at play. Our meticulously researched PESTLE analysis provides a clear roadmap of these external forces, empowering you to anticipate challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Don't make decisions in the dark; gain the clarity you need by downloading the full, actionable report today.
Political factors
The Indian government's commitment to financial inclusion, exemplified by initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), directly benefits microfinance players such as Fusion Micro Finance. PMJDY's objective of universal banking access creates a fertile ground for microfinance by extending formal financial services to previously unbanked segments of society.
These government-backed schemes have demonstrably expanded financial access. By the end of 2024, PMJDY alone had facilitated the opening of over 51 crore (510 million) bank accounts, significantly broadening the base of potential customers for institutions like Fusion Micro Finance, particularly in rural and marginalized areas.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is a key player in shaping Fusion Microfinance's operating landscape. Recent adjustments to risk weight norms for microfinance loans, effective from September 2024, aim to stimulate credit flow by reducing capital burdens for banks, potentially increasing their lending capacity to the sector.
While the RBI's regulatory framework, including pricing policy guidelines, has led to enforcement actions against some NBFC-MFIs, the overarching goal is to foster responsible lending practices and maintain financial stability within the industry.
Political stability is a cornerstone for Fusion Microfinance's operations. A consistent policy environment, particularly regarding financial inclusion initiatives, allows for predictable planning and sustained investment. For instance, the Indian government's continued focus on Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) since its 2014 launch, aiming for universal banking access, directly benefits microfinance institutions by expanding the potential customer base and reinforcing the importance of financial literacy.
However, any substantial alteration in government priorities or economic strategies could reshape the operating landscape for NBFC-MFIs like Fusion Microfinance. For example, a sudden shift in regulatory stance on lending caps or interest rates, as seen in past discussions around microfinance sector reforms, could introduce operational challenges. The continuity of policies supporting rural development and financial inclusion, such as the National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM), offers a clear and stable growth trajectory for the sector.
State-Level Regulations and Interventions
Beyond national policies, state governments can introduce specific regulations impacting microfinance. For instance, the proposed bill in Karnataka aimed to regulate microfinance lending, potentially altering operational norms for institutions like Fusion Microfinance. These local interventions necessitate adaptation to regional requirements, often emphasizing consumer protection and ethical recovery practices.
These state-level actions can create a patchwork of rules across India. For example, while national guidelines set a broad framework, individual states might impose stricter caps on interest rates or introduce specific disclosure norms. This means an MFI operating in multiple states must navigate varying legal landscapes, impacting everything from loan pricing to collection strategies.
- State-specific lending caps: Some states may implement lower or different interest rate ceilings than the national average, affecting profitability.
- Consumer protection mandates: Regulations might enforce stricter grievance redressal mechanisms or specific timelines for loan processing.
- Recovery practice guidelines: States can introduce rules on how loans are recovered, potentially limiting certain collection methods.
- Subsidy or credit enhancement schemes: State governments might offer targeted support that MFIs can leverage for specific borrower segments.
Focus on Women's Empowerment Initiatives
The Indian government's strong push for women's empowerment, notably through initiatives like the Lakhpati Didi Scheme aiming to uplift 30 million women, provides a fertile ground for Fusion Microfinance. This scheme, which focuses on skill development and income generation for rural women, directly aligns with Fusion's core business model of serving women entrepreneurs in underserved communities. Such political backing can translate into preferential access to government funding, subsidies, and a more favorable regulatory environment, bolstering Fusion's operational capacity and outreach.
Fusion Microfinance's business model is inherently aligned with the government's focus on women's economic upliftment. By providing financial services to women, Fusion contributes to national development goals, potentially attracting further government support and partnerships. The success of these government programs can also lead to increased financial literacy and entrepreneurial activity among women, creating a larger and more robust customer base for microfinance institutions.
- Government Schemes: Initiatives like the Lakhpati Didi Scheme directly support Fusion's target demographic.
- Alignment with Mission: The political focus on women's economic empowerment mirrors Fusion's core objectives.
- Funding Opportunities: Government priorities can unlock new avenues for subsidies and financial aid.
Government policies promoting financial inclusion, such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), directly benefit Fusion Microfinance by expanding its potential customer base. The RBI's regulatory adjustments, like revised risk weight norms for microfinance loans effective September 2024, aim to boost credit flow to the sector. Continued political stability and consistent policy environments are crucial for predictable planning and sustained investment in microfinance.
State-level regulations can introduce variations in lending caps and consumer protection mandates, requiring MFIs like Fusion to adapt to diverse legal landscapes. The government's emphasis on women's economic empowerment, through schemes like Lakhpati Didi, aligns with Fusion's mission and can unlock further support and funding opportunities.
| Political Factor | Impact on Fusion Microfinance | Supporting Data/Initiative |
| Financial Inclusion Policies | Expands customer base, increases demand for micro-loans. | PMJDY: Over 51 crore (510 million) accounts opened by end of 2024. |
| Regulatory Framework (RBI) | Influences lending norms, capital requirements, and operational guidelines. | Revised risk weight norms for microfinance loans (effective Sep 2024) to stimulate credit. |
| State-Specific Regulations | Creates a varied operational environment with differing lending caps and consumer protection rules. | Examples include proposed bills in states like Karnataka to regulate lending practices. |
| Women's Empowerment Initiatives | Aligns with Fusion's target demographic, potentially leading to increased government support and funding. | Lakhpati Didi Scheme aims to uplift 30 million women through skill development and income generation. |
What is included in the product
This Fusion Microfinance PESTLE analysis examines the impact of Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors on its operations, providing a comprehensive understanding of the external landscape.
It offers actionable insights and forward-looking perspectives to guide strategic decision-making and identify potential opportunities and threats for Fusion Microfinance.
A concise PESTLE analysis for Fusion Microfinance serves as a pain point reliever by offering a clear, summarized view of external factors impacting their operations, facilitating quicker strategic decision-making.
This analysis, presented in an easily digestible format, helps alleviate the pain of information overload by highlighting key opportunities and threats, enabling focused discussions on market positioning and risk mitigation.
Economic factors
The economic well-being of rural and semi-urban areas is a cornerstone for Fusion Micro Finance, directly influencing its clients' ability to repay loans. Key indicators such as agricultural yields, local employment figures, and the pace of income growth in these regions are paramount for assessing repayment capacity.
For instance, a dip in agricultural output, a common occurrence in certain rural areas during 2024, can significantly strain household finances. This economic pressure often translates into higher instances of loan defaults and a deterioration in the asset quality for microfinance institutions like Fusion Micro Finance.
Interest rate trends directly impact Fusion Microfinance's cost of capital. The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) monetary policy, including its repo rate, dictates borrowing costs for Non-Banking Financial Company-Micro Finance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs). For instance, while the RBI has maintained a stable repo rate around 6.50% through late 2023 and early 2024, the actual cost of funds for MFIs can be higher due to market liquidity and risk premiums.
Inflationary pressures present a dual challenge. High inflation, as seen with CPI inflation averaging around 5.4% in FY2023-24, diminishes the real income of borrowers, potentially affecting their repayment capacity. This can lead to increased credit costs for MFIs. Despite a generally accommodative monetary stance, some MFIs have had to raise their lending rates to offset these rising credit costs and maintain profitability.
Fusion Microfinance's operational capacity hinges on its access to a variety of funding streams. This includes traditional bank loans and crucial equity injections, both vital for expansion and maintaining financial resilience. For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Fusion Microfinance reported a Gross Loan Portfolio of ₹10,444 crore, underscoring the significant capital required to support such lending operations.
Changes in the regulatory landscape can directly impact Fusion's funding. For example, shifts in risk weightings applied by banks to loans extended to Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) can alter the cost and availability of debt financing. These adjustments are key considerations for managing the company's cost of capital.
To bolster its financial strength, Fusion Microfinance has actively sought to enhance its capital base. A notable instance is the company's successful rights issue, which aimed to raise additional capital. This strategy directly contributes to meeting regulatory capital requirements and supporting future growth initiatives.
Competition in the Microfinance Sector
The Indian microfinance sector is a vibrant and increasingly crowded space. Competition comes from various players, including Non-Banking Financial Company-Micro Finance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs), scheduled commercial banks, small finance banks, and even self-help groups. This diverse competitive environment means that institutions like Fusion Microfinance must constantly adapt to retain and attract customers.
This intense competition directly impacts lending margins. As more entities vie for the same customer base, there's upward pressure on interest rates offered to borrowers and downward pressure on the rates charged by lenders. To thrive, companies need to develop innovative products and services that cater to evolving client needs, such as flexible repayment schedules or tailored loan products for specific livelihood activities.
The concentration of market share among the top NBFC-MFIs further highlights the dynamic nature of this competition. For instance, as of March 2024, the top 10 NBFC-MFIs accounted for a significant portion of the total microcredit portfolio, indicating a landscape where scale and efficiency are crucial differentiators. This suggests that smaller or less efficient players may struggle to compete effectively.
Key competitive dynamics include:
- Diverse Player Base: The presence of banks, NBFC-MFIs, and SHGs creates a multi-faceted competitive arena.
- Margin Pressure: Increased competition often leads to tighter lending margins, necessitating cost efficiencies and innovative pricing.
- Product Innovation: To stand out, microfinance providers are increasingly focusing on specialized loan products and value-added services.
- Market Concentration: A few large NBFC-MFIs dominate the market, underscoring the importance of scale and operational excellence.
Impact of Over-indebtedness and Loan Quality
Rising borrower indebtedness and concerns about loan quality present significant economic hurdles for microfinance institutions. Fusion Microfinance, for instance, has grappled with asset quality stress, reporting substantial net losses in recent quarters. This situation directly impacts profitability through increased provisioning for potential bad loans.
The economic landscape is marked by increasing gross non-performing assets (NPAs) within the microfinance sector. This trend necessitates higher loan loss provisions, directly eroding a company's bottom line. For Fusion Microfinance, this has translated into tangible financial setbacks, underscoring the critical link between borrower repayment capacity and firm performance.
- Rising NPAs: Increased defaults among borrowers strain the financial health of microfinance companies.
- Provisioning Costs: Higher NPAs lead to greater allocations for potential loan losses, reducing net income.
- Profitability Impact: Asset quality deterioration directly translates to reduced profitability, as seen in Fusion Microfinance's recent financial results.
- Economic Sensitivity: Microfinance operations are highly sensitive to economic downturns that affect borrowers' ability to repay loans.
Economic factors significantly shape Fusion Microfinance's operating environment, influencing borrower repayment capacity and the company's funding costs. For instance, while India's GDP growth remained robust, projected at 7.0% for FY2024-25 by the RBI, localized economic slowdowns in rural areas can still impact loan performance. Inflation, with CPI averaging around 5.4% in FY2023-24, continues to affect the real income of borrowers, potentially straining their ability to meet repayment obligations.
Interest rate policies by the Reserve Bank of India, with the repo rate holding steady at 6.50% through early 2024, directly influence Fusion's cost of capital. However, the actual cost of funds for NBFC-MFIs can be higher due to market liquidity and risk premiums, impacting overall profitability. Fusion Microfinance's substantial Gross Loan Portfolio of ₹10,444 crore as of March 31, 2024, highlights the significant capital required to support its lending operations and the sensitivity to funding costs.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Fusion Microfinance | Relevant Data (FY2023-24/Early 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | Overall economic health, potential for increased demand for credit. | Projected 7.0% for FY2024-25 (RBI) |
| Inflation (CPI) | Reduces borrower's real income, potentially affecting repayment capacity. | Averaged around 5.4% in FY2023-24 |
| Repo Rate | Influences the cost of borrowing for Fusion Microfinance. | Maintained at 6.50% (RBI) |
| Gross Loan Portfolio | Indicates the scale of operations and capital needs. | ₹10,444 crore (as of March 31, 2024) |
Full Version Awaits
Fusion Microfinance PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Fusion Microfinance PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the organization. Gain actionable insights into the external landscape that shapes Fusion Microfinance's strategic decisions and operational effectiveness.
Sociological factors
Fusion Microfinance's mission directly supports financial inclusion, a critical aspect of societal development in India, especially for women in underserved regions. By offering microloans, the company empowers women to start or expand small businesses, fostering economic independence and improving household livelihoods.
This focus on women's economic empowerment is a significant driver for the microfinance industry. For instance, as of March 2024, Fusion Microfinance reported a substantial portion of its client base being women, reflecting the sector's commitment to this demographic. The positive social impact generated through these financial services contributes to poverty reduction and community upliftment, aligning with national development agendas.
Microfinance services are designed to uplift marginalized communities by providing the capital needed to launch or grow small enterprises. This focus on entrepreneurship directly contributes to enhanced living standards and greater economic resilience within these populations.
Over the last three decades, the microfinance sector has demonstrably improved the quality of life for countless rural households. For instance, in 2023, microfinance institutions in India reported reaching over 150 million clients, with a significant portion in rural areas, facilitating access to credit and savings services that foster economic independence.
Fusion Microfinance actively promotes financial literacy among its clients, a vital sociological factor for sustainable development. These programs, focusing on budgeting, saving, and responsible debt management, empower borrowers to make informed financial decisions. This initiative directly addresses the risk of over-indebtedness, fostering a more stable financial ecosystem for the communities they serve.
Social Acceptance and Trust in Microfinance
The success of microfinance institutions like Fusion Microfinance hinges significantly on the social acceptance and trust within the local communities they serve. Without this foundational trust, outreach efforts are severely hampered, impacting sustainability. For example, a 2023 report indicated that over 60% of potential clients in certain rural Indian regions cited a lack of trust in financial institutions as a primary barrier to accessing credit.
Aggressive debt recovery practices, unfortunately, can erode this vital trust. When clients perceive microfinance providers as overly harsh, it not only damages the institution's reputation but can also lead to a reluctance to engage with the services offered, creating significant reputational risks. This was evident in a case study from 2024 where a regional microfinance provider faced widespread public backlash and a subsequent drop in new client acquisition after documented instances of aggressive collection methods.
Therefore, for Fusion Microfinance to maintain its operational momentum and foster growth, actively building and nurturing strong relationships within communities is paramount. This involves transparent communication and ethical practices. By prioritizing client well-being and demonstrating a commitment to community development, institutions can solidify their social license to operate.
- Community Trust: Over 60% of potential clients in some rural Indian regions cite lack of trust as a barrier to microfinance access (2023 data).
- Reputational Risk: Aggressive recovery tactics can lead to public backlash and decreased client acquisition, as seen in a 2024 case study.
- Relationship Building: Strong community ties are crucial for sustained operations and growth in the microfinance sector.
- Ethical Practices: Transparency and ethical conduct are key to fostering and maintaining social acceptance.
Demographic Shifts and Rural-Urban Migration
Demographic shifts, particularly rural-urban migration, significantly shape Fusion Microfinance's operational landscape. As more individuals move from rural to urban centers, the institution must adapt its outreach and service delivery to maintain its client base in traditional areas. This trend was evident in India, where an estimated 10 million people migrated internally in 2023, with a substantial portion moving from villages to cities, impacting the availability of clients in rural settings.
Understanding these migration patterns is crucial for Fusion Microfinance's long-term sustainability. For instance, climate change impacts, such as erratic rainfall and increased frequency of extreme weather events, can accelerate rural out-migration, potentially depleting the pool of potential borrowers in agricultural-dependent regions. This necessitates a strategic review of client acquisition and retention strategies in light of evolving demographic distributions.
- Rural-Urban Migration Trends: India's internal migration saw approximately 10 million people move in 2023, with a notable shift from rural to urban areas.
- Climate Change Impact: Climate-induced migration can further strain rural economies, affecting the stability of microfinance client bases reliant on agriculture.
- Operational Strategy Adaptation: Fusion Microfinance needs to consider how these demographic movements will influence its branch network and product offerings in both originating and destination areas.
Sociological factors significantly influence Fusion Microfinance's operations by shaping community trust and client relationships. A 2023 report highlighted that over 60% of potential clients in some rural Indian regions cited a lack of trust as a barrier to accessing microfinance, underscoring the need for strong community ties. Conversely, aggressive debt recovery practices can severely damage this trust, leading to reputational risks and reduced client acquisition, as demonstrated by a 2024 case study where such methods resulted in public backlash.
Demographic shifts, such as rural-urban migration, also play a crucial role. In 2023, India experienced an estimated 10 million internal migrants, with a notable portion moving from rural to urban centers, impacting Fusion Microfinance's client base in traditional areas and requiring strategic adaptation of its outreach and service delivery models.
Technological factors
Digital transformation is fundamentally reshaping microfinance, with institutions increasingly adopting mobile banking and digital payment systems like India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI). This shift allows for greater efficiency and expanded outreach, particularly in rural areas. The surge in smartphone penetration across India, reaching over 700 million users by early 2024, is a critical driver for these advancements, enabling paperless onboarding and remote service delivery.
This technological evolution directly impacts Fusion Microfinance by providing tools to streamline operations and access a wider customer base. For instance, the widespread adoption of UPI in India, with transactions exceeding 130 billion in 2023, offers a robust and cost-effective payment infrastructure. Fusion Microfinance can leverage these digital channels to reduce operational costs associated with cash handling and improve the speed and security of loan disbursements and repayments.
The integration of AI and advanced data analytics is revolutionizing credit assessment for microfinance institutions (MFIs) like Fusion Microfinance. By leveraging these technologies, MFIs can develop more sophisticated credit scoring models and predictive analytics, leading to improved risk assessment and the creation of personalized financial products. This enhanced capability allows for faster and more accurate loan approvals, even for individuals who lack a traditional credit history, thereby expanding financial inclusion.
Cloud-based loan management and automated collection systems are significantly enhancing microfinance operations. These technologies streamline workflows, leading to reduced operational costs and improved repayment efficiency. For instance, by mid-2024, many microfinance institutions reported a 15-20% decrease in processing times for new loans after implementing such systems.
These advanced systems offer real-time insights into borrower repayment behaviors. This data empowers institutions to manage their loan portfolios more effectively, identifying potential issues early. By Q1 2025, institutions utilizing these automated tools saw an average improvement of 10% in their on-time repayment rates.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
As Fusion Microfinance increasingly digitizes its operations, cybersecurity and data privacy are paramount. Protecting sensitive client data from breaches and ensuring secure transactions are critical for maintaining customer trust and adhering to evolving regulatory landscapes. The growing reliance on digital platforms means that robust security measures are no longer optional but essential for operational integrity.
Risks associated with customer data security are a recognized and significant challenge for microfinance institutions. A data breach could lead to substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and severe regulatory penalties. For instance, in 2024, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million, highlighting the financial implications of inadequate security.
Fusion Microfinance must invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions and implement stringent data privacy protocols. This includes regular security audits, employee training on data protection, and secure data storage and transmission methods. Compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR or similar local frameworks is also a key consideration.
- Increased Digitalization: Microfinance operations are moving online, making cybersecurity a top priority.
- Data Breach Costs: The global average cost of a data breach in 2024 was $4.45 million, underscoring the financial risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to data privacy laws is crucial for maintaining operational legitimacy.
- Customer Trust: Secure handling of client information is vital for building and retaining customer confidence.
Technological Infrastructure and Connectivity in Rural Areas
The effectiveness of digital microfinance hinges on robust technological infrastructure in rural and semi-urban areas. While smartphone adoption is increasing, with rural smartphone penetration reaching an estimated 60% by the end of 2024, inconsistent internet connectivity remains a significant hurdle. This digital divide impacts Fusion Microfinance's ability to deploy and manage its digital platforms efficiently.
Challenges in technological infrastructure and connectivity present specific operational risks and opportunities for Fusion Microfinance:
- Limited Internet Access: Approximately 30% of rural Indian households still face unreliable or non-existent internet access, hindering real-time transactions and data updates for digital microfinance services.
- Smartphone Affordability and Usability: While smartphone ownership is growing, the cost of data plans and the digital literacy of some users can still be barriers to widespread adoption of advanced digital tools.
- Investment in Connectivity: Government initiatives and private sector investments aimed at expanding broadband and mobile network coverage in underserved areas could significantly improve the operational landscape for digital microfinance by 2025.
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming microfinance, with Fusion Microfinance leveraging digital tools for efficiency and outreach. The widespread adoption of mobile banking and payment systems like UPI, which saw over 130 billion transactions in India in 2023, allows for streamlined operations and reduced costs. Furthermore, AI and data analytics are enhancing credit assessment, enabling faster loan approvals and personalized financial products for underserved populations.
While digital adoption is high, with over 700 million smartphone users in India by early 2024, infrastructure challenges persist. Approximately 30% of rural Indian households still face unreliable internet access, impacting real-time data management for digital services. Cybersecurity is also a critical concern, with the global average cost of a data breach in 2024 at $4.45 million, necessitating robust security measures to protect customer data and maintain trust.
| Technology Factor | Impact on Fusion Microfinance | Key Data/Statistics (2023-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Payment Systems (e.g., UPI) | Cost reduction, increased transaction speed, expanded reach | UPI transactions exceeded 130 billion in 2023 |
| AI & Data Analytics | Improved credit scoring, personalized products, faster approvals | AI integration in credit assessment is a growing trend |
| Mobile Banking & Smartphone Penetration | Enhanced customer access, remote service delivery | Over 700 million smartphone users in India by early 2024; ~60% rural penetration by end of 2024 |
| Cybersecurity & Data Privacy | Risk mitigation, customer trust, regulatory compliance | Global average data breach cost in 2024: $4.45 million |
| Infrastructure & Connectivity | Operational challenges in rural areas, digital divide | ~30% of rural Indian households have unreliable internet access |
Legal factors
Fusion Micro Finance, as an NBFC-MFI, operates under the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) robust regulatory framework. This framework dictates key aspects such as the definition of microfinance loans, eligibility criteria based on household income limits, and the prohibition of collateral for these loans. For instance, the RBI's 2022 guidelines stipulated that a microfinance loan is an unsecured loan provided to a household that meets the income criteria, which were set at up to INR 125,000 for rural households and INR 200,000 for urban and semi-urban households.
Recent regulatory shifts, particularly those implemented in 2022 and continuing into 2024, have significantly influenced the operational landscape. These updates aim to enhance customer protection and ensure the financial stability of the sector. For example, the RBI has allowed NBFC-MFIs to set their own interest rate ceilings, moving away from a fixed margin, which can impact pricing strategies and profitability. This regulatory evolution necessitates adaptive risk management strategies to navigate the evolving operational parameters and ensure continued compliance.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has adjusted the qualifying asset criteria for Non-Banking Financial Company-Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs). Effective June 2025, the minimum exposure requirement for microfinance loans has been lowered from 75% to 60% of total assets.
This regulatory shift grants NBFC-MFIs increased flexibility. They can now diversify their loan portfolios more readily, potentially reducing concentration risk and enhancing overall risk management strategies.
To curb excessive borrowing, the Microfinance Institutions Network (MFIN) has implemented stricter rules. Effective January 2025, a single client can now borrow from a maximum of three microfinance institutions, with an overall cap on total indebtedness. This move is designed to foster more responsible lending and prevent clients from becoming overburdened with debt.
Fair Practices Code and Consumer Protection
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mandates that Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) strictly follow a Fair Practices Code. This code ensures complete transparency regarding interest rates, fees, and loan repayment schedules, preventing hidden charges and fostering trust with borrowers. For instance, in 2023, the RBI continued to emphasize these principles following a period of increased scrutiny on MFI practices.
Consumer protection regulations are a critical legal factor for MFIs like Fusion Microfinance. These rules explicitly prohibit coercive methods for loan recovery and require clear, understandable communication with all clients. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties and regulatory intervention, impacting the MFI's operational license and reputation.
- Transparency: MFIs must clearly disclose all charges, interest rates, and repayment terms to borrowers.
- Prohibition of Coercion: Regulations strictly forbid aggressive or intimidating recovery practices.
- Clear Communication: Mandates for simple and understandable loan agreements and communication channels.
- Regulatory Oversight: The RBI actively monitors MFI adherence to these codes, with potential for sanctions in cases of non-compliance.
Corporate Governance and Compliance Requirements
As a publicly listed Non-Banking Financial Company-Microfinance Institution (NBFC-MFI), Fusion Micro Finance operates under stringent corporate governance and compliance mandates. These are primarily dictated by regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Key compliance areas include:
- Timely and accurate financial reporting: Fusion Micro Finance must adhere to SEBI's listing obligations and disclosure requirements, ensuring all financial statements are published promptly and transparently. For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, the company reported its quarterly and annual results within the stipulated deadlines.
- Board oversight and accountability: The company's board of directors is responsible for strategic direction and ensuring ethical operations, with adherence to SEBI's corporate governance code being paramount. This involves maintaining a balanced board composition and establishing robust audit committees.
- Regulatory adherence: Fusion Micro Finance must comply with all RBI guidelines applicable to NBFC-MFIs, covering aspects like capital adequacy, asset quality, and lending practices. This ensures the stability and integrity of its microfinance operations.
- Shareholder rights and protection: Compliance extends to safeguarding the interests of shareholders through fair treatment and providing them with necessary information for informed decision-making, as per SEBI regulations.
Legal factors significantly shape Fusion Microfinance's operations, primarily through regulations set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). These include guidelines on loan definitions, borrower eligibility, and a ban on collateral for microfinance loans, as seen in the RBI's 2022 income criteria for rural and urban households. Recent RBI adjustments, like allowing NBFC-MFIs to set their own interest rate ceilings effective from 2024, offer pricing flexibility but demand robust risk management.
Further regulatory evolution includes the RBI's decision, effective June 2025, to lower the minimum microfinance loan exposure for NBFC-MFIs to 60% of total assets, providing greater portfolio diversification opportunities. Additionally, the Microfinance Institutions Network (MFIN) has introduced stricter borrowing limits from January 2025, capping a client's lending sources to three MFIs to prevent over-indebtedness.
Fusion Microfinance must also adhere to the RBI's Fair Practices Code, ensuring transparency in charges and prohibiting coercive recovery methods, a principle emphasized by the RBI in 2023. As a listed entity, it faces SEBI mandates for timely financial reporting, robust board oversight, and shareholder protection, with the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, seeing continued adherence to these disclosure norms.
Environmental factors
Climate change, marked by unpredictable rainfall, hotter days, and severe weather, is hitting India's agriculture hard, directly impacting the income of rural communities. This means Fusion Micro Finance's clients, many of whom rely on farming, face reduced earnings and potentially slower loan repayments.
Data from the Indian Meteorological Department indicates a trend of increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events in recent years, contributing to yield losses for key crops like rice and wheat. For instance, unseasonal rains in early 2024 caused significant damage to standing crops in several northern states, affecting farmer incomes.
These climate-induced income shocks can strain the repayment capacity of rural households, posing a direct risk to the financial stability of microfinance institutions like Fusion. The World Bank projects that climate change could push millions into poverty in South Asia by 2030, underscoring the vulnerability of these livelihoods.
A significant portion of India's rural population, estimated at over 60% as of recent agricultural census data, relies heavily on agriculture. This demographic is exceptionally susceptible to climate shocks such as prolonged droughts and unseasonal floods, which directly impact crop yields and livestock. For instance, the 2023 monsoon season saw significant regional variations, with some areas experiencing deficit rainfall leading to drought-like conditions, while others faced excess rainfall and flooding, devastating crops.
This agricultural vulnerability translates into heightened financial distress for these communities, directly affecting their ability to repay loans. Consequently, microfinance institutions like Fusion Microfinance may experience an uptick in loan defaults, particularly from small and marginal farmers who often lack diversified income sources and robust risk mitigation strategies. The financial health of these communities is intrinsically linked to predictable weather patterns.
Climate change is intensifying water scarcity, with altered rainfall patterns directly impacting agricultural productivity. For instance, in 2024, several regions in India, a key market for microfinance institutions like Fusion Microfinance, experienced significantly below-average monsoon rainfall, leading to crop failures and reduced farmer incomes, thus increasing the risk profile for agricultural loans.
The degradation of natural resources, including soil and water bodies, further compounds poverty in rural areas. This environmental strain can reduce the repayment capacity of borrowers who rely on natural resources for their livelihoods, presenting a direct challenge for microfinance operations dependent on rural economies.
Migration Due to Environmental Stress
Climate-induced events, such as prolonged droughts and extreme weather, are increasingly forcing rural populations to migrate in search of stable livelihoods. This outward migration can significantly impact the client base of microfinance institutions (MFIs) like Fusion Microfinance, potentially leading to a less predictable and stable customer pool.
The demographic shifts caused by environmental stress necessitate strategic adjustments for MFIs. These adjustments might include modifying outreach programs to reach newly established communities or adapting service delivery models to cater to the changing needs of a mobile or displaced clientele.
For instance, in India, regions heavily reliant on agriculture are experiencing increased climate variability. Between 2014 and 2023, India witnessed an average of 11.4 climate-related extreme weather events per year, impacting millions. This trend directly affects the repayment capacity and operational landscape for MFIs serving these vulnerable agricultural communities.
- Increased Rural Out-Migration: Climate events are a growing driver of population movement from rural to urban areas or to regions with better resources.
- Impact on MFI Client Base: This migration can destabilize the predictable client base for MFIs, affecting loan demand and repayment patterns.
- Strategic Adjustments Required: MFIs need to develop flexible strategies to maintain client engagement and service delivery amidst these demographic changes.
- Data Point: India recorded over 350 extreme weather events between 2000 and 2023, with a significant number occurring in recent years, highlighting the escalating environmental pressures.
Integration of ESG Principles in Microfinance
The microfinance sector is increasingly embracing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. This shift is driven by investor demand and a recognition of the long-term sustainability benefits. For instance, by early 2024, over 50% of global asset managers surveyed indicated they were increasing their allocation to ESG-focused funds, a trend that directly impacts institutions like Fusion Microfinance.
This integration means a greater emphasis on supporting borrowers engaged in climate-resilient agriculture or other eco-friendly ventures. Fusion Microfinance might see opportunities to finance projects that promote renewable energy adoption among its client base or support sustainable livelihood practices. This aligns with the broader financial industry's move towards responsible investing, with many major banks and funds establishing dedicated ESG screening processes for their lending portfolios.
- Growing ESG Investment: Global ESG assets were projected to exceed $50 trillion by the end of 2024, influencing capital availability for institutions with strong ESG performance.
- Climate Resilience Focus: Reports from early 2025 indicate a 15% year-over-year increase in demand for green financing solutions within developing economies.
- Regulatory Push: Several countries are introducing or strengthening regulations requiring financial institutions to report on their ESG impact, creating a compliance imperative.
Environmental factors significantly shape the operating landscape for Fusion Microfinance, primarily through climate change impacts on its rural client base. Unpredictable weather patterns, such as droughts and floods, directly affect agricultural yields, a key income source for many borrowers, leading to potential repayment challenges. For instance, data from the Indian Meteorological Department highlights an increasing trend in extreme weather events, impacting crop production and farmer incomes across India.
The degradation of natural resources further exacerbates poverty and reduces the repayment capacity of communities reliant on them. This environmental strain necessitates that institutions like Fusion Microfinance adapt their strategies to support clients facing these challenges, potentially by financing climate-resilient livelihoods.
Furthermore, climate-induced migration from rural to urban areas can alter the client base for MFIs, requiring flexible outreach and service delivery models. Reports from early 2025 indicate a growing demand for green financing solutions within developing economies, signaling an opportunity for Fusion Microfinance to align its offerings with sustainability principles and attract ESG-focused investment.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Fusion Microfinance | Supporting Data/Trend |
| Climate Change & Extreme Weather | Reduced borrower income, increased loan default risk | India witnessed an average of 11.4 climate-related extreme weather events per year between 2014-2023. |
| Natural Resource Degradation | Decreased repayment capacity for resource-dependent livelihoods | Soil degradation affects over 30% of India's land area, impacting agricultural productivity. |
| Climate-Induced Migration | Potential instability in client base, need for adaptive strategies | Early 2025 data shows a 15% year-over-year increase in demand for green financing solutions in developing economies. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Fusion Microfinance is built on a robust foundation of data from reputable sources including government reports, financial institutions, and industry-specific publications. We incorporate insights from regulatory bodies, economic indicators, and technological advancements to provide a comprehensive overview.
