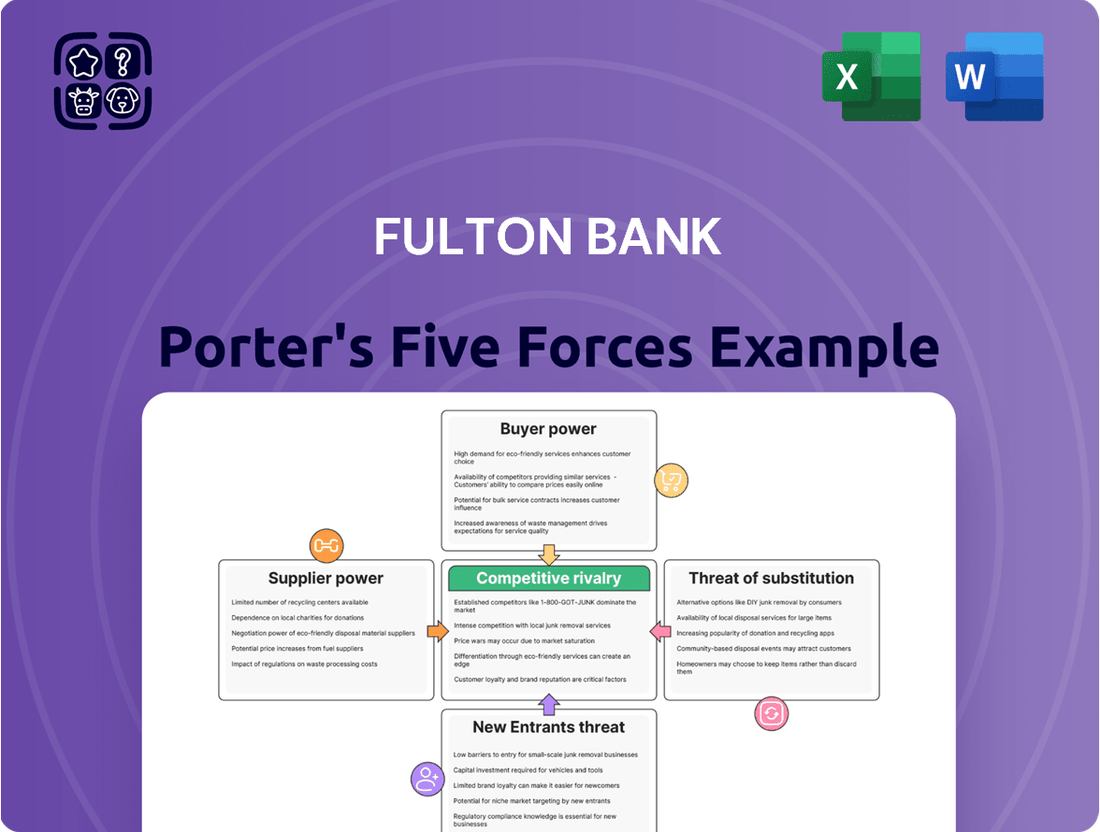
Fulton Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fulton Bank Bundle
Fulton Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing pressures from rivals and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of both its customers and suppliers is crucial for its strategic positioning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Fulton Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fulton Bank, like other financial institutions, depends on a range of suppliers for critical operations. These include technology vendors for core banking systems, cybersecurity solutions, and data analytics platforms, as well as providers of financial data and specialized professional services. The concentration of these suppliers significantly influences their leverage.
In 2024, the financial technology sector saw continued consolidation, with a few major players dominating the provision of cloud-based banking solutions and advanced analytics. For instance, the global banking software market, estimated to be worth billions, is characterized by the presence of several large, established firms. If these key technology providers or data service companies are highly concentrated, they can exert considerable bargaining power over Fulton Bank, potentially dictating pricing and service level agreements.
This concentration means Fulton Bank might face fewer alternatives when seeking essential services. A limited number of high-quality cybersecurity providers, for example, could command higher prices or impose stricter terms, directly impacting Fulton Bank's operational costs and its ability to negotiate favorable contracts for these vital inputs.
The ease or difficulty Fulton Bank faces when switching suppliers directly influences supplier power. For example, migrating core banking software is a significant undertaking. This involves complex data migration, intricate system integration, and extensive employee retraining, which can take months and cost millions. In 2024, the average cost for a mid-sized bank to switch core banking systems was estimated to be between $10 million and $50 million, underscoring the substantial switching costs.
The uniqueness of a supplier's offerings significantly impacts their bargaining power. If a supplier provides highly specialized or unique services that are critical to Fulton Bank's operations and cannot be easily replicated by other vendors, that supplier will possess greater leverage. This is especially relevant in areas like cutting-edge financial technologies or highly specialized consulting expertise, where alternatives are scarce.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While the banking sector typically sees less direct forward integration by suppliers compared to manufacturing, the potential for it exists, especially with specialized fintech providers. Imagine a major technology vendor that powers Fulton Bank's digital platforms deciding to launch its own direct-to-consumer banking services. This capability, even if not fully realized, grants them a degree of bargaining power.
This threat, though often low in traditional banking, can become more pronounced when dealing with critical technology and data service providers. For instance, a significant player in cloud computing or advanced data analytics, essential for modern banking operations, could leverage its position. As of early 2024, the fintech sector continues to grow, with significant investment flowing into companies specializing in AI-driven financial solutions and blockchain technology, increasing the potential for such integrations.
- Potential for Fintech Disruption: Specialized fintech firms providing core banking technologies could theoretically offer their services directly to consumers, bypassing traditional banks.
- Leverage for Key Tech Providers: Large technology and data analytics companies integral to a bank's operations hold leverage due to the critical nature of their services.
- Growing Fintech Investment: Significant venture capital funding in fintech in 2023 and early 2024 highlights the increasing capabilities and potential competitive threats from technology suppliers.
Importance of Fulton Bank to Suppliers
Fulton Bank's significance as a customer directly influences the bargaining power of its suppliers. If a supplier relies heavily on Fulton Bank for a substantial portion of its revenue, they are more likely to offer competitive pricing and favorable terms to secure and maintain that business. This dependence on Fulton Bank can significantly diminish the supplier's leverage.
For instance, consider a technology vendor providing core banking software. If Fulton Bank represents 30% of their annual sales, that vendor will likely be more accommodating during contract negotiations. This is a common dynamic in the financial services industry where large institutions can command better terms.
- Customer Dependence: Suppliers who derive a large percentage of their income from Fulton Bank have reduced bargaining power.
- Favorable Terms: This dependence incentivizes suppliers to offer better pricing and service to retain Fulton Bank's business.
- Industry Dynamics: In 2024, many specialized financial service providers cater to a limited number of large banks, amplifying this effect.
Suppliers to Fulton Bank, particularly in technology and data services, possess considerable bargaining power due to market concentration and high switching costs. In 2024, the fintech sector's consolidation means fewer providers for critical systems like core banking software. This scarcity, coupled with the millions of dollars and months required to switch vendors, gives these suppliers significant leverage over pricing and terms.
The uniqueness of offerings, such as advanced AI analytics or specialized cybersecurity solutions, further amplifies supplier power. While direct forward integration by suppliers is less common in banking, the potential exists with fintech firms, especially those receiving substantial investment as seen in 2023 and early 2024. Conversely, if Fulton Bank represents a large portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's power is diminished, leading to more favorable terms for the bank.
| Factor | Impact on Fulton Bank | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for dominant tech/data providers | Continued consolidation in fintech, few core system providers |
| Switching Costs | Limits alternatives, increases dependency | Millions of dollars and months for core banking system migration |
| Uniqueness of Offering | Stronger power for specialized services | High demand for AI analytics and advanced cybersecurity |
| Customer Dependence (Fulton Bank's share of supplier revenue) | Reduced supplier power if Fulton is a major client | Many specialized providers cater to a limited number of large banks |
What is included in the product
This analysis details the competitive forces impacting Fulton Bank, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry pressures, empowering proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fulton Bank's customer base is largely comprised of individual consumers and small to medium-sized businesses across the Mid-Atlantic region. This broad and fragmented customer base means that no single customer or small group of customers represents a substantial portion of the bank's overall revenue, which generally weakens customer bargaining power.
While most customers have limited individual leverage, Fulton Bank does serve larger corporate clients. These larger entities, due to the volume of their banking needs, may possess greater bargaining power, potentially influencing terms on services like treasury management or specialized lending.
Customer switching costs are a key factor in how much power customers have over Fulton Bank. If it's easy for customers to move their business to another bank, they have more leverage. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. saw a significant increase in digital banking adoption, with over 70% of consumers using mobile banking apps, making it simpler to manage accounts and potentially switch providers.
The growth of fintech and online banking platforms has dramatically reduced the effort involved in changing financial institutions. This ease of transition, often facilitated by streamlined account opening processes and digital transfer tools, empowers customers by giving them more options and reducing their reliance on any single bank.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Fulton Bank. In 2024, with interest rates fluctuating, consumers are keenly aware of the best deposit yields and loan rates. For instance, a difference of just 0.25% on a mortgage can translate to thousands of dollars over the loan's life, making customers highly attuned to pricing.
This sensitivity directly impacts Fulton Bank's bargaining power. If customers can easily switch between banks for better rates or lower fees, Fulton Bank faces pressure to maintain competitive pricing. This can limit the bank's ability to charge premium fees or command higher interest margins, especially when compared to institutions offering similar services at a lower cost.
Availability of Information to Customers
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, significantly boosting their bargaining power. Online comparison tools and readily available financial literacy resources empower individuals to thoroughly research banking products, interest rates, and fees. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of consumers actively used online platforms to compare banking services before making a decision, with many reporting that online reviews and rate comparisons heavily influenced their choices.
This transparency forces institutions like Fulton Bank to remain highly competitive. When customers can easily see which banks offer better terms or lower fees, they are more likely to switch, putting pressure on banks to offer attractive deals. This dynamic directly impacts pricing and service quality, as banks strive to retain and attract customers in an informed marketplace.
- Informed Consumer Base: The widespread availability of online financial comparison sites and educational content means customers are better equipped than ever to understand and evaluate banking offers.
- Increased Switching Propensity: Empowered by information, customers are more willing to switch providers to secure better rates or services, directly challenging customer loyalty.
- Competitive Pressure on Banks: This heightened customer awareness compels banks to offer more competitive pricing and superior service to maintain market share and profitability.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
For Fulton Bank, the threat of backward integration by customers is generally minimal. This would essentially mean customers creating their own banking institutions, a highly complex and regulated endeavor. However, very large corporations or consortiums might consider establishing in-house financial operations or specialized credit unions, which could indirectly influence pricing or service offerings from traditional banks.
While a full-scale bank creation is rare, some large entities do explore alternatives. For instance, large retailers or tech companies might develop their own payment systems or offer limited financial services, diverting some customer activity. In 2024, the trend of embedded finance, where financial services are integrated into non-financial platforms, saw continued growth, representing a form of customer-driven financial solutioning, though not direct backward integration into banking itself.
- Limited Direct Backward Integration: Customers starting their own banks is an extremely rare and impractical scenario for most.
- In-House Financial Solutions: Large corporations may develop internal treasury management or specialized credit facilities.
- Embedded Finance Growth: The rise of embedded finance in 2024 offers customers integrated financial tools, subtly impacting traditional banking relationships.
Fulton Bank's bargaining power with customers is moderate, influenced by an informed customer base and increasing ease of switching. While individual customers have limited power, larger corporate clients can negotiate better terms. The rise of fintech and digital banking in 2024, with over 70% of consumers using mobile banking, has lowered switching costs and increased customer price sensitivity.
| Factor | Impact on Fulton Bank | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low (fragmented base) | Individual customers represent a small portion of revenue. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate (decreasing due to digital) | Digital banking adoption >70% in 2023, simplifying account transfers. |
| Information Availability | High (empowers customers) | Consumers actively use online tools to compare rates and fees. |
| Price Sensitivity | High (especially for loans/deposits) | A 0.25% rate difference can significantly impact customer choice. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low (rare for banking) | Embedded finance growth in 2024 offers alternatives but not direct banking. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Fulton Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Fulton Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of industry competition, supplier and buyer power, threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitute products. You're looking at the actual document, ensuring you receive the exact, professionally crafted analysis the moment your purchase is complete, with no hidden surprises or placeholder content.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Fulton Bank operates in the Mid-Atlantic region, a landscape dotted with a varied competitive field. This includes formidable national players, other established regional banks, and a multitude of smaller community banks. The sheer number and the distribution of sizes among these competitors significantly shape the intensity of rivalry.
When many competitors are of similar size, the battle for market share tends to become more aggressive. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the U.S. banking industry had over 4,000 active commercial banks, with a significant portion of these operating regionally and competing directly with Fulton Bank's footprint. This density means Fulton Bank must constantly innovate and differentiate to maintain its position.
The banking sector, especially traditional community banking, often sees moderate growth. In 2024, the U.S. banking industry experienced a mixed growth environment, with some regions and segments showing resilience while others faced headwinds from higher interest rates and economic uncertainty. This moderate growth can lead to increased competitive rivalry as institutions vie for a larger slice of the existing customer base.
Fulton Bank offers a broad spectrum of financial services, from personal banking and mortgages to commercial lending and wealth management. The intensity of competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by how distinct these offerings are from those of its peers. For instance, a personalized approach to business lending or innovative digital banking features can set Fulton apart, potentially reducing direct price competition.
In 2024, the banking sector continues to see a trend towards commoditization in basic deposit and lending products, which naturally fuels price-based competition. However, banks that successfully differentiate through superior customer experience, specialized product development, or advanced technological solutions, like Fulton Bank aims to do, can mitigate this pressure. For example, in Q1 2024, Fulton Bank reported a 7% increase in its digital banking adoption rate, indicating a strategic focus on differentiating its service delivery.
Exit Barriers
Fulton Bank, like many financial institutions, faces significant exit barriers. These are the costs or difficulties a company encounters when trying to leave a market. For banks, these can include substantial investments in fixed assets like branches and technology infrastructure, which are hard to liquidate without significant loss.
Regulatory obligations also play a crucial role. Banks must adhere to strict capital requirements and consumer protection laws, making a swift exit complex and costly. Furthermore, long-standing customer relationships, built on trust and personalized service, create a sticky customer base that is difficult for competitors to dislodge, and for the bank itself to abandon easily.
These high exit barriers can trap even unprofitable banks in the market. This situation often results in market overcapacity, where there are more banks than the demand warrants. Consequently, this can fuel sustained price competition, as banks fight to retain market share rather than exiting, even at reduced profitability.
For instance, in 2024, the banking sector continued to grapple with the aftermath of interest rate hikes and evolving digital banking preferences. While some smaller or less efficient institutions might have considered consolidation or closure, the inherent costs and regulatory hurdles often kept them operational. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) reported in its Quarterly Banking Profile for Q1 2024 that while the number of problem banks remained low, the overall profitability for the industry was impacted by net interest margin compression for many. This environment underscores how difficult it is for even underperforming banks to simply shut down operations.
Key exit barriers for banks include:
- Significant Fixed Assets: Investment in physical branches, data centers, and IT systems represent substantial sunk costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent regulations regarding capital adequacy, liquidity, and consumer protection add complexity and cost to exiting the market.
- Customer Relationships: Long-term, established customer loyalty and the associated costs of acquiring new customers make it difficult to abandon existing relationships.
- Brand Reputation and Goodwill: The value placed on a bank's reputation can be a barrier to a disorderly exit that could damage its brand.
Acquisition and Consolidation Activity
The banking sector, particularly the regional segment, has experienced consistent merger and acquisition (M&A) activity. This consolidation trend can lead to a smaller competitor pool but simultaneously fosters larger, more powerful entities with enhanced market influence and expanded service portfolios. For instance, Fulton Bank’s acquisition of Republic First Bank in 2024 exemplifies this ongoing consolidation.
- Fulton Bank acquired Republic First Bank in April 2024.
- This acquisition added approximately $1.9 billion in assets and $1.5 billion in deposits to Fulton Bank.
- The deal was valued at $1.3 billion.
Fulton Bank faces intense rivalry from a broad spectrum of competitors, including large national banks, other regional players, and numerous community banks. This dense competitive landscape, with over 4,000 U.S. commercial banks in Q1 2024, forces Fulton to continually innovate and differentiate its offerings to capture market share. The banking sector's moderate growth in 2024 means that competition for existing customers is particularly fierce, often leading to price-based competition on basic products.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for traditional banks like Fulton Bank stems from fintech companies and their digital payment platforms. These innovators are steadily chipping away at market share by offering streamlined, often cheaper, alternatives for core banking functions.
Services like online lending, mobile wallets, personal finance management apps, and robo-advisors provide a compelling value proposition to consumers and businesses alike. For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at over $2.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift away from traditional payment methods.
These fintech solutions frequently boast enhanced convenience, lower transaction fees, and a more intuitive user experience, directly challenging the established banking model. As more consumers adopt these digital alternatives, the pressure on incumbent institutions to adapt and innovate intensifies.
Credit unions and a growing number of non-bank lenders present a significant threat of substitutes for Fulton Bank. Credit unions, operating as member-owned, not-for-profit entities, often provide competitive interest rates on loans and deposits, directly siphoning customers seeking better value. For instance, the credit union sector in the US held over $2.3 trillion in assets as of early 2024, demonstrating their substantial market presence.
Non-bank lenders, including fintech companies and specialized financing firms, offer alternative avenues for credit, particularly for small businesses and consumers who might find traditional bank requirements too stringent. These entities can be more agile in product development and underwriting, attracting borrowers who prioritize speed and flexibility. The alternative lending market saw significant growth in 2023, with transaction volumes in the billions, indicating a clear preference for these substitute options among certain customer segments.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms present a growing threat of substitution for traditional banking services like those offered by Fulton Bank. These platforms directly connect borrowers with lenders, often through online marketplaces, bypassing intermediaries. For instance, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $76.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $227.7 billion by 2030, indicating significant growth.
These alternative financing methods can offer competitive interest rates and faster approval processes compared to traditional bank loans, making them an attractive substitute for both individuals and small businesses seeking capital. Crowdfunding, in particular, allows businesses to raise funds from a large number of individuals, further diversifying funding sources away from banks.
In-house Corporate Finance Departments
Larger corporations often maintain robust in-house finance departments. These departments can handle a significant portion of their financial needs, including cash management, investment strategies, and even internal lending between subsidiaries. This capability directly reduces their reliance on external banking services for these functions.
For instance, in 2024, many large enterprises are leveraging advanced treasury management systems that integrate directly with their enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. This allows for sophisticated real-time cash flow forecasting and optimization, diminishing the need for banks to provide these core treasury services. Consequently, this presents a threat of substitution for Fulton Bank's commercial banking products.
- In-house treasury functions can manage liquidity and short-term investments, reducing the need for bank-provided treasury services.
- Internal corporate finance departments can facilitate intercompany loans, bypassing traditional commercial lending.
- Sophisticated treasury management systems are increasingly capable of handling complex financial operations, acting as a substitute for bank offerings.
- The trend towards **financial disintermediation** by large corporations directly impacts the demand for certain traditional banking services.
Cryptocurrencies and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
While still in early stages for widespread use, cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) present a growing threat of substitution for traditional banking services. These technologies offer alternative avenues for storing value, facilitating transactions, and engaging in financial investments, bypassing established institutions.
The potential for these digital assets to disrupt the financial landscape is significant. For instance, by mid-2024, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies had surpassed $2.5 trillion, indicating substantial capital flowing into these alternative systems.
DeFi platforms, in particular, are gaining traction by offering services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. The total value locked (TVL) in DeFi protocols reached over $100 billion in early 2024, demonstrating a clear shift towards decentralized financial solutions.
- Growing Market Capitalization: Cryptocurrencies' market cap exceeding $2.5 trillion by mid-2024 highlights significant user and investor adoption.
- DeFi's Total Value Locked (TVL): Over $100 billion in TVL in DeFi protocols by early 2024 signifies a substantial alternative to traditional financial services.
- Alternative Financial Services: DeFi platforms offer direct substitutes for banking functions like lending, borrowing, and asset management.
- Disruptive Potential: The increasing adoption and innovation in crypto and DeFi pose a long-term threat to incumbent financial institutions.
The threat of substitutes for Fulton Bank is substantial, primarily driven by the rise of fintech and digital alternatives. These digital platforms offer faster, cheaper, and more convenient services, directly competing with traditional banking functions.
Credit unions and non-bank lenders also present a significant challenge by offering competitive rates and more flexible terms, attracting customers seeking better value and accessibility. Furthermore, large corporations increasingly manage their financial needs internally, reducing their reliance on banks.
Emerging technologies like cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) are also developing as potential substitutes, offering alternative ways to manage assets and conduct transactions outside the traditional banking system.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | Market Indicator (2023/Early 2024 Data) | Impact on Banks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech & Digital Platforms | Digital Payments, Online Lending, Mobile Wallets, Robo-Advisors | Global Digital Payments Market: >$2.5 Trillion (2023) | Erosion of market share in core banking services |
| Credit Unions & Non-Bank Lenders | Competitive Deposit/Loan Rates, Agile Financing | US Credit Union Assets: >$2.3 Trillion (Early 2024) | Customer attrition, reduced lending volume |
| P2P Lending & Crowdfunding | Direct Borrower-Lender Connection, Alternative Capital Raising | Global P2P Lending Market: ~$76.2 Billion (2023) | Reduced demand for traditional loans and investment products |
| In-house Corporate Finance | Treasury Management, Intercompany Loans | Increased adoption of integrated ERP/Treasury Systems (2024) | Decreased demand for commercial banking and treasury services |
| Cryptocurrencies & DeFi | Alternative Asset Storage, Decentralized Financial Services | Crypto Market Cap: >$2.5 Trillion (Mid-2024), DeFi TVL: >$100 Billion (Early 2024) | Long-term potential disruption, shift in financial intermediation |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like Fulton Bank, faces substantial regulatory hurdles. Obtaining necessary licenses, adhering to complex compliance standards, and meeting significant capital requirements are all costly and time-consuming processes. These stringent rules effectively deter many potential new entrants, making it challenging for them to establish a foothold and compete with established players.
Starting a bank demands significant capital, often in the tens of millions, to satisfy stringent regulatory demands and build essential infrastructure. This high financial hurdle makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to enter the market and compete effectively.
For instance, Fulton Financial Corporation, a well-established player, boasts over $30 billion in assets as of early 2024, highlighting the scale of resources required to operate at a competitive level. Such substantial capital requirements act as a strong deterrent, limiting the threat of new entrants.
Existing institutions like Fulton Bank leverage significant economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs in areas like technology infrastructure, compliance, and marketing campaigns. For instance, in 2024, the average large U.S. bank reported a cost-to-efficiency ratio below 60%, a level difficult for a new entrant to match quickly.
New competitors face a steep challenge in replicating these operational efficiencies and cost advantages. Without substantial initial investment, they operate at a higher cost base, making it harder to compete on price or offer the same breadth of services as established players.
Furthermore, the experience curve plays a crucial role. Fulton Bank, with decades of operation, has refined its processes, risk management, and customer service protocols. This accumulated expertise translates into smoother operations and a deeper understanding of market dynamics, which new entrants lack.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
Fulton Bank benefits from its deep roots and established presence in the Mid-Atlantic region, cultivating strong brand loyalty and customer relationships. New competitors find it difficult to lure customers away from banks with a long-standing reputation and trusted connections.
Building that level of trust and attracting customers requires significant investment and time, making it a substantial barrier for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the average customer acquisition cost for a new bank account can range from $50 to $200, depending on the marketing channels used and the target demographic.
- Established Brand Recognition: Fulton Bank's long history translates to higher consumer trust and familiarity.
- Customer Retention: Existing strong relationships make it harder for new entrants to poach customers.
- High Customer Acquisition Costs: New banks must spend considerably to build a comparable customer base.
- Switching Costs: Customers often face minor inconveniences or potential fees when switching financial institutions.
Access to Distribution Channels
Traditional banks, like Fulton Bank, benefit from deeply entrenched distribution channels. Their extensive physical branch networks, combined with well-established digital banking platforms, provide a significant advantage in reaching and serving a broad customer base. For instance, as of Q1 2024, Fulton Bank reported over 200 branches across its operating footprint, facilitating easy customer access.
New entrants, particularly digital-only banks, face a considerable hurdle in replicating this reach. While they can sidestep the costs associated with physical branches, they must invest heavily in building robust digital distribution and sophisticated marketing strategies. This is crucial to effectively compete for market share against incumbent institutions that already possess strong customer relationships and brand recognition.
The challenge for new entrants is amplified by the high cost of customer acquisition in the digital space. Building trust and awareness to draw customers away from established players requires substantial marketing spend and innovative approaches to digital engagement. Without a compelling value proposition or seamless user experience, new entrants struggle to gain traction.
- Established Networks: Traditional banks leverage existing branch infrastructure and digital platforms, offering immediate customer access.
- Digital Entry Barriers: New digital banks must overcome significant marketing and customer acquisition costs to build comparable reach.
- Customer Loyalty: Entrenched competitors benefit from existing customer relationships and brand loyalty, making it harder for new entrants to gain market share.
The threat of new entrants for Fulton Bank is significantly mitigated by substantial barriers. High capital requirements, as evidenced by Fulton Financial Corporation's over $30 billion in assets in early 2024, make market entry prohibitively expensive for most. Regulatory compliance and licensing add further layers of difficulty and cost, demanding considerable time and financial resources that new players often lack.
Established players like Fulton Bank benefit from economies of scale, with average large U.S. banks reporting cost-to-efficiency ratios below 60% in 2024. This operational efficiency is difficult for newcomers to match, impacting their ability to compete on price. Furthermore, decades of experience and refined processes create an experience curve advantage that new entrants cannot quickly overcome.
Brand loyalty and customer relationships, cultivated over years, present another significant hurdle. The average customer acquisition cost for a new bank account in 2024 can range from $50 to $200, making it costly for new entrants to build a comparable customer base. Switching costs, though often minor, also contribute to customer retention for established institutions.
Fulton Bank's extensive distribution channels, including over 200 branches as of Q1 2024, provide a tangible advantage over digital-only entrants. While digital banks can avoid physical infrastructure costs, they must invest heavily in marketing and customer acquisition to achieve comparable reach and build trust in the competitive digital landscape.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Fulton Bank Advantage (Example Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Significant upfront investment needed for licenses, infrastructure, and regulatory compliance. | High barrier to entry. | $30+ billion in assets (early 2024). |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex compliance standards and licensing processes. | Time-consuming and costly to navigate. | Established compliance infrastructure. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high volume operations. | New entrants operate at a higher cost base. | Cost-to-efficiency ratio below 60% (average large U.S. bank, 2024). |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Established trust and customer relationships make switching difficult. | Challenging to attract and retain customers. | High customer retention rates. |
| Distribution Channels | Extensive branch networks and digital platforms. | New entrants struggle to match reach. | Over 200 branches (Q1 2024). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Fulton Bank is built upon a foundation of verified data, including the bank's annual reports, SEC filings, industry-specific research from financial analysts, and macroeconomic data from reputable sources to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
