1st Security Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
1st Security Bank Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape for 1st Security Bank is crucial for strategic planning. This analysis delves into the five key forces that shape its industry, revealing the underlying pressures and opportunities.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping 1st Security Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
1st Security Bank’s reliance on technology and software providers for essential functions like core banking systems and digital platforms grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. The growing sophistication of fintech and the critical need for advanced cybersecurity, particularly with the rise in data breaches, empower specialized tech vendors.
The trend of community banks adopting modern fintech solutions to boost efficiency and customer experience further solidifies supplier leverage; in fact, approximately 80% of community banks depend on fintech providers for their core systems, highlighting a significant dependency.
Suppliers of financial market data, economic forecasts, and credit rating services wield significant influence over banks like 1st Security Bank. These data providers offer essential inputs for risk management, investment strategies, and regulatory adherence. For instance, in 2024, the global financial data market was valued at over $30 billion, highlighting the scale and importance of these suppliers.
The proprietary nature and specialized content of many data services create high switching costs for financial institutions. Banks often integrate these data feeds deeply into their operational systems, making it costly and complex to change providers. This reliance on specific, often unique, data sets strengthens the bargaining power of these suppliers.
Regulatory compliance service providers wield considerable bargaining power over banks like 1st Security Bank, particularly as new regulations loom. With anticipated 2025 mandates focusing on cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and anti-money laundering (AML) efforts, banks face immense pressure to adapt. These specialized firms offer essential software, consulting, and auditing expertise, making them indispensable for navigating complex and evolving legal frameworks.
Human Capital (Skilled Employees)
The banking sector, including institutions like 1st Security Bank, relies heavily on a skilled workforce. Specialized areas such as wealth management, commercial lending, and the rapidly growing fields of technology and data analytics demand expertise. A scarcity of qualified individuals, especially in competitive regions like the Pacific Northwest, can significantly amplify the bargaining power of these skilled employees. This directly influences labor costs and the bank's ability to retain top talent.
This dynamic is evident as banks increasingly invest in talent development and upskilling programs. For instance, in 2024, many financial institutions reported increased spending on employee training to address skill gaps, particularly in digital banking and cybersecurity. This focus is crucial for meeting evolving customer expectations and maintaining a competitive edge.
- Talent Demand: The banking industry's need for specialized skills in areas like AI and machine learning is driving up demand for qualified professionals.
- Regional Competition: The Pacific Northwest's robust economy means 1st Security Bank faces competition for talent not just from other banks but also from tech companies.
- Upskilling Initiatives: Banks are prioritizing internal training and development to cultivate the necessary skills, aiming to mitigate reliance on external hiring and its associated costs.
- Labor Cost Impact: A tight labor market for skilled banking professionals can lead to higher salaries and benefits, directly impacting operational expenses for 1st Security Bank.
Infrastructure and Utility Providers
Infrastructure and utility providers, though often not the first suppliers considered, wield considerable bargaining power. For 1st Security Bank, with its focus on local branches across the Pacific Northwest, these providers are critical. Think of real estate lessors for branch locations and telecommunications companies for essential connectivity.
The bank's reliance on these services for its physical presence and day-to-day operations means that any significant price hikes or service disruptions from utility and infrastructure providers can directly affect its ability to serve customers. For instance, a substantial increase in commercial lease rates could pressure the bank's operating expenses, potentially impacting profitability or leading to branch consolidation.
In 2024, commercial real estate lease rates in major Pacific Northwest cities like Seattle and Portland have seen continued upward pressure due to demand. While specific figures for 1st Security Bank's leases aren't public, the broader market trend indicates a potential for increased supplier bargaining power in this sector. Similarly, telecommunications costs remain a significant operational expense for financial institutions.
- Real Estate Leases: The bank's physical branch network necessitates leasing commercial property, giving landlords bargaining power, especially in high-demand urban areas.
- Telecommunications Services: Reliable internet and phone services are crucial for banking operations, making telecom providers key suppliers with leverage.
- Utility Costs: Electricity, water, and other utilities are essential for branch operations, and their pricing can impact the bank's overhead.
The bargaining power of suppliers for 1st Security Bank is significant, particularly from technology providers, data services, and specialized regulatory compliance firms. The increasing reliance on advanced fintech solutions, the critical need for accurate financial data, and the complex regulatory landscape all empower these suppliers. In 2024, the global financial data market alone exceeded $30 billion, underscoring the immense value and influence of these essential service providers.
Furthermore, the bank's need for skilled talent, especially in emerging areas like AI and data analytics, gives employees considerable leverage, driving up labor costs. Even infrastructure providers like commercial lessors and telecommunication companies hold sway, particularly in competitive markets like the Pacific Northwest where lease rates and service costs can directly impact operational expenses.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependencies for 1st Security Bank | Factors Enhancing Bargaining Power (2024/2025 Outlook) | Impact on 1st Security Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers | Core banking systems, digital platforms, cybersecurity | Sophistication of fintech, rise in data breaches, need for advanced solutions | High switching costs, reliance on specialized vendors |
| Data & Research Services | Financial market data, economic forecasts, credit ratings | Global financial data market value >$30 billion (2024), proprietary content | Essential for risk management and strategy, costly to replace |
| Regulatory Compliance | Software, consulting for AML, AI, cybersecurity mandates | Anticipated 2025 mandates, complexity of evolving regulations | Indispensable for legal adherence, pressure to adopt new services |
| Skilled Labor | Wealth management, commercial lending, tech & data analytics talent | Scarcity of qualified professionals, regional competition (Pacific Northwest) | Increased labor costs, challenges in talent retention |
| Infrastructure & Utilities | Commercial real estate leases, telecommunications | Rising commercial lease rates in key cities, essential connectivity needs | Impact on operating expenses, potential for branch consolidation |
What is included in the product
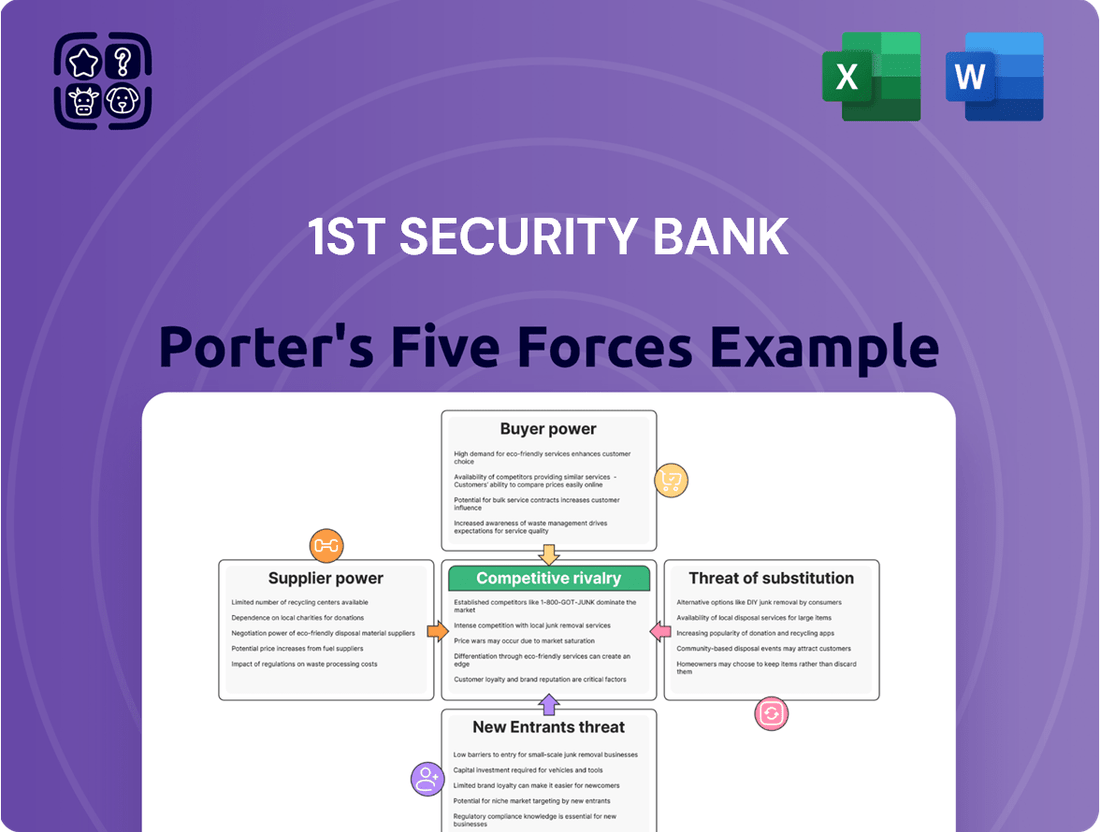
Tailored exclusively for 1st Security Bank, this analysis dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitutes within the banking sector.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, allowing 1st Security Bank to proactively adjust strategies.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual and small business deposit holders at banks like 1st Security Bank have a degree of bargaining power, particularly those with substantial balances or who use a range of banking products. The ease with which customers can move their accounts to a competitor offering better interest rates, reduced fees, or enhanced digital platforms fuels this power. For instance, in 2024, many community banks are investing heavily in digital account opening and related technologies, aiming to attract new customers and secure low-cost deposits in a competitive landscape.
Borrowers, especially those seeking significant commercial or real estate financing, frequently find themselves with a selection of banks and financial institutions. This ability to shop around for the best interest rates, loan terms, and overall service quality significantly bolsters their bargaining power. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage hovered around 6.7%, presenting a clear benchmark for comparison among lenders.
1st Security Bank actively works to counter this by emphasizing a relationship-driven approach and tailoring its services to local market demands. This strategy aims to foster loyalty and differentiate its value proposition beyond just pricing, thereby reducing the immediate leverage of loan applicants who might otherwise switch for a slightly better rate elsewhere.
Wealth management clients, especially high-net-worth individuals, wield significant bargaining power. Their substantial assets and the specialized nature of wealth management mean they can readily shift their business to competitors offering better returns, tailored advice, or more competitive fees. This forces firms like 1st Security Bank to constantly innovate and offer superior value.
Community and Relationship-Based Focus
1st Security Bank's commitment to community engagement and personalized service significantly dampens the bargaining power of individual customers. By focusing on building strong relationships and delivering exceptional experiences, the bank aims to cultivate loyalty that transcends mere price competition. This approach is underscored by their mission to consistently impress customers, fostering retention through value-added service rather than solely relying on competitive interest rates.
This customer-centric strategy can translate into tangible benefits for the bank:
- Enhanced Customer Retention: A strong community focus and personalized service can lead to higher customer retention rates, reducing the churn that often empowers customers to seek better deals elsewhere.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: When customers feel valued and connected to their bank, they may become less sensitive to minor price differences, diminishing their ability to bargain on rates alone.
- Positive Word-of-Mouth: Exceeding customer expectations, as suggested by their 'wow' mission, can generate positive word-of-mouth referrals, further strengthening the bank's market position and reducing reliance on attracting price-driven customers.
- Community Ties as a Differentiator: For the fiscal year ending December 31, 2023, 1st Security Bank reported a net interest margin of 3.25%, demonstrating a solid operational performance that allows for investment in relationship-building initiatives without compromising profitability.
Digital Sophistication and Open Banking
Customers are increasingly digitally sophisticated, readily comparing financial products and services across numerous providers. The rise of open banking further amplifies this, allowing easier access to and switching between financial institutions, including fintech innovators. This shift means banks must leverage advanced technologies like AI to enhance customer engagement and personalize offerings, as seen in the growing adoption of digital banking tools. For instance, a significant portion of retail banking transactions in 2024 occurred through digital channels, highlighting customer preference for convenient, accessible services.
- Digital Savvy: Customers are more informed and can easily compare offerings from various banks and fintechs.
- Open Banking Impact: Facilitates easier switching and access to diverse financial products, increasing customer leverage.
- AI-Driven Engagement: Banks are adopting AI to meet evolving customer expectations for personalized experiences and efficient service.
- Digital Transaction Growth: A substantial percentage of banking activities in 2024 were conducted digitally, underscoring customer reliance on these platforms.
Customers at banks like 1st Security Bank possess considerable bargaining power, especially those with large balances or who utilize multiple services. The ease of switching to competitors offering better rates or enhanced digital features fuels this leverage. For example, in 2024, many banks are focusing on digital onboarding to attract and retain low-cost deposits amidst fierce competition.
Borrowers, particularly for larger loans, can easily compare terms and interest rates across various institutions, significantly increasing their negotiating power. In Q1 2024, the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate was approximately 6.7%, serving as a key benchmark for borrowers.
1st Security Bank counters this by prioritizing relationship banking and tailoring services to local needs, aiming to build loyalty beyond just pricing. Wealthy clients, in particular, can shift substantial assets, compelling banks to continuously innovate their offerings and fee structures.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | 1st Security Bank's Counter-Strategy | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deposit Holders | Interest rates, fees, digital services | Relationship banking, personalized service | Digital account opening investment |
| Borrowers (Commercial/Real Estate) | Interest rates, loan terms, service quality | Tailored solutions, local market focus | Average 30-yr mortgage rate ~6.7% (Q1 2024) |
| Wealth Management Clients | Returns, advice quality, fees | Value-added services, innovation | High-net-worth individuals seek competitive advantages |
Same Document Delivered
1st Security Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for 1st Security Bank, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate usability. You can confidently expect this detailed report, covering all five forces, to be delivered instantly upon completion of your transaction.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Pacific Northwest, 1st Security Bank's core operating region, is home to substantial national and regional banks. These larger players possess extensive branch networks, significant marketing power, and a broad spectrum of financial products. For instance, in 2023, major national banks in the US reported average assets in the hundreds of billions, far exceeding community banks, allowing them to leverage economies of scale for competitive pricing and product innovation.
These financial giants can aggressively compete on both price and the sheer breadth of their offerings. Their ability to absorb costs and invest heavily in technology and customer acquisition means they can present a formidable challenge to smaller institutions like 1st Security Bank. This competitive pressure can impact market share and profitability for community banks that lack similar resources.
1st Security Bank faces intense competition from other community banks in the Pacific Northwest, all vying for local customers by emphasizing personalized service and community needs. This rivalry is particularly sharp for local deposits and loan opportunities.
While larger national banks pose a threat, the direct competition among community banks is a significant factor. These institutions are actively working to enhance their core profitability, a key challenge in today's market. For instance, many community banks are focusing on strategies to manage expenses effectively and secure low-cost deposits, which are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
In 2024, community banks are particularly focused on improving their net interest margins. As of the first quarter of 2024, the average net interest margin for community banks hovered around 3.2%, a figure that underscores the pressure to manage deposit costs and loan pricing effectively amidst this localized competition.
Fintech and digital-first challengers are significantly intensifying competition within the banking sector. Companies like Chime and Revolut, for instance, are attracting customers with innovative digital platforms, often offering more competitive interest rates and user-friendly interfaces than traditional banks. This trend is particularly evident as neobanks continue to grow their customer bases; Chime reported over 14 million users by early 2024, showcasing their disruptive potential.
These non-traditional players leverage advanced technology to provide seamless digital experiences, which can draw customers away from established institutions. For example, many fintechs excel at offering specialized services, such as faster payment processing or integrated budgeting tools, that traditional banks are still developing. This forces incumbents like 1st Security Bank to adapt rapidly.
To remain competitive, traditional banks are increasingly investing in AI and automation. These technologies are crucial for enhancing operational efficiencies, improving customer service, and developing new digital products. By streamlining processes and personalizing offerings, banks aim to match the agility and customer-centricity of their fintech rivals.
Interest Rate Environment
The prevailing interest rate environment is a critical driver of competitive rivalry among banks like 1st Security Bank. As of mid-2024, the Federal Reserve maintained a hawkish stance, with interest rates hovering at elevated levels, impacting net interest margins. This dynamic fuels intense competition for customer deposits, as individuals and businesses actively seek higher yields, often migrating funds to institutions offering more attractive rates.
This economic uncertainty, characterized by fluctuating rates, is compelling financial institutions to invest heavily in digital account opening and related technologies. The ability to offer a seamless, efficient digital onboarding experience becomes a key differentiator in attracting and retaining customers in a competitive landscape. Banks are prioritizing these technological advancements to capture market share and mitigate the impact of rate sensitivity.
- Interest Rate Impact: Elevated interest rates in 2024 pressure banks' net interest margins, intensifying competition for deposits.
- Customer Behavior: Customers are actively seeking higher yields, leading to deposit migration and a focus on competitive deposit rates.
- Digitalization Push: Economic uncertainty and rate sensitivity are accelerating investment in digital account opening and customer acquisition technologies.
- Competitive Advantage: Banks offering superior digital experiences are better positioned to attract and retain customers in this environment.
Product and Service Differentiation
1st Security Bank's competitive rivalry is significantly influenced by its product and service differentiation. The bank offers a wide spectrum of financial solutions, encompassing personal and business deposit accounts, diverse loan products, and wealth management services. This comprehensive offering allows them to cater to a broad customer base.
The bank emphasizes a relationship-based banking approach, fostering strong connections with its customers. This strategy, coupled with active community involvement, creates a unique value proposition. It aims to stand out from competitors that might focus more on sheer transaction volume rather than personalized client interactions.
- Product Breadth: Offering personal and business deposit accounts, various loan types, and wealth management.
- Service Focus: Prioritizing relationship-based banking and personalized customer service.
- Community Engagement: Leveraging local involvement to build a distinct brand identity.
- Value Proposition: Differentiating through personalized service over high transaction volume.
The competitive rivalry for 1st Security Bank is multifaceted, involving large national banks, other community banks, and increasingly, fintech challengers. National banks leverage scale and broad product offerings, while community banks compete on personalized service and local ties. Fintechs disrupt with digital-first, often rate-competitive solutions.
In 2024, the banking landscape continues to see intense competition, particularly driven by interest rate dynamics and the ongoing digital transformation. Community banks, like 1st Security Bank, are focused on managing net interest margins, which averaged around 3.2% in early 2024, and on retaining customers in a market where deposit migration is common.
The push for digital account opening and enhanced customer experiences is a key battleground, with fintechs like Chime, boasting over 14 million users by early 2024, setting a high bar. This forces traditional banks to invest in technology to maintain relevance and attract new clientele.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on 1st Security Bank | 2024 Focus for Banks |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Banks | Economies of scale, broad product range, large marketing budgets | Pressure on pricing, market share erosion for smaller players | Leveraging technology for efficiency and customer acquisition |
| Community Banks | Personalized service, local relationships, community focus | Intense competition for local deposits and loans | Improving net interest margins, managing deposit costs |
| Fintechs | Digital-first platforms, competitive rates, user experience | Customer acquisition through innovative digital offerings | Investing in digital capabilities, AI, and automation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Credit unions represent a notable threat of substitutes for 1st Security Bank, especially within its core operating regions like the Pacific Northwest. These member-owned institutions provide a full spectrum of banking services, mirroring those offered by 1st Security Bank, including deposit accounts and various loan products. Their community-centric approach and focus on member benefits can resonate strongly with consumers, presenting a direct alternative for banking needs.
The non-profit structure of credit unions often allows them to offer more attractive pricing, such as higher interest rates on savings or lower fees on checking accounts, compared to traditional banks. For instance, as of early 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts at credit unions often outpaced that of larger, for-profit banks, making them a compelling substitute for cost-conscious consumers. This competitive pricing directly challenges 1st Security Bank’s ability to attract and retain deposit customers.
Online-only banks and neobanks present a significant threat of substitution for traditional institutions like 1st Security Bank. These digital-first players offer a comprehensive suite of banking services, from checking accounts to loans, all accessible through intuitive mobile apps and websites. Their lower overhead costs often translate into more competitive pricing and innovative features, appealing strongly to a growing segment of digitally-savvy consumers.
The convenience factor is a major draw; customers can manage their finances anytime, anywhere, without needing to visit a physical branch. This shift in consumer preference means that for many, the need for a brick-and-mortar presence is diminishing. For instance, by the end of 2023, neobanks globally had amassed over 250 million customers, demonstrating their rapid adoption and ability to capture market share from incumbents.
Furthermore, the integration of generative AI is poised to enhance the efficiency and service offerings of these digital competitors. AI can power personalized customer support, streamline application processes, and even offer sophisticated financial advice, further eroding the traditional advantages of established banks. This technological edge allows neobanks to adapt quickly to market demands and customer expectations.
Fintech companies offering specialized financial services present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like 1st Security Bank. These firms, such as online lenders focusing on specific loan types or payment platforms like PayPal and Venmo, allow customers to bypass traditional banking for individual needs. This disaggregation means customers can cherry-pick services, weakening the all-in-one value proposition of a full-service bank.
Investment Firms and Brokerages
For wealth management and investment services, traditional investment firms, online brokerages, and robo-advisors present significant substitutes to a bank's offerings. These alternatives provide a wide array of investment products and advisory services, drawing in clients who might otherwise engage with a bank's wealth management division. The competitive landscape is further intensified by the growing investment in digital platforms and AI integration within the wealth management sector.
The threat of substitutes is particularly potent given the accessibility and evolving features of these alternative platforms. For instance, the global robo-advisor market was valued at approximately $2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong customer preference for digital-first investment solutions. This growth suggests that banks must innovate to retain clients.
- Online Brokerages: Platforms like Charles Schwab and Fidelity offer extensive research tools and a broad selection of investment options, directly competing for retail investors.
- Robo-Advisors: Companies such as Betterment and Wealthfront provide automated, algorithm-driven investment management at lower costs, appealing to tech-savvy and cost-conscious consumers.
- Traditional Investment Firms: Established players like Merrill Lynch and Morgan Stanley continue to attract high-net-worth individuals with personalized financial planning and advisory services.
- Digital Wealth Management: The increasing integration of AI and personalized digital experiences by these substitutes forces traditional banks to enhance their own digital capabilities to remain competitive.
Alternative Lending Platforms
Alternative lending platforms, such as peer-to-peer (P2P) lenders and other non-bank financial institutions, pose a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like 1st Security Bank. These platforms often offer more streamlined application processes and quicker funding times, appealing to borrowers seeking speed and convenience. For instance, in 2023, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $56.4 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, highlighting the increasing adoption of these alternatives.
These fintech disruptors frequently target specific market segments or offer specialized loan products that traditional banks might find less profitable or more complex to underwrite. This can divert loan origination volume away from 1st Security Bank, particularly from younger demographics or small businesses with unique funding needs. The ability of these platforms to leverage technology for lower operating costs also allows them to offer competitive interest rates, further intensifying the competitive pressure.
The impact on 1st Security Bank could manifest in reduced market share for certain loan types, such as personal loans or small business working capital. As of the first quarter of 2024, the non-bank mortgage origination share in the US was around 18%, demonstrating a tangible shift in lending channels. This trend underscores the need for 1st Security Bank to innovate and adapt its own lending processes to remain competitive against these agile alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for 1st Security Bank is substantial, encompassing credit unions, digital banks, and fintech companies. These alternatives offer comparable services, often with more competitive pricing or enhanced convenience, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Credit unions, with their member-focused approach and often lower fees, present a strong substitute, particularly for cost-sensitive consumers. Similarly, neobanks and online-only banks are rapidly gaining traction by leveraging technology for streamlined operations and superior user experiences, attracting a growing digitally-native customer base.
Fintech firms specializing in areas like lending, payments, and wealth management further fragment the market, allowing customers to bypass traditional banks for specific financial needs. This disaggregation, coupled with the increasing adoption of AI and digital platforms, necessitates continuous innovation from incumbent institutions like 1st Security Bank to maintain relevance and market share.
| Substitute Type | Key Offerings | Competitive Advantage | Market Trend (as of early 2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Unions | Deposit accounts, loans, community focus | Lower fees, higher savings rates, member benefits | Growing membership, often outperforming larger banks on customer satisfaction |
| Online-Only Banks/Neobanks | Checking, savings, loans, payments | Lower overhead, competitive pricing, user-friendly digital platforms | Rapid global customer acquisition, exceeding 250 million users by end of 2023 |
| Fintech (Lending, Payments, Wealth Management) | Specialized loans, digital payments, robo-advisory | Niche focus, speed, convenience, lower costs | P2P lending market valued at ~$56.4 billion in 2023; Robo-advisor market ~$2.1 billion in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces significant hurdles for newcomers due to extensive regulatory requirements. New entrants must meet substantial capital adequacy ratios, comply with stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, and secure multiple operating licenses, all of which demand considerable investment and expertise. For instance, in 2024, the Basel III endgame reforms continued to influence capital requirements, making it even more costly for potential new banks to establish themselves.
Establishing a new bank demands immense capital for everything from physical branches to advanced technology and initial operational expenses. For instance, 1st Security Bank operates 27 branches across Washington and Oregon, highlighting the scale required to be competitive.
Achieving a similar scale presents a formidable barrier for any newcomer aiming to challenge established institutions. The difficulty is underscored by the sharp decline in new bank charters, with an average of fewer than six new charters granted annually between 2010 and 2023, a significant drop following the 2008 financial crisis.
Building brand recognition and trust in banking is a long game. For instance, 1st Security Bank, with its deep roots and community ties, already has a solid foundation of customer loyalty and a reputation for dependability. Newcomers must overcome the significant hurdle of persuading customers to move their assets from institutions they already know and trust.
Technological Investment and Talent Acquisition
New entrants face substantial hurdles in technological investment and talent acquisition. To effectively compete, they must commit significant capital to developing robust digital banking platforms, advanced cybersecurity measures, and potentially artificial intelligence solutions. For instance, in 2024, the global fintech market saw continued heavy investment, with startups needing millions to build comparable infrastructure to established institutions.
Securing and retaining top-tier talent in the competitive banking and fintech sectors presents another major challenge. Banks are increasingly focusing their technology spending on efficiency drivers and sophisticated data analytics, making it difficult for new players to attract experienced professionals who are in high demand.
- New entrants require substantial investment in digital platforms and cybersecurity to match incumbents.
- Attracting and retaining skilled banking and fintech talent is a significant barrier.
- Banks are prioritizing efficiency and data analytics in their technology investments, raising the bar for new entrants.
Customer Acquisition Costs
Customer acquisition costs represent a significant barrier for new entrants in the banking sector. In a market as competitive as banking, attracting new customers, whether for deposits or loans, can be incredibly expensive. New banks often face the challenge of building brand recognition and trust from scratch, requiring substantial investment in marketing and advertising campaigns.
Established banks already possess a significant advantage due to their existing customer bases and well-developed marketing channels. These incumbents can leverage customer loyalty and existing relationships to retain business and attract new clients more cost-effectively. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to acquire a new checking account customer for many traditional banks hovered around $100 to $300, a figure that new entrants would need to match or exceed to gain market share.
To overcome this hurdle, new entrants must deploy highly innovative strategies and allocate considerable marketing budgets. This might involve offering attractive introductory rates, leveraging digital marketing and social media extensively, or partnering with other businesses to reach new customer segments. Without these efforts, new banks risk being outspent and outmaneuvered by established players with deeper pockets and existing customer loyalty.
- High Marketing Spend: New banks need significant investment to build brand awareness and attract customers in a crowded market.
- Established Customer Base: Incumbent banks benefit from existing relationships and loyalty, reducing their customer acquisition costs.
- Digital Strategy Importance: Innovative digital marketing and outreach are crucial for new entrants to compete effectively.
- Competitive Rates: Offering superior interest rates or fees can be a key differentiator for attracting initial customers.
The threat of new entrants for 1st Security Bank is moderate, primarily due to the high capital requirements and extensive regulatory landscape in banking. New players face significant upfront costs for licensing, technology, and compliance, which are substantial barriers to entry. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing implementation of stricter capital adequacy ratios under Basel III continued to make it more expensive for potential new banks to launch and operate.
The established brand loyalty and trust that 1st Security Bank enjoys, built over years of service, also present a considerable challenge for newcomers. Convincing customers to switch their banking relationships requires more than just competitive rates; it demands a proven track record and a strong reputation, which are difficult and time-consuming to build from scratch.
Furthermore, the need for significant investment in advanced technology, including robust digital platforms and cybersecurity, coupled with the challenge of attracting top-tier talent in a competitive market, further limits the ease with which new banks can emerge and compete effectively against established institutions like 1st Security Bank.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Relevance to 1st Security Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High; requires substantial initial investment. | Protects incumbents by increasing startup costs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | High; extensive licensing and adherence to AML/KYC. | Favors established banks with existing compliance infrastructure. |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Low for newcomers; takes time to build. | Strong asset for 1st Security Bank, making customer acquisition difficult for rivals. |
| Technological Investment | High; need for advanced digital platforms and cybersecurity. | Requires significant ongoing investment, a challenge for new entrants. |
| Talent Acquisition | Difficult; competition for skilled banking and fintech professionals. | Established banks can leverage existing talent pools and compensation packages. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for 1st Security Bank leverages data from their annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific research from IBISWorld and market intelligence from S&P Capital IQ.
