Fortive Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fortive Bundle
Fortive's competitive landscape is shaped by a complex interplay of forces, from the bargaining power of its customers to the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Fortive’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
A concentrated supplier base significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. If Fortive depends on a handful of providers for essential components or specialized software, those suppliers gain leverage. This is particularly true if the inputs are unique or proprietary, making it costly and disruptive for Fortive to find alternatives. For instance, in 2023, companies in the industrial automation sector, where Fortive operates, often faced supply chain constraints for advanced microchips, giving chip manufacturers considerable pricing power.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power for Fortive. If suppliers provide highly specialized or patented components, like those found in Fortive's advanced healthcare diagnostic equipment, their leverage grows. For instance, in 2024, companies relying on proprietary semiconductor designs for their core products often faced suppliers with substantial pricing power due to limited alternatives.
Fortive's suppliers can exert significant bargaining power if switching costs are high. These costs can involve substantial investments in retooling manufacturing lines, retraining employees on new systems, and rigorous re-qualification of components, all of which can be time-consuming and expensive. For instance, if a key supplier provides highly specialized components deeply integrated into Fortive's product designs, the effort and expense to find and implement an alternative could be prohibitive, thereby strengthening the supplier's hand.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Fortive's core business operations could significantly bolster their bargaining power. This scenario arises if a supplier develops unique capabilities that allow them to directly manufacture and sell products that compete with Fortive's existing offerings. For a diversified industrial technology firm like Fortive, this threat is generally lower, but it remains a critical factor to monitor, especially if a supplier gains a distinct technological advantage.
Consider the implications if a key component supplier, perhaps one providing specialized sensors or advanced software modules, were to develop a complete system that directly rivals a Fortive product. This would shift the supplier from a component provider to a direct competitor. For instance, if a supplier to Fortive's precision measurement segment were to launch a comparable, integrated measurement solution, their leverage over Fortive would dramatically increase.
While specific instances of forward integration by suppliers directly impacting Fortive are not widely publicized, the potential exists. For context, in the broader industrial technology sector, suppliers who possess proprietary technologies or significant intellectual property are more likely candidates for such a strategic move. This capability could allow them to capture more value by moving up the supply chain.
- Potential for Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers could leverage unique capabilities to enter Fortive's market, increasing their bargaining power.
- Impact on Fortive's Industry: This threat is less pronounced for diversified companies like Fortive but becomes relevant if a supplier develops a directly competing product.
- Supplier Leverage: A supplier moving into Fortive's space would gain significant leverage, potentially dictating terms or capturing market share.
Importance of Fortive to Supplier's Business
The significance of Fortive as a customer directly influences its suppliers' bargaining power. When Fortive constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier is more inclined to offer favorable terms and pricing to maintain the business relationship. For instance, if a key component supplier derives over 20% of its annual sales from Fortive, it would be highly motivated to accommodate Fortive's demands to secure that revenue stream.
Conversely, if Fortive represents a minor client for a large, diversified supplier, its individual leverage diminishes. A supplier generating the vast majority of its income from numerous other customers might be less accommodating to Fortive's specific requests, as losing Fortive's business would have a negligible impact on its overall financial performance. This asymmetry in customer reliance is a critical factor in supplier negotiations.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also shaped by the concentration of their customer base. If a supplier has a broad and diverse clientele, it is less dependent on any single customer like Fortive, thus increasing its ability to dictate terms. However, for suppliers heavily reliant on Fortive, their power is inherently constrained.
Fortive's suppliers hold considerable bargaining power when they provide unique or highly specialized inputs, as finding alternatives becomes difficult and costly. For example, in 2024, the scarcity of advanced semiconductors for industrial applications meant chip manufacturers could command higher prices from companies like Fortive, impacting their cost structures.
High switching costs, such as the need for extensive retooling or employee retraining, significantly empower Fortive's suppliers. If a supplier's components are deeply integrated into Fortive's product lines, the expense and time required to switch can make suppliers very influential. This was evident in 2023, where industries requiring custom-engineered parts faced suppliers with substantial leverage due to the prohibitive cost of sourcing elsewhere.
The bargaining power of Fortive's suppliers is also influenced by their own customer base concentration. If Fortive represents a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier is more likely to be accommodating. Conversely, if Fortive is a small client to a large supplier, the supplier's leverage increases, as demonstrated by suppliers in the electronics sector in 2024 who served a wide range of clients, reducing their dependence on any single buyer.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Relevance to Fortive (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High power if few suppliers exist. | Fortive faces this for specialized components. |
| Uniqueness of Input | High power if inputs are proprietary. | Crucial for Fortive's advanced technology segments. |
| Switching Costs | High power if changing suppliers is expensive/disruptive. | Significant for Fortive's integrated systems. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | High power if suppliers can compete directly. | A potential risk if suppliers gain technological edge. |
| Fortive's Importance to Supplier | Low power if Fortive is a major customer. | Fortive aims to be a key client for critical suppliers. |
What is included in the product
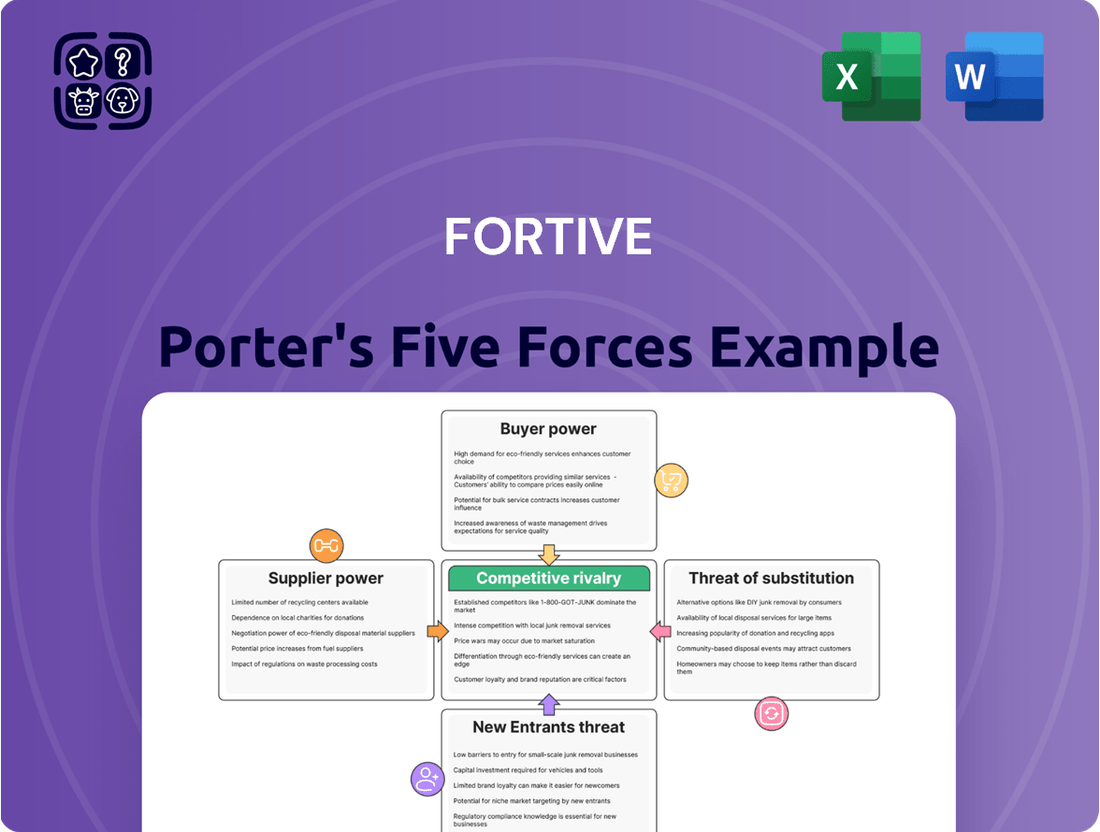
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Fortive, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the influence of substitutes within its diverse markets.
Fortive's Five Forces Analysis provides a structured framework to identify and mitigate competitive threats, transforming market uncertainty into actionable strategic insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
If Fortive's customer base is highly concentrated, with a few large clients generating a substantial portion of its sales, these key customers gain significant leverage. This allows them to negotiate for reduced pricing, enhanced service levels, or tailored product offerings, potentially impacting Fortive's profitability and margins.
Fortive's diverse industry exposure, serving sectors like industrial technology, healthcare, and environmental, potentially dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer. However, within specific product lines or regions, customer concentration could still be a notable factor influencing negotiations.
Customers' ability to switch to a competitor without much hassle directly impacts their bargaining power. If Fortive's customers can easily move to another provider with minimal cost, disruption, or need for new training, they gain leverage to negotiate better terms. This ease of switching is a key factor in how much power customers hold.
Fortive's emphasis on providing mission-critical workflow solutions hints at a deeper integration into their customers' operations. This embeddedness can potentially increase switching costs, as disrupting these solutions might be complex or expensive for clients. For instance, if a customer relies heavily on Fortive's integrated software for their entire production line, the effort and cost to replace that system could be substantial, thereby reducing the customer's bargaining power.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant lever in the bargaining power of buyers for Fortive. When Fortive's offerings are perceived as interchangeable or when clients operate under tight budgetary controls, particularly in sectors like certain manufacturing or healthcare segments, customers are more inclined to negotiate prices. This heightened sensitivity directly amplifies their ability to influence terms.
Conversely, the bargaining power of customers diminishes when Fortive provides highly specialized solutions or products critical for safety and operational integrity. In these scenarios, the value proposition extends beyond mere cost, making customers less sensitive to price and more focused on performance and reliability. For instance, in highly regulated industries, the cost of a component failure can far outweigh initial price differences, reducing customer price sensitivity.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers can significantly amplify their bargaining power against Fortive. If a substantial customer possesses the technical expertise and financial resources to produce Fortive's products or services internally, they gain leverage to negotiate better terms or potentially switch to in-house production. This is particularly relevant if customers can source key components or develop proprietary solutions that replicate Fortive's offerings.
While less common for highly specialized industrial technology and professional instrumentation, large enterprise clients might explore backward integration for specific, high-volume components or less complex service offerings. For instance, a very large manufacturing conglomerate could potentially develop in-house calibration services or manufacture certain standard sensor components if the cost-benefit analysis proves favorable.
- Customer Capability: Assesses if customers possess the technical knowledge and operational infrastructure to replicate Fortive's products or services.
- Cost of Integration: Evaluates the financial investment and ongoing operational costs for customers to undertake backward integration.
- Market Dynamics: Considers whether the market size and customer demand justify the significant undertaking of backward integration.
- Fortive's Value Proposition: Analyzes the unique value, innovation, and service Fortive provides that would be difficult for customers to replicate internally.
Information Availability to Customers
The more information customers possess regarding product costs, prevailing market prices, and the offerings of competing businesses, the stronger their negotiating leverage becomes. In markets characterized by high transparency, consumers can readily compare available choices and secure more favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the increasing availability of online reviews and price comparison tools across various industrial sectors has demonstrably empowered buyers.
Fortive operates within several industries where a degree of specialized knowledge historically limited perfect information symmetry. However, the ongoing digital transformation is progressively enhancing market transparency. This shift means customers are increasingly able to access data that was previously more guarded, directly impacting their ability to negotiate.
- Increased Online Information: In 2024, platforms offering detailed product specifications, user reviews, and price comparisons have become ubiquitous, significantly boosting customer awareness.
- Data Accessibility: Digitalization allows for easier access to cost structures and competitor analysis, reducing information asymmetry.
- Negotiation Leverage: Empowered customers can more effectively demand better pricing and terms, intensifying competitive pressure on suppliers like Fortive.
When Fortive's customers are concentrated, meaning a few major clients represent a significant portion of sales, these large buyers gain considerable power. They can push for lower prices or better service, directly affecting Fortive's profitability. For example, if a handful of industrial manufacturers account for over 30% of revenue in a specific product segment, their ability to negotiate is amplified.
The ease with which customers can switch to alternative suppliers is a critical factor. If switching involves minimal cost, disruption, or retraining, customers hold more sway in price and service negotiations. In 2024, the availability of cloud-based, interoperable solutions across many industrial sectors has generally lowered switching costs, increasing customer bargaining power.
Customers' price sensitivity directly impacts their bargaining power. When Fortive's offerings are seen as commodities or when clients operate under strict budgets, they are more likely to demand lower prices. For instance, in the more commoditized segments of the test and measurement market, price sensitivity can be quite high, giving buyers more leverage.
The bargaining power of Fortive's customers is influenced by their access to information. In 2024, increased market transparency through online platforms and data analytics empowers buyers to compare prices and product features more effectively. This readily available information allows customers to negotiate from a stronger position, demanding more competitive terms.
| Factor | Impact on Fortive | Example Scenario (2024) |
| Customer Concentration | High concentration increases buyer power. | A few large automotive manufacturers dominating orders for Fortive's precision tooling. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower buyers. | Clients easily migrating from Fortive's data acquisition software to a competitor's due to open-source compatibility. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity leads to greater buyer leverage. | Hospitals negotiating aggressively on the price of diagnostic equipment due to budget constraints. |
| Information Availability | Greater transparency enhances buyer power. | Buyers utilizing online comparison tools to identify the lowest-cost supplier for industrial sensors. |
Full Version Awaits
Fortive Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Fortive Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be delivered to you instantly upon purchase, ensuring complete transparency and immediate usability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial technology and connected workflow solutions sectors are populated by a substantial number of competitors. This includes large, diversified corporations alongside highly specialized firms, creating a dynamic and often crowded marketplace.
Key players such as Keysight, Teradyne, Rohde & Schwarz, AMETEK, Dover, and Roper Technologies actively compete with Fortive. For instance, in 2024, Keysight Technologies reported revenues of approximately $5.3 billion, showcasing the scale of some of these rivals.
This broad spectrum of competitors, each with unique strengths and market focuses, significantly heightens competitive rivalry. Companies must continuously innovate and differentiate to capture and maintain market share across the diverse segments within these industries.
The growth rate of the industries Fortive operates in plays a crucial role in shaping competitive rivalry. In markets experiencing slower growth or maturity, competition often intensifies as businesses vie for market share within a more limited expansion. However, high-growth sectors can provide opportunities for companies to scale without necessarily needing to gain ground directly from competitors. Fortive anticipates robust growth in its primary target markets through 2025, which could temper some of the more aggressive competitive pressures.
Fortive's competitive rivalry is shaped by how unique its offerings are and how difficult it is for customers to switch. If Fortive's products are highly distinct and customers face significant hurdles to change providers, the competition tends to be less fierce. For instance, many of Fortive's solutions are designed for 'mission-critical' operations, implying a level of integration and reliance that can deter switching.
While Fortive emphasizes differentiation through its focus on mission-critical applications and high-value services, competitors are also actively innovating. This means that even with some embeddedness, the threat of new or improved offerings from rivals can still pressure pricing and market share. For example, in the industrial technology sector, where Fortive operates, companies like Emerson Electric and Honeywell consistently invest in R&D to enhance their product portfolios and capture market share.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the industrial technology sector, where Fortive operates, can significantly fuel competitive rivalry. These barriers, often stemming from specialized, capital-intensive assets and long-term customer commitments, make it costly and difficult for firms to divest operations. For instance, the significant investment in manufacturing facilities and R&D required for products like precision measurement tools or industrial automation systems means companies are less likely to simply shut down or sell off these divisions when facing downturns.
When companies find it challenging to exit, they may persist in competing even with meager returns. This can manifest as aggressive pricing strategies or increased marketing efforts to maintain market share, ultimately eroding profitability for all players. In 2024, many industrial technology companies were still navigating supply chain complexities and fluctuating demand, potentially exacerbating the effects of high exit barriers by keeping less efficient players in the market longer.
- Specialized Assets: High upfront investment in unique machinery and intellectual property makes divestment difficult.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to customers for ongoing service and support can tie companies to a market.
- Emotional Attachment: Management or founder loyalty to specific product lines can hinder rational exit decisions.
- Government Regulations: Certain industries may have regulatory hurdles for exiting or divesting operations.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic stakes for competitors within the industrial technology sector, where Fortive operates, are exceptionally high, often fueling intense rivalry. Companies see market leadership and technological superiority not just as advantages but as essential for long-term viability and expansion. This can lead to aggressive competition, marked by substantial investments in research and development, aggressive pricing models, and strategic mergers and acquisitions to gain market share or acquire critical technologies.
For instance, the industrial automation market, a key area for Fortive, is projected to grow significantly, with some estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate of over 8% through 2028. This growth potential incentivizes players to outmaneuver rivals through innovation and market penetration. Companies are therefore willing to pour billions into developing next-generation solutions and securing key intellectual property.
- High Stakes Drive Aggression: Companies view market leadership in industrial technology as critical for survival, leading to aggressive competitive tactics.
- R&D as a Battleground: Significant investments in research and development are common as firms race to introduce cutting-edge products and solutions.
- Acquisitions for Advantage: Strategic acquisitions are frequently employed to consolidate market position, acquire new technologies, or eliminate competitive threats.
- Pricing and Market Share Focus: Aggressive pricing strategies are often used to gain market share, especially in rapidly growing segments of the industrial technology market.
The competitive rivalry within Fortive's operating sectors is intense due to a large number of players, including diversified giants and specialized firms. Key competitors like Keysight, Teradyne, and AMETEK are actively vying for market share. For example, in 2024, Keysight Technologies reported revenues of approximately $5.3 billion, demonstrating the significant scale of these rivals.
The presence of numerous competitors, each with distinct strengths, intensifies rivalry. Fortive's differentiation through mission-critical applications and customer integration can mitigate some pressure, but rivals like Emerson Electric and Honeywell continually invest in R&D to counter this. High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and long-term contracts, can also trap companies in markets, leading to sustained competitive pressure, especially when combined with fluctuating demand as seen in 2024.
| Competitor | 2024 Revenue (Approx.) | Sector Focus |
| Keysight Technologies | $5.3 billion | Electronic Test and Measurement |
| Teradyne | $2.7 billion | Semiconductor Test, Industrial Automation |
| AMETEK | $7.0 billion | Specialty Industrial Products, Electronic Instruments |
| Emerson Electric | $15.2 billion | Automation Solutions, Commercial & Residential Solutions |
| Honeywell | $42.0 billion | Aerospace, Building Technologies, Performance Materials, Safety & Productivity Solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Fortive's offerings hinges on whether customers can find alternative ways to meet their needs. This could mean using less sophisticated, manual methods instead of advanced instrumentation, or opting for different service providers that offer similar outcomes. For instance, a construction company might consider traditional surveying techniques rather than Fortive's connected workflow solutions for project management and data collection.
In 2024, the market for industrial and infrastructure solutions saw continued innovation in digital alternatives. Companies seeking efficiency gains might explore cloud-based project management software or even in-house developed systems, which could serve as substitutes for Fortive's specialized platforms. The cost-effectiveness and perceived reliability of these alternatives directly impact the pressure Fortive faces from substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Fortive's offerings hinges on their price-performance ratio. If alternative solutions provide similar or better functionality at a reduced cost, they represent a significant competitive challenge. For instance, in the industrial automation sector where Fortive operates, advancements in open-source software and more affordable hardware components can sometimes offer a compelling alternative to proprietary, high-cost systems.
Fortive's mission-critical, high-value products often justify a premium price. However, this premium must be continuously validated by superior performance and ongoing innovation. As of early 2024, the global industrial automation market is projected to reach over $200 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8-10%, indicating strong demand but also intense competition from both established players and emerging technologies that may offer a more attractive price point.
The threat of substitutes for Fortive's offerings is influenced by how easily customers can switch to alternative solutions. If switching is simple and low-cost, the threat is elevated. For instance, if a competitor offers a similar diagnostic tool that requires minimal integration effort and training, a customer might readily switch.
Fortive's strategy of providing integrated workflow solutions aims to increase switching costs for its customers. By embedding its products into a customer's operational processes, it becomes more complex and costly to adopt a substitute. This integration can involve significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and employee training, making a complete changeover a substantial undertaking.
For example, in the industrial technology sector, a company that has invested heavily in Fortive's connected manufacturing platform might face considerable disruption and expense if it were to switch to a less integrated competitor. This can include data migration challenges, retraining staff on new systems, and potential downtime during the transition, all of which contribute to higher switching costs and a lower threat of substitution.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customer propensity to substitute is a key consideration for Fortive, as evolving preferences and technological leaps can quickly render existing solutions less attractive. Factors like ease of use, the integration of new technologies, and shifts in industry best practices all play a significant role in how readily customers will switch to alternatives.
For example, the ongoing migration from traditional, on-premise software systems to more flexible and scalable cloud-based solutions represents a significant substitution threat. Similarly, in the instrumentation and diagnostics sectors where Fortive operates, the introduction of novel testing methodologies or more advanced analytical equipment can directly challenge established product lines. Fortive's strategic focus on expanding its software and connected solutions portfolio, as evidenced by its continued investment in these areas, is a direct response to mitigate these substitution risks by offering integrated, forward-looking alternatives.
Several factors influence customer propensity to substitute within Fortive's markets:
- Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of innovation, particularly in areas like AI and IoT, creates opportunities for new solutions to emerge that offer superior performance or functionality compared to existing products.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers regularly evaluate the total cost of ownership and the return on investment for their current solutions versus potential substitutes, factoring in not just purchase price but also maintenance, upgrades, and operational efficiency.
- Industry Standards and Regulations: Evolving industry standards or new regulatory requirements can necessitate the adoption of new technologies or methodologies, thereby increasing the propensity to substitute older systems.
- Convenience and Integration: Solutions that offer greater convenience, easier integration with existing workflows, or a more seamless user experience are more likely to attract customers away from less integrated or more cumbersome alternatives.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Rapid technological advancements in adjacent or unrelated industries can quickly spawn viable substitutes for Fortive's products and services. For instance, breakthroughs in AI and automation could create new ways for businesses to manage operations, potentially reducing reliance on Fortive's existing workflow solutions. The company's presence in fast-evolving sectors like healthcare diagnostics and industrial sensing means it must constantly monitor for disruptive innovations that offer superior performance or lower costs.
Consider the healthcare sector, where Fortive's businesses operate. In 2024, global healthcare IT spending was projected to reach over $200 billion, a significant portion of which is driven by innovation. If a new diagnostic technology emerges that is significantly faster, more accurate, and cheaper than current methods, it could directly substitute for some of Fortive's offerings in that space. Similarly, in transportation, advancements in autonomous driving systems could reduce the need for certain types of sensor technology that Fortive currently provides.
- Emergence of Disruptive Technologies: New technologies can rapidly create alternatives to existing solutions.
- Impact on Fortive's Markets: Fortive's core markets (healthcare, transportation, manufacturing) are highly susceptible to technological disruption.
- Need for Continuous Innovation: Companies like Fortive must invest heavily in research and development to stay ahead of potential substitutes.
- Portfolio Adaptation: Fortive's strategy must include evolving its product and service portfolio to address emerging technological trends and substitute threats.
The threat of substitutes for Fortive's offerings is moderate but growing, driven by technological advancements and cost-effectiveness. Customers can find alternatives through manual processes, different service providers, or emerging digital solutions. For example, cloud-based project management software in 2024 offers a substitute for Fortive's specialized platforms, particularly if it provides similar efficiency gains at a lower cost.
Entrants Threaten
The capital needed to even begin competing in the diversified industrial technology space, especially for companies like Fortive that focus on professional instrumentation and connected workflow solutions, is immense. Think about the costs involved in research and development to create cutting-edge products, building or acquiring modern manufacturing plants, establishing robust distribution channels, and then launching effective marketing campaigns. All of this requires significant upfront investment, easily running into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
Existing players like Fortive leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, allowing them to produce goods at a lower per-unit cost. For instance, in 2023, Fortive reported a gross profit margin of 55.1%, indicating efficient cost management. New entrants would find it difficult to match these cost efficiencies without substantial initial investment to achieve similar production volumes.
Fortive's emphasis on proprietary technology, evident in its portfolio of "iconic inventor brands" and active patenting, creates a formidable barrier to entry. As of early 2024, the company's ongoing investment in R&D, which has historically been a significant portion of its revenue, fuels this technological moat. Patents and specialized knowledge make it incredibly challenging and costly for newcomers to replicate Fortive's advanced solutions, thereby deterring potential competitors.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
Fortive's robust brand identity and deeply entrenched customer loyalty act as significant deterrents to new entrants. Years of operation in demanding sectors like healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing have solidified Fortive's reputation for reliability and safety. For instance, within the healthcare sector, where patient safety is paramount, switching to an unproven new supplier can be a high-risk proposition, particularly for critical medical equipment and diagnostic tools.
Customers in these essential industries often prioritize established service networks and proven performance over potentially lower initial costs from newcomers. This preference stems from the need for consistent uptime and readily available support, making it difficult for new companies to penetrate markets where Fortive has cultivated strong, long-term relationships. The cost and effort required for a new entrant to build comparable trust and demonstrate equivalent reliability are substantial.
- Established Brand Equity: Fortive's brands, such as Fluke and Tektronix, are recognized leaders in their respective fields, commanding premium pricing and customer preference.
- Customer Switching Costs: In industries like industrial automation and diagnostics, switching costs can be high due to integration with existing systems, employee training, and regulatory compliance requirements.
- Safety and Reliability Imperatives: Sectors like aerospace and automotive demand exceptionally high standards of reliability and safety, where a proven track record, like Fortive's, is a non-negotiable prerequisite.
Access to Distribution Channels
Gaining access to established distribution channels presents a significant hurdle for new entrants in Fortive's operating industries. Fortive benefits from its extensive sales forces, deep-rooted distributor relationships, and comprehensive service networks built over years.
New companies would need to invest heavily and overcome substantial challenges to replicate or access comparable distribution capabilities. This is particularly true in specialized sectors like industrial automation and healthcare, where trust and established relationships are paramount.
- Established Networks: Fortive's existing distribution channels, including its sales teams and third-party distributors, are a formidable barrier. For example, in the test and measurement segment, securing shelf space or preferred vendor status with major industrial suppliers can take years and significant investment.
- High Entry Costs: Building a new distribution network from scratch can cost millions, encompassing logistics, sales personnel training, and marketing efforts. A new entrant might face initial costs exceeding $10 million to establish a basic national distribution presence in a B2B industrial market.
- Market Penetration Challenges: Even with capital, new entrants struggle to gain traction against incumbents with proven track records and existing customer loyalty within these channels.
The threat of new entrants for Fortive is significantly low, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements and established competitive advantages. Building the necessary infrastructure, from advanced manufacturing facilities to extensive distribution networks, demands billions of dollars, making it prohibitively expensive for most newcomers.
Fortive's strong brand recognition and customer loyalty, cultivated over decades, further erects a formidable barrier. In critical sectors like healthcare, where reliability is paramount, the cost and risk associated with switching to an unproven supplier are immense, reinforcing Fortive's market position.
The company's proprietary technology, protected by patents and continuous R&D investment, creates a significant technological moat. This makes it exceptionally difficult and costly for new players to replicate Fortive's innovative solutions, effectively deterring potential competition.
Access to established distribution channels is another major hurdle. Fortive leverages its vast sales force and deep distributor relationships, which new entrants would find extremely challenging and expensive to replicate, further limiting their market penetration capabilities.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Fortive's Advantage (as of 2023/early 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Extremely High (Billions $) | Fortive operates with significant financial resources and economies of scale. |
| Brand Equity & Customer Loyalty | Difficult to Overcome | Established brands like Fluke and Tektronix command premium pricing and trust. |
| Proprietary Technology & Patents | High Replication Cost | Continuous R&D investment fuels a technological moat. |
| Distribution Channels | Challenging to Access/Build | Extensive sales force and deep distributor relationships. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Fortive Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings to understand internal strategies and financial health.
