Ford Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ford Motor Bundle
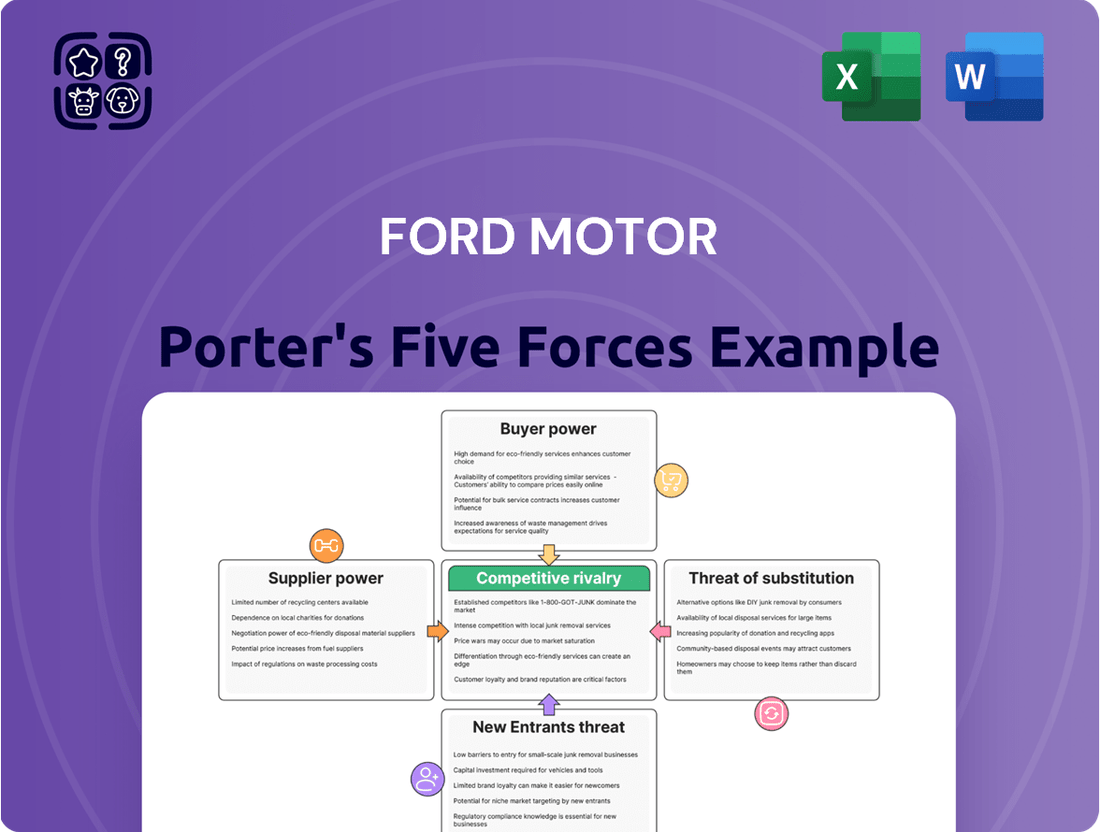
Ford Motor navigates a complex automotive landscape, facing intense rivalry, evolving buyer power, and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic success.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ford Motor’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ford's reliance on a limited number of specialized suppliers for critical automotive components significantly impacts its bargaining power. The automotive parts manufacturing market is quite concentrated, with approximately 10 major suppliers accounting for over 55% of the total market share. This means Ford often deals with a select group of companies that possess unique expertise and technology.
For high-value and technologically advanced parts, such as semiconductors and complex electronic systems, this supplier concentration translates into considerable leverage for these specialized providers. Ford may find it challenging to switch suppliers for these essential components without incurring substantial costs and production delays, thereby strengthening the suppliers' negotiating position.
Ford's reliance on specialized suppliers for critical automotive components significantly elevates supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs. For instance, re-engineering a complex powertrain or advanced driver-assistance system can cost Ford millions of dollars per component. This substantial financial and time investment acts as a formidable barrier, making it difficult and expensive for Ford to switch to alternative suppliers, thus empowering existing suppliers.
Ford's significant reliance on specific raw materials like steel and aluminum, alongside critical components such as semiconductors, directly impacts supplier bargaining power. These materials represent substantial procurement expenditures for the company, often running into billions of dollars annually.
The persistent global semiconductor shortage, which continued to affect automotive production throughout 2023 and into early 2024, clearly demonstrated the elevated influence of semiconductor suppliers. This vulnerability underscores how disruptions in these key material flows can significantly increase supplier leverage over Ford.
Suppliers' Low Forward Vertical Integration
Many automotive suppliers exhibit limited forward vertical integration, meaning they typically don't manage the distribution or direct sales of their components to the final car buyer. This reliance on manufacturers like Ford for market access inherently reduces their leverage.
In 2024, the automotive supply chain continued to show this trend, with a majority of Tier 1 suppliers focusing on component manufacturing rather than consumer-facing retail operations. Ford's own strategic investments in certain manufacturing processes, representing a degree of backward vertical integration, further consolidate its position, diminishing the suppliers' ability to dictate terms.
This dynamic means suppliers have less control over the final price and market penetration of their parts, as Ford and other automakers manage these crucial downstream aspects. Consequently, suppliers' bargaining power is constrained.
Key implications for Ford include:
- Reduced Cost Pressure: Ford can negotiate more favorable terms due to suppliers' limited market control.
- Supply Chain Stability: Dependence on Ford for sales provides Ford with some leverage in ensuring consistent supply.
- Limited Supplier Profitability: Suppliers' margins can be capped as they don't capture downstream value.
- Focus on Manufacturing Efficiency: Suppliers are incentivized to compete on production quality and cost rather than market access.
Supplier Relations and Industry Trends
Despite efforts to foster better supplier partnerships, Ford Motor Company faced a significant challenge in 2025, ranking second-to-last in a study evaluating North American automotive OEM-supplier working relationships. This low ranking suggests that the bargaining power of Ford's suppliers may remain substantial, potentially impacting cost negotiations and the reliability of the supply chain.
The ongoing strain in these relationships could translate into higher component costs for Ford, as suppliers may leverage their position to secure more favorable terms. This dynamic directly affects Ford's cost structure and, consequently, its profitability and competitive pricing strategies in the automotive market.
- Supplier Dependence: Ford's reliance on specific suppliers for critical components, such as semiconductors or advanced battery technology, can amplify supplier bargaining power.
- Market Concentration: If a particular supplier dominates the market for a key input, they possess greater leverage in price and supply volume negotiations.
- Switching Costs: The expense and time involved in qualifying and integrating new suppliers can deter Ford from seeking alternative sources, thus strengthening existing supplier positions.
Ford's bargaining power with suppliers is notably constrained by the concentration within the automotive parts industry, where a few key players often control specialized technologies. This situation was particularly evident in 2023 and 2024 due to ongoing supply chain disruptions, especially concerning semiconductors, where suppliers held significant leverage. The high costs and time required for Ford to switch suppliers for critical components further solidify these suppliers' negotiating positions.
The automotive supply chain in 2024 continued to see a limited degree of backward vertical integration among suppliers, meaning they rely heavily on automakers like Ford for market access. This dependence inherently weakens their ability to dictate terms, as Ford manages the critical downstream sales and distribution channels.
Ford's strategic investments in certain manufacturing processes in recent years have also helped consolidate its position, reducing the leverage of some suppliers who might otherwise seek to control more of the value chain.
Ford's relationships with its suppliers in North America were ranked second-to-last in a 2025 study, indicating persistent strains that could empower suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms, impacting Ford's costs and profitability.
| Factor | Impact on Ford's Supplier Bargaining Power | 2023-2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration for Critical Components | High | Approx. 10 major suppliers account for over 55% of the market for specialized parts. |
| Switching Costs for Key Components | High | Millions of dollars per component for re-engineering complex systems like powertrains or ADAS. |
| Supplier Forward Vertical Integration | Low | Majority of Tier 1 suppliers focus on manufacturing, not direct consumer sales. |
| Raw Material Dependence (e.g., Steel, Aluminum) | Moderate to High | Represents billions of dollars in annual procurement for Ford. |
| Semiconductor Supply Chain Vulnerability | High | Persistent shortage throughout 2023 and into 2024 significantly boosted semiconductor supplier leverage. |
| North American OEM-Supplier Relationship Ranking | Negative | Ford ranked second-to-last in a 2025 study, suggesting supplier leverage. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Ford Motor, examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes within the automotive industry.
Effortlessly assess competitive intensity and identify strategic vulnerabilities within the automotive industry, turning complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
While buyers can indeed switch between different automobile manufacturers, the costs involved in making that transition are generally considered moderate. This means that switching isn't prohibitively expensive, but it's not entirely free of consequence either.
A significant factor contributing to these moderate switching costs is the prevalence of existing car loans. Many consumers finance their vehicle purchases, and the process of selling a current car, paying off the loan, and then securing financing for a new vehicle can be a deterrent to frequent brand hopping. This financial tie-in provides a degree of stability for automakers like Ford, as it reduces the immediate likelihood of customers readily switching to a competitor.
For instance, in 2024, the average new car loan term in the United States was around 70 months, indicating a substantial financial commitment that anchors many buyers to their current vehicles and brands for a considerable period. This extended commitment naturally dampens the ease with which customers can switch, thus moderating their bargaining power.
Customers do have a moderate number of substitutes for Ford vehicles. Think about public transportation, the growing popularity of cycling, and even motorcycles. These can serve as alternatives, especially in urban areas or for shorter commutes.
However, these substitutes aren't always a perfect fit. For many, especially families or those needing to haul goods, public transport or bikes just don't offer the same convenience or utility as a car. This limitation on substitutes means customers can't exert overwhelming pressure on Ford's pricing or product offerings.
For instance, while ride-sharing services saw significant growth, with Uber reporting over 1 billion rides globally in 2023, they still largely complement private car ownership rather than fully replacing it for many demographics. This continued reliance on personal vehicles helps temper the bargaining power derived from alternative transportation.
The automotive market is highly price-sensitive, with consumers diligently comparing prices across various brands. In 2024, persistent economic pressures, including elevated interest rates and increasing vehicle prices, have amplified consumer budget consciousness, driving a stronger demand for transparent pricing and demonstrable value.
Evolving Consumer Preferences and Brand Loyalty
Consumer shopping trends for 2025 highlight a significant shift towards digital-first vehicle purchasing and servicing. This digital transformation means customers expect seamless online experiences, from research and configuration to financing and delivery. For instance, a late 2024 survey revealed that over 60% of potential car buyers preferred to complete at least half of the purchase process online.
Brand loyalty in the automotive sector is demonstrably waning. Data from early 2025 indicates that a substantial portion of consumers, estimated around 45%, are actively considering switching brands for their next vehicle purchase. This erosion of loyalty directly increases the bargaining power of customers, forcing manufacturers like Ford to innovate and offer compelling value propositions to retain their market share.
- Digital Dominance: 2025 consumer behavior shows a strong preference for online vehicle research, configuration, and even purchase.
- Shifting Loyalty: Approximately 45% of consumers are open to switching brands, increasing customer leverage.
- Eco-Conscious Choices: Growing environmental awareness influences purchasing decisions, demanding sustainable options from manufacturers.
Impact of EV Adoption and Hybrid Interest
Customer bargaining power is significantly influenced by evolving preferences in electric vehicle (EV) technology. While EV adoption is on an upward trajectory, a noticeable shift towards hybrid vehicles is occurring. This trend is largely driven by persistent concerns regarding the affordability of pure EVs, lingering range anxiety, and the still-developing charging infrastructure.
This growing customer preference for hybrids over pure EVs grants consumers more leverage. They are actively seeking a balanced solution that offers improved fuel efficiency without the perceived drawbacks of current EV technology. This dynamic directly impacts Ford's strategic decisions, pushing the company to adapt its product development pipeline and refine its pricing models to meet these changing customer demands.
- Hybrid Demand Surge: In early 2024, reports indicated a notable increase in consumer interest for hybrid vehicles, with some analysts observing a plateau or even a slight dip in demand for certain pure EV models.
- Affordability Gap: The average price difference between comparable hybrid and pure EV models remained a significant factor for many consumers throughout 2023 and into 2024, influencing purchasing decisions.
- Infrastructure Hesitation: Consumer surveys from late 2023 and early 2024 consistently highlighted charging availability and speed as key concerns for potential EV buyers, contributing to the appeal of hybrids.
Customers possess moderate bargaining power due to a combination of factors, including the availability of substitutes and price sensitivity. While brand loyalty is declining, the financial commitments tied to vehicle ownership, such as existing loans, somewhat temper customers' ability to switch easily.
The automotive market in 2024 and early 2025 saw consumers becoming increasingly budget-conscious, amplified by higher vehicle prices and interest rates. This heightened price sensitivity means customers are actively comparing options, which gives them leverage. For instance, a late 2024 survey indicated over 60% of car buyers preferred to handle at least half of the purchase process online, signaling a demand for transparent and accessible pricing.
Furthermore, evolving preferences, particularly the growing demand for hybrid vehicles over pure EVs due to affordability and infrastructure concerns, also empower customers. This trend, evident in early 2024 reports, forces manufacturers like Ford to adapt their offerings and pricing strategies to meet these shifting consumer needs.
| Factor | 2024/2025 Trend | Impact on Bargaining Power |
| Switching Costs (Loans) | Average new car loan term ~70 months (US, 2024) | Moderate, as financial commitment anchors buyers |
| Availability of Substitutes | Ride-sharing usage high, but complements ownership | Moderate, as personal vehicles remain essential for many |
| Price Sensitivity | Increased due to economic pressures | High, driving demand for value and transparent pricing |
| Brand Loyalty | Waning; ~45% open to switching brands (early 2025) | Increasing, forcing competitive offers |
| EV/Hybrid Preference | Growing demand for hybrids over pure EVs | Increasing, influencing product development and pricing |
Same Document Delivered
Ford Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Ford Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape of the automotive industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, all presented in a comprehensive and ready-to-use format.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ford operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, facing aggressive rivals like Toyota, General Motors, BMW, and Tesla. These global giants are constantly vying for market dominance through rapid innovation and aggressive marketing campaigns, making the automotive sector a battleground for market share.
In 2024, the automotive industry continues to see intense price competition and rapid product development cycles. For instance, Tesla's aggressive pricing strategies in early 2024 have pressured legacy automakers to adjust their own pricing, demonstrating the high degree of competitive rivalry.
The automotive sector, including players like Ford, faces significant exit barriers. Companies have made massive investments in manufacturing plants, specialized equipment, and global supply chains. For instance, Ford's capital expenditures in 2023 alone were $17.7 billion, reflecting the substantial ongoing commitment required to maintain operations.
These high fixed costs and specialized assets make it exceedingly difficult and costly for companies to leave the market. This situation naturally fosters a climate of persistent, intense competition among the remaining manufacturers, as shutting down operations would mean forfeiting these sunk costs.
While the global automotive landscape features numerous manufacturers, the market is notably concentrated among a moderate number of large, established companies. This means that intense competition isn't spread thinly but rather focused among a few dominant players, creating significant pressure for companies like Ford.
In 2023, the top 10 automotive groups, including giants like Toyota, Volkswagen Group, and Stellantis, accounted for approximately 65% of global vehicle sales. This concentration highlights how Ford faces formidable rivals with substantial market share and resources, intensifying the competitive rivalry.
Shift Towards Electric Vehicles and New Entrants
The automotive industry's rapid shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has dramatically intensified competitive rivalry. Established automakers like Ford are making substantial investments in EV technology and production, aiming to capture market share in this burgeoning segment. For instance, Ford's investment in EV production capacity, including its BlueOval City campus, highlights this commitment.
However, this transition also welcomes new, agile competitors. Companies like Tesla have already established a strong foothold, and emerging Chinese EV manufacturers are rapidly gaining traction globally, often with competitive pricing strategies. This dynamic creates significant pressure on legacy automakers to innovate quickly and manage costs effectively.
- Intensified Competition: The EV market sees fierce competition from both traditional automakers and new entrants, leading to price pressures.
- Ford's EV Investment: Ford is investing heavily in EV development and manufacturing, exemplified by its significant capital allocation to EV projects.
- Emerging Rivals: Chinese EV brands and Tesla are key competitors, pushing for innovation and market dominance.
- Price Wars: The competitive landscape has triggered price adjustments and potential price wars as companies vie for consumer attention and market share.
Focus on Differentiation and Technology
Ford is actively pursuing a differentiation strategy, focusing on product innovation and advanced technologies to stand out. This strategic shift is evident in their significant investments in areas like smart vehicle technologies and connected services, aiming to build a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving automotive landscape. For instance, Ford's commitment to electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving features are key differentiators.
The intensity of rivalry within the automotive sector is amplified by Ford's strategic pivot. Competitors are also heavily investing in similar technological advancements, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and sophisticated infotainment platforms. This creates a dynamic environment where continuous innovation is essential to maintain market share and attract customers.
- Ford's Q1 2024 revenue reached $42.8 billion, with a significant portion attributed to its improved product mix and technology features.
- Investments in ADAS and connected services are crucial for Ford to compete against rivals who are also enhancing their vehicle's technological capabilities.
- The company aims to differentiate through unique software and user experiences, moving beyond traditional hardware advantages.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of the automotive industry, impacting Ford significantly. The sector is dominated by a few large players, creating a concentrated market where intense competition is the norm. This rivalry is further fueled by substantial investments in new technologies, particularly electric vehicles (EVs), and aggressive pricing strategies by competitors like Tesla.
In 2024, this rivalry is evident in the ongoing price adjustments and rapid product development cycles. For example, Tesla's pricing actions early in the year forced other manufacturers to respond. Ford itself is making substantial investments in EV production, such as its BlueOval City campus, to keep pace with rivals who are also heavily investing in this transition.
The high fixed costs and specialized assets within the automotive industry create significant exit barriers, meaning companies are compelled to compete vigorously rather than withdraw. This leads to a sustained battle for market share among established giants and increasingly agile new entrants, including prominent Chinese EV manufacturers.
| Competitor | Global Market Share (Approx. 2023) | Key Competitive Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota | ~12% | Hybrid leadership, expanding EV offerings |
| Volkswagen Group | ~10% | Aggressive EV rollout, software development |
| General Motors | ~8% | Investing heavily in EVs and autonomous technology |
| Tesla | ~5% | Pioneering EV market, aggressive pricing, software integration |
| Stellantis | ~7% | Brand portfolio consolidation, EV platform development |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Direct substitutes for Ford vehicles, like public transit, bikes, and scooters, present a moderate threat. While these alternatives offer mobility, their practicality is often tied to specific geographic locations and user needs, meaning they don't fully replace the functionality of a car for many.
In 2024, the reliance on personal vehicles remains high in many regions, especially in suburban and rural areas where public transportation infrastructure is less developed. For instance, in the United States, personal vehicle miles traveled continue to be a significant metric, indicating the persistent demand for automobiles.
However, the growing popularity of ride-sharing services and the increasing adoption of electric scooters in urban centers in 2024 do offer more convenient alternatives for shorter commutes, impacting Ford's market share in specific segments.
The costs for consumers to switch from owning a personal vehicle to alternative transportation methods are generally moderate. While the initial purchase price and ongoing expenses like loan payments can be significant, the convenience and flexibility offered by personal car ownership often outweigh the immediate cost of switching for many buyers.
Many traditional substitutes for personal vehicles, such as public transportation or bicycles, often fall short in performance when considering convenience, flexibility, and safety. This is particularly true for longer commutes, transporting goods, or fulfilling specific professional requirements. For instance, in 2024, the average commute time in major metropolitan areas still significantly favors personal vehicles over public transit for many residents, highlighting the convenience factor.
Emergence of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) and Ride-Hailing
The rise of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) and ride-hailing platforms like Uber and Lyft presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional car ownership, a core offering for Ford. Younger demographics, in particular, are increasingly drawn to the flexibility and perceived cost-effectiveness of these services, potentially reducing demand for new vehicle purchases.
This shift is not merely theoretical. In 2024, ride-hailing services continue to see robust usage, with global ride-hailing revenues projected to reach over $200 billion. For instance, Uber reported a 24% increase in rides year-over-year in its Q1 2024 earnings. This indicates a growing segment of consumers who may opt out of owning a personal vehicle.
- Growing adoption of ride-sharing: Younger consumers are prioritizing access over ownership, viewing ride-hailing as a viable alternative to purchasing a car.
- Subscription models for vehicles: Some automakers are experimenting with car subscription services, offering flexible terms that could appeal to those hesitant about long-term ownership commitments.
- Impact on traditional sales: Increased reliance on MaaS and ride-hailing could lead to a decline in new car sales, especially in urban areas where these services are most prevalent.
Impact of Hybrid and Electric Bicycle Growth
The increasing adoption of electric bicycles and other advanced micromobility options presents a growing threat of substitution for traditional automobiles, particularly in urban settings. While not a direct replacement for longer journeys, these alternatives can chip away at the market for short-distance commutes, a segment often served by smaller, more fuel-efficient vehicles.
This trend is notable as more people opt for eco-friendly and cost-effective personal transportation. For instance, by 2024, the global e-bike market was projected to reach over $40 billion, indicating a significant shift in consumer preferences for shorter trips.
- E-bike market growth: The e-bike market is expanding rapidly, with projections suggesting continued strong growth through 2025.
- Urban commute shift: Micromobility solutions are increasingly favored for urban commutes, directly impacting the demand for cars in these areas.
- Reduced reliance on cars: For short trips, e-bikes and similar options offer a viable alternative, lessening the necessity of car ownership for some consumers.
- Cost and environmental factors: The lower operating costs and environmental benefits of e-bikes make them an attractive substitute for many urban dwellers.
The threat of substitutes for Ford vehicles is evolving, with ride-sharing and micromobility gaining traction, especially in urban areas. While personal vehicles remain dominant for many, particularly in suburban and rural settings, these alternatives are impacting shorter commute segments. The cost and convenience factors are key drivers in this shift.
In 2024, the global ride-hailing market is projected to exceed $200 billion, with companies like Uber reporting significant year-over-year growth in rides. Similarly, the e-bike market is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating it could surpass $40 billion by 2024, showcasing a clear consumer preference for alternative transportation for shorter distances.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Market Projection | Key Impact on Ford | Consumer Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ride-Sharing Services | >$200 billion (Global Revenue) | Reduces demand for new car ownership, particularly in urban areas. | Preference for access over ownership among younger demographics. |
| Electric Bicycles (E-bikes) | >$40 billion (Global Market) | Impacts sales of smaller, fuel-efficient vehicles for short commutes. | Growing adoption due to cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits. |
| Public Transportation | Varies by region | Moderate threat, largely dependent on infrastructure availability. | Still a primary option in areas with well-developed transit systems. |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive sector demands substantial capital for R&D, advanced manufacturing plants, and robust supply chains. For instance, developing a new vehicle platform can cost billions of dollars, as seen with Ford's significant investments in electric vehicle technology.
These substantial upfront financial requirements create a formidable barrier to entry for potential new competitors. Establishing a global manufacturing footprint and meeting stringent safety and emissions standards requires hundreds of millions, if not billions, in initial investment, effectively deterring many new players.
The immense cost and time required to build a reputable automotive brand present a significant barrier to new entrants. Ford, for instance, has invested billions over decades to cultivate its brand recognition and customer loyalty. This makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to establish a foothold and gain consumer trust against such deeply entrenched players.
New entrants into the automotive sector, like Ford, must contend with incredibly complex and stringent regulatory landscapes. These include rigorous safety certifications, such as those mandated by the NHTSA in the US, and increasingly demanding environmental standards, like the Euro 7 emissions regulations being phased in across Europe. Meeting these requirements necessitates substantial upfront investment in research, development, and extensive testing, significantly raising the barrier to entry.
Established Supply Chains and Distribution Networks
Ford, like other established automakers, benefits from deeply entrenched supply chains and distribution networks. These systems have been meticulously built over decades, allowing for efficient sourcing of parts and widespread vehicle availability. For instance, in 2024, Ford's global supply chain involves thousands of suppliers, a complex web that new entrants would find incredibly difficult and costly to replicate from scratch.
New companies entering the automotive market face substantial hurdles in establishing comparable supply chains and distribution channels. Replicating Ford's existing infrastructure would require immense capital investment and significant time to forge reliable relationships with component manufacturers and logistics providers. This barrier is a critical deterrent for potential new competitors.
The sheer scale and complexity of these established networks present a significant threat of new entrants. Consider the vast number of dealerships Ford operates globally; building a comparable retail and service footprint takes years and substantial investment. This existing infrastructure provides Ford with a competitive advantage in reaching and serving customers, making it harder for newcomers to gain market share.
- Established Supply Chains: Ford's global supply chain, a complex network of thousands of suppliers, is a significant barrier to entry.
- Extensive Distribution Networks: A vast dealership and service network provides a competitive advantage in customer reach and support.
- Replication Costs: New entrants face immense capital and time requirements to build similar supply and distribution capabilities.
- Logistical Expertise: Decades of experience in managing global logistics offer efficiency and cost advantages for incumbents.
Technological Advancements and Intellectual Property
The automotive industry is currently experiencing a technological revolution, particularly in areas like electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving, and connected car services. This rapid evolution demands substantial and ongoing investment in research and development. For instance, in 2024, major automakers are projected to spend billions on EV technology and autonomous systems, with Ford alone investing over $50 billion in EVs and autonomous vehicles through 2026.
Established companies like Ford possess extensive portfolios of patents and proprietary technologies, which act as significant barriers to entry for newcomers. Developing comparable capabilities and intellectual property from scratch is both time-consuming and incredibly expensive. This technological moat makes it challenging for new entrants to compete on a level playing field, especially concerning advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and battery technology.
- EV Investment: Global automakers are pouring hundreds of billions into EV development, with projections suggesting over $1.2 trillion will be invested by 2030.
- R&D Spending: In 2024, R&D expenditure for leading automotive manufacturers is expected to reach record highs, driven by the need to innovate in software and hardware.
- Patent Landscape: Companies with strong patent protection in areas like battery management systems and AI for autonomous driving can effectively deter new market entrants.
- Software Dominance: The increasing importance of software in vehicles means that companies with advanced software development capabilities and intellectual property have a distinct advantage.
The threat of new entrants for Ford is relatively low due to high capital requirements, established brand loyalty, and complex regulatory hurdles. For instance, the automotive industry demands billions in upfront investment for R&D, manufacturing, and global supply chains, a significant deterrent for newcomers. Ford's decades of brand building and customer trust, cultivated through substantial marketing and product development, create a formidable barrier.
New competitors must also navigate stringent safety and environmental regulations, such as evolving emissions standards and crash-test requirements, which necessitate extensive and costly compliance efforts. Furthermore, replicating Ford's deeply entrenched supply chains and extensive global distribution networks, built over many years and involving thousands of suppliers and dealerships, represents an immense challenge and financial burden for any potential entrant.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for Ford |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Massive upfront investment needed for R&D, manufacturing, and global operations. | Ford's $50 billion investment in EVs and autonomous vehicles through 2026. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Decades of brand building and customer trust are difficult to replicate. | Ford's long-standing reputation and established customer base. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting stringent safety, emissions, and environmental standards. | Adherence to NHTSA safety mandates and Euro 7 emissions regulations. |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | Complex, established networks of suppliers and dealerships. | Ford's global supply chain involving thousands of suppliers and extensive dealership network. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ford Motor leverages data from annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from firms like IHS Markit and JD Power. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics, supplier power, and buyer bargaining within the automotive sector.
