Frontier Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Frontier Airlines Bundle
Frontier Airlines operates in a highly competitive landscape shaped by intense rivalry among existing carriers, significant bargaining power of buyers, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) segment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Frontier Airlines’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The commercial aviation sector is heavily concentrated, with Airbus and Boeing dominating the market for new aircraft. This limited supplier base grants them substantial leverage when negotiating with airlines like Frontier, as viable alternatives are scarce.
The impact of this supplier power is amplified by ongoing supply chain disruptions affecting the industry. For instance, in 2024, airlines experienced significant delays in aircraft deliveries, directly hindering their ability to expand capacity and execute growth strategies.
Suppliers of highly specialized and certified aircraft components, like engines and avionics, wield significant bargaining power. This is due to the complex engineering and rigorous certification processes involved, making it difficult for airlines such as Frontier to readily switch providers. For instance, a major engine manufacturer could dictate terms, knowing that replacing their specialized parts across a fleet would be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming.
The airline industry's reliance on specialized skills, such as pilots and mechanics, means that labor unions hold considerable sway. These unions can negotiate for better pay, benefits, and working conditions, directly impacting airline operating costs. For example, in 2024, Frontier Airlines continued to navigate complex labor relations, with ongoing discussions and potential impacts on their cost structure stemming from agreements with their flight attendant union.
Fuel Suppliers' Influence
Jet fuel represents a substantial portion of an airline's operating costs, making its price fluctuations a critical factor in profitability. For instance, in 2023, jet fuel costs accounted for approximately 20-25% of total operating expenses for many major airlines.
Despite a seemingly large number of fuel suppliers, the market can consolidate, and global events like geopolitical instability or sudden shifts in supply and demand can significantly enhance suppliers' bargaining power. This concentration can limit an airline's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
Airlines possess few effective ways to counteract substantial increases in fuel prices, other than implementing hedging strategies to lock in prices or investing in more fuel-efficient aircraft. Even with these measures, the impact of sharp price hikes can be considerable.
- Significant Cost Component: Jet fuel costs often represent over 20% of an airline's operating budget.
- Market Concentration: While many suppliers exist, a few major players can dominate specific regions, increasing their leverage.
- Limited Alternatives: Airlines' ability to switch suppliers quickly or find substitutes for jet fuel is highly restricted.
- Hedging and Efficiency: Strategies like fuel hedging and fleet modernization are primary defenses against price volatility.
Airport Infrastructure and Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in airport infrastructure and services significantly impacts airlines like Frontier. Airport authorities and ground handling services often function as local monopolies or oligopolies, giving them considerable leverage in setting fees. For instance, major hub airports, where Frontier frequently operates, can command higher charges due to limited alternatives.
These supplier dynamics directly affect Frontier's operational costs and network planning. High landing fees, gate charges, and ground handling costs at key airports can reduce profitability and influence route selection. Frontier's strategy of focusing on specific routes and optimizing its network is therefore closely tied to the availability and cost of essential services at its chosen airports.
- Airport Fees: In 2024, average airport fees for airlines can represent a substantial portion of operating costs, with some major US airports charging upwards of $10 per passenger for landing and terminal usage.
- Ground Handling Costs: The cost of ground handling services, including baggage handling and aircraft servicing, can vary significantly by airport, impacting Frontier's per-flight expenses.
- Limited Competition: At many large airports, there may only be one or two primary ground handling providers, limiting airlines' ability to negotiate lower rates.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Frontier Airlines is significant, primarily due to the concentrated nature of aircraft manufacturing and the specialized components required. This limited supplier base, dominated by Boeing and Airbus, means airlines have few alternatives, granting these manufacturers considerable leverage in negotiations. Furthermore, the critical nature of specialized parts like engines and avionics, coupled with high switching costs and complex certification, solidifies supplier power.
Jet fuel is another area where supplier power is pronounced. While the fuel market appears broad, consolidation and global events can empower key suppliers, limiting airlines' ability to secure favorable pricing. This is compounded by the fact that fuel is a substantial operating cost, often representing 20-25% of an airline's expenses, and airlines have limited direct control over price fluctuations.
Airport infrastructure and services also contribute to supplier leverage. Airport authorities and ground handling providers can act as local monopolies or oligopolies, dictating fees for landing, gate usage, and ground services. For example, in 2024, major US airports could charge airlines upwards of $10 per passenger for terminal and landing fees, significantly impacting operational costs.
| Supplier Category | Key Suppliers | Impact on Frontier | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Manufacturing | Boeing, Airbus | High leverage due to limited competition; delays impact capacity. | Ongoing delivery delays in 2024 impacted airline fleet expansion plans. |
| Aircraft Components (Engines, Avionics) | General Electric, Rolls-Royce, Pratt & Whitney | High switching costs, specialized nature grants strong pricing power. | Complex certification and engineering make supplier changes difficult and expensive. |
| Jet Fuel | Major Oil Companies, Refiners | Significant cost driver (20-25% of operating expenses); price volatility impacts profitability. | Geopolitical events in 2024 continued to influence fuel price stability. |
| Airport Services & Infrastructure | Airport Authorities, Ground Handling Companies | Local monopolies/oligopolies lead to high fees (landing, gate, handling). | Average airport fees in 2024 could exceed $10 per passenger at major hubs. |
What is included in the product
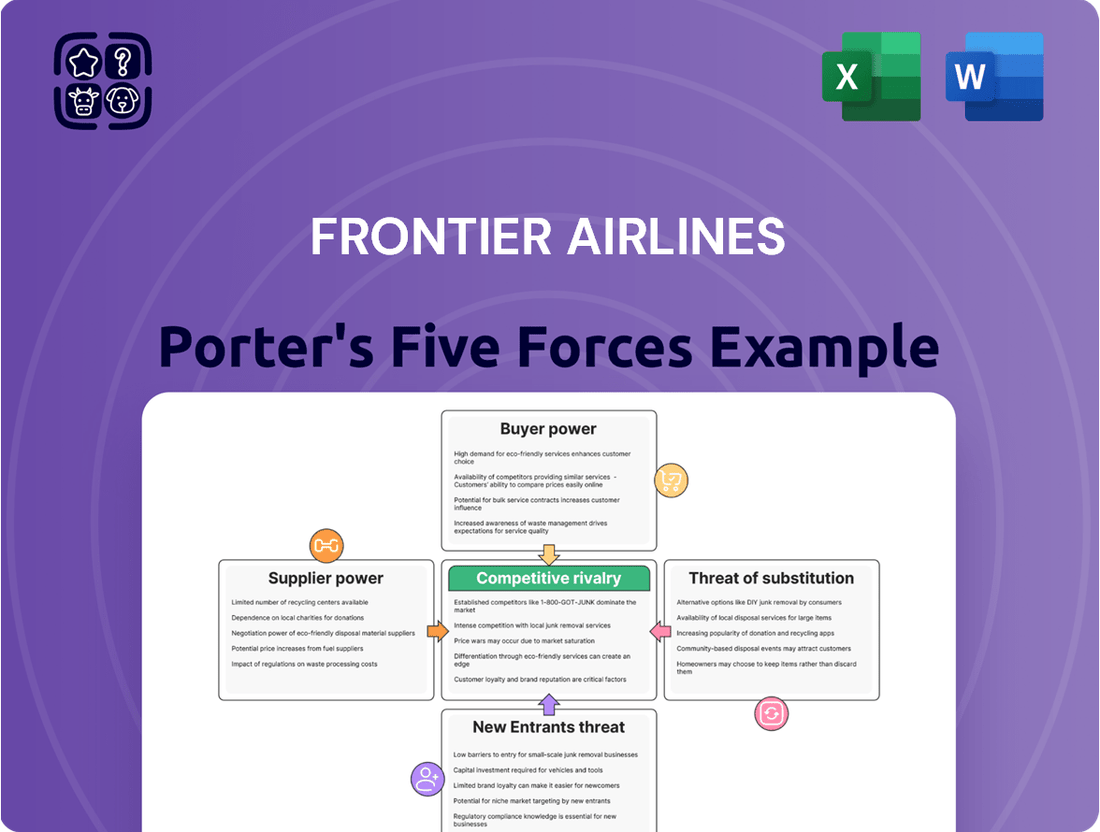
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Frontier Airlines, examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants, and the potential for substitute products.
Instantly visualize Frontier's competitive landscape with a clear, one-sheet Porter's Five Forces analysis, simplifying complex market pressures for strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Frontier Airlines' core customer base consists of leisure travelers, a segment known for its acute price sensitivity. This means that even small differences in ticket prices can heavily influence their purchasing decisions, giving them considerable bargaining power.
As an ultra-low-cost carrier, Frontier's strategy relies on attracting these price-conscious consumers with exceptionally low base fares. In 2024, the airline continued to compete aggressively on price, a strategy that amplifies customer power as they can easily shift to competitors offering even slightly cheaper options.
This high price sensitivity is particularly evident when other ultra-low-cost carriers or even traditional airlines offer comparable no-frills fares. Frontier's customers are adept at comparing prices across various airlines, making it crucial for Frontier to maintain its cost advantage to retain market share.
Frontier Airlines' unbundled service model, where extras like baggage and seat selection are additional fees, gives customers the power to customize their travel and only pay for what they need. This transparency in pricing, a core part of the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) model, empowers customers to compare total costs across airlines. For example, in 2024, the average ancillary revenue per passenger for ULCCs was significantly higher than for legacy carriers, highlighting how these fees are a substantial part of the customer's total outlay, and thus a point of negotiation or comparison.
The North American airline industry is characterized by a plethora of low-cost and ultra-low-cost carriers, such as Spirit Airlines and Allegiant Air. Even traditional carriers are now introducing basic economy fares, further intensifying competition. This wide array of choices, particularly on frequently traveled leisure routes, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power.
Online Travel Agencies and Price Comparison Sites
The widespread availability of online travel agencies (OTAs) and flight comparison websites significantly boosts the bargaining power of customers. These platforms allow travelers to effortlessly compare prices from various airlines, including Frontier, instantly. This heightened transparency fuels intense price competition, making it challenging for any airline to charge higher prices for its standard fares.
In 2024, the travel industry continued to see a strong reliance on these digital tools. For instance, platforms like Google Flights, Skyscanner, and Kayak allow consumers to sift through numerous options quickly. This accessibility means customers can easily identify the lowest available fares, putting pressure on airlines like Frontier to remain competitive on price. This dynamic directly translates to a reduced ability for Frontier to dictate terms or charge premium prices without facing immediate customer defection to a competitor offering a better deal.
- Increased Price Transparency: Customers can easily compare Frontier's fares against those of numerous other airlines, often in real-time.
- Reduced Switching Costs: It takes minimal effort for a customer to switch from one airline to another when booking through an OTA or comparison site.
- Focus on Price Sensitivity: The ease of comparison emphasizes price as a primary decision factor, diminishing the impact of brand loyalty for basic air travel.
- Market Pressure: Airlines like Frontier face constant pressure to offer competitive pricing to capture bookings through these popular online channels.
Impact of Negative Customer Experience
For ultra-low-cost carriers like Frontier Airlines, while price is a major draw, negative customer experiences can significantly erode loyalty. Issues such as frequent flight delays, cancellations, or unexpected fees can quickly sour a customer's perception, making them less likely to choose the airline again.
The widespread reach of social media amplifies the impact of these negative encounters. A single poor experience can go viral, rapidly damaging Frontier's brand image and leading to a substantial loss of potential and repeat customers. This highlights the critical importance of service quality, even for budget airlines.
In 2023, customer satisfaction scores for many airlines, including those in the ULCC segment, saw fluctuations. For instance, J.D. Power's North America Airline Satisfaction Study indicated that while overall satisfaction improved slightly, operational issues like delays and baggage mishandling remained key detriments to the customer experience.
- Price Sensitivity: ULCC customers are highly price-sensitive, but this doesn't negate the impact of poor service.
- Social Media Amplification: Negative reviews and complaints can spread rapidly online, influencing purchasing decisions for thousands.
- Reputational Damage: Consistent service failures can lead to a tarnished brand image, making customer acquisition more challenging and costly.
- Customer Churn: A history of negative experiences directly correlates with increased customer churn, impacting long-term revenue.
Frontier's customers, primarily leisure travelers, exhibit extreme price sensitivity. This means they readily switch to competitors offering even slightly lower fares. In 2024, the airline's continued reliance on aggressive low-price strategies directly empowers these consumers, as they can easily find comparable or cheaper options from numerous other carriers.
The proliferation of online travel agencies and flight comparison sites in 2024 means customers can effortlessly compare prices across airlines, including Frontier. This transparency intensifies price competition, limiting Frontier's ability to command premium pricing for its basic services.
While price is a key driver, poor customer experiences, such as frequent delays or cancellations, significantly impact loyalty. In 2023, operational issues remained a primary detractor from customer satisfaction across the airline industry, as noted in studies like the J.D. Power North America Airline Satisfaction Study, directly influencing customer choices and bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Frontier Airlines | Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High reliance on low base fares. | Very High. Customers readily switch for lower prices. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous ULCCs and basic economy fares from legacy carriers. | High. Easy to find comparable or cheaper options. |
| Online Comparison Tools | Widespread use of OTAs and comparison sites. | Very High. Instant price transparency and comparison. |
| Service Quality Perception | Negative experiences erode loyalty. | Moderate to High. Poor service can override price for some. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Frontier Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Frontier Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape within the airline industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive instantly upon purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Frontier Airlines operates within the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) sector, a space defined by fierce price competition. Airlines such as Spirit and Allegiant are direct rivals, frequently engaging in fare wars on overlapping routes to capture budget-conscious leisure travelers. This aggressive pricing strategy is fundamental to attracting and retaining customers in this segment.
Legacy carriers are increasingly adopting strategies that directly challenge Frontier's low-cost model. For instance, in 2024, major airlines like United and American continued to expand their basic economy offerings, often unbundling services like seat selection and checked baggage. This strategy allows them to compete on price, diluting Frontier's primary advantage.
This trend means Frontier isn't just competing with other ultra-low-cost carriers (ULCCs). It also faces pressure from established airlines that can leverage their vast networks, frequent flyer programs, and brand recognition. This broader competitive landscape can make it harder for Frontier to maintain its price leadership and customer loyalty solely on cost.
Frontier Airlines operates in a highly competitive landscape where route overlap is a significant challenge, with many of its routes directly contested by major carriers like Southwest, Delta, and United. This intense competition necessitates a keen focus on capacity management to ensure profitability.
Effective capacity management involves strategic adjustments, such as reducing flights on less busy days and concentrating resources on more lucrative 'trunk routes.' For instance, in 2024, airlines like Frontier have been actively adjusting their schedules to optimize load factors, a critical metric in the ultra-low-cost carrier model.
Brand Loyalty vs. Price Sensitivity
Frontier Airlines faces a constant battle between fostering brand loyalty and navigating the price sensitivity of its core customer base. While programs like the Unlimited Companion Travel Benefit aim to cultivate repeat business, the ultra-low-cost carrier model inherently attracts price-conscious travelers. This means that even loyal customers can be tempted away by slightly lower fares from rivals, making sustained loyalty a significant challenge.
The competitive landscape for Frontier is intensified by the fact that many of its customers prioritize the lowest possible ticket price. In 2024, the average domestic airfare in the U.S. saw fluctuations, but the demand for budget options remained strong. For instance, reports indicated that a substantial percentage of travelers considered price the primary factor in their booking decisions, underscoring the delicate balance Frontier must strike.
- Loyalty Programs: Frontier's 'Discount Den' and 'Unlimited Companion Pass' aim to build a loyal base, but their effectiveness is tested by competitor pricing.
- Price Sensitivity: The majority of Frontier's target demographic actively seeks the lowest fares, making them susceptible to switching for even minor savings.
- Perceived Value: Frontier must offer value beyond the base fare, such as convenient seating options like 'Upfront Plus', to retain customers in a highly competitive market.
- 2024 Market Dynamics: The ongoing competition among ultra-low-cost carriers and legacy airlines offering basic economy fares puts continuous pressure on Frontier's pricing strategy and loyalty initiatives.
Financial Performance and Strategic Adjustments of Competitors
The competitive rivalry within the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) segment is intensely shaped by the financial performance and strategic adjustments of key players. For instance, Spirit Airlines, a major competitor, filed for bankruptcy in mid-2023 and subsequently underwent significant capacity contractions, impacting the overall market dynamics. This move, alongside other airlines reducing their capacity, reflects a broader industry response to economic headwinds and a drive for greater profitability.
Frontier Airlines itself has implemented capacity cuts and is actively optimizing its route network. These actions are not isolated but are indicative of a sector-wide effort to navigate economic uncertainty and improve financial health. The need for such adjustments underscores the highly dynamic and responsive nature of the competitive environment, where airlines must continually adapt their strategies to maintain viability and achieve profitability amidst fluctuating market conditions.
- Spirit Airlines' Bankruptcy Filing: Spirit Airlines, a significant competitor to Frontier, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in June 2023, a move that signaled considerable financial distress within the ULCC sector.
- Capacity Adjustments: Following its bankruptcy filing, Spirit began contracting its capacity. This reduction in available seats by a major rival directly alters the competitive supply in the market.
- Industry-Wide Uncertainty: The strategic moves by both Spirit and Frontier, including Frontier's own capacity cuts and route optimization efforts, are responses to pervasive economic uncertainty impacting the airline industry.
- Focus on Profitability: The competitive landscape is characterized by a heightened focus on achieving profitability, forcing airlines like Frontier to make strategic adjustments to their operations and network planning.
Frontier Airlines faces intense rivalry from other ultra-low-cost carriers (ULCCs) like Spirit and Allegiant, who frequently engage in price wars. Legacy carriers are also intensifying competition by expanding their basic economy offerings, directly challenging Frontier's low-cost advantage.
In 2024, the airline industry saw continued pressure on pricing, with many travelers prioritizing cost. For example, domestic airfare fluctuations meant that even small savings could sway customer loyalty. Frontier's strategy to build loyalty through programs like the Unlimited Companion Travel Benefit is constantly tested by competitors' aggressive pricing.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by significant industry events. Spirit Airlines' mid-2023 bankruptcy filing and subsequent capacity reductions illustrate the financial pressures and strategic adjustments occurring within the ULCC sector. Frontier itself has responded with capacity cuts and route optimizations to improve profitability amidst this dynamic environment.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitors | Competitive Tactics | 2024 Market Impact |
| ULCC | Spirit Airlines, Allegiant Air | Price Wars, Fare Matching | Continued pressure on ticket prices, market share battles. Spirit's capacity adjustments influenced supply. |
| Legacy Carriers | Southwest Airlines, Delta Air Lines, United Airlines, American Airlines | Basic Economy Expansion, Unbundling Services | Dilution of ULCC price advantage, increased competition on price-sensitive routes. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For short to medium distances within the United States, driving a car is a strong substitute for flying, particularly impacting Frontier Airlines' customer base. The convenience of door-to-door service and the ability to carry more luggage without extra fees often outweigh the time savings of air travel for leisure trips. In 2024, the average cost of gasoline remained a factor, but the overall expense of driving for a family or group, including accommodation and meals, can still be more economical than four separate airline tickets, especially when Frontier’s ancillary fees are considered.
While less common for long hauls in the U.S. than in other regions, bus and rail services can still act as substitutes for Frontier Airlines, especially on shorter routes or for travelers prioritizing cost savings. For example, Amtrak's Acela service offers a premium rail option on the Northeast Corridor, directly competing with airlines on that busy segment. An increase in the frequency or a decrease in the price of these alternative transport modes could certainly siphon off some of Frontier's price-sensitive customer base.
The increasing prevalence of virtual communication and the normalization of remote work, significantly boosted by the COVID-19 pandemic, directly challenge the necessity of certain types of travel. While Frontier's core business is leisure, a societal move towards virtual interactions can subtly diminish the perceived need for air travel overall, particularly for shorter, less essential trips.
Alternative Vacation Options
For leisure travelers, a wide array of vacation alternatives exists beyond traditional air travel. Options like staycations, cruises, and road trips offer different experiences that can appeal to a broad segment of the market.
These alternatives can often be perceived as more budget-friendly or less hassle, particularly when travelers are mindful of increasing airfare costs or potential disruptions in air travel. For instance, in 2024, many consumers continued to explore domestic travel options, with road trips and local getaways seeing sustained popularity.
The appeal of these substitutes is amplified by factors such as the desire for more control over travel plans and the potential for unique, localized experiences. This broadens the competitive landscape for airlines like Frontier, as travelers may opt out of flying altogether.
Key alternative vacation options include:
- Staycations: Exploring local attractions and amenities, reducing travel time and costs.
- Cruises: Offering all-inclusive packages and diverse destinations without the need for multiple flights.
- Road Trips: Providing flexibility and the opportunity to discover new places at one's own pace.
Emerging Travel Technologies
Future transportation technologies, though currently in early stages, present a potential long-term threat of substitution for airlines like Frontier. The expansion of high-speed rail networks, for instance, could offer a competitive alternative for shorter routes, directly impacting passenger volume. Similarly, advancements in autonomous vehicle technology might eventually provide a convenient ground-based substitute for certain travel segments.
While these emerging options are not an immediate challenge for Frontier's current operations, the ongoing innovation in ground transportation warrants monitoring. A significant shift in consumer preference towards these alternatives, driven by factors like cost, convenience, or environmental concerns, could gradually erode demand for short and medium-haul flights over time.
- High-Speed Rail Expansion: Continued investment in high-speed rail infrastructure, particularly in densely populated corridors, could offer a viable alternative to short-haul flights. For example, the California High-Speed Rail project aims to connect major cities, potentially diverting some air travel.
- Autonomous Vehicle Development: As autonomous vehicle technology matures and becomes more widespread, it could offer a more convenient and potentially cost-effective door-to-door travel option for individuals and small groups, impacting shorter trips.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Environmental consciousness and the desire for more integrated travel experiences could lead consumers to favor ground transportation options that offer greater flexibility and a potentially lower carbon footprint compared to air travel.
The threat of substitutes for Frontier Airlines is significant, primarily from ground transportation like driving and rail, especially for shorter routes. In 2024, the persistent cost of gasoline, while a factor, still made driving a viable option for families and groups when compared to multiple airline tickets, particularly when Frontier's numerous ancillary fees are factored in. Furthermore, the growing acceptance of remote work and virtual communication subtly reduces the perceived need for some business and leisure travel, impacting airlines across the board.
Alternative vacation choices, such as staycations, cruises, and road trips, also present a strong substitute threat. These options are often viewed as more budget-friendly and less complicated than flying, especially as airfare costs fluctuate. In 2024, domestic travel, including road trips, maintained its popularity, indicating a consumer preference for flexibility and local exploration over air travel for certain segments.
Emerging technologies like high-speed rail and autonomous vehicles pose a longer-term substitution risk. Continued investment in high-speed rail corridors, like the California High-Speed Rail project, could divert significant passenger volume from short-haul flights. As autonomous vehicles mature, they may offer a more convenient and cost-effective door-to-door alternative for shorter trips, potentially impacting Frontier's market share.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Frontier Airlines | 2024 Relevance |
| Driving (Personal Vehicle) | High for short to medium distances; offers convenience and luggage flexibility. | Gasoline prices remained a consideration, but overall trip cost for groups often competitive with airfare + fees. |
| Bus and Rail Services | Moderate, especially on specific corridors (e.g., Northeast Corridor for Amtrak). | Price and frequency adjustments can attract cost-sensitive travelers. |
| Virtual Communication/Remote Work | Subtle but growing; reduces necessity for some travel. | Normalization of remote work continues to influence travel demand patterns. |
| Alternative Vacations (Staycations, Cruises, Road Trips) | High for leisure travelers; offers different experiences and perceived value. | Sustained popularity of domestic travel and road trips in 2024. |
| Future Technologies (High-Speed Rail, Autonomous Vehicles) | Low currently, but potential for significant long-term impact. | Ongoing infrastructure development and technological advancements warrant monitoring. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Frontier Airlines is significantly mitigated by the exceptionally high capital requirements inherent in the airline industry. Launching a new airline demands massive upfront investment, encompassing the acquisition or leasing of aircraft, the establishment of maintenance infrastructure, and the creation of essential operational support systems. For instance, a new wide-body aircraft can cost upwards of $300 million, and even a narrow-body jet, like those in Frontier's Airbus A320 family, represents a significant outlay.
These substantial financial barriers make it exceedingly difficult for new companies to enter the market and compete effectively. Even with a focus on a low-cost model, the sheer scale of initial funding needed for fleet, technology, and regulatory compliance acts as a formidable deterrent. This financial hurdle ensures that only well-capitalized entities can realistically consider entering the airline sector, thereby protecting existing players like Frontier from widespread new competition.
The airline industry faces significant regulatory hurdles, including stringent safety standards and operational requirements mandated by aviation authorities like the FAA. For instance, in 2024, airlines must adhere to evolving regulations concerning emissions and noise pollution, adding to compliance costs. These rigorous licensing, certification, and approval processes are complex and time-consuming, creating a substantial barrier for potential new entrants seeking to establish operations.
Securing desirable airport slots at congested airports presents a significant hurdle for new airlines like Frontier. Established carriers often possess preferential access, making it difficult for newcomers to establish competitive route networks, particularly at major hubs. For instance, in 2024, major airports like Denver International Airport (DEN), a key hub for Frontier, often operate at near-full capacity, with slot availability being a critical constraint.
Brand Recognition and Customer Trust
Brand recognition and customer trust present a significant barrier for new entrants in the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) market, even for price-sensitive travelers. Frontier Airlines, for instance, has cultivated a loyal customer base built on its established reputation for affordability.
New airlines would face substantial marketing expenses to build comparable brand awareness and convince consumers of their reliability and value proposition. For example, in 2023, the airline industry saw significant marketing spend, with major carriers investing millions to maintain and grow their market share.
- Established Brand Loyalty: Frontier has built trust over years of operation, making it difficult for newcomers to sway price-conscious customers.
- High Marketing Costs: New entrants must allocate considerable resources to marketing campaigns to build recognition and a positive reputation.
- Customer Trust Factor: Beyond price, customers value reliability and service, areas where established airlines like Frontier have a proven track record.
- ULCC Segment Competition: Even within the ULCC space, competition is fierce, requiring new players to offer a compelling and differentiated offering.
Intense Competition from Existing Players
The airline industry, especially the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) segment, is already saturated with intense competition. New entrants would immediately face aggressive pricing strategies and capacity adjustments from established players like Southwest Airlines and Spirit Airlines, making market penetration and profitability a significant challenge.
Established ULCCs and even legacy carriers offering competitive fares create a formidable barrier. For instance, in 2024, the average domestic airfare in the US remained a key battleground, with ULCCs constantly adjusting prices to capture market share.
- High Price Sensitivity: ULCC customers are primarily driven by price, meaning new entrants must offer significantly lower fares to attract them.
- Established Brand Loyalty: Existing carriers have built customer bases and loyalty programs that are difficult for newcomers to overcome.
- Economies of Scale: Larger airlines benefit from economies of scale in purchasing, maintenance, and operations, allowing them to undercut smaller competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Frontier Airlines is low due to immense capital requirements, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the difficulty in securing airport slots. Established brand loyalty and intense competition within the ULCC segment further deter newcomers.
For example, in 2024, the cost of a new narrow-body aircraft like the Airbus A320neo, a staple for ULCCs, can exceed $100 million, alongside substantial operational and certification expenses. Securing prime airport slots at hubs like Denver International Airport (DEN) is also a major challenge, as capacity is often maximized by incumbents.
| Barrier | Description | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for aircraft, infrastructure, and operations. | New narrow-body aircraft cost: ~$100+ million. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, safety standards, and compliance. | Ongoing compliance with evolving emissions standards. |
| Airport Slots | Limited access to desirable gates and takeoff/landing times at busy airports. | Major hubs like DEN operate near full capacity. |
| Brand & Trust | Building customer loyalty and a reputation for reliability. | Significant marketing investment required to compete. |
| Existing Competition | Intense price competition and capacity from established ULCCs. | Average domestic airfare remains a critical battleground. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Frontier Airlines Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of public financial filings, industry-specific market research reports, and news articles detailing competitor strategies and market trends.
We leverage data from airline industry trade publications, government aviation statistics, and company investor relations disclosures to comprehensively assess the competitive landscape.
