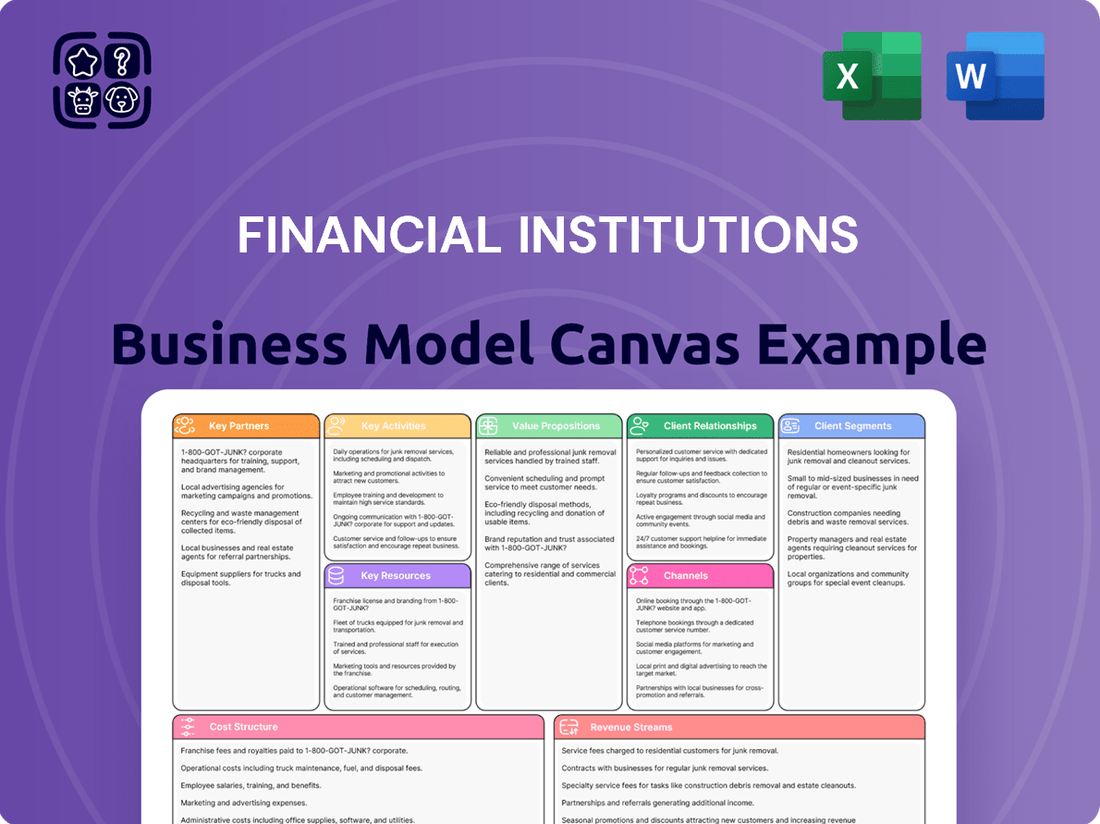
Financial Institutions Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Financial Institutions Bundle
Unlock the full strategic blueprint behind Financial Institutions’s innovative business model. This detailed Business Model Canvas reveals how they attract customers, generate revenue, and manage costs to achieve market dominance. It’s an essential tool for anyone seeking to understand their competitive edge.
Dive deeper into Financial Institutions’s operational genius with the complete Business Model Canvas. This professionally crafted document offers a crystal-clear view of their value proposition, key resources, and customer relationships, providing actionable insights for strategic growth.
See exactly how Financial Institutions constructs its success with our comprehensive Business Model Canvas. From identifying crucial partnerships to outlining revenue streams, this downloadable resource is perfect for strategic planning and competitive analysis.
Gain exclusive access to the complete Business Model Canvas that maps Financial Institutions’s pathway to profitability. This ready-to-use document is invaluable for business students and analysts eager to learn from industry leaders.
Transform your understanding of Financial Institutions’s market strategy with the full Business Model Canvas. Whether you're validating an idea or performing a competitive deep-dive, this template consolidates all essential strategic components.
Partnerships
Financial institutions are increasingly forging crucial partnerships with technology providers, particularly FinTech companies. These collaborations are instrumental in developing and implementing cutting-edge digital banking solutions, bolstering cybersecurity defenses, and leveraging advanced data analytics tools. By integrating these technologies, banks can significantly enhance their service delivery to customers.
The drive for improved operational efficiency is a major catalyst for these tech partnerships. For instance, in 2024, many financial firms invested heavily in cloud-based infrastructure and AI-powered customer service platforms, streamlining back-office operations and reducing processing times. These advancements directly contribute to a more agile and responsive business model.
Ensuring robust security for customer data and financial transactions is paramount in today's digital world. Partnerships with cybersecurity specialists provide access to state-of-the-art threat detection and prevention systems. Reports from 2024 indicate a substantial rise in sophisticated cyberattacks, underscoring the critical need for these protective alliances.
These strategic technology alliances enable financial institutions to remain competitive and compliant in a rapidly evolving market. Access to specialized FinTech expertise allows them to innovate faster, meet growing customer expectations for digital convenience, and safeguard sensitive information, which is vital for long-term success.
Financial institutions forge critical alliances with regulatory bodies and specialized compliance firms. These partnerships are essential for navigating the complex and ever-changing landscape of financial regulations, a necessity highlighted by the increasing scrutiny in 2024. For instance, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) continues to update its guidance on digital assets and cybersecurity, requiring financial firms to actively engage with these authorities.
Collaborating with entities like the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) or consulting with firms that offer regulatory technology solutions ensures ongoing adherence to legal frameworks. This proactive approach helps financial businesses avoid hefty fines, such as the millions levied in past years for non-compliance, and critically, it bolsters customer confidence by showcasing a commitment to sound, ethical practices.
Financial institutions can forge powerful alliances with local businesses and community organizations. These collaborations can take many forms, such as co-marketing campaigns that introduce new products or services to a broader audience. For instance, a bank might partner with a popular local restaurant for a special offer tied to using their debit card, driving both foot traffic and card usage. In 2024, data suggests that businesses engaging in local partnerships saw an average of 15% increase in customer acquisition through referral programs.
Beyond marketing, these partnerships can involve offering preferred banking services to employees of local businesses or sponsoring community development projects. A credit union supporting a local youth sports league not only enhances its brand image but also gains visibility among families within that community. This strengthens community ties and can lead to organic customer growth through local referrals, a strategy that proved effective for many community banks throughout 2024.
These local alliances also significantly bolster a financial institution's corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts. By investing in and supporting the local ecosystem, banks demonstrate a commitment that resonates deeply with consumers. For example, a partnership focused on financial literacy workshops for underserved communities in 2024 not only provided valuable education but also positioned the institution as a caring and responsible corporate citizen, attracting socially conscious customers.
Syndication Partners for Loans/Investments
Engaging with other financial institutions for loan syndication and co-investment is crucial for expanding reach and managing risk. This collaborative approach allows institutions to participate in larger deals than they might handle alone, effectively sharing the credit exposure. For example, in 2024, the syndicated loan market continued to be a significant avenue for large-scale financing across various sectors.
Syndication partners enable a financial institution to significantly increase its lending capacity. By pooling resources, they can underwrite larger loans for major projects, such as infrastructure development or corporate acquisitions, which might otherwise be beyond their individual risk appetite or capital limits. This also provides a pathway to diversify investment portfolios by participating in a broader range of credit opportunities.
The benefits extend to clients as well, who gain access to substantial capital for their ventures through a single, streamlined process. This partnership model is particularly vital in 2024 for facilitating complex transactions that require significant funding. The global syndicated loan market saw robust activity, with major global banks actively participating in these syndications to deploy capital efficiently.
- Increased Lending Capacity: Allows participation in larger deals, such as the multi-billion dollar infrastructure projects financed through syndication in 2024.
- Risk Sharing: Distributes credit risk across multiple institutions, mitigating potential losses for any single lender.
- Portfolio Diversification: Provides access to a wider array of investment opportunities and industries.
- Enhanced Client Service: Enables clients to secure larger financing packages more readily.
Payment Network Providers
Financial institutions rely heavily on partnerships with major payment network providers such as Visa, Mastercard, and Zelle. These collaborations are fundamental for enabling efficient and secure transaction processing for their banking clients. By integrating with these established networks, banks can offer a comprehensive suite of payment solutions that are both convenient and universally accepted.
These alliances are critical for extending operational reach and significantly improving the overall customer experience. For instance, Visa reported processing 238.5 billion transactions in 2023, highlighting the sheer volume and importance of these networks in the global economy. Mastercard also saw substantial growth, processing over 144 billion transactions in the same year. Such partnerships allow banks to provide their customers with the ability to make payments seamlessly across a vast array of merchants and platforms.
- Visa: Facilitates global card payments, enabling banks to offer debit and credit card services.
- Mastercard: Similar to Visa, it provides the infrastructure for widespread card transaction processing.
- Zelle: Offers peer-to-peer payment services, allowing for quick and easy money transfers between individuals through participating banks.
Key partnerships for financial institutions are diverse, encompassing technology providers, regulatory bodies, local businesses, and other financial entities. These alliances are crucial for innovation, compliance, market reach, and risk management. In 2024, the emphasis remained on leveraging FinTech for enhanced digital services and robust cybersecurity measures.
What is included in the product
A structured framework that breaks down the core components of a financial institution's operations, including customer segments, value propositions, revenue streams, and cost structures.
It provides a visual representation of how a financial firm creates, delivers, and captures value, serving as a strategic tool for analysis and planning.
Addresses the complexity of financial services by providing a structured framework to pinpoint and resolve operational inefficiencies.
Offers a clear, visual map to identify and alleviate the common pain points in financial institution operations and strategy.
Activities
Consumer & Commercial Banking Operations are the bedrock of a financial institution. This involves the meticulous management and processing of a wide array of financial products, including checking and savings accounts, personal loans, auto loans, mortgages, and various credit lines for both individuals and businesses. For instance, in 2023, U.S. commercial banks reported total deposits exceeding $17 trillion, highlighting the sheer volume of this crucial activity.
These operations directly contribute to the bank's liquidity, enabling it to fund its lending activities and provide essential financial services that fuel economic growth within the community. The efficiency and reliability of these processes are paramount, as they directly impact customer satisfaction and the institution's overall reputation. By handling over 90% of all payment transactions in many economies, these operations are vital.
Developing, underwriting, and selling a wide array of insurance products is a core function. This includes property, casualty, life, and health insurance, catering to diverse client needs and risk profiles.
These activities are crucial for diversifying the company's product portfolio and offering comprehensive risk management solutions. For example, in 2024, the global insurance market saw continued growth, with premium volumes projected to rise, underscoring the demand for these services.
Underwriting involves meticulously assessing and pricing risk to ensure profitability and solvency. This careful evaluation is vital for maintaining the financial health of the institution.
Sales efforts focus on reaching and acquiring customers, building relationships, and distributing these insurance products effectively through various channels, contributing directly to revenue generation.
Investment management and advisory services are central to financial institutions, encompassing wealth management, portfolio advice, and capital stewardship for a diverse client base. These services are built on rigorous market analysis, sophisticated asset allocation strategies, and bespoke financial planning designed to meet specific client objectives.
For instance, in 2024, the global wealth management industry saw significant shifts, with assets under management in actively managed funds reaching trillions. Financial advisors leverage deep market insights and data analytics to craft personalized investment portfolios, aiming to optimize risk-adjusted returns for both individual and institutional clients.
The core activities involve meticulous research into market trends, economic indicators, and investment vehicles. This data-driven approach informs strategic asset allocation decisions, ensuring portfolios are aligned with each client's unique financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, crucial for navigating volatile market conditions.
Digital Platform Development & Maintenance
Financial institutions are heavily invested in the continuous development, updating, and securing of their digital platforms. This includes everything from online and mobile banking interfaces to sophisticated investment portals and insurance management systems. By prioritizing these activities, institutions ensure their customers have convenient, accessible, and highly secure digital channels to manage their finances. In 2024, the focus remains on enhancing user experience and bolstering cybersecurity measures to combat evolving threats.
The importance of these digital channels is underscored by customer adoption rates. For instance, a significant majority of banking transactions now occur digitally. In 2023, mobile banking app usage saw a substantial increase, with many institutions reporting over 70% of their customer base actively using mobile platforms. This trend is expected to continue, making robust digital platform development a non-negotiable key activity for retaining and attracting customers.
- Platform Evolution: Ongoing investment in new features and user interface enhancements for online and mobile banking, investment, and insurance platforms.
- Security Fortification: Implementing advanced cybersecurity protocols and regular vulnerability assessments to protect sensitive customer data and financial assets.
- Performance Optimization: Ensuring platforms are fast, reliable, and scalable to handle increasing user traffic and transaction volumes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adapting platforms to meet evolving financial regulations and data privacy laws, such as those impacting digital identity verification.
Risk Management & Compliance
Risk management and compliance are paramount for financial institutions, involving the systematic identification, assessment, and mitigation of financial, operational, and regulatory risks. This proactive approach safeguards the institution's assets and reputation by embedding robust internal controls and conducting regular audits.
Staying informed about evolving regulations is critical; for instance, in 2024, financial institutions continued to navigate complex data privacy rules like GDPR and CCPA, alongside evolving anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) requirements. The cost of non-compliance can be substantial, with fines reaching millions for major breaches.
- Financial Risk Mitigation: Implementing hedging strategies and maintaining adequate capital reserves to buffer against market volatility and credit defaults.
- Operational Risk Management: Enhancing cybersecurity measures and business continuity plans to address potential disruptions from technology failures or cyberattacks. For example, the financial sector saw a significant increase in cyber threats in 2024, necessitating greater investment in defense.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to all legal and regulatory frameworks, including those related to consumer protection, fair lending, and financial reporting, to avoid penalties and maintain public trust.
Financial institutions engage in capital markets activities to facilitate trading, investment, and financing for clients. This includes underwriting securities, mergers and acquisitions advisory, and sales and trading of various financial instruments. In 2024, the global investment banking sector continued to see robust activity in M&A advisory, despite some economic headwinds.
These operations are vital for connecting capital-scarce entities with capital-rich investors, thereby fostering economic development. The complexity of these transactions requires deep market expertise and robust risk management frameworks. For instance, the IPO market, while fluctuating, remained a key area for capital raising in 2024.
Capital Markets Operations: Facilitating the issuance and trading of securities, providing M&A advisory, and engaging in structured finance. In 2024, global debt issuance remained strong, with corporate bonds playing a significant role in financing. The equity capital markets also saw considerable activity, particularly in technology and healthcare sectors.
Preview Before You Purchase
Business Model Canvas
The Financial Institutions Business Model Canvas you are previewing is the exact document you will receive upon purchase. This is not a sample or a mockup, but a direct representation of the comprehensive tool designed to map out your financial institution's strategy. Upon completion of your order, you will gain full access to this identical, professionally structured document, ready for immediate use and adaptation to your specific business needs.
Resources
Financial capital and reserves are the bedrock for any financial institution, acting as the fuel for all operations. This includes maintaining sufficient liquid assets, like cash and easily sellable securities, alongside robust equity and regulatory capital. These elements are critical for a bank to confidently extend loans, manage its obligations, and crucially, to absorb unexpected financial shocks.
As of early 2024, the global banking sector continues to navigate a complex economic landscape. For instance, the Basel III framework, fully phased in by many major economies, mandates higher capital ratios. Many large banks reported Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratios well above the regulatory minimums, with figures often exceeding 12%, demonstrating their capacity to withstand stress.
This robust capital base directly enables a financial institution to pursue its core business: lending. Without adequate reserves, a bank cannot underwrite loans effectively or manage the inherent risks associated with credit portfolios. For example, a bank with $10 billion in equity and reserves can support a much larger loan book than one with only $1 billion, directly impacting its revenue-generating potential.
A financial institution's skilled workforce is its backbone, encompassing everyone from advisors and underwriters to IT specialists. This human capital is absolutely critical for navigating complex financial landscapes, fostering robust client relationships, and ensuring smooth day-to-day operations. For instance, in 2024, the financial services sector continued to see high demand for data scientists and cybersecurity experts, reflecting the increasing reliance on technology and sophisticated analytics.
The expertise of a financial institution's team directly translates into the quality of services offered. Experienced financial advisors can provide tailored investment strategies, while proficient underwriters ensure sound risk assessment for loans. Reports from late 2023 indicated that banks with highly specialized lending teams often experienced lower default rates, underscoring the value of deep expertise.
Operational excellence is heavily reliant on this skilled human capital. From the efficiency of loan processing to the security of digital platforms, the capabilities of the workforce are paramount. By mid-2024, many institutions were investing heavily in training programs to upskill their employees in areas like regulatory compliance and digital banking, recognizing its direct impact on performance.
Robust IT systems are the backbone of modern financial institutions, ensuring seamless operations and secure data handling. In 2024, investments in technology infrastructure are critical, with many banks allocating significant portions of their budgets to upgrades and maintenance. These systems support everything from customer account management to complex trading algorithms.
Secure data centers are paramount for protecting sensitive financial information and maintaining customer trust. Financial firms are increasingly investing in advanced cybersecurity tools and protocols to defend against evolving threats. For instance, the global cybersecurity market for financial services was projected to reach over $30 billion in 2024, highlighting the industry's focus on security.
Specialized banking software and sophisticated trading platforms are essential for efficient service delivery and competitive market participation. These platforms enable real-time transaction processing, risk management, and the execution of trades, often across global markets. The adoption of cloud-based solutions is also accelerating, offering scalability and cost efficiencies.
Advanced cybersecurity tools are non-negotiable for financial institutions. The rise of sophisticated cyberattacks means continuous investment in areas like threat detection, data encryption, and identity management is crucial. Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA further mandates robust security measures, making cybersecurity a core component of the business model.
Branch Network & Physical Assets
Physical bank branches, offices for insurance agents, and investment service centers are crucial tangible touchpoints. These locations, along with a widespread ATM network, offer customers direct interaction and accessibility. For instance, in 2024, many large banks continued to optimize their physical footprint, closing some branches while investing in enhanced in-branch technology and customer service experiences to cater to evolving customer needs. The presence of these physical assets is vital for building trust and facilitating complex financial transactions or personalized advice that digital channels may not fully replicate.
Despite the surge in digital banking, a physical presence remains a significant differentiator. It’s where customers can receive in-depth personal consultations, crucial for major financial decisions like mortgages or investment planning. Moreover, these branches and offices contribute significantly to brand visibility and customer loyalty. Data from 2024 suggests that while foot traffic may have shifted, the strategic placement of branches in high-traffic areas and their role in community engagement continue to be valuable assets.
- Physical Locations: Bank branches, insurance offices, investment centers.
- ATM Network: Essential for convenient cash access and basic transactions.
- Customer Interaction: Facilitates personal consultations and complex service needs.
- Brand Visibility: Tangible presence reinforces brand trust and recognition.
- Strategic Importance: Balances digital convenience with the need for physical touchpoints.
Customer Data & Intellectual Property
Customer data and intellectual property are cornerstones for financial institutions, forming critical key resources. Proprietary customer information, such as transaction history and financial preferences, enables highly personalized service offerings and the development of targeted financial products. For instance, in 2024, many leading banks leveraged advanced analytics on customer spending habits to proactively offer tailored savings plans and investment opportunities. This data-driven approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also drives product adoption and revenue growth.
Intellectual property, encompassing proprietary financial models, unique investment strategies, and robust algorithms, provides a significant competitive edge. These intangible assets allow institutions to outperform competitors by identifying market inefficiencies or developing innovative financial solutions. Furthermore, a strong brand reputation, built on trust and consistent delivery of value, acts as a key resource, attracting new clients and retaining existing ones. In 2023, the global financial services industry saw significant investment in AI and machine learning for developing proprietary trading algorithms, highlighting the increasing importance of IP in this sector.
- Proprietary Customer Information Leveraged for personalized service and targeted product development.
- Financial Models & Algorithms Drive competitive advantage through unique analytical capabilities.
- Investment Strategies Differentiate offerings and potentially enhance returns.
- Brand Reputation Fosters trust and client loyalty, a critical intangible asset.
Intellectual property, including unique financial models and algorithms, offers a distinct competitive advantage. For instance, in 2024, many financial institutions intensified their focus on developing proprietary AI-driven trading strategies, aiming to capture market opportunities more effectively. This intellectual capital is crucial for innovation and maintaining market leadership.
Value Propositions
Financial institutions are increasingly offering comprehensive solutions, acting as a one-stop shop for banking, insurance, and investment management. This integrated approach simplifies financial planning for clients, saving them valuable time and effort. For instance, in 2024, many large banks have expanded their wealth management divisions, integrating advisory services with retail banking products to offer a more cohesive client experience.
This holistic offering provides unparalleled convenience and a unified view of an individual's financial landscape. By consolidating services under one trusted provider, customers can streamline their financial management, from everyday banking to long-term investment strategies. This convenience is a significant draw, especially for busy professionals and families navigating complex financial needs.
The market for integrated financial services is robust, with customer demand for convenience driving innovation. In 2024, reports indicate that customers who utilize multiple services from a single financial institution tend to have higher engagement and satisfaction rates compared to those who use separate providers for different needs.
Personalized client advisory is a cornerstone for financial institutions, offering tailored advice and customized product solutions through dedicated advisors. This approach ensures that financial strategies and product offerings, from investment portfolios to business financing, precisely match individual and business needs, fostering deeper client relationships.
In 2024, a significant trend saw financial firms investing heavily in advisor technology to enhance personalization. For example, client relationship management (CRM) systems are now integrated with AI-driven analytics to predict client needs. This allows advisors to proactively offer solutions, like customized retirement plans or tailored business loan packages, leading to improved client retention.
The effectiveness of personalized advice is evident in client satisfaction and asset growth. Studies from early 2024 indicate that clients receiving personalized financial guidance are 30% more likely to increase their investment with the institution compared to those receiving generic advice. This emphasis on a personal touch builds trust and drives long-term financial success for both the client and the institution.
Secure & Reliable Financial Services are the bedrock of any financial institution's value proposition. In 2024, this translates to safeguarding client assets and sensitive data through advanced cybersecurity protocols and by strictly adhering to evolving regulatory frameworks. For instance, the global cybersecurity market is projected to reach $345.4 billion by 2026, highlighting the significant investment financial institutions are making in this area to maintain trust.
This unwavering commitment to security and compliance directly fosters client trust and confidence, which is absolutely critical in the financial sector. Banks and investment firms that demonstrate robust data protection and regulatory adherence, such as those meeting GDPR or CCPA standards, often see higher customer retention rates. In fact, a 2023 survey indicated that over 70% of consumers consider data security a primary factor when choosing a financial provider.
Convenient Access & Digital Innovation
Financial institutions are increasingly prioritizing convenient access and digital innovation to meet evolving customer expectations. This approach blends the reliability of physical branches and ATMs with the seamlessness of advanced digital platforms, offering a flexible banking experience. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of banking transactions, estimated to be over 80%, were conducted through digital channels, highlighting the growing reliance on these innovations.
This hybrid model ensures customers can manage their finances anytime and anywhere, catering to a wide range of preferences and needs. The digital push isn't just about convenience; it’s also about enhancing security and personalization. Banks are investing heavily in AI and machine learning to offer tailored financial advice and fraud detection, with global spending on AI in banking projected to reach tens of billions by 2024.
- Digital Channels Dominance: By 2024, digital channels are handling the majority of banking transactions, reflecting a clear shift in customer behavior.
- Investment in AI: Financial institutions are significantly increasing their investments in artificial intelligence to improve customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Customer-Centricity: The focus is on providing flexible access points, combining physical and digital touchpoints to cater to diverse customer preferences.
- Enhanced Security: Digital innovation includes robust security measures, with advancements in biometric authentication and real-time fraud monitoring becoming standard.
Community-Focused & Local Expertise
Financial institutions that prioritize community focus and local expertise build a powerful value proposition. This means having a deep understanding of what makes a specific geographic area tick, its economic drivers, and the unique needs of its residents and businesses. By tailoring services and actively participating in local initiatives, these institutions foster a sense of trust and loyalty that goes beyond transactional banking.
This commitment translates into tangible benefits for the community. For example, a bank actively supporting local small businesses might offer specialized lending programs or workshops. In 2024, data indicated that community banks, often characterized by their local focus, continued to outperform larger national banks in terms of customer satisfaction, with many reporting Net Promoter Scores above 50, a significant indicator of strong customer loyalty and advocacy.
- Deep Understanding of Local Market Dynamics: Institutions leverage granular data on local employment trends, industry concentrations, and demographic shifts to inform their product development and lending strategies.
- Commitment to Supporting Community Growth: This is demonstrated through initiatives like sponsoring local events, offering financial literacy programs in schools, and partnering with local non-profits.
- Accessible Services: Maintaining a visible branch presence or offering robust digital tools that cater to local user preferences ensures ease of access for all community members.
- Building Strong Community Ties: Local expertise allows for more personalized advice and support, fostering long-term relationships that are mutually beneficial.
Financial institutions are increasingly offering comprehensive, integrated solutions, simplifying financial planning and providing a unified view of a client's financial landscape. This holistic approach, driven by customer demand for convenience, fosters deeper engagement and higher satisfaction rates. In 2024, many institutions expanded wealth management services, embedding advisory capabilities within retail banking to create a more cohesive client experience.
Customer Relationships
Financial institutions are increasingly focusing on building lasting connections by offering dedicated financial advisors and relationship managers. This personalized approach ensures clients receive tailored guidance, fostering trust and loyalty. For instance, many wealth management firms reported that over 60% of their new client acquisition in 2024 was driven by referrals from existing clients who valued this direct, supportive relationship.
Personalized consultations are key to understanding and addressing individual financial goals. This often involves regular check-ins and proactive advice, especially as clients' needs change. A survey of retail banking customers in early 2025 revealed that 75% of respondents felt more confident in their financial decisions when they had a dedicated point of contact who understood their personal circumstances.
Financial institutions are increasingly focusing on digital self-service to enhance customer relationships. Robust online and mobile platforms allow customers to independently manage accounts, perform transactions, and access crucial information. This digital empowerment offers unparalleled convenience and control, a significant draw for today's digitally native consumers.
By providing these self-service options, banks and credit unions can significantly reduce operational costs associated with traditional in-branch or phone support. For instance, digital channels can handle a vast majority of routine inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex issues. This efficiency translates directly to better resource allocation and improved customer experience.
To complement self-service, institutions are integrating digital support channels such as AI-powered chatbots and comprehensive Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) sections. These tools offer instant assistance, answering common queries 24/7 without human intervention. This dual approach of self-service and readily available digital support fosters stronger, more responsive customer relationships.
In 2024, customer expectations for seamless digital interactions continue to rise. A significant percentage of banking transactions are now conducted digitally, highlighting the critical need for intuitive and efficient self-service portals. Institutions that excel in this area are likely to see higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Financial institutions are increasingly adopting proactive communication strategies to deepen client relationships. This involves regularly informing clients about evolving market trends, such as the projected 4.5% growth in global wealth management assets in 2024, and introducing new product offerings designed to meet changing investment needs.
By providing access to financial literacy resources, like educational webinars and articles on topics such as sustainable investing which saw a 15% increase in investor interest in early 2024, firms position themselves as trusted advisors. This approach not only keeps clients engaged but also empowers them with the knowledge to make more informed financial decisions, fostering loyalty.
Community Engagement & Local Presence
Financial institutions are increasingly prioritizing community engagement to build deeper connections with their customer base. This approach goes beyond simple banking services, focusing on creating a tangible local presence that resonates with individuals and businesses alike. By actively participating in community events and offering sponsorships, these institutions demonstrate a commitment that fosters trust and loyalty, reinforcing their role as integral parts of the local economy.
The impact of this strategy can be seen in customer retention and acquisition. For instance, banks that invest in local initiatives often report higher customer satisfaction and a stronger brand image within their operating regions. This localized approach helps differentiate them in a competitive market, making them the preferred choice for financial services.
- Local Branch Interactions: Many customers still value face-to-face interactions. In 2024, a significant portion of banking customers, particularly in rural areas, continue to rely on physical branches for personalized service and complex transactions.
- Community Events and Sponsorships: Supporting local events, from school fairs to business expos, enhances brand visibility and goodwill. Data from 2024 suggests that sponsorships in arts and community development programs yield higher positive sentiment compared to purely commercial advertising for financial institutions.
- Strengthening Local Bonds: Commitment to local communities translates into stronger customer relationships. A 2024 survey indicated that customers are more likely to remain with a financial institution that actively contributes to their local area's well-being.
- Beyond Financial Transactions: Positioning the institution as a community partner, not just a service provider, builds enduring loyalty. This human-centric approach is crucial for long-term customer retention in the evolving financial landscape.
Problem Resolution & Complaint Handling
Financial institutions must establish efficient and empathetic processes for addressing customer inquiries, issues, and complaints promptly. In 2024, a significant driver of customer retention for banks was effective complaint resolution, with studies indicating that companies excelling in this area saw an average 10% increase in customer loyalty.
Effective problem resolution reinforces trust and satisfaction, turning potentially negative experiences into opportunities to demonstrate commitment to customer service. For example, a major retail bank reported in early 2025 that resolving customer complaints within 24 hours led to a 15% higher Net Promoter Score (NPS) compared to those taking longer.
- Speed of Resolution: Aim to resolve customer issues on first contact whenever possible.
- Empathy and Understanding: Train staff to actively listen and show genuine concern for customer problems.
- Clear Communication Channels: Offer multiple, easily accessible channels for customers to voice concerns.
- Feedback Loop for Improvement: Utilize complaint data to identify systemic issues and improve services.
Financial institutions are increasingly focusing on building lasting connections through personalized advice and digital self-service. Proactive communication, community engagement, and efficient problem resolution are key to fostering trust and loyalty. In 2024, customer expectations for seamless digital interactions and responsive support continued to shape these relationships.
| Customer Relationship Strategy | Description | 2024/2025 Data/Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Advice | Dedicated advisors and relationship managers offer tailored guidance. | 60% of new client acquisition in wealth management driven by referrals in 2024. |
| Digital Self-Service | Robust online and mobile platforms for account management and transactions. | 75% of retail banking customers in early 2025 felt more confident with a dedicated contact. |
| Proactive Communication | Informing clients about market trends and new products. | 15% increase in investor interest in sustainable investing in early 2024. |
| Community Engagement | Active participation in local events and sponsorships. | Banks investing in local initiatives report higher customer satisfaction and brand image. |
| Problem Resolution | Efficient and empathetic processes for addressing customer issues. | Resolving complaints within 24 hours led to a 15% higher NPS for a major retail bank in early 2025. |
Channels
Physical branch networks act as the bedrock for many financial institutions, serving as the primary touchpoint for customers seeking in-person transactions, personalized consultations, and the initiation of new accounts. This tangible presence fosters a sense of community trust and allows for a level of bespoke service that digital channels often can't replicate.
In 2024, the role of physical branches is evolving, with many institutions optimizing their footprint rather than abandoning it entirely. For instance, while the number of bank branches in the US has seen a steady decline over the past decade, the remaining branches are often repurposed to offer more advisory services and less transactional processing. This strategic shift acknowledges the continued importance of face-to-face interaction for complex financial needs.
The value proposition of a physical branch network extends beyond mere transactions. It's about building relationships and providing a secure, accessible hub for financial guidance. A significant portion of customers, particularly older demographics or those with intricate financial planning needs, still prioritize the ability to speak with a banker directly, reinforcing the branch's role in customer retention and acquisition.
Online banking and mobile applications are crucial components of a financial institution's business model, offering customers 24/7 access to manage accounts, conduct transactions, and even handle investments and insurance. This digital accessibility is paramount in today's fast-paced world, meeting the demand for convenience. In 2024, a significant portion of banking interactions, estimated to be over 80% for many institutions, occurred through these digital channels.
These platforms aren't just for basic banking; they increasingly integrate sophisticated features like personalized financial advice, budgeting tools, and seamless investment management. The adoption rate for mobile banking apps continues to climb, with global mobile banking users projected to surpass 2.5 billion by the end of 2024, highlighting their central role in customer engagement.
The efficiency gains for financial institutions are substantial, reducing the need for physical branch visits and lowering operational costs. For instance, many banks report a significant decrease in teller transactions as customers migrate to digital self-service options, a trend that accelerated through 2024.
Dedicated Relationship Managers/Advisors serve as a crucial direct human interaction channel, particularly for high-net-worth individuals, commercial clients, and those seeking investment management services. These personal contacts are designed to deliver highly tailored advice and cultivate deep, long-term relationships, fostering trust and loyalty.
In 2024, many private banks and wealth management firms continued to invest heavily in these channels. For example, a significant portion of advisory fees for firms like UBS and Morgan Stanley are directly tied to the personalized advice and ongoing management provided by relationship managers. These professionals often manage portfolios worth tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, demonstrating the immense value placed on this human touch in financial services.
Customer Service Call Centers
Customer service call centers function as the primary hub for financial institutions to manage phone inquiries, technical assistance, and general customer support. These centralized operations are crucial for providing immediate assistance and resolving a broad spectrum of customer issues, from account inquiries to transaction disputes.
In 2024, the demand for efficient customer service in financial institutions remained high, with many customers still preferring phone interactions for complex issues. The average handling time for customer service calls in the financial sector was around 7 minutes, highlighting the need for well-trained agents and robust support systems.
- Cost Efficiency: While essential, call centers represent a significant operational cost for financial institutions, often comprising a large portion of customer support budgets.
- Customer Satisfaction: Effective call center operations directly impact customer satisfaction and loyalty, with studies indicating that 75% of customers expect a response within 5 minutes for customer service inquiries.
- Technology Integration: The integration of AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants within call centers is a growing trend, aiming to handle routine queries and free up human agents for more complex problems. In 2024, many institutions invested heavily in these technologies.
- Data Collection: Call center interactions are a rich source of customer data, providing valuable insights into customer needs, pain points, and emerging trends, which can inform product development and service improvements.
Strategic Partnerships & Referrals
Financial institutions can significantly boost customer acquisition by cultivating strategic partnerships and referral programs. These collaborations leverage the trust and existing networks of third parties to introduce new clients. For instance, partnering with local businesses or real estate agents can tap into customer bases already seeking financial services related to property transactions.
Financial planners are another key group for referrals, as their clients often have diverse financial needs that a broader financial institution can fulfill. In 2024, many firms are actively seeking these synergistic relationships to expand their market reach. The effectiveness of these channels is often measured by the cost of acquiring a customer through a referral compared to other marketing efforts, with referral costs typically being lower.
- Leverage Local Business Tie-ins: Collaborate with businesses like car dealerships or home renovation companies for cross-promotional opportunities.
- Engage Real Estate Agents: Offer incentives for agents referring clients for mortgages or home equity loans.
- Build Financial Planner Networks: Establish referral agreements with independent financial advisors who can benefit from your institution's broader product suite.
- Track Referral Success: Implement systems to monitor the volume and quality of customers acquired through each partnership.
Strategic partnerships and referral programs are vital channels for customer acquisition, tapping into established networks to introduce new clients. For example, collaborations with real estate agents can directly link institutions with individuals needing mortgages or related financial products.
Financial planners also represent a significant referral source, as their clients often require a wider array of financial services. In 2024, many financial institutions actively pursued these alliances to broaden their market presence, recognizing that referral-based customer acquisition often yields a lower cost per customer compared to other marketing strategies.
| Partnership Type | Example Collaboration | Customer Acquisition Benefit | 2024 Trend Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real Estate | Mortgage referrals from agents | Direct access to home buyers | Increased mortgage originations through agent networks |
| Financial Planning | Referrals for investment management | Access to clients with diverse financial needs | Growth in wealth management AUM from advisor referrals |
| Local Businesses | Cross-promotion with car dealerships | Targeted client segments for auto loans | Higher conversion rates for specific loan products |
Customer Segments
Individual consumers represent a foundational customer segment for retail banking, primarily seeking essential financial tools like checking and savings accounts, mortgages, personal loans, and credit cards. Their financial decisions are often driven by a need for convenience, competitive interest rates, and dependable access to fundamental banking services to manage their day-to-day finances effectively. In 2024, the average savings account interest rate hovered around 0.46% APY, highlighting the importance of competitive rates for this group.
This segment relies heavily on accessible channels, whether physical branches or robust digital platforms, for transactions and account management. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 70% of banking customers reported using mobile banking apps, underscoring the demand for digital convenience. They look for banks that simplify their financial lives, offering user-friendly interfaces and responsive customer support for their personal banking needs.
Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) represent a crucial customer segment for financial institutions, often requiring a suite of commercial banking services. These enterprises typically need commercial loans for working capital or expansion, robust business checking accounts for day-to-day transactions, and sophisticated treasury management solutions to optimize cash flow. In 2024, the demand for these services remains high, with many SMBs actively seeking growth capital. For instance, a significant portion of the nearly 33 million SMBs in the United States are likely to be in the market for financing to support their operational needs and strategic growth initiatives.
Beyond core banking, SMBs also frequently require specialized insurance products to mitigate various business risks, from property damage to liability. They are looking for financial partners who can offer efficient digital tools to streamline their banking processes and provide access to growth capital, whether through traditional loans or alternative financing options. Tailored advice from financial professionals is also highly valued, as SMBs often lack dedicated internal finance departments and rely on external expertise to navigate financial planning and investment opportunities to manage their operations and fuel expansion.
High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIs) are a crucial customer segment for financial institutions, requiring highly specialized wealth management, investment advisory, and estate planning. These affluent clients, often defined by having investable assets of $1 million or more, seek personalized attention and expert guidance. As of late 2024, the global HNWI population surpassed 23 million individuals, collectively holding over $90 trillion in wealth, presenting a significant opportunity for institutions offering bespoke financial solutions and exclusive access to complex investment vehicles like private equity and hedge funds.
Commercial & Corporate Clients
Commercial and corporate clients represent a significant segment for financial institutions, often requiring sophisticated and tailored financial solutions. These are typically larger businesses and corporations that necessitate complex financing arrangements, such as syndicated loans, which involve multiple lenders. In 2024, the global syndicated loan market continued to be a vital source of capital for large corporations, facilitating mergers, acquisitions, and major capital expenditures.
These clients also demand robust treasury services to manage their cash flow, liquidity, and payment operations efficiently. Furthermore, comprehensive insurance solutions are crucial for risk mitigation, covering a wide range of potential business disruptions. Financial institutions catering to this segment focus on providing scalable solutions that can adapt to the evolving needs of these growing enterprises.
Key needs for commercial and corporate clients include:
- Complex Financing: Access to syndicated loans and large-scale credit facilities to fund major projects and expansions. For instance, in the first half of 2024, global syndicated loan issuance reached approximately $2.5 trillion, with a substantial portion directed towards corporate borrowers.
- Treasury and Cash Management: Efficient tools and services for managing international payments, foreign exchange, and optimizing working capital.
- Risk Management: Tailored insurance products, hedging strategies, and advisory services to protect against financial and operational risks.
- Strategic Partnerships: A desire for long-term relationships with financial institutions that can offer strategic financial advice and support business growth initiatives.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as endowments, foundations, and pension funds, represent a critical customer segment for financial institutions. These entities are not simply looking for returns; they are entrusted with managing vast sums of capital for the long-term benefit of their beneficiaries. This means they demand a high level of professional investment management and robust advisory services, with a keen focus on fiduciary responsibility.
Their investment objectives are fundamentally centered on long-term asset growth and capital preservation. Consequently, they require specialized portfolio management expertise tailored to their unique risk tolerances and time horizons. For instance, in 2024, many pension funds are navigating complex market conditions, seeking strategies that balance inflation hedging with growth potential.
- Fiduciary Duty: Institutions operate under a legal and ethical obligation to act in the best interest of their beneficiaries, demanding transparency and accountability from their financial partners.
- Long-Term Horizon: Investment strategies are typically designed over decades, not quarters, emphasizing sustainable growth and risk management.
- Specialized Expertise: They require deep knowledge in areas like alternative investments, liability-driven investing (LDI), and ESG integration.
Customer segments in financial institutions are diverse, ranging from individual consumers needing basic banking to sophisticated institutional investors managing vast assets. Each segment has unique requirements for products, services, and advisory support. Financial institutions must effectively identify and cater to these distinct needs to remain competitive and profitable.
Cost Structure
Personnel and employee salaries represent a significant portion of a financial institution's cost structure. This includes compensation for a wide range of roles, from high-earning bankers and advisors to essential IT staff, administrative personnel, and senior management.
Labor costs are inherently a primary expense for service-oriented businesses like financial institutions, as the delivery of financial services relies heavily on skilled human capital. For example, in 2024, the average salary for a financial advisor in the United States was approximately $96,500, with experienced professionals earning considerably more.
Furthermore, the technology infrastructure required to support modern financial services necessitates substantial investment in IT professionals, whose salaries can range from $80,000 for entry-level positions to over $150,000 for specialized cybersecurity experts.
The overall compensation packages, including base salaries, bonuses, and benefits, directly reflect the value and expertise of the workforce, making personnel costs a critical factor in profitability and operational efficiency.
Technology and infrastructure costs are a significant expense for financial institutions, covering everything from essential IT systems to advanced cybersecurity. In 2024, these expenditures are crucial for supporting digital banking platforms, cloud services, and robust data management. For instance, major banks are investing billions annually in technology upgrades to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. These investments are vital for maintaining competitiveness and ensuring the secure handling of sensitive financial data.
Branch and office operations represent a substantial cost for financial institutions, encompassing expenses like rent for physical locations, utilities to power them, ongoing maintenance, and security systems to protect assets and personnel. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to invest heavily in their branch networks, with the average cost of operating a single branch often running into hundreds of thousands of dollars annually, depending on size and location.
Maintaining this physical footprint is crucial for customer accessibility and serves as vital operational hubs for various services. While digital channels are growing, many customers still prefer in-person interactions for complex transactions or personalized advice, justifying these significant overheads.
The trend in 2024 saw some consolidation of smaller, less trafficked branches, but the overall cost structure related to office space and essential branch infrastructure remained a core component of a financial institution's budget. These costs are directly tied to the physical delivery of services and the operational backbone of the business.
Marketing & Sales Expenses
Marketing and sales expenses are crucial for financial institutions to gain visibility and attract clients. These include significant investments in advertising, promotional campaigns, and strengthening brand presence. For instance, in 2024, many leading banks allocated substantial budgets to digital marketing, with reports indicating a 15% year-over-year increase in spending on social media and search engine marketing to reach a wider audience.
These outlays are directly tied to customer acquisition and retention efforts across all service lines, from retail banking to wealth management. Sales commissions are a key component, directly incentivizing teams to bring in new business and maintain existing relationships. This focus on market penetration is vital for sustained growth in a competitive financial landscape.
Key components of these expenses include:
- Advertising & Promotions: Funds dedicated to campaigns across various media to highlight products and services.
- Branding Initiatives: Investments in building and maintaining a strong, recognizable brand identity.
- Sales Force Costs: Including salaries, commissions, and training for sales teams.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Technology and efforts to nurture and retain customer relationships.
Regulatory Compliance & Legal Fees
Financial institutions face significant costs to meet stringent regulatory requirements. These expenses include legal fees for counsel on compliance matters, costs for internal and external audits, and the substantial effort involved in preparing and submitting various compliance reports to governing bodies. For instance, in 2024, the global financial services industry is projected to spend billions on compliance, with a significant portion allocated to technology solutions and personnel dedicated to regulatory adherence.
Maintaining compliance is not just a cost center; it’s a critical investment that protects the firm from substantial penalties, litigation, and reputational damage. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines, license revocation, and a loss of customer trust. In 2023, fines levied against financial institutions for compliance breaches globally exceeded tens of billions of dollars, underscoring the financial imperative of robust compliance programs.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Expenses related to adhering to laws and industry standards.
- Legal Counsel: Fees paid to lawyers specializing in financial regulations and corporate law.
- Audits: Costs for internal and external audits to ensure adherence to regulations and financial reporting standards.
- Compliance Reporting: Expenditures on systems and personnel for generating and submitting regulatory reports.
Financial institutions incur substantial costs related to funding their operations and lending activities. These primarily include interest expenses paid on deposits, borrowed funds, and other debt instruments. For example, in 2024, the net interest margin remains a critical profitability driver, with many banks adjusting their rates in response to central bank monetary policies. The cost of capital directly impacts the institution's ability to offer competitive loan products and generate returns.
Operational costs encompass a broad range of expenses beyond personnel and technology, including things like transaction processing fees, data analytics tools, and the ongoing costs of managing complex financial instruments. For instance, the increasing reliance on real-time payment systems in 2024 necessitates investment in robust infrastructure and incurs associated transaction fees. These operational expenditures are vital for the smooth functioning of day-to-day business and the efficient execution of financial transactions.
| Cost Category | 2024 Estimates/Data | Key Components |
| Personnel Costs | Avg. Financial Advisor Salary: ~$96,500 (US) | Salaries, bonuses, benefits for all staff |
| Technology & Infrastructure | Billions invested annually by major banks | IT systems, cybersecurity, cloud services |
| Branch & Office Operations | Hundreds of thousands annually per branch (avg.) | Rent, utilities, maintenance, security |
| Marketing & Sales | 15% YoY increase in digital marketing spend (reports) | Advertising, promotions, CRM, sales commissions |
| Regulatory Compliance | Billions spent globally by financial services | Legal, audits, reporting, compliance technology |
| Funding Costs | Net Interest Margin critical driver | Interest on deposits, borrowings, debt |
| Operational Costs | Increasing due to real-time payment systems | Transaction processing, data analytics, instrument management |
Revenue Streams
Net interest income is the lifeblood of most financial institutions, representing the profit made from lending and borrowing activities. It's essentially the spread between what a bank earns on its assets, like loans and securities, and what it pays out on its liabilities, such as customer deposits. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to see significant net interest income, driven by higher interest rates. JPMorgan Chase reported its net interest income for the first quarter of 2024 was $23.9 billion, up substantially from the previous year, illustrating this core revenue stream's power.
Service charges and fees represent a crucial revenue stream for financial institutions, encompassing income generated from a wide array of banking services. These include everyday transactional charges like account maintenance fees, ATM usage fees, and wire transfer costs, alongside less predictable but often significant revenue from overdraft charges. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to rely on these fees, with overdraft fees alone contributing billions annually to their top lines, though regulatory scrutiny and consumer advocacy are increasingly influencing fee structures and volumes.
Insurance premiums are the fundamental revenue stream for SDN Insurance Agency, representing the money collected from clients for all the different insurance policies they offer. This income is crucial for the agency's core operations, allowing them to cover the costs associated with potential claims that policyholders might make and, importantly, to generate profit.
In 2024, the global insurance market continued its upward trajectory, with premiums for property and casualty insurance alone projected to reach approximately $2.9 trillion. For a company like SDN Insurance Agency, this means a significant opportunity to capture market share by offering competitive and comprehensive policy options.
Investment Management Fees
Investment management fees are a core revenue driver, typically calculated as a percentage of the total assets clients entrust to the firm, known as assets under management or AUM. This model directly aligns the firm's success with the growth of its clients' portfolios. For instance, in 2024, firms specializing in wealth and asset management, like Courier Capital and HNP Capital, heavily rely on this stream, demonstrating their value proposition in navigating financial markets.
- AUM-Based Fees: A common structure where fees are a percentage of the assets managed, often tiered based on AUM size.
- Performance Fees: Additional fees earned when investment performance exceeds a predetermined benchmark or hurdle rate.
- Crucial for Wealth Managers: This revenue stream underpins the profitability of firms focused on managing and growing client wealth.
- 2024 Market Context: The stability and growth of AUM fees in 2024 reflect investor confidence and the ongoing demand for professional investment guidance.
Loan Origination & Servicing Fees
Financial institutions generate revenue through loan origination fees, which are charges for processing new loans, including mortgages and credit lines. These fees are a crucial component of their revenue model, supplementing interest income and covering the upfront administrative burdens of underwriting and closing. For example, in 2024, origination fees on residential mortgages often ranged from 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount.
Servicing fees represent another significant revenue stream. These are ongoing charges for managing existing loans, which involve collecting payments, managing escrow accounts, and handling delinquencies. These fees are typically a percentage of the outstanding loan balance, providing a consistent revenue flow. In 2024, servicing fees for mortgage-backed securities often fell between 0.25% and 0.45% annually.
- Loan Origination Fees: Charges for setting up new loans, covering processing and underwriting costs.
- Servicing Fees: Ongoing revenue from managing existing loans, including payment collection and account administration.
- Diversification of Revenue: These fees provide income beyond interest, enhancing profitability and stability.
- Administrative Cost Coverage: Fees directly offset the expenses associated with lending operations.
Trading and investment gains are vital for financial institutions, encompassing profits from buying and selling securities like stocks, bonds, and derivatives. These activities can generate substantial returns, especially in volatile markets, but also carry inherent risks. For instance, in 2024, many investment banks saw significant gains from their trading desks, particularly in fixed-income and currency markets.
Commissions are another key revenue source, earned from facilitating transactions for clients, such as executing stock trades or selling financial products like mutual funds. These fees are typically a fixed amount per trade or a percentage of the transaction value. In 2024, online brokerages continued to attract a high volume of retail trades, contributing significantly to their commission revenue.
| Revenue Stream | Description | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Gains | Profits from buying and selling securities. | Investment banks reported strong trading revenues in Q1 2024, with many seeing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year in their markets divisions. |
| Commissions | Fees earned from facilitating client transactions. | Online brokerage platforms saw an average commission per trade decrease slightly in 2024 due to increased competition, but overall trading volumes remained robust. |
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The Financial Institutions Business Model Canvas is built upon a foundation of regulatory filings, internal financial statements, and extensive market research. These sources provide the critical data necessary to accurately define customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structures within the financial services industry.
