FibroGen Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
FibroGen Bundle
FibroGen faces significant competitive pressures, with the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers posing key challenges. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate the biopharmaceutical landscape. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore FibroGen’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
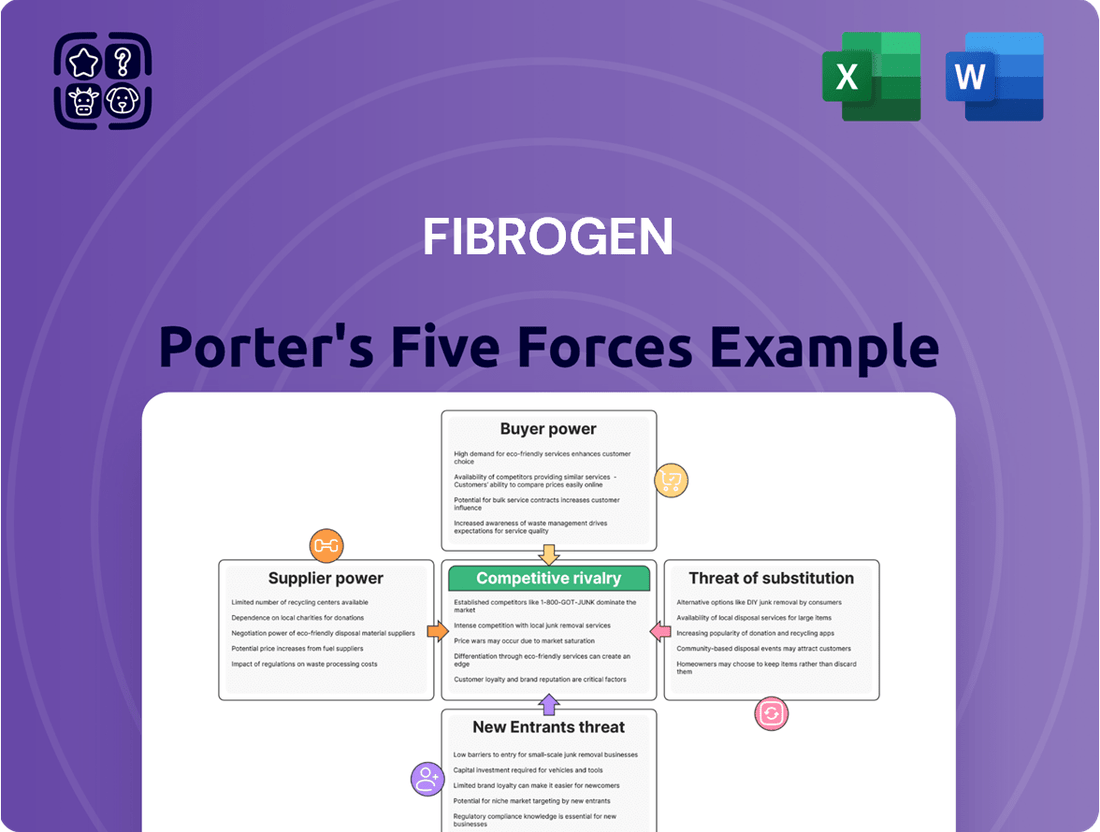
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The biopharmaceutical sector, including companies like FibroGen, frequently depends on a small group of specialized suppliers for essential components such as raw materials, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), and intricate manufacturing processes. This limited supplier pool grants these entities considerable influence, particularly when dealing with proprietary materials or specialized technological needs.
This concentrated supplier market was highlighted as a growing concern within the pharmaceutical industry, with projections indicating a substantial impact by 2025. For instance, the global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market, a key area for specialized services, was valued at approximately $170 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow, underscoring the importance of these supplier relationships.
FibroGen faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the exceptionally high costs associated with switching suppliers in the biopharmaceutical industry. These costs include rigorous validation, obtaining new regulatory approvals, and the inherent risk of production interruptions. For instance, changing a key supplier for an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) could necessitate an entirely new drug master file submission to regulatory bodies like the FDA, a process that can take months and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Suppliers possessing patents or proprietary technologies crucial for FibroGen's drug development and manufacturing wield significant bargaining power. This intellectual property necessitates licensing agreements or the costly pursuit of less effective alternatives for FibroGen. The biotech sector's rapid innovation, with a surge in R&D, amplifies the value of these unique supplier capabilities.
Supplier's Importance to FibroGen's Product Quality and Efficacy
The quality and consistency of raw materials are paramount for FibroGen's biologic therapies, directly influencing their safety and efficacy. Any lapse in supplier quality control can trigger significant regulatory hurdles, costly product recalls, and severe damage to FibroGen's reputation, underscoring a substantial reliance on dependable suppliers.
This inherent dependence grants suppliers considerable bargaining power, as FibroGen's operational integrity and market standing are intrinsically linked to the reliability of its supply chain.
- Impact on Product: Supplier material quality directly affects the safety and efficacy of FibroGen's biologic drugs.
- Risk of Compromise: Substandard materials can lead to regulatory problems, recalls, and reputational harm.
- Dependency Factor: FibroGen's reliance on consistent, high-quality inputs strengthens supplier leverage.
- Financial Implication: In 2023, the pharmaceutical industry saw increased scrutiny on supply chain integrity, with recalls often costing millions in lost revenue and remediation.
Limited Forward Integration Threat from Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward to compete directly with FibroGen is notably low. Developing and bringing a new drug to market requires immense capital, navigating complex regulatory pathways like FDA approvals, and possessing highly specialized scientific and commercial expertise. These significant barriers to entry in the pharmaceutical sector effectively deter most suppliers from attempting such a move.
These high barriers mean that suppliers are unlikely to become direct competitors. For instance, the average cost to develop a new drug from discovery to market approval in 2024 is estimated to be over $2 billion, a figure that is prohibitive for most entities not already established in the biopharmaceutical industry.
- High Capital Investment: Pharmaceutical R&D and commercialization demand billions in funding, a substantial barrier for potential supplier entrants.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating agencies like the FDA involves lengthy, expensive, and uncertain approval processes.
- Specialized Expertise: Success requires deep scientific knowledge, clinical trial management, and sophisticated marketing capabilities.
FibroGen faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers due to the specialized nature of raw materials and manufacturing processes in the biopharmaceutical sector. The high cost and complexity of switching suppliers, often involving extensive validation and regulatory re-approvals, solidify this supplier leverage. For example, changing a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) supplier can incur hundreds of thousands of dollars and months of regulatory work.
Suppliers holding patents or proprietary technologies essential for FibroGen's operations further enhance their influence. This dependence means FibroGen must often secure licensing agreements or seek less effective alternatives, a situation amplified by the rapid innovation characteristic of the biotech industry. The critical importance of consistent, high-quality inputs for drug safety and efficacy means any supplier quality lapse can lead to severe regulatory issues, recalls, and reputational damage.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward to become direct competitors to FibroGen is very low. The immense capital, complex regulatory navigation, and specialized scientific and commercial expertise required to bring a drug to market, estimated at over $2 billion in 2024, act as significant deterrents for most suppliers.
| Factor | FibroGen's Situation | Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Relies on a few specialized suppliers for critical components. | High |
| Switching Costs | High costs for validation, regulatory approval, and production continuity. | High |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers possess essential patents and unique capabilities. | High |
| Quality Dependence | Critical for drug safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance. | High |
| Forward Integration Threat | Very low due to high barriers to entry in drug development. | Low |
What is included in the product
FibroGen's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the presence of substitutes impacting its pharmaceutical market position.
Instantly identify competitive threats and opportunities within the FibroGen landscape, streamlining strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
FibroGen's primary customers are healthcare systems, hospitals, and government and private payers. These entities often buy drugs in substantial quantities, giving them considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. government, a major payer, continued to negotiate aggressively on drug prices, reflecting a broader trend of cost containment within the healthcare sector.
These consolidated buyers, particularly large insurance companies and national healthcare systems, wield significant bargaining power. Their ability to negotiate bulk discounts and favorable terms can heavily influence drug pricing strategies. This is amplified as employers, anticipating escalating health expenses, are increasingly pushing for lower pharmaceutical spending, directly impacting drug manufacturers like FibroGen.
Customers, particularly those managing chronic conditions like CKD anemia, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This heightened awareness of cost is driven by the increasing strain on global healthcare budgets, making long-term treatment affordability a critical concern.
The anemia treatment market, while projected for growth, faces persistent pricing challenges. For instance, in 2024, the global anemia treatment market was valued at approximately $40 billion, with ongoing negotiations and reimbursement policies directly impacting the effective price of therapies.
For chronic kidney disease (CKD) anemia, FibroGen’s roxadustat faces significant customer bargaining power due to a range of alternative treatments. These include established erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) and various iron preparations, offering patients and healthcare providers multiple choices.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by the presence of other hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors (HIF-PHIs), such as vadadustat and daprodustat. This availability of comparable treatments directly limits FibroGen's ability to dictate pricing, as customers can readily switch to more cost-effective or preferred alternatives.
Formulary Inclusion and Reimbursement Decisions
The bargaining power of customers, particularly in the pharmaceutical sector, is significantly influenced by formulary inclusion and reimbursement decisions. Hospital formulary committees and health insurance providers act as powerful gatekeepers, determining which drugs make it onto their preferred lists and at what price. For FibroGen, exclusion from these formularies can drastically curtail market access and dampen sales potential. For instance, in 2024, many insurers continued to tighten their formularies, demanding strong evidence of comparative effectiveness and cost-effectiveness before approving new treatments.
These committees wield considerable influence because their decisions directly impact patient access and physician prescribing habits. A drug not listed on a formulary often means higher out-of-pocket costs for patients or outright denial of coverage, making it less attractive. This dynamic places substantial pressure on pharmaceutical companies like FibroGen to demonstrate clear value propositions to these powerful customer groups.
Furthermore, the growing trend of direct-to-consumer (DTC) advertising for pharmaceuticals is beginning to shift some power towards individual patients. While still regulated, DTC campaigns can create demand that influences physician conversations and, indirectly, formulary considerations. This evolving landscape means FibroGen must navigate both institutional and individual customer preferences.
- Formulary Gatekeepers: Hospitals and insurers control drug access via inclusion on preferred drug lists.
- Reimbursement Leverage: Decisions on reimbursement levels directly impact a drug's affordability and market penetration.
- Market Access Barriers: Formulary exclusion can severely limit sales for pharmaceutical products.
- Evolving Patient Influence: Direct-to-consumer marketing is starting to empower individual patient demand.
Patient Advocacy and Awareness
While patients aren't direct purchasers of FibroGen's products, their influence is significant. Informed patients and advocacy groups can sway prescribing habits and reimbursement decisions by advocating for specific treatments or pushing back on high drug prices. This indirect pressure amplifies customer power, impacting healthcare providers and payers alike.
The growing strength of patient advocacy groups, particularly in the rare disease space where FibroGen operates, is a key trend. These groups are increasingly sophisticated in their lobbying efforts and their ability to mobilize public opinion. For instance, in 2024, several major patient advocacy organizations reported record levels of engagement and successful campaigns influencing policy decisions related to drug access and affordability.
- Increased Patient Engagement: Patient advocacy groups are becoming more organized and vocal, directly impacting market access and pricing discussions.
- Reimbursement Influence: Advocacy efforts can lead to payer decisions that either facilitate or restrict patient access to medications, a critical factor for FibroGen.
- Cost Awareness: Patients and their representatives are increasingly scrutinizing drug costs, creating pressure for more transparent and value-based pricing models.
FibroGen's customers, primarily large healthcare systems and payers, exert considerable bargaining power due to their purchasing volume and ability to negotiate pricing. In 2024, the ongoing focus on healthcare cost containment meant these entities actively sought discounts and favorable terms, directly impacting drug pricing strategies.
The availability of alternative treatments, including established ESAs and other HIF-PHIs, further strengthens customer leverage by providing viable options. This competitive landscape limits FibroGen's pricing flexibility, as customers can readily switch to more cost-effective or preferred therapies.
Formulary gatekeepers, such as hospital committees and insurance providers, significantly influence market access and pricing through their inclusion and reimbursement decisions. In 2024, many insurers tightened formularies, demanding strong evidence of value, which puts pressure on FibroGen to demonstrate clear benefits.
Patient advocacy groups are also increasingly influential, advocating for affordability and access, which indirectly impacts payer and provider decisions. This growing patient voice, amplified by direct-to-consumer marketing, adds another layer to customer bargaining power.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on FibroGen |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Systems & Hospitals | Bulk purchasing, formulary control | Negotiated discounts, market access restrictions |
| Payers (Insurers, Government) | Reimbursement decisions, cost containment focus | Pricing pressure, evidence of cost-effectiveness required |
| Individual Patients & Advocacy Groups | Price sensitivity, demand for affordability | Indirect influence on prescribing and payer policies |
Full Version Awaits
FibroGen Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete FibroGen Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. You're viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring no surprises. This comprehensive analysis is ready for immediate use, providing valuable insights into the industry's dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
FibroGen faces intense competition from established pharmaceutical giants boasting substantial R&D budgets and expansive commercial networks. These behemoths, with their diversified portfolios, can leverage existing market access and brand recognition to outmaneuver smaller players.
Companies such as AstraZeneca and Astellas Pharma, despite being FibroGen's partners for roxadustat in specific territories, also represent direct rivals in other therapeutic areas. For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical market reached an estimated $1.6 trillion, a testament to the scale and resources of these major players.
FibroGen's strategic focus on areas with high unmet medical needs, such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) anemia and oncology, naturally draws in formidable competition. This intense rivalry stems from numerous biopharmaceutical firms vying to pioneer groundbreaking treatments, driving substantial research and development expenditures industry-wide. For instance, the market for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is characterized by a pronounced unmet clinical need, fueling extensive research and development efforts from multiple players.
Competitive rivalry in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly for companies like FibroGen, is intensely fueled by the success of clinical trials and the ongoing development of pipeline products. The ability to bring new, effective treatments to market is paramount.
FibroGen itself has a pipeline, including FG-3246 targeting prostate cancer, but this is just one piece of a much larger competitive landscape. Other companies are also actively developing treatments for similar or even more advanced conditions, creating a dynamic race for innovation and market share.
For instance, in 2024, the oncology drug development space saw significant activity, with numerous companies reporting trial results. Companies with robust pipelines and compelling clinical data are better positioned to gain a competitive edge and secure market leadership.
Patent Expirations and Biosimilar/Generic Competition
Patent expirations are a major disruptor in the biopharmaceutical sector, opening the door for more affordable biosimilar and generic alternatives. FibroGen's flagship drug, Roxadustat, faces this reality as its primary patents are approaching their end dates in key markets.
This shift will likely intensify competition and put downward pressure on Roxadustat's pricing as biosimilar manufacturers enter the market. For instance, in 2024, the global biosimilar market was valued at approximately $25.5 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, highlighting the significant impact of patent cliffs on established drug revenues.
- Patent Expirations: Roxadustat's core patents are expiring in several major jurisdictions, creating an opportunity for generic and biosimilar entry.
- Increased Competition: The arrival of biosimilars will directly challenge FibroGen's market share and pricing power for Roxadustat.
- Price Erosion: Historically, biosimilar entry can lead to significant price reductions, impacting revenue streams for originator drugs.
- Market Dynamics: The increasing maturity of the biosimilar market, evidenced by its $25.5 billion valuation in 2024, underscores the competitive threat FibroGen faces.
Strategic Alliances and Acquisitions
FibroGen’s competitive rivalry is intensified by strategic alliances and acquisitions, as companies seek to bolster their market standing and diversify their product portfolios. These partnerships are crucial for navigating the complex pharmaceutical landscape.
A prime example is FibroGen's collaboration with AstraZeneca and Astellas for the development and commercialization of roxadustat. This alliance highlights the industry's reliance on such strategic moves to share risks and leverage complementary expertise, especially in bringing novel therapies to market.
The roxadustat market, in particular, has been a focal point for mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity. This trend underscores the intense competition and the drive for consolidation among biopharmaceutical firms aiming to secure significant market share and intellectual property.
- Strategic Partnerships: FibroGen’s alliance with AstraZeneca and Astellas for roxadustat is a key strategy to compete in the competitive anemia treatment market.
- M&A Activity: The global pharmaceutical M&A market saw significant activity in 2024, with deal values reaching hundreds of billions of dollars, reflecting the broader trend of consolidation that impacts companies like FibroGen.
- Market Expansion: Collaborations and acquisitions allow companies to expand their geographic reach and therapeutic areas, thereby strengthening their competitive position against rivals.
FibroGen operates within a highly competitive pharmaceutical landscape, facing rivals with substantial R&D budgets and established market presence. The sheer scale of global pharmaceutical giants, with the market valued at approximately $1.6 trillion in 2024, means they can readily outmaneuver smaller entities through existing infrastructure and brand recognition.
The company's focus on therapeutic areas with significant unmet needs, such as chronic kidney disease and oncology, inherently attracts intense competition from numerous biopharmaceutical firms. This dynamic environment fuels extensive research and development, with companies racing to bring innovative treatments to market.
Patent expirations, a recurring challenge in the sector, directly impact FibroGen's flagship drug, roxadustat. As core patents expire, the market anticipates the entry of biosimilar manufacturers, a trend underscored by the biosimilar market's $25.5 billion valuation in 2024, which is expected to grow substantially.
These biosimilar entrants will likely exert downward pressure on roxadustat's pricing and erode market share, a common outcome following patent cliffs. FibroGen's strategic alliances, such as its partnership with AstraZeneca and Astellas for roxadustat, are critical for navigating this competitive terrain and sharing development risks.
| Rivalry Factor | Impact on FibroGen | Supporting Data (2024 Estimates/Figures) |
| Established Pharmaceutical Giants | Significant competitive disadvantage due to scale and resources. | Global pharmaceutical market size: ~$1.6 trillion. |
| Pipeline Competition | Intensified R&D race in key therapeutic areas like CKD and oncology. | High investment in oncology drug development. |
| Patent Expirations & Biosimilars | Threat of price erosion and market share loss for roxadustat. | Biosimilar market valuation: ~$25.5 billion; projected growth. |
| Strategic Alliances & M&A | Need for partnerships to compete; risk of being outmaneuvered by consolidated entities. | Global pharmaceutical M&A deal values in the hundreds of billions. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), established treatments like erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) and iron supplements are strong substitutes for FibroGen's roxadustat. These therapies are familiar to both patients and physicians, with proven effectiveness and safety records. For instance, injectable ESAs continue to hold a dominant position in the overall anemia treatment landscape, representing a significant competitive threat.
The threat of substitutes for FibroGen's HIF-PHI products, like roxadustat, is significant due to the emergence of other HIF-PHIs. Companies are developing and have already launched drugs such as vadadustat and daprodustat. These offer a similar mechanism of action, directly competing with roxadustat's core functionality.
These alternative HIF-PHIs, including vadadustat and daprodustat, have demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials, proving their ability to effectively raise hemoglobin levels. This similarity in therapeutic outcome means patients and physicians have viable alternatives, intensifying the competitive landscape for FibroGen.
For certain anemias, like iron deficiency anemia, dietary changes and supplements act as substitutes. For instance, in 2024, the global iron supplements market was valued at approximately $4.5 billion, indicating a significant demand for these readily available alternatives.
These accessible options can reduce the need for more specialized and costly pharmaceutical treatments offered by companies like FibroGen, potentially impacting the addressable market for their advanced therapies.
Alternative Therapies for Fibrotic Diseases and Cancer
The threat of substitutes for FibroGen's therapies, particularly in fibrosis and cancer, is significant. For fibrotic diseases, established antifibrotic drugs such as pirfenidone and nintedanib already serve as direct substitutes. Furthermore, the landscape is dynamic with numerous other experimental therapies actively progressing through clinical trials, potentially offering alternative treatment avenues.
In the oncology space, the substitute threat is even more pronounced. FibroGen faces competition from a broad spectrum of established cancer treatments. These include traditional modalities like chemotherapy and radiation therapy, surgical interventions, and a growing array of targeted therapies and immunotherapies that are continuously evolving.
- Fibrosis Substitutes: Pirfenidone and nintedanib are current market alternatives, with ongoing development of novel antifibrotic agents posing future threats.
- Cancer Substitutes: The oncology market is highly competitive, featuring chemotherapy, radiation, surgery, and a wide range of targeted and immunotherapies.
- Pipeline Impact: The success of FibroGen's pipeline in these areas will be measured against the efficacy and accessibility of these numerous existing and emerging substitutes.
Potential for Gene Therapies and Advanced Modalities
The long-term threat of substitutes for FibroGen's products, particularly those addressing anemia, includes the burgeoning field of gene therapies. These advanced modalities aim to correct the underlying genetic causes of diseases, offering a potentially curative approach rather than symptomatic management. While still in developmental stages for many of FibroGen's current therapeutic areas, gene therapies represent a significant disruptive force for the future.
Specifically, advancements in gene therapy for anemia are a major trend to watch. For instance, by mid-2024, several gene therapy candidates for inherited anemias like sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia have shown promising clinical trial results, with some even receiving regulatory approvals in certain markets. This suggests a future where the need for drugs like FibroGen's roxadustat (Evrenzo) could be diminished if gene therapies become widely accessible and effective for broader anemia indications.
- Gene Therapy for Anemia: Emerging treatments aim to correct genetic defects causing anemia, potentially offering a one-time cure.
- Disruptive Potential: While currently in early stages for many conditions, gene therapies could fundamentally alter the treatment landscape.
- Market Trends: By mid-2024, several gene therapies for inherited anemias have advanced significantly in clinical trials and regulatory pathways.
- Competitive Landscape: The success of gene therapies could reduce demand for existing anemia treatments, impacting companies like FibroGen.
The threat of substitutes for FibroGen's anemia treatments is substantial, with established therapies like injectable erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) and iron supplements remaining dominant. These existing treatments are well-understood by healthcare providers and patients, offering proven efficacy and safety profiles.
Beyond traditional methods, new oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors (HIF-PHIs), such as vadadustat and daprodustat, directly compete with FibroGen's roxadustat. These emerging drugs offer similar mechanisms of action, providing viable alternatives that can capture market share.
The market for iron supplements alone was approximately $4.5 billion in 2024, highlighting the accessibility and demand for these basic substitutes. Furthermore, the advancement of gene therapies, particularly for inherited anemias, presents a long-term disruptive threat, potentially offering curative solutions that could diminish the need for ongoing pharmaceutical interventions.
| Therapy Type | Examples | Market Status/Trend | Threat Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Established Anemia Treatments | Injectable ESAs, Iron Supplements | Dominant, familiar, proven efficacy | High |
| Alternative HIF-PHIs | Vadadustat, Daprodustat | Emerging, similar mechanism of action | High |
| Dietary/Supplements | Dietary changes, oral iron | Accessible, cost-effective | Moderate |
| Gene Therapies | For inherited anemias | Advancing rapidly, potential for cures | High (Long-term) |
Entrants Threaten
The biopharmaceutical sector presents formidable barriers to entry, primarily due to rigorous regulatory landscapes. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandates extensive clinical trials and data submission, making the path to market exceptionally challenging and costly.
Developing and gaining approval for a new drug typically spans 10 to 15 years and can cost upwards of $2.6 billion. This extended timeline and substantial financial investment act as significant deterrents for potential new competitors seeking to enter the market.
Recent trends indicate the FDA is increasing its scrutiny and raising the standards for drug approval. This heightened regulatory environment further solidifies the threat of new entrants by demanding even more robust evidence of safety and efficacy.
Developing novel therapeutics demands enormous investment in research and development, clinical trials, and specialized scientific talent. FibroGen, for instance, dedicates substantial resources to its drug pipeline. This significant financial commitment, coupled with the high attrition rate of drug candidates during clinical testing, presents a formidable barrier for any new company aiming to enter the biopharmaceutical market.
FibroGen's robust patent portfolio, covering its key drug candidates and approved therapies like roxadustat, significantly deters new entrants. These intellectual property rights create substantial barriers, forcing potential competitors to either invest heavily in developing distinct products or incur substantial costs for licensing. The threat is amplified as patent expiry for biologics, a common challenge in the pharmaceutical industry, can open doors for biosimilar competition, although the complexity of biologics often still presents hurdles.
Need for Established Distribution and Commercialization Networks
Beyond the complex process of drug discovery and approval, new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector face a substantial hurdle in establishing robust distribution and commercialization channels. This involves building out costly sales forces, extensive marketing operations, and intricate logistics to effectively reach healthcare providers and patients.
Companies like FibroGen have historically relied on strategic partnerships, such as their collaborations with AstraZeneca and Astellas, to gain access to these established networks. For instance, the collaboration with AstraZeneca for roxadustat in certain territories provided immediate access to a global commercial infrastructure.
The significant capital investment and time required to replicate these established networks present a formidable barrier to entry for smaller, emerging companies.
- High Cost of Sales and Marketing Infrastructure: Building a dedicated sales force and marketing teams for specialized biopharmaceuticals can cost hundreds of millions of dollars annually.
- Access to Prescribers: Gaining access to physicians and key opinion leaders in the medical community requires established relationships and a proven track record, which new entrants lack.
- Distribution Logistics: Ensuring the safe, efficient, and compliant delivery of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals to pharmacies and hospitals is a complex undertaking.
- Regulatory Compliance in Commercialization: Navigating the intricate regulatory landscape for drug promotion and marketing adds another layer of complexity and cost.
Economies of Scale and Brand Recognition
The threat of new entrants for a company like FibroGen is significantly influenced by substantial economies of scale enjoyed by established pharmaceutical giants. These incumbents can leverage their size to achieve lower per-unit costs in critical areas such as research and development, manufacturing, and marketing. For instance, in 2024, major pharmaceutical firms often reported R&D expenditures in the billions of dollars, a scale difficult for newcomers to match.
Furthermore, deep-rooted brand recognition and trust within the healthcare ecosystem present a formidable barrier. Years of successful product launches and consistent engagement with physicians and patients build a reputation that new entrants struggle to replicate quickly. This established trust translates into preferential prescribing habits and patient adherence, making it challenging for emerging companies to carve out market share.
- Economies of Scale: Large pharmaceutical companies can spread R&D, manufacturing, and marketing costs over a wider product base, reducing per-unit expenses.
- Brand Recognition: Established brands benefit from trust and familiarity among healthcare providers and patients, a significant hurdle for new market entrants.
- Capital Requirements: The immense capital needed for drug development, clinical trials, and regulatory approval acts as a substantial barrier to entry.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex and lengthy regulatory approval processes, such as those overseen by the FDA, requires expertise and resources that new entrants may lack.
The threat of new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector, impacting companies like FibroGen, remains low due to extremely high barriers. These include the immense cost and time required for drug development, with estimated costs for bringing a new drug to market often exceeding $2.6 billion and timelines stretching over a decade. Furthermore, stringent regulatory requirements from bodies like the FDA demand extensive clinical trials and data, adding significant complexity and expense for any new player.
FibroGen benefits from substantial intellectual property protection through its patent portfolio, which deters competitors from easily replicating its therapies. The need for established distribution and commercialization networks, often built through costly partnerships, further limits new entrants. For instance, major pharmaceutical firms in 2024 reported R&D spending in the billions, highlighting the economies of scale that newcomers struggle to match.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Impact on New Entrants |
| Regulatory Approval | Rigorous FDA processes, extensive clinical trials | High cost (>$2.6B), long timelines (10-15 years) |
| Capital Requirements | R&D, manufacturing, marketing investment | Billions of dollars, difficult for new firms to raise |
| Intellectual Property | Patents on drug candidates and therapies | Requires licensing or development of distinct products |
| Commercialization Infrastructure | Sales forces, marketing, distribution networks | Hundreds of millions in annual costs, requires established relationships |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our FibroGen Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including FibroGen's SEC filings, investor presentations, and annual reports. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific market research reports and publications from reputable sources like FierceBiotech and EvaluatePharma to capture the competitive landscape.
