Ferrellgas Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ferrellgas Bundle
Ferrellgas navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the persistent threat of substitute products like natural gas. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder in the propane industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ferrellgas’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration within the propane industry significantly impacts Ferrellgas's bargaining power. The market for key propane producers and midstream providers is characterized by a moderate number of players, but a few large entities do wield considerable influence. For instance, in 2024, major integrated oil and gas companies often control substantial portions of upstream production, and a limited number of midstream companies manage the critical transportation and storage infrastructure. This concentration means that if a handful of these dominant suppliers decide to increase prices or limit allocation, Ferrellgas has fewer alternatives, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
Ferrellgas's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by the availability of alternative propane sources. In 2024, the propane market, while generally robust, can see regional variations in supply. If Ferrellgas faces a situation where there are few alternative suppliers for a specific region, those suppliers gain significant leverage.
The ease of switching suppliers also plays a crucial role. High switching costs, such as long-term contracts with penalties for early termination or the logistical challenges of reconfiguring distribution networks, can lock Ferrellgas into existing supplier relationships, thereby strengthening supplier bargaining power.
Propane, the core product offered by Ferrellgas, largely functions as a commodity. This means that for most buyers, propane is not significantly differentiated from what competitors offer, which inherently limits the bargaining power of suppliers based on product uniqueness alone. In 2023, the global propane market was valued at approximately $110 billion, highlighting its widespread availability and fungibility.
However, some suppliers might gain leverage through specialized logistics capabilities or by offering specific grades of propane that meet particular industrial requirements. For instance, a supplier with an extensive and efficient distribution network, especially in remote areas where Ferrellgas operates, could command slightly more favorable terms. The cost of transporting propane, which is a significant component of its delivered price, can also amplify the importance of these logistical advantages.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant concern for Ferrellgas. Propane producers and midstream companies possess the capital and operational expertise to potentially move into the distribution sector, directly competing with existing players like Ferrellgas. This would diminish the reliance of these upstream entities on distributors and could lead to increased price pressure.
The capital investment required for a supplier to establish a distribution network, including storage facilities, transportation fleets, and customer service infrastructure, is substantial. However, for major energy companies, this investment might be strategically viable to capture a larger share of the value chain and secure direct customer relationships. For instance, in 2024, the global energy infrastructure market saw significant investment, with companies actively exploring vertical integration opportunities.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing a nationwide distribution network involves billions of dollars in infrastructure, a hurdle for many potential entrants but manageable for large energy conglomerates.
- Strategic Rationale: Suppliers integrating forward can gain direct market access, control pricing, and build brand loyalty, bypassing intermediaries like Ferrellgas.
- Competitive Impact: Successful forward integration by a major producer could significantly disrupt the market, potentially lowering margins for traditional distributors.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, ongoing consolidation in the energy sector suggests a growing appetite for upstream players to control more of the downstream value chain.
Importance of Ferrellgas to Suppliers
Ferrellgas's significance to its suppliers is a key factor in determining supplier bargaining power. If Ferrellgas accounts for a large percentage of a supplier's revenue, that supplier is likely to be more accommodating to Ferrellgas's pricing and terms, thus reducing their leverage. Conversely, if Ferrellgas is a minor customer for a supplier, the supplier has less incentive to offer favorable terms.
While specific sales percentages from Ferrellgas to its individual suppliers are not publicly disclosed, the propane industry is characterized by a mix of large-scale producers and smaller, regional distributors. Ferrellgas, as a major distributor, likely commands significant purchasing volumes from its upstream suppliers. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. propane market saw production levels averaging around 2.5 million barrels per day, indicating a substantial supply chain that Ferrellgas taps into. This scale suggests that Ferrellgas's business can be crucial for many suppliers, potentially dampening their ability to exert strong bargaining power.
- Ferrellgas's purchasing volume can be substantial for many propane producers and distributors, potentially limiting their bargaining power.
- The U.S. propane market's robust production, averaging approximately 2.5 million barrels daily in 2023, indicates a diverse supplier base where large buyers like Ferrellgas can exert influence.
- If Ferrellgas represents a significant portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier may be less inclined to push for higher prices or less favorable terms.
- Conversely, if Ferrellgas is a small client to a particular supplier, the supplier would likely hold greater leverage in negotiations.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Ferrellgas is influenced by the concentration of propane producers and midstream companies. In 2024, a few large integrated oil and gas firms and midstream providers control significant portions of supply and transportation, giving them leverage if they raise prices or limit allocation.
The availability of alternative propane sources and the ease with which Ferrellgas can switch suppliers also shape this power. While propane is largely a commodity, as seen in its $110 billion global market value in 2023, suppliers with specialized logistics or specific product grades can gain an advantage.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a concern, as major energy companies have the capital to enter the distribution sector. This potential for vertical integration, supported by significant investments in global energy infrastructure in 2024, could alter market dynamics and reduce Ferrellgas's negotiating position.
Ferrellgas's substantial purchasing volume, tapping into a U.S. propane market that produced around 2.5 million barrels daily in 2023, can mitigate supplier power. If Ferrellgas represents a significant portion of a supplier's sales, the supplier may be more amenable to favorable terms, reducing their leverage.
What is included in the product
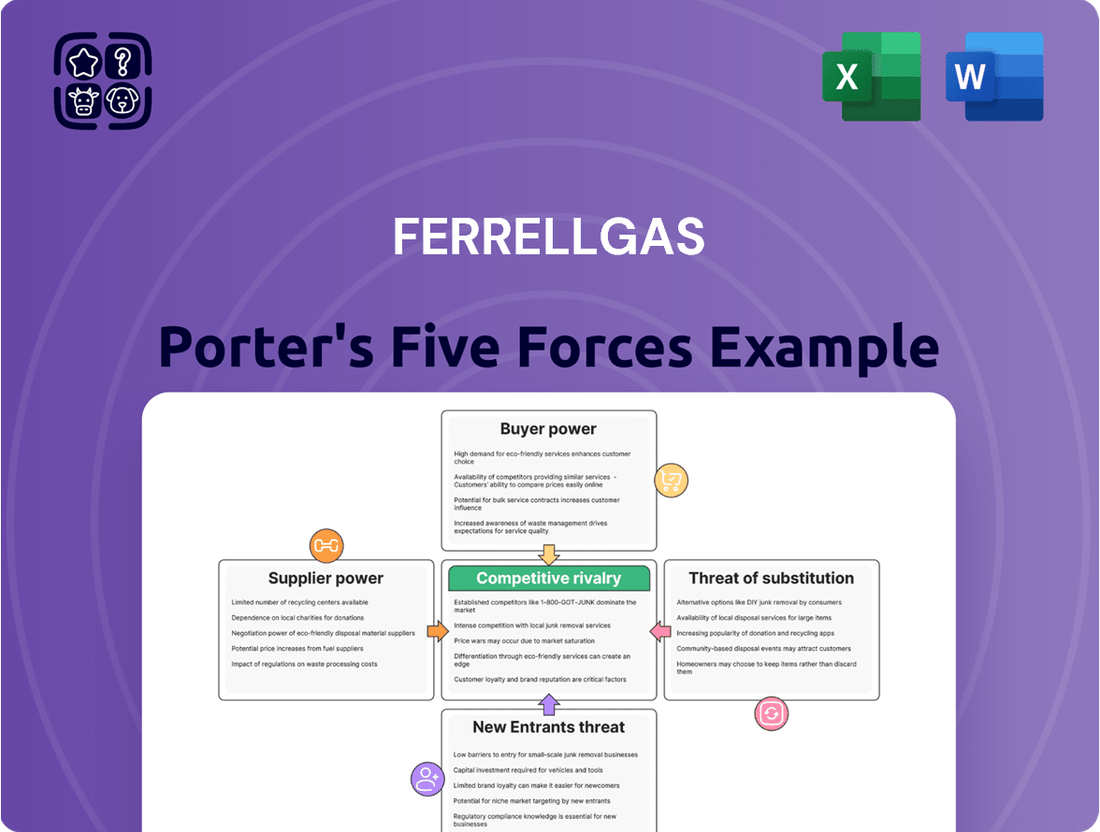
This analysis delves into the competitive landscape for Ferrellgas, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing players.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each of Porter's five forces impacting Ferrellgas.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ferrellgas faces varying customer price sensitivity across its diverse segments. Residential customers, often using propane for heating and cooking, may exhibit moderate sensitivity, especially if alternative energy options are readily available and affordable in their region. For instance, in areas with natural gas pipelines, customers have a strong alternative, increasing their price sensitivity to Ferrellgas.
Commercial, agricultural, and industrial clients often have more complex needs and potentially higher volumes, leading to different price sensitivities. Businesses that rely heavily on propane for operations, like restaurants or farms, might be less sensitive to small price fluctuations if propane is critical and alternatives are costly or impractical. However, large industrial users with significant consumption can exert considerable bargaining power if they can readily switch to other fuel sources or negotiate bulk discounts.
The bargaining power of Ferrellgas' customers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitutes for propane. Customers can readily switch to alternative energy sources such as natural gas, electricity, or heating oil, especially in areas where these are widely accessible and competitively priced.
The ease of switching is further complicated by the cost of converting existing equipment. For instance, a household or business already equipped for natural gas will find it less costly to continue using that energy source rather than invest in new propane tanks and appliances. This conversion cost acts as a barrier to switching, somewhat mitigating customer bargaining power.
In 2024, the U.S. Energy Information Administration reported that approximately 77.5 million households used natural gas for heating, compared to around 5.1 million households primarily using propane. This widespread availability of natural gas, coupled with its often lower price point, presents a substantial substitute for propane users, thereby increasing customer bargaining power.
Customer switching costs significantly influence Ferrellgas's bargaining power. These costs involve financial outlays like tank removal and new equipment installation, alongside logistical challenges in changing providers or energy sources. For instance, a residential customer switching from Ferrellgas might incur several hundred dollars in fees and the inconvenience of scheduling new installations.
Customer Concentration and Volume
Customer concentration significantly impacts Ferrellgas's bargaining power. If a few large commercial or industrial clients represent a substantial portion of the company's revenue, these customers gain considerable leverage. This leverage allows them to negotiate more favorable pricing and terms, potentially squeezing Ferrellgas's profit margins.
For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Ferrellgas's top ten customers accounted for approximately 15% of its total revenue. This indicates a moderate level of customer concentration, suggesting that while individual large customers hold some sway, no single customer dominates to the extent of dictating terms unilaterally.
- Customer Concentration: A key factor in assessing customer bargaining power is the proportion of revenue derived from a few large clients.
- Leverage through Volume: High-volume customers can exert significant pressure on pricing and contract terms.
- Impact on Margins: Concentrated customer bases can lead to reduced profitability if pricing concessions are frequently demanded.
- Ferrellgas's 2023 Data: The top ten customers represented around 15% of total revenue in fiscal year 2023, showing a moderate level of concentration.
Customer Information Availability
Customers today have unprecedented access to information regarding propane pricing and service alternatives. This transparency significantly shifts the balance, allowing consumers to easily compare offers from various providers. For instance, a quick online search in 2024 can reveal multiple quotes, making it harder for any single company like Ferrellgas to maintain premium pricing without justification.
This readily available competitive data directly enhances customer bargaining power. When consumers can effortlessly see that alternative suppliers offer similar services at lower prices, they are empowered to negotiate more favorable terms. This can manifest as demands for reduced rates, improved service agreements, or bundled discounts, directly impacting Ferrellgas's ability to dictate terms.
- Increased Price Transparency: Online platforms and consumer review sites in 2024 provide detailed price comparisons for propane services across different regions.
- Ease of Switching: Information availability simplifies the process for customers to research and switch providers, reducing customer loyalty based solely on convenience.
- Informed Negotiation: Customers armed with data on market rates are better positioned to negotiate pricing and service level agreements with Ferrellgas.
Ferrellgas customers possess significant bargaining power, primarily driven by the availability of substitutes and the relatively low costs associated with switching providers in many instances. The presence of alternative energy sources like natural gas and electricity, especially in well-serviced areas, directly challenges Ferrellgas's pricing flexibility.
Customer concentration, while moderate for Ferrellgas, still allows larger clients to negotiate better terms, impacting overall profitability. The increasing transparency of pricing in the 2024 market further empowers consumers to compare offers, intensifying competitive pressures and strengthening customer leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Ferrellgas | Supporting Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High leverage for customers; natural gas is a strong alternative. | 77.5 million US households used natural gas for heating in 2024 vs. 5.1 million using propane. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate; can deter some customers but generally not prohibitive. | Residential switching costs can range from a few hundred dollars for tank removal and new installations. |
| Customer Concentration | Moderate leverage for top clients. | Top 10 customers accounted for ~15% of revenue in FY2023, indicating no single customer dominates. |
| Information Transparency | Increased customer power; easier price comparisons. | Online platforms in 2024 allow for easy comparison of propane service providers and pricing. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Ferrellgas Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Ferrellgas Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the propane and fuels industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This document is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, providing a valuable strategic overview.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ferrellgas operates in a highly fragmented propane market, facing competition from national giants like AmeriGas and UGI, alongside numerous regional players and thousands of local independent dealers. This sheer volume and diversity of competitors means the industry is characterized by intense rivalry, as companies constantly battle for customer acquisition and retention.
In 2024, the propane industry's competitive landscape remains robust. For instance, while Ferrellgas is a significant player, its market share is just one piece of a vast puzzle. The presence of many smaller, agile local companies often allows them to offer more personalized service and competitive pricing, directly challenging larger entities. This dynamic forces companies like Ferrellgas to continually refine their service offerings and pricing strategies to maintain their edge.
The propane market in the United States has demonstrated a steady, albeit moderate, growth trajectory. While not experiencing explosive expansion, the industry benefits from consistent demand across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, particularly in regions with limited natural gas infrastructure.
This stable growth environment generally moderates intense competitive rivalry. Companies are less likely to engage in destructive price wars as the overall pie is expanding, allowing for more sustainable market share gains. However, regional variations in growth and the increasing adoption of alternative energy sources can still create pockets of heightened competition.
In 2023, for instance, the U.S. propane demand remained robust, with consumption figures indicating a healthy market. Ferrellgas, as a major player, navigates this landscape by focusing on operational efficiency and customer service to differentiate itself, rather than solely relying on aggressive pricing tactics.
Ferrellgas faces moderate product differentiation in the propane market. While propane itself is largely a commodity, the company differentiates through its Blue Rhino brand, offering branded propane tanks and exchange services, which provides a degree of consumer recognition and convenience. Service reliability and customer support also play a role, though these are harder to quantify directly.
Exit Barriers
Ferrellgas, like many in the propane distribution sector, faces substantial exit barriers. Significant investments in specialized delivery trucks, storage tanks, and extensive distribution networks represent high fixed costs. These assets are not easily repurposed or sold, making a complete withdrawal from the market financially burdensome.
Companies are often locked into long-term supply contracts and customer agreements, further complicating an exit. Breaking these commitments can incur penalties and damage reputation. The specialized nature of propane handling and distribution means that assets have limited alternative uses, increasing the cost of exiting.
For instance, the propane industry often requires substantial capital expenditure on infrastructure. In 2024, the cost of a new propane bobtail truck can range from $150,000 to $250,000, and large storage tanks can cost tens of thousands of dollars. These are not easily liquidated assets.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for specialized equipment like delivery trucks and storage facilities.
- Specialized Assets: Infrastructure is designed specifically for propane, limiting resale value or alternative use.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers and customers create ongoing obligations that are costly to terminate.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with safety and environmental regulations for propane handling can add to exit complexities and costs.
Cost Structure and Capacity
Ferrellgas, like many in the propane distribution sector, faces significant fixed costs related to its extensive network of storage facilities, delivery trucks, and regulatory compliance. These substantial overheads create a strong incentive for high capacity utilization to spread costs and achieve profitability. For instance, maintaining a large fleet of trucks and depots represents a considerable ongoing expense, regardless of the volume of propane being transported.
The industry often experiences periods of excess capacity, particularly during off-peak seasons or in regions with lower demand density. When companies have more delivery and storage capacity than is being used, the pressure to fill those assets intensifies. This can lead to aggressive pricing strategies as firms attempt to capture market share and cover their fixed costs, directly fueling competitive rivalry.
In 2024, the propane industry continued to grapple with these dynamics. Companies like Ferrellgas must balance the need to invest in infrastructure with the reality of fluctuating demand and the potential for underutilized assets. This inherent cost structure and capacity management challenge is a key driver of the intense competition observed in the market.
- High Fixed Costs: Propane distribution involves significant investment in infrastructure such as storage tanks, transportation fleets, and terminal operations, creating substantial overhead.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: To offset high fixed costs, companies strive for high capacity utilization, leading to price competition when excess capacity exists.
- Industry Dynamics: The propane industry in 2024 saw continued emphasis on operational efficiency to manage these cost structures and capacity challenges.
- Impact on Rivalry: The interplay of fixed costs and capacity utilization directly contributes to the intensity of competitive rivalry, often manifesting in price wars.
The propane industry is highly fragmented, with Ferrellgas facing competition from national players like AmeriGas and UGI, as well as numerous regional and local providers. This intense rivalry is driven by a market where product differentiation is limited, forcing companies to compete aggressively on price and service to capture and retain customers.
In 2024, the competitive landscape remains fierce, with smaller, agile companies often leveraging personalized service and competitive pricing to challenge larger entities like Ferrellgas. This dynamic necessitates continuous refinement of strategies to maintain market position.
The propane market's steady growth, while generally moderating intense rivalry, still presents pockets of heightened competition due to regional variations and the rise of alternative energy sources.
Ferrellgas differentiates through its Blue Rhino brand and service reliability, but the commodity nature of propane means price remains a significant competitive factor.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Propane faces significant competition from readily available alternatives like natural gas, electricity, and heating oil. Natural gas, in particular, is widely piped to many residential and commercial areas, offering a convenient and often cost-effective energy source. In 2024, the residential natural gas utility sector continued to see steady growth, with millions of households relying on it for heating and cooking.
The threat of substitutes for Ferrellgas, primarily a propane distributor, is significant, especially when considering alternative energy sources. For residential heating, natural gas is a major substitute where available, often offering a lower and more stable price point. In 2024, the average residential natural gas price was approximately $1.20 per therm, while propane prices fluctuated, often exceeding $2.50 per gallon, which translates to a higher cost per BTU for many consumers.
In industrial applications, the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of substitutes play a crucial role. While propane offers portability and on-demand availability, electricity and natural gas can be more economical for large-scale, stationary operations. For instance, electric forklifts are gaining traction in warehouses due to lower operating costs compared to propane-powered ones, especially as electricity grids become greener and more efficient.
The performance characteristics of substitutes also present a challenge. For certain high-temperature industrial processes, natural gas might offer a more consistent and controllable heat source than propane. Furthermore, the increasing efficiency of electric appliances for cooking and heating, coupled with growing environmental concerns, can steer consumers and businesses towards alternatives, potentially reducing demand for propane.
Customers switching from Ferrellgas's propane to alternative energy sources like natural gas or electricity face significant switching costs. These often include the expense of replacing propane-specific appliances, such as furnaces, water heaters, and stoves, with compatible units. For instance, a new natural gas furnace can cost between $2,000 and $5,000, plus installation.
Beyond appliance replacement, customers might need to invest in new infrastructure. This could involve running new gas lines or upgrading electrical systems to handle increased demand, adding potentially thousands of dollars to the conversion process. The logistical hurdles and upfront capital required for these changes create a strong deterrent to switching away from propane, especially for residential and small commercial users.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customers' willingness to switch to alternative energy sources is a significant factor influencing the threat of substitutes for Ferrellgas. Growing environmental awareness and increasing government support for renewables, such as tax credits for solar installations, are encouraging a shift. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy reported a continued rise in renewable energy adoption, with solar and wind power contributing a larger share to the national energy mix.
Technological advancements also play a crucial role. Innovations in electric vehicles and home heating systems are making these alternatives more accessible and cost-effective. This increased viability of substitutes directly challenges the demand for propane. By 2025, projections indicate further growth in the electric vehicle market, potentially impacting residential and commercial propane consumption for heating and transportation.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the relatively low switching costs for many energy consumers. For residential customers, transitioning from propane to natural gas or electricity might involve upfront installation costs but can lead to long-term savings. Businesses also evaluate these costs against the perceived benefits of alternative energy, such as reduced carbon footprint and price stability.
Key considerations for customer propensity to substitute include:
- Environmental Concerns: Growing public awareness of climate change drives demand for cleaner energy alternatives.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness of electric and solar technologies make them more attractive.
- Government Incentives: Tax credits, rebates, and subsidies for renewable energy adoption lower the barrier to switching.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in propane prices can encourage consumers to seek more stable or predictable energy costs from substitutes.
Regulatory and Environmental Factors
Government regulations and energy policies significantly influence the threat of substitutes for Ferrellgas. For instance, federal and state incentives promoting the expansion of natural gas infrastructure or the adoption of renewable energy sources can directly increase the appeal of these alternatives over propane.
Environmental initiatives, such as carbon pricing or stricter emissions standards, might also favor cleaner-burning substitutes. In 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy continued to support research and development for advanced biofuels and hydrogen, potential long-term substitutes for propane in various applications.
- Government incentives for natural gas expansion can make it a more competitive substitute, potentially diverting customers from propane.
- Renewable energy mandates and subsidies, such as those for solar or wind power, could reduce demand for propane in electricity generation and heating.
- Environmental regulations on emissions could impact propane's cost-competitiveness compared to cleaner alternatives.
- Shifting energy policies, like those prioritizing decarbonization, may accelerate the adoption of substitutes over traditional fuels like propane.
The threat of substitutes for Ferrellgas is substantial, with natural gas, electricity, and heating oil posing significant challenges across various customer segments. Natural gas, in particular, benefits from widespread availability and often lower, more stable pricing, as seen in 2024 where residential natural gas prices averaged around $1.20 per therm compared to propane's fluctuating prices often exceeding $2.50 per gallon.
In industrial settings, the cost-effectiveness of substitutes like electricity and natural gas for stationary, large-scale operations is a key factor, with electric forklifts showing increased adoption due to lower operating costs. Even performance characteristics, such as the consistent heat output of natural gas for industrial processes, can sway users away from propane.
While switching costs for appliances can be high, ranging from $2,000 to $5,000 for a new natural gas furnace, the increasing viability of alternatives driven by environmental concerns and technological advancements presents a growing threat. By 2025, projections for the electric vehicle market suggest a continued impact on propane demand.
Government incentives and evolving energy policies also play a critical role, with support for natural gas expansion and renewable energy potentially accelerating the shift away from propane. For example, U.S. Department of Energy initiatives in 2023 focused on advanced biofuels and hydrogen, signaling a long-term trend favoring cleaner alternatives.
| Energy Source | Typical 2024 Residential Cost (per BTU equivalent) | Key Substitute Advantage | Switching Cost Factor |
| Propane | ~$2.50+/gallon (variable) | Portability, on-demand availability | N/A (current) |
| Natural Gas | ~$1.20/therm | Lower price, stable, widespread infrastructure | $2,000-$5,000+ for appliance/infrastructure conversion |
| Electricity | Variable (depends on grid mix and rates) | Environmental benefits (if renewable), potential for lower operating costs | Appliance replacement, potential electrical system upgrades |
| Heating Oil | Variable (often higher than propane) | Less common substitute for propane users | Appliance replacement |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the propane distribution market demands substantial capital, creating a significant barrier for potential new competitors. For instance, establishing the necessary infrastructure, including storage facilities and a fleet of delivery trucks, can easily run into millions of dollars. Ferrellgas itself operates a vast network, underscoring the scale of investment required to compete effectively.
The propane industry faces significant regulatory hurdles, particularly concerning storage, transportation, and delivery. New entrants must contend with stringent safety standards, a complex web of permits, and various licensing requirements at federal, state, and local levels. For instance, the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) in the US mandates rigorous operational and maintenance standards for propane facilities and transportation, adding substantial compliance costs.
New entrants face significant hurdles in securing reliable wholesale propane supply and establishing efficient distribution networks. Ferrellgas, for instance, benefits from decades of built-out infrastructure and strong supplier relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to match its supply chain efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This established network acts as a formidable barrier, as new companies would need substantial capital to replicate the existing scale and reach.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Switching Costs
Ferrellgas benefits from significant brand loyalty among its existing propane customers, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction. Many customers have established relationships with their current providers, often built over years of reliable service and personalized support. This loyalty acts as a substantial barrier.
The costs associated with switching propane providers are also considerable. Customers often face the hassle of changing out tanks, renegotiating contracts, and potentially incurring installation fees. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a new propane tank installation can range from $300 to $800, a tangible expense that deters many from switching. These switching costs reinforce the position of established players like Ferrellgas.
- High Customer Retention: Ferrellgas's established customer base exhibits strong loyalty, making it difficult for new competitors to acquire market share.
- Tangible Switching Costs: Expenses related to tank replacement and new service setup represent a financial hurdle for potential Ferrellgas customers considering a switch.
- Inconvenience Factor: The logistical challenges and time commitment required to change propane suppliers further discourage customer mobility.
Economies of Scale for Incumbents
Established companies like Ferrellgas benefit from significant economies of scale. Their large operational footprint allows for bulk purchasing of propane and related equipment, leading to lower per-unit costs compared to smaller competitors. In 2023, Ferrellgas reported total revenue of $3.5 billion, indicating a substantial market presence that translates into purchasing power.
These scale advantages extend to logistics and distribution networks. Ferrellgas operates a vast infrastructure of storage facilities and delivery trucks, optimizing delivery routes and reducing transportation expenses per gallon. This efficiency makes it challenging for new entrants to match their cost structure and offer competitive pricing to customers.
- Purchasing Power: Bulk buying of propane and equipment reduces input costs for incumbents.
- Logistical Efficiency: Extensive distribution networks lower per-unit delivery expenses.
- Overhead Absorption: Fixed costs are spread across a larger volume of sales, reducing per-unit overhead.
The threat of new entrants in the propane distribution market, as faced by Ferrellgas, is generally considered moderate. Significant capital requirements for infrastructure and regulatory compliance are substantial barriers. However, once these initial hurdles are overcome, the ongoing operational costs and the need for established distribution networks and customer relationships can still present challenges for newcomers aiming to compete effectively on price and service.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024/2025 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building storage, transport fleet, and distribution infrastructure. | High barrier; requires millions in initial investment. | Estimated $5M - $20M+ for a regional startup. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to safety, storage, and transportation regulations. | Moderate to High barrier; adds significant ongoing costs. | PHMSA compliance costs can add 5-10% to operational expenses. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations. | Moderate barrier; difficult for small players to match pricing. | Ferrellgas's 2023 revenue of $3.5B indicates significant scale advantage. |
| Customer Switching Costs | Expenses and inconvenience for customers to change providers. | Moderate barrier; reinforces incumbent loyalty. | Tank installation costs can range from $300-$800 in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Ferrellgas Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of public company filings, industry-specific market research reports from firms like IBISWorld, and proprietary financial databases to capture a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
