Fagron Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fagron Bundle
Fagron's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants, all of which impact its profitability and strategic positioning. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone looking to grasp Fagron's market realities.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Fagron’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fagron's dependence on highly specialized pharmaceutical raw materials positions suppliers of unique or patented ingredients to wield considerable influence. For instance, if a critical active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is sourced from a single supplier with exclusive rights, Fagron's ability to negotiate pricing and terms is significantly diminished.
The consistent availability and unwavering quality of these specific raw materials are paramount for Fagron to manufacture its compounded medications. Any disruption or compromise in quality directly impacts patient safety and the efficacy of the final products, making suppliers of these essential components powerful.
In the pharmaceutical sector, stringent regulatory hurdles frequently narrow the pool of acceptable suppliers for crucial active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients. For instance, as of early 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) maintains rigorous approval processes, meaning only a handful of manufacturers may meet the exacting standards for specific compounds.
This limited approved supplier landscape grants these entities significant pricing power and control over contract terms. The substantial investment in time and resources required to qualify new suppliers, coupled with the inherent risks of regulatory non-compliance, makes switching a formidable challenge for pharmaceutical companies, thereby amplifying supplier leverage.
Suppliers who consistently meet Fagron's rigorous quality control and regulatory compliance standards, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), hold significant sway. Fagron's reliance on these high-quality inputs is critical for maintaining product integrity and satisfying global health authorities. Suppliers unable to demonstrate robust compliance are simply not an option for Fagron, further concentrating power among those who can reliably deliver.
Switching Costs for Raw Materials
Switching suppliers for critical raw materials presents substantial switching costs for Fagron. These costs encompass the rigorous re-validation of new materials, obtaining necessary regulatory approvals, and the potential for significant disruption to ongoing production schedules. For instance, in the pharmaceutical sector, the process of qualifying a new supplier for an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) can take 12-18 months and cost upwards of $100,000 to $500,000 depending on the complexity and regulatory oversight.
These elevated switching costs inherently diminish Fagron's operational flexibility. Consequently, this situation amplifies the bargaining power of existing suppliers. The sheer effort and financial outlay required to transition to an alternative supplier can often be prohibitive, leaving Fagron with fewer viable options and strengthening the supplier's negotiating position.
- Re-validation Processes: Ensuring new raw materials meet stringent quality and performance standards.
- Regulatory Approvals: Obtaining necessary certifications and clearances from health authorities.
- Production Disruption: Potential downtime and loss of output during the transition period.
- Associated Costs: Including research, testing, and potential inventory write-offs.
Supplier Concentration in Niche Markets
In specialized areas of pharmaceutical compounding, such as certain niche active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), the supply chain can be highly concentrated. This means a small number of global manufacturers might be the sole producers of critical raw materials essential for Fagron's personalized medicine solutions.
This limited supplier base for unique or rare compounds significantly amplifies their bargaining power. When Fagron relies on these highly specialized ingredients, these suppliers can dictate terms, impacting Fagron's costs and production capabilities.
- Supplier Concentration: In 2024, some niche pharmaceutical compounding ingredients are sourced from as few as 1-3 global manufacturers.
- Critical Ingredients: Fagron's ability to offer unique personalized medications often depends on these specialized, single-source raw materials.
- Impact on Fagron: High supplier concentration for vital components can lead to increased input costs and potential supply chain disruptions for Fagron.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Fagron is considerable, particularly for specialized pharmaceutical raw materials. When Fagron requires unique or patented ingredients, suppliers with exclusive rights can dictate terms, significantly limiting Fagron's negotiation leverage. This is amplified by the fact that in 2024, certain niche pharmaceutical compounding ingredients are sourced from as few as one to three global manufacturers, making these suppliers highly influential.
Fagron's reliance on suppliers who consistently meet stringent quality and regulatory standards, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), is critical. Suppliers unable to demonstrate robust compliance are not viable options, further concentrating power among those who can reliably deliver. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) maintains rigorous approval processes in 2024, meaning only a limited number of manufacturers may meet the exacting standards for specific compounds, enhancing supplier leverage.
Switching suppliers for critical raw materials involves substantial costs for Fagron, including re-validation, regulatory approvals, and potential production disruptions. These elevated switching costs, which can range from $100,000 to $500,000 and take 12-18 months for APIs, diminish Fagron's operational flexibility and strengthen the supplier's negotiating position.
| Factor | Impact on Fagron | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration for Niche APIs | High dependence on few suppliers | Strong |
| Regulatory Hurdles for New Suppliers | Extended qualification time and cost | Strong |
| Switching Costs (Re-validation, Approvals) | Significant financial and operational burden | Strong |
| Quality and Compliance Requirements | Limited supplier pool meeting standards | Strong |
What is included in the product
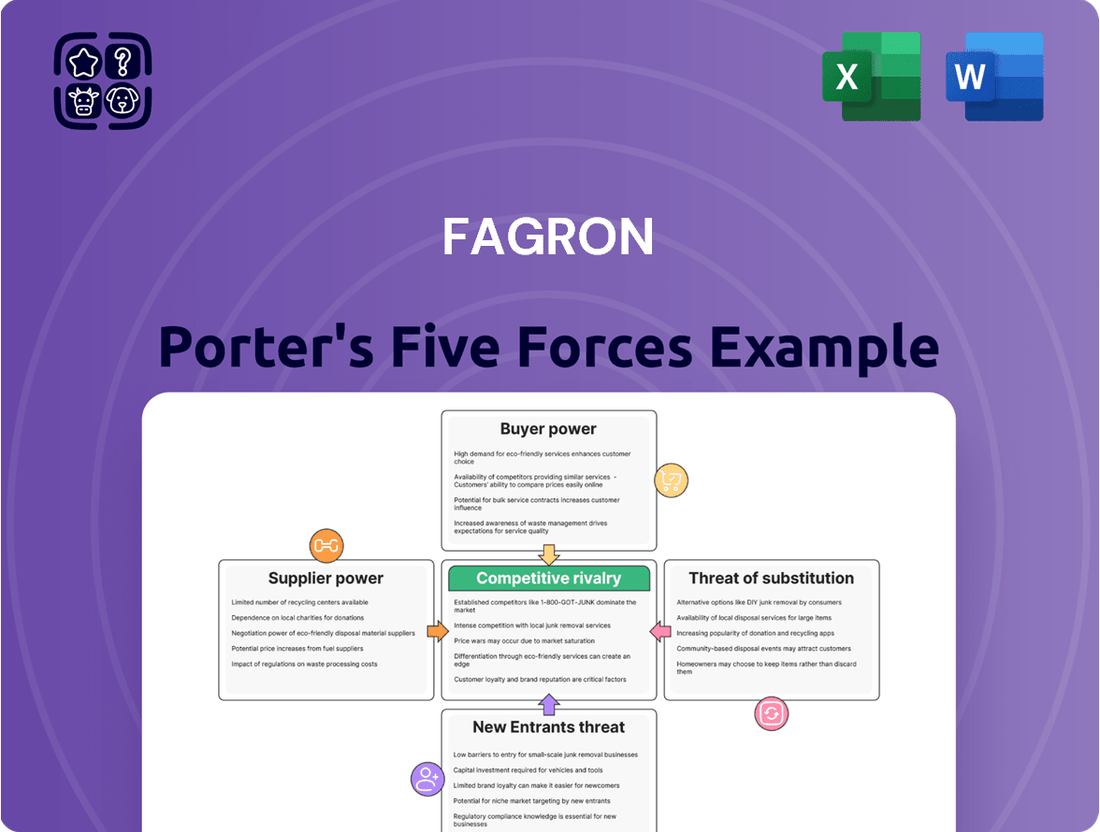
This analysis dissects Fagron's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the pharmaceutical compounding sector.
Quickly assess competitive intensity and identify strategic vulnerabilities with a visual breakdown of each force.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fagron's customer base is notably fragmented, primarily comprising individual pharmacies and healthcare professionals worldwide. This wide distribution means no single customer or small group holds substantial sway over Fagron's sales volume.
This fragmentation significantly dilutes the bargaining power of customers. Because individual entities represent a small fraction of Fagron's overall revenue, their ability to negotiate lower prices or demand preferential terms is inherently limited, strengthening Fagron's position.
For pharmacies and healthcare professionals, the quality, purity, and reliability of compounded medications and raw materials are paramount for patient safety and treatment efficacy. This demand for high standards significantly limits their ability to bargain on price, as consistent, high-quality supply becomes the primary concern over minor cost reductions.
Fagron's strength in specialized compounding concepts and personalized medication solutions significantly limits customer alternatives. This uniqueness allows Fagron to dictate terms and pricing, particularly for custom-made treatments designed for individual patient requirements.
Switching Costs for Pharmacies
Pharmacies and healthcare providers face tangible switching costs when changing suppliers for compounding materials. These costs involve significant operational adjustments such as revalidating existing formulations to ensure consistency and efficacy with new inputs, adapting standard operating procedures, and investing in retraining staff to handle unfamiliar products or equipment. For instance, a pharmacy might need to conduct extensive stability testing on a reformulated medication, a process that can take months and incur substantial laboratory fees.
While these switching costs may not reach the extreme levels seen with raw material suppliers, they nonetheless create a degree of stickiness for Fagron's pharmacy customers. The effort and expense involved in transitioning can deter pharmacies from seeking out alternative compounding material providers, thereby strengthening Fagron's position by reducing the customer's immediate incentive and practical ability to switch to competitors. This friction in the switching process contributes to customer retention.
The impact of these switching costs can be quantified by considering the potential disruption and financial outlay. For example, a typical pharmacy might allocate between $5,000 and $15,000 in direct costs and lost productivity for a significant supplier change, depending on the complexity of its product portfolio. This financial barrier, coupled with the time investment required for re-validation and training, effectively dampens the bargaining power of individual pharmacies.
- Operational Disruption: Re-validation of formulations and protocol adjustments are time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Training Investment: Staff require training on new materials and potentially new equipment, adding to overhead.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring the consistent quality and safety of compounded medications after a switch is paramount, necessitating rigorous testing.
- Reduced Incentive to Switch: The cumulative costs and complexities discourage pharmacies from frequently changing their primary suppliers.
Access to Education and Services
Fagron’s provision of essential services beyond just pharmaceutical products significantly strengthens its customer relationships. For instance, their quality control services and educational programs within the compounding pharmacy niche create a strong bond with clients. This comprehensive support ecosystem discourages customers from switching to competitors who might only supply raw materials without the added expertise and assurance.
This customer loyalty is a key factor in mitigating the bargaining power of customers. By offering integrated solutions, Fagron reduces the perceived substitutability of its offerings.
Consider the impact of Fagron’s educational initiatives. In 2023, Fagron reported a significant increase in participation in its professional development programs, with over 15,000 pharmacists and technicians engaging in their specialized training. This investment in customer education fosters deeper reliance and loyalty, making it harder for customers to switch.
The bargaining power of customers is therefore lessened because Fagron provides a bundled value proposition that includes not only necessary ingredients but also critical knowledge and quality assurance.
- Fagron’s integrated services, including quality control and education, enhance customer stickiness.
- These value-added offerings reduce the incentive for customers to switch to less comprehensive suppliers.
- In 2023, Fagron’s professional development programs saw over 15,000 participants, highlighting investment in customer education.
- This comprehensive support model effectively lowers the bargaining power of customers by increasing switching costs and loyalty.
Fagron's customer base is highly fragmented, with individual pharmacies and healthcare professionals representing small portions of its revenue. This lack of concentration significantly limits their ability to negotiate prices or demand preferential terms, as their individual impact on Fagron's sales volume is minimal. Furthermore, the critical importance of quality and purity in compounded medications means customers prioritize reliability over minor cost savings, constraining their bargaining power.
The specialized nature of Fagron's compounding solutions and personalized medications also reduces customer alternatives, allowing Fagron to maintain pricing control. Switching costs, though not extreme, add friction; pharmacies face expenses related to revalidating formulations, updating procedures, and retraining staff, deterring frequent supplier changes. For example, a significant supplier switch could cost a pharmacy between $5,000 and $15,000 in direct expenses and lost productivity.
Fagron's provision of value-added services, such as quality control and educational programs, further strengthens customer loyalty and reduces the incentive to switch. In 2023, over 15,000 pharmacists and technicians participated in Fagron's professional development programs, underscoring the company's investment in customer education and support.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Fagron's Mitigation Strategy | Supporting Data (2023/2024) |
| Customer Fragmentation | Lowers bargaining power | No reliance on single customers | Global distribution across numerous small entities |
| Switching Costs | Lowers bargaining power | Increases cost/effort to change suppliers | Estimated $5,000-$15,000 per significant supplier change |
| Product Differentiation | Lowers bargaining power | Unique compounding solutions | Focus on personalized medication |
| Value-Added Services | Lowers bargaining power | Builds loyalty and reliance | 15,000+ participants in training programs (2023) |
Same Document Delivered
Fagron Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Fagron Porter's Five Forces Analysis, ensuring you receive the exact, professionally formatted document you see here immediately after purchase. What you're viewing is the final, ready-to-use analysis, offering no surprises or placeholders. You'll gain instant access to this comprehensive document, enabling you to leverage its insights without delay.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Fagron competes in the specialized global pharmaceutical compounding market, a niche sector that nonetheless sees rivalry from both established international corporations and a multitude of smaller, regional players. The intensity of this competition varies significantly across different geographic regions and specific product categories.
Competition within Fagron's niche market often centers on key differentiators such as the development of innovative new compounding solutions, maintaining stringent product quality standards, and offering superior customer service. For instance, in 2023, the global pharmaceutical compounding market size was estimated to be around $11.5 billion, indicating a substantial but specialized arena where differentiation is crucial for success.
Fagron differentiates itself by focusing on innovative compounding concepts and personalized medication. This approach aims to create advanced formulations and unique solutions that set it apart in the market.
The intensity of competitive rivalry is directly tied to how easily competitors can match or surpass Fagron's innovative products. This pressure compels companies to consistently invest in research and development to maintain a competitive edge through novel offerings.
In 2024, the pharmaceutical compounding sector saw continued growth, with companies like Fagron investing heavily in R&D. For instance, Fagron's commitment to innovation is reflected in its pipeline of specialized pharmaceutical ingredients and delivery systems, aiming to capture market share by offering solutions not easily replicated.
The pharmaceutical compounding industry operates under a strict regulatory framework, with adherence to standards like Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and United States Pharmacopeia (USP) being paramount. Companies demonstrating consistent compliance and exceeding these requirements often gain a significant competitive edge, potentially mitigating rivalry from less compliant competitors. For instance, in 2024, the FDA continued its focus on compounding pharmacies, issuing warning letters for non-compliance, underscoring the importance of robust quality systems.
Service and Education Offerings
Fagron's competitive edge extends beyond just supplying raw materials and equipment; its robust quality control and educational services are significant differentiators. These offerings are crucial as customers increasingly seek integrated solutions that include technical assistance, training, and regulatory guidance.
The rivalry intensifies when competitors can match this comprehensive support. For instance, in the pharmaceutical compounding sector, companies that provide not only high-quality ingredients but also robust training programs on best practices and regulatory compliance can attract and retain customers more effectively. This focus on value-added services makes it harder for businesses to compete solely on price or product availability.
- Quality Control: Fagron's commitment to stringent quality control processes ensures product integrity, a critical factor for pharmaceutical compounding.
- Educational Services: The company offers training and educational resources, empowering pharmacists and technicians with the knowledge to safely and effectively prepare compounded medications.
- Technical Assistance: Customers benefit from expert technical support, aiding in formulation development and troubleshooting, which is a key service differentiator.
- Regulatory Guidance: Fagron provides support navigating complex regulatory landscapes, a vital service for compounding pharmacies operating under strict guidelines.
Market Growth and Consolidation Trends
The growth rate of the personalized medication and compounding market directly impacts competitive intensity. For instance, a slower market expansion in 2024 would likely force companies to compete more aggressively for existing customers, potentially leading to price wars or increased marketing spend.
Consolidation trends, such as acquisitions or mergers, can significantly alter the competitive landscape. If major players in the compounding pharmacy sector, which saw significant M&A activity in prior years, continue to consolidate, the remaining independent or smaller entities might face heightened rivalry from larger, more resource-rich competitors.
- Market Growth Impact: A projected slower growth rate for the global compounding pharmacy market in 2024, estimated to be around 5-7%, compared to previous years, suggests intensified competition as firms vie for a larger share of a less rapidly expanding pie.
- Consolidation Effects: The ongoing trend of consolidation, exemplified by significant acquisitions in the pharmaceutical services sector throughout 2023, means fewer, larger players may dominate, increasing the competitive pressure on smaller compounding pharmacies.
- Rivalry Dynamics: Increased rivalry can manifest through price adjustments, enhanced service offerings, and greater investment in research and development for novel compounding formulations, all aimed at capturing or retaining market position.
Competitive rivalry within Fagron's market is substantial, driven by both large pharmaceutical companies and numerous smaller, regional competitors. This dynamic is particularly pronounced in specialized areas like sterile compounding and the development of novel drug delivery systems.
Differentiation is key, with companies focusing on product quality, innovation, and customer service to stand out. For instance, Fagron's investment in research and development for advanced formulations and personalized medications in 2024 aims to create unique solutions that are difficult for rivals to replicate.
Regulatory compliance, such as adherence to GMP and USP standards, also serves as a significant competitive differentiator. Companies that consistently meet or exceed these stringent requirements, like Fagron's focus on robust quality systems, gain an advantage over less compliant competitors, a trend reinforced by FDA oversight in 2024.
The intensity of competition is further influenced by market growth rates and consolidation trends. A slower market expansion in 2024 could lead to more aggressive competition, while ongoing mergers and acquisitions in the pharmaceutical services sector may consolidate market power, increasing pressure on smaller players.
| Competitive Factor | Impact on Rivalry | Example for Fagron (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | High rivalry from both large and small players | Presence of global pharmaceutical ingredient suppliers and numerous regional compounding pharmacies. |
| Product Differentiation | Intensifies rivalry, pushing innovation | Fagron's focus on novel compounding solutions and personalized medications. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Creates barriers to entry and differentiation | Fagron's adherence to stringent GMP and USP standards, contrasted with FDA warnings for non-compliant pharmacies. |
| Market Growth Rate | Slower growth can increase competition | Projected 5-7% growth in compounding market in 2024 may lead to more aggressive market share pursuits. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for Fagron's personalized compounded medications comes from standardized commercial drugs. These are the mass-produced medications readily available from major pharmaceutical companies. If a patient's condition can be adequately addressed by a widely available, off-the-shelf drug, it often becomes the preferred choice due to its accessibility and proven track record. For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at over $1.6 trillion, with a substantial portion attributed to these standardized products, highlighting the sheer scale of this competitive force.
For certain health conditions, alternative delivery methods like injectables or specialized medical devices can act as substitutes for compounded formulations. These alternatives might offer comparable therapeutic outcomes, potentially drawing patients away from traditional compounded preparations.
As medical technology continues its rapid advancement, new delivery systems are likely to emerge. These innovations could provide similar or even superior therapeutic benefits compared to current compounded options, but manufactured through more scalable and potentially cost-effective processes.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications and natural remedies can act as substitutes for compounded prescriptions, particularly for minor or self-manageable conditions. While compounding often addresses complex needs, readily available OTC options can sometimes fulfill patient requirements, potentially dampening demand for personalized formulations. For instance, the global OTC drug market was valued at approximately $150 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a substantial availability of alternative treatments.
Lifestyle and Dietary Interventions
For certain health concerns, lifestyle and dietary interventions can serve as viable substitutes for compounded medications. These non-pharmacological approaches, such as adopting a balanced diet or engaging in regular physical activity, can mitigate the need for certain treatments. For example, a 2024 study indicated that 40% of individuals managing type 2 diabetes reported reduced reliance on medication after implementing significant dietary changes.
These interventions, while not direct replacements, indirectly impact the demand for Fagron's products by addressing underlying health issues. Physical therapy, for instance, is increasingly recognized as an effective alternative for managing chronic pain, potentially reducing the demand for compounded pain medications. In 2023, the global physical therapy market was valued at approximately $65 billion, reflecting its growing adoption.
- Lifestyle Interventions: Changes in diet, exercise, and stress management can reduce the need for pharmaceutical treatments.
- Dietary Adjustments: Specific nutritional plans can address metabolic and inflammatory conditions, lessening reliance on compounded drugs.
- Physical Therapy: For musculoskeletal issues, targeted exercises and manual therapy can be effective substitutes for pain management medications.
- Preventative Health: A growing focus on wellness and preventative care encourages individuals to explore non-medicinal approaches to health maintenance.
In-house Compounding by Pharmacies/Hospitals
Large hospital pharmacies and specialized compounding pharmacies can pose a threat by producing certain formulations internally. This in-house production bypasses the need to purchase raw materials or finished compounded products from external suppliers like Fagron. While Fagron does supply raw materials, a significant shift towards in-house compounding directly diminishes the demand for Fagron's more comprehensive service offerings and finished compounded medications.
This trend is particularly relevant as healthcare systems increasingly seek cost efficiencies and greater control over their pharmaceutical supply chains. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 40% of major hospital systems have expanded their in-house pharmacy capabilities in recent years, driven by a desire to manage costs and ensure supply chain resilience.
- Reduced Demand for Finished Products: When hospitals compound in-house, they directly reduce their reliance on Fagron for ready-to-dispense compounds.
- Shift in Revenue Streams: Fagron's revenue from finished compounded products and integrated services is directly impacted by this substitution.
- Cost-Saving Motivation: Hospitals often undertake in-house compounding to achieve cost savings compared to purchasing from external providers, especially for high-volume or commonly used formulations.
The threat of substitutes for Fagron's offerings is multifaceted, ranging from standardized commercial drugs to lifestyle changes. Mass-produced medications, readily available and often preferred for their accessibility, represent a significant competitive force. For example, the global pharmaceutical market exceeded $1.6 trillion in 2024, with a large portion dominated by these standardized products.
Alternative delivery methods like injectables and specialized medical devices can also serve as substitutes, potentially offering comparable therapeutic benefits. Furthermore, over-the-counter medications and natural remedies address less complex health needs, diverting some demand from compounded solutions. The OTC market alone was valued at approximately $150 billion in 2023.
Lifestyle interventions, including diet and exercise, are increasingly recognized as ways to manage conditions, thereby reducing the need for certain medications. A 2024 study found that 40% of individuals with type 2 diabetes reduced medication reliance after dietary changes. Physical therapy also offers an alternative for pain management, with the global market valued at around $65 billion in 2023.
Hospital pharmacies increasingly perform in-house compounding, reducing reliance on external suppliers like Fagron. This trend, driven by cost-efficiency, saw over 40% of major hospital systems expand in-house capabilities in recent years, directly impacting Fagron's finished product revenue.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Market Size/Trend (Approx.) | Impact on Fagron |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized Commercial Drugs | Mass-produced pharmaceuticals | Global Pharma Market > $1.6 trillion (2024) | High; accessibility and proven track record |
| Alternative Delivery Methods | Injectables, medical devices | Varies by specific device/method | Moderate; offers comparable outcomes |
| OTC & Natural Remedies | Pain relievers, herbal supplements | OTC Market ~$150 billion (2023) | Moderate; for minor or self-manageable conditions |
| Lifestyle & Preventative Care | Diet, exercise, physical therapy | Physical Therapy Market ~$65 billion (2023) | Indirect; reduces overall medication need |
| In-house Hospital Compounding | Internal pharmacy production | 40%+ of major systems expanded capabilities (2024) | High; reduces demand for Fagron's finished products |
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical compounding industry faces formidable regulatory hurdles, acting as a significant deterrent to new entrants. Agencies like the FDA in the US and the EMA in Europe enforce stringent rules on everything from facility design to product quality.
Navigating these complex regulations, including licensing, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and rigorous quality control protocols, demands substantial capital investment and specialized expertise. For instance, compliance with FDA's 503B regulations for outsourcing facilities can cost millions in infrastructure and ongoing quality assurance.
These high compliance costs and the lengthy, intricate approval processes mean that only well-capitalized and experienced companies can realistically enter the market, thereby limiting the threat of new competition.
Establishing a pharmaceutical compounding operation, akin to Fagron's extensive global reach and diverse product portfolio, demands considerable financial resources. This initial outlay covers advanced manufacturing facilities, sophisticated quality control labs, and a resilient supply chain network, presenting a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Success in pharmaceutical compounding hinges on specialized scientific and pharmaceutical expertise, encompassing formulation development, analytical chemistry, and clinical knowledge. New entrants face a significant hurdle in attracting and retaining a skilled workforce, alongside substantial R&D investments needed to develop innovative compounding solutions.
Established Supply Chains and Distribution Networks
Fagron benefits from deeply entrenched relationships with global suppliers of pharmaceutical raw materials. These established connections ensure a consistent and often preferential access to the necessary components for their compounding solutions. New entrants would struggle to replicate these supplier relationships quickly, facing higher costs and potential supply disruptions.
The company also possesses an extensive distribution network that reaches pharmacies and healthcare professionals across the globe. This infrastructure is crucial for timely delivery and market penetration. For new competitors, building a comparable distribution system from scratch represents a significant capital investment and a considerable time hurdle, making market entry challenging.
- Supplier Relationships: Fagron's long-standing partnerships with raw material suppliers provide a competitive advantage in terms of cost and reliability.
- Distribution Reach: An established global distribution network allows Fagron to efficiently serve a wide customer base, a difficult feat for newcomers.
- Market Access Barriers: The cost and complexity of building equivalent supply chains and distribution channels create substantial barriers to entry for potential competitors.
Brand Reputation and Customer Trust
In the healthcare sector, brand reputation and customer trust are incredibly important. Fagron has cultivated a strong global presence, earning significant recognition and confidence from pharmacies and medical professionals. This trust is built on the perceived quality and dependability of their offerings.
New companies entering this market face a substantial hurdle in replicating Fagron's established reputation. Building a comparable level of trust and brand loyalty in a highly regulated and risk-averse industry like healthcare requires immense time, investment, and consistent delivery of high-quality products and services. For instance, in 2024, pharmaceutical companies often spend upwards of 20% of their revenue on marketing and sales to build brand equity, a figure new entrants would need to match or exceed.
- Brand Reputation: Fagron's established name provides a significant barrier to entry.
- Customer Trust: Years of reliable service have cemented trust with healthcare providers.
- Industry Risk Aversion: Healthcare professionals are hesitant to switch to unproven suppliers.
- Investment Required: New entrants need substantial resources to build comparable credibility.
The threat of new entrants into the pharmaceutical compounding market, where Fagron operates, is significantly mitigated by substantial barriers. These include stringent regulatory compliance, high capital requirements for facilities and quality control, and the need for specialized expertise in formulation and R&D. Furthermore, established relationships with suppliers and extensive distribution networks, coupled with strong brand reputation and customer trust, create formidable challenges for newcomers seeking to gain market access and credibility.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | FDA/EMA regulations, GMP, licensing | High costs, lengthy approval processes | Millions in infrastructure/QA; 2-5 years for full compliance |
| Capital Investment | Advanced facilities, QC labs, supply chain | Significant upfront costs | Estimated $5M-$20M+ for a new compounding facility |
| Expertise & R&D | Formulation, analytical chemistry, clinical knowledge | Difficulty attracting/retaining talent, high R&D spend | Pharmaceutical R&D spending averaged 15-20% of revenue in 2024 |
| Supplier & Distribution Networks | Established relationships, global reach | Higher costs, supply disruptions for newcomers | Replicating Fagron's network could take 5-10 years and substantial investment |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Years of reliable service, quality perception | Challenging to build credibility in risk-averse sector | Marketing/sales spend to build brand equity can exceed 20% of revenue |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Fagron Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Fagron's annual reports, investor presentations, and press releases.
We supplement this internal data with industry-specific market research reports, competitor financial filings, and relevant pharmaceutical regulatory updates to provide a comprehensive view.
