Enterprise Bank & Trust Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Enterprise Bank & Trust Bundle
Enterprise Bank & Trust operates in a dynamic financial landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer expectations. Understanding the underlying forces at play is crucial for navigating this market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Enterprise Bank & Trust’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Depositors exert moderate bargaining power over Enterprise Bank & Trust. This power is largely influenced by prevailing market interest rates and the broader economic climate, which dictate the attractiveness and cost of capital. While individual retail depositors have minimal leverage, larger corporate and institutional clients can negotiate better terms, directly affecting the bank's cost of funds.
Enterprise Bank & Trust experienced robust deposit growth in 2024, with total deposits reaching $71.9 billion by the end of the first quarter. This strong performance suggests a stable, yet competitive, landscape for attracting and retaining capital from depositors, indicating that while depositors have influence, the bank's solid financial standing allows it to manage this power effectively.
Skilled employees, especially in areas like commercial lending and wealth management, hold considerable sway. Enterprise Bank & Trust, like its peers, needs to provide attractive pay, benefits, and growth paths to secure and keep top performers.
The banking industry's need for expertise in digital transformation and AI is a key factor, increasing the leverage of these specialized workers. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 10% growth for information technology managers between 2022 and 2032, a rate faster than average, highlighting the demand for tech talent.
Technology providers wield significant bargaining power over banks like Enterprise Bank & Trust as digital transformation accelerates. The increasing reliance on advanced platforms for core banking, wealth management, and crucial cybersecurity necessitates dependence on these specialized vendors, giving them leverage.
The growing importance of AI in banking, coupled with the associated compliance costs, further amplifies supplier power. For instance, the projected increase in AI compliance expenses for financial institutions between 2024 and 2025 underscores the financial impact of this trend, highlighting the critical need for banks to secure and maintain relationships with capable technology partners.
Information and Data Providers
Information and data providers are critical suppliers for Enterprise Bank & Trust, offering essential financial data, market intelligence, and credit assessment tools. The quality and timeliness of these inputs directly impact the bank's ability to analyze market trends, manage risk, and make strategic decisions. For instance, in 2024, the demand for real-time, AI-ready data feeds from providers like Bloomberg and Refinitiv has intensified, reflecting the increasing reliance on advanced analytics for competitive advantage.
- Data quality and accuracy: Enterprise Bank & Trust relies on providers for accurate market data, credit scores, and economic indicators.
- Timeliness of information: The speed at which data is delivered is crucial for timely decision-making in fast-moving markets.
- Provider concentration: A limited number of dominant data providers can increase their bargaining power.
- AI and analytics integration: The growing need for sophisticated AI-driven insights elevates the importance of data providers who can supply comprehensive and structured datasets.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) and state banking authorities, wield considerable influence over Enterprise Bank & Trust, even though they are not traditional suppliers. These entities establish the operational landscape and enforce critical rules.
Their mandates, covering capital adequacy, liquidity management, and risk protocols, directly impact the bank's strategic decisions and financial outlays. For instance, in 2024, the FDIC continued to emphasize robust cybersecurity measures, requiring significant investment from financial institutions like Enterprise Bank & Trust to protect customer data and maintain system integrity.
- Stringent Capital Requirements: Regulatory bodies dictate minimum capital ratios, forcing banks to hold more capital, which can impact profitability and lending capacity.
- Liquidity Mandates: Compliance with liquidity coverage ratios and net stable funding ratios necessitates careful management of assets and liabilities.
- Evolving Compliance Costs: New regulations, particularly around areas like artificial intelligence in financial services, demand ongoing investment in technology and expertise.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: The threat of fines and sanctions for failing to meet regulatory standards reinforces the bargaining power of these authorities.
Technology providers and data vendors represent a significant source of bargaining power for Enterprise Bank & Trust. The increasing reliance on specialized software for core banking operations, cybersecurity, and advanced analytics means the bank is dependent on these external entities. This dependence is amplified by the growing complexity and cost associated with integrating new technologies, especially in areas like artificial intelligence, which requires specialized expertise and robust data infrastructure.
In 2024, the demand for cloud-based banking solutions and AI-driven customer service platforms continued to rise, giving technology vendors considerable leverage. Banks must invest heavily in these systems to remain competitive, making vendor relationships critical. For example, the market for financial technology (FinTech) solutions is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong demand that empowers providers.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependencies for Enterprise Bank & Trust | Impact of Bargaining Power | 2024/2025 Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers | Core banking software, cybersecurity platforms, AI/analytics tools | Increased costs for essential systems, potential vendor lock-in | Rising demand for cloud-native banking solutions |
| Data & Information Providers | Market data feeds, credit scoring services, economic intelligence | Reliance on data accuracy for risk management and decision-making | Intensified need for real-time, AI-ready data from providers like Bloomberg |
What is included in the product
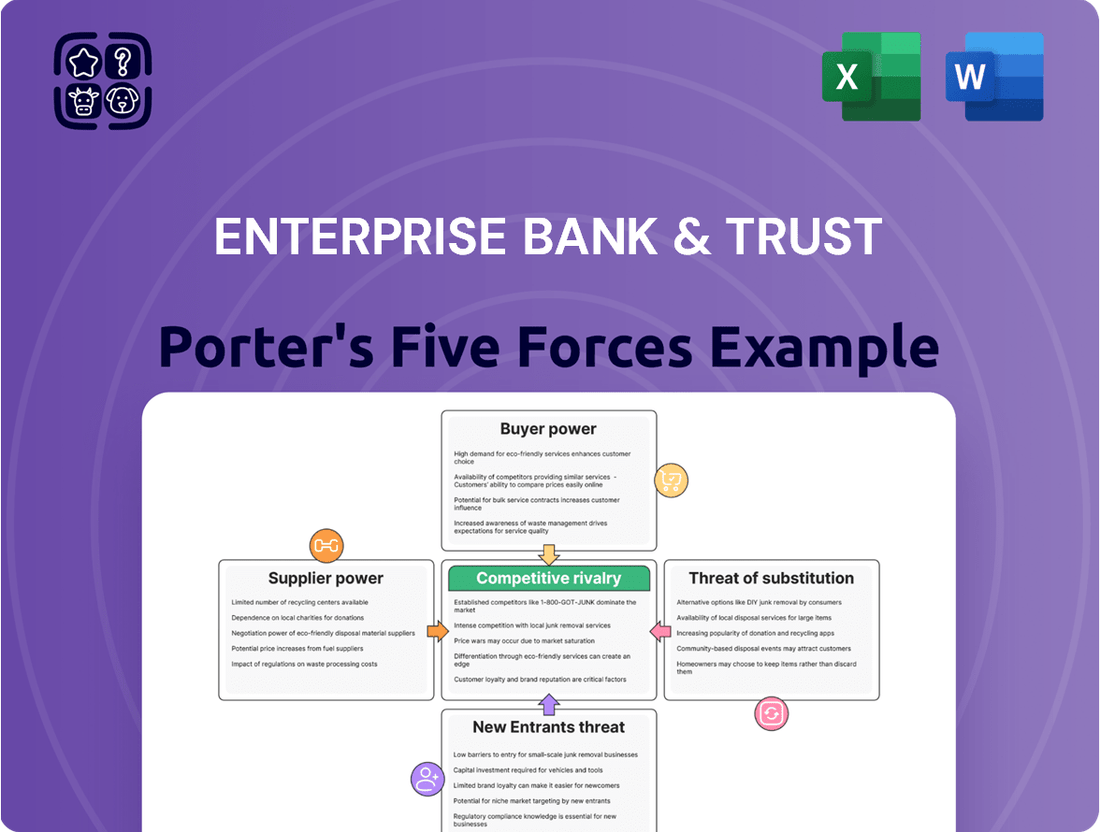
Tailored exclusively for Enterprise Bank & Trust, this analysis dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products within its operating environment.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry dynamics, empowering Enterprise Bank & Trust to proactively address market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Retail and small business customers hold moderate bargaining power. With many banks and credit unions available, and low costs to switch basic accounts, they can easily move their money if unsatisfied. For instance, in 2024, the average customer retention rate for regional banks hovered around 85-90%, indicating that a significant portion of customers do switch annually.
The rise of digital banking has amplified this power. Customers can now effortlessly compare interest rates, fees, and services online, making it simpler than ever to find better deals. This ease of comparison means banks like Enterprise Bank & Trust need to consistently offer competitive digital tools and personalized service to keep these customers engaged and prevent them from looking elsewhere.
Commercial and corporate clients, particularly those with substantial banking needs like large businesses, wield significant bargaining power. They often demand tailored financial solutions, from commercial and retail loans to sophisticated treasury management services, and can leverage the volume and complexity of their business to negotiate favorable terms.
Enterprise Bank & Trust's strategic focus on privately-held businesses amplifies the importance of these client relationships. In 2023, for instance, the bank reported total loans of $13.9 billion, a substantial portion of which would likely come from these larger corporate entities, giving them considerable leverage in discussions about pricing and service agreements.
Wealth management clients, particularly high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors, wield considerable bargaining power. They expect highly customized investment strategies, sophisticated digital platforms, and transparent, competitive fees. For instance, in 2024, many wealth management firms are enhancing their digital offerings to meet client demand, with a significant portion of clients indicating a willingness to switch providers for superior digital experiences and personalized advice.
Price Sensitivity and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, making them highly price-sensitive. Online comparison tools and readily available data allow consumers to easily benchmark rates for loans, deposits, and various banking fees. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage fluctuated around 6.6%, a figure easily verifiable by potential borrowers, directly impacting their decision-making process.
This heightened transparency significantly boosts customer bargaining power. They can swiftly identify the most competitive offers across the market, pushing banks like Enterprise Bank & Trust to maintain aggressive pricing strategies. This necessitates a focus on differentiating through value-added services and cultivating robust customer relationships to retain business.
- Increased Price Transparency: Online platforms allow for easy comparison of banking product pricing.
- Customer Bargaining Power: Customers can readily identify the best rates for loans and deposits.
- Competitive Pressure: Banks must offer competitive pricing or emphasize superior service.
- Focus on Value: Enterprise Bank & Trust needs to highlight its unique offerings beyond just price.
Demand for Digital and Personalized Experiences
Customers increasingly expect digital-first, personalized banking experiences. This demand for seamless online interactions and tailored services, including AI-driven insights and proactive solutions, amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of consumers consider digital banking capabilities a key factor when choosing a financial institution.
Financial institutions like Enterprise Bank & Trust face pressure to invest in advanced technologies to meet these evolving customer expectations. Failure to provide hyper-personalized services and instant access can lead to customer attrition, particularly to nimble fintech competitors.
- Digital Expectations: A significant majority of banking customers now prioritize digital channels for transactions and service.
- Personalization Demand: Customers expect financial services tailored to their individual needs and preferences.
- Competitive Pressure: Fintechs and digitally advanced banks are setting new benchmarks for customer experience, increasing pressure on traditional institutions.
- Investment Imperative: Banks must invest in technology to remain competitive and retain customers in this evolving landscape.
The bargaining power of customers for Enterprise Bank & Trust is significant, driven by increased price transparency and evolving digital expectations. Customers can easily compare offerings, pushing banks to be competitive on rates and fees. This necessitates a strong focus on delivering superior value and personalized experiences to retain client loyalty. In 2024, the average consumer spends over 3 hours per week managing their finances online, highlighting the importance of digital engagement.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Drivers | Impact on Enterprise Bank & Trust |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & Small Business | Moderate to High | Low switching costs, ease of online comparison, availability of alternatives | Pressure on pricing, need for competitive digital offerings and service |
| Commercial & Corporate | High | Large transaction volumes, demand for tailored solutions, negotiation leverage | Need for specialized services, relationship management, competitive pricing on complex products |
| Wealth Management | High | Demand for customization, sophisticated platforms, fee sensitivity | Focus on personalized strategies, advanced digital tools, transparent fee structures |
Same Document Delivered
Enterprise Bank & Trust Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Enterprise Bank & Trust Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector. This detailed analysis is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Enterprise Bank & Trust faces a highly fragmented and diverse competitive environment. The banking sector includes large national institutions, numerous regional banks, and a vast number of community banks and credit unions, all vying for customers across commercial, retail, and wealth management services. This broad spectrum of players means Enterprise Bank & Trust must consistently differentiate itself to capture and retain market share.
For many standard banking products, offerings can appear quite similar across different institutions. This often means that competition heats up based on price, like interest rates, or the fees charged for services. For example, in 2024, the average interest rate on a new car loan hovered around 7.5%, a figure that banks actively adjust to attract customers.
While Enterprise Bank & Trust strives to stand out by offering a broad range of services and focusing on building strong customer relationships, the fundamental similarity of core banking products like checking accounts or mortgages makes differentiation crucial. This similarity intensifies the need for exceptional customer service and continuous innovation to retain and attract clients in a crowded market.
The banking sector is experiencing a significant surge in competitive rivalry driven by rapid digitalization and innovation. Banks are locked in a fierce race to leverage advancements in artificial intelligence and digital platforms to deliver superior customer experiences, making convenience and efficiency paramount. For Enterprise Bank & Trust, this means a constant need to invest in technology to stay competitive and meet customer demands for seamless digital interactions.
This technological arms race is not just about offering new features; it's about fundamentally reshaping how banking services are delivered. For instance, in 2024, many traditional banks are investing heavily in AI-powered chatbots and personalized financial advice tools, mirroring the capabilities of fintech disruptors. The pressure to innovate means continuous upgrades to mobile banking apps, online account management, and secure payment systems, all while managing the associated costs and cybersecurity risks.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are reshaping the banking and wealth management sectors, as firms pursue consolidation for greater scale and market influence. This heightened activity signals a competitive environment where strategic partnerships are crucial for survival and growth.
Enterprise Bank & Trust's own strategic move, its planned merger with Rockland Trust slated for completion by July 2025, directly reflects this industry-wide trend. This combination aims to bolster Enterprise Bank & Trust's competitive standing and operational capabilities.
- Industry Consolidation: The banking sector saw a significant number of M&A deals in 2024, with over 200 announced transactions, indicating a strong push towards consolidation.
- Scale and Efficiency: Mergers often aim to achieve economies of scale, reduce operating costs, and expand service offerings, thereby enhancing competitiveness.
- Market Position: By merging, institutions like Enterprise Bank & Trust and Rockland Trust seek to strengthen their market share and geographic reach.
- Strategic Imperative: The M&A surge is a direct response to evolving customer demands, technological advancements, and increasing regulatory pressures, making strategic combinations a necessity.
Focus on Niche Markets and Specialization
Banks often compete intensely by honing in on specific market niches. Enterprise Bank & Trust, for instance, strategically targets privately-held businesses and their owners. This specialization creates a distinct competitive landscape where deep industry knowledge and customized financial services become crucial for standing out against both broad-market competitors and other specialized institutions.
This niche focus means rivalry isn't just about price, but about the quality of tailored advice and solutions. For example, in 2024, many regional banks saw increased competition for middle-market businesses seeking specialized treasury management or commercial real estate financing, areas where Enterprise Bank & Trust likely competes directly.
- Specialization as a Differentiator: Enterprise Bank & Trust's focus on privately-held businesses and their owners allows for highly tailored services, distinguishing it from more generalist banks.
- Expertise in Niche Markets: Competition within these specialized segments often hinges on the depth of expertise and understanding of specific client needs, such as succession planning or capital raising for closely-held companies.
- Targeted Competitive Arena: This creates a competitive arena where banks that can offer specialized knowledge and relationship-driven service have an advantage over those with a broader, less focused approach.
The competitive rivalry for Enterprise Bank & Trust is intense, fueled by a fragmented market and the commoditization of standard banking products. Banks compete heavily on interest rates and fees, with average new car loan rates around 7.5% in 2024, highlighting price sensitivity.
Digitalization is a major driver, pushing banks to invest in AI and digital platforms for better customer experience, as seen with the rise of AI-powered chatbots and personalized financial tools in 2024.
Industry consolidation, with over 200 M&A deals in 2024, is reshaping the landscape, forcing institutions like Enterprise Bank & Trust to merge to gain scale and market share, as exemplified by its planned merger with Rockland Trust.
Enterprise Bank & Trust also faces rivalry in its niche focus on privately-held businesses, where competition centers on specialized knowledge and tailored solutions rather than just price.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech firms are increasingly offering specialized financial services that can replace traditional banking products. Think of peer-to-peer lending platforms, digital payment apps like Venmo or Zelle, and online investment advisors. These alternatives often boast superior convenience, faster transaction times, and more competitive pricing, directly challenging Enterprise Bank & Trust's established services.
The threat is substantial, as evidenced by the rapid growth in fintech adoption. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at over $11 trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach $33 trillion by 2030, highlighting a significant shift in consumer preference towards these digital solutions.
Commercial clients increasingly bypass traditional bank loans for direct capital market access. In 2024, the U.S. corporate bond market saw robust issuance, with investment-grade companies raising over $1.5 trillion, demonstrating a significant alternative to bank financing for larger enterprises.
This trend is further amplified by the growth of private equity and venture capital funding. For instance, venture capital firms invested approximately $150 billion in U.S. startups and growth-stage companies throughout 2024, providing substantial capital without requiring commercial bank intermediation.
Consequently, the ability of businesses to directly tap into these capital markets serves as a potent substitute for commercial banking services, particularly for those with strong credit profiles or innovative business models seeking growth capital.
Independent financial advisors and robo-advisors present a significant threat of substitutes for Enterprise Bank & Trust's wealth management services. These non-bank providers often cater to specific client needs with specialized investment strategies or more competitive fee structures, drawing away potential or existing bank clients. For instance, the independent advisor channel in the U.S. managed approximately $5.1 trillion in assets as of the end of 2023, demonstrating its substantial market presence.
Direct-to-consumer investment platforms, like those offering fractional shares or commission-free trading, also act as potent substitutes. These platforms appeal to a growing segment of investors, particularly younger demographics, who prioritize accessibility and lower costs over traditional, full-service banking relationships. The continued growth in assets managed by these platforms, which saw significant inflows in 2023, underscores their appeal as alternatives to bank-led wealth management.
Embedded Finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
The increasing prevalence of embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banks like Enterprise Bank & Trust. Non-financial companies can now offer banking services directly within their own ecosystems, making traditional banking channels less necessary for many transactions. This shift allows businesses to provide financial products, like lending or payments, without needing to be a licensed bank themselves.
This evolution means that customers might opt for integrated financial solutions offered by their preferred tech platforms rather than engaging directly with a bank. For instance, a retail company could offer point-of-sale financing or loyalty-based payment options, effectively substituting a bank's role in those specific customer interactions. The BaaS model, in particular, lowers the barrier to entry for financial service provision, allowing a wider array of companies to compete with banks.
- Embedded Finance Growth: Projections indicate the embedded finance market could reach $7 trillion globally by 2030, a substantial increase from current figures, highlighting the scale of potential substitution.
- BaaS Adoption: Major financial institutions are increasingly partnering with BaaS providers, signaling a recognition of this trend and its potential to disrupt traditional banking models.
- Customer Convenience: Studies show consumers value seamless, integrated experiences, making them more likely to adopt financial services embedded within platforms they already use regularly.
- New Entrants: Fintech companies leveraging BaaS are enabling non-financial brands to launch financial products, creating a new competitive landscape for traditional banks.
Regulatory Shifts and Alternative Lending
Regulatory shifts can significantly impact the competitive landscape for banks like Enterprise Bank & Trust. When regulations become more stringent for traditional banks, it can inadvertently create an opening for alternative lending platforms and non-bank financial institutions.
These substitute providers often face fewer compliance hurdles, making them a more attractive and accessible option for borrowers. For instance, in 2024, the rise of fintech lenders offering streamlined digital onboarding and faster loan approvals highlights this trend, as they can bypass some of the legacy compliance burdens faced by established banks.
This dynamic directly increases the threat of substitutes, as borrowers may opt for these less regulated, yet potentially more efficient, financing channels. The global alternative lending market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion by 2024, demonstrating its substantial and growing presence as a substitute for traditional bank loans.
- Increased Competition: Stricter bank regulations can drive borrowers to alternative lenders, increasing competitive pressure.
- Fintech Advantage: Fintech platforms, with their digital focus and potentially lighter regulatory load, offer a compelling substitute.
- Market Growth: The significant growth in the alternative lending market, exceeding $1.1 trillion in 2024, underscores the threat.
The threat of substitutes for Enterprise Bank & Trust is significant, stemming from a diverse range of non-traditional financial service providers. These alternatives often leverage technology to offer greater convenience, lower costs, and specialized services that directly compete with the bank's offerings.
Fintech firms, for example, provide services like peer-to-peer lending and digital payments, challenging traditional banking models. The global fintech market's projected growth to $33 trillion by 2030 underscores this shift. Furthermore, commercial clients increasingly access capital markets directly, with U.S. corporate bond issuance exceeding $1.5 trillion in 2024, bypassing bank loans.
Wealth management services are also under pressure from independent and robo-advisors, managing approximately $5.1 trillion in assets as of late 2023. Embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) further dilute traditional banking roles, with the embedded finance market potentially reaching $7 trillion globally by 2030.
Regulatory disparities can also favor substitutes, as seen with fintech lenders in 2024 offering faster approvals by navigating fewer compliance burdens. The alternative lending market's projected size of over $1.1 trillion in 2024 highlights this competitive pressure.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | Market Size/Growth Indicator (2023-2024 Data) | Impact on Enterprise Bank & Trust |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Platforms | P2P Lending, Digital Payments, Robo-Advisors | Global Fintech Market: >$11T (2023), projected $33T by 2030 | Erosion of retail and wealth management customer base |
| Capital Markets | Corporate Bonds, Private Equity, Venture Capital | U.S. Investment Grade Bonds: >$1.5T issuance (2024); VC Funding: ~$150B (2024) | Reduced demand for commercial loans from creditworthy firms |
| Embedded Finance & BaaS | Financial services within non-financial platforms | Embedded Finance Market: Projected $7T by 2030 | Disintermediation of banking services in everyday transactions |
| Alternative Lenders | Streamlined digital loan origination | Global Alternative Lending Market: >$1.1T (2024) | Competition for loan origination, especially with lighter regulation |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like Enterprise Bank & Trust, presents significant hurdles for newcomers due to high capital requirements. New entrants must not only meet substantial initial investment needs but also maintain ongoing regulatory capital reserves, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, to ensure solvency and stability.
Building a strong deposit base and securing diverse funding sources, critical for any bank's operational success, is a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. Enterprise Bank & Trust, for instance, has cultivated a broad and stable funding profile over years of operation, a feat that is difficult and costly for a new player to replicate quickly.
The banking industry is notoriously difficult to enter due to significant regulatory barriers. New companies must obtain extensive licenses and adhere to a complex web of compliance and oversight rules, which can be a massive undertaking. For instance, in 2024, the cost of regulatory compliance for financial institutions continued to climb, with many reporting budgets in the tens of millions of dollars annually just to stay afloat with evolving regulations.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on cybersecurity and anti-money laundering (AML) protocols adds layers of complexity and expense. The need for robust systems to protect customer data and prevent illicit financial activities means that potential new entrants face substantial upfront investment in technology and expertise. This increased demand for specialized compliance functions, particularly around AI governance in 2024, effectively raises the bar and deters many from even attempting to enter the market.
Established banks like Enterprise Bank & Trust have cultivated trust and loyalty over many years, making it difficult for new players to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, customer retention rates for incumbent banks often exceeded 90% for core checking and savings accounts, a testament to ingrained habits and established relationships.
New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and incentives to even begin chipping away at this entrenched loyalty, a costly endeavor when competing against institutions with decades of community presence and proven reliability.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Existing financial institutions like Enterprise Bank & Trust often leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can spread their costs across a larger volume of transactions and customers, leading to lower per-unit costs for services. For instance, in 2024, the average operating cost per dollar of assets for large U.S. banks was notably lower than for smaller institutions, reflecting this scale advantage.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Building the necessary technology infrastructure, marketing reach, and operational capacity to compete with established players requires immense upfront investment. Without an existing, large customer base, a new bank cannot immediately achieve the same cost per transaction, making it difficult to offer competitive rates or fees.
Furthermore, network effects play a crucial role. Established banks have extensive branch networks, ATM access, and deeply integrated digital platforms that create value for customers. A new entrant must invest heavily to replicate even a fraction of this accessibility, a challenge compounded by the fact that customers often prefer the convenience and familiarity of incumbent institutions.
- Economies of Scale: Large banks in 2024 typically operated with lower cost-to-income ratios due to their size.
- Network Effects: Customer loyalty and convenience are enhanced by established physical and digital networks.
- Initial Investment: New entrants require substantial capital to build comparable infrastructure and market presence.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Lack of scale and network initially puts new banks at a pricing and service offering disadvantage.
Technological Investment and Talent Acquisition
The threat of new entrants into the banking sector, particularly for established players like Enterprise Bank & Trust, is significantly influenced by the capital and expertise required for technological advancement. Building a sophisticated digital banking and wealth management platform demands substantial and ongoing financial commitment. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to allocate billions towards digital transformation initiatives, with some reports suggesting that the average investment in IT infrastructure and cybersecurity for financial institutions exceeded $10 billion annually.
Furthermore, the ability of new entrants to attract and retain top-tier technology talent presents a considerable hurdle. The demand for skilled professionals in areas like AI, blockchain, and cybersecurity remains exceptionally high. In 2024, the average salary for a senior software engineer in the fintech sector often surpassed $150,000, reflecting the competitive landscape for acquiring this specialized workforce.
- Massive Capital Outlay: Developing robust digital banking and wealth management capabilities requires immense and sustained investment, often in the billions of dollars, to compete with established infrastructure.
- Talent Scarcity: Attracting and retaining specialized tech talent, crucial for building and maintaining advanced platforms, is a significant challenge due to high demand and competitive compensation packages.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must also invest heavily in ensuring compliance with stringent financial regulations, adding another layer of cost and complexity to market entry.
- Brand Trust and Reputation: Building the necessary trust and reputation in the financial services industry takes considerable time and resources, which new entrants often lack compared to established institutions.
The threat of new entrants for Enterprise Bank & Trust is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements, often in the hundreds of millions, are essential for regulatory compliance and operational stability. Building a strong, diversified funding base and securing customer trust, cultivated over years, are incredibly difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate.
Regulatory hurdles are immense, demanding extensive licenses and adherence to complex rules, with compliance costs for financial institutions in 2024 reaching tens of millions annually. Furthermore, the need for robust cybersecurity and anti-money laundering systems, including AI governance in 2024, adds significant upfront investment, deterring potential entrants.
Established banks benefit from significant economies of scale, leading to lower operating costs per dollar of assets compared to smaller entities, a cost advantage new entrants struggle to match. Network effects, from extensive branch and ATM access to integrated digital platforms, further solidify customer loyalty, making it challenging for new players to offer comparable convenience.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Impact/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Substantial initial investment and ongoing regulatory capital reserves needed. | Hundreds of millions of dollars required for solvency. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Obtaining licenses and adhering to complex rules. | Annual compliance budgets often in the tens of millions for financial institutions. |
| Brand Trust & Loyalty | Years of operation build customer relationships and habits. | Customer retention rates for incumbent banks often exceed 90% for core accounts. |
| Economies of Scale | Spreading costs over larger transaction volumes leads to lower per-unit costs. | Large U.S. banks had lower average operating costs per dollar of assets. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Enterprise Bank & Trust Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including public financial filings, industry-specific market research reports, and insights from reputable financial news outlets.
We leverage data from regulatory bodies, economic indicators, and proprietary market intelligence platforms to provide a comprehensive assessment of the competitive landscape.
