Northfield Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Northfield Bank Bundle
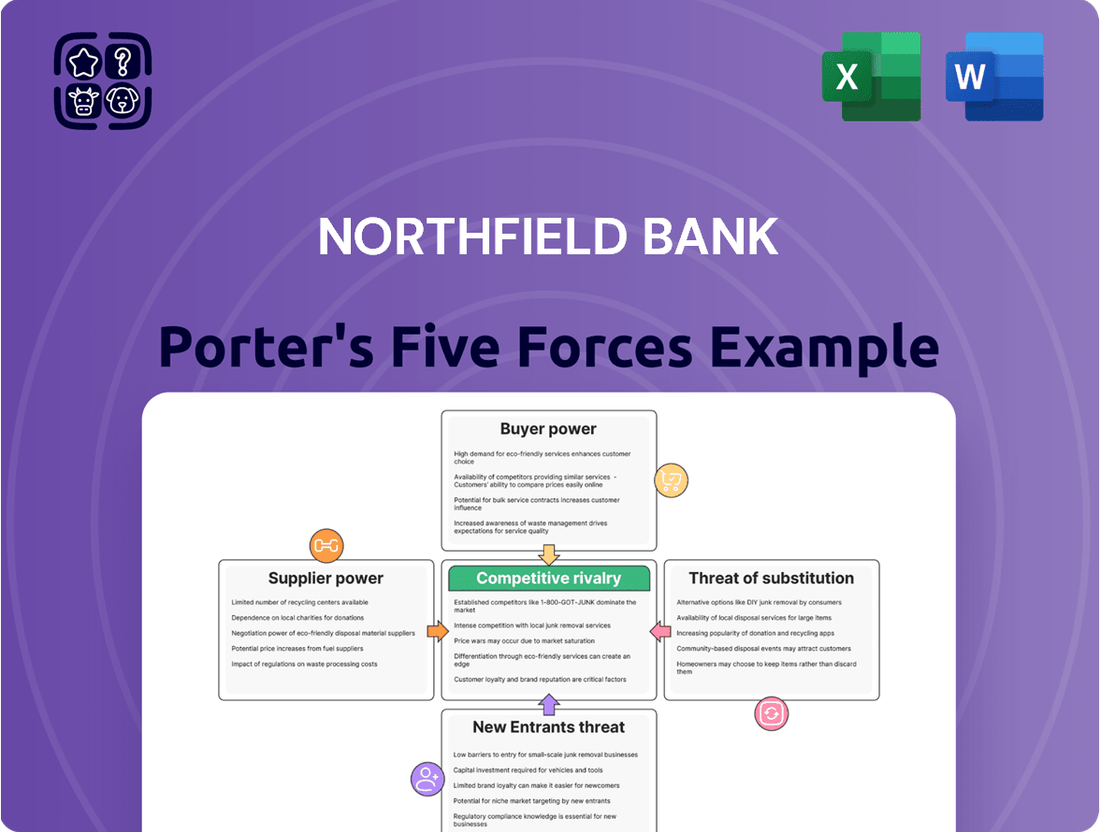
Northfield Bank navigates a landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the ever-present threat of new entrants, but the intensity of rivalry is a key concern. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the bank's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Northfield Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
For Northfield Bank, individual and business depositors are essentially the suppliers of its core capital. Their ability to influence terms hinges on factors like current interest rates and how easily they can switch their money to competitors offering better returns or more appealing services. This is a critical dynamic for any bank.
While Northfield Bank saw its cost of deposits fall to 1.95% by the end of 2024, this doesn't eliminate the underlying pressure. Consumers actively seeking higher yields can still push banks to offer more competitive rates, especially when alternative investment options are readily available and attractive.
Northfield Bank's digital transformation hinges on technology and software vendors, who supply everything from core banking platforms to advanced cybersecurity. The specialized and rapidly evolving nature of these technologies, often proprietary, means vendors can wield considerable bargaining power, especially when integration is complex. The broader banking sector's aggressive push into AI and automation, with global spending on financial technology projected to reach hundreds of billions by 2025, further amplifies demand and can drive up costs for these essential supplier services.
The availability of skilled professionals, particularly in fields like cybersecurity, data analytics, and AI, grants significant power to these talent pools as suppliers to Northfield Bank. In 2024, the demand for such expertise continues to outstrip supply, driving up compensation expectations and recruitment expenses for financial institutions aiming to stay competitive.
Wholesale Funding Markets
Northfield Bank, like many financial institutions, relies on wholesale funding markets beyond traditional retail deposits. These include sources such as Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) advances and brokered deposits. The cost and accessibility of these funds are heavily influenced by overall financial market conditions, central bank interest rate policies, and the bank's own perceived creditworthiness, granting these institutional suppliers significant leverage.
In 2024, Northfield Bank experienced a notable shift in its funding structure. While total borrowings saw an increase, this was accompanied by a decrease in FHLB advances and other forms of borrowing. This dynamic suggests a potential recalibration of their reliance on different wholesale channels, possibly in response to changing market costs or strategic decisions regarding their funding mix.
- Wholesale Funding Reliance: Banks like Northfield utilize FHLB advances and brokered deposits to supplement retail deposits for liquidity and lending.
- Supplier Power Factors: The bargaining power of these wholesale funding providers is derived from market conditions, interest rate policies, and the bank's credit standing.
- 2024 Funding Trends: Northfield Bank observed an increase in overall borrowings in 2024, but this was counterbalanced by a reduction in FHLB advances and other borrowings.
Regulatory Bodies (Implicit Suppliers of Operating License)
Regulatory bodies such as the Federal Reserve, FDIC, and state banking departments function as implicit suppliers to Northfield Bank by providing essential operating licenses and defining the regulatory landscape. Their influence is substantial, as evolving compliance requirements and capital mandates directly affect operational costs and strategic flexibility. For instance, ongoing adjustments to Basel III, which aim to strengthen bank capital requirements and risk management, necessitate significant investment and adaptation from institutions like Northfield Bank.
The bargaining power of these regulatory bodies is amplified by their ability to grant or revoke operating licenses, thereby controlling market access. Increased scrutiny and the constant evolution of compliance standards, particularly concerning areas like cybersecurity and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, impose direct costs on banks. In 2024, the financial services industry continued to grapple with heightened regulatory expectations, with institutions dedicating substantial resources to meeting these evolving demands.
- Regulatory Mandates: Federal Reserve, FDIC, and state agencies dictate operational frameworks and licensing, acting as crucial gatekeepers for market participation.
- Compliance Costs: Adherence to evolving regulations, including Basel III adjustments and enhanced risk management protocols, directly increases operating expenses for banks.
- Capital Requirements: Regulatory bodies set capital adequacy ratios, influencing how much capital banks must hold, which impacts lending capacity and profitability.
- Market Access Control: The power to grant, modify, or revoke operating licenses gives regulators significant leverage over a bank's ability to conduct business.
Northfield Bank's suppliers of capital, primarily depositors, wield significant bargaining power. This power is influenced by prevailing interest rates and the ease with which depositors can move funds to competitors offering better returns or services. While Northfield Bank lowered its cost of deposits to 1.95% by the close of 2024, competitive market conditions and attractive alternative investments mean depositors can still exert pressure for higher yields.
Technology and software vendors represent another key supplier group, providing essential platforms and cybersecurity solutions. The specialized nature of these offerings and the complexity of integration allow vendors considerable leverage. The banking sector's substantial investment in AI and automation, with global fintech spending projected to exceed hundreds of billions by 2025, further increases demand and can drive up costs for these critical services.
The market for skilled professionals in areas like cybersecurity and data analytics remains tight, granting these talent pools considerable bargaining power. In 2024, the persistent demand for such expertise outstripped supply, leading to increased compensation expectations and recruitment costs for financial institutions like Northfield Bank.
Northfield Bank also relies on wholesale funding markets, including FHLB advances and brokered deposits. The cost and availability of these funds are sensitive to overall market conditions, central bank policies, and the bank's creditworthiness. In 2024, Northfield Bank saw an increase in total borrowings, but this was accompanied by a decrease in FHLB advances and other borrowed funds, indicating a strategic adjustment in its funding mix.
| Supplier Group | Key Leverage Factors | Impact on Northfield Bank (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Depositors | Interest rates, ease of switching | Cost of deposits at 1.95%; ongoing pressure for higher yields |
| Technology Vendors | Specialized offerings, integration complexity | Increased demand due to fintech investment, potential cost escalation |
| Skilled Professionals | High demand, low supply | Increased recruitment costs and compensation expectations |
| Wholesale Funding Markets | Market conditions, central bank policy, creditworthiness | Shift in funding mix with increased total borrowings but reduced FHLB advances |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Northfield Bank, this analysis dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products on its market position and profitability.
Instantly understand competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, allowing Northfield Bank to proactively address threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Deposit customers, those looking for checking, savings, or certificate of deposit accounts, wield significant bargaining power. This is largely because switching banks is relatively easy and inexpensive for them, and there are many banking options available.
These customers are highly attuned to interest rates, the ease of digital banking, and the quality of personalized service they receive. For Northfield Bank, attracting and keeping these deposits hinges on providing competitive interest rates and an excellent customer experience, particularly as consumers continue to seek higher yields on their savings.
In 2024, for instance, the average interest rate on savings accounts across major US banks remained relatively low, often below 0.5%, while some online banks and credit unions offered rates exceeding 4%, highlighting customer sensitivity to yield. This disparity underscores the pressure on traditional banks like Northfield to offer more competitive terms to retain their deposit base.
Loan customers, including individuals seeking mortgages and businesses requiring commercial loans, wield considerable bargaining power. This is largely due to the competitive landscape, with numerous traditional banks and an increasing number of non-bank lenders offering attractive rates, adaptable terms, and expedited approval timelines. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage fluctuated, creating opportunities for borrowers to negotiate favorable terms.
Wealth management clients at Northfield Bank possess significant bargaining power due to their financial sophistication and substantial assets. These clients expect tailored advice, diverse investment options, clear fees, and proven performance. In 2024, the average assets under management for high-net-worth individuals, a key demographic for wealth management, continued to grow, underscoring their leverage.
Digital-First Consumers
Digital-first consumers, especially in urban centers, hold significant sway over Northfield Bank. They demand intuitive, mobile-centric banking with instant transactions and AI support, mirroring trends seen across the financial sector. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that 75% of banking customers prefer mobile apps for everyday transactions.
This preference means that if Northfield Bank's digital offerings lag, these tech-savvy customers can readily switch to competitors providing superior online platforms. This ease of switching amplifies their collective bargaining power, forcing banks to continuously invest in digital innovation to retain their business.
- Digital Expectations: Consumers increasingly expect seamless, mobile-first banking experiences.
- Switching Costs: Low switching costs for digital banking empower customers to move to better platforms.
- Competitive Landscape: Competitors offering advanced digital features can attract customers away from less advanced banks.
- Data Insights: In 2023, over 80% of financial institutions reported increased investment in digital transformation to meet customer demands.
Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs)
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), a crucial customer base for community banks like Northfield, are exercising greater bargaining power. They are actively seeking more personalized financial products, quicker loan approvals, and seamless digital banking experiences. This shift is driven by the expanding availability of alternative financing options.
The rise of fintech lenders and digital-only business banking platforms has significantly broadened the choices available to SMBs. For instance, by the end of 2023, the small business lending market saw continued growth in alternative lending, with some reports indicating that fintechs accounted for a substantial portion of new small business loans, putting pressure on traditional institutions to adapt.
- Increased Demand for Tailored Services: SMBs are no longer satisfied with one-size-fits-all banking.
- Access to Alternative Lenders: Fintechs offer faster approvals and specialized solutions, increasing SMB options.
- Digital Expectations: Businesses expect integrated, user-friendly digital banking platforms.
- Price Sensitivity: Competition among lenders can lead to SMBs negotiating for better rates and fees.
Customers at Northfield Bank possess considerable bargaining power, particularly as switching costs remain low across many banking services. This leverage is amplified by the increasing availability of diverse financial providers, from traditional banks to fintechs, offering competitive rates and enhanced digital experiences. For instance, by mid-2024, many online banks continued to offer savings account yields significantly higher than traditional brick-and-mortar institutions, often exceeding 4.5% APY, directly influencing deposit customer expectations and their willingness to switch for better returns.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | Northfield Bank's Challenge | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deposit Customers | Interest rates, ease of digital banking, personalized service | Offering competitive yields and superior customer experience | Average savings account APY at major banks ~0.3%, online banks ~4.5% |
| Loan Customers | Interest rates, loan terms, approval speed | Matching or exceeding competitor offerings in pricing and efficiency | 30-year fixed mortgage rates fluctuated, creating negotiation opportunities |
| Wealth Management Clients | Tailored advice, investment performance, fee transparency | Demonstrating value through expertise and consistent returns | Continued growth in high-net-worth individual assets |
| Digital-First Consumers | Mobile app functionality, transaction speed, AI support | Investing in and maintaining cutting-edge digital platforms | 75% of banking customers prefer mobile apps for daily transactions |
| Small & Medium Businesses (SMBs) | Personalized products, loan speed, digital integration, pricing | Adapting to fintech offerings and providing tailored business solutions | Fintechs capturing a significant share of new small business loans |
Same Document Delivered
Northfield Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Northfield Bank, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You will receive this exact, professionally formatted analysis, providing actionable insights into Northfield Bank's market position and potential challenges.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The New York and New Jersey banking landscape is incredibly crowded. Northfield Bank operates in a region saturated with financial institutions, from massive national players like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America to a multitude of regional and community banks. This sheer density means intense competition for every customer and every dollar.
This high concentration of competitors directly impacts Northfield Bank by creating significant pressure on pricing for loans and deposit accounts. To attract and retain customers, banks often have to offer more competitive rates, which can squeeze profit margins. For instance, as of early 2024, average savings account APYs across major national banks hovered around 0.35-0.45%, while some competitive online banks and credit unions were offering upwards of 4.50%, highlighting the rate pressure.
Beyond pricing, Northfield Bank must also focus on service differentiation to stand out. The intense rivalry forces the bank to innovate and offer unique value propositions, whether through personalized customer service, specialized lending products, or advanced digital banking solutions. Failing to do so means risking losing market share to competitors who are better positioned to meet evolving customer demands in this dynamic market.
Northfield Bank, like all financial institutions, finds itself in a fierce digital transformation race. Banks are pouring significant capital into artificial intelligence, automation, and sophisticated digital platforms. This intense focus aims to elevate customer experiences and streamline internal operations. For instance, in 2024, the global banking sector's IT spending was projected to reach over $200 billion, highlighting the scale of this investment.
This relentless pursuit of innovation means constant competition to deliver the most cutting-edge and user-friendly digital services. Failure to keep pace risks obsolescence. Northfield Bank's strategic initiatives, including its ongoing cloud migration, are direct responses to this pressure, ensuring it remains competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Fluctuating interest rates, especially a downward trend, can squeeze a bank's net interest margin, which is the profit made from lending versus what's paid on deposits. This heightened competition for profitable loans and deposits can be particularly challenging for community banks like Northfield. Larger, more diversified banks often have an easier time adjusting their deposit rates to maintain margins.
While Northfield Bank saw its net interest margin improve in the second quarter of 2025, the broader banking landscape remains intensely competitive. This environment necessitates careful management of both lending strategies and deposit acquisition to ensure sustained profitability amidst shifting economic conditions.
Product and Service Overlap
Most banks, including Northfield Bank, offer a very similar set of core products like checking and savings accounts, mortgages, and various business loans. This similarity means customers can easily switch between banks for these basic services, making product substitutability a significant factor.
Because of this overlap, Northfield Bank must differentiate itself by focusing on aspects beyond just the products themselves. This includes offering superior customer service, demonstrating deep knowledge of the local market, providing faster transaction speeds, and developing specialized financial solutions tailored to specific customer needs.
- High Product Substitutability: Core banking products are largely commoditized, allowing easy switching for customers.
- Competition on Non-Product Factors: Banks like Northfield must excel in service, local expertise, and speed.
- Differentiation Strategy: Success hinges on offering unique value propositions beyond standard banking services.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity within the banking sector, especially among community and regional banks, is a significant factor influencing competitive rivalry. This trend is driven by a need for greater scale and efficiency in an increasingly digital and competitive landscape.
Consolidation results in larger, more robust competitors possessing enhanced resources, broader market reach, and greater financial capacity. This can intensify the competitive pressure on smaller, independent institutions like Northfield Bank.
- Increased Consolidation: In 2024, the banking industry continued to witness strategic M&A as institutions sought to bolster their market position and operational capabilities.
- Scale Advantages: Larger, merged entities often benefit from economies of scale in technology investment, regulatory compliance, and product development, creating an uneven playing field.
- Market Share Shifts: Successful mergers can significantly alter market share dynamics, concentrating more power in the hands of fewer, larger players.
Northfield Bank faces intense competition from a wide array of financial institutions, from national giants to local community banks, all vying for customers in a saturated market. This rivalry pressures banks to offer competitive rates, driving down profit margins, as evidenced by the significant gap between national bank savings rates and those offered by more aggressive institutions in early 2024. To survive and thrive, Northfield must differentiate itself through superior customer service, specialized products, and advanced digital offerings, a strategy reinforced by the ongoing digital transformation race across the banking sector, with global IT spending projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Tactics | Impact on Northfield Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Large National Banks | Aggressive pricing, extensive digital platforms, broad product offerings | Rate pressure, need for digital parity |
| Regional/Community Banks | Personalized service, local market knowledge, niche products | Competition for local deposits and loans, need for service differentiation |
| Online Banks/Credit Unions | High-yield deposit accounts, lower loan rates, digital convenience | Direct competition on price and digital experience |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies and digital-only banks present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Northfield Bank. These agile competitors offer specialized services, such as streamlined payment apps and peer-to-peer lending, often with a superior digital experience and lower fees.
For instance, by mid-2024, neobanks and fintech platforms had captured a notable share of the digital payments market, with transaction volumes continuing to surge. Their ability to attract younger, digitally-savvy customers by offering faster, more convenient, and often cheaper alternatives directly challenges Northfield Bank's established customer base and service model.
The increasing prevalence of non-bank lenders, such as specialized mortgage companies and burgeoning online platforms, presents a substantial threat by directly competing with Northfield Bank's core lending business. These alternative lenders are adept at filling financing voids traditional banks may overlook, offering more agile and customized loan products.
Private credit firms, in particular, have seen significant growth, with global private debt assets projected to reach $2.7 trillion by 2028, up from $1.3 trillion in 2022, according to Preqin. This expansion means more capital is available outside traditional banking channels, often with faster decision-making and less stringent regulatory oversight, directly siphoning potential borrowers from Northfield Bank.
Online investment platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat to traditional banks like Northfield Bank in wealth management. These digital alternatives often boast lower management fees, with many robo-advisors charging around 0.25% annually, compared to potentially higher fees for human advisors at traditional institutions. This cost advantage, coupled with user-friendly interfaces and automated portfolio rebalancing, makes them attractive substitutes for individuals seeking to grow their savings and investments.
The accessibility and convenience of these platforms are also key drivers of their threat. For instance, many online brokerages allow users to open accounts and start investing with minimal initial capital, sometimes as low as $0 or $100, democratizing access to wealth management. This ease of entry and the availability of a wide array of investment options, from stocks and bonds to ETFs, directly compete with the services offered by Northfield Bank’s wealth management division.
Alternative Payment Systems and Digital Wallets
The rise of alternative payment systems and digital wallets presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. Platforms like Apple Pay and Google Pay, alongside peer-to-peer payment apps such as Venmo and Zelle, are increasingly becoming the go-to methods for everyday transactions. This trend is particularly evident in the younger demographic, with a notable shift away from traditional methods.
These digital alternatives offer enhanced convenience and speed, directly challenging the utility of checking accounts, debit cards, and even wire transfers for many consumers. For instance, by mid-2024, Zelle reported processing over $800 billion in payments annually, showcasing its substantial adoption. This widespread use diminishes the necessity for customers to rely on Northfield Bank's established payment infrastructure for routine financial activities.
The ease of use and integration into daily life provided by these substitute systems can lead to customer attrition, especially if banks do not adapt their own offerings. Consider the following impacts:
- Increased transaction volume for non-bank platforms: Digital wallets and P2P apps are capturing a larger share of consumer spending.
- Reduced interchange fees for banks: As more transactions bypass traditional card networks, banks see a decline in revenue.
- Customer loyalty shift: Users may develop a stronger affinity for the convenience of digital payment providers.
- Data privacy concerns: While convenient, the use of third-party digital wallets raises questions about data security and how personal financial information is handled.
Emerging Technologies (Blockchain, CBDCs, Crypto)
Emerging technologies like blockchain and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) pose a long-term threat of substitution for traditional banking services. While their widespread adoption for everyday transactions is still developing, these innovations could bypass intermediaries like Northfield Bank. For instance, the potential for direct, secure, and transparent financial exchanges could reduce reliance on established banking infrastructure.
The development of stablecoins and potential CBDCs could offer alternative payment rails, impacting transaction fee income for banks. As of early 2024, many countries are actively exploring or piloting CBDCs, indicating a serious consideration of these digital alternatives. This shift could enable peer-to-peer transactions that bypass traditional correspondent banking networks.
- Blockchain and DLTs: Offer potential for faster, cheaper cross-border payments and more efficient trade finance, reducing the need for traditional bank intermediation.
- Stablecoins: Provide a digital medium of exchange that can be used for payments and remittances, potentially competing with bank-provided payment services.
- CBDCs: Could offer a direct digital alternative to commercial bank deposits, potentially impacting banks' funding base and role in monetary transmission.
- Disintermediation Risk: These technologies could facilitate direct financial interactions between individuals and businesses, reducing the need for banks as trusted intermediaries.
The threat of substitutes for Northfield Bank is substantial, stemming from a variety of non-traditional financial service providers. Fintech companies and digital-only banks offer streamlined services and superior digital experiences, capturing market share in areas like payments and lending. For example, by mid-2024, neobanks had significantly increased their transaction volumes, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces substantial hurdles for newcomers due to stringent regulatory frameworks. Prospective institutions must successfully navigate complex licensing processes and satisfy rigorous capital adequacy requirements, which can be financially daunting.
Compliance with a vast array of rules covering consumer protection, anti-money laundering protocols, and data security further solidifies these barriers, discouraging many potential entrants. For instance, US banks are mandated to maintain specific minimum capital ratios, with new regulations anticipated to take effect between 2024 and 2025, increasing the financial commitment for new players.
Establishing a new bank, even a community-focused one like Northfield Bank, demands substantial capital. Regulatory bodies mandate significant minimum capital reserves to ensure stability and protect depositors. For instance, in 2024, new bank charters often require millions in initial capital, a figure that can easily climb into the tens or hundreds of millions depending on the scope and planned services.
Beyond regulatory hurdles, new entrants must fund the creation of robust physical and digital infrastructure. This includes branches, ATMs, sophisticated online banking platforms, and cybersecurity measures. Attracting initial deposits also requires marketing and competitive interest rates, adding to the upfront financial burden. Northfield Bank, for example, has historically focused on a strong community bank leverage ratio, indicating a prudent approach to capital management which new entrants would need to replicate or exceed.
Established banks like Northfield Bank, with a history dating back to 1887, possess a formidable advantage in brand trust and customer loyalty. This long-standing presence allows them to cultivate deep relationships and a recognized name, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
New entrants struggle to replicate this ingrained trust, a critical factor in the banking sector where customers prioritize security and reliability. For instance, in 2024, customer acquisition costs for traditional banks can be significantly higher than for digital-only banks, but the retention rates for established institutions often remain superior due to this trust advantage.
High Technology and Infrastructure Investment
New entrants face substantial hurdles due to the immense capital required for technology and infrastructure. Establishing competitive digital banking platforms, advanced cybersecurity, and AI-driven analytics demands significant upfront investment. For instance, major banks are consistently increasing their IT spending; in 2024, the banking sector globally was projected to invest over $300 billion in technology.
This high cost of entry acts as a powerful deterrent. Developing and maintaining these sophisticated systems, from cloud computing to data management, requires ongoing expenditure and specialized expertise, making it difficult for smaller or newer players to keep pace with established institutions.
- High Capital Outlay: Significant investment needed for digital platforms, cybersecurity, and AI.
- Technological Sophistication: Requirement for cutting-edge and constantly updated systems.
- Operational Infrastructure: Building and maintaining efficient, scalable backend operations.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: Continuous expenditure for system upgrades and security patches.
Niche Entry by Fintechs
While establishing a full-service bank remains a high barrier to entry, the threat from new entrants is significantly amplified by agile fintech companies. These firms often target specific, profitable niches within financial services, such as digital payments or specialized small business lending. For instance, by early 2024, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $300 billion, showcasing substantial growth and investment in these specialized areas.
These niche players can achieve rapid scaling within their chosen segments, building significant customer bases and brand recognition. As they mature, there's a clear potential for these fintechs to broaden their service portfolios, directly challenging established institutions like Northfield Bank in more comprehensive ways. The ease of digital customer acquisition and lower overheads compared to traditional banks allow for aggressive pricing and innovation.
- Fintech Niche Dominance: Fintechs are carving out significant market share in areas like digital payments, with global transaction volumes expected to exceed $10 trillion by 2025.
- Rapid Scalability: Companies like Square and Stripe have demonstrated the ability to scale operations globally within a few years by focusing on specific merchant services.
- Evolving Competitive Landscape: The increasing sophistication of fintech offerings means that specialized entrants can gradually expand their services, becoming more direct competitors to traditional banks.
The threat of new entrants for Northfield Bank is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital requirements and rigorous regulatory landscape inherent in the banking industry. New banks must secure millions in initial capital, a figure that is projected to increase with evolving regulations between 2024 and 2025, demanding robust financial backing for even community-focused institutions.
Furthermore, the need for extensive operational infrastructure, including advanced digital platforms and cybersecurity, coupled with the challenge of building brand trust and customer loyalty against established players, creates formidable barriers. For instance, global banking technology spending was anticipated to surpass $300 billion in 2024, highlighting the immense investment required to compete technologically.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example (2024/2025 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Licensing, capital adequacy, consumer protection, AML, data security. | US banks facing new capital ratio regulations impacting new entrants. |
| Capital Requirements | Minimum reserves for stability and depositor protection. | New bank charters often requiring millions to hundreds of millions in initial capital. |
| Infrastructure Investment | Physical branches, ATMs, digital platforms, cybersecurity. | Global banking IT spending projected over $300 billion in 2024. |
| Brand Trust & Loyalty | Established reputation and customer relationships. | Higher customer acquisition costs for new banks vs. established ones, with better retention for the latter. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Northfield Bank is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor relations materials, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and reputable financial news outlets to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
