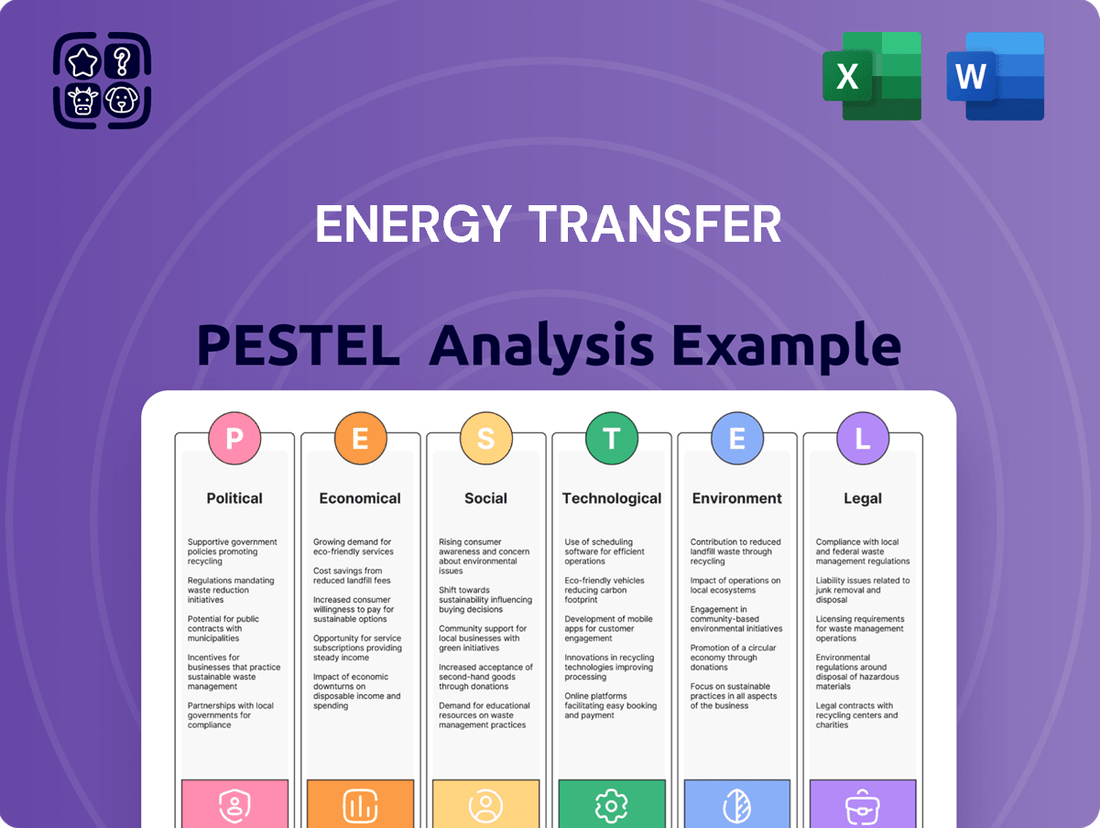
Energy Transfer PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Energy Transfer Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces impacting Energy Transfer with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping its operations and future growth. Gain a critical edge in your strategic planning and investment decisions. Download the full report now for actionable intelligence.
Political factors
Energy Transfer's vast infrastructure, encompassing over 130,000 miles of pipelines across 44 states, operates under a web of federal and state regulations. These rules dictate everything from initial project approvals to ongoing safety protocols.
Shifts in environmental standards, permitting requirements, and operational safety mandates can directly affect project schedules and expenses. For example, the development of pipelines like the Hugh Brinson Pipeline faces stringent government scrutiny, influencing its feasibility and cost.
Global trade policies are a significant consideration for Energy Transfer, directly influencing its import/export terminal operations and future growth. The company's recent success in securing substantial long-term LNG Sale and Purchase Agreements highlights its commitment to expanding its presence in international markets. For instance, by mid-2025, the demand for U.S. LNG exports is projected to reach new highs, making favorable trade agreements critical for profitability.
International political stability and ongoing conflicts directly influence global energy supply and demand, leading to price volatility and disruptions in critical supply chains. For instance, the ongoing geopolitical tensions in Eastern Europe in 2024 continue to reshape global energy flows, with significant implications for crude oil and natural gas prices.
As a major North American energy transporter, Energy Transfer's operations are indirectly impacted by these geopolitical shifts. Fluctuations in global energy prices and supply reliability can alter the demand for its midstream services, affecting volumes transported and storage needs.
Energy Transfer's diversified asset base, spanning crude oil, natural gas, NGLs, and refined products, provides a degree of resilience against these broader market risks. This diversification helps to buffer the company from sector-specific downturns caused by geopolitical events, as seen in its ability to maintain steady throughput volumes in certain segments even amidst global energy market uncertainty in 2024.
Energy transition policies and support for traditional energy
Government initiatives promoting renewable energy and policies aimed at phasing out fossil fuels present a significant long-term political risk for traditional energy companies. Energy Transfer, while focused on natural gas, crude oil, and NGLs, also participates in renewable energy projects, acknowledging natural gas's role as a backup for renewables. The evolving regulatory environment will heavily influence future investment and operational strategies.
For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 in the United States provides substantial tax credits and incentives for renewable energy development, potentially accelerating the shift away from fossil fuels. This policy landscape directly impacts the demand for and profitability of traditional energy infrastructure.
- Policy Risk: Government mandates and incentives for renewables can reduce demand for fossil fuel transportation and storage.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Shifting political priorities can lead to unpredictable changes in environmental regulations and carbon pricing.
- Investment Shifts: Public and private capital may increasingly flow towards green energy, impacting funding for traditional energy projects.
Tax policies and incentives for the energy sector
Changes in tax laws directly impact Energy Transfer's financial health and its ability to distribute cash to unitholders. For instance, modifications to the tax treatment of master limited partnerships (MLPs) can alter profitability and investor returns. Investors closely monitor the existing tax landscape and any emerging incentives or penalties related to energy infrastructure projects.
Energy Transfer has a track record of rewarding investors, evidenced by its consistent growth in quarterly cash distributions. For example, in the first quarter of 2024, the company announced a cash distribution of $0.33 per limited partner unit, representing a 2.5% increase from the previous quarter and a 10% increase year-over-year, underscoring their commitment to unitholder value.
- Tax Law Impact: Alterations in tax legislation, particularly those affecting MLPs, can significantly influence Energy Transfer's net income and the cash available for distributions.
- Investor Scrutiny: The current tax climate and potential future policy shifts regarding energy infrastructure are key factors for investors assessing the company's long-term viability and attractiveness.
- Distribution Growth: Energy Transfer's commitment to increasing its quarterly cash distributions, as seen with its Q1 2024 payout, signals confidence in its operational performance and financial stability.
Government policies and regulations significantly shape Energy Transfer's operational landscape, influencing everything from pipeline construction permits to environmental compliance. Shifts in political priorities, such as increased emphasis on renewable energy, can create policy risks by potentially reducing demand for fossil fuel transportation services. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 offers substantial incentives for green energy, which could indirectly impact the long-term outlook for traditional midstream infrastructure.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors influencing Energy Transfer, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
It offers actionable insights and forward-looking perspectives to guide strategic decision-making and identify opportunities within the dynamic energy sector.
Provides a concise version of the Energy Transfer PESTLE analysis that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions, simplifying complex external factors.
Easily shareable summary format ideal for quick alignment across teams or departments, ensuring everyone understands the key external drivers impacting energy transfer strategies.
Economic factors
Energy Transfer's financial performance, though largely driven by fees, remains sensitive to global energy demand and the fluctuating prices of commodities like crude oil and natural gas. The company’s Q1 2025 results highlighted robust volumes across its key transportation segments, demonstrating a healthy appetite for energy products.
This strong demand, reflected in their midstream segment's significant growth in early 2025, underscores Energy Transfer's strategic positioning within an evolving energy landscape. The company's ability to move substantial volumes of crude oil, natural gas, and NGLs is directly tied to the underlying global consumption trends and the resulting commodity price environment.
Interest rate fluctuations directly influence Energy Transfer's borrowing expenses, a significant factor given its considerable capital expenditure plans. For instance, the company anticipates capital expenditures of around $5.0 billion in 2025, underscoring the need for cost-effective financing.
The company's capacity to tap into capital markets at competitive rates is paramount for financing its ambitious growth strategies. Maintaining strong credit ratings from agencies such as S&P Global and Moody's is essential for securing these favorable borrowing costs.
Rising inflation directly impacts Energy Transfer's operational costs. Increased prices for essential materials like steel, higher wages for skilled labor, and rising service costs for transportation and maintenance can squeeze profit margins. This is a critical consideration for a company heavily involved in infrastructure development and upkeep.
Energy Transfer's diverse asset base provides some insulation, but managing these inflationary headwinds is key to maintaining healthy Adjusted EBITDA margins. For instance, in Q1 2025, the company managed to increase its Adjusted EBITDA to $3.4 billion, showcasing its ability to navigate such pressures effectively, even as input costs potentially climb.
Economic growth and industrial activity
Robust economic growth fuels demand for energy, directly benefiting Energy Transfer's core services. As industries expand and consumer spending rises, the need for transporting and processing natural gas, crude oil, and NGLs increases significantly.
Energy Transfer's operational performance in 2024 and early 2025 reflects this positive correlation. The company reported record volumes in several key segments, demonstrating its ability to capitalize on a strong economic environment.
- Increased Throughput: Higher industrial production drives greater volumes of natural gas and crude oil through Energy Transfer's pipelines.
- Record Performance: The company achieved record volumes in its NGL and refined products transportation and services segments during Q1 2025.
- Economic Sensitivity: Energy Transfer's financial results are closely tied to the health of the broader economy and industrial activity.
- Infrastructure Utilization: Economic expansion leads to higher utilization rates for Energy Transfer's extensive midstream infrastructure.
Capital expenditure plans and financial performance
Energy Transfer's capital expenditure plans are a significant driver of its future financial performance. For 2025, the company has outlined ambitious growth capital expenditures totaling approximately $5.0 billion. These investments are strategically focused on expanding its existing infrastructure and increasing its market presence.
These planned investments, which include the development of new processing facilities and the expansion of critical pipeline networks, are designed to foster substantial future growth and improve overall profitability. The company's financial trajectory supports these investments, as evidenced by its recent performance metrics.
- Projected 2025 Capital Expenditures: Approximately $5.0 billion.
- Investment Focus: Infrastructure expansion and market reach enhancement.
- Key Projects: New processing plants and pipeline expansions.
- Financial Indicator: Consistent year-over-year increases in Adjusted EBITDA.
Economic growth directly correlates with increased energy demand, benefiting Energy Transfer's transportation and services. The company's Q1 2025 results showed strong volumes, indicating a healthy economic environment. This trend is expected to continue as industrial output and consumer spending rise through 2025.
Inflationary pressures, however, can increase operational costs for Energy Transfer. Despite rising input prices, the company demonstrated resilience in Q1 2025, achieving $3.4 billion in Adjusted EBITDA. Strategic management of these costs will be crucial for maintaining profitability as capital expenditures for 2025 are projected at $5.0 billion.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Energy Transfer | 2024/2025 Data Points |
| Economic Growth | Increased demand for energy products, higher pipeline throughput. | Record volumes in NGL and refined products transportation in Q1 2025. |
| Inflation | Higher operational costs (materials, labor, services). | Projected capital expenditures of $5.0 billion for 2025. Adjusted EBITDA of $3.4 billion in Q1 2025. |
| Interest Rates | Increased borrowing costs for capital expenditures. | Company focuses on maintaining strong credit ratings for favorable financing. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Energy Transfer PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Energy Transfer PESTLE Analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the energy sector. It provides a robust framework for understanding the dynamic landscape of energy transfer and its associated challenges and opportunities.
Sociological factors
Public sentiment towards fossil fuel infrastructure is a major driver of regulatory decisions and project approvals for companies like Energy Transfer. Growing environmental activism, amplified by social media, puts significant pressure on the company's operations and expansion plans, impacting its social license to operate.
Environmental groups and local communities frequently scrutinize Energy Transfer's operations, focusing on potential impacts like spills and emissions. For instance, in 2023, the company faced continued opposition to certain pipeline projects, leading to increased legal challenges and project delays, as highlighted in numerous news reports and court filings.
Energy Transfer addresses these concerns in its corporate responsibility reports, detailing efforts in environmental stewardship and community engagement. The company reported investing $250 million in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives in 2023, aiming to mitigate impacts and foster positive relationships.
Energy Transfer's ability to maintain its social license to operate hinges on fostering positive community relationships across its extensive network. In 2023, the company reported engaging with over 1,500 communities, highlighting the scale of this undertaking. Transparent communication and proactive issue resolution are vital for both ongoing operations and future expansion plans, especially given its presence in all 44 states.
Energy Transfer's operations heavily rely on a skilled workforce for constructing, maintaining, and operating its vast energy infrastructure. The availability of qualified personnel, from engineers to field technicians, directly impacts project timelines and operational reliability. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 5% growth in pipeline transport occupations between 2022 and 2032, indicating a competitive labor market.
Labor relations present a critical dynamic for Energy Transfer. The potential for labor disputes, such as strikes or wage negotiations, can disrupt operations and escalate project expenses. In 2023, the average hourly wage for pipeline workers saw an increase, reflecting ongoing labor market pressures. Maintaining positive relationships with unions and ensuring fair compensation are vital for operational continuity.
Safety concerns and public trust
Incidents involving pipeline safety, such as leaks or ruptures, can significantly damage public trust. This erosion of confidence often results in heightened regulatory scrutiny, costly legal battles, and strong community opposition to new projects. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. experienced multiple pipeline incidents that led to environmental damage and increased calls for stricter safety standards.
Energy Transfer actively manages these risks through comprehensive safety programs. The company emphasizes robust risk management to maintain the integrity and reliability of its extensive pipeline network. By prioritizing safety, Energy Transfer aims to prevent disruptions and safeguard its public reputation.
- 2023 Pipeline Incidents: Reports indicated an increase in minor pipeline leaks across the US, though major ruptures remained infrequent.
- Regulatory Focus: Agencies like the PHMSA (Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration) continue to update regulations, impacting operational procedures.
- Public Perception: Community engagement and transparent safety reporting are crucial for building and maintaining public trust in energy infrastructure projects.
Demographic shifts influencing energy consumption
Long-term demographic trends are reshaping energy demand, with population growth and increasing urbanization driving consumption. Energy Transfer is adapting its strategy to these shifts, anticipating a rise in demand for natural gas, particularly for power generation and liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports. For instance, the company secured new agreements in 2024 to supply natural gas to burgeoning data centers, a sector experiencing exponential growth fueled by digital transformation.
The company's strategic focus on meeting evolving energy needs is further exemplified by its advancement of the Lake Charles LNG project. This project is designed to capitalize on the increasing global demand for natural gas, with projections indicating continued robust growth in LNG markets through 2025 and beyond. This positions Energy Transfer to benefit from these demographic-driven consumption patterns.
Key demographic influences include:
- Population Growth: Global population is projected to reach 8.1 billion by 2025, increasing overall energy requirements.
- Urbanization: As more people move to cities, concentrated energy demand for residential, commercial, and industrial use intensifies.
- Aging Populations: In some developed nations, aging demographics may lead to shifts in consumption patterns, though overall demand often remains high.
- Emerging Economies: Rapid economic development and population growth in emerging markets are significant drivers of increased energy consumption.
Public perception and community acceptance are paramount for Energy Transfer, influencing regulatory approvals and operational expansion. Negative sentiment, often fueled by environmental concerns and past incidents, can lead to significant project delays and increased legal challenges, as seen in ongoing opposition to certain pipeline projects in 2023. The company's investment of $250 million in ESG initiatives in 2023 underscores its commitment to mitigating environmental impacts and fostering positive community relations across the 1,500+ communities it serves.
Technological factors
Energy Transfer is heavily invested in advanced technologies for pipeline integrity, with a focus on continuous monitoring and inspection. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to deploy smart pigging technologies and aerial surveillance, including drone usage, to identify potential issues proactively. These efforts are directly tied to their pipeline safety management programs, which aim to mitigate risks and ensure operational continuity across their extensive infrastructure.
Energy Transfer, while rooted in traditional midstream operations, is actively exploring and integrating new energy transfer technologies to boost efficiency and broaden its asset base. This forward-looking approach includes investigating advancements in carbon capture, hydrogen transportation, and other nascent energy solutions.
In 2024, the company continued to focus on optimizing its existing infrastructure through technological upgrades, a key component of its organic growth strategy. For instance, investments in digital monitoring systems for pipelines aim to improve leak detection and operational safety, directly impacting transfer efficiency.
While specific financial figures for R&D into entirely new energy transfer methods are not always broken out, Energy Transfer's capital expenditure plans for 2024 and 2025 allocate significant portions to infrastructure modernization and efficiency improvements, which inherently encompass technological adoption.
The energy sector is rapidly embracing digitalization and automation. For companies like Energy Transfer, this means integrating advanced data analytics, AI, and robotic process automation into their core operations. These technologies are designed to streamline processes, reduce manual intervention, and boost overall productivity.
By implementing these digital tools, Energy Transfer can expect significant improvements in operational efficiency and a reduction in costs. For instance, predictive maintenance powered by AI can forecast equipment failures, minimizing downtime and costly emergency repairs, a critical factor in the capital-intensive pipeline industry. This proactive approach ensures smoother operations and greater reliability.
In 2024, the energy industry saw a notable increase in spending on digital transformation initiatives, with projections indicating continued growth. Energy Transfer's strategic focus on leveraging these innovations is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. The company is investing in technologies that optimize flow rates across its extensive network and enhance overall network management, aiming for smarter, more responsive infrastructure.
Innovations in carbon capture and emissions reduction
Innovations in carbon capture and emissions reduction are increasingly vital as global attention on climate change intensifies. Energy Transfer's commitment to sustainability is evident in its corporate responsibility reports, detailing ongoing emissions reduction programs and renewable energy initiatives. For instance, in 2023, the company reported a reduction in its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions intensity by 15% compared to a 2019 baseline.
Adopting advanced carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies presents a significant strategic opportunity for Energy Transfer. This move would not only align the company with stringent evolving environmental standards but also bolster its long-term sustainability profile. The global CCUS market is projected to grow substantially, with estimates suggesting it could reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2030, driven by policy support and technological advancements.
- Technological Advancements: Development of more efficient and cost-effective CCUS technologies, including direct air capture (DAC) and enhanced oil recovery (EOR) integration.
- Regulatory Tailwinds: Government incentives and carbon pricing mechanisms are making CCUS projects more economically viable. For example, the Inflation Reduction Act in the US offers significant tax credits for carbon capture.
- Industry Collaboration: Partnerships and joint ventures are emerging to share the costs and risks associated with deploying large-scale CCUS infrastructure.
- Energy Transfer's Role: Potential for Energy Transfer to leverage its existing pipeline infrastructure for CO2 transportation and storage, creating new business lines.
Cybersecurity threats to critical infrastructure
Energy Transfer's operations, like much of the energy sector, are increasingly reliant on digital control systems and interconnected networks. This digital transformation, while enhancing efficiency, also exposes the company to sophisticated cyberattacks. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy has highlighted the growing threat landscape, with reports indicating a significant rise in attempted cyber intrusions against energy infrastructure in recent years.
Protecting its vast network of pipelines, storage facilities, and critical operational data from evolving cyber threats represents a paramount technological challenge for Energy Transfer. A successful breach could disrupt supply chains, compromise sensitive information, and lead to significant financial and reputational damage. The potential for cascading effects across interconnected systems underscores the urgency of robust defense mechanisms.
Implementing and maintaining advanced cybersecurity measures is essential for ensuring operational continuity, safeguarding data integrity, and ultimately protecting national energy security. Investments in areas like threat detection, incident response, and employee training are crucial. The financial sector, for example, saw cybersecurity spending projected to reach over $270 billion globally in 2024, indicating the scale of investment required in critical industries.
- Increased Vulnerability: The digital backbone of energy infrastructure, including Energy Transfer's assets, presents a larger attack surface for cyber adversaries.
- Data Integrity and Operational Continuity: Protecting sensitive operational data and ensuring uninterrupted service delivery are critical functions threatened by cyberattacks.
- National Security Implications: Disruptions to energy infrastructure can have far-reaching consequences for national security and economic stability.
- Investment in Defense: Companies are compelled to invest heavily in advanced cybersecurity technologies and protocols to mitigate these growing risks.
Technological advancements are reshaping energy transfer, with a focus on digital integration and efficiency. Energy Transfer is actively deploying smart technologies for pipeline monitoring and inspection, utilizing drone surveillance and advanced leak detection systems in 2024 to enhance safety and operational continuity.
The company is also exploring new energy transfer methods, including carbon capture and hydrogen transport, aligning with broader industry trends toward decarbonization and diversified energy solutions. Investments in infrastructure modernization for 2024 and 2025 reflect a commitment to technological upgrades that boost efficiency and safety across its network.
Cybersecurity remains a critical technological factor, as the increasing digitalization of energy infrastructure, including Energy Transfer's assets, expands the attack surface for cyber threats. Robust defense mechanisms are essential to protect operational continuity and data integrity, with significant investments being made across the sector to counter these evolving risks.
| Technology Area | Focus for Energy Transfer | Industry Trend/Impact | Data Point/Example (2024/2025 Focus) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline Integrity & Monitoring | Smart pigging, aerial surveillance (drones) | Proactive issue identification, safety enhancement | Continued deployment of smart pigging in 2024 for pipeline inspection. |
| New Energy Transfer | Carbon capture, hydrogen transport | Diversification, decarbonization efforts | Investigation into advancements in CCUS technologies. |
| Digitalization & Automation | Data analytics, AI for predictive maintenance | Efficiency gains, cost reduction, operational optimization | Investments in digital monitoring systems to improve leak detection. |
| Cybersecurity | Threat detection, incident response | Protecting critical infrastructure from cyberattacks | Increased focus on advanced cybersecurity measures due to rising threat landscape. |
Legal factors
Energy Transfer navigates a complex web of environmental regulations governing air emissions, water quality, and waste management, critical for avoiding costly penalties and operational interruptions. For instance, in 2023, the company reported $28 million in environmental penalties, underscoring the financial impact of non-compliance.
Maintaining compliance is paramount, as violations can lead to significant fines and legal entanglements, impacting financial performance and public trust. Energy Transfer's 2024 sustainability report details ongoing investments in emission reduction technologies, aiming to further mitigate environmental risks.
Securing permits for Energy Transfer's new projects, like pipeline expansions or processing plant builds, is a legally intricate and lengthy endeavor. This often requires detailed environmental impact studies and public consultations, which can lead to significant project delays and increased expenses.
For instance, in 2023, the average time to obtain major infrastructure permits in the US saw an increase, with some energy projects facing review periods exceeding two years. Energy Transfer's strategic growth, including its ongoing investments in natural gas liquids infrastructure, is directly tied to its ability to efficiently navigate these complex regulatory landscapes.
Energy Transfer navigates significant litigation risks, often stemming from environmental incidents, land use conflicts, and contractual disputes. These legal battles can lead to substantial financial penalties, operational interruptions, and damage to the company's public image.
A prime example is the ongoing legal fallout from Winter Storm Uri, which has placed considerable financial burdens on Energy Transfer, particularly within its intrastate operations. As of early 2024, the company has continued to manage these liabilities, highlighting the persistent financial impact of such events.
Antitrust regulations and market competition
Antitrust regulations are crucial for Energy Transfer, a major North American energy infrastructure company, to ensure fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices across its extensive network. Regulatory bodies closely scrutinize its operations and strategic moves, like the significant 2024 acquisition of NuStar Energy, to uphold these principles.
These reviews are vital as Energy Transfer's substantial market share and diversified portfolio, including midstream assets and NGL transportation, place it under considerable antitrust scrutiny. For instance, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) actively monitors mergers and acquisitions in the energy sector to maintain a competitive landscape.
- Antitrust Compliance: Energy Transfer must navigate complex antitrust laws to operate its vast midstream infrastructure.
- Merger Scrutiny: Acquisitions like the NuStar deal (valued at approximately $7.3 billion in 2024) undergo rigorous review by antitrust authorities.
- Market Power: The company's significant presence in natural gas and NGL transportation necessitates adherence to regulations preventing market dominance.
- Competitive Landscape: Antitrust oversight ensures a level playing field for other energy participants, fostering innovation and consumer choice.
Land use and eminent domain laws
Energy Transfer's extensive operations, covering 44 states as of early 2024, necessitate constant engagement with land use and eminent domain laws. The acquisition of rights-of-way for pipeline construction and expansion is a critical, yet legally intricate, process.
These legal frameworks can directly impact project timelines and budgets. Disputes with landowners over compensation or property rights, and challenges from environmental groups citing land impact, are common occurrences that can lead to significant delays and cost overruns. For instance, eminent domain proceedings, while a tool for public infrastructure development, often involve protracted legal battles.
Navigating these complex land-related legalities is a core operational challenge for Energy Transfer. The company's ability to effectively manage these legal aspects is crucial for maintaining its operational integrity and growth trajectory.
- Land Acquisition Complexity: Energy Transfer's 44-state footprint means it must comply with a patchwork of state and federal land use regulations, impacting pipeline routing and construction.
- Eminent Domain Impact: The potential use of eminent domain for acquiring necessary easements can lead to protracted legal disputes, increasing project costs and timelines.
- Stakeholder Disputes: Conflicts with landowners and environmental organizations over land acquisition and usage are a persistent factor, influencing project feasibility and public perception.
Energy Transfer must adhere to stringent labor laws and workplace safety regulations, impacting its workforce management and operational costs. In 2023, the company reported a total recordable incident rate of 0.78, reflecting its commitment to safety protocols and compliance with OSHA standards.
Compliance with these legal frameworks is essential for maintaining a safe working environment and avoiding penalties. The company's 2024 safety initiatives include enhanced training programs for its approximately 10,000 employees, underscoring the ongoing focus on legal and ethical labor practices.
The energy sector is subject to evolving cybersecurity laws and data privacy regulations, requiring Energy Transfer to invest in robust protection measures for its critical infrastructure and sensitive customer information. As of early 2024, the company continues to update its cybersecurity protocols in line with emerging threats and regulatory guidance.
Failure to comply with these digital security mandates can result in significant fines and reputational damage. Energy Transfer's ongoing digital transformation efforts are designed to integrate advanced security features, ensuring compliance with regulations like the Cybersecurity Enhancement Act.
| Legal Factor | Relevance to Energy Transfer | 2023/2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Compliance | Adherence to emissions, water, and waste regulations. | $28 million in environmental penalties in 2023; ongoing investments in emission reduction. |
| Permitting Processes | Securing permits for new infrastructure projects. | Average US permit times increased; projects can face >2 year reviews. |
| Litigation Risk | Handling disputes from environmental incidents, land use, and contracts. | Continued management of liabilities from Winter Storm Uri as of early 2024. |
| Antitrust Regulations | Ensuring fair competition in its extensive network. | Scrutiny of the ~$7.3 billion NuStar Energy acquisition in 2024 by antitrust authorities. |
| Land Use & Eminent Domain | Acquiring rights-of-way for pipelines across 44 states. | Protracted legal battles common in eminent domain proceedings for easements. |
| Labor & Safety Laws | Workforce management and workplace safety compliance. | Total recordable incident rate of 0.78 in 2023; ~10,000 employees. |
| Cybersecurity & Data Privacy | Protecting critical infrastructure and customer data. | Ongoing updates to cybersecurity protocols in line with emerging threats. |
Environmental factors
The intensifying global and national commitment to combating climate change is leading to more stringent emissions targets and policies. This shift directly impacts the long-term viability and operational strategies for fossil fuel infrastructure, a core component of Energy Transfer's business. For instance, the U.S. rejoined the Paris Agreement in 2021, signaling a renewed commitment to emissions reduction, with national goals aiming for a 50-52% reduction from 2005 levels by 2030.
Energy Transfer acknowledges this evolving landscape, actively integrating initiatives to lessen its environmental impact. The company's strategic planning recognizes the transitional role of natural gas in the global energy mix as countries move towards lower-carbon alternatives. This is reflected in their efforts to improve operational efficiency and explore infrastructure that supports cleaner energy sources.
Insights into Energy Transfer's commitment to emissions reduction can be found in their corporate responsibility reports. These reports detail specific programs and progress made in areas such as methane leak detection and repair, and investments in carbon capture technologies. For example, in their 2023 reporting, Energy Transfer highlighted a continued focus on reducing Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions across their extensive network.
Pipeline construction and ongoing operations by Energy Transfer can significantly disrupt local ecosystems, impacting wildlife habitats and overall biodiversity. For instance, the Mariner East project faced scrutiny regarding its potential effects on sensitive waterways and the Chesapeake Bay watershed. Energy Transfer is committed to mitigating these impacts through measures like meticulous route planning to avoid critical habitats and implementing comprehensive restoration plans post-construction, aligning with environmental regulations.
Energy Transfer's extensive operations, especially in natural gas processing and NGL fractionation, inherently involve significant water consumption and the production of wastewater. For instance, in 2023, the company reported water withdrawal activities across its various segments, underscoring the need for robust management strategies.
Effective water management is paramount for Energy Transfer to ensure environmental compliance and maintain sustainable operations. This includes responsible sourcing of water, minimizing its use, and employing advanced treatment technologies for wastewater before discharge, aligning with regulatory standards and best practices.
The company's dedication to environmental stewardship directly addresses these water-related challenges. By investing in and implementing improved water sourcing and wastewater treatment processes, Energy Transfer aims to mitigate its environmental footprint and operate responsibly within the communities it serves.
Risk of spills and leaks
Energy Transfer's extensive pipeline network, crucial for transporting crude oil, natural gas, and natural gas liquids, faces the inherent risk of spills and leaks. These incidents can trigger significant environmental damage, impacting ecosystems and communities. The company actively manages these risks through robust pipeline safety programs and detailed emergency response protocols, acknowledging that minimizing environmental impact is vital for operational stability and public trust.
In 2023, Energy Transfer reported that its pipeline integrity programs and leak detection systems contributed to a reduction in reportable incidents. For instance, the company invested over $1.5 billion in capital expenditures related to safety and environmental stewardship in 2023, a figure that underscores its commitment to mitigating these risks. These efforts are essential for maintaining regulatory compliance and safeguarding the company's reputation.
- Pipeline Safety Investment: Energy Transfer allocated approximately $1.5 billion to safety and environmental initiatives in 2023.
- Incident Reduction Focus: Continuous improvement in pipeline integrity management and leak detection technology is a key operational priority.
- Environmental Stewardship: The company's commitment to preventing spills and leaks is directly linked to its operational integrity and public perception.
Renewable energy integration and diversification
Energy Transfer is strategically broadening its portfolio beyond traditional midstream, recognizing the growing importance of renewable energy. The company commissioned natural gas-fired electric generation facilities in 2024 to bolster its own operational efficiency and sustainability. This move reflects a commitment to adapting to the evolving energy market and supporting environmental objectives.
The integration of natural gas is particularly crucial as it acts as a vital complementary fuel source for intermittent renewables like solar and wind. By providing reliable power when renewable sources are unavailable, natural gas infrastructure ensures grid stability. For instance, in 2024, the company's investments in gas-fired generation aim to reduce reliance on less efficient or more carbon-intensive power sources for its extensive operations.
This diversification strategy is not just about environmental alignment but also about future-proofing the business. As the global energy transition accelerates, companies that can bridge traditional and renewable energy sectors will be better positioned for long-term growth. Energy Transfer's engagement in these areas highlights a proactive approach to managing environmental factors and capitalizing on new market opportunities.
Key aspects of Energy Transfer's renewable energy integration include:
- Commissioning of natural gas-fired electric generation facilities in 2024 to support operations.
- Exploration of renewable energy initiatives to diversify its business model.
- Leveraging natural gas as a complementary fuel for intermittent renewable sources.
- Alignment with broader environmental sustainability goals and the energy transition.
The increasing global focus on sustainability and climate change directly impacts Energy Transfer's operations. Stricter environmental regulations, such as those aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, necessitate significant investment in cleaner technologies and operational adjustments. For example, national commitments to emissions reduction targets, like the U.S. goal of a 50-52% reduction from 2005 levels by 2030, create a challenging yet opportunity-rich environment for midstream companies.
Energy Transfer is actively addressing environmental concerns through initiatives like methane leak detection and repair, and exploring carbon capture technologies. Their 2023 reporting highlighted continued efforts to reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions across their infrastructure. The company's commitment to environmental stewardship also extends to responsible water management, ensuring compliance with stringent wastewater treatment standards.
The company's proactive approach includes investing in pipeline safety, with approximately $1.5 billion allocated to safety and environmental initiatives in 2023. This investment underscores a dedication to minimizing environmental impact and maintaining operational integrity. Furthermore, Energy Transfer is diversifying its portfolio, commissioning natural gas-fired electric generation facilities in 2024 to enhance operational efficiency and support the broader energy transition.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Energy Transfer PESTLE analysis is meticulously constructed using data from governmental energy departments, international climate organizations, and reputable financial institutions. We incorporate insights from energy market reports, technological innovation databases, and socio-economic trend analyses.
