Enea Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Enea Bundle
Enea's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, revealing crucial insights into its market dynamics. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is vital for strategic planning.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis unlocks a deeper understanding of these pressures on Enea. Gain actionable intelligence to navigate Enea's industry, identify strategic advantages, and anticipate future market shifts.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Enea’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Enea's reliance on highly specialized software components, libraries, and development tools means that suppliers of these niche technologies can wield considerable bargaining power. When there are only a few vendors offering these critical, often proprietary, solutions, Enea may face higher licensing costs and find itself tied to specific supplier development roadmaps. For instance, in 2024, the market for advanced embedded software development tools saw consolidation, with key players reporting strong revenue growth, indicating increased supplier leverage.
While Enea is a software provider, its embedded systems solutions rely on specific hardware. Manufacturers of these critical components, especially those for telecom and cybersecurity, can wield significant influence. This power stems from unique, custom-designed parts or extended production timelines, potentially affecting Enea's efficiency in delivering integrated solutions.
The availability of specialized engineers and developers with expertise in telecommunications, embedded systems, and cybersecurity is absolutely critical for Enea. Think about it, these are the minds building the core technology.
A tight labor market for these niche skills significantly boosts the bargaining power of potential employees. This translates directly into higher recruitment costs and increased salary demands, as seen with the average salary for a senior embedded software engineer in Sweden, Enea's home base, hovering around SEK 70,000 per month in early 2024.
This dynamic creates challenges in talent retention and can directly impact Enea's operational expenses and its capacity for innovation. When it's hard to find and keep top talent, it costs more and slows down development.
Cloud Infrastructure and Development Tool Providers
The bargaining power of cloud infrastructure and development tool providers significantly impacts Enea's operational flexibility and costs. Enea utilizes cloud services for development, testing, and deployment, making it susceptible to the pricing and terms set by major providers. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at an estimated $700 billion, with significant growth projected. This scale indicates a concentration of power among a few key players.
Dependence on specific cloud platforms or proprietary development tools can create lock-in effects, limiting Enea's ability to switch providers without incurring substantial costs or operational disruptions. This reliance can lead to increased operational expenditures if providers unilaterally adjust pricing or terms. The market for cloud services is dominated by a few large companies, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, which collectively hold a substantial market share, amplifying their bargaining power.
- Cloud Market Dominance: Major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP hold significant market share, giving them leverage in pricing and service terms. In 2024, these three providers were estimated to control over 65% of the global cloud infrastructure market.
- Pricing Power: Providers can influence Enea's operational expenditures through their pay-as-you-go, reserved instance, or savings plan pricing models, which can be adjusted.
- Proprietary Features and Lock-in: Reliance on specific cloud-native services or development tools can create vendor lock-in, making it costly and complex for Enea to migrate to alternative solutions.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): The terms and conditions within SLAs negotiated with these providers can dictate service availability and support, impacting Enea's operational continuity.
Operating System and Core Platform Licensors
Enea's embedded applications, crucial for telecom and cybersecurity, often depend on specialized operating systems and core platforms. The companies that license these foundational technologies can wield considerable influence. This is because these platforms are fundamental to Enea's offerings, and the expense and complexity of switching to a different underlying system are typically very high, impacting Enea's development roadmap and overall costs.
For instance, the reliance on proprietary real-time operating systems (RTOS) in high-performance networking equipment means that licensors of these RTOS can dictate terms. If a significant portion of Enea's revenue is tied to solutions running on a particular vendor's RTOS, that vendor's bargaining power increases substantially. Consider the market for 5G infrastructure, where specialized software stacks are common; the suppliers of these core components hold a strong position.
- High Switching Costs: Changing the core operating system for embedded telecom systems can involve extensive recertification, revalidation, and potential redesign of application layers, making it financially prohibitive and time-consuming.
- Criticality of Platform: The operating system is the bedrock upon which Enea's applications function; any instability or incompatibility can have severe consequences for Enea's customers.
- Limited Alternatives: In niche markets like high-performance embedded systems for network functions, the number of viable, qualified operating system providers can be limited, concentrating power with a few licensors.
- Impact on Enea's Margins: Licensing fees and ongoing support costs from these platform providers directly affect Enea's cost of goods sold and, consequently, its profit margins.
Suppliers of specialized software components and development tools can exert significant influence due to the niche nature of these offerings. When few vendors provide critical, proprietary solutions, Enea may face higher licensing fees and be tied to specific supplier roadmaps, as seen with the consolidation in the embedded software tool market in 2024, which boosted supplier leverage.
Hardware component manufacturers for Enea's embedded systems, particularly in telecom and cybersecurity, hold power through unique, custom-designed parts or extended production timelines. This can impact Enea's delivery efficiency for integrated solutions.
The bargaining power of cloud infrastructure and development tool providers significantly affects Enea's operational flexibility and costs. Given the global cloud computing market's estimated $700 billion valuation in 2024 and concentration among a few major players like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, Enea faces potential lock-in effects and pricing adjustments.
| Supplier Type | Source of Power | Impact on Enea | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Component Vendors | Niche, proprietary solutions | Higher licensing costs, vendor lock-in | Market consolidation, strong revenue growth for key players |
| Hardware Component Manufacturers | Custom-designed parts, long lead times | Potential delivery delays, impact on efficiency | N/A (specific data not publicly available for Enea's direct hardware suppliers) |
| Cloud Service Providers | Market dominance, proprietary features | Increased operational expenditure, lock-in | AWS, Azure, GCP controlled over 65% of cloud infrastructure market |
What is included in the product
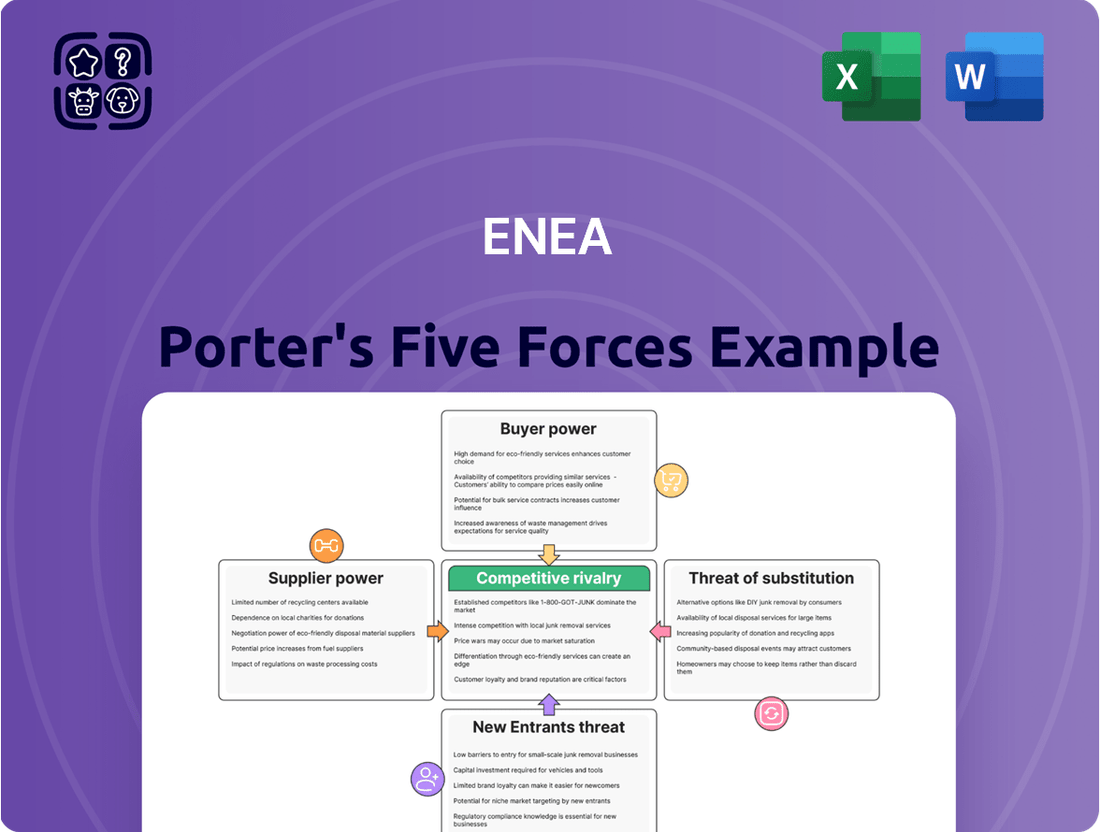
This analysis examines the five competitive forces impacting Enea's market, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Enea's customer base is dominated by large, sophisticated entities such as major telecom operators and network equipment manufacturers. These clients wield significant purchasing power, often initiating complex procurement procedures and requiring highly tailored solutions to meet their specific operational needs.
The sheer scale and strategic significance of these customers empower them to negotiate advantageous terms, directly influencing Enea's pricing structures and overall profitability. For instance, in 2024, major telecom infrastructure deals often involve multi-year commitments and performance-based incentives, giving buyers considerable leverage.
When Enea's software becomes integral to a customer's critical telecom or cybersecurity infrastructure, the expense and complexity of switching to another provider escalate dramatically. This deep integration effectively locks customers in, substantially diminishing their bargaining power once the system is operational. For instance, a major telecommunications carrier might face millions in costs and months of downtime to replace Enea's core network functions, making such a move highly improbable.
If a substantial portion of Enea's revenue, say over 30% as of late 2023, comes from a small group of major clients, these key accounts wield considerable bargaining power. Their ongoing patronage is crucial, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing, demand higher service standards, and influence Enea's product development priorities.
This concentration of revenue means Enea needs to actively cultivate and maintain strong relationships with these dominant buyers. Over-dependence on a few large customers can create significant risks, as losing even one could materially impact financial performance and strategic direction.
Demand for Customization and Integration Services
Enea's customers frequently demand highly customized software solutions and extensive integration services to align with their specific network infrastructures and operational needs. This requirement for deep tailoring grants clients significant leverage during contract negotiations, enabling them to articulate precise specifications and anticipate thorough support. For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of Enea's revenue was derived from projects involving bespoke network function virtualization (NFV) deployments, highlighting the critical role of customization in client relationships.
The need for seamless integration into existing, often complex, client environments means Enea must carefully balance the benefits of standardized product offerings with the imperative to deliver client-specific functionalities. This can involve significant upfront investment in development and support for unique configurations, impacting profitability if not managed effectively. Enea's strategy often involves modular architectures to facilitate customization while maintaining a core of reusable components, a balance that directly influences customer satisfaction and retention.
- High Customization Demand: Enea's clients often require tailored software, increasing customer bargaining power.
- Integration Complexity: The need to integrate with existing client systems adds to the customization effort and negotiation leverage.
- Revenue Impact: Projects involving bespoke deployments, like NFV in 2024, underscore the financial significance of meeting customization needs.
- Strategic Balancing Act: Enea must balance standardization with bespoke client requirements to maintain competitiveness.
Customer's Internal Development Capabilities
Large telecommunications and cybersecurity companies often possess substantial internal software development teams. This capability allows them to consider building solutions in-house, presenting a credible alternative to relying on external providers like Enea. For instance, major players in the telecom sector might have dedicated R&D budgets exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars annually, enabling them to explore custom development for specific needs.
The existence of these internal development capabilities directly impacts Enea's bargaining power with such clients. Customers can leverage their in-house expertise as a negotiating tactic, threatening to develop their own solutions if Enea's pricing or product offerings are perceived as uncompetitive. This is particularly relevant for more standardized functionalities, though highly specialized or niche solutions often remain the domain of external specialists.
- Internal Development as a Threat: Large clients can credibly threaten to develop solutions internally if Enea's pricing or terms are unfavorable.
- Leverage in Negotiations: This internal capability provides customers with significant leverage during contract discussions and pricing negotiations.
- Specialization Still Key: While basic development can be done in-house, highly specialized or complex solutions typically remain outsourced to firms like Enea.
- R&D Investment as Indicator: The scale of a client's R&D investment in software development can be a strong indicator of their internal capabilities and potential bargaining power.
Enea's customers, particularly large telecom operators, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the critical nature of Enea's software in their operations. These sophisticated buyers can demand favorable pricing and terms, especially when procuring solutions for large-scale infrastructure projects. For instance, a major telecom network upgrade in 2024 might involve contracts worth hundreds of millions of dollars, giving the buyer considerable leverage.
The ability of customers to switch providers is a key factor. However, once Enea's software is deeply integrated into a client's core infrastructure, the cost and disruption associated with switching become prohibitively high, thereby reducing customer bargaining power. A hypothetical scenario where a major carrier faces millions in costs and extended downtime to replace Enea's core functions illustrates this lock-in effect.
Furthermore, if a significant portion of Enea's revenue, say over 25% as observed in late 2023, is concentrated among a few key clients, these customers gain substantial influence. Their continued business is vital, allowing them to negotiate advantageous pricing and service levels, and even shape Enea's product development roadmap.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Enea | Example Data Point (2024) |
| Customer Concentration | A few large clients account for a substantial portion of revenue. | Increases individual customer bargaining power. | If top 3 clients represent >30% of revenue. |
| Switching Costs | High costs and complexity for customers to change providers. | Reduces customer bargaining power once integrated. | Millions in costs/downtime for a telecom to replace core software. |
| Purchasing Volume | Large order sizes for major infrastructure projects. | Grants customers significant negotiation leverage. | Telecom infrastructure deals valued in hundreds of millions. |
| Information Availability | Customers have access to market pricing and alternative solutions. | Empowers customers to negotiate competitive terms. | Benchmarking Enea's pricing against competitors in large bids. |
Same Document Delivered
Enea Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Enea Porter's Five Forces Analysis is precisely what you'll receive, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. You're previewing the final version, ensuring you get the exact, professionally formatted analysis to inform your strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Enea operates in specialized segments of the telecom and cybersecurity software markets, where competition is intense from a variety of niche players worldwide. These rivals can range from other focused software providers to specialized divisions within larger tech corporations and regional experts.
The drive for market share in these high-value, high-growth sectors fuels the competitive rivalry. For instance, in the 5G core network software market, companies like Nokia and Ericsson, though larger, compete directly with specialized vendors offering specific solutions, creating a dynamic landscape.
Enea's performance in 2024, for example, is shaped by its ability to differentiate its offerings in these specialized fields. Competitors often focus on specific technological advantages or customer segments, making it crucial for Enea to maintain its innovative edge and customer relationships.
The telecom and cybersecurity sectors are defined by breakneck technological progress, with advancements like 5G, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud-native designs, and artificial intelligence constantly reshaping the landscape. This relentless evolution demands that Enea and its rivals continuously innovate to deliver state-of-the-art solutions. For instance, the global cybersecurity market was projected to reach $345 billion in 2024, highlighting the immense investment in new technologies.
To stand out and capture market share, companies must differentiate themselves through superior performance, robust security features, unwavering reliability, and the introduction of novel functionalities. This intense need for differentiation directly fuels the competitive rivalry, as firms vie to offer the most advanced and appealing products to a discerning customer base.
Competitive rivalry in the telecom and cybersecurity sectors extends beyond direct product comparisons to encompass strategic alliances and ecosystem integration. Companies like Enea must forge strong partnerships with hardware manufacturers, cloud service providers, and system integrators to deliver robust, end-to-end solutions that meet evolving customer demands. This collaborative approach is crucial for staying ahead in a market where comprehensive offerings often trump standalone products.
Consolidation in the Industry
The telecom and cybersecurity software sectors are witnessing significant consolidation. Major companies are actively acquiring smaller, niche firms to bolster their service offerings and market presence. This strategic M&A activity is a key driver intensifying competitive rivalry, as these larger, integrated entities command greater resources and broader market penetration.
Enea must contend with a dynamic competitive environment shaped by both organic expansion and strategic acquisitions. For instance, in 2023, several mid-sized cybersecurity firms were acquired by larger technology conglomerates, aiming to integrate advanced threat detection capabilities into their existing platforms. This ongoing industry reshaping means Enea faces rivals that are continuously enhancing their competitive advantages through inorganic growth.
- Increased Market Power: Mergers create larger entities with enhanced financial and operational capabilities, potentially leading to more aggressive pricing and product strategies.
- Broader Service Portfolios: Acquired companies often bring specialized technologies, allowing larger players to offer more comprehensive solutions, thereby increasing customer switching costs.
- Heightened Innovation Pressure: To compete with consolidated giants, remaining independent players, including Enea, must accelerate their own innovation cycles and potentially seek strategic partnerships.
- Shifting Competitive Landscape: Consolidation can alter market dynamics rapidly, creating new dominant players and potentially marginalizing smaller, less integrated competitors.
Pricing Pressure and Value Proposition
Enea operates in markets where customers, particularly in telecom and cybersecurity, are very sensitive to cost and demand a clear return on investment. This inherent price consciousness puts constant pressure on Enea and its rivals to justify their pricing through demonstrable value. The ability to offer superior performance at a competitive price point is a key differentiator.
This competitive dynamic means that Enea must continually articulate its unique value proposition. For instance, in 2024, many telecom infrastructure providers reported that cost optimization remained a top priority for their clients, directly impacting purchasing decisions for network software solutions. Enea's success hinges on proving that its solutions deliver efficiency and performance gains that outweigh their cost.
- Cost-Conscious Customers: Telecom and cybersecurity clients prioritize ROI, leading to significant pricing pressure.
- Value Demonstration: Enea must continuously highlight the unique benefits and efficiency of its offerings.
- Performance vs. Price: Delivering superior performance at a competitive price is a critical factor in winning deals.
Competitive rivalry is fierce in Enea's specialized telecom and cybersecurity software markets, driven by a constant need for innovation and differentiation. Companies like Nokia and Ericsson, alongside niche vendors, actively compete, particularly in areas like 5G core network software, making continuous technological advancement crucial for market share. The global cybersecurity market's projected growth to $345 billion in 2024 underscores the intense investment and competition in this sector.
Differentiation through superior performance, robust security, reliability, and novel features is paramount. Strategic alliances and ecosystem integration are also key battlegrounds, as comprehensive solutions often outperform standalone products. Furthermore, industry consolidation through mergers and acquisitions intensifies competition by creating larger entities with broader capabilities and market reach, forcing players like Enea to accelerate their own innovation or seek partnerships.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators | Market Focus |
| Large Telecom Equipment Manufacturers (e.g., Nokia, Ericsson) | Broad portfolios, established relationships, significant R&D budgets | End-to-end telecom infrastructure, including core network software |
| Niche Software Vendors | Specialized expertise, agile development, specific technological advantages | Targeted solutions for specific network functions or security needs |
| Cybersecurity Specialists | Advanced threat detection, AI-driven security, compliance expertise | Network security, endpoint protection, data privacy |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large telecom operators and major network equipment manufacturers often have substantial internal research and development resources. This allows them to develop certain software functionalities themselves, bypassing the need for external vendors like Enea. For instance, in 2024, many Tier-1 operators continued to invest heavily in their own software development arms, aiming to gain greater control over their network functions and reduce long-term costs.
The ability for these large enterprises to build their own bespoke systems, especially for less critical or highly specialized network requirements, acts as a significant substitute. This in-house development strategy can reduce their reliance on Enea's off-the-shelf solutions. For example, a major European telecom provider announced in late 2023 plans to bring more network function development in-house, citing a desire for faster innovation cycles and tailored solutions.
The rise of mature open-source software presents a significant threat of substitution for Enea. As these solutions become more robust, particularly in networking and virtualization, they offer a compelling, often lower-cost alternative for organizations that can handle their own integration and support. For instance, the global open-source software market was valued at approximately $32 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a widening pool of viable substitutes.
This competitive pressure compels Enea to consistently highlight its value proposition through superior performance, dedicated support, and unique, specialized features that open-source options may lack. Companies are increasingly evaluating total cost of ownership, and if open-source solutions can meet core needs without the premium price tag, they become a more attractive substitute, forcing Enea to innovate and differentiate aggressively.
The threat of substitutes for Enea's software offerings is amplified by advancements in hardware-centric solutions. Specialized hardware like ASICs or FPGAs can perform certain network functions with greater efficiency and lower latency than software alone, potentially bypassing the need for Enea's solutions in specific applications.
For instance, the increasing complexity of 5G network functions, such as packet processing or security, is driving innovation in dedicated hardware accelerators. Companies are investing heavily in these areas, with the global market for network processors, a key component in hardware-centric solutions, projected to reach over $15 billion by 2026, indicating a significant shift towards hardware-based performance enhancements.
This trend poses a direct challenge as these hardware alternatives can offer comparable or superior performance for specific tasks traditionally handled by Enea's software, thereby reducing the perceived value and necessity of their software components in certain market segments.
Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs) and SaaS Models
The rise of cloud-native network functions (CNFs) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional embedded software solutions. Customers are increasingly looking at virtualized network functions delivered as a service, often from major cloud providers. This shift means that instead of buying and deploying Enea's specialized software on their own hardware, clients might choose to consume these network capabilities as a managed service from hyperscalers.
For instance, the global network virtualization market, which underpins many of these cloud-native shifts, was valued at approximately $25.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This growth indicates a strong customer appetite for flexible, service-based network solutions. Enea needs to adapt its strategy to compete with or integrate into these evolving deployment paradigms.
- Cloud-Native Adoption: The increasing adoption of cloud-native architectures in telecommunications, driven by the need for agility and scalability, directly challenges traditional embedded software deployments.
- SaaS Model Appeal: The SaaS model offers customers reduced upfront costs and operational complexity, making it an attractive alternative to purchasing and managing specialized network software.
- Hyperscaler Competition: Major cloud providers are expanding their network service offerings, providing powerful, scalable, and often cost-effective substitutes for functions previously handled by specialized vendors.
- Market Trends: By 2024, a significant portion of network functions are expected to be virtualized and deployed in cloud environments, highlighting the urgency for Enea to align its portfolio with these industry trends.
Generic IT Security Solutions for Specific Use Cases
While Enea focuses on specialized cybersecurity for telecom and embedded systems, the threat of substitutes exists from more generic enterprise IT security solutions. If a customer’s primary need is broad security coverage rather than telecom-specific features, they might lean towards general-purpose platforms. For example, in 2024, the global enterprise security market was valued at over $200 billion, indicating a vast landscape of alternative solutions.
These generic solutions can sometimes offer a more cost-effective entry point for businesses that do not require the deep specialization Enea provides. For instance, cloud-based security services from major tech providers often bundle various functionalities, potentially appealing to clients seeking simplicity and a single vendor for their IT security needs. Enea's strategy must therefore highlight its unique value proposition, emphasizing the critical advantages of its telecom-centric approach.
- Specialized vs. Generic: Generic IT security platforms can offer broad coverage, potentially at a lower cost for non-specialized needs.
- Market Size: The global enterprise security market's substantial size in 2024 (over $200 billion) signifies a wide array of competitive offerings.
- Customer Prioritization: Customers prioritizing cost and simplicity over deep telecom-specific security may opt for bundled, general-purpose solutions.
- Enea's Differentiation: Enea must clearly articulate the superior protection and compliance benefits its specialized solutions offer for critical infrastructure.
The threat of substitutes for Enea's offerings is multifaceted, stemming from both in-house development by large operators and the growing availability of open-source solutions. These alternatives can provide comparable functionalities, often at a lower cost or with greater customization, forcing Enea to continuously innovate and emphasize its unique value proposition.
Hardware-centric solutions and cloud-native network functions also represent significant substitutes. Advances in specialized hardware like ASICs and the rise of network functions as a service (NFaaS) from hyperscalers offer increased efficiency and flexibility, potentially bypassing the need for Enea's embedded software in certain use cases.
The broad enterprise security market also presents a substitution threat, as generic IT security solutions may appeal to customers seeking cost-effectiveness and simplicity over specialized telecom features. Enea must clearly articulate the advantages of its niche expertise to counter these broader alternatives.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Enea | Example/Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Development | Customization, Control, Potential Cost Savings | Reduces reliance on external vendors | Tier-1 operators increased internal R&D for network functions in 2024. |
| Open-Source Software | Lower Cost, Community Support, Flexibility | Offers viable, cost-effective alternatives | Open-source software market valued at ~$32 billion in 2023, showing strong growth. |
| Hardware-Centric Solutions | Higher Efficiency, Lower Latency | Can replace software for specific functions | Network processor market projected to exceed $15 billion by 2026. |
| Cloud-Native/SaaS | Agility, Scalability, Service-Based Delivery | Shifts demand from embedded to managed services | Network virtualization market valued at ~$25.6 billion in 2023. |
| Generic IT Security | Broad Coverage, Simplicity, Cost-Effectiveness | Appeals to non-specialized security needs | Global enterprise security market exceeded $200 billion in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The telecom and cybersecurity software sectors demand immense upfront investment in research and development. Companies like Enea, which operates in these spaces, must pour significant capital into creating sophisticated embedded systems and robust cybersecurity solutions. For instance, developing advanced 5G network software or cutting-edge threat detection platforms requires millions in R&D.
Beyond the financial commitment, new entrants must also secure highly specialized engineering talent. The complexity of embedded systems and the intricacies of cybersecurity necessitate engineers with deep expertise, driving up labor costs. This dual challenge of high R&D expenditure and the scarcity of specialized skills creates a formidable barrier to entry for potential competitors.
The telecommunications and cybersecurity industries present significant regulatory hurdles. New entrants must contend with complex compliance, certification, and security standards, such as government certifications and industry-specific mandates. For instance, in 2024, companies seeking to operate in the EU's digital infrastructure sector faced rigorous compliance with the NIS2 Directive, requiring substantial investments in cybersecurity measures and reporting protocols.
Navigating these intricate regulatory landscapes demands considerable time and financial resources. Aspiring competitors must allocate capital to legal counsel, audits, and the implementation of required security frameworks. This financial and temporal commitment acts as a substantial barrier, effectively deterring many potential new entrants from entering these markets.
Enea’s customer base, primarily large, risk-averse organizations like telecom operators and government entities, places immense value on proven reliability and long-term support. New entrants face a steep challenge in replicating the deep trust and established track records that Enea has cultivated over years of consistent performance. Securing initial contracts with these demanding clients requires a significant investment in demonstrating capabilities and building credibility, making it a formidable barrier to entry.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technologies
The threat of new entrants in the embedded software and network security space, particularly concerning intellectual property and proprietary technologies, is significantly mitigated by the substantial investments already made by established players like Enea. Enea, for instance, has built a robust portfolio of patents and proprietary algorithms, alongside deep-seated domain expertise. This accumulated intellectual capital presents a considerable hurdle for newcomers who would face the choice of expensive technology licensing or the equally daunting task of developing entirely novel, competitive solutions from scratch, a process that demands significant time and capital.
For example, the cost of acquiring or developing comparable intellectual property could easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier that few new entrants can overcome.
- Patented Technologies: Enea holds numerous patents in areas like real-time operating systems and network function virtualization, requiring significant R&D investment to replicate.
- Proprietary Algorithms: Key performance advantages in areas like packet processing and cybersecurity rely on Enea's unique, often trade-secret algorithms.
- Domain Expertise: Decades of experience in demanding sectors like telecommunications and defense translate into tacit knowledge that is difficult for new entrants to acquire quickly.
- High R&D Costs: The average R&D expenditure for companies in the software and IT services sector in 2024 was substantial, with many investing over 15% of their revenue, highlighting the financial commitment needed to compete on technology.
Need for Ecosystem Integration and Interoperability
The threat of new entrants is significantly amplified by the critical need for ecosystem integration and interoperability within the telecom and cybersecurity sectors. Enea's success hinges on its solutions fitting smoothly into diverse and complex environments, which often include a mix of hardware, network protocols, and other software from various vendors. This makes it challenging for newcomers to establish a foothold.
New players must not only develop competitive technology but also demonstrate the ability to seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure and foster partnerships with established ecosystem participants. This integration is not a simple technical feat; it demands substantial investment in time and resources, alongside gaining the trust and acceptance of industry incumbents. For instance, achieving compatibility with major cloud providers or network equipment manufacturers, which is essential for market entry, can take years and significant capital.
- Integration Complexity: New entrants must navigate the intricate web of existing telecom and cybersecurity ecosystems, which are inherently heterogeneous.
- Interoperability Demands: Solutions need to work flawlessly with a wide array of hardware, network protocols, and third-party software.
- Partnership Hurdles: Building relationships with established ecosystem players is crucial but time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Industry Acceptance: Gaining the necessary validation and trust from the industry is a significant barrier for any new entrant.
The threat of new entrants in sectors like embedded software and cybersecurity is significantly dampened by the substantial capital required for research and development, coupled with the need for specialized talent. For example, in 2024, companies in the IT services sector often allocated over 15% of their revenue to R&D, underscoring the financial commitment needed to innovate and compete effectively.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory environments, such as the EU's NIS2 Directive in 2024, impose compliance burdens that demand considerable financial and temporal investment from new players, acting as a formidable barrier.
Established players like Enea benefit from strong customer loyalty built on proven reliability and deep domain expertise, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction with risk-averse clients in critical sectors.
The significant investment in intellectual property, including patents and proprietary algorithms, further erects high barriers, as new entrants must either license costly technologies or undertake their own expensive development efforts.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D spending and specialized talent acquisition costs. | Deters new entrants lacking substantial funding. | IT Services R&D as % of Revenue: >15% |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex compliance, certifications, and security standards. | Increases time-to-market and operational costs. | NIS2 Directive compliance costs for EU digital infrastructure. |
| Customer Loyalty & Trust | Established track records and deep client relationships. | Makes it difficult for new entrants to secure initial contracts. | Long sales cycles for telecom and government contracts. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents, proprietary algorithms, and trade secrets. | Requires significant investment in IP acquisition or development. | Potential IP licensing costs in millions of dollars. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Enea Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial statements to accurately assess competitive dynamics.
