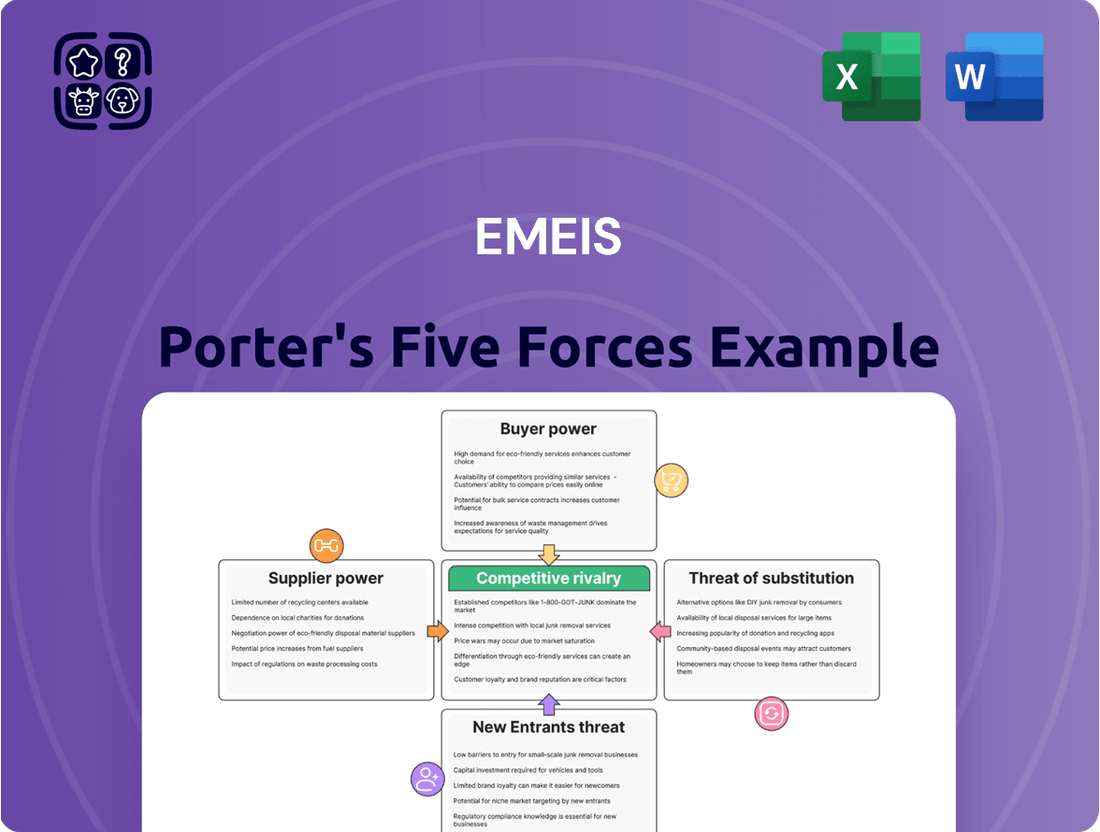
Emeis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Emeis Bundle
Emeis Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the underlying competitive landscape, detailing the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating Emeis's market effectively. Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Emeis’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The healthcare sector, especially long-term care and rehabilitation facilities, is grappling with ongoing staffing shortages for crucial roles such as nurses, therapists, and caregivers. This scarcity directly amplifies the bargaining power of these skilled professionals. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated a national nursing shortage projected to worsen, with some estimates suggesting a deficit of over 400,000 registered nurses by 2030. This situation forces employers like Emeis to compete more aggressively for talent, potentially driving up labor costs.
These persistent shortages empower specialized labor suppliers to negotiate for improved compensation packages, including higher wages, enhanced benefits, and more flexible working conditions. Emeis, like other healthcare providers, may find itself compelled to meet these demands to secure and retain essential staff. The increasing cost of labor due to these negotiations can directly impact Emeis's operational expenses and profitability, a critical factor in its overall competitive standing.
Emeis relies heavily on specialized medical equipment and technology, such as advanced rehabilitation devices and remote monitoring systems. Suppliers of these critical, often proprietary, technologies can wield substantial bargaining power, particularly when Emeis faces limited alternative vendors or incurs high costs to switch providers.
For instance, in 2024, the global medical device market was valued at approximately $530 billion, with significant growth driven by technological advancements. Companies that develop unique, patented rehabilitation technologies or integrated electronic health record systems often find themselves in a strong negotiating position due to the specialized nature of their offerings and the investment required for Emeis to adopt new systems.
As a major healthcare provider, Emeis relies heavily on a steady flow of pharmaceuticals. The bargaining power of pharmaceutical suppliers is often significant, especially when dealing with patented drugs or essential medicines that lack readily available generic substitutes. This can directly influence Emeis's operational expenses.
In 2024, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at approximately $1.6 trillion, with a substantial portion attributed to patented drugs. For instance, the average price of a new brand-name drug launched in the US in 2023 was over $100,000 per year, highlighting the potential cost pressure on purchasers like Emeis.
Real Estate and Facility Management Services
Emeis Porter's network of nursing homes and hospitals relies on real estate and facility management services, making these suppliers a potential source of bargaining power. In markets with high property values or a scarcity of appropriate healthcare facilities, landlords and service providers can command higher prices or more favorable lease terms. For instance, in 2024, commercial real estate vacancy rates for healthcare properties in major metropolitan areas remained low, often below 5%, indicating a tight market where suppliers have leverage.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified when Emeis has limited alternatives for acquiring or managing its physical locations. In regions where specialized healthcare real estate is in high demand and few options exist, suppliers can dictate terms more effectively. This is particularly true for facilities requiring specific layouts or regulatory compliance, narrowing the pool of available properties and service providers.
- Limited Availability: In 2024, the supply of specialized healthcare real estate in many urban centers remained constrained, with vacancy rates for medical office buildings averaging around 8.5% nationally, according to industry reports.
- High Property Values: Prime locations, especially in densely populated areas, command premium rental rates, increasing the bargaining power of property owners.
- Specialized Services: Facility management for healthcare settings requires specific expertise and compliance, concentrating power among a few qualified providers.
- Lease Renewal Terms: As leases come up for renewal, suppliers can leverage current market conditions to negotiate increased rents or service fees, impacting Emeis's operational costs.
Specialized Service Providers (e.g., IT, Consulting)
Emeis, a significant player in the healthcare sector, likely relies on specialized external firms for critical functions like IT, cybersecurity, and strategic consulting. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be considerable if their expertise is highly specialized or if switching costs are substantial for Emeis.
For instance, in 2024, the global IT services market was valued at over $1.3 trillion, with cybersecurity services alone projected to reach $231.7 billion. This indicates a robust market where providers with unique skill sets, particularly in areas like AI-driven cybersecurity or complex healthcare IT integrations, can command higher prices and more favorable terms.
- High Integration Costs: Implementing new IT systems or cybersecurity protocols often involves significant upfront investment and lengthy integration periods, making it costly and disruptive for Emeis to switch providers.
- Niche Expertise: Suppliers offering specialized knowledge in areas such as healthcare data analytics, HIPAA-compliant cloud solutions, or advanced medical imaging software possess a distinct advantage.
- Limited Supplier Pool: The availability of a small number of highly qualified providers for certain niche services can concentrate bargaining power in the hands of the suppliers.
- Industry Demand: The increasing demand for digital transformation and enhanced cybersecurity in healthcare, as evidenced by rising market valuations, strengthens the position of capable service providers.
Suppliers possess significant bargaining power when their products or services are critical, unique, or when there are few alternatives. This power allows them to influence pricing and terms, impacting a company's costs and profitability. For Emeis, this is evident in areas like specialized medical equipment, pharmaceuticals, and skilled labor, where scarcity and high switching costs empower suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key component of Porter's Five Forces, shaping the competitive landscape. When suppliers have leverage, they can demand higher prices, reduce quality, or limit availability, directly affecting a firm's ability to compete and generate profits. Understanding and managing this power is crucial for strategic decision-making.
In 2024, the healthcare sector continued to face challenges from powerful supplier groups. For instance, the persistent shortage of registered nurses, projected to exceed 400,000 by 2030, significantly boosted the bargaining power of nursing staff and staffing agencies. Similarly, the high cost of patented pharmaceuticals, with some new drugs exceeding $100,000 annually, demonstrated the leverage held by pharmaceutical manufacturers.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Emeis (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Skilled Labor (Nurses, Therapists) | Severe shortages, high demand, specialized skills | Increased wage pressures, higher staffing costs |
| Specialized Medical Equipment | Proprietary technology, high switching costs, limited vendors | Higher equipment purchase/lease prices, potential service contract costs |
| Pharmaceuticals | Patented drugs, lack of generic alternatives, high R&D costs | Increased drug procurement expenses, potential impact on patient care costs |
| Real Estate (Healthcare Facilities) | Low vacancy rates in prime locations, specialized facility needs | Higher rental costs, increased facility management expenses |
| IT & Cybersecurity Services | Niche expertise, high integration costs, increasing industry demand | Higher service fees, potential for long-term contracts |
What is included in the product
Emeis Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive framework to assess the competitive intensity and attractiveness of the healthcare market, detailing the power of buyers, suppliers, new entrants, existing rivals, and substitute products for Emeis.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Patients and their families now have a wider array of choices in healthcare, from specialized rehabilitation to in-home care and assisted living. This increased availability of options significantly boosts their bargaining power.
Emeis's customers, particularly those seeking long-term care or rehabilitation, can leverage their choices to select providers offering superior personalized care, demonstrably better health outcomes, or more competitive pricing structures. The emphasis on patient experience is a critical factor in retaining this empowered customer base.
For instance, the home healthcare market alone is projected to reach over $500 billion globally by 2027, indicating a strong consumer shift towards alternative care settings. In 2024, reports suggest that patient satisfaction scores are increasingly influencing provider selection, with many patients actively comparing quality metrics and cost-effectiveness before committing to a service.
Government payers like Medicare and Medicaid represent a substantial portion of Emeis's revenue. In 2024, Medicare and Medicaid accounted for a significant percentage of hospital and healthcare provider revenue nationwide, influencing pricing and operational decisions across the industry.
These large government entities wield considerable bargaining power. They dictate reimbursement rates, which directly impacts Emeis's profitability, and also set care standards that can shape service offerings and operational costs.
Private insurance companies hold significant bargaining power with Emeis, as they represent a substantial customer base. In 2024, the healthcare insurance market saw continued consolidation, with larger insurers wielding more influence in negotiations. This power allows them to negotiate for lower reimbursement rates, potentially limiting Emeis's revenue per patient.
Furthermore, these insurers can restrict network access for certain procedures or providers, directly impacting Emeis's patient volume and service utilization. Their ability to influence which services are covered and at what level also shapes Emeis's operational decisions and profitability. For instance, a major insurer deciding to reduce coverage for a specific Emeis service could lead to a significant drop in demand for that offering.
Referral Networks and Healthcare Systems
Referral networks significantly influence the bargaining power of customers within healthcare systems like Emeis. These networks, often comprising hospitals, physicians, and other healthcare providers, act as gatekeepers, directing patient flow. In 2024, the increasing consolidation of healthcare systems means fewer, larger referral entities can exert considerable influence over provider choice.
The ability of these referral sources to steer patients towards specific facilities, based on factors like quality metrics, cost efficiency, and existing contractual agreements, effectively translates them into powerful customers for Emeis. For instance, a major hospital system's decision to prioritize referrals to a particular Emeis facility can directly impact its patient volume and revenue.
- Referral Power: Hospitals and physician groups can direct significant patient volumes, acting as key customers for Emeis.
- Partnership Influence: Established relationships and contractual terms between referral sources and Emeis shape patient choice.
- Quality and Cost Focus: Referral sources increasingly evaluate providers on clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness, increasing customer leverage.
Demand for Value-Based Care
Customers are increasingly shifting their focus towards value-based care, prioritizing measurable health outcomes and overall cost-effectiveness over the sheer volume of medical services received. This trend is significantly amplifying their bargaining power, as they now have clearer benchmarks to assess the quality and affordability of healthcare providers.
For Emeis Porter, demonstrating a clear advantage in patient outcomes and delivering cost-efficient care models will be paramount. For instance, a 2024 report by the Health Care Payment Learning & Action Network indicated that the share of healthcare payments made under value-based arrangements reached 60% in 2023, highlighting the growing market demand.
- Focus on Outcomes: Emeis must showcase data proving superior patient recovery rates and reduced readmission percentages.
- Cost Efficiency: Highlighting reduced per-patient costs without compromising quality is essential.
- Patient Satisfaction: Demonstrating high patient satisfaction scores, often linked to better outcomes and communication, strengthens Emeis's position.
- Transparency: Providing clear pricing and outcome data empowers patients to make informed choices, increasing their leverage.
Customers, including patients, their families, and major payers like government entities and private insurers, hold significant sway over Emeis. This power stems from increased choice, a focus on value-based care, and the ability to negotiate pricing and service terms.
In 2024, the healthcare landscape continued to see patients actively comparing providers based on outcomes and cost. Government payers like Medicare and Medicaid, which represent a substantial portion of revenue for many healthcare providers, dictate reimbursement rates and care standards, directly impacting profitability and operational decisions.
Private insurers, often consolidated and wielding considerable influence, negotiate lower reimbursement rates and can restrict network access, affecting patient volume. Referral networks, increasingly consolidated themselves, act as gatekeepers, directing patient flow based on quality and cost metrics.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Emeis |
|---|---|---|
| Patients/Families | Increased choice, focus on outcomes, satisfaction | Drives demand for quality and patient-centric care |
| Government Payers (Medicare/Medicaid) | Large volume, rate setting, standards | Significant revenue influence, operational constraints |
| Private Insurers | Market share, negotiation power, network control | Affects reimbursement rates and patient access |
| Referral Networks | Patient volume control, quality/cost evaluation | Influences patient flow and provider selection |
What You See Is What You Get
Emeis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within an industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The long-term care, rehabilitation, and mental health sectors are characterized by a fragmented market structure. This means there are many local and regional providers competing with larger national and international entities, creating a dynamic landscape for service delivery.
This high degree of fragmentation often fuels intense price competition among providers. To stand out, companies are compelled to differentiate their services, focusing on specialized care, patient experience, or technological integration. For example, in 2024, the US home healthcare market alone, a significant part of long-term care, was valued at over $150 billion, illustrating the vast number of players vying for market share.
Competitors in the healthcare sector, such as Amedisys and LHC Group, present a broad spectrum of services. These include home health, assisted living, specialized clinics, and outpatient care, some of which directly challenge Emeis's core business.
Brookdale Senior Living, another major competitor, also offers a diverse portfolio that often overlaps with Emeis's patient base and service areas. This wide range of offerings intensifies the competitive landscape, requiring Emeis to differentiate its value proposition effectively.
Competitive rivalry in healthcare, particularly in specialized sectors like elderly and mental health care, is intensely shaped by the perceived quality of care, actual patient outcomes, and the overall reputation of providers. Emeis, recognizing this, strategically emphasizes its commitment to personalized care and patient well-being, positioning these as crucial differentiators in a crowded market.
Technological Advancements as a Competitive Edge
Competitors in the healthcare sector are rapidly integrating advanced technologies like telehealth, artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and remote patient monitoring. These innovations are crucial for enhancing patient care, boosting operational efficiency, and attracting a broader patient base. For Emeis, staying ahead means not just adopting these technologies but strategically investing in them to maintain its competitive edge.
The push towards digital health solutions is a defining characteristic of the current competitive landscape. For instance, in 2024, the global telehealth market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, showcasing the significant shift in how healthcare is delivered and accessed. Emeis needs to ensure its technological infrastructure supports these evolving patient expectations and service delivery models.
- Telehealth Adoption: Competitors are expanding telehealth services, increasing patient convenience and reach.
- AI in Diagnostics: AI-powered tools are being used for faster and more accurate diagnoses, a key differentiator.
- Robotics in Surgery: Robotic-assisted surgeries offer precision and faster recovery times, attracting specialized patient segments.
- Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems allow for continuous patient oversight, improving chronic disease management.
Consolidation and Mergers & Acquisitions
The competitive landscape is being reshaped by a wave of consolidation, primarily driven by mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Larger companies are actively acquiring smaller competitors to broaden their operational territories, enhance their service offerings, and capture a greater slice of the market. This strategic move, while beneficial for the acquiring entities, can significantly escalate competitive pressures by creating more powerful and resource-rich market players.
This trend is particularly evident in sectors like technology and finance. For instance, in 2024, the technology sector saw a notable increase in M&A activity, with deal values reaching hundreds of billions of dollars globally. This consolidation often leads to fewer, but larger, competitors, intensifying the rivalry for market share and customer loyalty.
- Increased Market Concentration: Consolidation leads to fewer, larger players, intensifying direct competition.
- Enhanced Economies of Scale: Merged entities can leverage greater scale, potentially leading to more aggressive pricing.
- Broader Service Portfolios: Acquisitions allow companies to offer a wider range of products or services, creating more comprehensive solutions.
- Geographic Expansion: M&A is a key strategy for companies looking to enter new markets or strengthen their presence in existing ones.
The competitive rivalry within Emeis's operating sectors is fierce, driven by numerous providers offering similar services. This fragmentation means companies constantly vie for patient attention and market share through service quality and innovation. For example, the US long-term care market, a key area for Emeis, is highly competitive, with many local and national players. In 2024, the home healthcare segment alone was valued at over $150 billion, underscoring the intense competition for patients and revenue.
Competitors are actively differentiating themselves by focusing on specialized care, patient experience, and technological advancements. The rapid integration of telehealth, AI, and remote monitoring by rivals like Amedisys and Brookdale Senior Living highlights the industry's shift towards digital solutions. This technological race is crucial for enhancing patient care and operational efficiency, with the global telehealth market projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in 2024.
Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is further intensifying this rivalry, creating larger, more formidable competitors. Companies are acquiring smaller entities to expand their reach and service portfolios, leading to increased market concentration. This trend, prominent across various sectors including technology, means Emeis faces pressure from well-resourced giants, necessitating strategic investment and differentiation to maintain its competitive edge.
| Key Competitor | Service Overlap | Competitive Strategy Example | 2024 Market Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amedisys | Home health, rehabilitation | Expanding specialized care programs | Growth in post-acute care |
| LHC Group | Home health, hospice | Acquisitions for geographic expansion | Integration of acquired entities |
| Brookdale Senior Living | Senior living, assisted living | Enhancing resident experience | Focus on memory care services |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Home healthcare services present a significant threat to traditional institutional long-term care and rehabilitation facilities. This is because individuals can receive necessary medical attention and support within the comfort of their own homes, often at a lower cost.
The preference for home-based care is growing, especially among seniors, fueled by advancements in remote monitoring technology. For instance, by 2024, the global remote patient monitoring market was projected to reach approximately $60 billion, indicating a strong trend towards in-home care solutions.
Assisted living facilities present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional nursing homes. These facilities offer a less intensive and often more independent living option, catering to individuals who require some assistance with daily activities but not the constant, skilled nursing care provided by nursing homes. This distinction makes them a viable alternative for a growing segment of the senior population.
In 2024, the number of assisted living facilities across the United States continued to expand, reflecting increasing demand. Data from the National Center for Assisted Living indicated that over 30,000 assisted living communities were operating, serving approximately 1 million residents. This widespread availability and the perceived lower cost compared to skilled nursing care make them a compelling substitute.
The appeal of assisted living also stems from its focus on resident autonomy and social engagement, which can be more attractive than the more medically-oriented environment of nursing homes. For many seniors, the ability to maintain a degree of independence while receiving support is a primary driver for choosing assisted living over more intensive care options, thereby directly impacting the market share of nursing homes.
Adult day care programs present a significant threat of substitutes for full-time institutional care, offering a middle ground for seniors and individuals needing support. These programs provide essential supervision, engaging social activities, and basic care services during the day, enabling participants to reside in their own homes overnight. This flexibility and reduced cost structure make them an attractive alternative to more intensive, round-the-clock residential facilities.
The market for adult day care is growing, reflecting this shift. In 2023, the U.S. adult day care services market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion, with projections indicating continued expansion. This growth is driven by the desire for aging in place and the cost-effectiveness compared to nursing homes, which can exceed $8,000 per month. Adult day care, by contrast, often costs between $1,000 and $3,000 per month, making it a more accessible option for many families.
Informal Caregivers and Family Support
The availability of informal caregiving, often provided by family members and friends, presents a significant threat of substitutes for formal care services like those offered by Emeis. These informal caregivers frequently step in, especially for the elderly and individuals with chronic conditions, reducing the need for professional assistance. For instance, in 2024, an estimated 53 million adults in the U.S. provided unpaid care to an adult or child, demonstrating the widespread reliance on family support systems.
This extensive informal care network can directly impact the demand for Emeis's services by offering a lower-cost, readily accessible alternative. The willingness and capacity of family members to provide care can therefore limit the market share and pricing power of formal care providers. Statistics from 2023 indicated that the economic value of unpaid caregiving in the U.S. was estimated to be $522 billion, highlighting the substantial contribution of informal support.
- Informal Caregiving's Scale: Millions of Americans provide unpaid care, acting as a significant substitute for professional services.
- Cost Advantage: Informal care is typically free, making it a highly attractive alternative to paid care.
- Emotional Connection: Family caregivers often provide a level of emotional support that can be difficult for formal providers to replicate.
- Market Impact: The strong presence of informal caregivers can cap the growth and pricing flexibility of companies like Emeis.
Technology-Enabled Self-Management Solutions
Technology-enabled self-management solutions are increasingly posing a threat. Advancements in digital health, wearables, and AI-powered platforms allow individuals to monitor and manage aspects of their health and rehabilitation at home, bypassing traditional facility-based services.
These digital tools can substitute for certain in-person therapies or consultations. For instance, the global digital health market was valued at over $200 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift towards home-based, tech-driven health management.
- Digital Health Market Growth: The digital health sector is experiencing rapid expansion, with projections suggesting continued strong growth through 2025 and beyond.
- Wearable Technology Adoption: Increased consumer adoption of wearable devices for health tracking provides a foundation for self-management solutions. In 2024, it's estimated that over 1 billion people worldwide use health and fitness wearables.
- AI in Healthcare: Artificial intelligence is being integrated into various health applications, offering personalized insights and guidance that can reduce reliance on external providers for routine care or monitoring.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: The rise of remote patient monitoring platforms allows for continuous data collection and analysis outside of clinical settings, directly substituting for some in-facility check-ups.
The threat of substitutes for traditional nursing homes and rehabilitation facilities is multifaceted, encompassing home healthcare, assisted living, adult day care, informal caregiving, and technology-enabled self-management. These alternatives often present a more cost-effective, convenient, or preferred option for individuals seeking care.
Home healthcare services are a direct substitute, allowing individuals to receive medical attention at home, often at a lower cost. By 2024, the global remote patient monitoring market was projected to reach approximately $60 billion, underscoring the trend towards in-home care solutions.
Assisted living facilities offer a less intensive, more independent living environment, appealing to those who need some daily assistance but not constant skilled nursing. In 2024, over 30,000 assisted living communities were operating in the U.S., serving about 1 million residents.
Adult day care programs provide daytime supervision and activities, enabling participants to live at home, offering a cost-effective alternative to full-time care. The U.S. adult day care services market was valued at around $3.5 billion in 2023.
Informal caregiving by family and friends is a substantial substitute, reducing demand for professional services. An estimated 53 million adults in the U.S. provided unpaid care in 2024, with the economic value of this care estimated at $522 billion in 2023.
Technology-enabled self-management, including wearables and AI platforms, allows individuals to monitor and manage health at home. The global digital health market exceeded $200 billion in 2023, indicating a strong shift towards tech-driven health management.
| Substitute Type | Key Offering | 2024/2023 Data Point | Estimated Cost (Monthly) |
| Home Healthcare | Medical attention at home | Remote Patient Monitoring Market: ~$60 billion (projected) | Varies, often lower than facilities |
| Assisted Living | Independent living with assistance | 30,000+ U.S. facilities, ~1 million residents | $3,000 - $6,000+ |
| Adult Day Care | Daytime supervision and activities | U.S. Market Value: ~$3.5 billion (2023) | $1,000 - $3,000 |
| Informal Caregiving | Unpaid family/friend support | 53 million U.S. caregivers (2024); $522 billion economic value (2023) | $0 (unpaid) |
| Tech Self-Management | Digital health, wearables, AI | Digital Health Market: >$200 billion (2023) | Varies (device/subscription costs) |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing and running facilities for long-term care, rehabilitation, and psychiatric services demands immense capital. This includes significant outlays for real estate, specialized medical equipment, and a highly trained workforce. For instance, the average cost to build a new skilled nursing facility can range from $15 million to $30 million, depending on size and location.
Furthermore, the healthcare industry is burdened by extensive regulations. New entrants face formidable licensing, accreditation, and ongoing compliance mandates. In 2024, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continued to emphasize rigorous quality reporting and patient safety standards, adding complexity and cost for any new provider seeking to enter the market.
Brand reputation and trust are incredibly important in healthcare, especially when dealing with people who might be more vulnerable. Emeis, being a major global player, already has a strong reputation built over time. This makes it tough for newcomers to quickly earn the same level of trust and credibility with patients and their loved ones.
The ongoing shortage of skilled healthcare professionals, including nurses, therapists, and doctors, presents a significant barrier for new entrants in the healthcare sector. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a need for over 200,000 new registered nurses annually over the next decade, highlighting the intense competition for qualified staff. This scarcity makes it challenging for new facilities to quickly assemble a competent workforce, which is essential for providing high-quality patient care and establishing a reputation.
Established Referral Networks and Partnerships
Established referral networks represent a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to compete with companies like Emeis. Existing players have cultivated deep relationships with hospitals, physicians, and other healthcare entities, ensuring a consistent stream of patients. For instance, in 2024, the healthcare referral market continued to be dominated by established providers who leverage these long-standing partnerships.
Building comparable referral networks requires substantial investment in time, personnel, and relationship management. Newcomers face the challenge of not only identifying potential referrers but also demonstrating value and reliability to earn their trust. This process can take years, during which established companies continue to solidify their market position.
- Established referral networks are a key competitive advantage.
- New entrants must invest heavily to replicate existing partnerships.
- The healthcare referral market in 2024 showed continued dominance by established players due to these networks.
- Building trust and demonstrating value are critical for new entrants to gain referrals.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
The threat of new entrants for a company like Emeis is significantly influenced by existing economies of scale and cost advantages. Established players often achieve lower per-unit costs through high-volume production, bulk purchasing power, and streamlined administrative processes. For instance, in 2024, major players in the global healthcare and services sector, where Emeis operates, often reported operating margins that benefited from these efficiencies, sometimes exceeding 10% for well-established entities.
New companies entering this market would likely struggle to match these cost efficiencies from the outset. They would probably incur higher initial costs for raw materials, marketing, and setting up operations. This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price with established firms, effectively acting as a barrier to entry.
Consider these points:
- Economies of Scale: Emeis likely benefits from significant cost reductions per unit as its operational volume increases, a feat difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Purchasing Power: Large-scale procurement allows Emeis to negotiate better prices with suppliers, a leverage new, smaller competitors cannot easily access.
- Operational Efficiency: Established processes and optimized supply chains contribute to lower overheads for Emeis compared to a startup.
- Capital Intensity: The healthcare and services sector often requires substantial upfront investment in infrastructure and technology, which can deter new entrants lacking significant capital.
The threat of new entrants in the long-term care and rehabilitation sector, where Emeis operates, is generally moderate to high, but significantly mitigated by substantial barriers. These include the immense capital required for facilities, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the critical importance of brand reputation and trust. Furthermore, the scarcity of skilled healthcare professionals and the established nature of referral networks present considerable challenges for any new player attempting to gain a foothold.
New entrants face significant hurdles due to the high capital investment needed for healthcare facilities, often running into tens of millions of dollars for construction and specialized equipment. Regulatory compliance, including licensing and quality standards, adds another layer of complexity and cost, with agencies like CMS in 2024 continuing to enforce rigorous patient safety protocols. Building a trusted brand and assembling a qualified workforce, especially given the projected demand for over 200,000 new registered nurses annually in the US through 2034, are also formidable tasks.
Established referral networks, cultivated over years by companies like Emeis, are a major deterrent. Newcomers must invest heavily in time and resources to build similar relationships with hospitals and physicians, a process that can take years. This, coupled with the cost advantages derived from economies of scale and purchasing power enjoyed by established entities in 2024, makes it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively on price or service delivery.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for real estate, equipment, and staffing. Example: $15M-$30M for a skilled nursing facility. | Significant financial barrier, requiring substantial upfront investment. |
| Regulation | Complex licensing, accreditation, and compliance mandates. CMS standards in 2024 emphasize quality reporting. | Increases operational costs and time-to-market; potential for non-compliance penalties. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Essential for patient confidence, especially for vulnerable populations. Emeis's global presence builds inherent trust. | New entrants struggle to quickly establish credibility and attract patients. |
| Workforce Scarcity | Shortage of skilled professionals like nurses and therapists. US projected need: 200,000+ RNs annually through 2034. | Challenges in assembling a competent team, impacting service quality and reputation. |
| Referral Networks | Established relationships with hospitals and physicians ensure patient flow. | New entrants must invest heavily to replicate these deep-seated partnerships. |
| Economies of Scale | Established players benefit from lower per-unit costs due to high volume and purchasing power. | New entrants face higher initial costs, making price competition difficult. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data, including publicly available company financial statements, industry association reports, and market research databases. We also incorporate insights from news articles and trade publications to capture current market dynamics and competitive strategies.
