EMC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
EMC Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and EMC is no exception. A Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a powerful framework to dissect the industry's inherent profitability and identify key strategic challenges and opportunities.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore EMC’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The market for specialized raw materials crucial for high-performance EMC/RF components, such as specific magnetic alloys or advanced conductive polymers, can be highly concentrated. This means a limited number of suppliers control the supply chain for these critical inputs. For instance, in 2024, the global market for rare earth elements, vital for many advanced electronic components, was dominated by a few key producing nations, creating inherent supplier leverage.
This concentration grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. They can dictate pricing and terms, particularly for proprietary or high-purity materials. Companies like EMC Technology Co., Ltd. may encounter substantial challenges when these essential materials have few or no viable alternative sources, impacting their cost structure and production capabilities.
Despite general improvements in supply chain efficiency, EMC Technology Co., Ltd. is still facing challenges with certain electronic components. For instance, lead times for advanced analog integrated circuits (ICs), specialized sensors, and certain memory modules remain extended or unpredictable. This situation directly impacts EMC's ability to secure necessary materials promptly.
This ongoing variability in lead times for critical components significantly bolsters the bargaining power of suppliers. When EMC faces limited immediate sourcing options due to these extended timelines, suppliers can leverage this scarcity. They might dictate terms more aggressively, potentially leading to increased component costs for EMC Technology Co., Ltd. This is a key factor in the 2024 landscape, as semiconductor supply chains continue to navigate demand shifts and production capacities.
Suppliers pushing the envelope with advanced materials for EMI shielding, such as graphene or MXenes, can significantly boost their bargaining power. These innovations offer enhanced performance and novel features, making them attractive to companies like EMC Technology Co., Ltd.
EMC Technology Co., Ltd. might find itself increasingly dependent on these forward-thinking suppliers if adopting their superior materials becomes crucial for staying competitive in the evolving EMC shielding market. For example, the global market for advanced materials, including those used in EMI shielding, has seen consistent growth, with projections indicating continued expansion through 2028, driven by demand in electronics and telecommunications.
Global supply chain disruptions and geopolitical factors
Ongoing global supply chain challenges, amplified by geopolitical tensions and export controls on critical minerals, directly impact the availability and pricing of essential components for companies like EMC Technology Co., Ltd. This creates significant uncertainty in procurement, potentially strengthening the bargaining power of suppliers in regions offering stable production or possessing unique resources.
For instance, in 2024, continued geopolitical instability in Eastern Europe and parts of Asia has led to increased lead times and price volatility for certain electronic components. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) noted in its April 2024 World Economic Outlook that supply chain pressures, while easing from pandemic peaks, remain a concern, particularly for specialized inputs. This situation allows suppliers with diversified production bases or exclusive access to key raw materials, such as rare earth elements, to command higher prices and more favorable terms.
- Geopolitical Impact: Export controls on critical minerals, such as those affecting lithium and cobalt, can restrict supply and drive up costs for manufacturers.
- Supply Chain Volatility: Disruptions in shipping routes and manufacturing hubs in 2024 have extended delivery times for semiconductors and other vital electronic parts.
- Supplier Leverage: Suppliers in politically stable regions or those with proprietary technology for essential materials gain considerable leverage in price negotiations.
- EMC's Procurement Strategy: EMC Technology Co., Ltd. faces increased pressure to secure stable supply agreements and explore alternative sourcing to mitigate these supplier-driven risks.
Supplier consolidation in the electronics industry
Supplier consolidation in the electronics industry is a significant factor influencing the bargaining power of suppliers. As companies merge or acquire others, the number of independent component vendors decreases. This reduction in competition directly benefits the remaining suppliers, as they face less pressure to offer competitive pricing and more favorable terms to their customers, such as EMC Technology Co., Ltd.
This trend can lead to less flexibility for buyers. With fewer options, EMC Technology Co., Ltd. may find it harder to negotiate price reductions or customized payment schedules. Suppliers, holding a stronger market position due to consolidation, can exert more control over the terms of sale, potentially increasing costs for EMC.
For instance, the semiconductor industry has seen notable consolidation. In 2023, the market experienced significant M&A activity, with major players acquiring smaller firms to expand their portfolios and market share. This pattern suggests that by mid-2025, EMC Technology Co., Ltd. might face a landscape with fewer, larger, and potentially more dominant component suppliers.
- Reduced Vendor Choice: Consolidation shrinks the pool of available suppliers, limiting options for buyers like EMC.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: Fewer competitors mean suppliers can dictate terms more easily, impacting pricing and flexibility for EMC.
- Potential for Higher Costs: Less competition can translate to higher component prices for EMC Technology Co., Ltd.
- Strategic Sourcing Challenges: EMC may need to adapt its sourcing strategies to navigate a more concentrated supplier market.
A concentrated market for specialized raw materials, like rare earth elements vital for advanced electronics, grants suppliers significant leverage. This concentration, evident in the few key producing nations dominating the rare earth market in 2024, allows suppliers to dictate pricing and terms, especially for proprietary or high-purity inputs. Companies like EMC Technology Co., Ltd. face challenges securing these critical materials at favorable costs when alternatives are scarce.
Extended lead times for essential electronic components, such as advanced analog ICs and specialized sensors, further amplify supplier bargaining power. This unpredictability in sourcing, a persistent issue in 2024 semiconductor supply chains navigating demand shifts, enables suppliers to impose more stringent terms and potentially higher prices on buyers like EMC.
The introduction of innovative materials for EMI shielding, like graphene, also enhances supplier leverage. As these advanced materials become crucial for competitive performance, companies such as EMC Technology Co., Ltd. may find themselves increasingly dependent on suppliers offering these cutting-edge solutions, which are part of a growing global advanced materials market projected to expand through 2028.
Geopolitical tensions and export controls on critical minerals in 2024, as highlighted by the IMF's April 2024 World Economic Outlook, continue to create supply chain volatility. This environment allows suppliers with diversified production or exclusive access to key resources to command higher prices and more favorable terms, impacting EMC's procurement stability.
| Factor | Impact on EMC | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration (Rare Earths) | Increased supplier pricing power | Few nations dominate global supply, impacting raw material costs. |
| Extended Lead Times (ICs, Sensors) | Reduced buyer flexibility, potential for higher component costs | Semiconductor supply chains still managing demand/capacity, leading to unpredictable delivery. |
| Advanced Material Adoption (Graphene) | Growing dependence on innovative suppliers | Global advanced materials market expanding, driven by electronics demand. |
| Geopolitical Instability | Supply chain volatility, price increases for critical minerals | IMF notes persistent supply chain pressures, impacting availability and pricing. |
What is included in the product
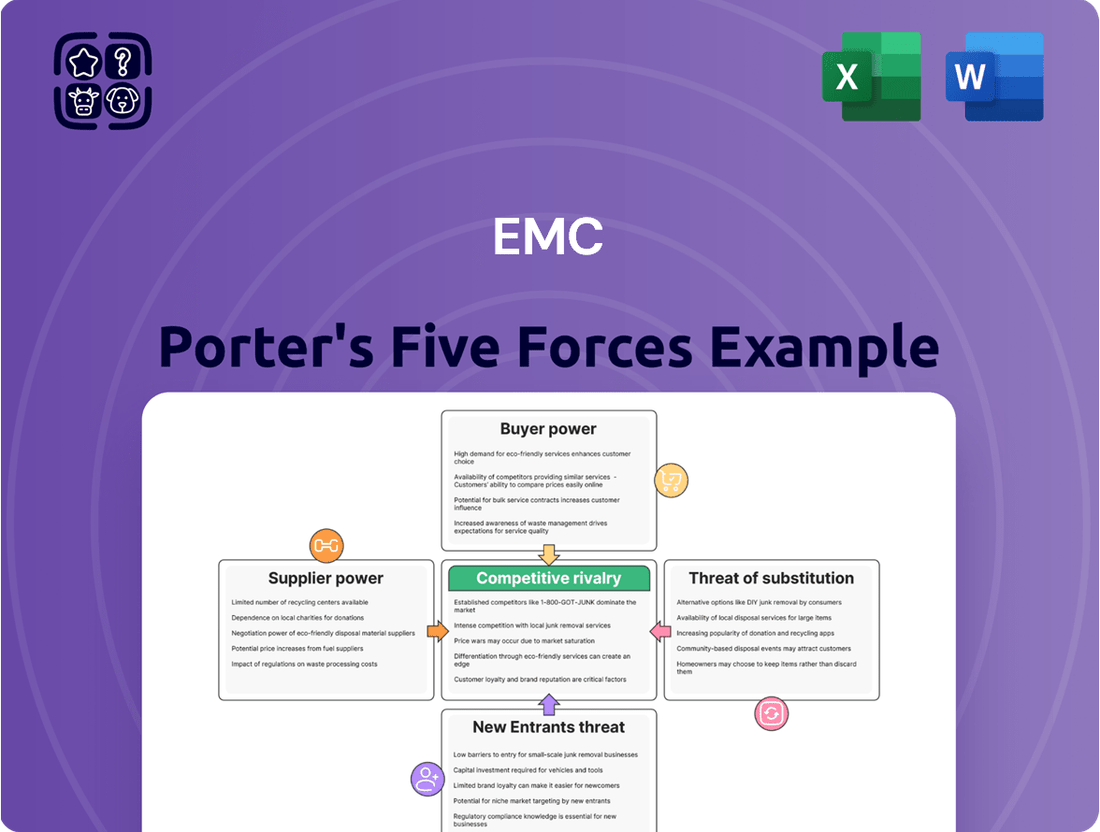
Analyzes the intensity of competition, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes for EMC.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
EMC Technology Co., Ltd. caters to a broad spectrum of industries, from telecommunications and automotive to consumer electronics and industrial applications. This wide reach means that no single customer segment dominates the company's sales, which can help to mitigate individual customer leverage.
While major clients in sectors like automotive, which saw global vehicle production reach approximately 78.5 million units in 2023, might possess considerable bargaining power due to high volume purchases, the sheer diversity of EMC's customer base is a key counterbalancing factor. Different industries have unique needs and purchasing scales, preventing a monolithic customer front from dictating terms.
For electronic manufacturers, achieving ElectroMagnetic Compatibility (EMC) compliance is not just a regulatory hurdle; it's a fundamental requirement for product reliability and market access. In 2024, the increasing complexity of electronic devices and the proliferation of wireless technologies have made robust EMC performance even more critical. Failure to meet these standards can lead to product failures, costly redesigns, and significant delays in bringing products to market, impacting brand reputation and future sales.
This critical need elevates EMC components from mere commodities to essential, value-adding inputs. Customers recognize that compromising on the quality of EMC solutions can result in far greater expenses down the line, whether through product recalls or lost sales due to performance issues. Consequently, their bargaining power is somewhat diminished, as they are less likely to prioritize price over the assurance of reliable compliance and market-ready products.
The electronic components market, encompassing EMC and RF filters, is characterized by a vast global network of manufacturers and distributors. This abundance of suppliers means customers can readily find alternatives if current terms are unsatisfactory, significantly enhancing their negotiating leverage.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for electronic components was estimated to be worth hundreds of billions of dollars, with a substantial portion dedicated to passive components like filters. This sheer volume and competition among suppliers empower buyers to seek out more competitive pricing and favorable terms.
Customer price sensitivity in competitive end-markets
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor, especially in competitive end-markets like consumer electronics. When many alternatives exist, buyers naturally focus more on price. This puts considerable pressure on companies like EMC Technology Co., Ltd. to maintain competitive pricing for their components. For instance, in 2024, the average selling price for many consumer electronic components saw a slight decrease due to oversupply in certain segments, directly impacting revenue for component manufacturers.
EMC Tech must therefore strike a delicate balance. It's not just about offering the lowest price; it's about providing value that justifies the cost. This means ensuring their components offer superior performance or unique features that differentiate them from competitors, even at a slightly higher price point. A recent industry report indicated that while 65% of consumer electronics buyers consider price a primary factor, 40% are willing to pay a premium for enhanced durability or advanced functionality.
- Price Sensitivity: High in competitive consumer electronics markets.
- Impact on EMC Tech: Direct pressure to lower component prices.
- Strategic Imperative: Balancing cost-effectiveness with performance differentiation.
- Consumer Behavior: Price is key, but performance and durability also influence purchasing decisions.
Potential for backward integration by large customers
Very large electronic manufacturers, particularly those with substantial R&D budgets and manufacturing capabilities, could theoretically explore developing certain custom EMC/RF components in-house. This is especially true for highly specialized applications where off-the-shelf solutions are insufficient.
While the barriers to entry for custom component manufacturing, including specialized equipment and expertise, are significant, the mere potential for such backward integration grants considerable bargaining power to these major customers. For instance, a company like Apple, with its vast resources, could potentially invest in in-house development for critical, proprietary shielding or filtering technologies, thereby influencing pricing and product specifications from its EMC component suppliers.
- Backward Integration Threat: Large customers like major electronics OEMs possess the financial and technical wherewithal to consider developing custom EMC components internally.
- Specialized Needs Drive Integration: This threat is amplified when customers have highly specific performance or integration requirements not readily met by existing market offerings.
- Bargaining Leverage: The credible threat of backward integration enhances customer negotiation power, potentially leading to lower prices or more favorable terms for suppliers.
- Example Scenario: A leading smartphone manufacturer might explore in-house development of advanced EMI shielding solutions for its flagship devices, signaling its intent to suppliers.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to the abundance of suppliers in the electronic components market, including those for EMC and RF filters. This competitive landscape, valued in the hundreds of billions of dollars globally in 2024, allows buyers to readily seek alternatives and negotiate favorable terms, particularly in price-sensitive sectors like consumer electronics. While 65% of consumer electronics buyers prioritize price, a notable 40% are willing to pay more for enhanced durability or advanced features, creating a dynamic where EMC Tech must balance cost with differentiation.
The threat of backward integration by large, well-resourced customers, such as major electronics OEMs with substantial R&D capabilities, further amplifies customer leverage. The potential for these entities to develop specialized EMC components in-house, especially for unique applications, can influence supplier pricing and product specifications, as seen with large entities like Apple exploring proprietary shielding technologies.
| Factor | Impact on EMC Tech | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Abundance | Pressure on pricing and margins | High |
| Price Sensitivity (Consumer Electronics) | Need for cost-competitive solutions | High |
| Willingness to Pay Premium (Performance/Durability) | Opportunity for value-based pricing | Moderate |
| Backward Integration Potential | Threat to sales volume and pricing power | High (for large OEMs) |
What You See Is What You Get
EMC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete EMC Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive and market forces impacting the company. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring you get precisely what you need for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The EMC and RF component market is highly competitive, featuring a broad spectrum of global giants and niche regional specialists. This means EMC Technology Co., Ltd. faces significant rivalry from established players like Schaffner, Murata, and TDK, who command substantial market share and technological expertise.
The competitive landscape for EMC Technology Co., Ltd. is intensely shaped by rapid technological advancements. The proliferation of 5G, the Internet of Things (IoT), and sophisticated automotive electronics fuels a constant need for innovation, pushing competitors to introduce cutting-edge products. For instance, the market for advanced Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) and Bulk Acoustic Wave (BAW) filters, crucial components in these technologies, demands significant and ongoing research and development investment.
The global RF filter market is experiencing robust expansion, with projected compound annual growth rates (CAGRs) between 14% and over 17% extending to 2034. This impressive growth trajectory, fueled by the widespread adoption of 5G technology and the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), is a significant magnet for both established companies and emerging entrants.
Consequently, the high market growth inherently intensifies competitive rivalry. Existing players are compelled to scale their operations and innovate to maintain market share, while the lucrative growth prospects actively draw new competitors into the RF filter landscape, further heating up the competitive environment.
Increasing importance of meeting stringent regulatory standards
The global regulatory landscape for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is becoming increasingly demanding. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter standards, and in 2024, we've seen a notable trend of these regulations extending to cover lower frequency ranges. This means components previously exempt now require rigorous testing and validation, forcing manufacturers to adapt their designs and invest more in research and development. For example, the European Union's EMC Directive continues to evolve, pushing for higher performance thresholds across a broader spectrum of electronic devices.
This heightened regulatory environment directly fuels competitive rivalry within the electronics industry. Companies that can proactively meet and exceed these evolving EMC standards gain a significant advantage. In 2024, the cost of non-compliance can be substantial, ranging from product recalls to market access denial. Consequently, significant capital expenditure is being channeled into advanced testing equipment and specialized engineering talent to ensure products meet the latest requirements. This investment barrier naturally favors larger, more established players, intensifying competition among those striving for market leadership.
- Evolving Standards: EMC regulations are tightening globally, with a focus on lower frequencies in 2024.
- Increased Investment: Companies must invest heavily in compliance and R&D to meet these new demands.
- Market Access: Failure to comply can lead to product recalls and exclusion from key markets.
- Competitive Advantage: Proactive compliance offers a distinct edge in a crowded marketplace.
Product differentiation through specialized solutions
While core electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) components can become commodities, differentiation thrives through specialized solutions. Companies like EMC Technology Co., Ltd. achieve this by offering miniaturized, high-performance products tailored for demanding sectors such as electric vehicles (EVs) and aerospace, where stringent requirements justify premium pricing. This focus on custom solutions and adherence to international standards, like those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), allows them to carve out a competitive edge.
For instance, the automotive sector, particularly the burgeoning EV market, demands increasingly sophisticated EMC solutions to manage the complex electromagnetic interactions within vehicles. By 2024, the global automotive EMC testing market was projected to reach significant figures, highlighting the demand for specialized expertise and components. Companies that can provide integrated, high-performance filtering and shielding solutions for these applications are well-positioned to capture market share.
- Specialized solutions command higher margins in sectors like EVs and aerospace.
- Miniaturization and enhanced performance are key differentiators.
- Adherence to international standards like IEC is crucial for market access and trust.
The competitive rivalry in the EMC and RF component market is intense, driven by a mix of large, established global players and agile niche specialists. Companies like Schaffner, Murata, and TDK possess significant market share and advanced technological capabilities, setting a high bar for competitors. This dynamic forces all participants, including EMC Technology Co., Ltd., to continuously innovate and optimize their offerings to remain relevant and capture market share in a crowded field.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Engineers are increasingly adopting sophisticated PCB design techniques to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI), thereby reducing the need for external filtering components. Optimized PCB layouts, effective grounding strategies, and the implementation of multilayer PCBs with ground stitching are becoming standard practices. This shift directly challenges the market for dedicated EMI suppression devices, as these internal design solutions offer a more integrated and cost-effective approach to compliance.
The development of advanced materials like graphene-based composite films, MXenes, and conductive inks presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) components. These innovations enable integrated shielding solutions, embedding protection directly into device structures or packaging, thereby bypassing the need for discrete shielding parts.
These novel materials offer a compelling alternative by providing lightweight and highly effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. For instance, research in 2024 highlights the potential of MXenes to achieve shielding effectiveness exceeding 50 dB at specific frequencies, a performance comparable to conventional shielding methods but with added advantages in weight and integration flexibility.
This shift towards embedded shielding can reduce manufacturing complexity and costs associated with assembling separate EMC components. Companies are increasingly exploring these materials to meet stringent regulatory requirements for EMI/EMC while simultaneously pursuing miniaturization and enhanced performance in electronic devices, impacting the demand for legacy shielding solutions.
Software-based interference mitigation presents a unique threat of substitutes for traditional hardware solutions in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). By employing advanced algorithms and adaptive filtering, software can actively manage and reduce electromagnetic noise within electronic systems. This can lessen reliance on physical shielding, ferrite beads, or specialized filtering components.
For instance, in the automotive sector, which is a significant market for EMC solutions, sophisticated software techniques are increasingly being used to manage EMI in complex electronic control units. This trend is driven by the growing density of electronic components and the need for cost-effective solutions. The global market for automotive EMC testing services alone was valued at over USD 1.5 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of investment in ensuring signal integrity.
Passive filtering techniques versus active solutions
Customers facing electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) challenges can sometimes opt for simpler, less integrated solutions. For instance, basic passive filtering techniques, like ferrite beads or common-mode chokes, can address certain EMI issues without requiring specialized components from EMC Technology Co., Ltd. This availability of alternative, often less complex, approaches represents a significant threat of substitutes.
Furthermore, the choice of core components can inherently mitigate EMC problems. Selecting linear power supplies over switch-mode power supplies, for example, can reduce the need for extensive external filtering. This strategic component selection by designers broadens customer options, creating a viable substitute for dedicated EMC solutions.
The market for EMC solutions is impacted by the accessibility of these alternative methods. For example, in 2024, the global passive components market, which includes many of these simpler filtering solutions, was valued at over $25 billion. This substantial market size underscores the significant presence of substitutes available to customers.
- Passive Filtering: Simpler solutions like ferrite beads and capacitors can address basic EMI needs.
- Component Selection: Choosing inherently lower-EMI components (e.g., linear power supplies) reduces reliance on external filtering.
- Cost-Effectiveness: These alternatives often present a lower upfront cost compared to specialized EMC components.
- Market Size of Substitutes: The broad market for passive electronic components, exceeding $25 billion in 2024, highlights the availability of alternatives.
Shift towards system-in-package (SiP) architectures
The increasing adoption of system-in-package (SiP) architectures presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) components. As devices become smaller and more integrated, the demand for standalone EMC solutions like shielded enclosures or filters may decline.
SiP designs often incorporate shielding directly into the package, effectively embedding EMC functionality. This trend, driven by miniaturization, means that the need for separate, often bulky, EMC components is reduced. For instance, in the 2024 semiconductor market, the growth of advanced packaging technologies like SiP is a key driver for innovation, potentially displacing older component-based approaches.
- Miniaturization: SiP enables smaller, more compact electronic devices, reducing the physical space available for traditional EMC components.
- Integration: Shielding and filtering can be built directly into SiP modules, making standalone EMC solutions redundant.
- Cost Efficiency: Integrated solutions can potentially offer cost savings compared to sourcing and assembling separate EMC parts.
- Performance Gains: Embedding EMC features within SiP can lead to improved performance by minimizing signal path lengths and reducing parasitic effects.
The threat of substitutes for traditional EMC components is substantial, driven by advancements in design, materials, and system integration. These substitutes often offer integrated solutions, cost efficiencies, and improved performance, directly challenging the market for standalone EMC parts.
Sophisticated PCB design techniques, novel materials like MXenes, and system-in-package (SiP) architectures are key substitutes. For example, MXenes demonstrated shielding effectiveness over 50 dB in 2024 research, matching conventional methods but with added benefits. Similarly, the passive components market, valued over $25 billion in 2024, indicates a strong availability of simpler, alternative filtering solutions.
Software-based interference mitigation and strategic component selection, such as using linear power supplies, further reduce the need for dedicated EMC hardware. This broadens customer options, making these alternatives a significant competitive force.
| Substitute Category | Key Innovations/Approaches | 2024 Market Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated Design | Optimized PCB layouts, grounding strategies | Standard practice for EMI reduction |
| Advanced Materials | Graphene, MXenes, conductive inks | MXenes: Shielding >50 dB (research); Lightweight, integrated shielding |
| Software Mitigation | Algorithmic interference management | Growing adoption in automotive ECUs; Automotive EMC testing market >$1.5 billion (2023) |
| Passive Filtering & Component Choice | Ferrite beads, capacitors, linear power supplies | Passive components market >$25 billion (2024) |
| System-in-Package (SiP) | Embedded shielding within packages | Key driver in semiconductor advanced packaging |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in the EMC and RF components market is significantly mitigated by the exceptionally high capital investment required for research and development (R&D) and manufacturing. Developing cutting-edge EMC and RF solutions demands substantial financial resources for advanced R&D, specialized testing equipment, and the establishment of sterile, high-precision manufacturing environments. For instance, setting up a state-of-the-art semiconductor fabrication facility, often necessary for advanced RF components, can easily run into billions of dollars. This immense financial hurdle acts as a formidable barrier, discouraging many potential new players from entering the market and challenging established firms.
New entrants face significant hurdles due to stringent regulatory compliance and testing requirements. Navigating complex and evolving international Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standards demands substantial investment in specialized testing and certification processes. For instance, in 2024, the cost of obtaining CE marking for electronic products, which includes EMC testing, can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on product complexity and the number of tests required.
These rigorous regulatory hurdles directly increase the cost and time-to-market for new players. Companies must allocate considerable resources to ensure their products meet standards like FCC Part 15 in the US or EN 55032 in Europe. Failure to comply can result in product recalls or market access denial, making adherence a critical, albeit costly, barrier to entry.
Established relationships are a significant barrier for new entrants in the electronic components market. Companies like EMC Technology Co., Ltd. have cultivated deep ties with major electronic manufacturers, providing not just products but also specialized solutions and ongoing technical support. This existing rapport makes it challenging for newcomers to break in, as manufacturers often prefer the reliability and proven performance of their current suppliers.
Furthermore, customer switching costs play a crucial role. When a manufacturer decides to change component suppliers, they face substantial expenses and risks. These include the time and cost associated with re-qualifying new components, redesigning their products to accommodate different specifications, and building trust with an unfamiliar vendor. For instance, a single component change in a complex electronic device could necessitate extensive testing and certification, potentially delaying product launches and incurring significant engineering overhead.
Proprietary technology and specialized expertise
The threat of new entrants in the EMC/RF components market is significantly mitigated by the deep-seated need for proprietary technology and specialized expertise. The intricate design and manufacturing of these components demand advanced knowledge in material science, component architecture, and electromagnetic principles, creating substantial hurdles for potential newcomers. For instance, companies like Murata Manufacturing, a leader in ceramic capacitors and filters, invest heavily in R&D, with their 2024 R&D expenditure projected to be substantial, reflecting the continuous innovation required to maintain a competitive edge. This technological moat makes it exceedingly difficult for new players to enter and compete effectively without significant upfront investment and time to develop comparable capabilities.
Newcomers face a steep learning curve and considerable capital requirements to replicate the specialized engineering skills and proprietary technologies that established players possess. This includes mastery over:
- Material Science: Developing or sourcing advanced materials with specific dielectric, magnetic, or conductive properties is critical for high-performance EMC/RF components.
- Component Design: Expertise in miniaturization, impedance matching, and thermal management for compact and efficient designs is paramount.
- Electromagnetic Theory: A profound understanding of electromagnetic wave propagation, shielding, and interference mitigation is essential for product efficacy.
Economies of scale for existing manufacturers
Established manufacturers of electronic medical components (EMCs) enjoy significant economies of scale. This means they can produce, purchase raw materials, and distribute their products at a lower cost per unit than a new company just starting out. For instance, in 2024, major EMC suppliers often operate massive, highly automated factories, allowing them to spread fixed costs over a much larger output volume.
New entrants would struggle to match these cost efficiencies. Without the same production volume, their per-unit costs for manufacturing and sourcing critical components would be considerably higher. This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for new players to compete on price with established firms, especially in markets where price sensitivity is a key factor for buyers.
- Economies of scale in production: Existing manufacturers leverage large-scale operations to reduce per-unit manufacturing costs.
- Procurement advantages: Established players secure bulk discounts on raw materials and components, further lowering their cost base.
- Distribution efficiencies: Larger volumes allow for more cost-effective logistics and supply chain management.
- Barrier to entry: New entrants face higher initial costs, hindering their ability to compete on price against incumbents.
The threat of new entrants in the EMC and RF components market is significantly dampened by substantial capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, stringent regulatory compliance, and the need for specialized expertise. Established players benefit from economies of scale and strong customer relationships, creating formidable barriers for newcomers. For example, setting up a semiconductor fabrication facility can cost billions, and obtaining necessary certifications like CE marking in 2024 can cost tens of thousands of dollars.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D and manufacturing facilities. | Semiconductor fab setup: Billions USD. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting complex international standards and testing. | CE Marking: Thousands to tens of thousands USD. |
| Proprietary Technology & Expertise | Need for specialized knowledge in material science, design, and EM theory. | Significant R&D investment by market leaders like Murata. |
| Customer Relationships | Deep-seated ties with major manufacturers. | Established suppliers offer proven reliability and support. |
| Switching Costs | Expenses and risks associated with changing suppliers. | Re-qualification, redesign, and trust-building for new components. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | Automated factories spread fixed costs over larger output. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial statements. We also leverage insights from trade publications and economic indicators to capture the full competitive landscape.
