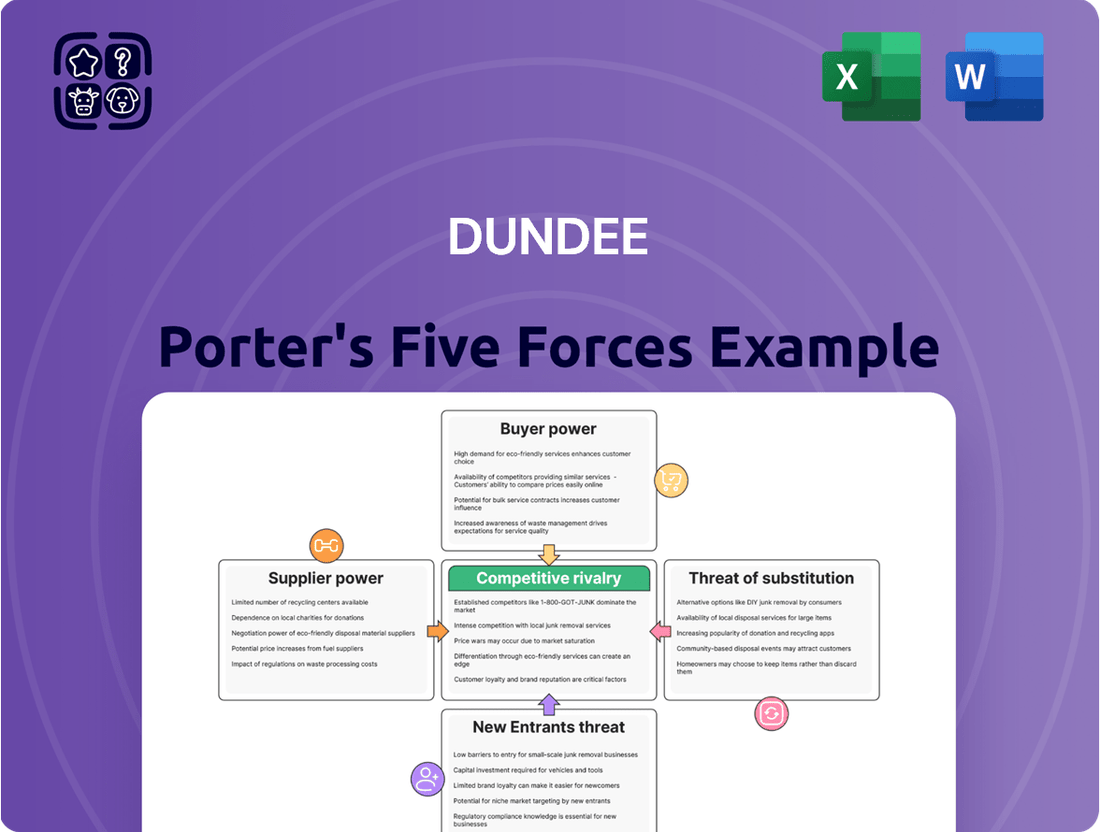
Dundee Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dundee Bundle
Dundee's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dundee’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The mining sector's dependence on highly specialized equipment for exploration and extraction significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. Dundee Precious Metals Inc. (DPM) likely encounters this, as a handful of global manufacturers dominate the production of essential machinery.
The substantial investment required for this technology, coupled with its critical role in operational efficiency, means DPM has limited alternatives. For instance, the average cost of a large-scale mining truck can range from $500,000 to over $1 million, and specialized drilling rigs can cost millions more.
Furthermore, the high switching costs associated with changing major equipment suppliers, due to integration complexities and extensive training needs, further consolidate supplier leverage. This reliance on proprietary technology and the expense of replacement make it challenging for DPM to negotiate favorable terms.
Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) relies heavily on a specialized workforce, including geologists, mining engineers, and skilled operators, for its operations in Bulgaria, Namibia, and Serbia. The availability of this talent is a key factor in the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly when specialized expertise is scarce in a particular region.
In 2024, the global mining sector continued to face challenges in attracting and retaining skilled labor. For instance, reports indicated a significant shortage of experienced mining engineers in several key mining jurisdictions, which naturally drives up compensation expectations. This scarcity directly impacts DPM's operational costs and project timelines, enhancing the leverage of these skilled professionals.
DPM's success in securing and keeping top-tier talent is therefore paramount. Their ability to offer competitive remuneration packages and foster a positive work environment directly influences their capacity to mitigate the bargaining power of suppliers in the skilled labor market, ensuring operational continuity and progress on growth initiatives.
Energy, such as electricity and fuel, along with consumables like processing chemicals, represent substantial costs for mining companies like Dundee Precious Metals (DPM). Suppliers of these critical inputs wield significant bargaining power, especially when global energy prices are volatile or when local supply options are restricted. For instance, in 2024, global oil prices saw fluctuations, impacting fuel costs for transportation and machinery.
DPM's commitment to sustainability, including energy efficiency measures, helps mitigate some exposure, but the company remains susceptible to the external pricing pressures exerted by energy and consumable suppliers. The cost of electricity, a major operational expense, can be directly influenced by the pricing strategies of utility providers or fuel suppliers, impacting DPM's overall profitability.
Financing and Capital Providers
Mining projects, like those undertaken by Dundee Precious Metals (DPM), are inherently capital-intensive, demanding significant upfront investment for exploration, development, and sustained operations. In 2023, DPM reported capital expenditures of $214.9 million, highlighting the scale of investment required.
The bargaining power of financing and capital providers can be substantial, particularly when the pool of lenders or investors willing to fund large-scale mining ventures is limited. This scarcity allows these providers to dictate terms, influencing interest rates and loan covenants for projects such as DPM's Čoka Rakita and Loma Larga developments.
For instance, during the development phase of its Timok Project, a major copper-gold mine, a significant portion of its funding came from debt facilities, demonstrating the reliance on external capital providers. The terms negotiated for such facilities directly impact project profitability and DPM's overall financial flexibility.
- Capital Intensity: Mining operations require substantial capital for exploration, development, and ongoing extraction.
- Limited Financing Pool: A restricted number of financial institutions or investors willing to finance large mining projects increases their leverage.
- Influence on Terms: Capital providers can exert significant influence over interest rates, repayment schedules, and other loan conditions.
- Project Viability: Favorable financing terms are crucial for the economic viability of new mining ventures like Čoka Rakita and Loma Larga.
Regulatory and Environmental Services
Suppliers of regulatory and environmental services wield considerable bargaining power over Dundee Precious Metals (DPM). This stems from DPM's dedication to sustainable mining and the strict environmental laws in its operational regions. These services are essential for DPM to maintain its social license to operate and to lessen its environmental footprint.
DPM's reliance on specialized providers for environmental consulting, compliance, and remediation is amplified by its commitment to industry-leading Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards. For instance, S&P Global's recognition of DPM's ESG performance underscores the necessity of engaging these expert suppliers. The critical nature of these services means DPM has limited room to negotiate terms, granting suppliers significant leverage.
- Essential Services: Environmental compliance and remediation are non-negotiable for DPM's operations.
- Regulatory Dependence: Stringent environmental regulations necessitate the use of specialized external expertise.
- ESG Commitments: Adherence to high ESG standards, like those recognized by S&P Global, increases reliance on these suppliers.
- Limited Substitutability: The specialized nature of these services reduces the availability of readily substitutable suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) is significant due to the capital-intensive nature of mining, reliance on specialized equipment and labor, and the critical role of energy and regulatory services. In 2023, DPM's capital expenditures reached $214.9 million, highlighting the substantial investment needed for its operations. This financial commitment means DPM is often dependent on a limited pool of financing providers who can dictate terms, impacting project viability.
Moreover, the scarcity of skilled mining professionals, a trend continuing into 2024 with reported shortages of experienced engineers, grants considerable leverage to labor suppliers. Similarly, the specialized nature of mining equipment, with large machinery costing upwards of $1 million, and the high costs associated with switching suppliers, further empower equipment manufacturers. Energy and consumable suppliers also hold sway, especially during periods of price volatility, as seen with fluctuating oil prices in 2024.
Finally, DPM's commitment to stringent ESG standards and the complex regulatory environment in its operating regions amplify the bargaining power of environmental and regulatory service providers. These factors collectively limit DPM's ability to negotiate favorable terms across several key supplier categories.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on DPM | Example Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment Manufacturers | High specialization, high switching costs, substantial capital investment required for machinery | Limited negotiation flexibility, potential for higher equipment costs | Large mining trucks can cost $500,000 - $1M+; specialized drilling rigs cost millions. |
| Skilled Labor | Scarcity of specialized expertise (e.g., mining engineers), high demand | Increased labor costs, potential project delays if talent is unavailable | Shortage of experienced mining engineers reported in key jurisdictions in 2024. |
| Energy & Consumables | Price volatility of global commodities, reliance on essential inputs (fuel, electricity, chemicals) | Exposure to fluctuating operational costs, impact on profitability | Global oil price fluctuations in 2024 affected fuel costs. |
| Financing & Capital Providers | Capital-intensive nature of mining, limited pool of willing investors/lenders | Ability to dictate loan terms, interest rates, and covenants; impacts project financing | DPM's 2023 capital expenditures were $214.9 million. Reliance on debt facilities for projects. |
| Regulatory & Environmental Services | Strict environmental laws, DPM's ESG commitments, specialized nature of services | Limited negotiation power, essential for maintaining social license to operate | S&P Global recognition of DPM's ESG performance necessitates engagement with expert providers. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Dundee's specific industry context.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of each force, making strategic planning more effective.
Customers Bargaining Power
The commodity nature of gold and precious metals significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Because these metals are largely undifferentiated, buyers see little distinction between what Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) and its competitors offer. This fungibility means switching costs for customers are very low; they can readily shift to another supplier if DPM's pricing or terms aren't competitive.
DPM's revenue is intrinsically linked to global metal prices, which are driven by overarching market demand rather than specific producer attributes. For instance, in 2024, the average price of gold fluctuated, reaching highs of over $2,400 per ounce at certain points, demonstrating the market's sensitivity to broader economic and geopolitical factors, which in turn empowers buyers to seek the best available price.
While the global demand for gold is diverse, encompassing investors, central banks, and the jewelry sector, Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) likely sells its gold and copper concentrates to a more limited set of direct buyers, such as specialized refiners and traders. This concentration among immediate off-takers can grant them greater bargaining power, potentially influencing pricing and contract conditions.
For example, if DPM has only a few key customers for its concentrates, those customers might be able to negotiate more favorable terms. However, the robust and consistent demand for gold from central banks and major institutional investors, which reached record levels in recent years, can serve as a significant counterbalance. In 2023, central bank net purchases of gold were substantial, providing a strong underlying market that can reduce the leverage of any single buyer.
The global precious metal market, including gold and platinum, exhibits significant price transparency. For instance, as of mid-2024, spot gold prices are readily accessible through numerous financial news outlets and trading platforms, allowing any buyer to ascertain the current market value. This easy access to information means Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) faces substantial customer bargaining power stemming from price transparency.
Customers, armed with real-time global price data, can easily compare DPM's offerings against prevailing market rates. This makes it difficult for DPM to charge prices significantly above these benchmarks without losing business. For example, if DPM's platinum price is 2% higher than the London Metal Exchange spot price, informed buyers are likely to seek alternatives.
Consequently, DPM's ability to achieve strong profit margins is less about dictating prices to customers and more about excelling in operational efficiency and maximizing production output. In 2023, DPM reported a total gold production of 325,500 ounces and copper production of 49,200 tonnes, demonstrating a focus on volume to drive profitability.
Importance of Product to Buyer's Business
The importance of gold as a raw material or investment vehicle significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Buyers, particularly large industrial users and institutional investors, are acutely aware of gold's price sensitivity and actively pursue the most advantageous terms.
For instance, in 2024, fluctuations in global gold prices directly impacted purchasing decisions for jewelry manufacturers and central banks alike. Companies relying heavily on gold for production, such as high-end watchmakers or electronics firms, will exert considerable pressure to secure favorable pricing and supply agreements.
- Critical Input: Gold's role as a fundamental component in various industries increases buyer leverage.
- Price Sensitivity: Buyers are highly attuned to market price shifts, driving demand for cost-effective sourcing.
- Negotiation Power: Large-volume purchasers possess significant ability to negotiate terms, impacting supplier margins.
Global Demand Dynamics
Global demand for gold, influenced by geopolitical events and inflation concerns, plays a crucial role in shaping customer bargaining power. For instance, during periods of heightened uncertainty, such as the geopolitical shifts observed in early to mid-2024, demand for gold as a safe-haven asset typically surges. This increased demand, as projected to continue into 2025, tends to diminish the bargaining power of individual customers, allowing producers to maintain or even increase prices.
When demand is robust, as anticipated for gold in the 2024-2025 period, buyers have fewer alternatives and are more willing to accept prevailing market prices. This scenario strengthens the position of gold producers. Conversely, a significant drop in global demand would empower customers, giving them more leverage to negotiate lower prices.
- Increased demand reduces customer leverage: During 2024, gold prices saw significant upward movement, reflecting strong investor demand amidst global economic uncertainty.
- Central bank policies impact demand: Central banks' decisions to increase gold reserves, a trend observed in 2024, further bolsters demand and reduces customer bargaining power.
- Inflationary pressures drive demand: As inflation concerns persisted through 2024 and into 2025, gold's appeal as an inflation hedge intensified, strengthening producer pricing power.
The bargaining power of customers for Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) is significantly influenced by the commodity nature and price transparency of gold and copper. Low switching costs and readily available market pricing empower buyers to seek competitive terms, making operational efficiency crucial for DPM's profitability. While concentrated buyer groups can exert leverage, strong global demand, particularly from central banks, can mitigate this power.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024/2025 Projections) |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Nature & Fungibility | High | Gold and copper are largely undifferentiated, allowing easy substitution between suppliers. |
| Price Transparency | High | Real-time spot prices for gold and copper are widely accessible, enabling informed purchasing decisions. For example, gold prices in mid-2024 were readily available on financial platforms. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Minimal costs are associated with changing suppliers for these raw materials. |
| Concentration of Buyers | Potentially High | A limited number of direct off-takers for concentrates can increase their negotiation leverage. |
| Global Demand (e.g., Central Banks) | Lowers Customer Power | Record central bank gold purchases in recent years, continuing into 2024, create a strong underlying market that reduces individual buyer influence. |
| Operational Efficiency & Production Volume | Mitigates Customer Power | DPM's focus on production volume, such as 325,500 ounces of gold in 2023, helps offset customer pricing pressure. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Dundee Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Dundee Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces shaping the industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises. You're looking at the actual document, providing you with immediate access to actionable insights upon completing your transaction.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global gold mining sector is quite crowded, with major players like Newmont Corporation, Barrick Gold Corporation, and Agnico Eagle Mines Limited. These giants, along with a substantial number of mid-tier and junior exploration companies, create a highly fragmented and competitive environment. For Dundee Precious Metals (DPM), this means facing intense rivalry for crucial resources, investment capital, and market positioning.
DPM, as a mid-tier producer, finds itself in direct competition with both larger, more established miners and smaller, agile junior companies. This dynamic forces DPM to constantly vie for access to promising exploration sites, secure financing for its projects, and capture market share, all within a landscape populated by entities of varying scales and capabilities.
The competitive rivalry in the gold market, where products are largely undifferentiated commodities, is intense and primarily driven by price. Companies like Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) must focus on cost efficiency to maintain profitability and market share. DPM's strategy of low-cost production and high margins, evidenced by their consistent ability to meet cost guidance, positions them well in this price-sensitive landscape.
The gold market's robust performance in 2024-2025, marked by substantial price increases and significant investment, has created a more favorable environment for industry participants. This surge, fueled by global economic unease and increased purchasing by central banks, means there's more revenue available for everyone, which can slightly ease the intensity of direct competition.
However, this period of expansion also acts as a catalyst for increased production and aggressive pursuit of market share among competitors. For instance, major gold producers like Barrick Gold and Newmont Corporation have reported strong earnings in early 2024, reflecting this market buoyancy, and are likely to reinvest in exploration and development, thereby sustaining underlying competitive pressures.
High Exit Barriers
Dundee Corporation faces significant competitive rivalry due to high exit barriers inherent in the mining sector. These barriers stem from the massive, specialized fixed assets required for mining operations and the long-term commitments involved, making it difficult and costly for companies to cease operations.
Even when facing financial difficulties, mining companies often continue to operate to recoup sunk costs, thereby intensifying competition. This situation can lead to prolonged periods of oversupply or price pressure as firms fight to survive or maintain market share. For instance, the significant capital expenditure for exploration, development, and processing equipment, coupled with substantial environmental rehabilitation obligations, creates a strong disincentive to exit the industry.
- High Capital Intensity: The mining industry demands enormous upfront investment in machinery, infrastructure, and exploration, often running into billions of dollars.
- Long-Term Commitments: Mining leases and permits can span decades, obligating companies to maintain operations and associated costs.
- Environmental Rehabilitation Costs: Post-mining land restoration and environmental cleanup can cost millions, acting as a significant financial deterrent to exiting.
- Specialized Assets: Mining equipment and facilities are highly specialized and have limited resale value outside the industry, increasing exit costs.
Strategic Differentiation through ESG and Innovation
Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) actively seeks to differentiate itself in the mining sector through a strong emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles and a commitment to innovation. This strategic focus allows DPM to carve out a unique position in an industry often characterized by commodity-driven competition.
DPM's dedication to sustainability is a key differentiator, attracting investors who prioritize responsible mining. For instance, in 2024, DPM continued to report strong ESG performance, aiming to lead its peers in this crucial area. This commitment can translate into a competitive advantage by appealing to a growing segment of the investment community that values ethical production and long-term sustainability.
- Peer-Leading ESG Performance: DPM's consistent efforts in sustainability reporting and practice aim to set it apart from competitors.
- Investor Attraction: A strong ESG profile can draw capital from a widening pool of environmentally and socially conscious investors.
- Market Differentiation: In a market where many products are viewed as commodities, DPM's ethical approach provides a distinct value proposition.
- Stakeholder Appeal: The focus on ESG resonates with a broader range of stakeholders, including local communities and employees, fostering stronger relationships and a positive brand image.
The gold mining sector is intensely competitive, with numerous players vying for resources and market share. Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) faces this rivalry from both larger corporations and smaller exploration firms. This competition is amplified by the commodity nature of gold, where price is a primary driver, making cost efficiency crucial for DPM's profitability and market standing.
Despite a favorable market in 2024-2025 with rising gold prices, competition remains robust as companies reinvest in growth. High capital intensity, long-term commitments, and significant environmental rehabilitation costs create substantial exit barriers, compelling companies to persist even during challenging times. DPM differentiates itself through a strong ESG focus, attracting investors and building a unique market position.
| Competitor | Market Cap (Approx. USD Billion, Mid-2024) | 2024 Production Guidance (Moz) | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Newmont Corporation | ~$50 | 6.0 - 6.4 | Scale and diversified portfolio |
| Barrick Gold Corporation | ~$25 | 4.2 - 4.6 | Focus on high-quality assets |
| Agnico Eagle Mines Limited | ~$15 | 3.1 - 3.3 | Strong operational efficiency and growth pipeline |
| Dundee Precious Metals (DPM) | ~$1.5 | 0.45 - 0.50 | ESG leadership and low-cost operations |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For investors looking for stability, gold faces significant competition from other assets. Government bonds, especially those from stable economies, are a traditional safe haven. In 2024, yields on U.S. Treasury bonds remained attractive, offering a steady income stream that can rival gold's appeal during uncertain times.
Certain currencies, like the Swiss franc and the Japanese yen, also serve as safe-haven assets. Their stability can draw capital away from gold, particularly when global economic or political risks escalate. The performance of these currencies is closely watched by investors seeking to preserve wealth.
Even cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, have emerged as a perceived store of value for some investors, especially younger demographics. While volatile, Bitcoin's digital scarcity and decentralized nature have led some to view it as a modern-day alternative to gold. Its market capitalization in 2024 continued to be a significant factor in investor consideration.
In industrial settings, the threat of substitutes for metals like gold and copper is a constant consideration. If cheaper alternatives can perform similar functions, demand for these precious metals can decrease. For instance, advancements in material science are continually exploring new composites and alloys that could potentially replace copper in certain electrical applications.
While gold and copper boast unique properties, particularly in conductivity and corrosion resistance, technological progress might unlock new materials for specific roles. However, for highly critical applications, such as those found in advanced electronics and specialized medical devices, the inherent advantages of gold and copper often make viable substitutes scarce. For example, in 2024, the demand for high-purity copper in the burgeoning electric vehicle battery sector remained robust, underscoring its current indispensability in key growth areas.
Consumers in the jewelry market have numerous alternatives to gold, including platinum, silver, various gemstones, and fashion jewelry crafted from less costly materials. This broad spectrum of choices can exert pressure on gold jewelry demand, especially during economic slowdowns or shifts in consumer tastes. For instance, while gold jewelry demand in value terms saw growth in Q1 2025 even with record prices, the availability of attractive substitutes remains a constant consideration.
Impact of Central Bank Policies
Central bank policies significantly shape the threat of substitutes for gold. For instance, decisions on interest rates directly impact gold's appeal. When central banks signal lower interest rates, as seen in many developed economies during periods of economic uncertainty, non-yielding assets like gold become more attractive relative to interest-bearing investments. This was evident in early 2024, where anticipation of rate cuts by the US Federal Reserve supported gold prices.
Currency management by central banks also plays a crucial role. A stronger US dollar, often a result of tightening monetary policy or perceived economic strength, can make gold more expensive for investors holding other currencies, potentially reducing demand. Conversely, a weaker dollar can boost gold's attractiveness. The US Dollar Index (DXY) movements often correlate inversely with gold prices, highlighting this dynamic.
Furthermore, central bank gold purchases represent a direct demand driver, acting as a significant factor in reinforcing gold's value proposition against fiat currencies. In 2023, central banks continued to be substantial net buyers of gold, with official sector net purchases reaching approximately 1,037 tonnes, according to the World Gold Council. This sustained buying by institutions underscores gold's role as a store of value and a hedge against currency depreciation, influencing its attractiveness as a substitute investment.
- Interest Rate Environment: Lower expected interest rates increase gold's appeal as a non-yielding asset.
- Currency Fluctuations: A weaker US dollar generally makes gold more affordable and attractive globally.
- Central Bank Demand: Significant gold purchases by central banks, like the 1,037 tonnes bought in 2023, bolster its perceived value and reduce the threat from other assets.
Perceived Value and Store of Wealth
Gold's historical position as a store of value, particularly as a hedge against inflation and currency debasement, significantly limits the threat of substitutes. This perception of intrinsic worth is deeply ingrained, making it challenging for other assets to fully replicate its role. For instance, while cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are sometimes touted as digital gold, their extreme volatility and regulatory uncertainty in 2024 still prevent them from offering the same level of stable wealth preservation as physical gold for many investors.
Furthermore, gold's low correlation with traditional financial assets like stocks and bonds makes it an attractive diversifier, especially during periods of market turbulence. In 2024, as geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties persisted, gold's ability to hold its value when other markets declined reinforced its unique position. This inherent diversification benefit acts as a substantial barrier against substitutes that do not offer similar uncorrelated performance characteristics.
The market sentiment surrounding gold as a safe-haven asset is a critical factor. Even with the rise of alternative investments, the psychological comfort and established trust associated with gold are difficult to overcome. This deep-seated belief in gold's enduring value creates a formidable defense against direct substitution by newer or less proven asset classes.
- Gold's historical role as a store of wealth is a primary defense against substitutes.
- Low correlation with other assets enhances gold's diversification appeal in volatile markets, a trait difficult for substitutes to match.
- Investor perception and trust in gold as a safe haven present a significant barrier to substitution.
The threat of substitutes for gold is moderate, primarily due to its unique combination of properties and entrenched market position. While other assets like government bonds and certain currencies offer safe-haven characteristics, they often lack gold's historical store of value and inflation-hedging capabilities. Emerging digital assets, while gaining traction, still face volatility and regulatory hurdles that limit their direct substitution for gold's stability.
Entrants Threaten
The gold mining industry presents formidable barriers to entry, primarily due to the immense capital required. Developing a new gold mine involves substantial upfront costs for exploration, feasibility studies, mine construction, and processing plant setup. These expenditures can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, making it exceedingly difficult for new players to enter the market.
For instance, Dundee Precious Metals' significant investment in its Čoka Rakita project, a key growth initiative, underscores the scale of capital commitment necessary. Such high capital requirements effectively deter many potential competitors, thereby reducing the threat of new entrants in the gold mining sector.
New mining ventures are often bogged down by extensive regulatory and permitting processes. These can include rigorous environmental impact assessments, complex land acquisition procedures, and the need to secure numerous operational permits. Such hurdles can stretch for many years, demanding significant financial investment and carrying inherent uncertainties, effectively acting as a substantial barrier to entry for aspiring mining companies.
The threat of new entrants due to access to scarce resources is significant for gold mining companies like Dundee Precious Metals (DPM). Identifying and securing economically viable gold reserves is becoming increasingly difficult, as the most accessible deposits have largely been discovered. This makes it tough for new players to enter the market and find high-quality mineral assets, which are typically already controlled by established mining firms.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players in the market, such as Dundee Precious Metals (DPM), leverage significant economies of scale. This advantage translates into lower per-unit costs across operations, procurement, and processing. For instance, DPM’s established infrastructure and high-volume output allow for more efficient resource utilization compared to a new entrant starting at a smaller scale.
New entrants would likely face a substantial cost disadvantage. Operating at a smaller scale initially means higher fixed costs spread over fewer units, making it challenging to compete on price with established, larger-volume producers. This initial cost barrier is a significant deterrent.
DPM’s decade-long operational track record, as of 2024, highlights the benefits derived from the experience curve. This history demonstrates consistent cost performance and operational efficiency, further entrenching their competitive position and making it harder for newcomers to match their cost structure and reliability.
- Economies of Scale: DPM’s large-scale operations reduce per-unit costs in mining, processing, and logistics.
- Experience Curve: DPM's ten years of operational history (as of 2024) have refined processes, leading to improved efficiency and lower costs.
- Procurement Power: Larger volumes allow DPM to negotiate better prices for raw materials and equipment.
- Capital Intensity: New entrants would require substantial upfront capital for similar-scale operations, increasing financial risk.
Established Infrastructure and Supply Chains
Developing the necessary infrastructure, such as roads, power, and water, and establishing reliable supply chains in remote mining locations presents a substantial barrier for new entrants. These new players would need to construct these vital components from the ground up, leading to immense capital expenditure and complex logistical hurdles. For instance, the cost of developing a new mine in a frontier region can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
Established mining companies, like Dundee Precious Metals (DPM), have already made significant investments in and have optimized their existing infrastructure and supply networks within their operating regions. DPM's operations in Bulgaria, for example, benefit from decades of investment in road networks, power access, and established relationships with local suppliers, giving them a considerable cost and efficiency advantage.
- Significant Capital Outlay: New entrants face massive upfront costs for infrastructure development, estimated to be in the hundreds of millions for a medium-sized mine.
- Logistical Complexity: Establishing efficient and cost-effective supply chains in remote areas is a major operational challenge.
- Existing Network Advantage: Established firms possess optimized infrastructure and supplier relationships, reducing operational costs and lead times.
- Time to Market: Building new infrastructure can add years to the time it takes for a new entrant to become operational, compared to leveraging existing assets.
The threat of new entrants in the gold mining sector, including for companies like Dundee Precious Metals (DPM), is significantly mitigated by several factors. The sheer capital intensity required for exploration, mine development, and processing facilities, often running into hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars, acts as a primary deterrent. For example, the development of a new gold mine typically demands substantial upfront investment before any revenue is generated.
Furthermore, navigating the complex web of regulatory approvals, environmental impact assessments, and land acquisition processes can be a lengthy and costly endeavor, often taking many years. This bureaucratic labyrinth, coupled with the increasing difficulty in discovering new, economically viable gold reserves, favors established players who have already secured access to prime mineral assets. Dundee Precious Metals, with its established operations and expertise, is well-positioned to manage these challenges.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Immense upfront investment for exploration, mine construction, and processing. | High financial risk and limited access to funding for new players. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Extensive permitting, environmental reviews, and land acquisition processes. | Significant delays, increased costs, and project uncertainty. |
| Resource Scarcity | Difficulty in finding and securing economically viable gold deposits. | New entrants struggle to acquire quality mineral assets, often already controlled by incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Dundee Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating insights from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from key players, and relevant trade association publications to capture the competitive landscape.
