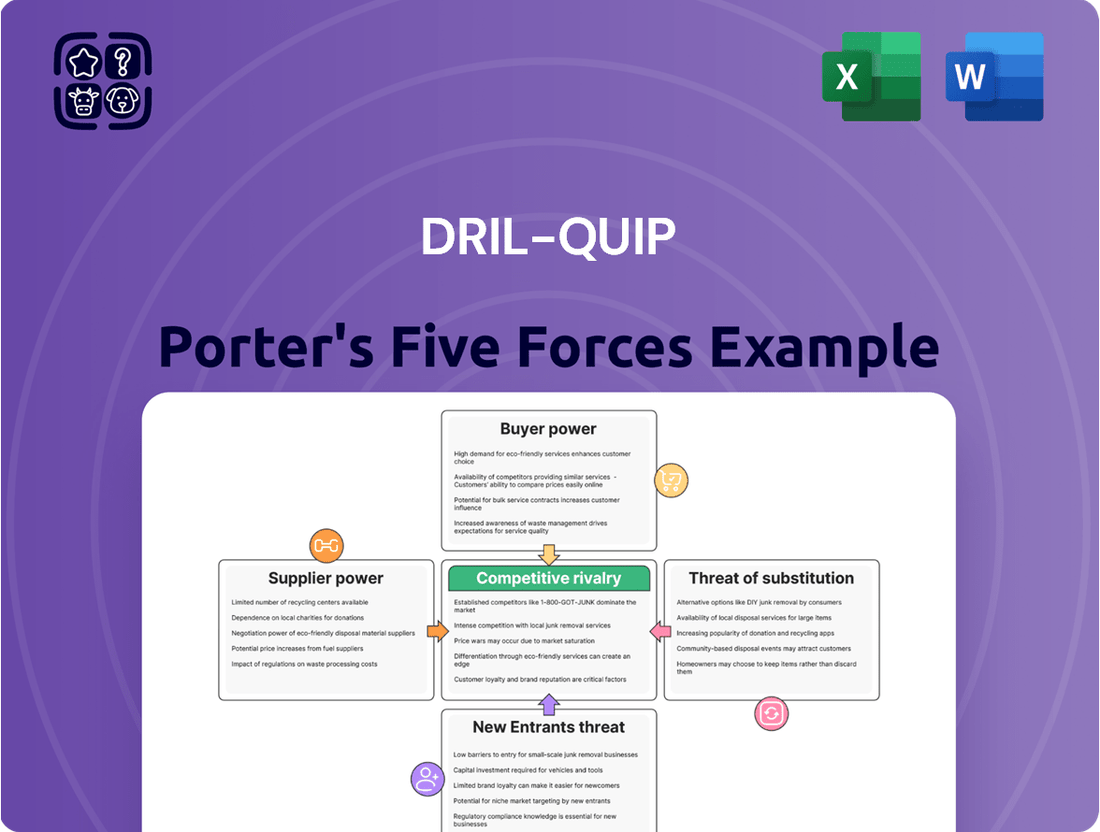
Dril-Quip Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dril-Quip Bundle
Dril-Quip's competitive landscape is shaped by significant supplier power and the intense rivalry among existing players in the offshore drilling equipment market. Understanding these forces is crucial for grasping the company's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dril-Quip’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Dril-Quip's dependence on highly specialized components and raw materials for its advanced drilling equipment, especially for deepwater operations, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. The intricate nature of these inputs often means only a limited number of suppliers can meet Dril-Quip's stringent quality and technical specifications.
This exclusivity grants these suppliers considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the oil and gas sector experienced notable supply chain volatility, impacting the availability and pricing of critical materials. Projections for 2025 suggest this trend may continue, potentially increasing costs for Dril-Quip and highlighting the suppliers' enhanced bargaining position.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technologies or advanced manufacturing for critical subsea components like wellheads and riser systems wield considerable influence. Dril-Quip's reliance on these cutting-edge solutions for deepwater and challenging projects often translates into supplier leverage regarding pricing and contractual terms. For instance, in 2024, the market for specialized subsea equipment saw continued consolidation, with a few key technology providers dominating specific segments, further amplifying their bargaining power.
Supplier concentration significantly impacts Dril-Quip's bargaining power. If a few dominant suppliers control essential components for oil and gas equipment, they can dictate terms. For instance, in 2024, the market for certain advanced drilling components saw consolidation, with the top three suppliers holding an estimated 60% market share, increasing their leverage.
Switching Costs for Dril-Quip
Switching suppliers for Dril-Quip's highly engineered and integrated equipment presents significant hurdles. These can include substantial costs associated with re-tooling manufacturing processes, the lengthy and complex re-qualification of new suppliers, and the inherent risk of production schedule disruptions. These factors collectively empower existing suppliers by limiting Dril-Quip's ability to easily change vendors.
The financial implications of these switching costs are considerable. For instance, a single change in a critical component supplier could necessitate millions in new capital expenditure for specialized machinery and extensive testing protocols. This financial commitment, coupled with the potential for lost revenue during any transition, directly strengthens the supplier's leverage in negotiations.
- High Re-tooling Expenses: Acquiring new, specialized machinery to accommodate different supplier specifications can run into the millions of dollars for complex drilling equipment.
- Lengthy Re-qualification Periods: The process of vetting and approving a new supplier for critical components can take many months, impacting production timelines.
- Production Disruption Risks: Unforeseen issues during a supplier transition can lead to costly downtime and missed delivery targets, directly affecting revenue.
- Loss of Supplier-Specific Expertise: Existing suppliers often possess deep knowledge of Dril-Quip's specific operational needs, which is difficult and time-consuming to transfer to a new partner.
Forward Integration Threat by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Dril-Quip's manufacturing operations, while less common, presents a significant potential shift in bargaining power. If a supplier possesses the technical capability and strategic motivation to produce the same specialized equipment Dril-Quip offers, it could drastically alter the supplier-customer dynamic.
This potential for forward integration compels Dril-Quip to actively cultivate strong, collaborative relationships with its critical suppliers. Maintaining competitive pricing and favorable contract terms becomes paramount to mitigate this risk.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers may leverage their capabilities to produce Dril-Quip's final products, increasing their leverage.
- Supplier Incentive: Suppliers with high margins or market share in their own segment might see forward integration as a growth opportunity.
- Dril-Quip's Response: Maintaining strong supplier relationships and competitive terms is crucial to deter this threat.
- Impact on Margins: Successful supplier forward integration could lead to increased input costs or reduced pricing power for Dril-Quip.
Dril-Quip faces considerable supplier bargaining power due to the specialized nature of its drilling equipment components. The limited number of suppliers capable of meeting stringent technical and quality demands, particularly for deepwater operations, grants these vendors significant leverage. This situation was underscored in 2024 by ongoing supply chain volatility in the oil and gas sector, which drove up prices for critical materials, a trend anticipated to persist into 2025.
Suppliers holding proprietary technologies for essential subsea components, such as wellheads and riser systems, wield substantial influence. Dril-Quip's reliance on these advanced solutions for challenging projects often translates into suppliers dictating pricing and contractual terms. The market consolidation observed in 2024 within specialized subsea equipment further amplified the bargaining power of key technology providers.
| Factor | Impact on Dril-Quip | 2024 Data/Trend | 2025 Outlook |
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for dominant suppliers | Top 3 suppliers held ~60% market share for certain components | Continued consolidation likely |
| Switching Costs | Limits Dril-Quip's ability to change vendors | Millions in re-tooling, lengthy re-qualification periods | High costs remain a barrier |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers dictate terms for critical subsea parts | Few key providers dominate specific segments | Dominance expected to continue |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Dril-Quip's competitive landscape identifies the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products on its market position.
Dril-Quip's Porter's Five Forces Analysis eliminates the pain of complex competitive research by providing a visually intuitive spider chart, instantly revealing strategic pressure points.
This tool simplifies the understanding of market dynamics, allowing for swift adjustments to strategy without the need for extensive data manipulation or specialized software.
Customers Bargaining Power
Dril-Quip's customer base is concentrated among major integrated, independent, and foreign national oil and gas companies worldwide. This consolidation means a significant portion of their revenue comes from a relatively small number of large, sophisticated buyers.
These major players operate on a global scale and purchase equipment in substantial volumes, granting them considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the top 10 customers for many oilfield service providers typically accounted for over 60% of their total revenue, a testament to customer concentration.
Their size and purchasing power enable these customers to negotiate aggressively on pricing, demand favorable contract terms, and require highly customized product specifications. This can put pressure on Dril-Quip's profit margins and necessitate significant investment in tailored solutions.
Customers in the oil and gas sector, particularly those involved in deepwater operations, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they closely scrutinize the cost of equipment like Dril-Quip's. For instance, in 2023, capital expenditures by major oil companies saw a notable increase, but this was often tied to cost management and efficiency improvements, underscoring the ongoing pressure on suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
The standardization of products significantly impacts customer bargaining power. While Dril-Quip focuses on specialized, engineered solutions for the oil and gas industry, the potential for certain components or less complex product lines to become more commoditized exists. If this standardization occurs, customers gain the ability to more easily switch between suppliers, which naturally increases their leverage and puts downward pressure on prices.
For instance, if a particular type of casing or a standard connector becomes widely available from multiple manufacturers, buyers can then shop around for the best deal. This shift from unique, engineered solutions to more off-the-shelf products empowers customers, as the switching costs diminish. Dril-Quip's strategy to counter this involves continuous investment in proprietary technology and innovative designs, aiming to maintain a competitive edge that transcends mere product standardization.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Backward
Large oil and gas companies, Dril-Quip's primary customers, possess significant financial muscle and technical capabilities. This allows them to consider backward integration, meaning they could potentially produce certain components or even entire drilling systems in-house, or acquire existing manufacturers. This inherent possibility acts as a powerful lever in their negotiations with Dril-Quip, as they can threaten to bypass the supplier altogether.
For instance, major energy players often have substantial capital expenditures. In 2023, the top global oil and gas companies reported billions in profits, providing ample resources for such strategic moves. This financial clout directly translates into enhanced bargaining power when negotiating pricing and terms with equipment providers like Dril-Quip.
- Customer's Financial Strength: Major oil and gas firms often have revenues in the tens or hundreds of billions of dollars, enabling them to invest in in-house production or acquisitions.
- Technical Expertise: These companies employ highly skilled engineers and have access to advanced manufacturing technologies, reducing the barrier to self-production.
- Potential for Backward Integration: The ability to produce components or systems internally or through acquisition directly challenges Dril-Quip's market position and pricing power.
- Negotiating Leverage: The credible threat of backward integration gives customers significant leverage to demand lower prices or more favorable contract terms from Dril-Quip.
Impact of Product on Customer's Cost Structure
Dril-Quip's specialized drilling equipment is a cornerstone for deepwater operations, making it a substantial capital expenditure for its clientele. This critical nature means customers, despite the necessity, will meticulously evaluate the entire cost of ownership. They focus on optimizing project economics by considering not just the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance expenses and the long-term operational efficiency of the equipment.
The significant investment required for Dril-Quip's deepwater solutions directly impacts a customer's cost structure. For example, a single deepwater drilling rig can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, with the specialized equipment forming a large portion of that. Customers, such as major oil and gas producers, are highly sensitive to any factor that could inflate their project breakeven costs. Therefore, they actively seek equipment that offers reliability and reduces downtime, as these directly translate into lower operating expenses and improved profitability for their exploration and production activities.
- High Initial Investment: Dril-Quip's deepwater drilling equipment represents a significant capital outlay for oil and gas companies.
- Total Cost of Ownership Scrutiny: Customers analyze purchase price, maintenance, and operational efficiency to manage project economics.
- Impact on Project Breakeven: Equipment reliability and uptime directly influence the cost-effectiveness of deepwater exploration and production.
- Customer Sensitivity to Costs: Oil majors are motivated to reduce overall project expenses, making them price-sensitive and value-focused.
Dril-Quip's customers, primarily large oil and gas companies, wield considerable bargaining power due to their concentrated purchasing volume and significant financial resources. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly impacting Dril-Quip's profitability.
The potential for these major players to integrate backward, either by producing components in-house or acquiring manufacturers, presents a constant threat that enhances their negotiating position. For instance, in 2024, many oilfield service companies reported that their top 10 customers accounted for over 60% of revenue, highlighting the dependency and resulting customer power.
Furthermore, the high cost of Dril-Quip's specialized deepwater equipment makes customers exceptionally sensitive to the total cost of ownership. They actively seek to optimize project economics, driving demand for reliable, efficient, and competitively priced solutions.
| Factor | Impact on Dril-Quip | Customer Action |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Reduced pricing power, pressure on margins | Negotiate aggressive pricing, demand favorable terms |
| Backward Integration Potential | Threat to market share and pricing | Consider in-house production or acquisition of competitors |
| Price Sensitivity (Deepwater Ops) | Need for cost-competitive solutions | Scrutinize total cost of ownership, seek efficiency gains |
What You See Is What You Get
Dril-Quip Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Dril-Quip Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive instantly upon purchase, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes. Our commitment is to transparency, ensuring you get the complete, professional analysis without any discrepancies.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The market for engineered drilling and production equipment, especially for deepwater projects, is characterized by a few large, established global competitors. These major players, including Baker Hughes, TechnipFMC, and SLB, possess considerable scale and resources, intensifying the competition for securing contracts and expanding their market presence.
The deepwater drilling and subsea equipment sectors are anticipated to experience robust growth, but the pace of this expansion directly impacts how fiercely companies compete. A more measured growth rate often intensifies rivalry as businesses vie more aggressively for a limited pool of opportunities. Conversely, rapid expansion can dilute competitive pressures as companies focus on capturing new market segments.
Looking ahead, the subsea equipment market is forecast to see substantial growth between 2025 and 2034. This upward trend suggests opportunities for expansion, but also means companies will need to innovate and differentiate to secure their share of this expanding market.
Dril-Quip distinguishes itself by providing highly engineered solutions specifically designed for deepwater, harsh operating conditions, and complex drilling applications. This focus on superior technology and reliability allows them to sidestep direct price wars and build a significant competitive edge.
In 2024, the oil and gas industry continued to see demand for specialized equipment that can withstand extreme environments. Dril-Quip’s commitment to innovation in these niche areas, such as their advanced subsea wellhead systems, is key to maintaining this differentiation and commanding premium pricing.
Exit Barriers
High fixed costs associated with specialized manufacturing equipment and facilities in the oil and gas sector, like those for Dril-Quip's advanced drilling systems, can make exiting the market prohibitively expensive. These sunk costs, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, mean companies must continue operating even in challenging periods to avoid substantial losses.
The presence of specialized assets, such as proprietary drilling technology or unique manufacturing capabilities, further entrenches companies within the industry. Selling these assets at a significant discount or repurposing them for other industries is often not feasible, effectively locking companies into the oil and gas market.
Long-term contracts, common in large-scale energy projects, also act as significant exit barriers. Companies like Dril-Quip are contractually obligated to fulfill these agreements, which can span several years, preventing them from withdrawing even when market conditions deteriorate. For instance, in 2023, the oil and gas equipment sector saw companies struggling with order backlogs that extended well into 2024, highlighting the commitment tied to existing contracts.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant capital investment in specialized machinery and plants.
- Specialized Assets: Equipment designed for specific oil and gas applications, with limited alternative uses.
- Long-Term Contracts: Binding agreements that require continued operation and delivery.
- Industry Downturns: Companies may continue production despite low demand to cover fixed costs, intensifying price competition.
Strategic Alliances and Mergers
Strategic alliances and mergers are reshaping the competitive landscape. Dril-Quip's merger with Innovex International, completed in September 2024, is a prime example of this trend. This consolidation aims to broaden service portfolios and capitalize on synergistic advantages.
These strategic moves intensify rivalry by creating larger, more integrated entities. For instance, the combined entity can offer a more comprehensive suite of products and services, putting pressure on competitors to adapt or face market share erosion.
- Industry Consolidation: The oil and gas equipment sector, including companies like Dril-Quip, has experienced significant consolidation.
- Merger Impact: The Dril-Quip and Innovex International merger in September 2024 created a larger player with enhanced capabilities.
- Competitive Intensification: Such mergers lead to increased competition as consolidated firms leverage combined strengths and broader offerings.
Competitive rivalry in the engineered drilling and production equipment market remains intense, driven by the presence of large, established global players like SLB, Baker Hughes, and TechnipFMC. These companies leverage their scale and resources to compete fiercely for contracts, particularly in the growing deepwater sector. Dril-Quip differentiates itself through highly engineered, specialized solutions for demanding environments, aiming to avoid direct price competition and command premium pricing.
The industry is characterized by high fixed costs and specialized assets, creating significant exit barriers that encourage companies to remain competitive even during downturns. This persistence, coupled with ongoing consolidation, such as Dril-Quip's September 2024 merger with Innovex International, intensifies the competitive landscape by creating larger, more integrated entities with broader service portfolios.
| Competitor | Market Focus | 2024 Estimated Revenue (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|
| SLB | Integrated energy services and equipment | ~33.0 |
| Baker Hughes | Oilfield services, equipment, and digital solutions | ~23.0 |
| TechnipFMC | Subsea, surface, and onshore/offshore services | ~13.0 |
| Dril-Quip | Deepwater and harsh environment drilling and production equipment | ~0.6 (Pre-merger estimate) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most substantial long-term threat of substitutes for Dril-Quip arises from the global movement towards renewable and alternative energy sources. This energy transition, driven by decarbonization efforts, could diminish the demand for oil and gas extraction, impacting the need for drilling equipment.
Despite this shift, traditional energy sources are projected to remain a significant part of the global energy mix through 2025 and beyond. For instance, in 2023, oil and gas still accounted for approximately 50% of global primary energy consumption, indicating continued demand for related services and equipment.
The rise of onshore drilling and production, especially in shale and unconventional resources, presents a significant threat of substitutes for offshore deepwater exploration. This shift is driven by advancements in hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling, making onshore extraction more economical and accessible. For instance, U.S. crude oil production reached an estimated 13.2 million barrels per day in 2024, a testament to the strength of onshore operations.
Dril-Quip, while historically focused on deepwater, recognizes this trend and has strategically expanded its onshore capabilities. The acquisition of Great North, a key player in the North American onshore market, diversifies Dril-Quip's revenue streams and allows it to compete in this growing segment. This diversification is crucial as onshore production continues to capture market share, potentially reducing the demand for highly specialized deepwater equipment.
Technological advancements in existing oil and gas operations pose a significant threat of substitution for Dril-Quip. For instance, improvements in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques, such as chemical flooding or thermal methods, can unlock production from mature fields. This reduces the imperative for companies to invest in new, capital-intensive deepwater exploration and development projects, thereby lessening demand for Dril-Quip's specialized subsea drilling and production equipment.
Changes in Energy Consumption Patterns
A significant shift in global energy consumption patterns presents a substantial threat of substitution for Dril-Quip. If demand for hydrocarbons, the primary market for Dril-Quip's drilling and production equipment, were to decrease substantially, the need for their specialized products would diminish. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in their 2024 outlook that while oil demand is projected to grow modestly, the long-term trajectory is influenced by the accelerating adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy sources. This broad market-level substitution impacts the entire oil and gas equipment sector, not just Dril-Quip.
The increasing global focus on decarbonization and the transition to cleaner energy sources directly impacts the demand for traditional oil and gas extraction equipment.
- Shifting energy mix: Projections suggest a continued rise in renewable energy capacity, potentially displacing fossil fuels.
- Electrification trends: The growing adoption of electric vehicles and industrial electrification reduces the need for oil and gas.
- Government policies: Stricter environmental regulations and carbon pricing mechanisms incentivize a move away from hydrocarbons.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in energy storage and alternative fuels could further accelerate the decline in fossil fuel demand.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The cost-effectiveness of substitutes is a key determinant of their threat to deepwater oil and gas production. For instance, as solar and wind power technologies advance, their levelized cost of energy (LCOE) continues to decrease, making them increasingly competitive. By the end of 2023, the global average LCOE for new utility-scale solar PV projects was around $39 per megawatt-hour, while onshore wind was approximately $33 per megawatt-hour, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). This contrasts with the often higher operational expenditures for deepwater oil and gas extraction, which can fluctuate significantly with market conditions.
The economic viability of alternatives directly impacts their ability to displace traditional energy sources. When the upfront investment and ongoing operational costs of substitutes, such as advanced battery storage or geothermal energy systems, are high, their adoption rate slows. This can limit their immediate threat to established deepwater production. For example, while hydrogen fuel cell technology offers promise, the current infrastructure and production costs remain a significant barrier to widespread commercial use, especially compared to the established infrastructure for oil and gas.
Conversely, as the technology for renewable energy sources matures and scales, their cost-effectiveness improves, amplifying the threat they pose. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in 2024 that renewables are set to account for over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion in the coming years. This trend suggests that substitutes will become increasingly attractive, potentially reducing demand for deepwater oil and gas.
- Decreasing LCOE for Renewables: Global average LCOE for solar PV and onshore wind hovered around $39/MWh and $33/MWh respectively by late 2023, per IRENA.
- High Initial Costs of Alternatives: Technologies like hydrogen fuel cells face significant upfront investment and infrastructure challenges.
- Renewable Dominance in Capacity Expansion: Over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion is expected to come from renewables in the near future, according to the IEA.
The threat of substitutes for Dril-Quip is significant, primarily driven by the global energy transition away from fossil fuels. While traditional energy sources remain dominant, the accelerating adoption of renewables and electric vehicles curtails long-term demand for oil and gas extraction, impacting the need for Dril-Quip's specialized equipment.
Onshore drilling advancements also present a substitute threat, particularly for deepwater operations, as evidenced by the robust U.S. crude oil production reaching an estimated 13.2 million barrels per day in 2024. Furthermore, improved enhanced oil recovery techniques can reduce the necessity for new, capital-intensive deepwater projects, thereby lessening demand for Dril-Quip's offerings.
The cost-competitiveness of renewable energy sources, with solar and wind LCOEs around $39/MWh and $33/MWh respectively by late 2023, increasingly challenges the economics of deepwater extraction. This trend, coupled with renewables accounting for over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion, signals a growing substitution threat.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the highly specialized deepwater drilling and production equipment market demands immense capital. Newcomers face substantial upfront costs for advanced manufacturing facilities, cutting-edge research and development, and rigorous testing infrastructure. For instance, the average cost to build a new offshore drilling rig can range from $500 million to over $1 billion, presenting a formidable financial hurdle.
Dril-Quip's substantial portfolio of proprietary technologies and patents, particularly in intricate subsea systems and wellhead connectors, presents a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to leverage its extensive intellectual property to maintain its market position. The sheer investment in research and development required to replicate this technological depth would be a significant hurdle, demanding years and substantial capital for any new entrant aiming to compete effectively.
The oil and gas sector, particularly for deepwater drilling, is burdened with rigorous environmental regulations, demanding safety protocols, and extensive certification processes. New companies entering this arena would find it incredibly difficult to navigate and comply with these intricate and constantly changing legal frameworks.
For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE) imposes strict oversight on offshore operations, with compliance costs for new entrants potentially running into millions of dollars before any revenue is generated. These substantial upfront investments act as a significant barrier, deterring potential competitors from entering the market.
Established Customer Relationships and Reputation
Dril-Quip's established customer relationships with major oil and gas companies, including integrated, independent, and foreign national entities, present a formidable barrier to new entrants. These clients often prioritize reliability and proven performance, leading to long-standing supplier partnerships. For instance, securing initial contracts with such risk-averse customers requires significant time and demonstrated success.
The deep trust and proven track record that Dril-Quip has cultivated over years of operation are crucial deterrents. Newcomers must not only match Dril-Quip's product quality but also overcome the ingrained preference for established, dependable suppliers. This loyalty is a significant hurdle for any potential competitor attempting to gain market share.
- Long-term contracts: Many of Dril-Quip's clients operate under multi-year supply agreements, limiting immediate opportunities for new players.
- Supplier qualification processes: Oil and gas majors have rigorous vetting procedures that new entrants must navigate, often requiring extensive operational history and safety records.
- Brand loyalty: Decades of reliable service have fostered strong brand loyalty, making it difficult for new companies to displace incumbent suppliers.
Supply Chain and Distribution Networks
The threat of new entrants concerning supply chain and distribution networks for highly engineered oilfield equipment like Dril-Quip's is significantly low. Building and maintaining an extensive global infrastructure, complete with specialized logistics for remote offshore operations and comprehensive after-sales support, represents a formidable barrier. For instance, in 2024, the cost of establishing such a network, including warehousing, transportation, and skilled personnel, can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a capital investment that deters most new players.
Newcomers would face immense difficulty in matching the established incumbents' capabilities, which have been honed over decades. This includes securing reliable suppliers for specialized components, navigating complex international shipping regulations, and developing the necessary service infrastructure in challenging environments. The sheer scale and complexity of Dril-Quip's existing operations, which service a global customer base, create a significant competitive advantage that is not easily replicated.
Furthermore, the need for specialized certifications and long-term relationships with key clients in the oil and gas sector add further layers of difficulty. These relationships are crucial for securing contracts and understanding the evolving needs of the industry, which new entrants would lack. The high upfront investment and the time required to build trust and operational expertise make the threat of new entrants in this specific area relatively weak.
The threat of new entrants in Dril-Quip's specialized market is considerably low due to the substantial capital investment required for advanced manufacturing and R&D. New companies would also struggle to replicate Dril-Quip's extensive intellectual property and navigate the complex regulatory landscape. Established customer relationships and brand loyalty further fortify this barrier.
The deepwater drilling equipment sector demands immense upfront capital, with new offshore drilling rigs costing upwards of $500 million to over $1 billion. This financial hurdle, coupled with the need for proprietary technologies and compliance with stringent regulations like those from the BSEE, significantly deters new market participants.
Dril-Quip's established global supply chain and distribution networks, vital for servicing remote offshore operations, represent another formidable barrier. Building a comparable infrastructure, including specialized logistics and after-sales support, can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. This, combined with the time needed to build trust and operational expertise, makes the threat of new entrants relatively weak.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building advanced manufacturing facilities and R&D centers. | $500 million - $1 billion+ for a new offshore drilling rig. |
| Proprietary Technology & IP | Replicating Dril-Quip's patented subsea systems and wellhead connectors. | Years of R&D investment and substantial capital. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating environmental regulations and safety protocols (e.g., BSEE). | Millions of dollars in upfront compliance costs. |
| Customer Relationships & Brand Loyalty | Overcoming established trust and long-term contracts with major oil companies. | Significant time and demonstrated success required to gain initial contracts. |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | Establishing a global infrastructure for specialized logistics and after-sales support. | Hundreds of millions of dollars in capital investment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Dril-Quip leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate insights from industry trade publications, market research reports, and financial analyst assessments to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
