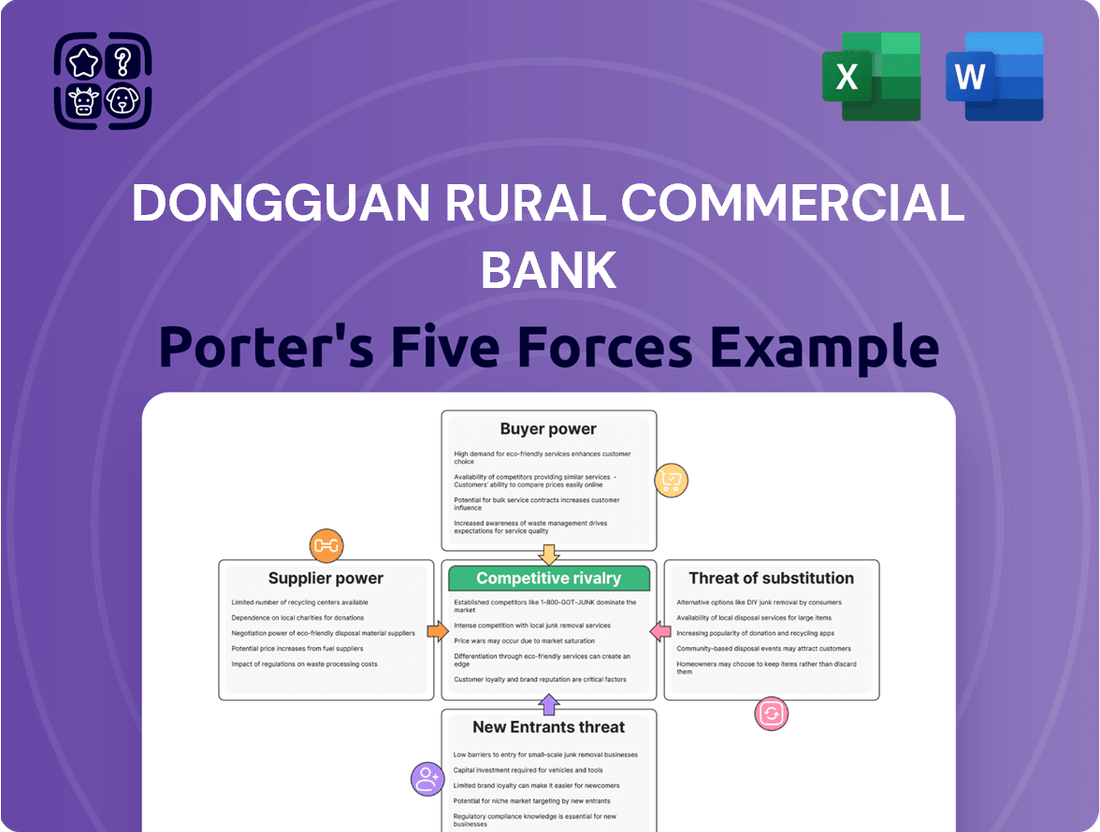
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank Bundle
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank operates in a landscape shaped by intense rivalry among existing players and the constant threat of new entrants eager to capture market share. Understanding the bargaining power of both its customers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this competitive environment.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual depositors at Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank is typically low. This is because the depositor base is highly fragmented, meaning no single depositor holds significant sway. Furthermore, the deposit products themselves are often standardized, offering little differentiation for customers to leverage in negotiations.
However, a collective shift in depositor behavior can influence interest rates, particularly when banks are actively competing for stable funding. Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's reliance on its local deposit base underscores the importance of these individuals as crucial funding sources, even if their individual power is limited.
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's reliance on the interbank market for liquidity and short-term funding means that other financial institutions acting as suppliers hold considerable sway. The overall liquidity in the market, heavily influenced by central bank policies and broader economic conditions, directly impacts the bank's cost of obtaining these crucial funds. For instance, during periods of tight liquidity, the interest rates demanded by these interbank suppliers can rise significantly, increasing the bank's cost of funds and potentially squeezing profit margins.
Specialized technology and software vendors, especially those providing core banking platforms and cybersecurity solutions, wield significant bargaining power. These providers often have high switching costs for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, as implementing new systems is complex and disruptive. For instance, the global market for core banking software is dominated by a few key players, allowing them to command premium pricing and dictate terms, impacting the bank's operational efficiency and its ability to innovate.
Skilled Labor Market
The availability of skilled professionals in finance, technology, and risk management is a key factor influencing the bargaining power of suppliers for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank. In a competitive talent market, employees possessing specialized expertise, particularly in areas like digital banking and cybersecurity, can command higher salaries and better benefits. This upward pressure on labor costs is a direct consequence of their increased bargaining power.
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank faces a significant challenge in attracting and retaining top talent, as it must compete not only with other regional financial institutions but also with larger national banks and agile fintech firms that often offer more attractive compensation packages and cutting-edge work environments. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a senior software engineer in China's financial sector saw a notable increase, reflecting the high demand for these skills.
- Talent Competition: Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank must contend with major players like ICBC and Ant Group for skilled financial and tech professionals.
- Wage Inflation: The demand for specialized skills in areas such as AI and data analytics in banking is driving up wage expectations for qualified candidates.
- Retention Challenges: High turnover among tech-savvy employees can increase recruitment and training costs, impacting operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance Providers
Regulatory compliance providers, including legal and audit firms, significantly influence Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's operations. These entities, while not traditional suppliers, effectively supply the framework and standards the bank must adhere to, dictating processes and capital needs. In 2024, the cost of compliance for Chinese banks continued to be a substantial operational expense, with many investing heavily in technology and personnel to meet evolving requirements.
The stringent nature of Chinese banking regulations, enforced by bodies like the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), means that adherence is mandatory. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, including fines and operational restrictions, making these regulatory dictates a powerful force shaping the bank's strategic decisions and resource allocation.
- Mandatory Adherence: Chinese banking regulations are non-negotiable, impacting all aspects of Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's business.
- Cost of Compliance: The financial burden of meeting regulatory standards, including fees for external audit and legal services, is significant.
- Operational Influence: Compliance requirements directly shape the bank's operational processes, risk management, and capital planning.
Suppliers of capital, particularly those in the interbank market and providers of specialized technology, exert considerable bargaining power over Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank. The bank's dependence on these external sources for liquidity and essential operational systems means that supplier terms can significantly impact its cost of funds and efficiency.
The market for core banking software is concentrated, with a few dominant players dictating terms. In 2024, the ongoing need for digital transformation and enhanced cybersecurity meant that Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, like many financial institutions, faced premium pricing from these critical technology vendors, leading to substantial capital outlays.
Furthermore, the competition for skilled labor, especially in areas like fintech and risk management, allows employees to negotiate higher compensation. For instance, data from 2024 indicated a competitive landscape for AI specialists within China's financial sector, pushing up salary expectations and increasing the bank's personnel costs.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interbank Lenders | Market Liquidity & Central Bank Policy | Influences cost of short-term funding | Tight liquidity periods in 2024 increased borrowing costs. |
| Core Banking Software Vendors | High Switching Costs & Market Concentration | Dictates pricing for essential IT infrastructure | Premium pricing for advanced platforms remained a significant expense. |
| Skilled Financial & Tech Professionals | High Demand & Specialized Expertise | Drives up labor costs and impacts talent retention | Salaries for AI and data analytics roles saw notable increases in 2024. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's competitive landscape reveals the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, perfect for quick decision-making and identifying key pain points.
This analysis allows for customized pressure level adjustments based on new data or evolving market trends, directly addressing the pain point of uncertainty.
Customers Bargaining Power
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank (DRCB) caters to a broad spectrum of clients, from everyday individuals to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and even substantial corporations. This wide reach means the bank must understand that not all customers wield the same influence.
For instance, individual retail customers, while numerous, generally have limited bargaining power due to the standardized nature of their banking needs and the availability of numerous alternative providers. In contrast, larger corporate clients, often requiring more complex financial solutions like syndicated loans or specialized treasury services, and possessing greater access to alternative capital sources, can negotiate more favorable terms, potentially impacting DRCB's margins.
In 2023, DRCB reported that its retail deposit base continued to be a significant contributor to its funding, highlighting the importance of retaining these customers despite their individual lower bargaining power. Conversely, the bank's focus on corporate lending saw growth in its loan portfolio, indicating active engagement with larger clients who do possess more leverage.
For basic banking services like checking and savings accounts, Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank faces customers with low switching costs. This is particularly true as digital banking platforms become more prevalent, allowing individuals to easily move funds or open new accounts with competitors offering more attractive interest rates or enhanced digital features. In 2024, reports indicated that a significant percentage of banking customers consider switching providers for better digital experiences or higher yields on deposits, directly impacting the bank's ability to retain these customers without competitive offerings.
SMEs often prioritize stable, long-term relationships with their local banks, which can temper their immediate bargaining power on loan conditions. This is particularly true for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, which has a strong local presence and understanding of its SME clients' needs.
However, if Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's offerings become less competitive or fail to meet evolving SME requirements, these businesses can explore alternatives. The availability of other regional banks or specialized non-bank lenders can significantly increase the bargaining power of SMEs.
Access to Multiple Financial Providers
Customers, especially larger corporate clients, benefit from a highly competitive financial landscape in China. As of late 2024, the banking sector includes over 4,000 financial institutions, offering a vast selection beyond regional players like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank. This extensive choice empowers customers to negotiate better rates and terms, as they can easily compare offerings from state-owned giants, national joint-stock banks, and increasingly, foreign banks with a presence in the market.
The sheer volume of choices available means customers can actively seek out the most advantageous financial products and services. This dynamic forces banks to compete not just on price but also on service quality, innovation, and specialized offerings. For Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, this translates to a significant need to differentiate its value proposition to retain and attract clients in a crowded market.
- Increased Customer Choice: Over 4,000 financial institutions operate in China, providing ample alternatives to Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's customers.
- Negotiating Power: Clients can leverage this competition to secure more favorable interest rates, fees, and service packages.
- Differentiator Imperative: Banks must move beyond basic pricing to offer unique services and build strong customer relationships to counter this power.
Digital Empowerment of Customers
The digital age has significantly shifted the balance of power towards customers, especially in the banking sector. With a plethora of digital banking channels and comparison websites readily available, consumers can effortlessly access and compare offerings from various financial institutions. This heightened transparency drastically reduces their search costs, enabling swift decisions based on competitive rates, fees, and service features. For instance, in 2024, the number of active mobile banking users globally continued its upward trajectory, with projections indicating over 2.5 billion users by the end of the year, illustrating the widespread adoption and reliance on digital platforms.
This digital empowerment directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers. They are no longer confined to a single bank's offerings and can easily switch providers if they find a better deal elsewhere. Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank must therefore prioritize investments in robust and competitive digital platforms to retain and attract customers in this dynamic environment. Failing to do so risks losing market share to more digitally agile competitors.
- Increased Information Access: Customers can easily compare rates, fees, and services across multiple banks online.
- Lowered Switching Costs: Digital platforms facilitate quick account opening and transfers, reducing the effort to switch banks.
- Demand for Competitive Pricing: Transparency drives customers to seek the best value, pressuring banks on pricing.
- Focus on Digital Experience: Banks need to invest in user-friendly apps and online services to meet customer expectations.
The bargaining power of customers for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank is influenced by the vast number of financial institutions in China and the increasing ease of switching due to digital platforms. While individual retail customers have limited individual sway, their collective ability to compare and switch based on better rates or digital experiences poses a challenge. Corporate clients, however, can leverage their larger transaction volumes and access to diverse funding sources to negotiate more favorable terms, directly impacting the bank's profitability.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Influencing Factors |
| Retail Customers | Low to Moderate | Standardized needs, ease of digital switching, availability of numerous alternatives. |
| SMEs | Moderate | Desire for stable relationships, but increasing availability of alternative lenders and competitive offerings. |
| Corporate Clients | High | Complex needs, access to diverse capital markets, ability to negotiate terms based on transaction volume. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This in-depth examination provides actionable insights into the bank's strategic positioning and potential challenges within the rural commercial banking sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank contends with the formidable presence of large state-owned commercial banks like ICBC and China Construction Bank. These giants boast extensive branch networks, substantial capital reserves, and deeply ingrained brand loyalty, allowing them to serve a broad customer base across all financial segments.
These national players often benefit from lower funding costs due to government backing, enabling them to offer more competitive pricing on loans and other financial products. This scale advantage translates into a significant competitive edge, particularly in attracting both individual and corporate clients.
For instance, as of the end of 2023, the total assets of China's five largest state-owned banks exceeded 100 trillion RMB, dwarfing the asset size of regional banks. This sheer financial muscle empowers them to invest heavily in technology and marketing, further solidifying their market dominance and making it challenging for smaller institutions like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank to compete effectively on price and product breadth.
Dongguan's banking landscape is densely populated with numerous regional and city commercial banks, all fiercely competing for the same pool of individual and small to medium-sized enterprise (SME) customers. This intense rivalry frequently escalates into price wars, particularly concerning deposit interest rates and loan pricing. For instance, as of early 2024, the average lending rate for SMEs in China hovered around 4.5% to 5.5%, creating a tight margin for all players.
Banks in this environment must differentiate themselves beyond mere pricing. Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, like its peers, is challenged to stand out through superior service quality and innovative product offerings tailored to local needs. Success hinges on leveraging deep local market knowledge and fostering strong, personalized customer relationships, especially with the vital SME segment that drives much of the regional economy.
Joint-stock commercial banks, though smaller than their state-owned counterparts, are demonstrating a notable drive for expansion throughout China. These institutions are increasingly entering or bolstering their presence in regional markets like Dongguan, introducing innovative products and digital services that directly challenge established local banks. For instance, by mid-2024, several joint-stock banks reported double-digit year-over-year growth in digital customer acquisition, a trend that directly impacts how rural commercial banks must compete for market share.
Emergence of Fintech Companies
The rise of fintech companies presents a significant competitive challenge. These firms, while not operating as traditional banks, excel at offering specialized financial services such as streamlined online payments, peer-to-peer lending platforms, and accessible digital wealth management tools. For instance, by mid-2024, China's digital payment market, dominated by players like Alipay and WeChat Pay, processed trillions of dollars in transactions, directly impacting traditional banking fee income.
These specialized fintech players can effectively disrupt established banking revenue streams by attracting a growing segment of tech-savvy customers who value convenience and lower costs. This increased competition puts pressure on incumbent institutions like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank to innovate. By early 2024, fintech adoption rates among Chinese consumers were reported to be over 80% for mobile payments, highlighting the shift in customer preference.
- Fintech Specialization: Fintechs offer niche services like online payments and P2P lending, directly competing with traditional banking functions.
- Revenue Stream Disruption: Specialized fintech offerings can erode established banks' fee-based income.
- Customer Acquisition: Tech-savvy consumers are increasingly drawn to the convenience and cost-effectiveness of fintech solutions.
- Competitive Pressure: The overall market becomes more competitive, forcing traditional banks to adapt and integrate technology to retain customers and market share.
Price and Service Competition
Competition among banks, including Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, is fierce, primarily focusing on pricing and service offerings. Banks frequently engage in price wars, especially concerning interest rates for loans and deposits, which can significantly impact profitability. In 2023, the average lending rate for small and medium-sized enterprises in China saw a slight decrease, reflecting this competitive pressure.
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank needs to differentiate itself beyond just price. This means focusing on the quality and range of services provided, enhancing customer convenience, and cultivating strong, trusted relationships with clients. For instance, offering specialized digital banking solutions or personalized financial advice can create a competitive edge.
- Price Competition: Banks compete on interest rates for loans and deposits, and service fees.
- Service Competition: Differentiation through the quality, breadth, and convenience of services offered.
- Relationship Banking: Building trust and personalized service as a key differentiator against price-focused competition.
Competitive rivalry is intense for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, facing pressure from large state-owned banks with vast resources and smaller regional players in a crowded market. Fintech companies also pose a significant threat by offering specialized, convenient digital services that attract tech-savvy customers.
This environment forces banks to compete not only on pricing but also on service quality and innovation. Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank must leverage its local market knowledge and customer relationships to stand out, particularly within the crucial SME segment.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Large State-Owned Banks (e.g., ICBC, CCB) | Extensive networks, large capital reserves, government backing, lower funding costs | Dominant market share, ability to offer competitive pricing and a broad product range |
| Regional/City Commercial Banks | Agility, local market focus, personalized service | Intense competition for local customers, potential price wars on rates and fees |
| Joint-Stock Commercial Banks | Expansion drive, innovative products, digital services | Increasingly challenging regional banks with new offerings and digital capabilities |
| Fintech Companies | Specialized services (payments, lending), digital convenience, lower costs | Disrupting traditional revenue streams, attracting tech-savvy customers, forcing digital adaptation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For larger corporate clients, capital markets present a significant substitute to traditional bank financing. These companies can bypass banks by directly raising funds through issuing corporate bonds or selling equity. This direct financing model reduces their dependence on bank credit, thereby diminishing the bank's intermediary role and potentially impacting its lending volumes.
Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's primary customer base consists of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These businesses typically have more limited access to capital markets compared to larger corporations. However, for the bank's larger local corporate clients, the availability of bond and equity markets as alternative funding sources represents a tangible threat to its traditional lending business.
The threat of substitutes for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank comes from a growing array of non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs). These include leasing companies, asset management firms, and micro-lenders, all of which offer specialized financial services that can directly compete with traditional banking products. For instance, leasing companies provide equipment financing, an alternative to business loans, while asset management firms offer investment vehicles that substitute for savings accounts or fixed deposits.
NBFIs often operate with lighter regulatory burdens compared to traditional banks. This flexibility allows them to innovate and offer more tailored or niche financial solutions. For example, some micro-lenders cater specifically to small businesses or individuals underserved by conventional banks, providing accessible credit and financial management tools. This diversification of financial service providers broadens customer choices significantly, presenting a tangible substitute for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's offerings.
Fintech lending and crowdfunding platforms present a substantial threat of substitution for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank. These online channels, including peer-to-peer lending and crowdfunding, provide alternative avenues for individuals and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to secure financing, effectively bypassing traditional banking institutions. For instance, by mid-2024, the global P2P lending market was projected to reach over $200 billion, highlighting its growing influence.
The inherent advantages of these fintech platforms, such as accelerated approval processes and tailored loan terms, make them particularly appealing. Their technological underpinnings allow for greater efficiency and customization, which can be a significant draw, especially for smaller loan amounts where traditional bank processes might be perceived as cumbersome. The sheer convenience and speed offered by these digital alternatives can attract specific customer segments away from established banks.
Informal Lending Channels
Informal lending channels, like private lenders and community financing groups, act as substitutes for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, especially for those who don't qualify for traditional loans. These options can provide faster access to capital, though they often come with higher risks and less regulatory oversight. In 2024, while formal financial inclusion efforts are growing, a significant portion of the population in developing regions still relies on these informal networks for quick cash injections, particularly for immediate needs or small-scale ventures.
These informal channels can siphon off customers seeking speed and flexibility, bypassing the more structured processes of established banks. For instance, in some emerging markets, peer-to-peer lending platforms, though increasingly regulated, also represent a growing substitute, offering alternative avenues for borrowing and lending outside traditional banking systems.
- Prevalence: Informal lending remains a significant factor in certain local markets, particularly in less developed areas.
- Customer Base: These channels often cater to individuals and small businesses that may not meet the stringent criteria of formal banking institutions.
- Key Advantage: Speed and simplified access to funds are the primary drawcards of informal lending.
- Risk Factor: Despite the convenience, informal lending typically carries a higher risk profile for both lenders and borrowers compared to regulated banking services.
Emerging Digital Currencies and Blockchain Finance
The rise of digital currencies and blockchain technology presents a long-term threat to traditional banking services. These innovations could potentially replace established payment and settlement systems, and even impact lending activities. While widespread adoption in mainstream banking is still developing, these technologies have the potential to fundamentally reshape financial transactions by reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries.
For instance, China's central bank digital currency, the digital yuan, is actively being tested and expanded. As of early 2024, pilot programs for the digital yuan have included millions of users and thousands of merchants across various cities, demonstrating a clear move towards digitalizing currency. The evolving regulatory landscape in China regarding cryptocurrencies and blockchain applications will be a critical factor in how significantly these technologies disrupt established financial institutions like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank.
- Digital Yuan Pilots: By late 2023, over 260 million individuals and 6 million merchants were involved in digital yuan pilot programs in China.
- Transaction Volume: In the first half of 2024, the cumulative transaction volume for the digital yuan exceeded 2 trillion yuan (approximately $278 billion USD).
- Blockchain Adoption: Global investment in blockchain technology is projected to reach over $150 billion by 2024, indicating growing interest and development in the space.
Fintech lending and crowdfunding platforms offer a significant substitute for traditional bank financing, particularly for SMEs. These online channels provide faster, more tailored loan terms, attracting customers seeking efficiency. By mid-2024, the global P2P lending market was projected to exceed $200 billion, underscoring the growing appeal of these alternatives.
Non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) like leasing companies and micro-lenders provide specialized services that directly compete with bank products. Operating with lighter regulatory burdens, they can offer more niche solutions, such as equipment financing or credit for underserved segments. This broadens customer choices, presenting a tangible alternative to Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank's offerings.
Informal lending channels, including private lenders and community groups, serve as substitutes, especially for those who do not qualify for traditional loans. These options offer quicker access to capital, though often with higher risks and less oversight. In 2024, these networks remain crucial for immediate needs in many developing regions.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank | 2024 Market Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Markets | Direct fund raising via bonds/equity | Reduces dependence on bank credit for larger corporates | N/A (Corporate Finance) |
| Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NBFIs) | Specialized services (leasing, micro-lending) | Offers alternative financing, competes for niche markets | Growing market share in specialized lending |
| Fintech Lending & Crowdfunding | Online platforms, faster approvals, tailored terms | Siphons off SME and individual borrowers | Global P2P lending market projected >$200 billion |
| Informal Lending | Fast access, simplified processes, higher risk | Serves unbanked/underbanked, bypasses formal channels | Significant reliance in certain developing regions |
| Digital Currencies/Blockchain | Potential to replace payment/settlement systems | Long-term disruption of traditional intermediaries | Digital Yuan pilots involve >260 million users; Blockchain investment projected >$150 billion |
Entrants Threaten
The Chinese banking sector, including institutions like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, is characterized by exceptionally high regulatory barriers. These include substantial capital requirements, rigorous licensing procedures, and continuous adherence to evolving compliance standards set by bodies such as the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC). For instance, in 2023, the minimum registered capital for rural commercial banks varied by region, but generally remained in the hundreds of millions of RMB, a significant hurdle for aspiring entrants.
These stringent requirements act as a powerful deterrent, effectively limiting the influx of new competitors. The process of obtaining a banking license is notoriously complex and time-consuming, often spanning several years and demanding extensive documentation and proof of financial stability and operational capacity. This makes it exceedingly difficult for new players to establish a foothold and challenge established entities.
Establishing a commercial bank, even a regional one like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank, requires substantial capital. This includes significant investments in physical infrastructure, advanced technology systems, and crucially, meeting stringent capital adequacy ratios mandated by regulators. For instance, as of early 2024, many jurisdictions require Tier 1 capital ratios to be well above 10%, a considerable hurdle for new players.
These high financial prerequisites act as a powerful barrier to entry. Very few organizations possess the sheer volume of resources and the appetite for such a massive initial outlay. The sheer cost of setting up and operating a compliant financial institution is a major deterrent, effectively limiting the pool of potential new competitors.
Established brand loyalty and trust present a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to compete with incumbent institutions like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank. These established banks often boast decades of service, fostering deep community relationships and a reputation for reliability. For instance, in 2023, major state-owned banks in China, which often have long histories, maintained a dominant market share, reflecting the enduring power of brand recognition and customer confidence in the financial sector.
Difficulty in Building Distribution Networks
Building a widespread distribution network, crucial for customer accessibility and service delivery in banking, presents a significant barrier for new entrants targeting Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank. Establishing a physical branch network and ATM infrastructure requires immense capital investment and considerable time. For instance, by the end of 2023, Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank operated a substantial number of branches and self-service terminals across its service area, a network built over years. This extensive physical presence is a formidable hurdle for newcomers aiming to replicate its reach and customer touchpoints.
While digital-only banks can potentially circumvent some of the capital expenditure associated with physical branches, they still face the challenge of developing sophisticated digital platforms and implementing effective customer acquisition strategies to gain market share. Even with digital innovation, reaching a broad customer base comparable to established players like Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank demands significant marketing and technological investment. The existing distribution channels, both physical and digital, of incumbent banks offer a substantial competitive advantage that new entrants must overcome.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the sheer difficulty and expense of replicating the distribution capabilities of established institutions. Consider the following points:
- Capital Intensity: The cost of establishing a nationwide or even a regionally significant branch and ATM network can run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
- Time to Market: Building brand recognition and customer trust alongside a physical network takes years, if not decades.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining licenses and approvals to operate a banking network involves stringent regulatory compliance, adding to the time and cost.
- Digital Infrastructure Costs: Even digital-first banks require substantial investment in secure, scalable, and user-friendly online and mobile banking platforms.
Talent Acquisition Challenges
New entrants into the banking sector, particularly in a competitive market like Dongguan, face considerable hurdles in attracting skilled personnel. This includes securing experienced loan officers, robust risk managers, essential IT specialists, and diligent compliance experts.
The scarcity of top-tier talent, coupled with intense competition from established financial institutions, makes the process of talent acquisition both a significant and potentially very expensive challenge for any new bank. This difficulty is amplified because specialized banking expertise is not easily replicated or quickly developed.
- Talent Scarcity: Reports from 2024 indicate a persistent shortage of experienced financial professionals across China, with demand often outstripping supply, especially in specialized roles.
- Competition for Expertise: Established banks in regions like Guangdong province often offer competitive compensation packages and career advancement opportunities, making it difficult for new entrants to lure away seasoned employees.
- High Acquisition Costs: The need for competitive salaries, signing bonuses, and extensive training programs can significantly increase the initial operating costs for new banks, impacting their profitability and market entry strategy.
The threat of new entrants for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank is significantly low due to the immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory landscape in China's banking sector. Aspiring banks need to meet substantial capital adequacy ratios, with Tier 1 capital often needing to exceed 10% as of early 2024, a substantial barrier for newcomers. Furthermore, the complex and lengthy licensing process, demanding years of compliance and proof of stability, effectively deters potential competitors from entering the market.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Dongguan Rural Commercial Bank is built upon a foundation of official financial statements, regulatory filings from Chinese banking authorities, and industry-specific reports from reputable financial data providers. We also incorporate market share data and competitor analysis from leading economic research firms to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
