Drax Group plc Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Drax Group plc Bundle
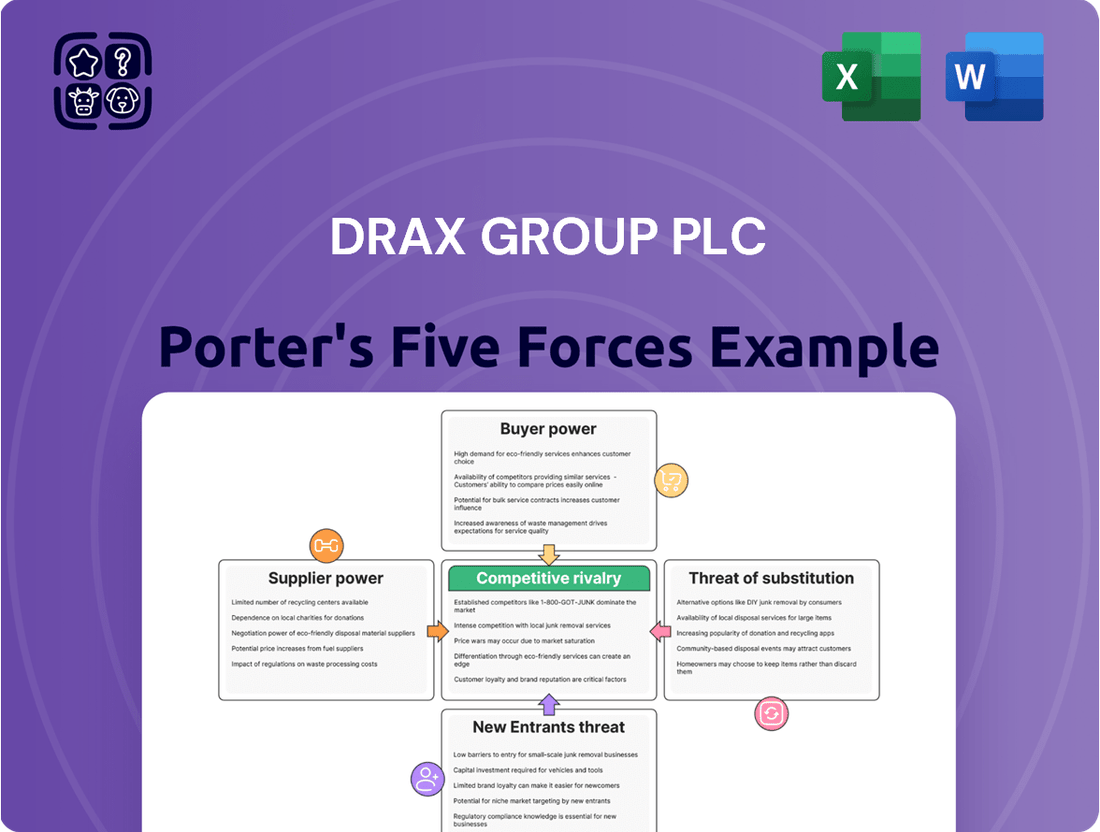
Drax Group plc navigates a complex energy landscape, where intense competition from rivals and the looming threat of substitute energy sources significantly shape its market position. Understanding the power of buyers and the influence of suppliers is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Drax Group plc’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Drax Group plc's reliance on sustainable biomass, around 9 million tonnes in 2024, makes the concentration of its suppliers a critical factor in their bargaining power. With the majority of this fibre, approximately 66.7%, originating from the United States and another 23.4% from Canada, the supplier landscape in North America is particularly influential.
If a few dominant, specialized biomass providers control a significant portion of this supply, they could leverage their position to dictate higher prices or more stringent contract terms to Drax. This concentration means Drax has fewer alternatives, thereby increasing the suppliers' ability to exert pressure.
The unique sustainability criteria for biomass, including UK Government standards, Forest Europe criteria, and UK Timber Regulation, along with a preference for Sustainable Biomass Program (SBP) certification, create a specialized supply chain. This specialization narrows the field of eligible suppliers, potentially boosting the bargaining power of those who meet these rigorous requirements.
Drax's proactive supplier engagement, including site visits and audits, aims to foster strong relationships and ensure compliance. This deep integration makes it costly for Drax to switch biomass suppliers. The financial year 2023 saw Drax's biomass procurement costs rise, highlighting the importance of these supplier relationships.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by biomass suppliers poses a potential increase in their bargaining power against Drax Group. If suppliers were to enter electricity generation or carbon removal, they could capture more of the value chain, making Drax more dependent on them.
While direct biomass suppliers are unlikely to integrate forward due to the high capital costs of power generation, larger, more diversified forestry companies might consider such a strategic move. This would allow them to directly benefit from the energy market and potentially carbon credit revenues.
For instance, a major forestry conglomerate with significant landholdings and existing processing capabilities could invest in biomass power plants or carbon capture facilities. This would shift the power dynamic, as Drax would then be competing with its own suppliers for market share and profitability in these related sectors.
The capital expenditure required for establishing electricity generation facilities is substantial, acting as a significant deterrent for many smaller biomass suppliers. However, for established players in the forestry sector, this barrier might be surmountable, especially with favorable government incentives for renewable energy and carbon capture technologies. For example, in 2023, the UK government continued to offer Contracts for Difference (CfD) for renewable electricity generation, which could make forward integration more attractive for large biomass producers.
Availability of Substitute Inputs for Drax
The availability of substitute inputs for Drax significantly impacts the bargaining power of its biomass suppliers. If alternative fuel sources or energy inputs become readily available and economically viable for Drax's power stations, the leverage held by current biomass suppliers would diminish. This is crucial as Drax's primary generation relies heavily on biomass.
Drax's operational diversification, including its hydro and pumped storage assets, further dilutes the bargaining power of biomass suppliers. While biomass is central to its thermal generation, these other generation methods mean Drax is not entirely dependent on a single fuel source for its overall energy output. This reduces the overall pressure from any single group of suppliers.
- Biomass Dependency: Drax's core business is heavily reliant on biomass, making its primary suppliers influential.
- Substitute Input Viability: The economic feasibility and availability of alternative fuels for its power stations directly counter supplier power.
- Diversified Generation Portfolio: Drax's operation of hydro and pumped storage assets reduces its overall reliance on biomass suppliers for its entire energy generation.
- Mitigation of Supplier Leverage: By having multiple energy sources, Drax can negotiate more effectively with individual fuel suppliers, including those for biomass.
Drax Group's significant reliance on biomass, estimated at around 9 million tonnes for 2024, places considerable influence in the hands of its suppliers, particularly those concentrated in North America where approximately 90.1% of its fibre originates. The specialized nature of biomass, requiring adherence to stringent sustainability and certification standards such as SBP, further concentrates the supplier base, empowering those who meet these criteria. Drax's deep integration and the rising costs of biomass procurement, noted in FY 2023, underscore the substantial bargaining power held by its key biomass providers.
| Biomass Supply Source (2024 Estimate) | Percentage of Drax's Fibre |
|---|---|
| United States | 66.7% |
| Canada | 23.4% |
| Other Regions | 9.9% |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Drax Group plc dissects the competitive forces shaping its industry, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces for Drax Group plc.
Customers Bargaining Power
Drax Group plc's customer base includes large industrial and commercial energy users in the UK. The concentration of these significant consumers can translate into substantial bargaining power, particularly if they have the flexibility to switch suppliers or consider on-site energy generation.
For instance, in 2024, the UK's industrial electricity consumption represented a notable portion of the overall market. Large industrial clients, often operating with tight margins, are highly sensitive to energy costs and are therefore motivated to negotiate favorable terms, potentially leveraging alternative energy sources or supplier competition.
The UK energy market offers customers a growing array of energy sources, from wind and solar to nuclear and gas. This diversification directly impacts customer bargaining power. In 2024, renewables accounted for over 50% of the UK's electricity generation, providing consumers with more alternatives to traditional providers like Drax.
For large industrial or commercial customers of Drax Group, the physical costs associated with switching electricity providers are generally quite low. While there are administrative and contractual steps involved, the actual process of changing suppliers doesn't typically require significant investment in new equipment or infrastructure.
This low switching barrier directly translates into increased bargaining power for these customers. They can easily explore and move to competitors that offer more favorable pricing, better service level agreements, or more attractive contract terms, putting pressure on Drax to remain competitive.
For instance, in the UK energy market, where Drax operates, the ease of switching has been a key feature, with Ofgem reporting millions of consumers switching suppliers annually. This high churn rate underscores the limited lock-in effect for customers, enhancing their ability to negotiate.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers, particularly large industrial consumers, exhibit significant price sensitivity. Fluctuations in electricity prices directly impact their operational expenditures, making cost a primary decision-making factor. This sensitivity means Drax must maintain competitive pricing to retain these crucial clients.
The UK wholesale power market has seen price declines in recent years. For instance, average wholesale electricity prices in the UK were around £45-£55 per megawatt-hour (MWh) for much of 2023, down from peaks seen in 2022. This downward trend directly affects Drax's revenue and profit margins, underscoring the importance of managing costs and offering attractive pricing to customers.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: Industrial customers are highly attuned to electricity costs, as these represent a substantial portion of their operating expenses.
- Impact of Falling Wholesale Prices: Declining wholesale power prices in the UK, observed in 2023, have put pressure on Drax's profitability, highlighting customer demands for lower rates.
- Competitive Landscape: Drax operates in a market where customers can switch suppliers, making price a key differentiator and a critical factor in maintaining market share.
Potential for Backward Integration by Customers
While uncommon, very large industrial consumers with substantial energy needs could consider generating their own power, for example, through on-site renewable installations. This potential for backward integration, even if rarely exercised, can serve as a latent source of bargaining power for customers.
For instance, a major industrial player might evaluate the economics of installing solar farms or small-scale wind turbines to offset a portion of their electricity consumption from suppliers like Drax Group. This capability, even if theoretical, forces energy providers to remain competitive on pricing and service to retain such clients.
- Potential for backward integration by large industrial consumers.
- On-site renewable installations as an example.
- Serves as a latent source of bargaining power.
- Incentivizes competitive pricing from energy providers.
Drax Group's large industrial and commercial customers wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial energy consumption and the availability of alternatives. In 2024, the UK energy market's increasing reliance on renewables, which constituted over 50% of generation, provided these customers with more options beyond traditional suppliers like Drax. This, coupled with low switching costs, incentivizes competitive pricing and service from Drax.
The price sensitivity of these customers is a key factor. For example, a drop in UK wholesale electricity prices to around £45-£55 per MWh in 2023, down from previous highs, directly influences their negotiation stance. Furthermore, the potential for large consumers to explore on-site generation, while not always exercised, acts as a latent pressure point, compelling Drax to maintain attractive offers.
| Factor | Impact on Drax | Customer Action/Leverage | 2024 Data/Context |
| Customer Concentration | High | Large buyers can negotiate bulk discounts. | Significant portion of UK industrial users are large-scale consumers. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Moderate | Customers can switch to competitors or alternative energy sources. | Renewables >50% of UK generation in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Customers can easily change suppliers to secure better terms. | Millions of UK consumers switch suppliers annually. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Customers demand lower prices, impacting Drax's margins. | Wholesale prices fell to £45-£55/MWh in 2023. |
| Potential for Backward Integration | Low (Latent) | Customers may consider self-generation, pressuring prices. | On-site solar/wind installations are feasible for large users. |
What You See Is What You Get
Drax Group plc Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Drax Group plc, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company within the energy sector. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights without any placeholders or surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The UK energy sector features a dynamic competitive landscape. Drax faces rivals ranging from established utilities like EDF Energy and RWE to a growing number of renewable energy developers focused on wind and solar power.
In 2024, the UK government continued to push for decarbonization, intensifying competition among diverse energy sources. Drax’s biomass and flexible generation assets compete directly with the expanding capacity of offshore wind farms, which saw significant investment throughout the year, and the ongoing contributions from nuclear and gas-fired power plants.
The United Kingdom's electricity demand is on an upward trajectory, fueled by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and heat pumps, alongside the burgeoning needs of AI and data centers. This surge necessitates substantial investment in new power generation capacity.
While this expanding market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, it also sharpens competitive pressures. Companies are actively competing to secure market share within these evolving and growing sectors of the energy landscape.
Drax Group plc distinguishes itself by focusing on dispatchable renewable power derived from sustainable biomass. Its ambitious development of Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) technology positions it as a leader aiming for carbon negativity, a significant differentiator in the energy market.
While BECCS can lessen direct competition with traditional power generators, Drax still faces rivalry within the broader renewable and low-carbon energy sector. For instance, in 2024, the UK government continued to support various renewable technologies, including offshore wind and solar, through competitive auctions, creating a landscape where multiple low-carbon solutions vie for market share and policy support.
Exit Barriers
Drax Group faces substantial exit barriers due to the immense capital tied up in its power generation assets. For instance, the construction and maintenance of its biomass power stations represent significant, long-term investments. These high upfront costs and specialized nature of the infrastructure make it exceptionally difficult and costly to divest or repurpose these assets.
These considerable exit barriers mean that companies like Drax are often locked into the industry, even when market conditions are unfavorable. This persistence can intensify competitive rivalry, as firms are less likely to exit during periods of low profitability, instead choosing to continue operating, potentially leading to price wars or a struggle for market share.
- High Capital Intensity: Drax's investment in biomass pellet plants and associated logistics, such as its own pellet production facilities, represents billions in capital expenditure, creating a significant hurdle for exiting the market.
- Specialized Assets: Power generation infrastructure, particularly for specific fuel types like biomass, is highly specialized and lacks readily available alternative uses, increasing the cost and difficulty of disposal.
- Industry Persistence: The inability to easily exit forces companies to remain competitive, potentially exacerbating rivalry as firms strive to maintain profitability despite challenging market dynamics.
Strategic Commitments and Future Investments
Drax's substantial strategic commitments, including its focus on Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) and flexible generation, alongside securing government contracts for difference (CfDs), clearly signal its long-term competitive posture. For instance, Drax has invested £2 million in its BECCS development pipeline. This forward-looking strategy directly influences the competitive landscape.
The energy sector is characterized by intense rivalry as other major players are also making significant investments in a range of low-carbon technologies. These include substantial outlays in offshore wind, solar power, and other renewable energy solutions. For example, in 2023, the UK government announced plans to invest £20 billion in offshore wind projects, highlighting the scale of this competition.
- BECCS Investment: Drax's commitment to BECCS, aiming for negative emissions, positions it uniquely but also invites competition from other carbon reduction technologies.
- Flexible Generation: The emphasis on flexible generation is crucial in a grid increasingly reliant on intermittent renewables, requiring ongoing innovation and investment.
- Pellet Production Expansion: Expanding pellet production capacity, a key feedstock for its biomass generation, is a strategic move to secure supply chains, a factor other energy producers also consider.
- Government Support: Securing CfDs provides a revenue certainty that influences investment decisions and competitive advantages for Drax, a model other renewable developers seek to emulate.
Competitive rivalry within the UK energy sector remains intense, with Drax Group plc navigating a landscape populated by established utilities and emerging renewable energy firms. The drive towards decarbonization, a key government objective in 2024, fuels this rivalry as diverse energy sources compete for market share and policy support.
Drax's strategic focus on dispatchable biomass power, particularly its investment in Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS), differentiates it but doesn't eliminate competition. Other players are heavily investing in offshore wind, solar, and nuclear power, creating a multi-faceted competitive environment. For instance, the UK's commitment to offshore wind saw significant investment in 2023, with plans for £20 billion in projects.
The high capital intensity and specialized nature of power generation assets create significant exit barriers for companies like Drax, fostering industry persistence. This means firms are less likely to withdraw during periods of lower profitability, potentially leading to sustained competitive pressure and a continuous effort to secure market share and favorable government contracts.
| Competitor Type | Key Focus Areas | 2024 Competitive Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Established Utilities (e.g., EDF, RWE) | Diverse generation portfolios, grid infrastructure | Maintaining market share, adapting to decarbonization mandates |
| Renewable Developers (Wind, Solar) | Intermittent renewable generation, grid connection | Securing CfDs, expanding capacity through auctions |
| Other Low-Carbon Solutions | Nuclear, hydrogen, energy storage | Developing new technologies, seeking policy support |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The UK's renewable energy sector is booming, with substantial growth in wind and solar power. These technologies are increasingly affordable and directly compete with biomass electricity, particularly as the grid accommodates more variable renewable sources.
The threat of substitutes for Drax Group plc is significantly influenced by the rapid advancement of new energy technologies and storage solutions. For instance, the increasing efficiency and decreasing cost of large-scale battery storage systems, like those deployed by companies such as Tesla, directly challenge the need for traditional dispatchable power sources. These battery farms can store excess renewable energy and release it when demand peaks or when intermittent sources like wind and solar are unavailable, effectively substituting the grid balancing services Drax's biomass plants provide.
Furthermore, the development of long-duration energy storage systems, such as compressed air energy storage (CAES) or flow batteries, offers a more direct substitute for the continuous power generation capabilities of biomass. These technologies are gaining traction, with projects like the Advancion Energy Storage project in the UK demonstrating the growing capacity of battery storage to meet grid demands. As these storage solutions become more widespread and cost-effective, they diminish the unique value proposition of dispatchable power generation, posing a substantial threat to Drax's market position.
Government policy significantly shapes the energy landscape, impacting the attractiveness of biomass as an energy source. While the UK government has historically offered transitional support for large-scale biomass operations, such as Drax's conversion to biomass, there's a clear and accelerating push towards other clean energy technologies. For instance, the UK's commitment to offshore wind, with targets for significant capacity increases by 2030, and continued investment in nuclear power, presents strong alternative pathways for decarbonization.
Public Perception and Environmental Concerns
Public and scientific scrutiny regarding the sustainability of large-scale biomass burning, like that undertaken by Drax, can significantly elevate the perceived viability of alternative renewable energy sources. For instance, in 2023, the UK government's Department for Energy Security and Net Zero reported that solar power generation increased by 12% compared to 2022, reaching new highs. This growing acceptance of solar and wind, often viewed as unequivocally clean, presents a potent substitute threat.
Negative public perception or the imposition of stricter environmental regulations could further accelerate the shift towards these alternatives. Companies heavily reliant on biomass may face increased operational costs or reduced market share if public sentiment turns against their primary energy source. The increasing global focus on carbon neutrality, with many nations setting ambitious targets, means that energy sources perceived as having a higher environmental impact will likely face greater pressure.
- Growing acceptance of solar and wind power: In 2023, solar PV capacity in the EU grew by over 25 GW, demonstrating a strong market trend towards these alternatives.
- Increased regulatory scrutiny: Future regulations on carbon emissions and land-use for biomass sourcing could increase costs for Drax, making substitutes more competitive.
- Public perception as a driver of change: A significant portion of the public now favors renewable energy sources with lower perceived environmental footprints, influencing investment and policy decisions.
Decentralized Energy Generation
The increasing adoption of decentralized energy generation presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional power providers like Drax Group. Rooftop solar installations and community energy schemes empower consumers to generate their own electricity, directly reducing demand for grid-supplied power.
In 2024, the UK saw continued growth in distributed energy resources. For instance, the total installed capacity of solar PV in the UK reached approximately 15 GW by the end of 2023, with residential rooftop solar being a substantial contributor. This trend is expected to accelerate as battery storage costs decrease, making self-consumption more viable.
- Growing Rooftop Solar Capacity: Residential solar PV installations continue to expand, offering a direct alternative to grid electricity.
- Community Energy Projects: Localized energy generation and sharing models reduce reliance on large, centralized power plants.
- Falling Storage Costs: Advancements in battery technology are making it more economical for consumers to store and use their own generated power.
- Policy Support: Government incentives and supportive regulations in various regions encourage the uptake of decentralized energy solutions.
The surge in renewable energy sources, especially wind and solar, directly challenges biomass. These technologies are becoming more efficient and affordable, and the grid is better equipped to handle their variability. For example, in 2024, the UK's installed offshore wind capacity continued its upward trajectory, providing a substantial source of clean electricity that competes for market share.
The increasing viability of energy storage solutions, like advanced battery systems, offers another potent substitute. These systems can store excess renewable energy and release it when needed, mimicking the dispatchable nature of biomass and reducing the need for Drax's services. The UK government's ongoing support for grid-scale battery projects, with several gigawatt-scale installations coming online, underscores this trend.
Technological advancements in long-duration storage, such as compressed air or flow batteries, further strengthen the threat of substitutes. These are emerging as viable alternatives for providing consistent power, directly impacting the value proposition of traditional baseload power generation. As these technologies mature and become more cost-effective, they will increasingly displace incumbent solutions.
| Energy Source | 2023 UK Capacity (GW) | Growth Trend | Substitute Threat Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offshore Wind | ~14.7 | Strongly Increasing | High |
| Solar PV | ~15.0 (end of 2023) | Increasing | Medium to High |
| Battery Storage | Growing rapidly (specific figures vary by project) | Strongly Increasing | Medium to High |
Entrants Threaten
The capital intensity of power generation presents a significant barrier to new entrants in the sector. Establishing large-scale facilities, particularly those utilizing advanced technologies like biomass conversion or carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS), demands immense financial resources. For instance, Drax Group plc's own strategic investments in pellet production facilities and its ambitious Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) projects underscore the substantial capital outlay required to enter and compete effectively in this market.
The UK energy sector's stringent regulatory environment acts as a considerable barrier to new entrants. Obtaining the necessary licenses, environmental permits, and adhering to grid connection standards demands significant investment and expertise. For instance, new power generation projects, especially those exploring innovative technologies like Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS), face a complex and lengthy approval process. This regulatory maze effectively deters many potential competitors from entering the market, thereby protecting established players like Drax Group plc.
The threat of new entrants regarding access to sustainable biomass supply chains for Drax Group is moderate. Drax has invested heavily in developing a global, integrated supply chain, including its own pellet production facilities, ensuring a stable and sustainable source of fuel. For instance, in 2023, Drax continued to expand its pellet production capacity, with its pellet plants in the US and Canada playing a crucial role in its biomass supply.
New competitors would face significant hurdles in replicating this established infrastructure and securing the necessary volume of sustainably sourced biomass. Meeting stringent sustainability certifications and navigating complex international logistics for biomass procurement presents a substantial barrier to entry, requiring considerable capital investment and expertise.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Drax Group plc benefits significantly from substantial economies of scale, particularly in operating the UK's largest biomass power station. This operational scale translates into lower per-unit production costs. For instance, in 2023, Drax's biomass generation capacity stood at 2.6 GW, a considerable advantage.
The experience curve effect also plays a crucial role. Having operated and optimized its biomass facilities for years, Drax has developed efficiencies and expertise that are difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly. This accumulated knowledge allows for smoother operations and better cost management.
Potential new entrants would likely face considerably higher per-unit costs during their initial operational phases. Without achieving a similar scale of operations or the benefit of years of experience, competing on price with Drax would be a significant challenge.
- Economies of Scale: Drax operates the UK's largest biomass power station, a significant asset that allows for cost efficiencies not easily matched by smaller operations.
- Experience Curve: Years of operational experience in biomass conversion and fuel sourcing have honed Drax's efficiency, reducing costs through learning and optimization.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: New players would likely incur higher initial operating costs due to a lack of scale and established operational expertise, hindering price competitiveness.
- Biomass Pellet Production: Drax's integrated biomass pellet production further enhances its economies of scale, providing a cost advantage in fuel sourcing.
Government Support and Incumbency Advantage
Drax benefits from existing government support, like Contracts for Difference (CfDs), which offer revenue certainty for its biomass operations. For instance, in 2023, Drax announced a £1.5 billion investment in its UK biomass operations, partly supported by these mechanisms. These long-term revenue support schemes are crucial for large capital-intensive projects, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on a level playing field.
The evolving regulatory landscape and the need for substantial, long-term government backing for new renewable energy projects present a significant barrier. Incumbents like Drax have established relationships and a track record that often facilitates access to such support, creating an incumbency advantage. This makes it challenging for potential new entrants to secure the necessary financial and regulatory backing for comparable large-scale developments.
The threat of new entrants for Drax Group plc is generally considered low due to substantial capital requirements for power generation facilities and the complex regulatory environment in the UK energy sector. These factors, combined with Drax's established economies of scale and experience curve advantages in biomass operations, create significant barriers to entry.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Drax Group plc is built upon a foundation of publicly available information, including their annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate industry-specific data from market research reports and trade publications.
