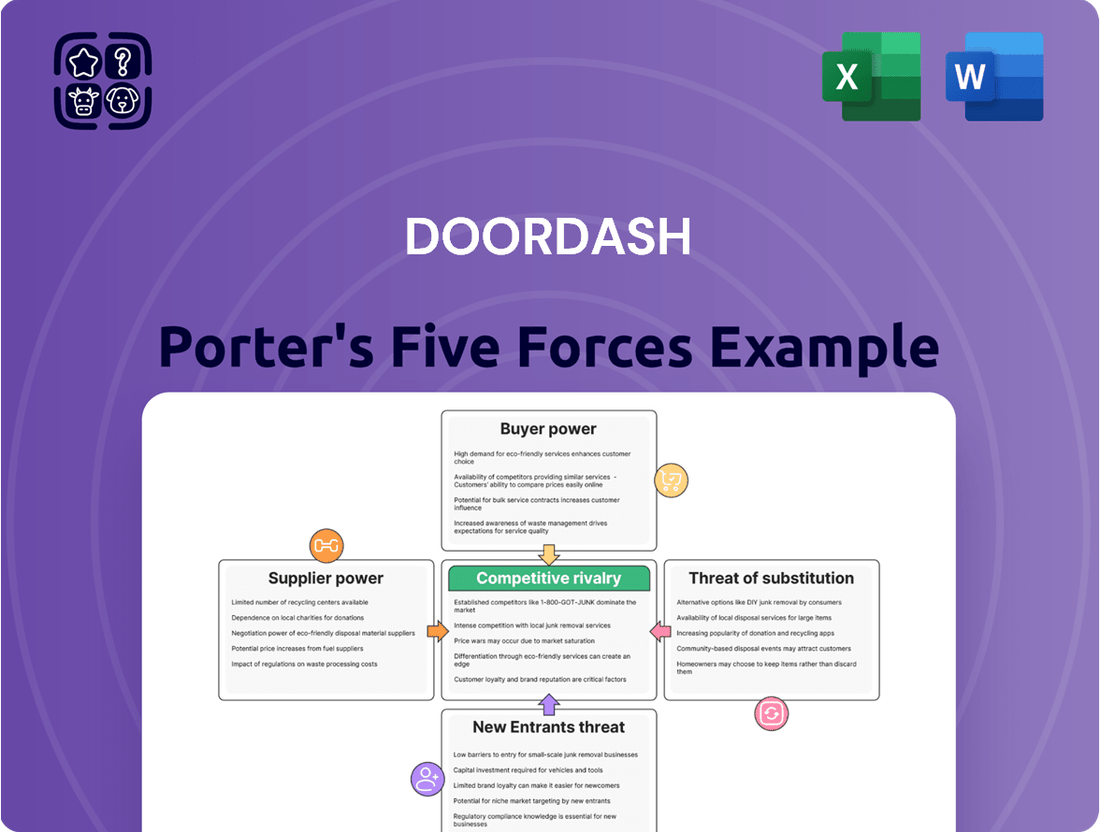
DoorDash Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DoorDash Bundle
DoorDash navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the ever-present threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for anyone looking to grasp DoorDash's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping DoorDash’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Major restaurant chains, leveraging their strong brand recognition and substantial order volumes, can negotiate more favorable commission structures with DoorDash. This bargaining power is significant, as DoorDash's standard commission fees often fall between 15% and 30% of each order's value, making these rates a crucial point of discussion.
Furthermore, the widespread practice of merchants listing their services across multiple delivery platforms inherently diminishes their reliance on any single provider. This multi-platform presence grants them increased leverage in negotiations, allowing them to play platforms against each other to secure better terms.
Dashers, classified as independent contractors, wield significant bargaining power because they are the very engine of DoorDash's service. Their willingness to accept deliveries directly dictates DoorDash's ability to fulfill orders promptly and maintain service quality. In 2024, DoorDash continued to navigate discussions around Dasher pay and benefits, a key factor influencing driver retention and operational expenses.
The ease with which Dashers can switch between delivery platforms presents a substantial challenge to DoorDash. With minimal switching costs, drivers can readily opt for competitors offering more favorable pay structures or working conditions. This mobility means DoorDash must constantly compete for driver availability, impacting its capacity to scale operations efficiently.
DoorDash's reliance on technology providers for mapping, payments, and cloud services means these suppliers hold a degree of bargaining power, particularly if their offerings are specialized or crucial to operations. The company's substantial technology investments, reaching $820 million in the fourth quarter of 2023, underscore this dependence on specialized tech partners.
While DoorDash's considerable market presence can provide some leverage in negotiations, the indispensable nature of certain technology providers ensures they retain influence over the platform. This dynamic is key to understanding the operational costs and strategic partnerships within the food delivery sector.
Grocery and New Vertical Partners
DoorDash's expansion into grocery and new verticals significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. Major grocery chains, with their established customer bases and substantial order volumes, can negotiate favorable terms due to their market presence. For instance, in 2024, large supermarket chains continued to be key partners, and their ability to direct significant consumer demand to DoorDash gives them leverage in commission rate discussions.
The success of DoorDash in these new segments hinges on striking a balance. DoorDash needs to secure partnerships with these merchants on terms that ensure the merchants remain profitable while simultaneously offering competitive pricing to end consumers. This dynamic is crucial for DoorDash's growth strategy beyond its core restaurant delivery business.
- Merchant Leverage: Large grocery chains and major retailers possess significant bargaining power due to their brand recognition and the potential for high order volumes, influencing DoorDash's commission structures and service level agreements.
- Partnership Dependence: DoorDash's ability to attract and retain customers in new verticals like grocery and convenience is directly tied to its partnerships with these merchants, making favorable terms essential.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: DoorDash must balance the need for merchant profitability with the imperative to offer competitive delivery prices to consumers, a key factor in supplier negotiations.
Labor Market Conditions
Labor market conditions significantly impact DoorDash's bargaining power with its suppliers, which in this case are the Dashers. When the overall labor market is tight, or when there's widespread dissatisfaction with gig economy pay, DoorDash faces increased pressure. This can force them to offer better compensation to attract and retain enough delivery drivers.
For instance, in 2024, many gig workers expressed concerns about stagnant pay rates despite rising inflation. This sentiment can translate into a reduced willingness to work for DoorDash unless incentives or base pay are improved. Such a scenario directly increases DoorDash's operating expenses.
- Labor Shortages: A general shortage of available workers in the broader economy can make it harder for DoorDash to recruit and retain Dashers, giving existing Dashers more leverage.
- Gig Worker Sentiment: Widespread dissatisfaction with pay-per-delivery rates, as observed in various reports throughout 2024, can lead to a reduced supply of Dashers, pushing DoorDash to offer higher compensation.
- Alternative Opportunities: The availability of other gig work or traditional employment with better benefits and pay can draw Dashers away from DoorDash, weakening DoorDash's control over its delivery workforce.
The bargaining power of suppliers, primarily Dashers and technology providers, significantly influences DoorDash's operational costs and strategic flexibility. Dashers, as independent contractors, can exert considerable leverage, especially in tight labor markets. In 2024, DoorDash faced ongoing discussions regarding driver compensation and benefits, directly impacting its ability to maintain a sufficient and motivated delivery fleet.
Technology suppliers also hold sway, particularly those offering specialized services critical to DoorDash's platform functionality. The company's substantial investments in technology, exemplified by the $820 million expenditure in Q4 2023, highlight its dependence on these partners and the associated bargaining power they possess.
Major restaurant and grocery chain partners also wield significant influence. Their substantial order volumes and brand recognition allow them to negotiate more favorable commission rates, often between 15% and 30%, affecting DoorDash's revenue streams. This is particularly evident in DoorDash's expansion into new verticals like grocery delivery, where large chains can leverage their market position.
| Supplier Type | Key Leverage Factors | Impact on DoorDash |
|---|---|---|
| Dashers (Gig Workers) | Labor market tightness, driver satisfaction, availability of alternative work | Influences driver recruitment, retention, and compensation costs. In 2024, concerns over pay rates impacted driver supply. |
| Technology Providers | Specialized services, platform integration, switching costs | Affects operational efficiency and costs. DoorDash's $820M tech investment in Q4 2023 underscores reliance. |
| Merchants (Restaurants & Grocers) | Brand recognition, order volume, multi-platform presence | Dictates commission structures (15-30%), partnership terms, and service level agreements. Large chains have significant negotiating power. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the five competitive forces impacting DoorDash, examining supplier power, buyer bargaining power, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the food delivery industry.
Leverage DoorDash's Porter's Five Forces analysis to instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats, ensuring a robust strategy for sustained market leadership.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers hold significant sway over DoorDash due to their low switching costs. It takes mere minutes for a consumer to download and navigate alternative food delivery apps, such as Uber Eats or Grubhub, making it incredibly easy to compare options.
This ease of switching means customers can readily shop around for the best prices, fastest delivery times, or a wider restaurant selection without much effort or expense. This directly fuels competition among delivery platforms, as they must constantly vie for customer attention and loyalty.
In 2024, the food delivery market remains highly competitive, with DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Grubhub all actively engaging in promotional activities and price adjustments to attract and retain users, underscoring the impact of low switching costs.
Customers today have an abundance of choices, with a significant 87% of food delivery app users in 2024 having multiple platforms on their phones. This widespread multi-homing means consumers can easily compare and select the best deal for each order, be it a discount, quicker delivery, or a preferred restaurant. This accessibility to alternatives directly amplifies customer bargaining power against platforms like DoorDash.
DoorDash and its competitors frequently offer promotions and discounts, a key factor that significantly enhances the bargaining power of customers. These incentives, including new user bonuses, are a major driver in attracting and keeping users on their platforms. DoorDash's substantial marketing investment in 2024 directly supports this approach, ensuring customers can often find attractive deals, thereby reducing their effective spending.
Direct Ordering from Restaurants
Customers can exert significant bargaining power by choosing to order directly from restaurants, bypassing third-party delivery platforms like DoorDash. This direct channel is particularly appealing for those who prefer dining in or picking up their food themselves. By ordering directly, consumers can often avoid service fees charged by delivery apps and may gain access to exclusive restaurant promotions or loyalty rewards. In 2024, it’s estimated that around 30% of all restaurant orders were placed directly with the establishment, highlighting this as a substantial alternative that can influence platform usage.
- Direct Ordering as a Substitute: Customers can bypass platform fees by ordering directly from restaurants.
- Access to Exclusive Benefits: Direct orders may unlock restaurant-specific loyalty programs and discounts.
- Market Share of Direct Orders: Approximately 30% of restaurant orders in 2024 were placed directly, indicating significant customer preference for this channel.
Price Sensitivity and Delivery Fees
Customers are often quite sensitive to the total cost of their food delivery orders, with delivery fees and service charges playing a significant role in their decision-making. This means DoorDash must carefully manage its pricing to stay competitive. For instance, a significant portion of customers might abandon their carts if the delivery fee exceeds a certain threshold, impacting order volume.
This price sensitivity directly influences DoorDash's strategy. They need to strike a delicate balance between keeping fees low enough to attract and retain customers and high enough to cover operational costs and generate profit. If delivery costs become too burdensome, customers are likely to explore alternatives, such as picking up food themselves or opting for rival delivery services with lower fees.
- Price Sensitivity: DoorDash customers frequently compare total order costs, including delivery and service fees, across different platforms.
- Fee Impact: High delivery fees can lead to cart abandonment, with studies indicating that over 60% of consumers are likely to cancel an order due to high delivery costs.
- Competitive Pressure: DoorDash must continually evaluate its fee structure against competitors to maintain market share, especially in price-sensitive urban areas.
The bargaining power of customers is a significant force impacting DoorDash. Their ability to easily switch between delivery platforms, often driven by price sensitivity and the availability of promotions, means DoorDash must remain competitive. The prevalence of customers using multiple apps in 2024, with 87% having more than one platform on their phones, highlights this ease of comparison and choice.
| Factor | Impact on DoorDash | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Customers can easily move to competitors like Uber Eats or Grubhub. | 87% of users have multiple food delivery apps installed. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are highly aware of total order costs, including fees. | Over 60% of consumers abandon carts due to high delivery fees. |
| Direct Ordering Alternative | Customers can bypass platforms by ordering directly from restaurants. | Approximately 30% of restaurant orders are placed directly. |
| Promotional Reliance | Discounts and offers are key to customer acquisition and retention. | DoorDash invests heavily in marketing and promotions to attract users. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
DoorDash Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact DoorDash Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. Understand the strategic landscape and competitive pressures impacting DoorDash with this comprehensive, ready-to-use document.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. food delivery landscape is a battleground dominated by a few key players. DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Grubhub are the primary forces, constantly vying for supremacy.
DoorDash has solidified its position as the market leader in the United States, commanding an impressive market share estimated between 60% and 67% in 2024-2025. However, this strong standing is continually tested by the aggressive tactics and strategic maneuvers of its closest competitors, Uber Eats and Grubhub.
The intense market concentration means that any significant move by one of these giants, such as DoorDash's expansion into new services or Uber Eats' promotional campaigns, directly influences the strategies and market share of the others, creating a dynamic and highly competitive environment.
Competitive rivalry within the food delivery sector, including DoorDash, is fierce, driven by aggressive pricing and frequent promotional wars. This includes widespread discounts, free delivery initiatives, and subscription services like DashPass, all aimed at capturing and keeping customers. DoorDash's significant marketing expenditures highlight the intensity of these efforts, which are essential given the low customer switching costs.
These constant incentives, while attracting users, put considerable pressure on profit margins for all players in the market. For instance, DoorDash reported marketing and sales expenses of $1.1 billion in 2023, a testament to the ongoing battle for market share through customer acquisition and retention programs.
Competitive rivalry is intensifying as major platforms like DoorDash expand beyond their core restaurant delivery into new verticals such as groceries, convenience store items, and alcohol. This diversification means competitors are now vying for market share across a broader range of local commerce services, further intensifying the competitive landscape.
In 2024, DoorDash's expansion into grocery delivery saw significant growth, with the company reporting a substantial increase in the number of grocery partners and order volume. This strategic move directly pits DoorDash against established grocery retailers and other delivery platforms, creating a more crowded and competitive market for last-mile delivery services.
Technological Innovation and Operational Efficiency
DoorDash's competitive rivalry is heavily influenced by technological innovation and operational efficiency. Companies in the food delivery space constantly pour resources into developing better logistics, smarter routing, and more user-friendly apps to stand out. DoorDash's significant investment in its technology platform, which underpins its efficient service and customer experience, acts as a crucial differentiator and a hurdle for new entrants.
The company’s operational expertise is a key factor in its ability to manage a vast network of restaurants and delivery personnel effectively. For instance, DoorDash reported an increase in Gross Order Value (GOV) to $18.0 billion in the first quarter of 2024, showcasing the scale of its operations. Maintaining a lead in technology and efficiency is paramount for DoorDash to sustain its market position against competitors like Uber Eats and Grubhub, which are also heavily investing in these areas.
- Technological Advancement: DoorDash continuously refines its algorithms for optimal delivery routes, aiming to reduce delivery times and costs, a critical factor in customer retention.
- Operational Scale: The company’s ability to manage a large volume of orders efficiently, as evidenced by its growing GOV, provides a competitive advantage through economies of scale.
- User Experience: Investments in app functionality and customer service are vital for attracting and keeping both consumers and Dashers, directly impacting market share.
- Investment in R&D: Ongoing research and development in areas like AI-powered logistics and new delivery models are essential to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving sector.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
DoorDash actively shapes its competitive environment through strategic acquisitions and partnerships, aiming to broaden its operational footprint and deepen its service capabilities. The company's acquisition of Wolt in 2022 for approximately $8 billion, for instance, significantly expanded its presence in Europe and other international markets. These moves are crucial for consolidating market power and creating more robust network effects.
These strategic maneuvers are designed to directly counter the growth of rivals by increasing DoorDash's market share and diversifying its revenue streams. By integrating new services and customer bases, DoorDash aims to build a more resilient and dominant position in the on-demand delivery sector. For example, partnerships with major retailers enhance the platform's appeal beyond just restaurant delivery.
- Acquisition of Wolt: Closed in 2022 for roughly $8 billion, expanding DoorDash's global reach.
- Partnerships with Retailers: Collaborations with companies like Target and Sephora integrate grocery and retail delivery, broadening service offerings.
- Loyalty Program Integrations: Efforts to link with existing loyalty programs aim to increase customer stickiness and acquisition.
The competitive rivalry in food delivery is intense, marked by aggressive pricing and frequent promotional offers. DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Grubhub are locked in a constant battle for market share, utilizing discounts, free delivery, and subscription services to attract and retain customers. DoorDash's substantial marketing spend, reaching $1.1 billion in 2023, underscores the high cost of this competition.
This rivalry extends beyond core restaurant delivery as platforms diversify into groceries and convenience items. DoorDash's expansion into grocery delivery in 2024, partnering with numerous retailers, directly challenges competitors and established grocery chains. This broadens the competitive arena, demanding continuous innovation in logistics and customer experience to maintain an edge.
Technological advancement and operational efficiency are key battlegrounds, with significant investments in algorithms, routing, and app functionality. DoorDash's Gross Order Value (GOV) reaching $18.0 billion in Q1 2024 highlights its operational scale, a critical advantage in this market. Competitors are also heavily investing in these areas, making sustained technological leadership essential.
Strategic moves like DoorDash's 2022 acquisition of Wolt for approximately $8 billion further intensify competition by expanding global reach and consolidating market power. These acquisitions, alongside partnerships with major retailers, aim to create stronger network effects and a more diversified service offering, directly impacting rivals' strategies and market positions.
| Competitor | Estimated U.S. Market Share (2024-2025) | Key Competitive Actions |
|---|---|---|
| DoorDash | 60%-67% | Aggressive promotions, DashPass subscription, expansion into groceries/convenience, technological investment. |
| Uber Eats | ~20%-25% | Leveraging ride-sharing network, promotional pricing, expanding into new verticals. |
| Grubhub | ~5%-10% | Focus on specific markets, partnerships, potential consolidation. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The option for consumers to dine in at restaurants or pick up orders directly acts as a significant substitute to third-party delivery services like DoorDash. This bypasses delivery fees and service charges, often leading to a lower total cost for the customer. For instance, the National Restaurant Association reported a 4.4% increase in restaurant sales in early 2024 compared to the previous year, highlighting a resilient consumer preference for traditional dining and takeout.
The convenience of grocery delivery platforms like Instacart and meal kit services such as HelloFresh poses a significant threat to DoorDash. These alternatives directly compete by offering consumers easy ways to prepare meals at home, often emphasizing cost-effectiveness or healthier options compared to restaurant delivery.
The meal kit sector alone was valued at around $8.5 billion in 2024, demonstrating the substantial market share these substitutes capture. This growth indicates a clear consumer preference for at-home meal solutions, which can divert spending away from DoorDash's core prepared food delivery business.
The threat of cooking at home as a substitute for food delivery services like DoorDash remains a significant factor. In 2024, with ongoing inflation impacting grocery prices, consumers are increasingly weighing the cost of delivery fees and restaurant markups against the expense of home ingredients. For instance, the US Consumer Price Index for food away from home saw a notable increase in early 2024, making home cooking a more economically appealing option for many.
Restaurant-Specific Apps and Websites
Many restaurants, especially larger ones, are creating their own apps and websites for ordering. These platforms often feature special discounts or loyalty rewards to encourage customers to order directly. For instance, in 2024, many national fast-food chains reported significant growth in direct digital orders, bypassing third-party services.
This trend allows customers to skip delivery apps like DoorDash altogether, potentially leading to a more personalized and cost-effective experience for those who frequently patronize a particular establishment. By offering exclusive benefits, these direct channels can siphon off a portion of the order volume that might otherwise go through DoorDash.
- Direct Ordering Growth: Many restaurant chains saw double-digit percentage increases in direct digital orders throughout 2024.
- Loyalty Program Impact: Restaurants with robust loyalty programs saw higher retention rates for direct orders compared to third-party platforms.
- Customer Bypass: The ability for customers to easily access restaurant-specific ordering reduces reliance on aggregators.
Other On-Demand Delivery Services
The expansion of other on-demand delivery services, particularly from giants like Amazon and Walmart, presents a significant threat to DoorDash. These companies are increasingly offering delivery for general retail items and groceries, leveraging their vast logistics networks and established customer loyalty.
The potential for these players to pivot into prepared food delivery is substantial. For instance, Amazon's existing Prime Now and Fresh services demonstrate a robust capability in rapid delivery, which could be readily adapted to include restaurant meals. This broadens the competitive landscape beyond traditional food delivery platforms, offering consumers convenience that extends beyond just restaurant orders.
- Amazon's Grocery Delivery Reach: As of early 2024, Amazon Fresh and Whole Foods Market delivery services are available in hundreds of U.S. cities, providing a strong foundation for expanding into prepared food delivery.
- Walmart's Delivery Network: Walmart, with its extensive store footprint, offers same-day grocery delivery in over 3,000 locations, a significant logistical advantage that could be applied to other delivery categories.
- Customer Base Overlap: Both Amazon and Walmart boast massive customer bases, many of whom already utilize their delivery services for everyday needs, making it easier to introduce and gain adoption for new offerings.
The threat of substitutes for DoorDash is multifaceted, encompassing direct restaurant ordering, home cooking, grocery delivery, and meal kits. Consumers can bypass third-party delivery fees by dining in or picking up orders themselves, a trend supported by the National Restaurant Association's report of a 4.4% increase in restaurant sales in early 2024. Furthermore, the growing popularity of grocery delivery and meal kit services, with the meal kit sector alone valued at approximately $8.5 billion in 2024, offers consumers convenient and often more economical alternatives for at-home dining.
| Substitute Category | Key Drivers | 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Restaurant Ordering | Cost savings, loyalty programs, personalized experience | Double-digit percentage increases in direct digital orders reported by many chains. |
| Home Cooking | Cost-effectiveness, inflation impact on dining out | US Consumer Price Index for food away from home increased, making home cooking more appealing. |
| Grocery Delivery & Meal Kits | Convenience, cost-effectiveness, healthier options | Meal kit sector valued at ~$8.5 billion; Amazon Fresh/Whole Foods delivery in hundreds of U.S. cities. |
Entrants Threaten
The food delivery sector presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its significant capital and technology demands. Establishing a competitive platform requires substantial upfront investment in advanced technology, efficient logistics networks, and widespread marketing efforts. DoorDash's substantial spending, with technology and development costs reaching approximately $820 million in the fourth quarter of 2023, underscores the high financial hurdle for newcomers aiming to compete effectively.
Established players like DoorDash benefit from powerful network effects. A large customer base attracts more restaurants and drivers, which in turn attracts even more customers. This virtuous cycle creates a significant competitive moat, making it incredibly difficult for new entrants to build the necessary critical mass of users, merchants, and Dashers to compete effectively.
DoorDash benefits from significant brand recognition and a substantial, loyal customer base. In 2024, the company boasted over 42 million monthly active users and 22 million members across its DashPass and Wolt+ subscription programs. This established loyalty presents a considerable barrier for new entrants.
New competitors would face the daunting task of investing heavily in marketing and promotional activities to even begin chipping away at DoorDash's entrenched customer loyalty. Overcoming this existing consumer trust and awareness requires a disproportionately large expenditure, making initial market penetration a slow and costly endeavor.
Difficulty Securing Merchant Partnerships
Securing partnerships with a broad range of restaurants is a significant hurdle for new delivery platforms. Established players like DoorDash, which boasted over 300,000 restaurant partners by the end of 2023, have built strong, often exclusive, relationships. This makes it difficult for newcomers to attract desirable merchants and offer a competitive variety of choices to consumers.
Restaurants might be reluctant to partner with unproven platforms due to concerns about reliability, reach, and commission structures. DoorDash's extensive customer base and marketing power provide a strong incentive for restaurants to join, a benefit that new entrants struggle to replicate. This difficulty in establishing a robust merchant network directly impacts a new platform's ability to compete on service offerings and customer appeal.
- Established Network Advantage: DoorDash's extensive network of over 300,000 restaurant partners as of late 2023 creates a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Exclusive Agreements: Existing platforms often have exclusive deals with popular restaurants, limiting the options available to competitors.
- Restaurant Hesitation: Merchants may be wary of partnering with new, unproven delivery services, preferring the established reach and marketing capabilities of incumbents.
- Service Variety Impact: The inability to secure diverse merchant partnerships directly hinders a new platform's ability to offer a competitive selection of food options.
Operational Complexity and Regulatory Landscape
The operational complexity of managing a vast network of couriers and restaurants, coupled with the intricacies of real-time order dispatch and dynamic routing, creates a substantial barrier for new entrants. DoorDash, for instance, has refined its algorithms and operational processes over years of experience, making it difficult for newcomers to match its efficiency and scale in 2024.
Furthermore, the constantly shifting regulatory landscape, particularly concerning the classification and compensation of gig economy workers, introduces significant uncertainty and potential compliance costs. New companies must contend with varying local and national labor laws, which can impact business models and profitability. For example, ongoing debates and legal challenges regarding worker status in various jurisdictions, including potential mandates for benefits or minimum wage adjustments, add a layer of risk that established players have learned to navigate.
- Operational Hurdles: DoorDash's sophisticated logistics platform, honed through years of operation, involves complex real-time order matching, efficient routing, and managing a fluctuating fleet of independent contractors, presenting a significant challenge for new entrants aiming to achieve comparable efficiency and speed.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Navigating the evolving regulatory environment, especially concerning gig economy worker classification and compensation laws, adds complexity and potential costs. Changes in these laws could significantly impact the operational model and financial viability of new delivery platforms.
- Cost of Compliance: New entrants face substantial costs in ensuring compliance with diverse and changing labor laws, which can include providing benefits or adhering to minimum wage requirements, thereby increasing their operational expenses compared to established competitors who have already absorbed these costs.
The threat of new entrants in the food delivery market is moderate, largely due to substantial barriers like high capital requirements for technology and logistics, alongside the powerful network effects enjoyed by incumbents like DoorDash. Building brand recognition and securing restaurant partnerships also present significant challenges for newcomers.
DoorDash's substantial user base, exceeding 42 million monthly active users in 2024, and its extensive network of over 300,000 restaurant partners as of late 2023, create strong competitive moats. New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing and operations to gain comparable traction.
Operational complexity and evolving regulations, particularly concerning gig workers, further deter new entrants. DoorDash's established efficiency and experience in navigating these complexities provide a distinct advantage.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for technology, logistics, and marketing. | Significant hurdle for new players. |
| Network Effects | More users attract more restaurants/drivers, creating a virtuous cycle. | Difficult for newcomers to achieve critical mass. |
| Brand Recognition & Loyalty | Established trust and customer base. | Requires substantial marketing spend to overcome. |
| Restaurant Partnerships | Securing a wide range of merchant agreements. | Incumbents have strong, often exclusive, relationships. |
| Operational Complexity | Managing logistics, dispatch, and courier networks efficiently. | Requires sophisticated technology and experience. |
| Regulatory Landscape | Navigating evolving labor laws for gig workers. | Adds uncertainty and potential compliance costs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our DoorDash Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data, including DoorDash's own SEC filings, investor reports, and earnings call transcripts. We also leverage industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld, alongside data on consumer spending habits and labor market trends.
